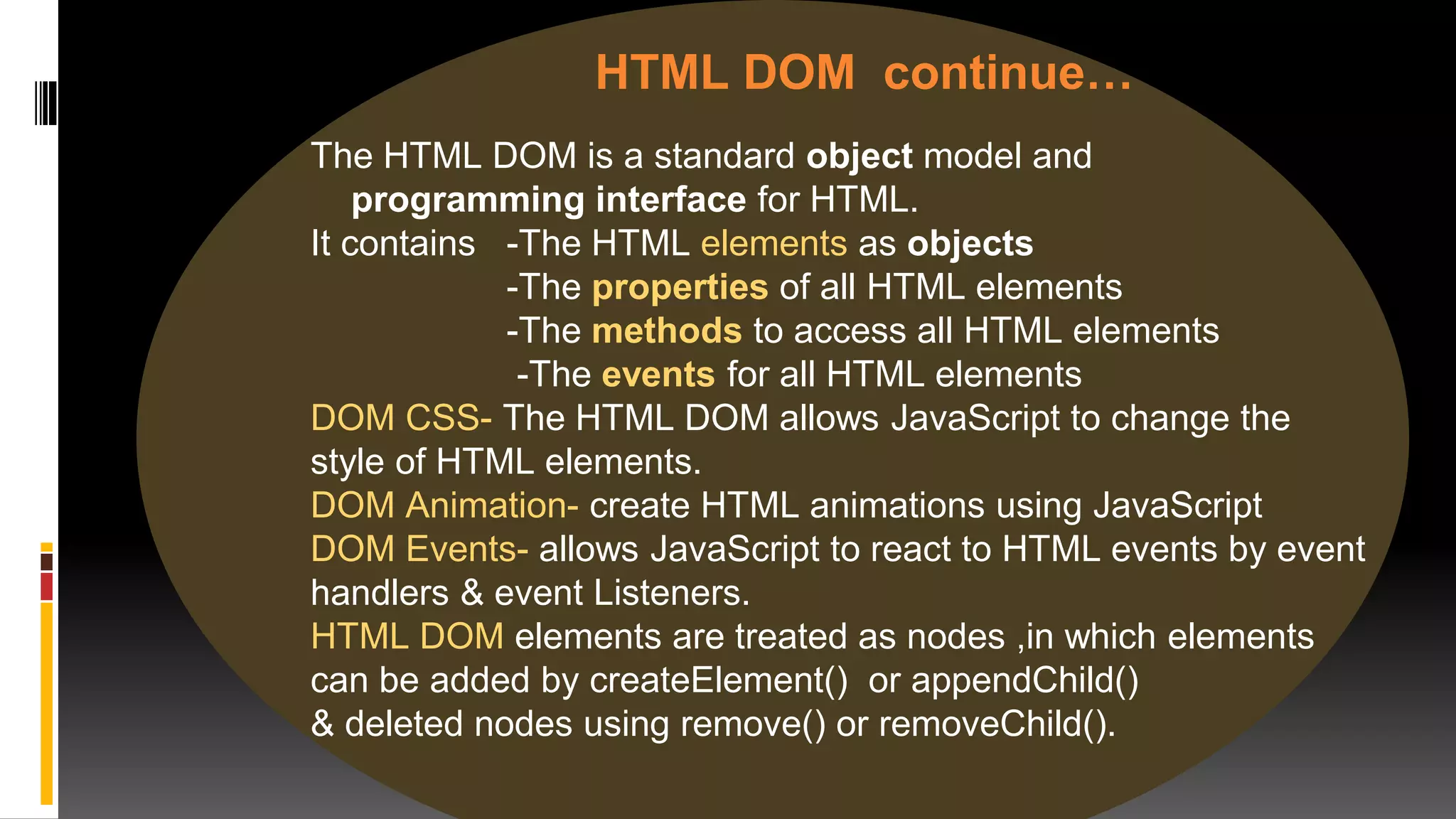
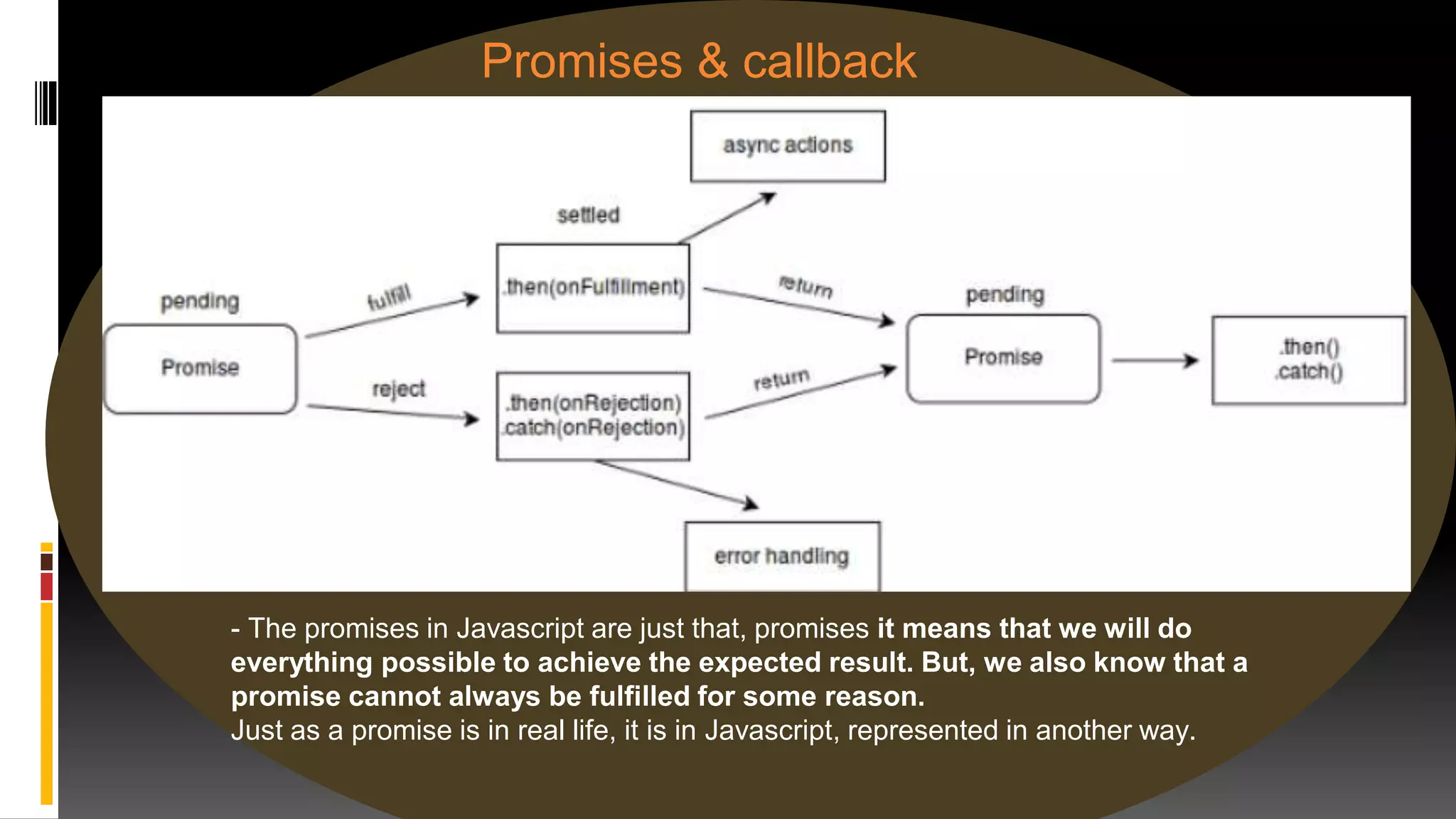
The document discusses various web frameworks including Node.js, Express.js, and Django. It provides an introduction to each framework, explaining what they are used for and some of their main features. Node.js is introduced as a framework for running JavaScript on the server and some of its core modules are described. Express.js is presented as a web application framework built on Node.js. Django is introduced as a Python web framework that allows for quick development with minimal code.





