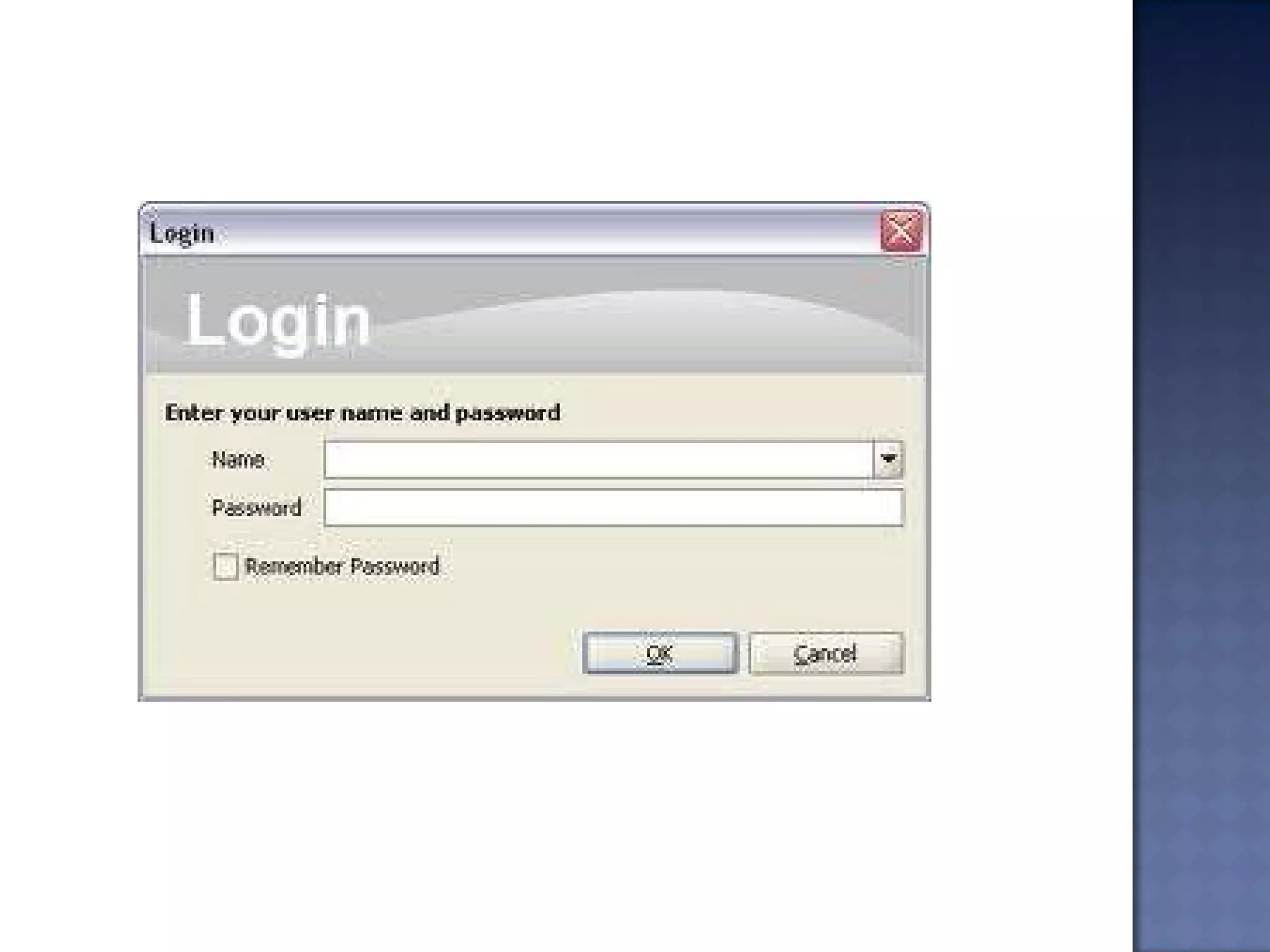
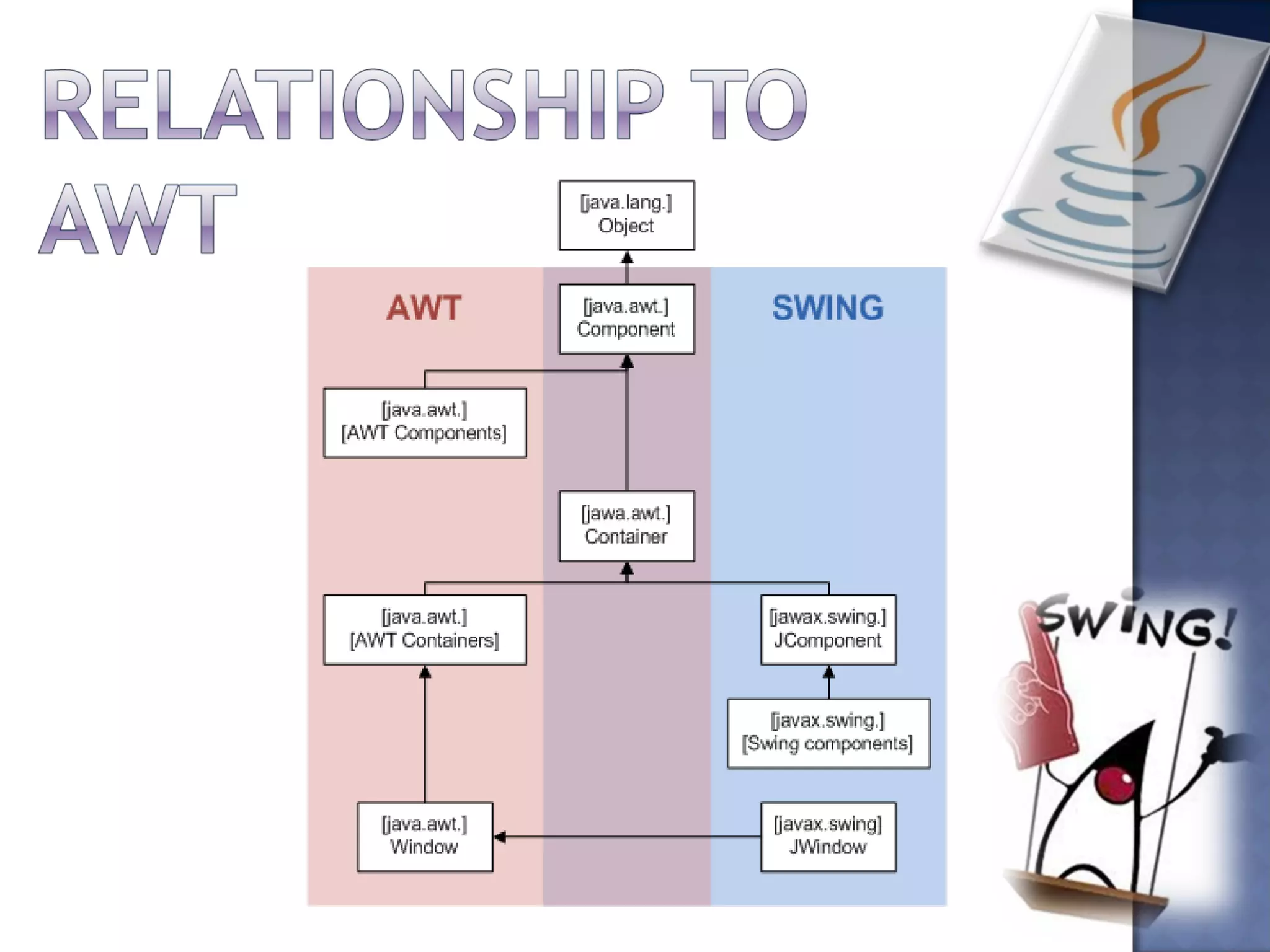
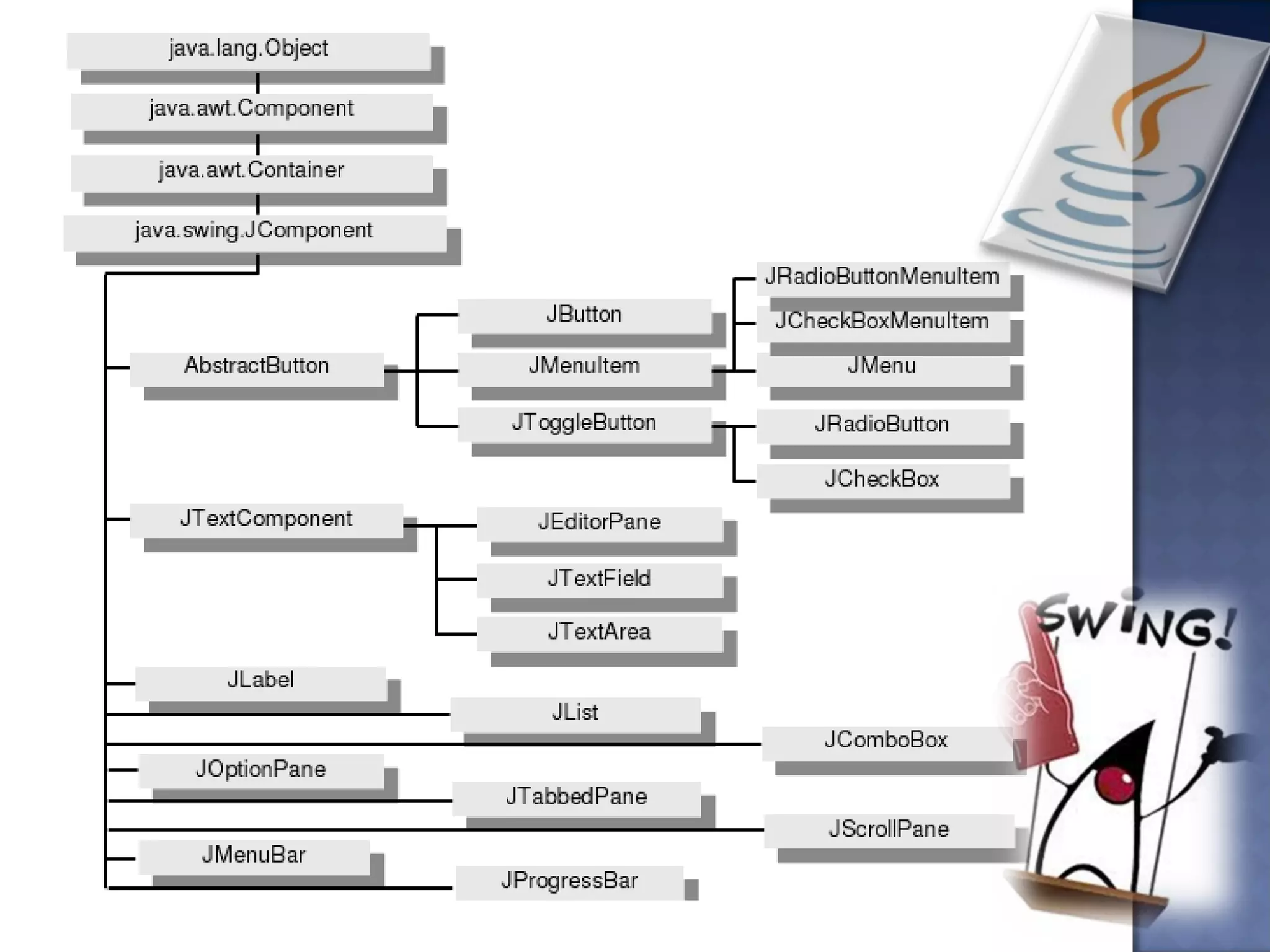
