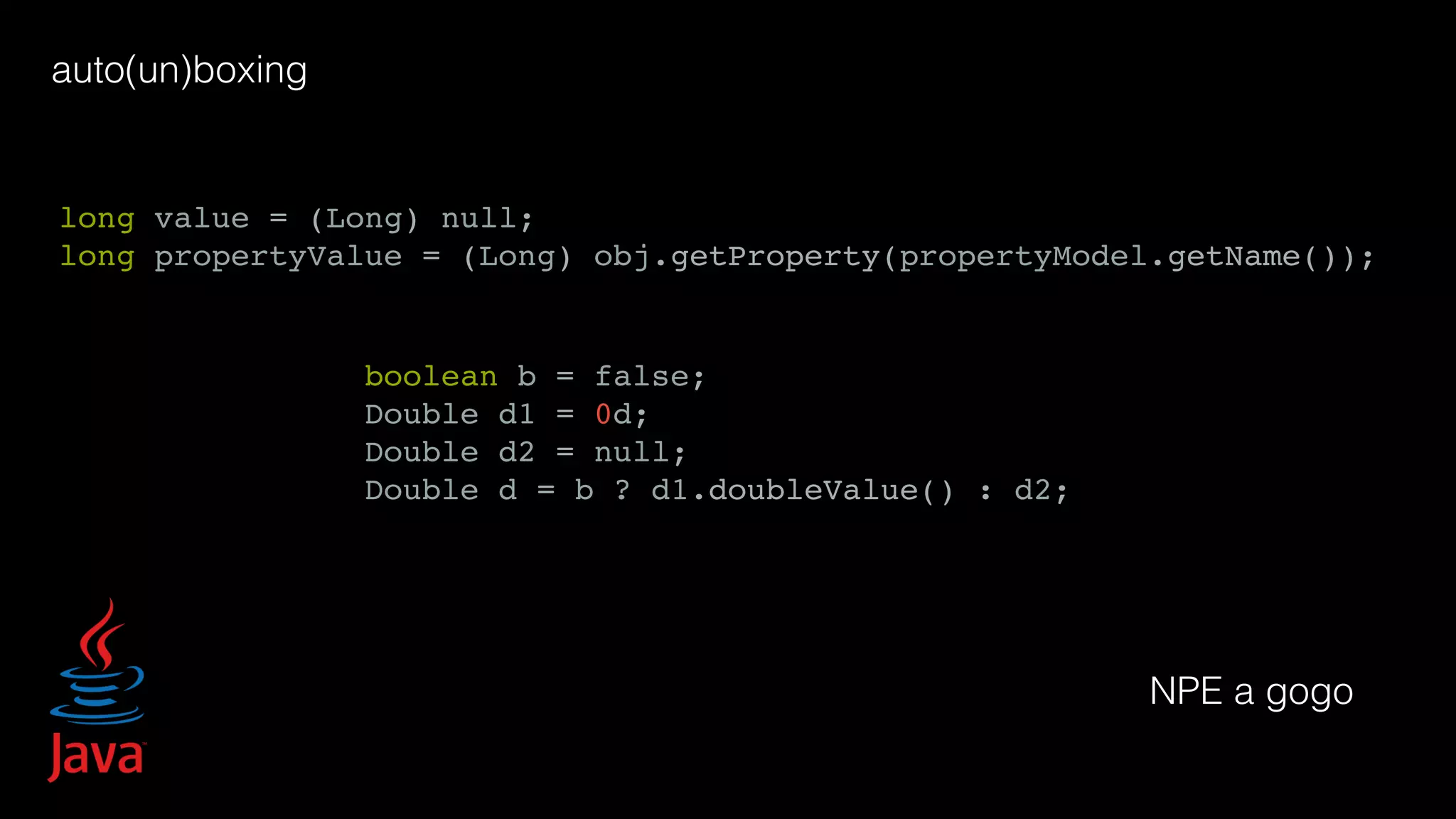
1. The code sample provided defines a simple Java class called HelloWorld with a main method that prints "Epic Fail". 2. The class contains a single public static void main method that takes an array of String arguments. 3. Within the main method it prints the text "Epic Fail" without any other processing or output.