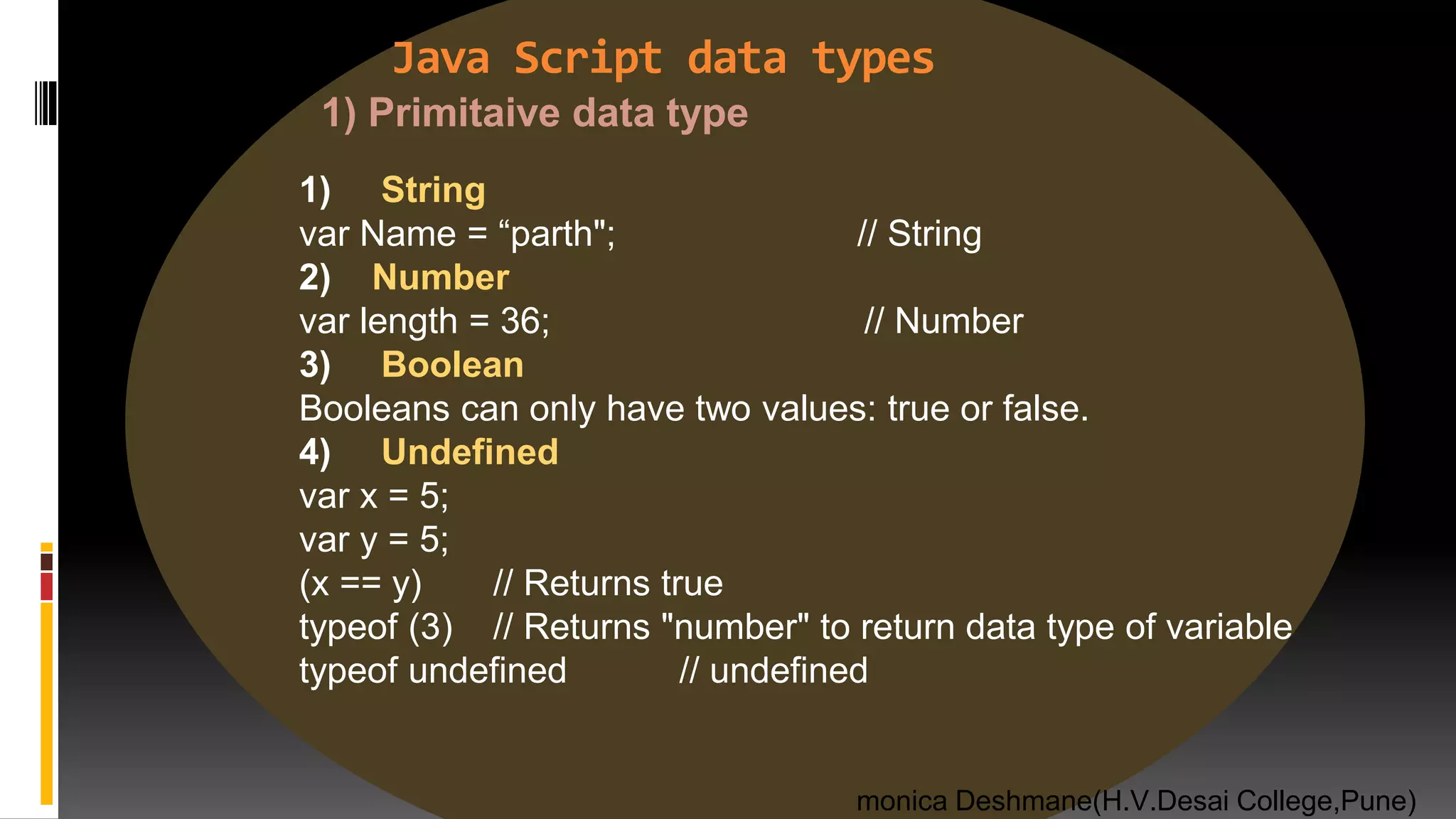
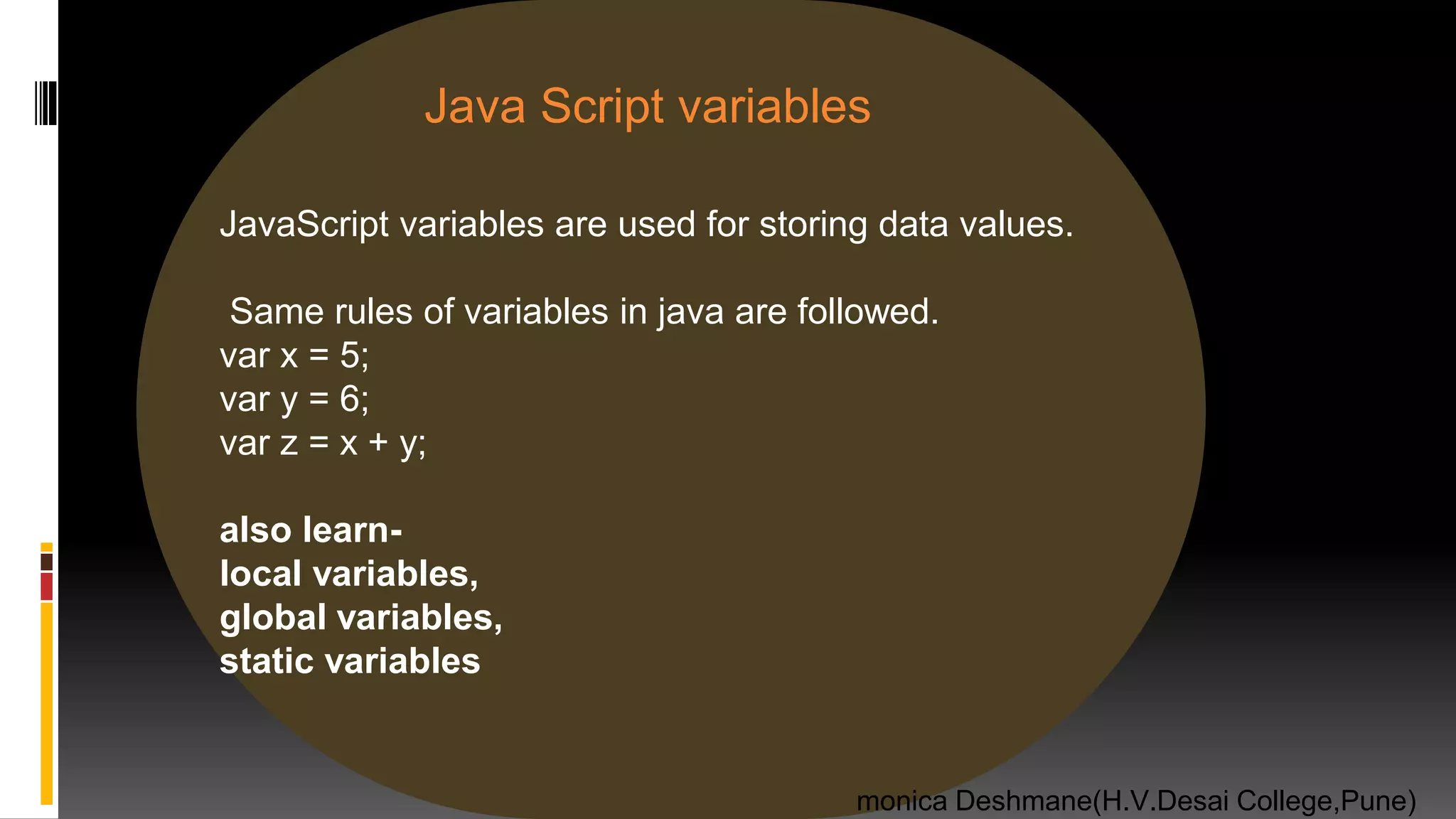
![Java Script data types 1) Function function myFunction() { } 2) Object var x = {firstName:"John", lastName:“Ray"}; // Object 3) Array var cars = [“suzuki", "VagonR", "BMW"]; //array var person = null; //null //diffrence between null & undefined 1) typeof undefined // undefined typeof null // object 2) null === undefined // false null == undefined // true monica Deshmane(H.V.Desai College,Pune) 2)complex data types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-10-2048.jpg)
![JS Types:Revise You can divide JavaScript types into 2 groups 1) primitive - are number, Boolean, string, null 2) complex -are array ,functions ,and objects //primitive Var A=5; Var B=A; B=6; A; //5 B; //6 //complex or reference types Var A=[2,3]; Var B=A; B[0]=3; A[0]; //3 B[0]; //3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-11-2048.jpg)
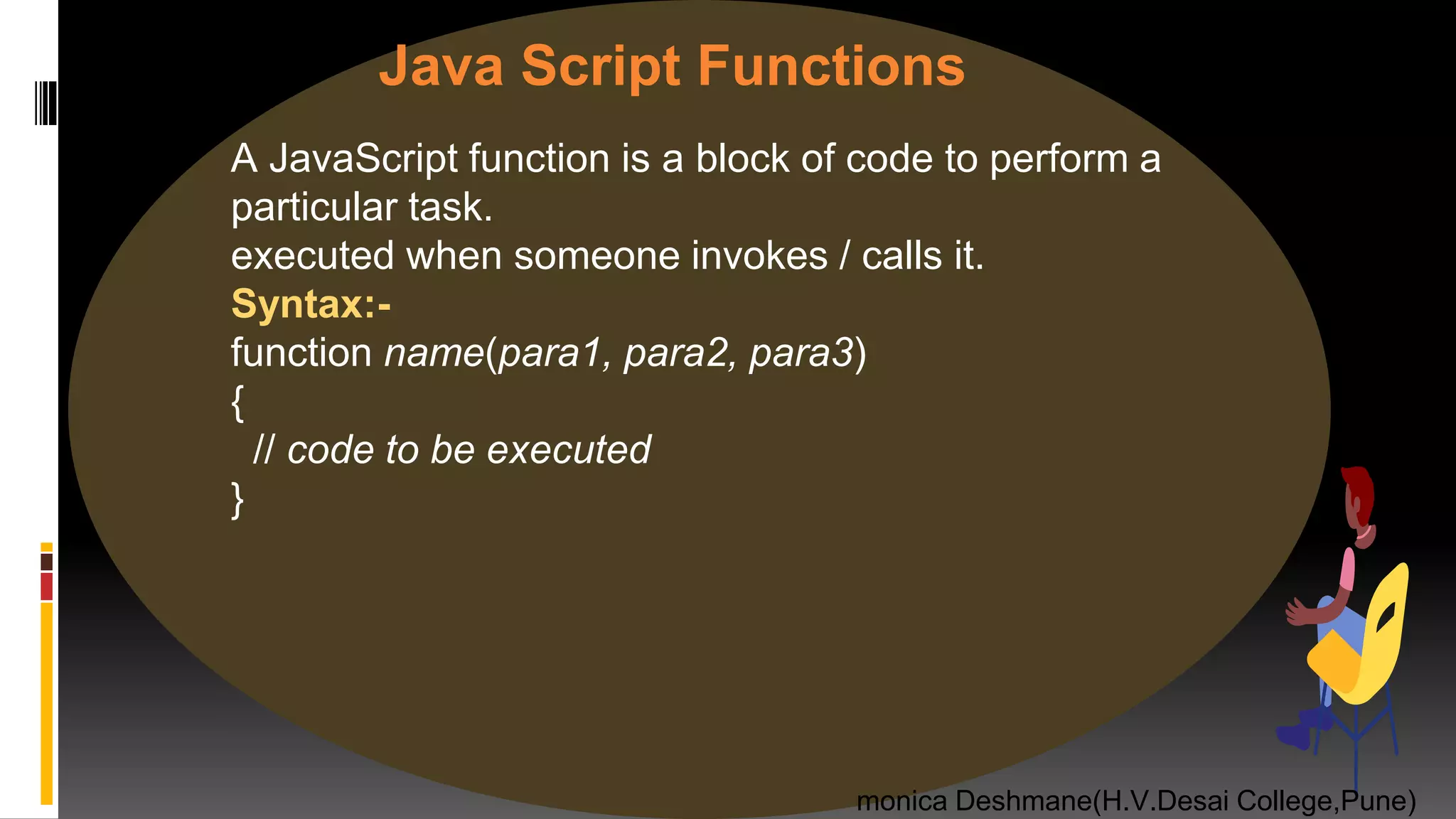

![var f=function f() { typeof f== “function”; //true window==this; //true //as this is global object } .call & .apply method-To change reference of this to any other object when calling function. function a() {this.a==‘b’; //true} funcation a(b,c){ b==‘first’; //true c==‘second’; //true } a.call((a:’b’),’first’,’second’); //call