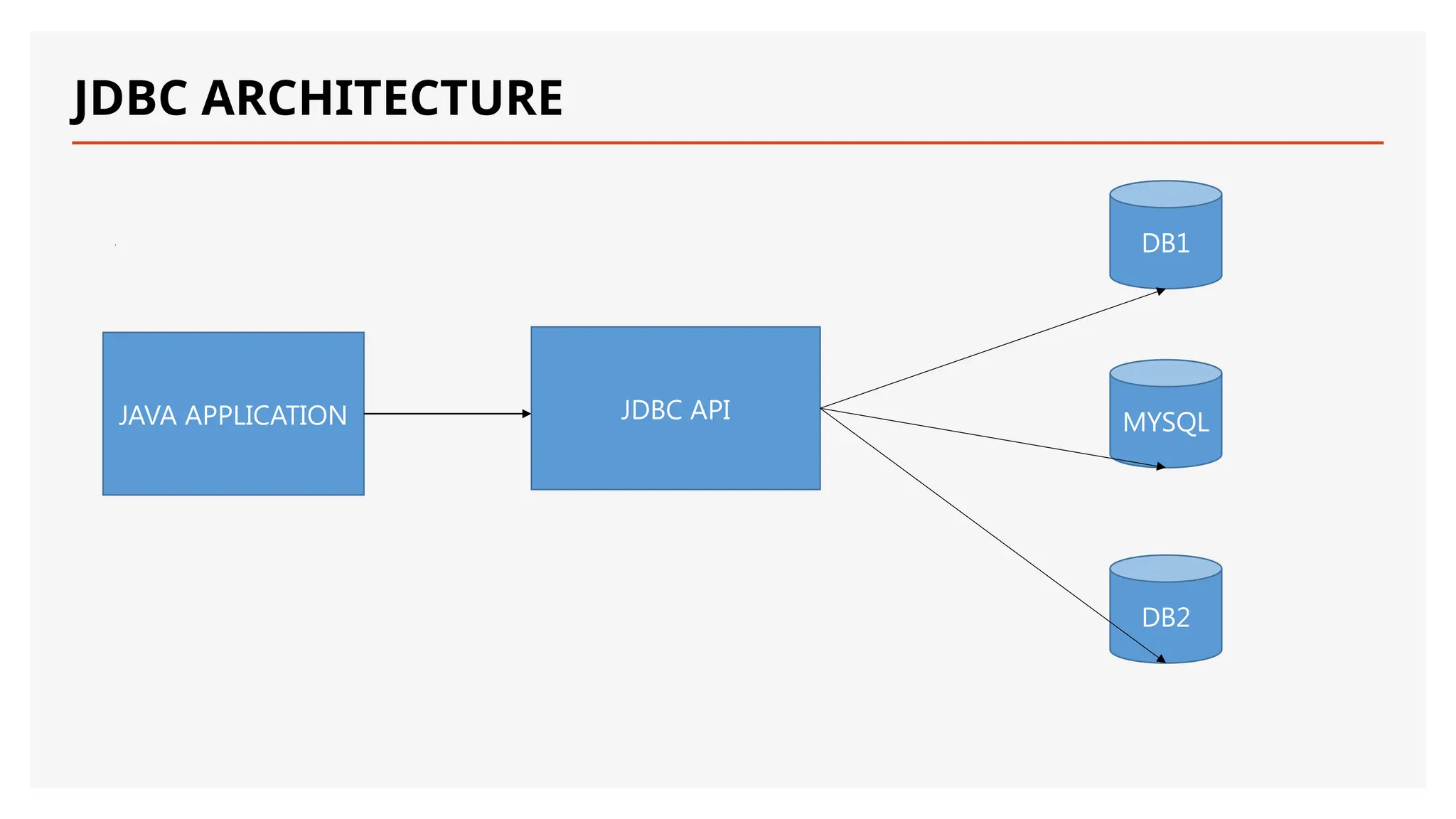
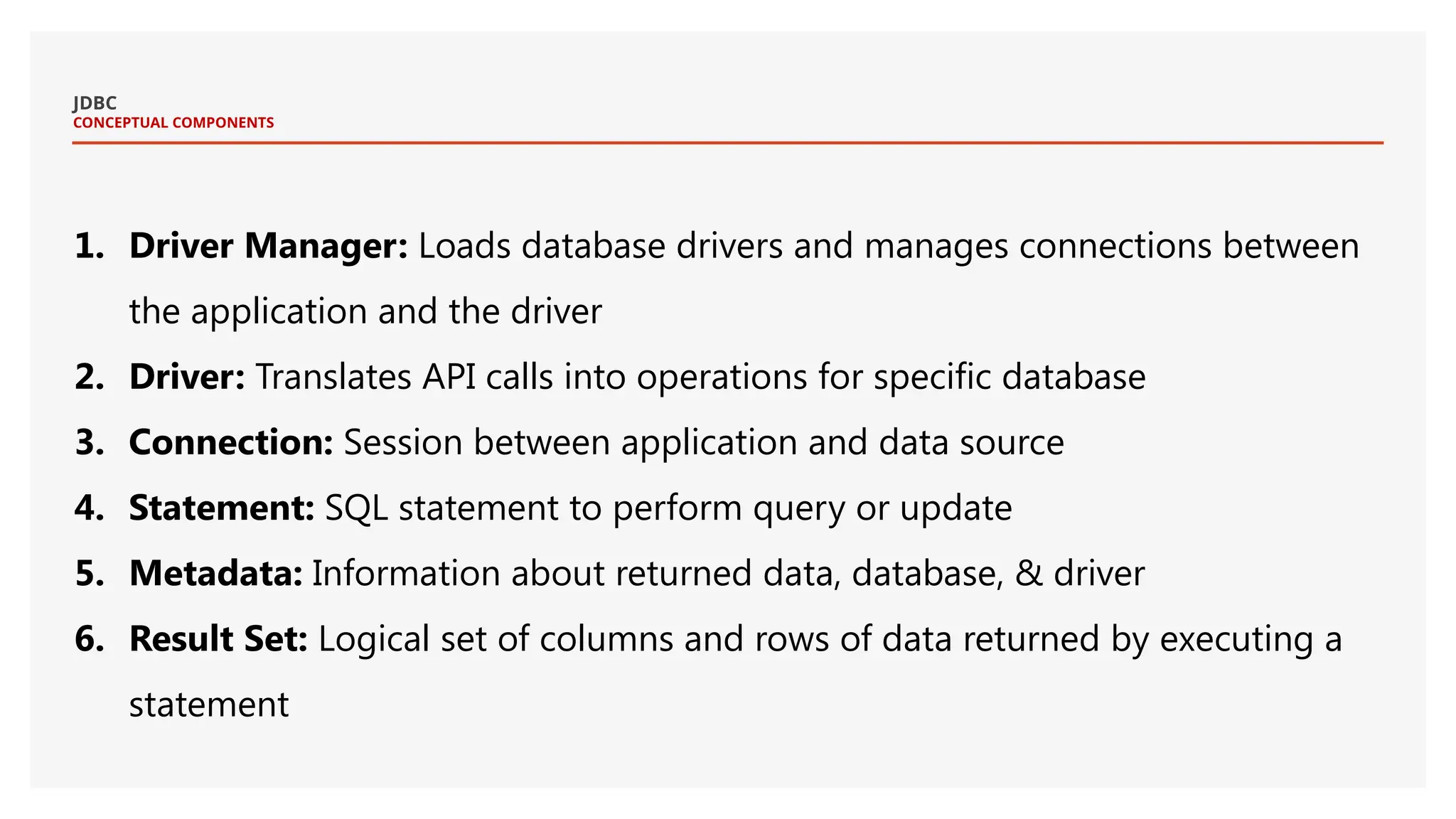
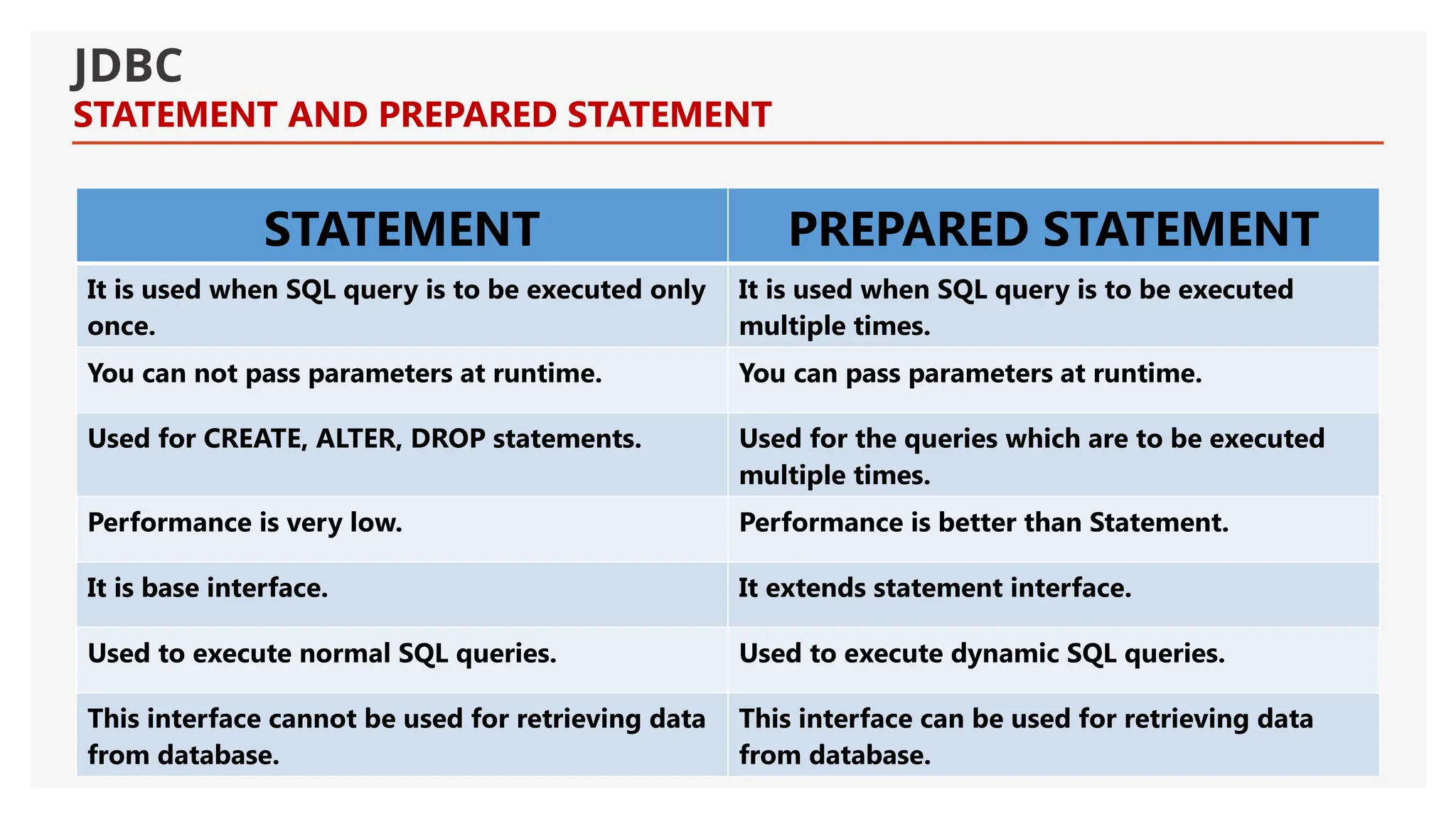
The document provides an introduction to Java Database Connectivity (JDBC), explaining its purpose as an API for connecting and interacting with databases using Java. It covers key components such as the DriverManager, drivers, connections, statements, and result sets, along with the different types of JDBC drivers. Additionally, it includes examples of establishing connections, executing SQL statements, and utilizing prepared statements for efficient database operations.