![1 public class HelloWorld { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 print "Epic Fail" 4 } 5 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-1-2048.jpg)

















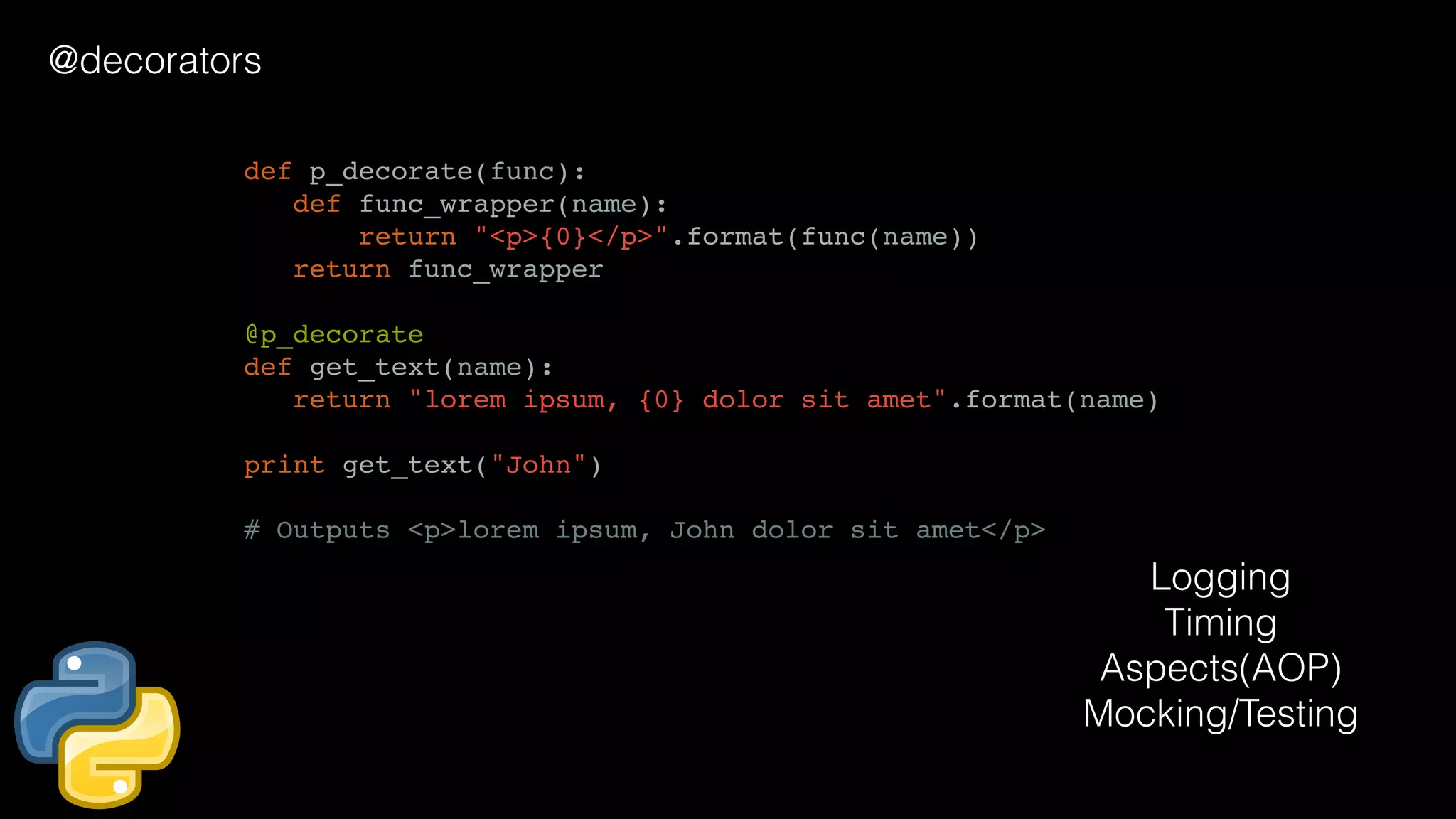
![@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface Test { public boolean enabled() default true; } public class T { @Test(enabled = false) void testB() { throw new RuntimeException("This test always passed"); } } public class M { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { for (Method method : T.class.getDeclaredMethods()) { if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Test.class)) { Annotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(Test.class); Test test = (Test) annotation; if (test.enabled()) { method.invoke(obj.newInstance()); }}}}} @annotation/metadata/reflection Logging Timing Aspects(AOP) Mocking/Testing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-34-2048.jpg)
![streams IntStream natural = IntStream.iterate(0, i -> i + 1); natural.limit(10000).sum(); LongStream fibs = Stream.iterate( new long[]{1, 1}, f -> new long[]{f[1], f[0] + f[1]}) .mapToLong(f -> f[0]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-37-2048.jpg)
![lambda f = lambda x, y : x + y f = lambda x: x**2 + 2*x - 5 mult3 = filter(lambda x: x % 3 == 0, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) square_rt = lambda x: math.sqrt(x) def sqroot(x): return math.sqrt(x) Celsius = [39.2, 36.5, 37.3, 37.8] Fahrenheit = map(lambda x: (float(9)/5)*x + 32, Celsius) reduce(lambda x,y: x+y, [47,11,42,13]) sorted(list, key=lambda i: i.last_name)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-40-2048.jpg)
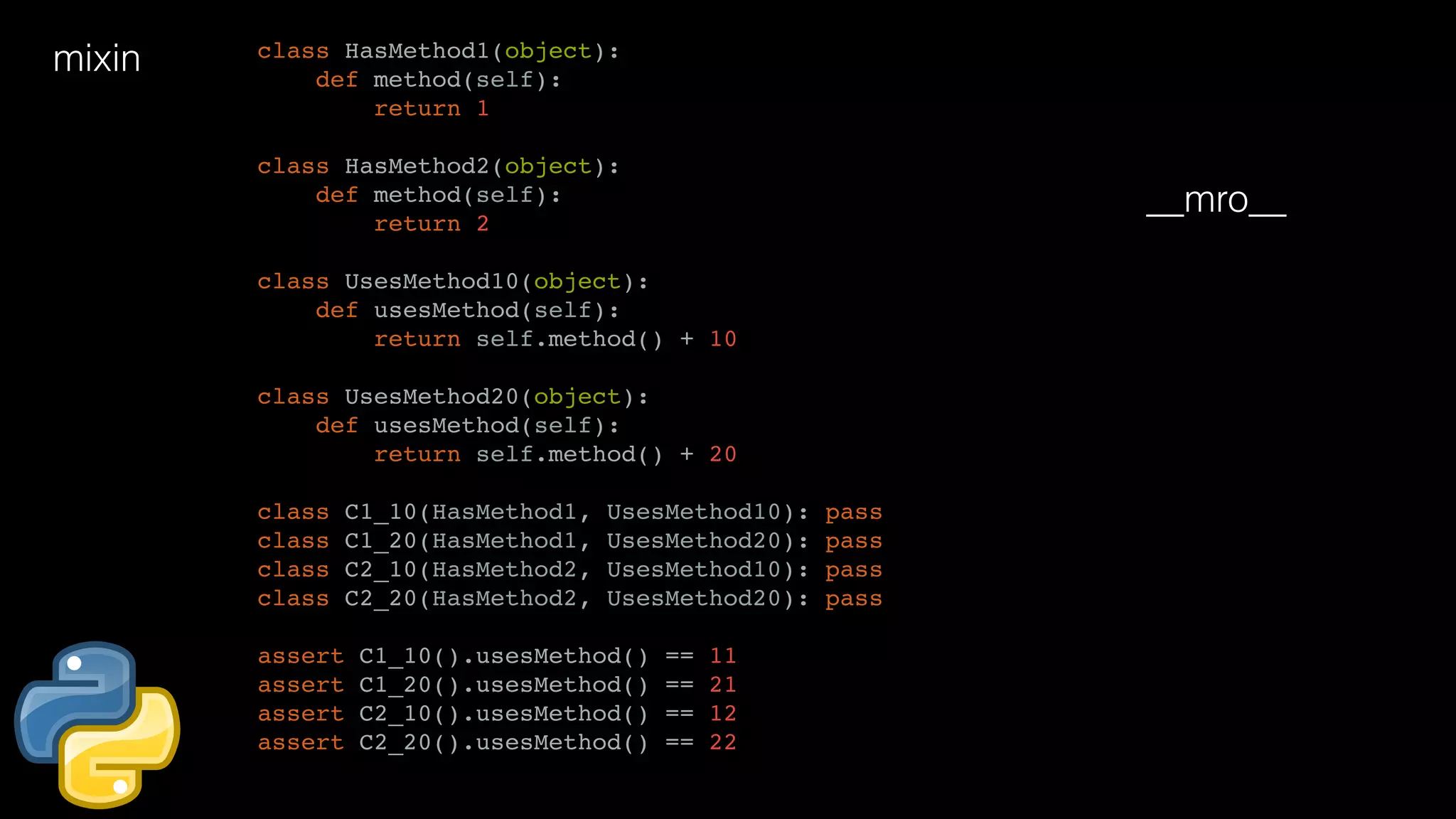
![closures def generate_power_func(n): print "id(n): %X" % id(n) def nth_power(x): return x**n print "id(nth_power): %X" % id(nth_power) return nth_power raised_to_4 = generate_power_func(4) del generate_power_func raised_to_4.__closure__ raised_to_4.__closure__[0].cell_contents](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-43-2048.jpg)
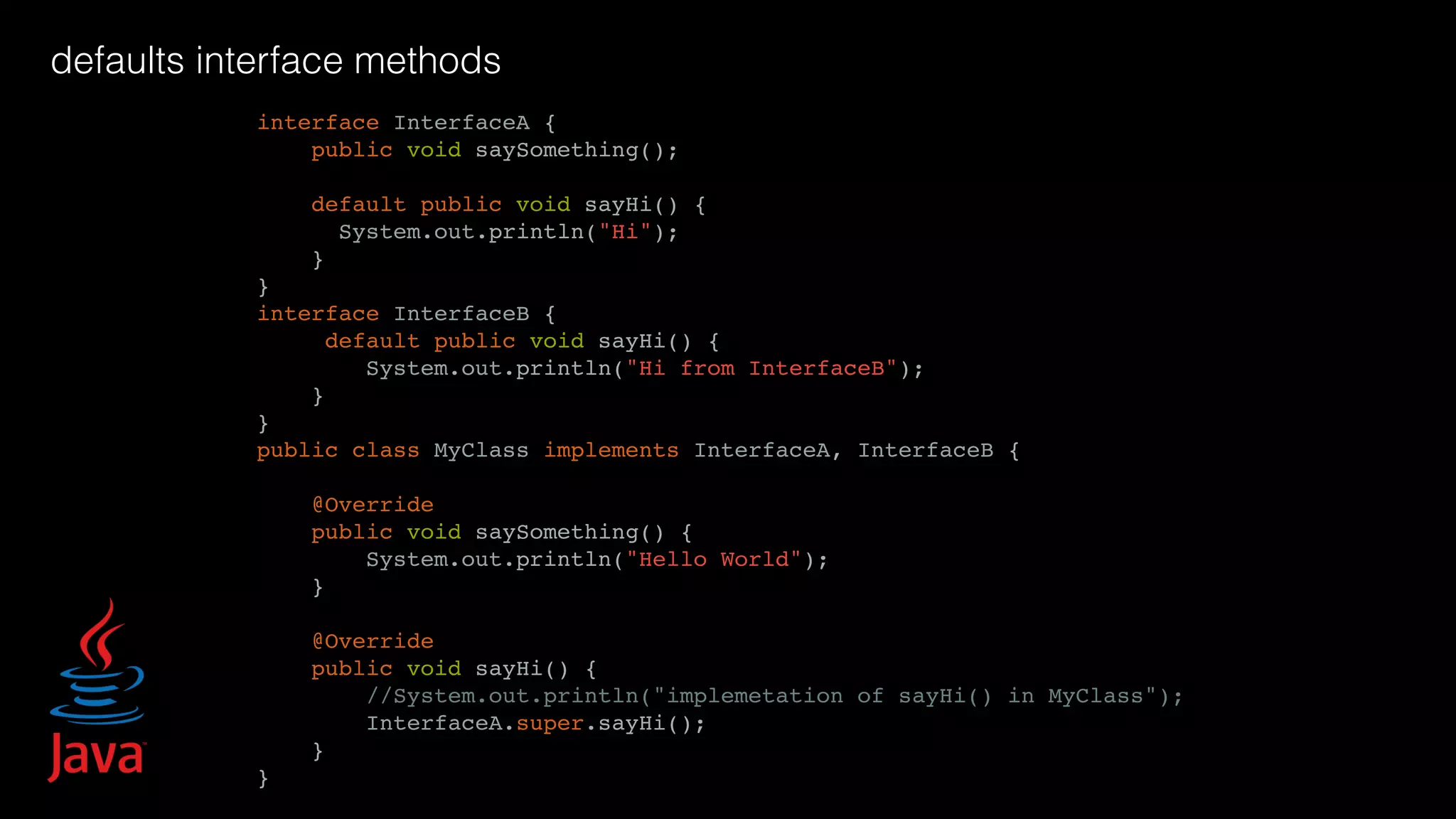
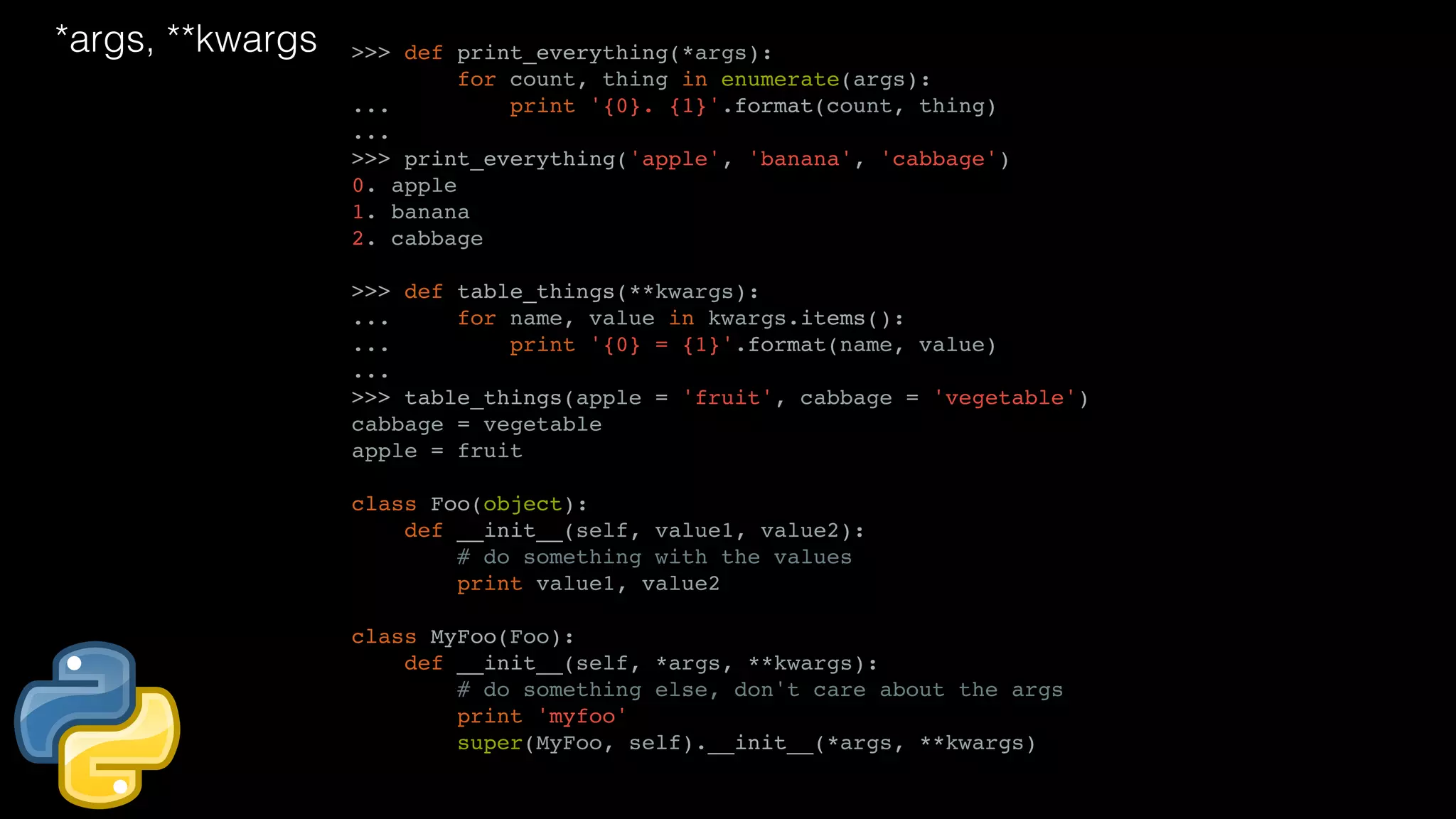
![unpacking def my_function(): return 1, 2 a, b = my_function() a = my_function()[0] import datetime t= (2010, 10, 2, 11, 4, 0, 2, 41, 0) dt = datetime.datetime(t[0], t[1], t[2], t[3], t[4], t[5], t[6]) t = (2010, 10, 2, 11, 4, 0, 2, 41, 0) dt = datetime.datetime(*t[:7]) >>> def parrot(voltage, state='a stiff', action='voom'): ... print "-- This parrot wouldn't", action, ... print "if you put", voltage, "volts through it.", ... print "E's", state, "!" ... >>> d = {"voltage": "four million", "state": "bleedin' demised", "action": "VOOM"} >>> parrot(**d) -- This parrot wouldn't VOOM if you put four million volts through it. E's bleedin' demised !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-46-2048.jpg)
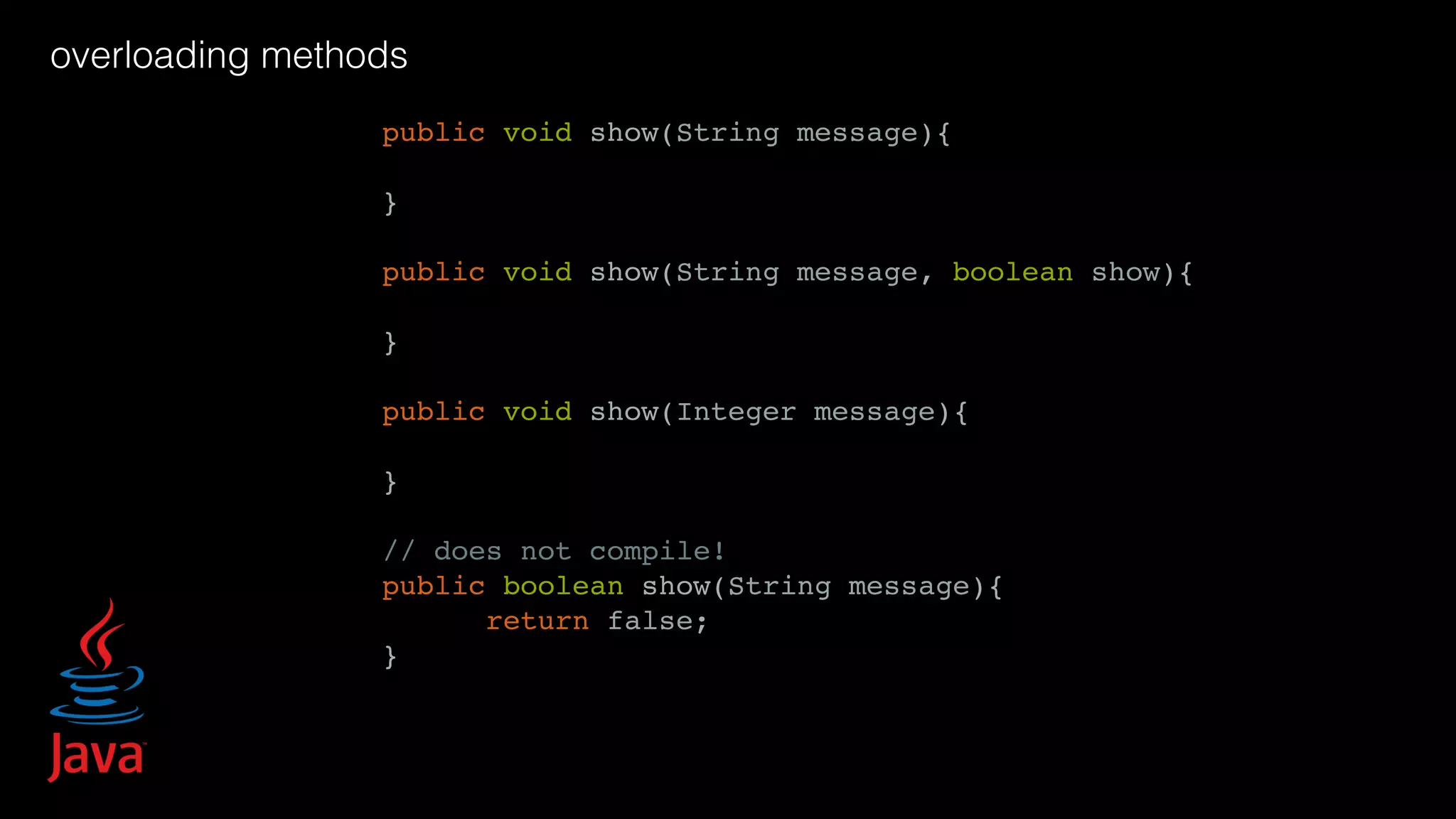
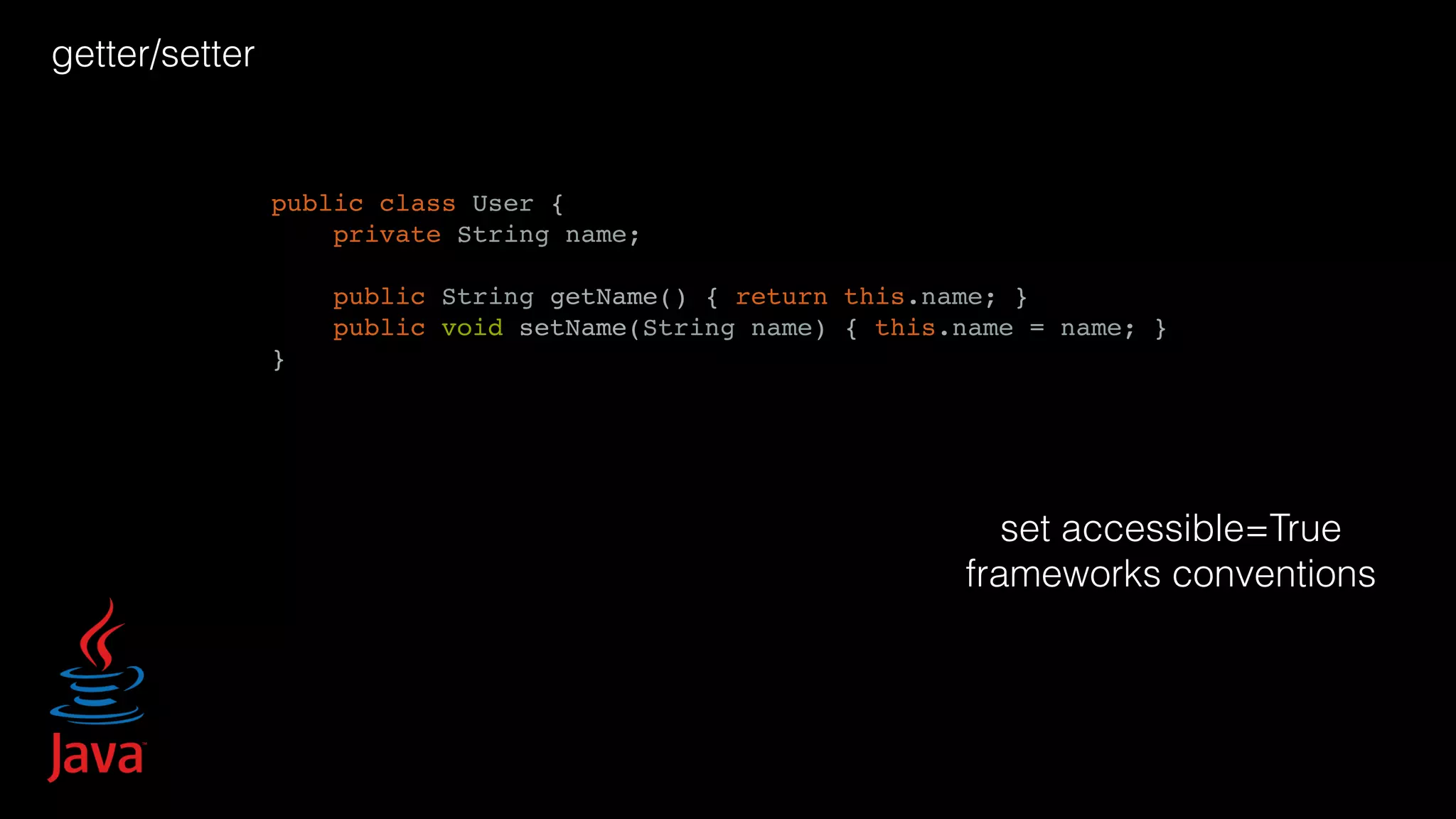
![varargs… public class HelloWorldVarargs { public static void main(String args[]) { test(215, "India", "Delhi"); test(147, "United