takes list of parameters to pass function a.apply({a:’b’},[’first’,’second’]); //apply takes array of parameters to pass function monica Deshmane(H.V.Desai College,Pune) Some concepts about function..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-15-2048.jpg)



![Patterns Character classes [:alum:] Alphanumeric characters [0-9a-zA-Z] [:alpha:] Alphabetic characters [a-zA-Z] [:blank:] space and tab [ t] [:digit:] Digits [0-9] [:lower:] Lower case letters [a-z] [:upper:] Uppercase letters [A-Z] [:xdigit:] Hexadecimal digit [0-9a-fA-F] range of characters ex. [‘aeiou’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-19-2048.jpg)

![Array in Java Script monica Deshmane(H.V.Desai College,Pune) 1. Array creation • var arr1 = new Array(); OR • var arr2 = [ ]; arr2.push(1); arr2.push(2); //[1,2] arr1.sort(); • var arr3 = [ ‘mat', 'rat', 'bat' ]; 2. Length arr2.length; console.log(arr2); 3. To delete element from array arr3.splice(2, 2); arr.pop(); //see demo on JS.do](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-22-2048.jpg)
![Array splice in Java Script monica Deshmane(H.V.Desai College,Pune) <script> var lang = ["HTML", "CSS", "JS", "Bootstrap"]; document.write(lang + "<br>"); var removed = lang.splice(2, 1, 'PHP', ‘python') document.write(lang + "<br>"); // HTML,CSS,JS,Bootstrap