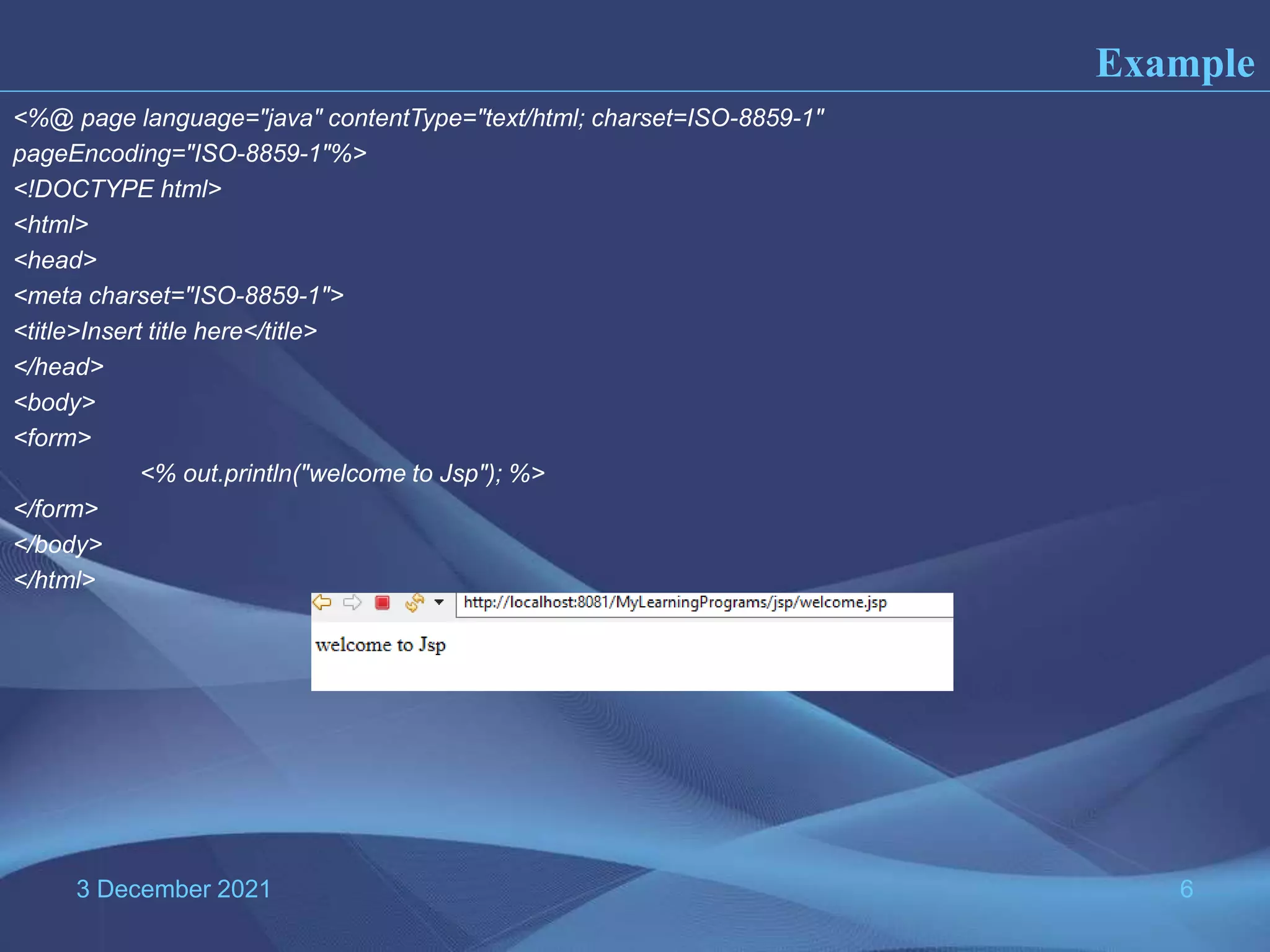
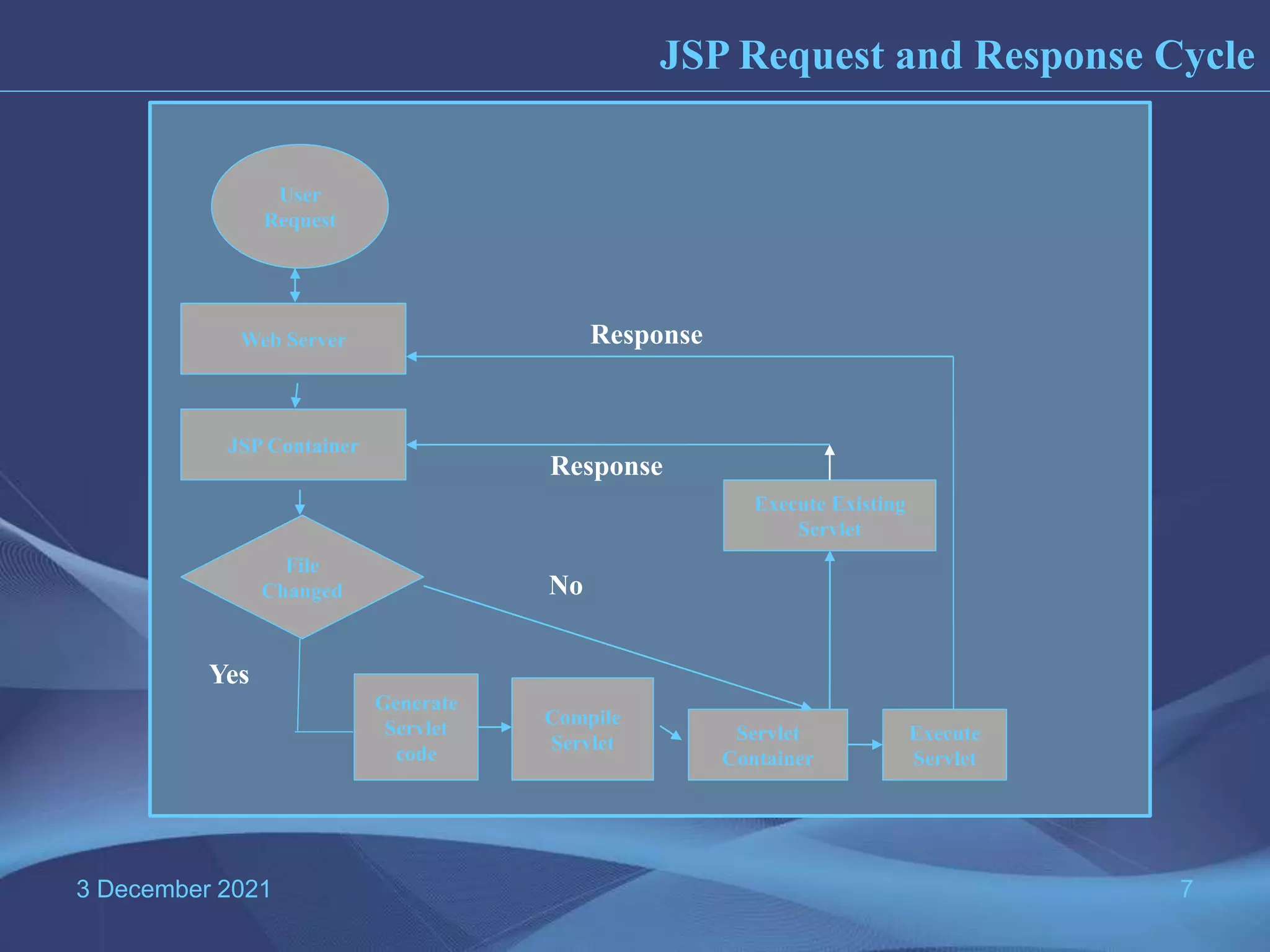
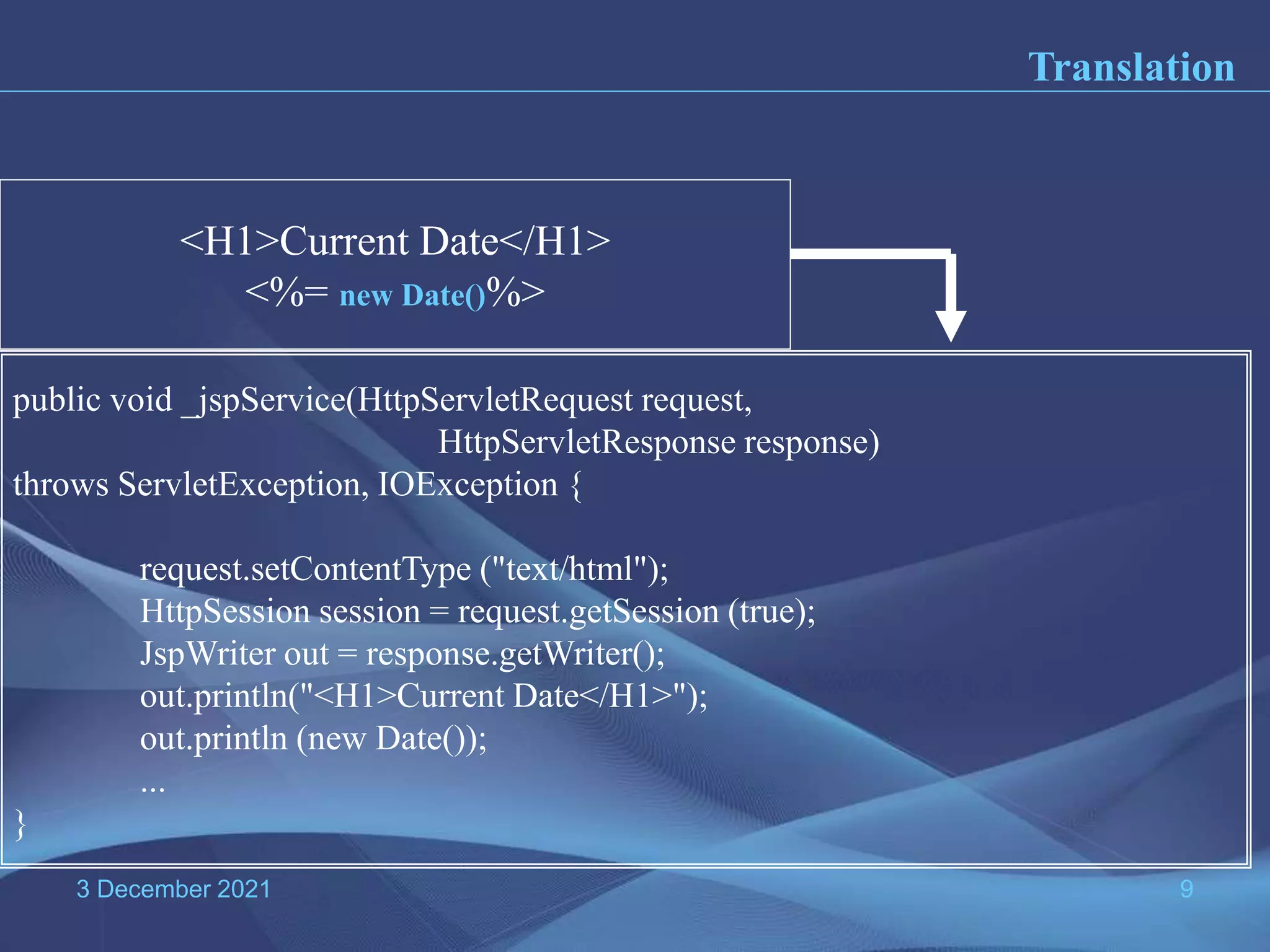
