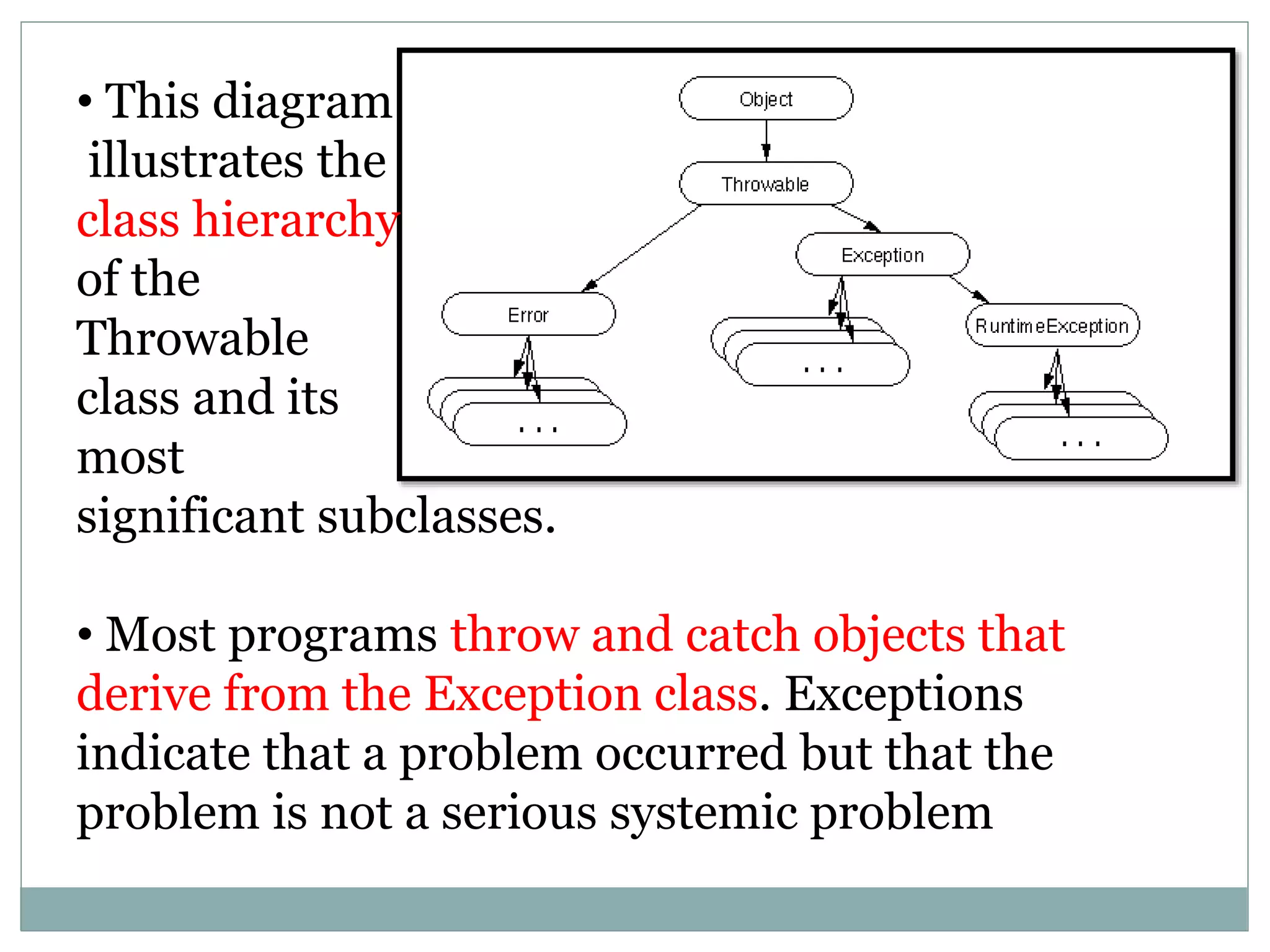
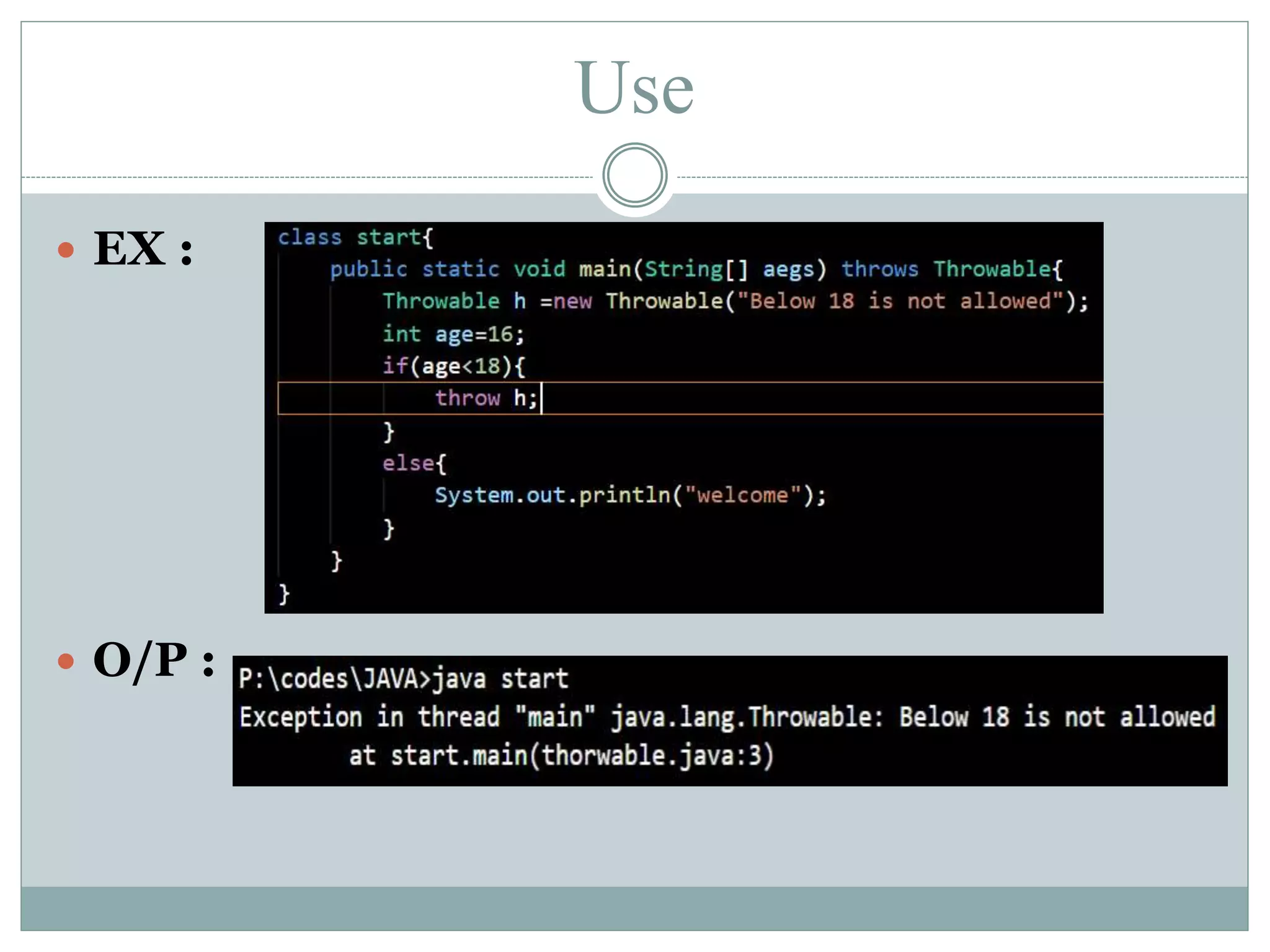
The document explains the Throwable class in Java, which serves as the superclass for all errors and exceptions. It details the class's constructors, methods, and its role in exception handling, emphasizing that only instances of this class and its subclasses can be thrown or caught in Java. The document also includes examples of constructors and methods associated with Throwable.