document.write(removed + "<br>"); // HTML,CSS,PHP,python,Bootstrap // No Removing only Insertion from 2nd index from the ending lang.splice(-2, 0, 'React') // JS document.write(lang) // HTML,CSS,PHP,React,python,Bootstrap </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-23-2048.jpg)
![Array continue… monica Deshmane(H.V.Desai College,Pune) Array is like u so before the typeof operator will return “object” for arrays more times however you want to check that array is actually an array. Array.isArray returns true for arrays and False for any other values. Array.isArray( new array) // true Array.isArray( [ ] ) // true Array.isArray( null) // false Array.isArray(arguments ) //false](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-24-2048.jpg)
![Array continue… monica Deshmane(H.V.Desai College,Pune) See –tutorials point javascript arrays array methods • to loop over an array you can use for each (Similar to jquery $.each) [1,2,3].foreach(function value) { console.log (value ); } •To filter elements out of array you can use filter (similar two jQuery grep) [1,2,3].foreach(function value) { return value < 3; } //will return [ 1, 2] •to change value of of each item you can use map (similar to Jquery map) [ 5,10 ,15].map function (value) { return value*2; } // will return [10 ,20 ,30] • also available but less commonly used are the methods- reduce , reduceRight and lastIndexOf.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-25-2048.jpg)
![Array continue… monica Deshmane(H.V.Desai College,Pune) •reduceRight:-Subtract the numbers in the array, starting from the right: <script> var numberarr= [175, 50, 25]; document.getElementById(“p1").innerHTML = numberarr.reduceRight(myFunc); function myFunc(total, num) { return total - num; } •Reduce-from left to right •lastIndexOf- const animals = ['Dog', 'Tiger', 'Penguin','Dog']; console.log(animals.lastIndexOf('Dog'));// expected output: 3 console.log(animals.lastIndexOf('Tiger'));// expected output: 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-26-2048.jpg)
![•Object Creation var obj1 = new Object(); var obj2 = { }; var subject = { first_name: "HTML", last_name: "CSS“ , reference: 320 ,website: "java2s.com" }; •add a new property subject.name= "brown"; OR subject["name"] = "brown"; •To delete a new property delete subject.name; •To get all keys from object var obj={a:’aaa’, b:’bbb’ ,c:’ccc’}; Object.keys(obj); //[‘a’ ,’b’, ‘c’] Objects in Java Script](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1javascriptwebframeworkfinallydoneslideshare-200721174547/75/java-script-27-2048.jpg)