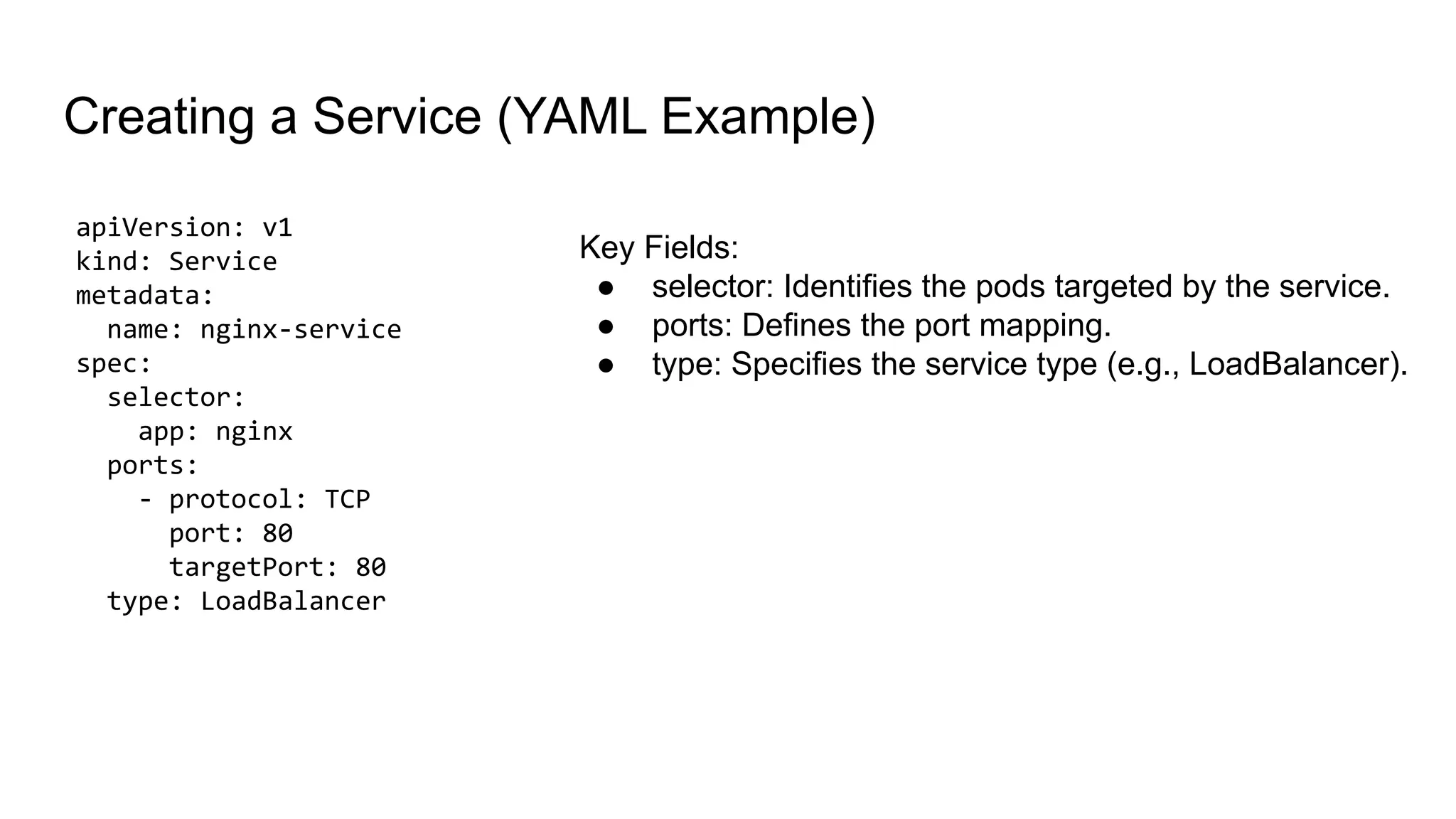
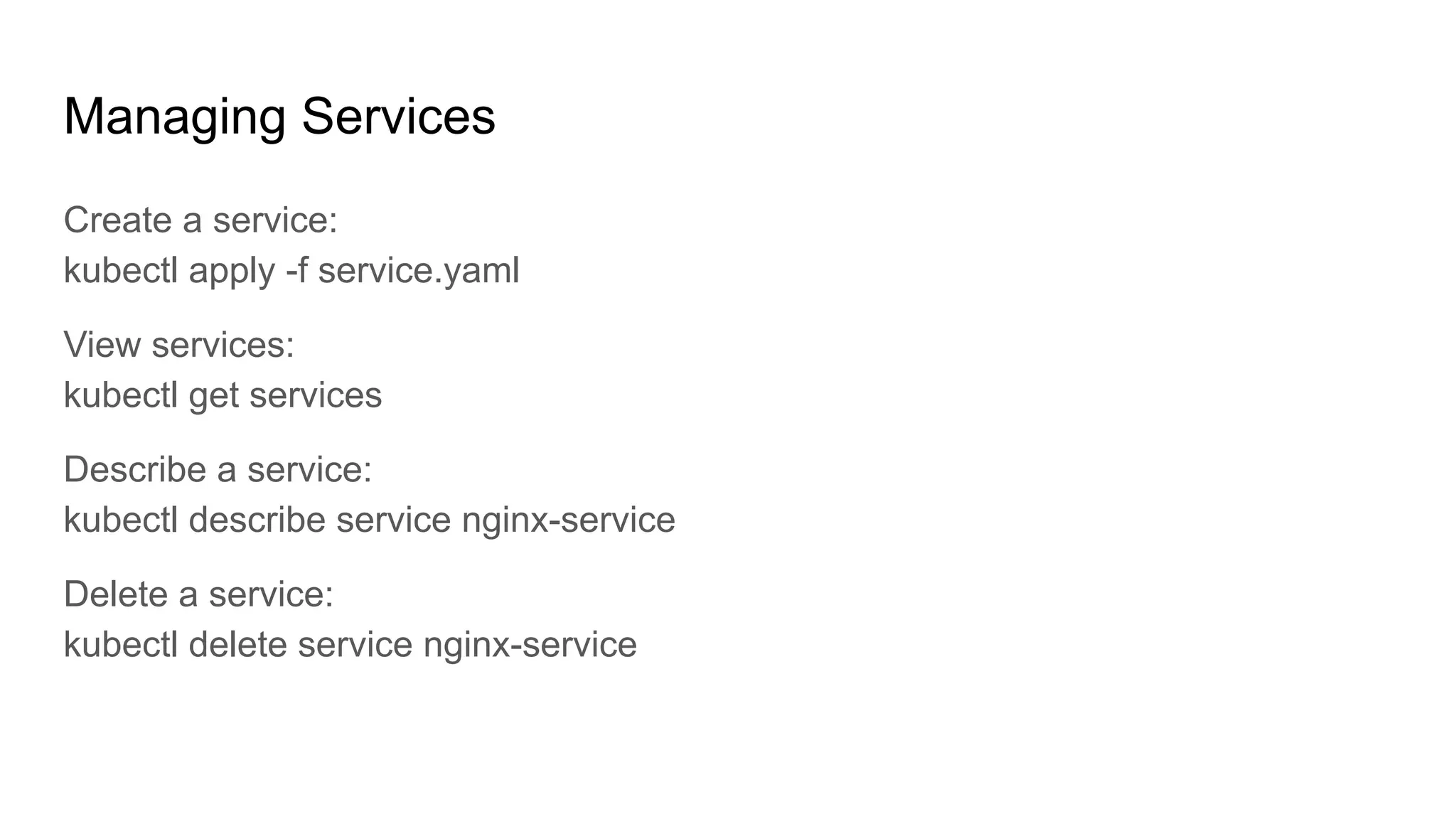
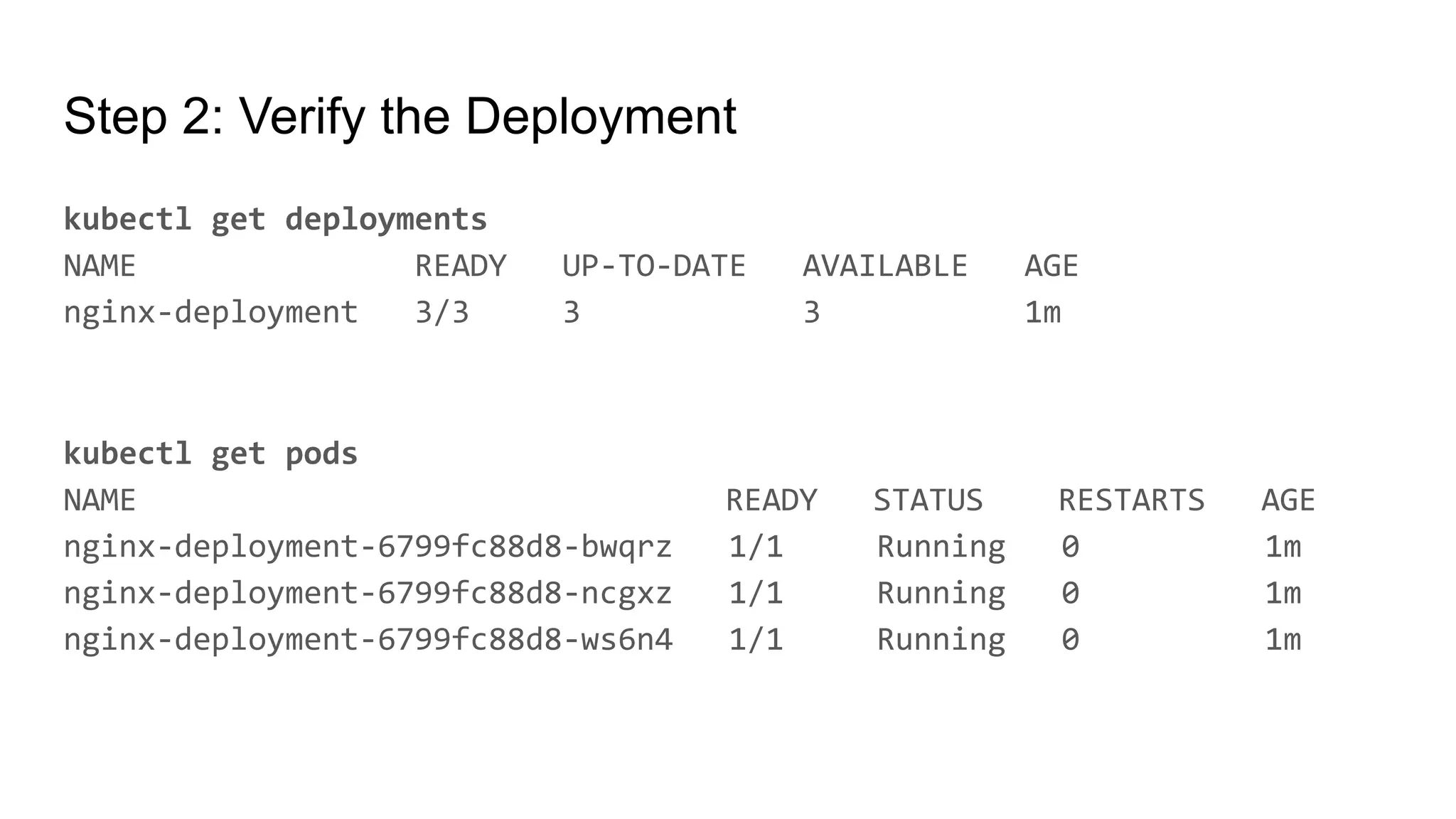
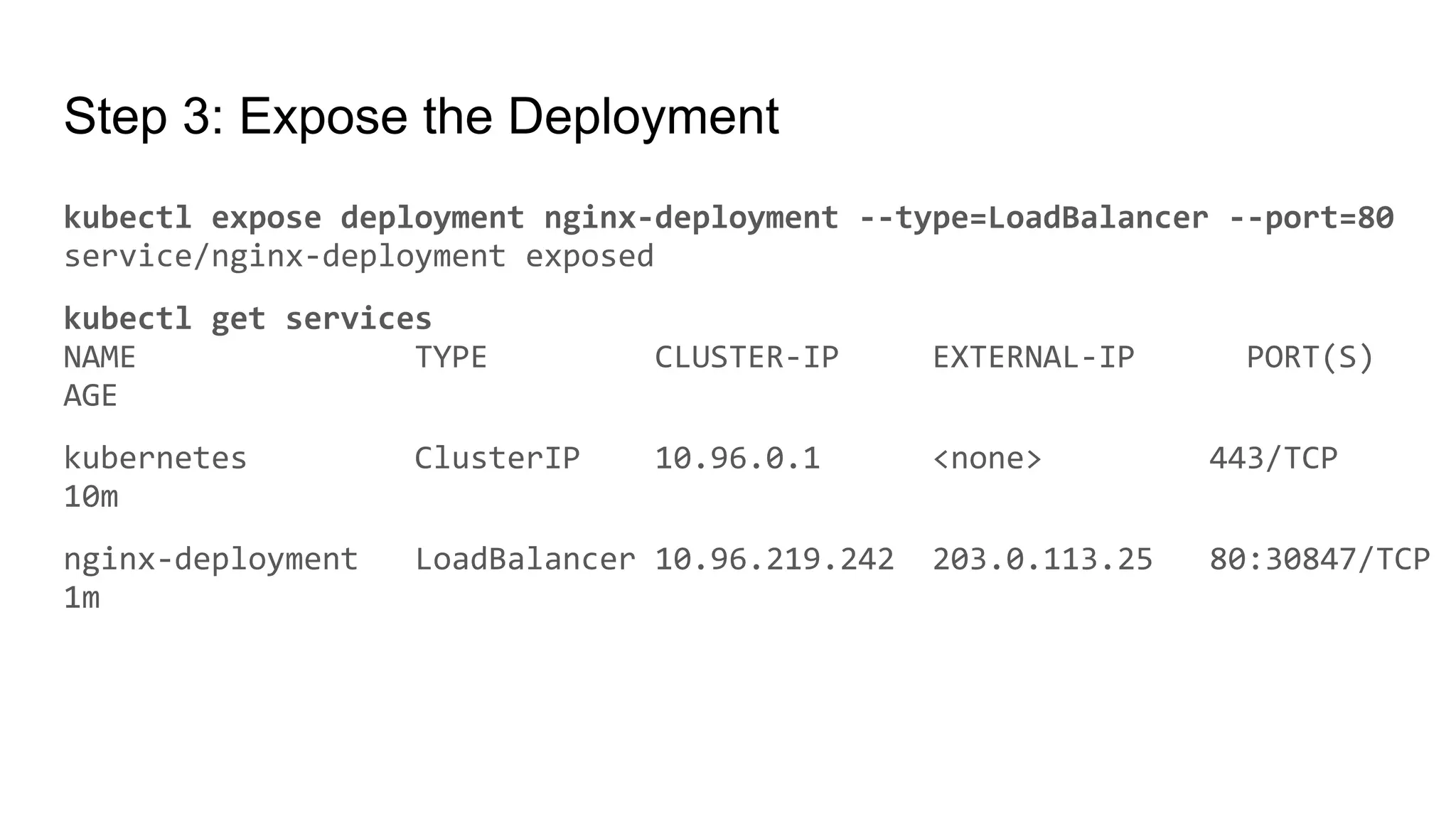
The document provides a comprehensive overview of managing applications in Kubernetes, including key concepts such as deployments and services. It details the features and benefits of Kubernetes deployments, along with commands for creating, scaling, updating, and rolling back deployments. Additionally, it explains the definition, purpose, and types of Kubernetes services, along with commands for managing these services.