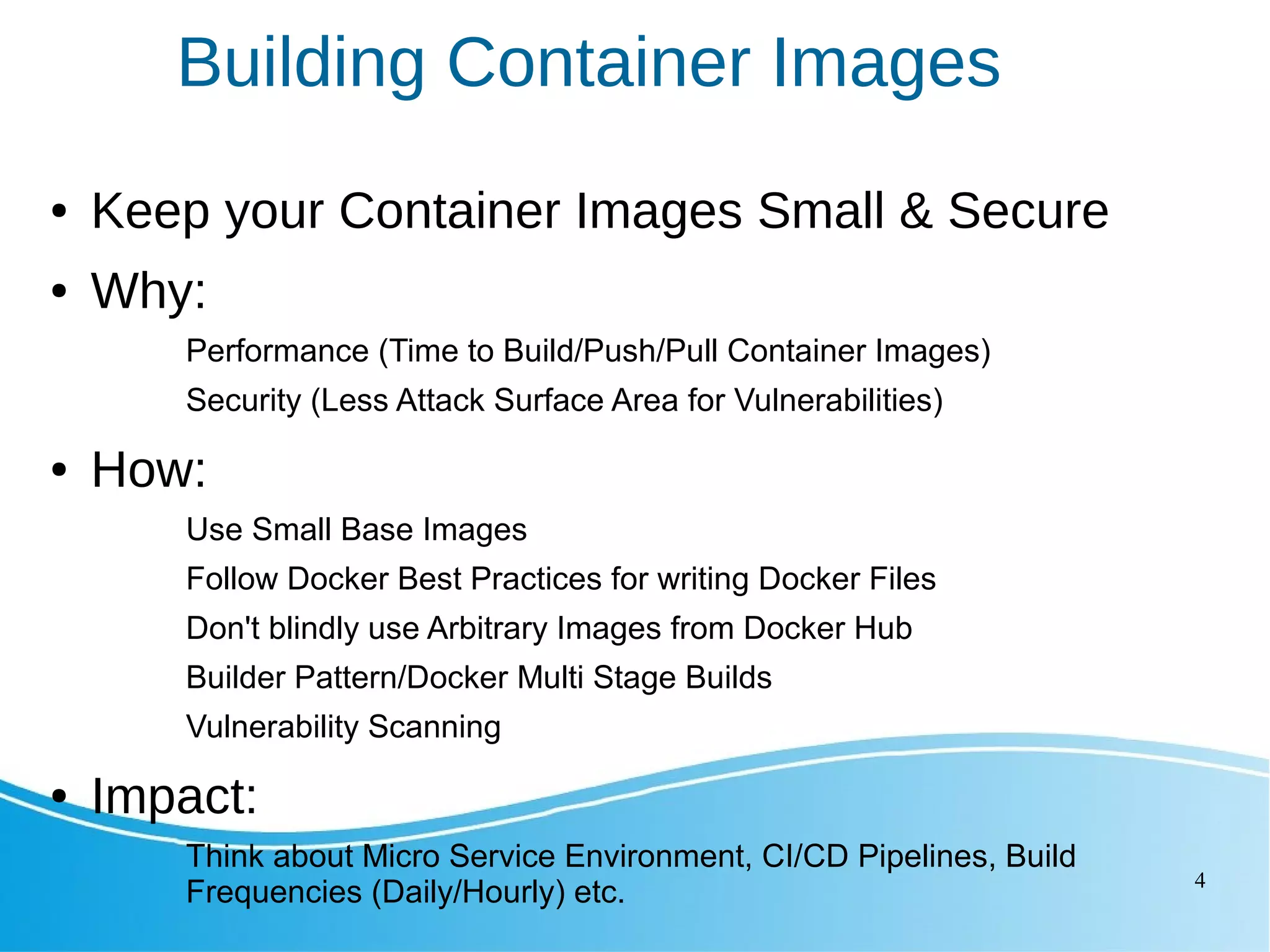
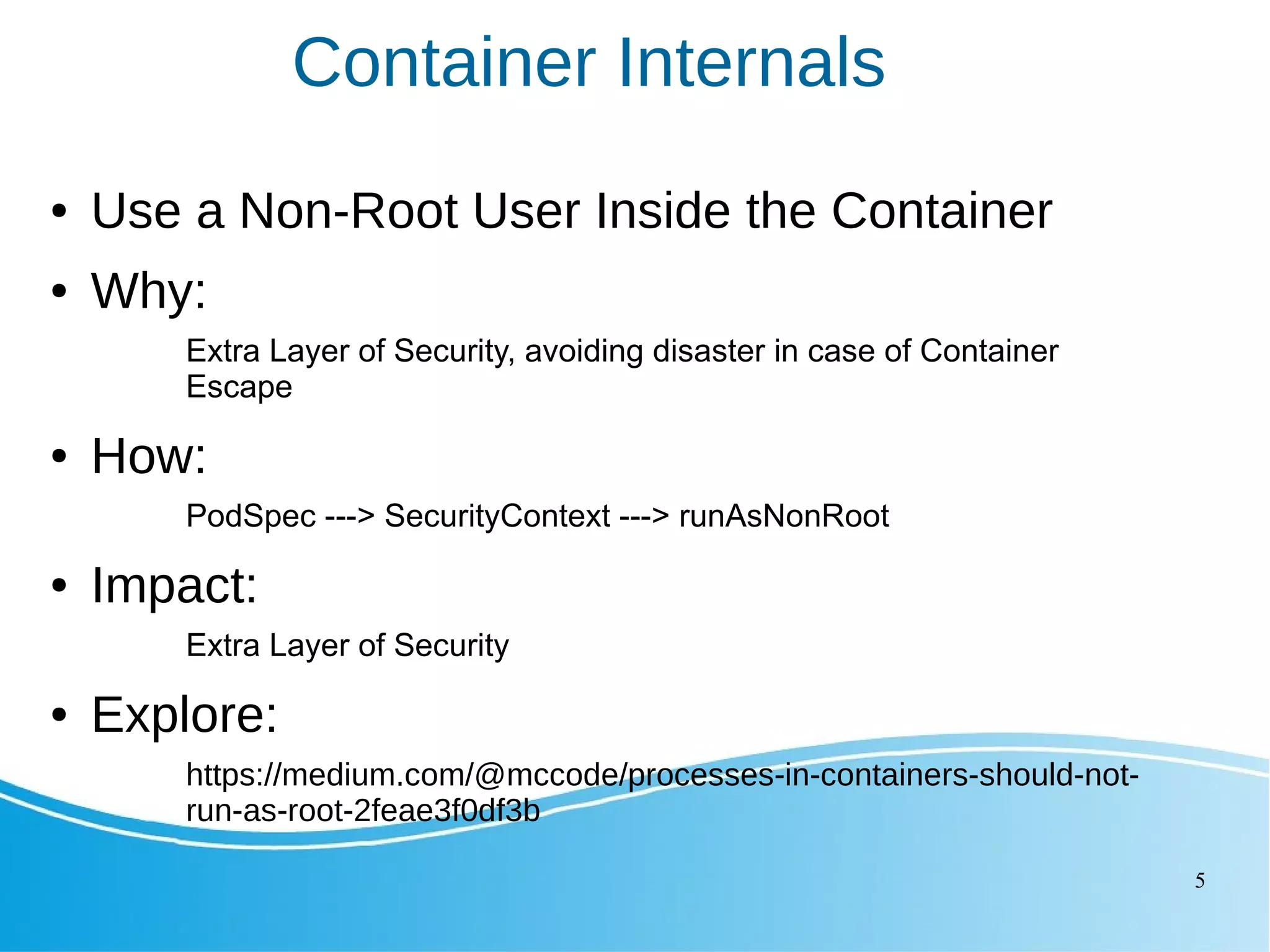
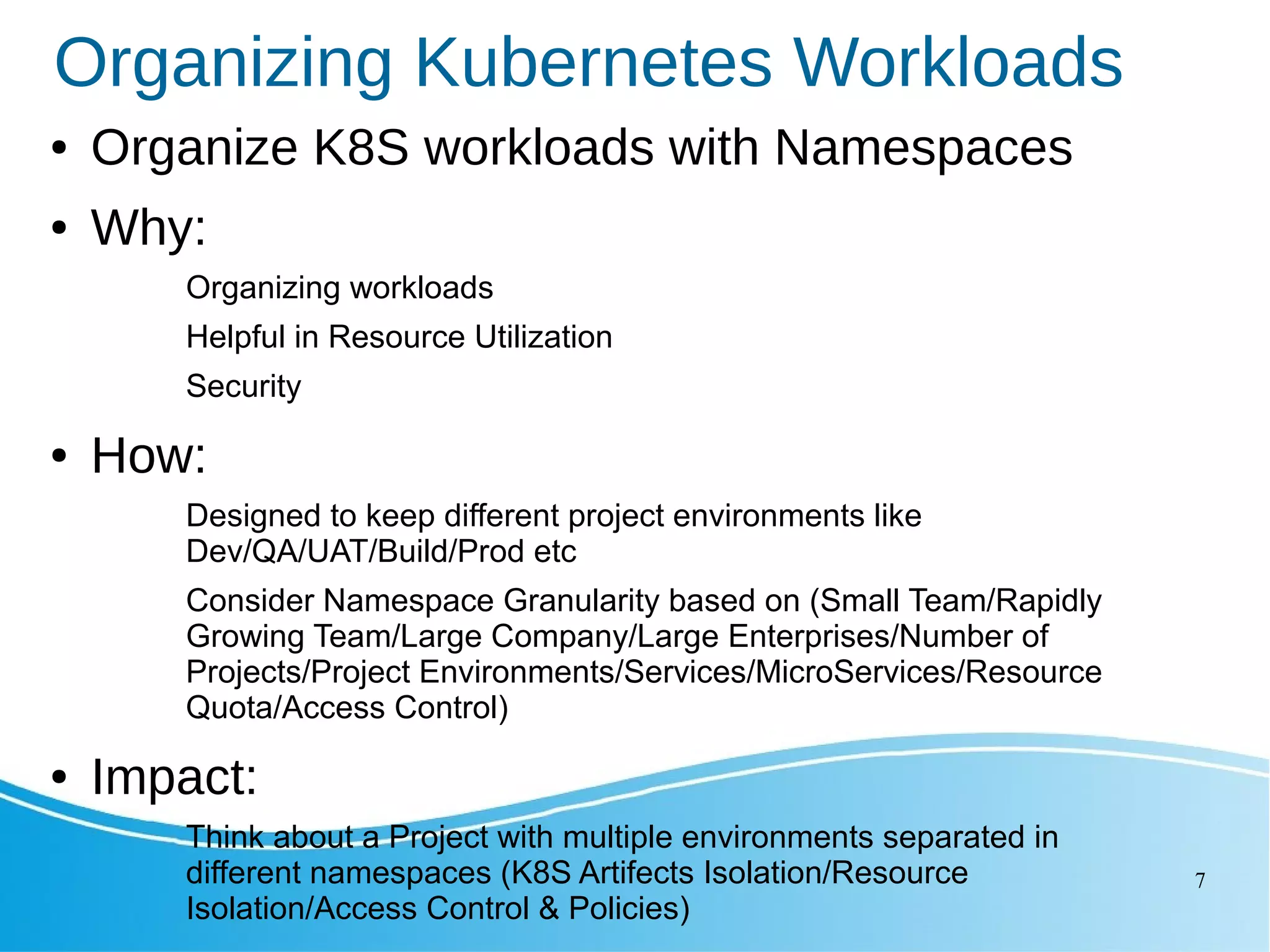
