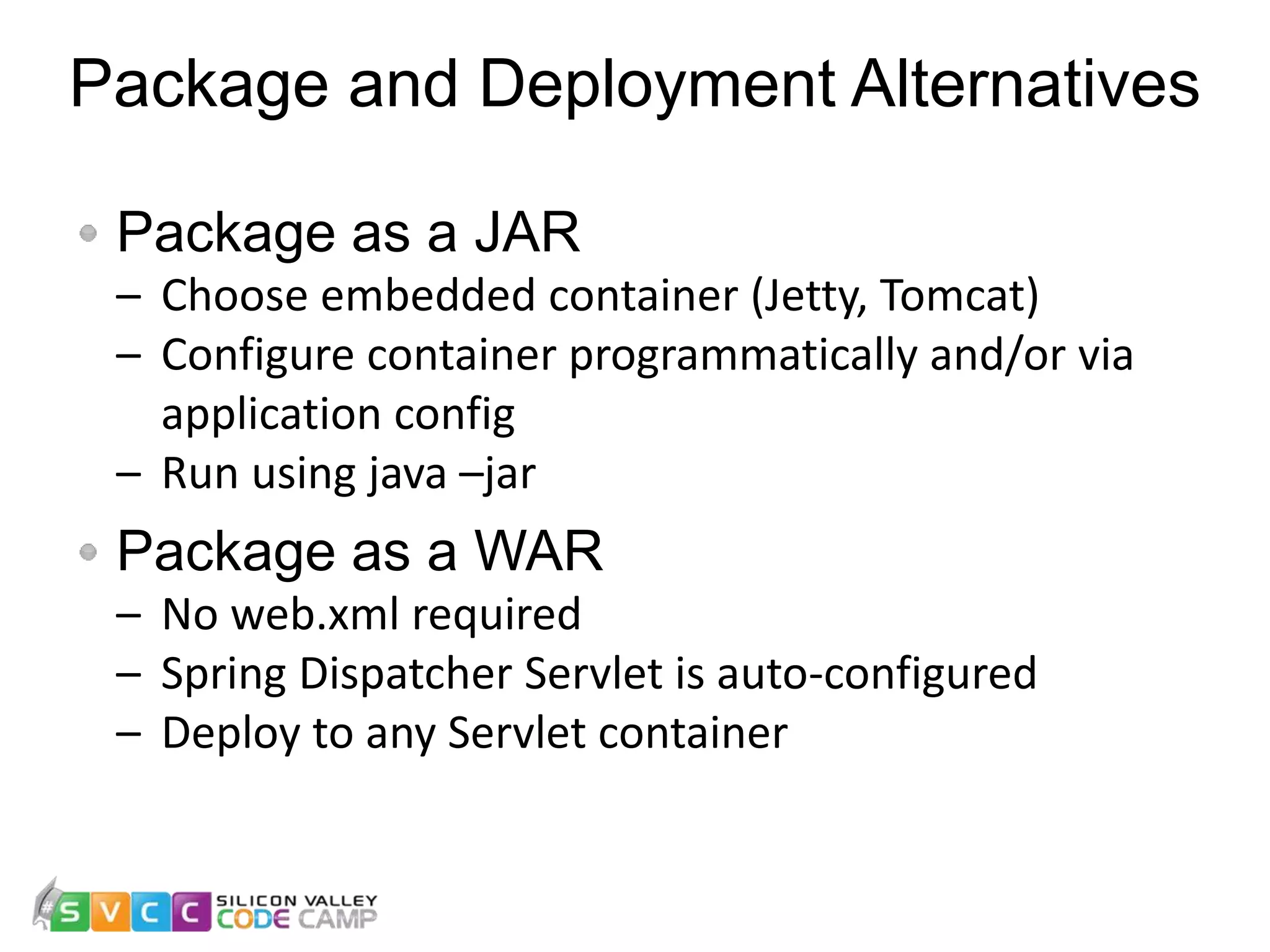
Tim Hobson presented on using Spring Boot for rapid application development. He discussed why Spring Boot helps enable rapid development through its use of auto-configuration, starter dependencies, and built-in production-ready features. He showed how an application can be developed quickly with Spring Boot by focusing on domain logic rather than infrastructure configuration. His code example demonstrated exploring Spring Boot features like controllers, security, persistence, and monitoring in just a few days of development.