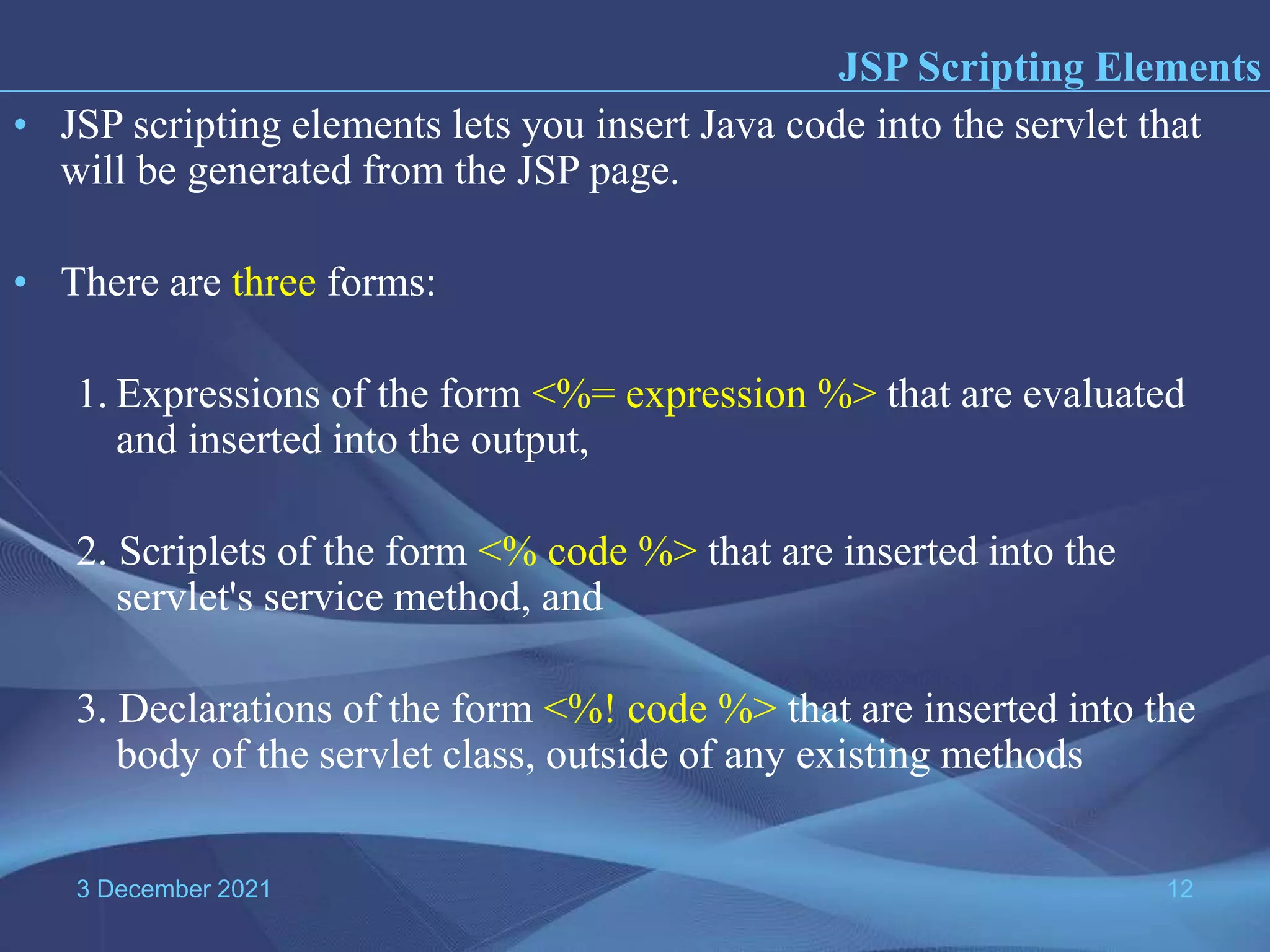
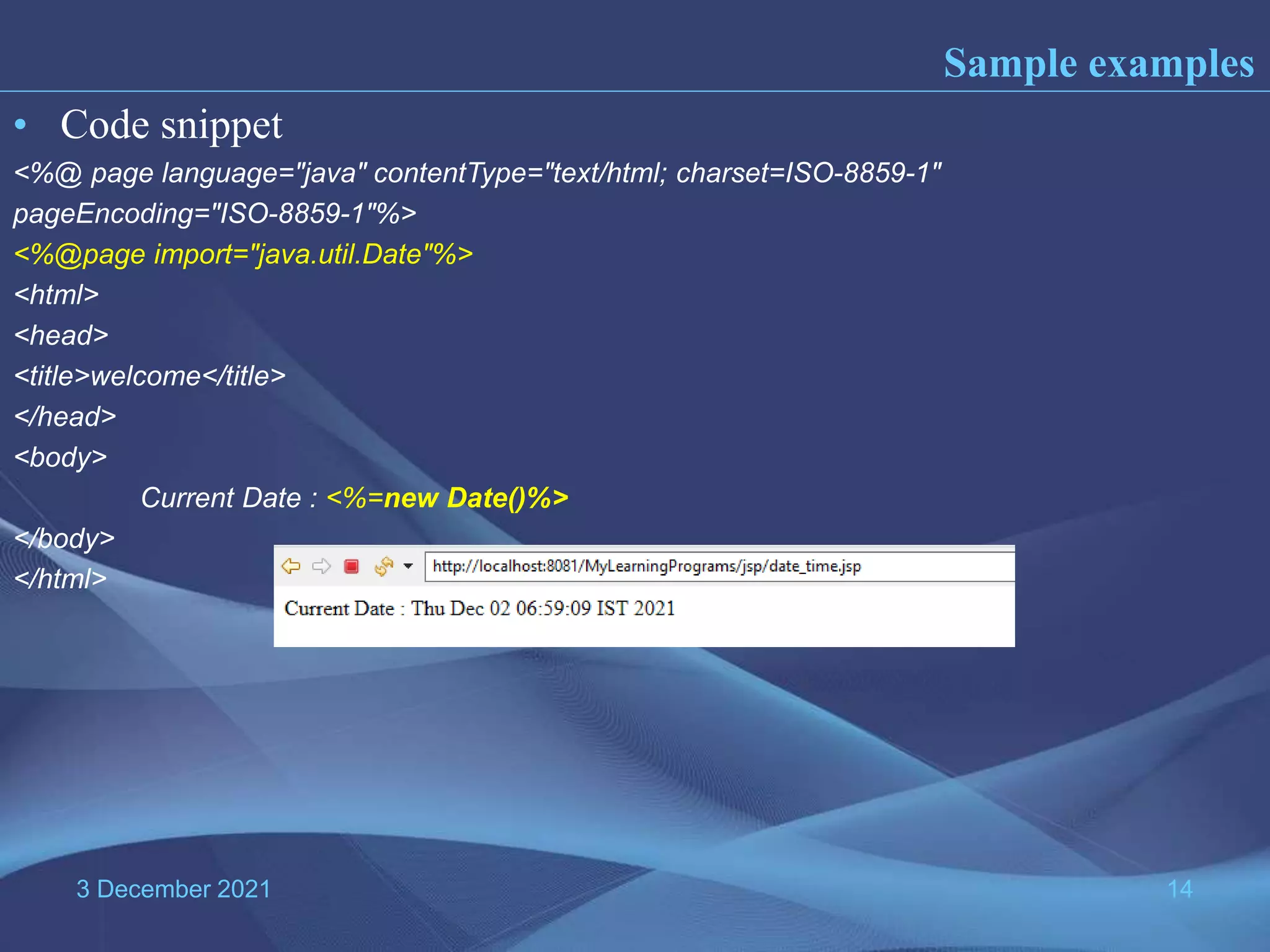
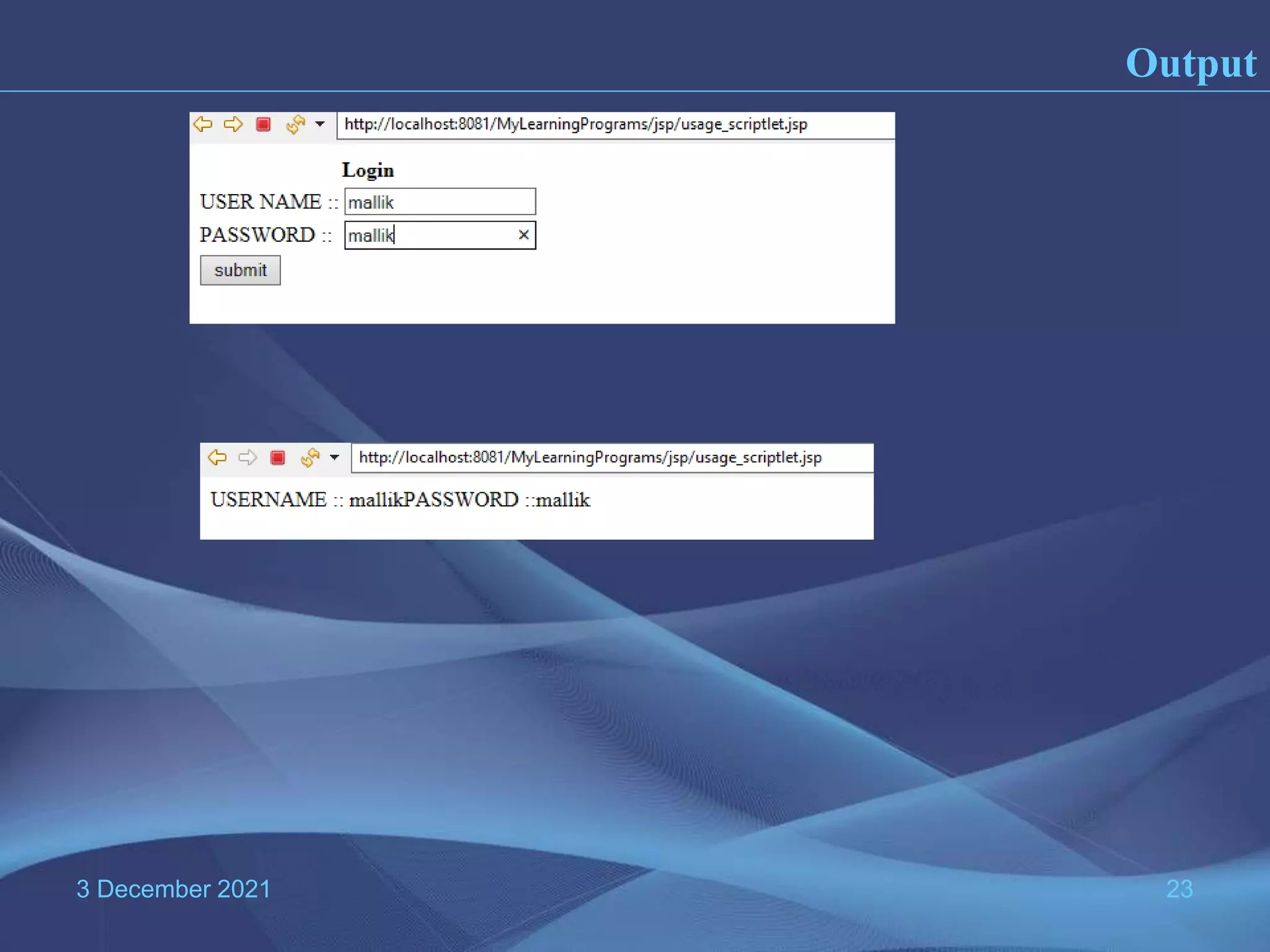
