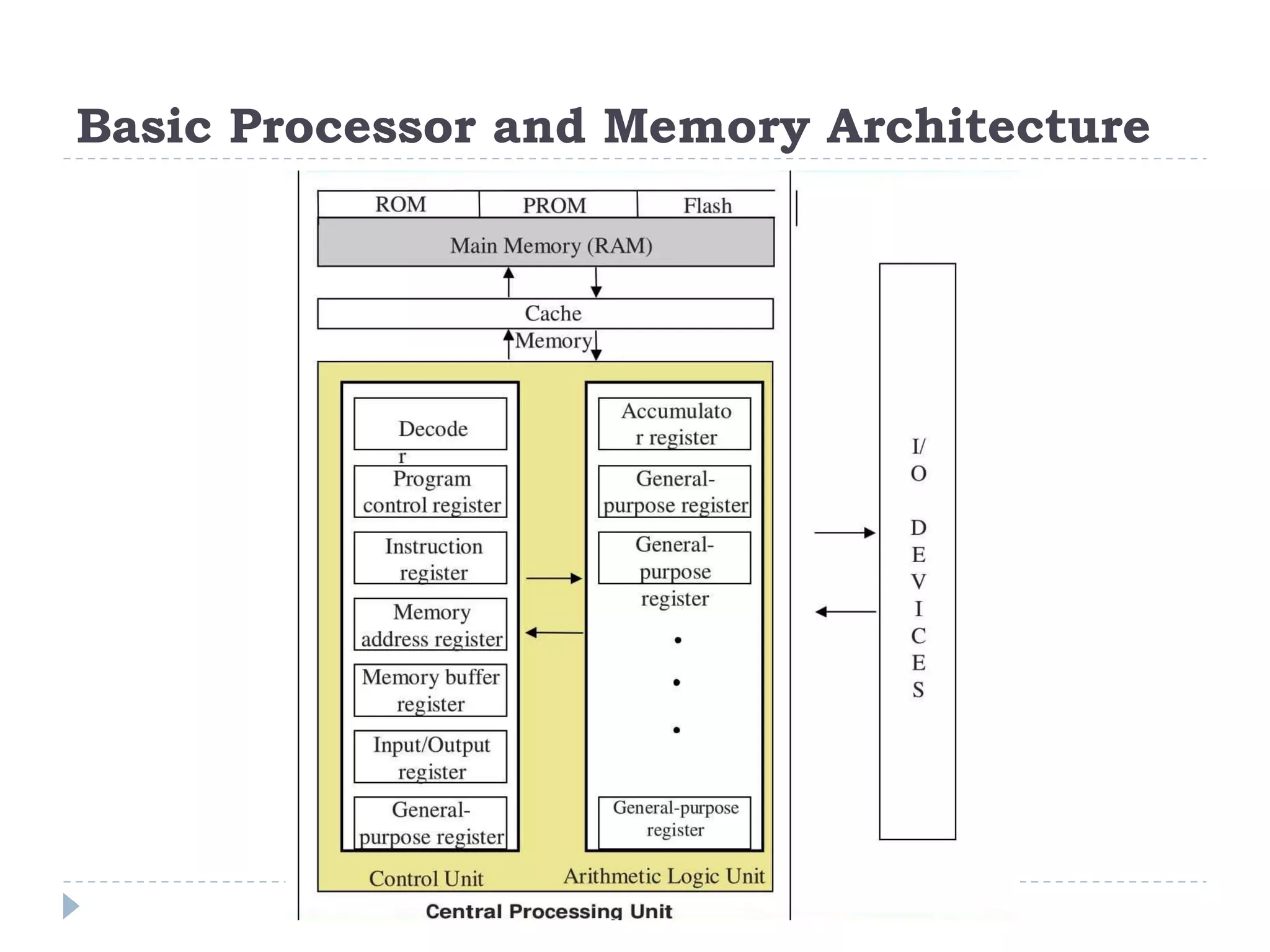
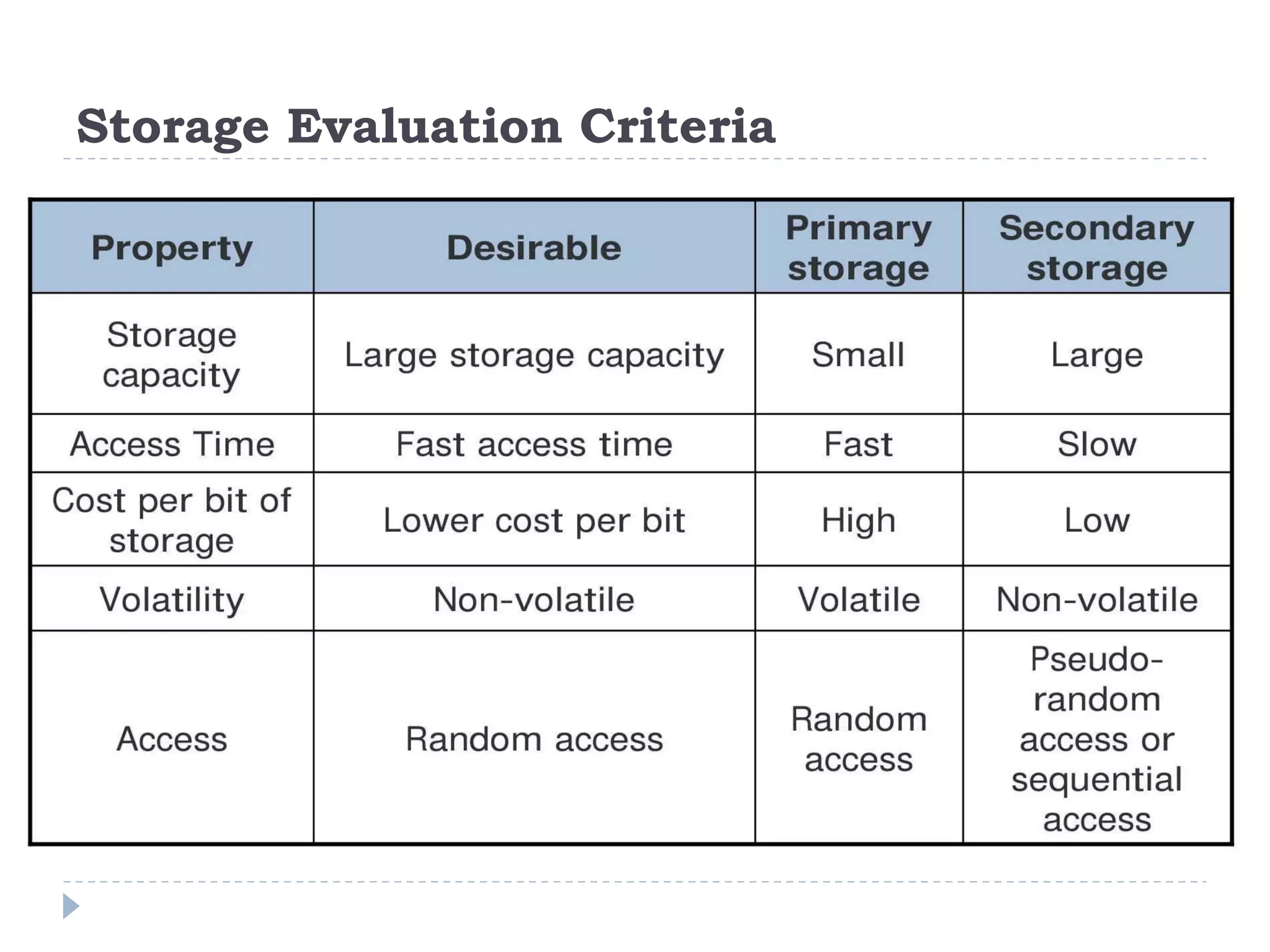
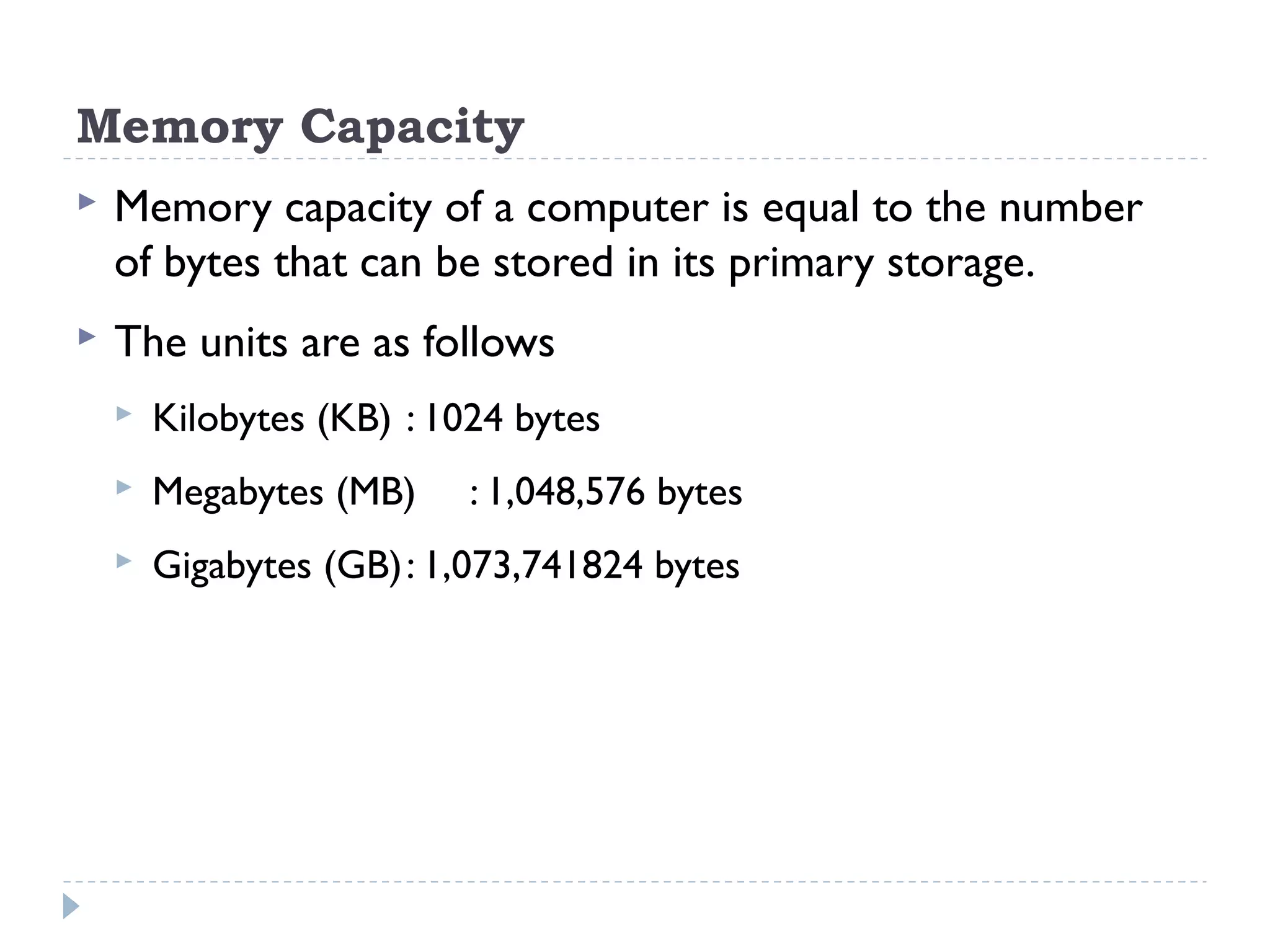
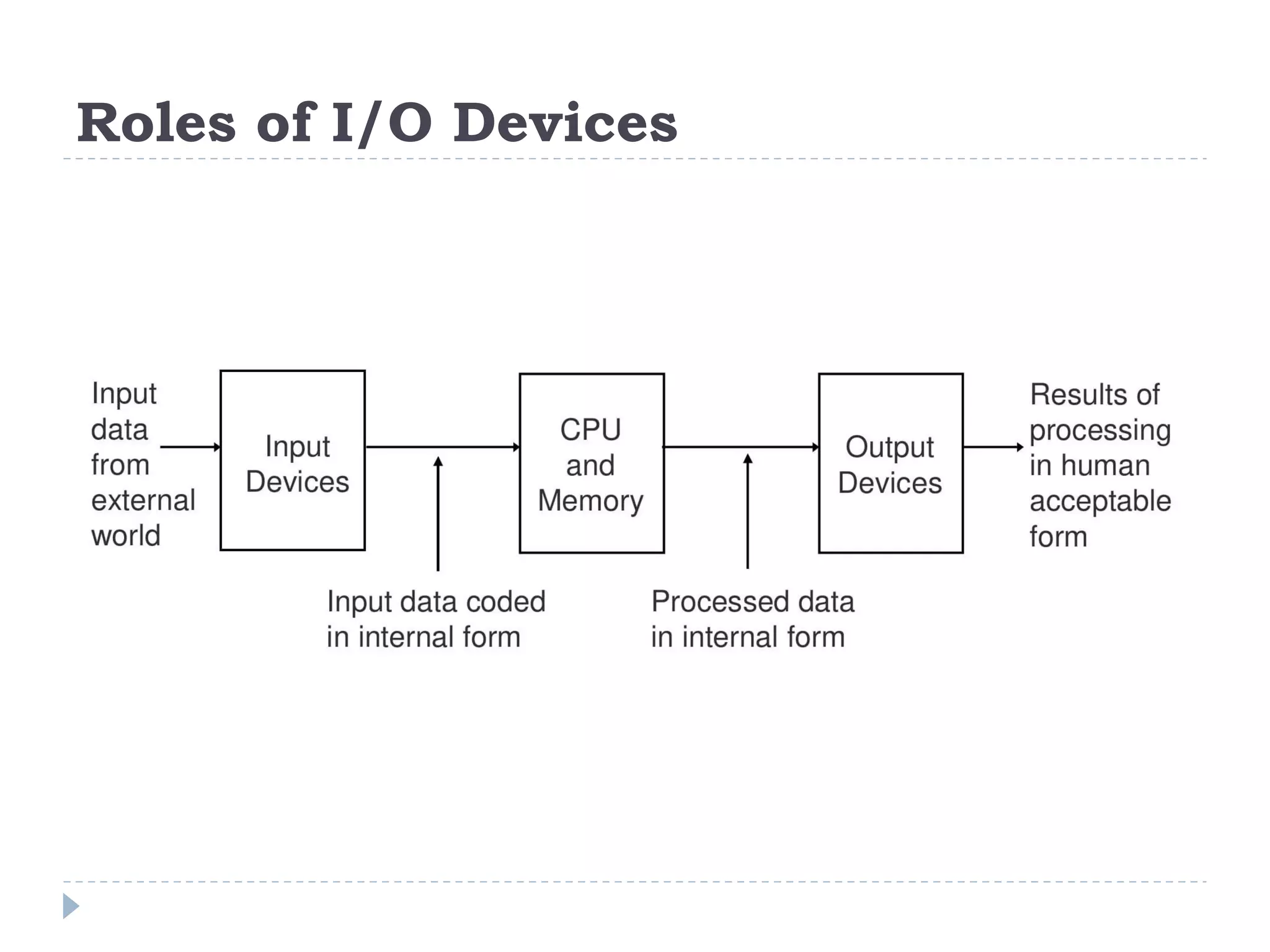
The document discusses the architecture and components of computer processors and memory, focusing on the Central Processing Unit (CPU), including its two main components: the Control Unit (CU) and Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). It details the functions of registers, main memory, and secondary storage, emphasizing the differences in volatility and capacity. Additionally, the document outlines various input and output devices that facilitate communication between the computer and users.