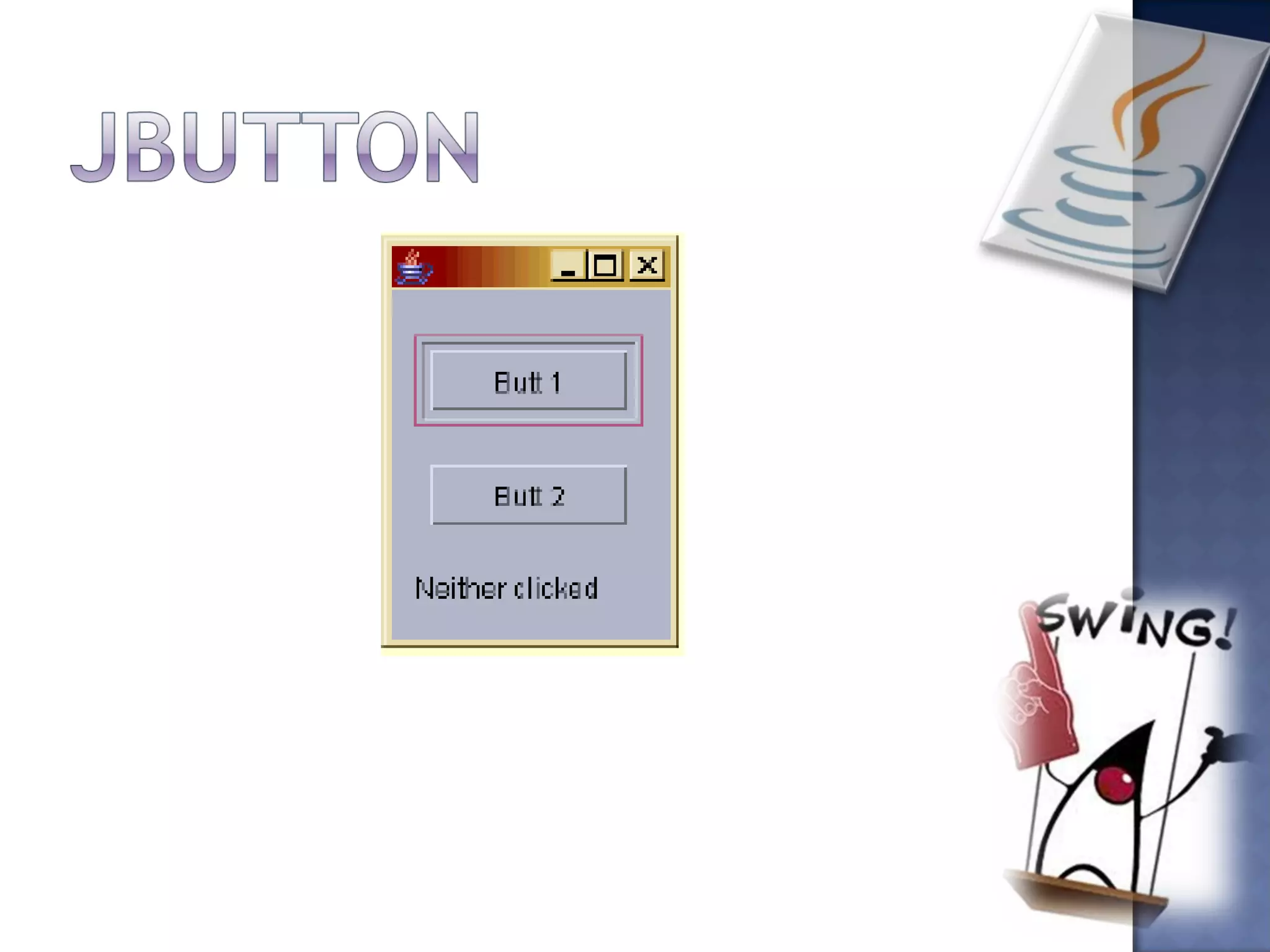
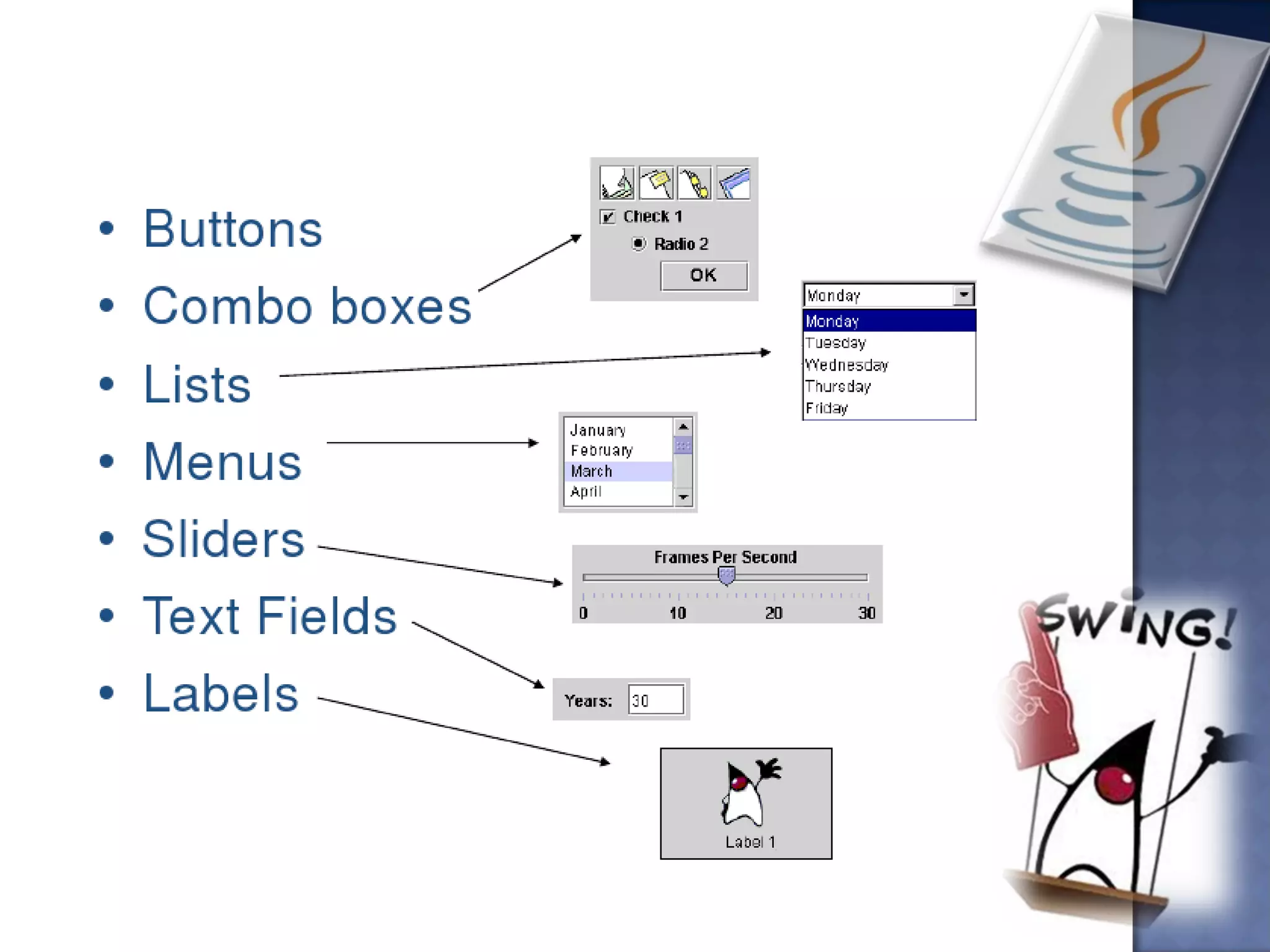
Swing is the primary Java GUI widget toolkit. It is highly customizable and extensible, allowing users to override default implementations and extend the framework. Swing components are lightweight because they do not require allocating native operating system resources. Common Swing components include buttons, lists, menus, frames, and panels.