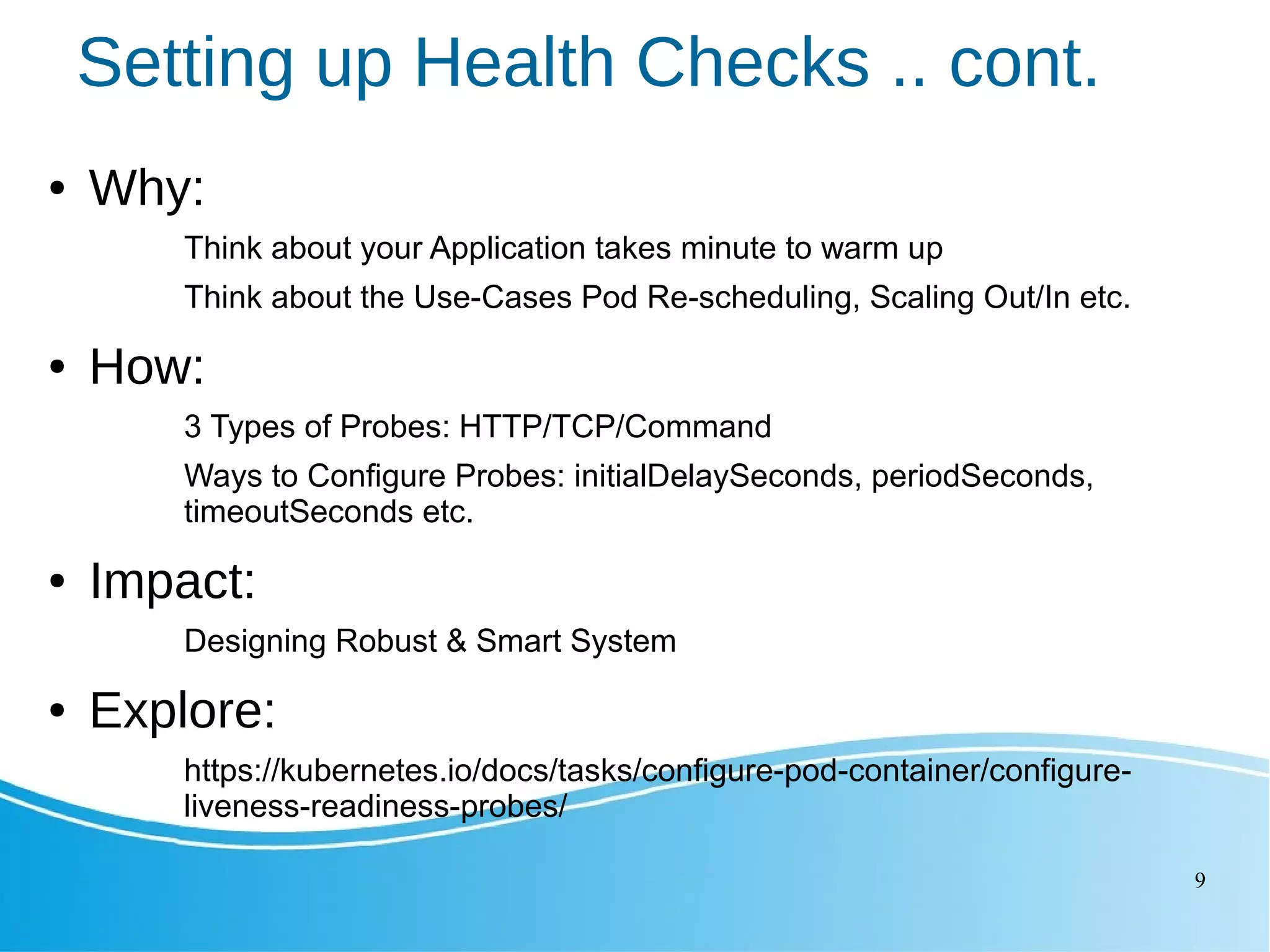
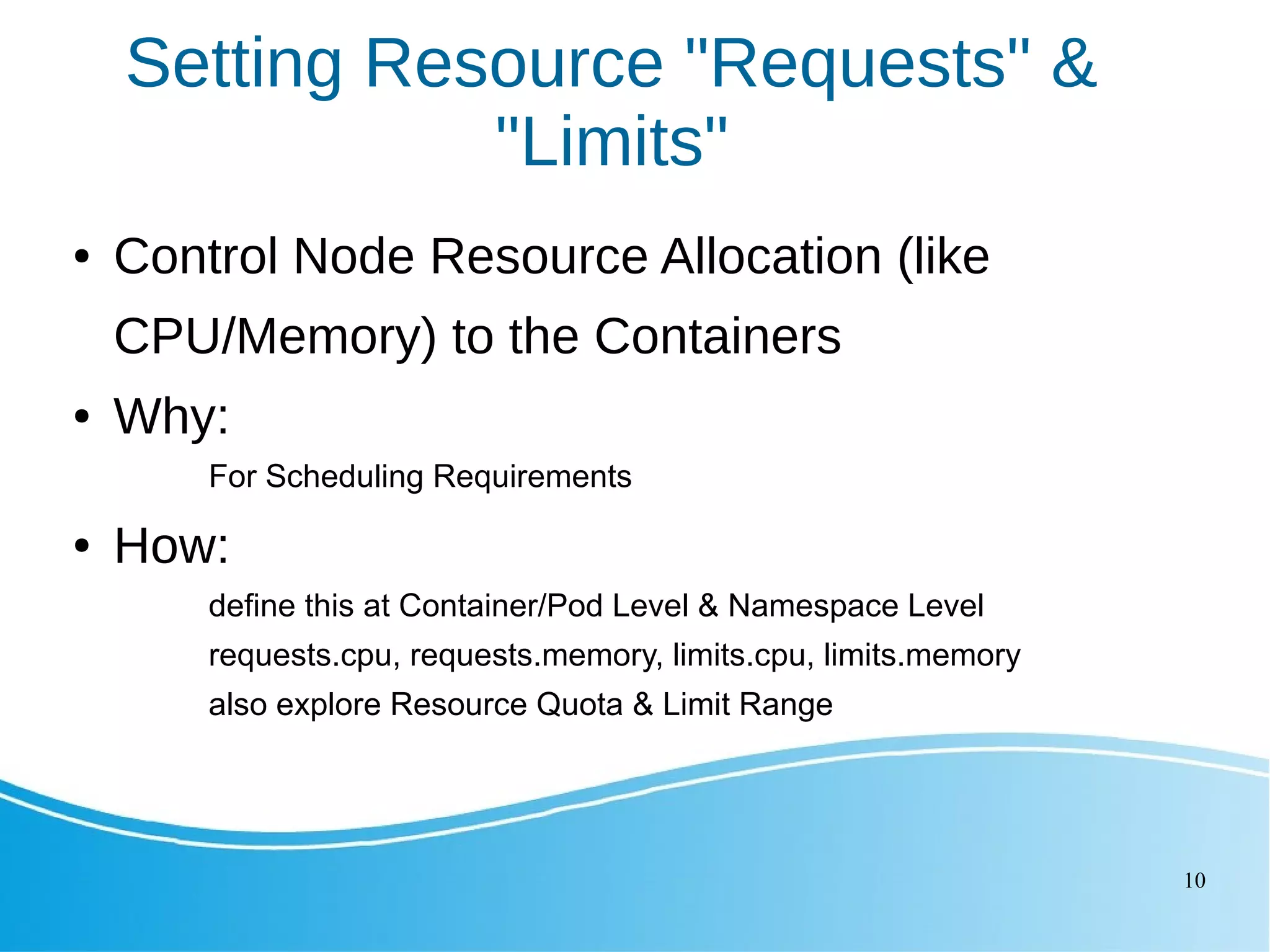
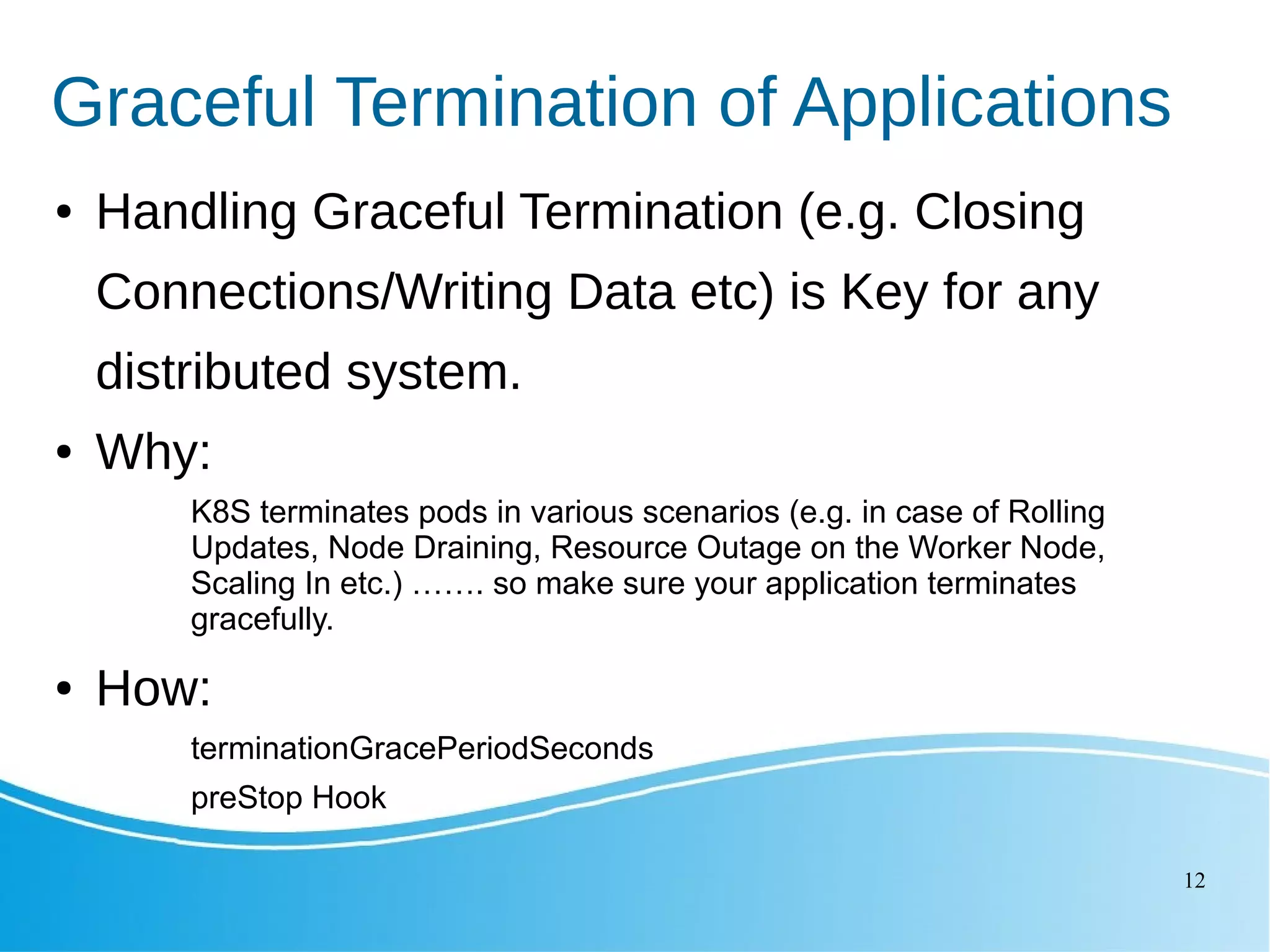
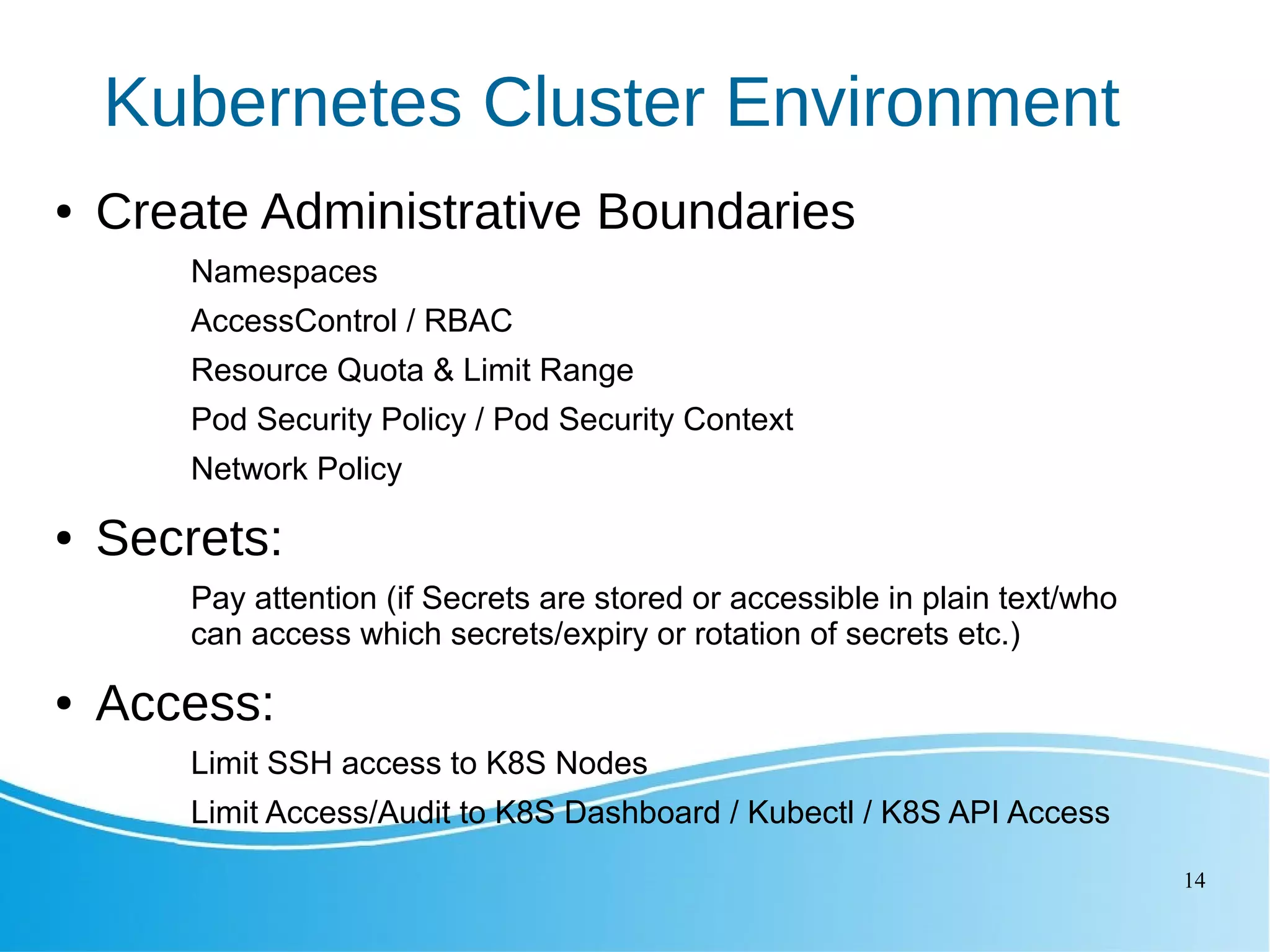
This document outlines several Kubernetes best practices including: - Using small, secure container images to improve performance and security - Running containers as non-root users for an extra layer of security - Organizing workloads into namespaces for isolation, resource utilization, and security - Implementing liveness and readiness probes to ensure instances are ready to receive traffic - Setting resource requests and limits to control node resource allocation - Ensuring applications terminate gracefully through termination grace periods and pre-stop hooks - Implementing administrative boundaries through namespaces, RBAC, quotas, and policies