States", "New York", "California"); } public static void test(int some, String... args) { System.out.print("n" + some); for(String arg: args) { System.out.print(", " + arg); } } } class Logger { void error(Marker marker, String message, Object... params) }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-49-2048.jpg)
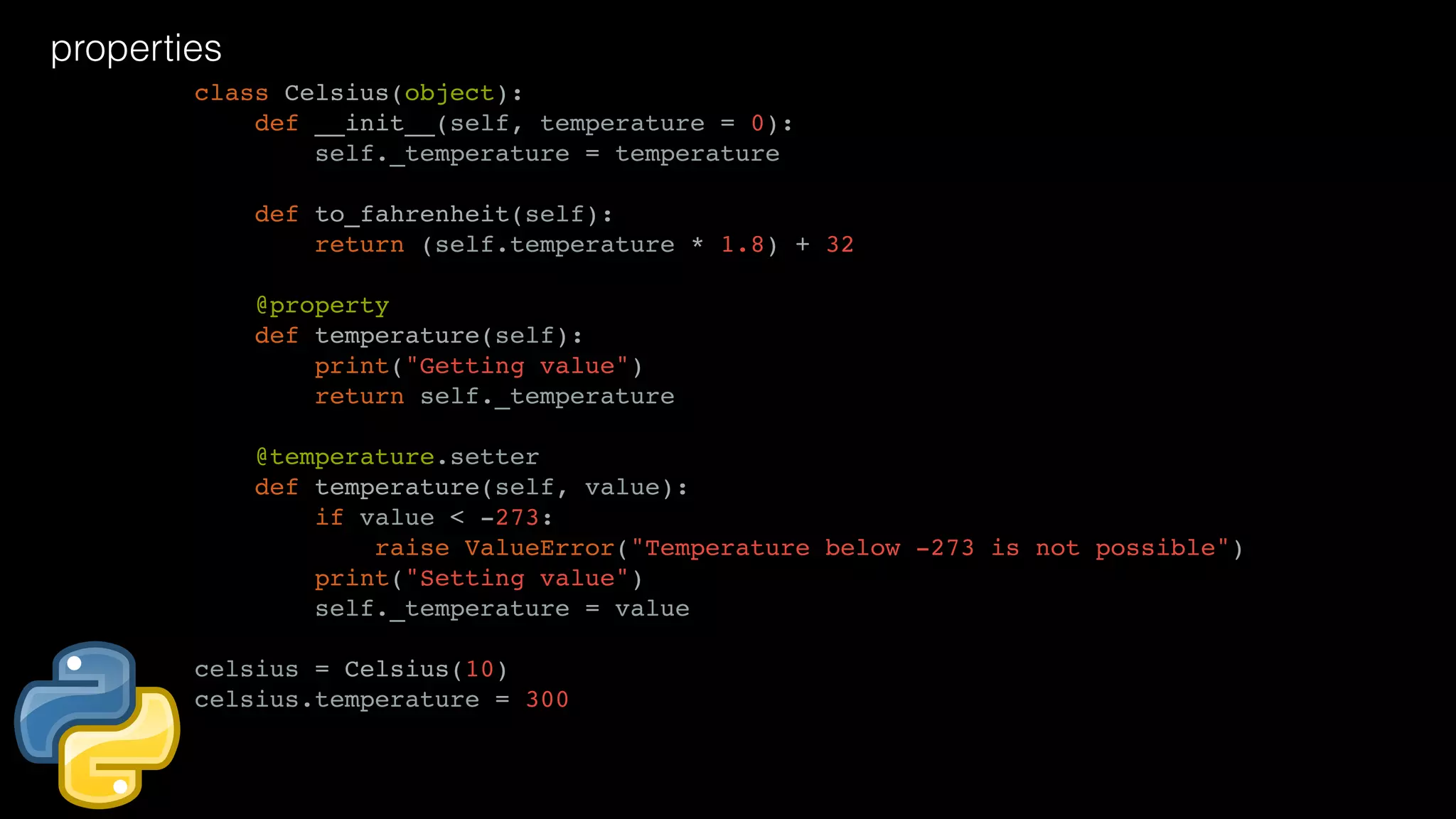
![list comprehension >>> S = [x**2 for x in range(10)] >>> V = [2**i for i in range(13)] >>> M = [x for x in S if x % 2 == 0] >>> noprimes = [j for i in range(2, 8) for j in range(i*2, 50, i)] >>> primes = [x for x in range(2, 50) if x not in noprimes] >>> print primes [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47] >>> words = 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog'.split() >>> stuff = [[w.upper(), w.lower(), len(w)] for w in words] ['THE', 'the', 3] ['QUICK', 'quick', 5] ... l = [['40', '20', '10', '30'], ['20', '20', '20'], ['100', '100'], ['100', '100', '100']] [[float(y) for y in x] for x in l] >>> d = {n: n**2 for n in range(5)} >>> print d {0: 0, 1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 4: 16}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-53-2048.jpg)
![list slicing a[start:end] # items start through end-1 a[start:] # items start through the rest of the array a[:end] # items from the beginning through end-1 a[:] # a copy of the whole array There is also the step value, which can be used with any of the above: a[start:end:step] # start through not past end, by step a[-1] # last item in the array a[-2:] # last two items in the array a[:-2] # everything except the last two items](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-54-2048.jpg)
![__metaclass__ >>> class Printable(type): ... def whoami(cls): print "I am a", cls.__name__ ... >>> Foo = Printable('Foo',(),{}) >>> Foo.whoami() I am a Foo >>> Printable.whoami() Traceback (most recent call last): TypeError: unbound method whoami() [...] >>> class Bar: ... __metaclass__ = Printable ... def foomethod(self): print 'foo' ... >>> Bar.whoami() I am a Bar >>> Bar().foomethod() foo # metaclass magic methods # def __new__(cls, name, bases, dict): # def __init__(self, name, bases, dict):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapython-151126213736-lva1-app6892/75/Java-VS-Python-56-2048.jpg)