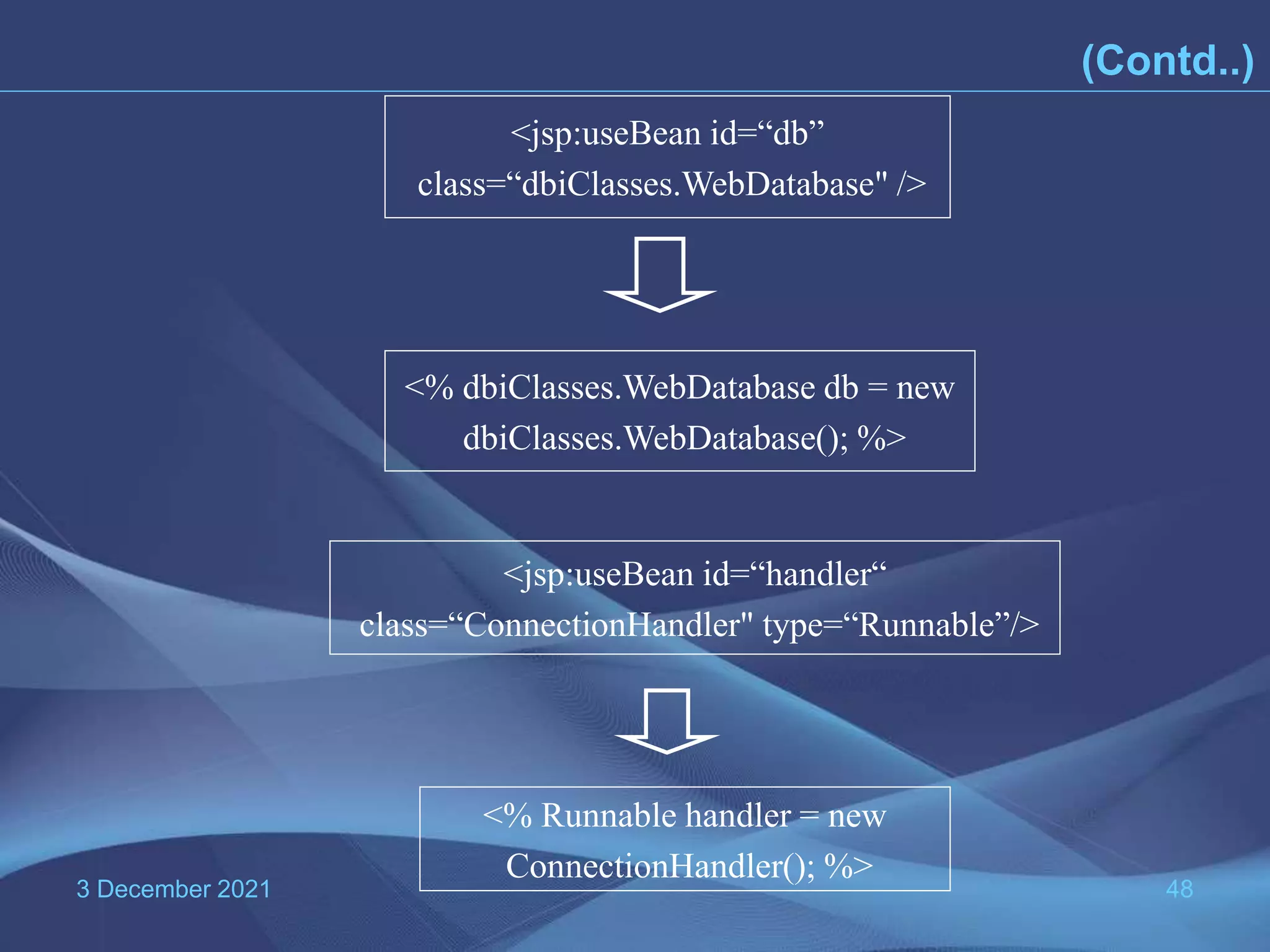
The document provides information about Java Server Pages (JSP) technology: - JSP separates the graphical design from dynamic content and allows Java code to be embedded in HTML pages, helping to develop dynamic web applications. - It benefits web designers and programmers by allowing each to focus on their specialties without needing to learn the other's language. - JSP pages are converted to servlets by the JSP container, with the Java code embedded in the servlet's _jspService() method. This process compiles and runs the page each time it is requested.