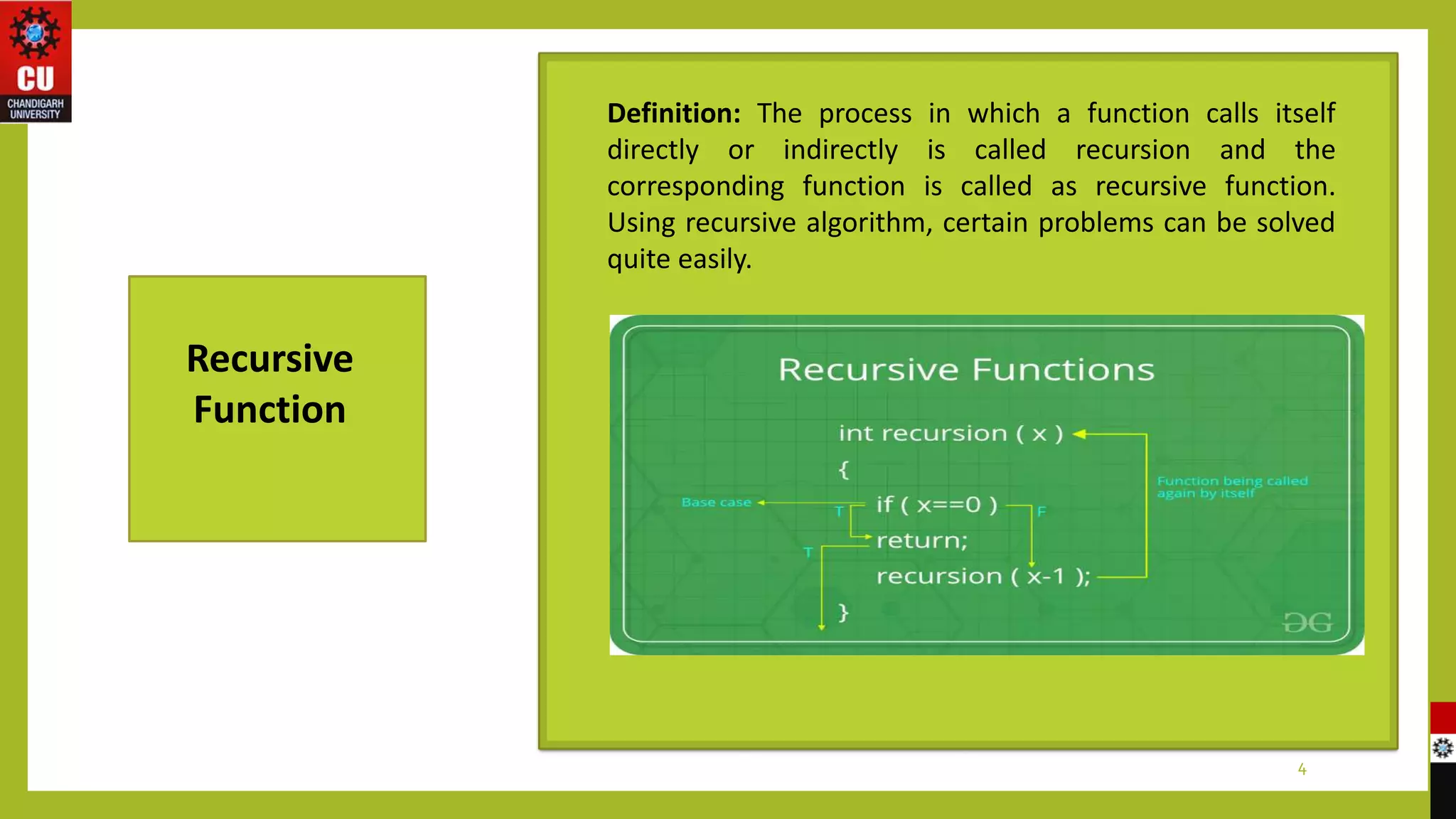
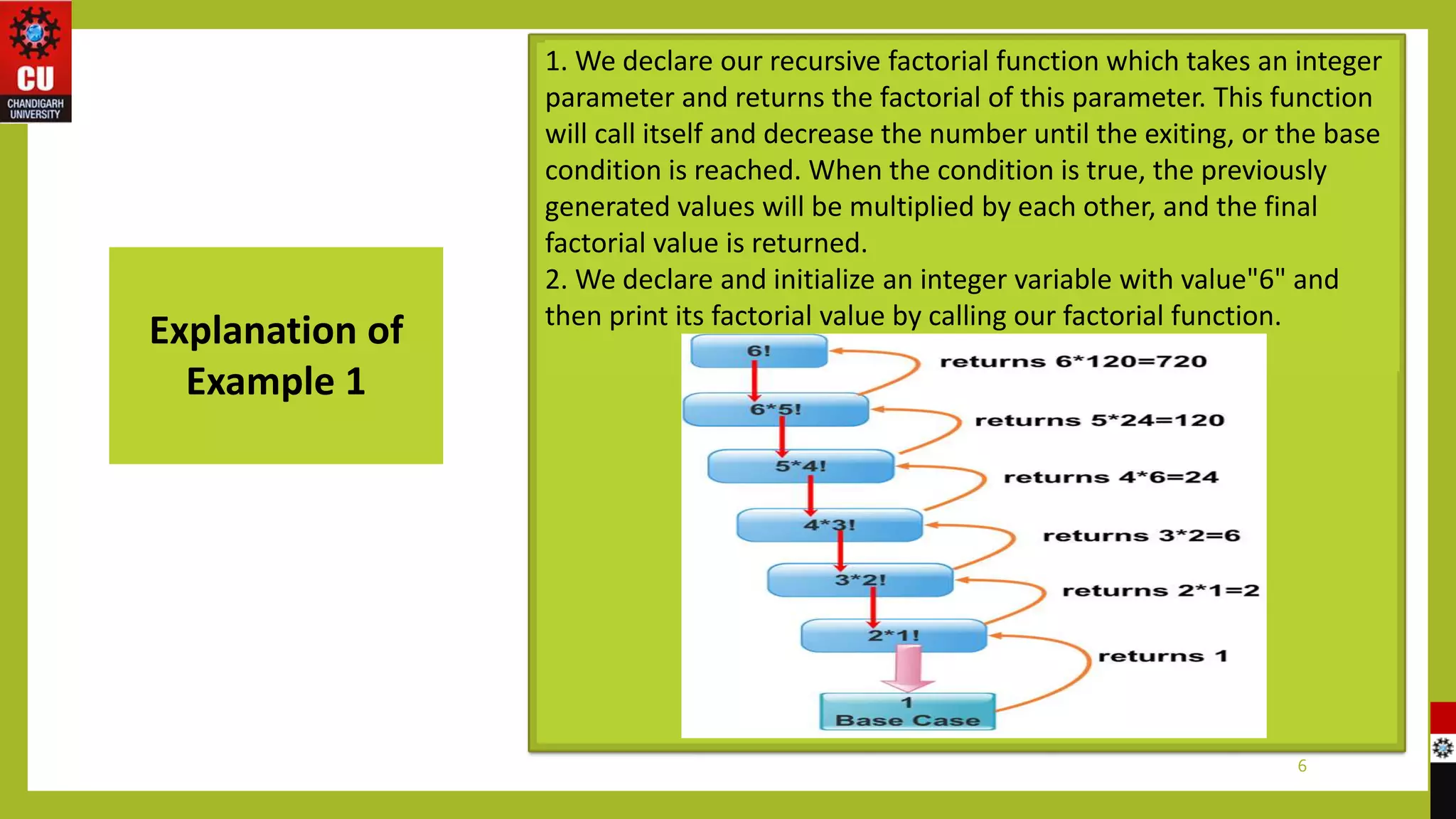
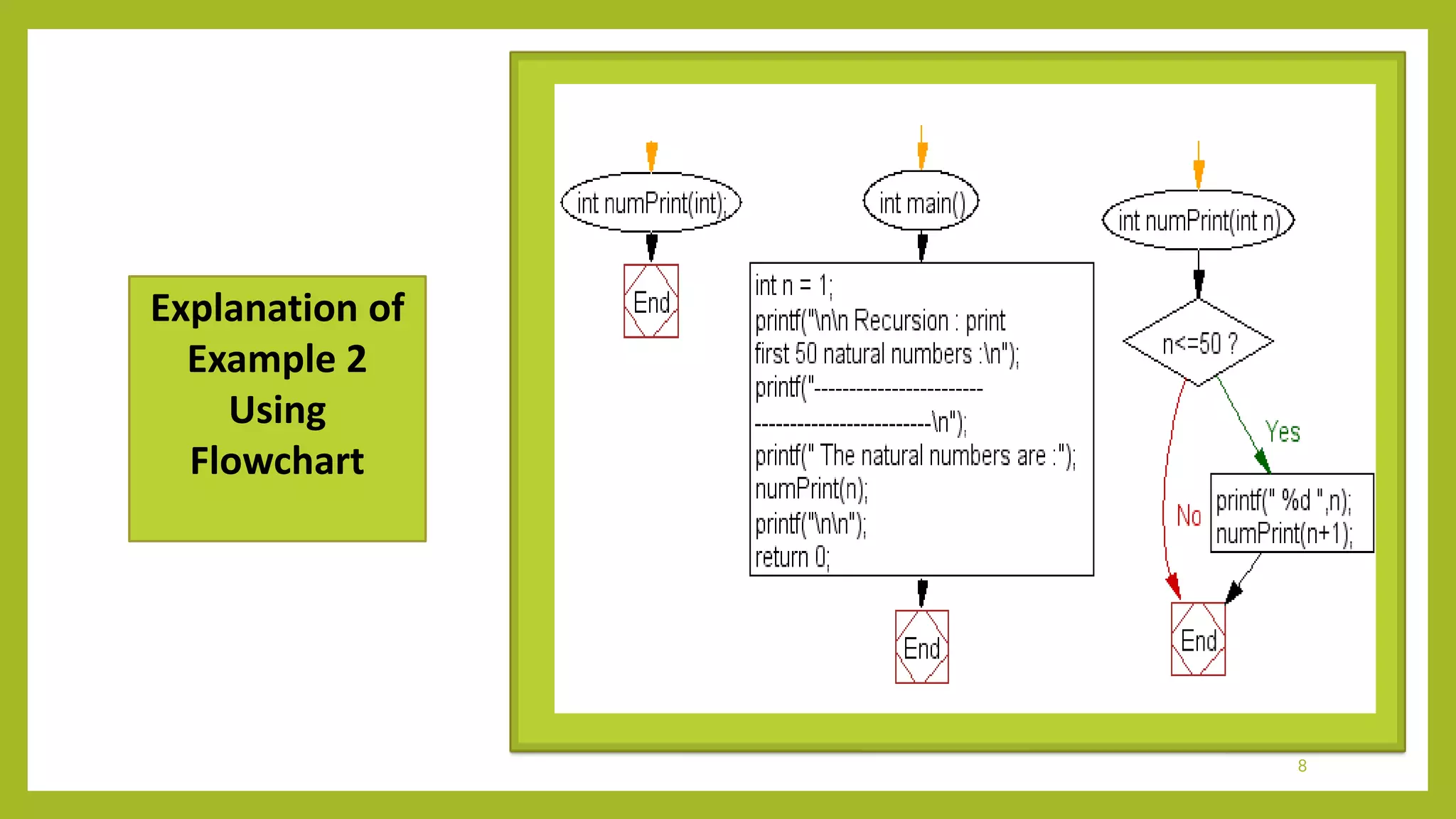
The document covers topics on functions and macros in C programming. It discusses recursive functions, providing examples to calculate the factorial of a number and print the first 50 natural numbers recursively. It also defines macros as code fragments that are replaced by their defined values, and provides an example to calculate the area of a circle using a macro for PI. The document aims to provide exposure to problem solving with programming and raise programming skills with the C language.