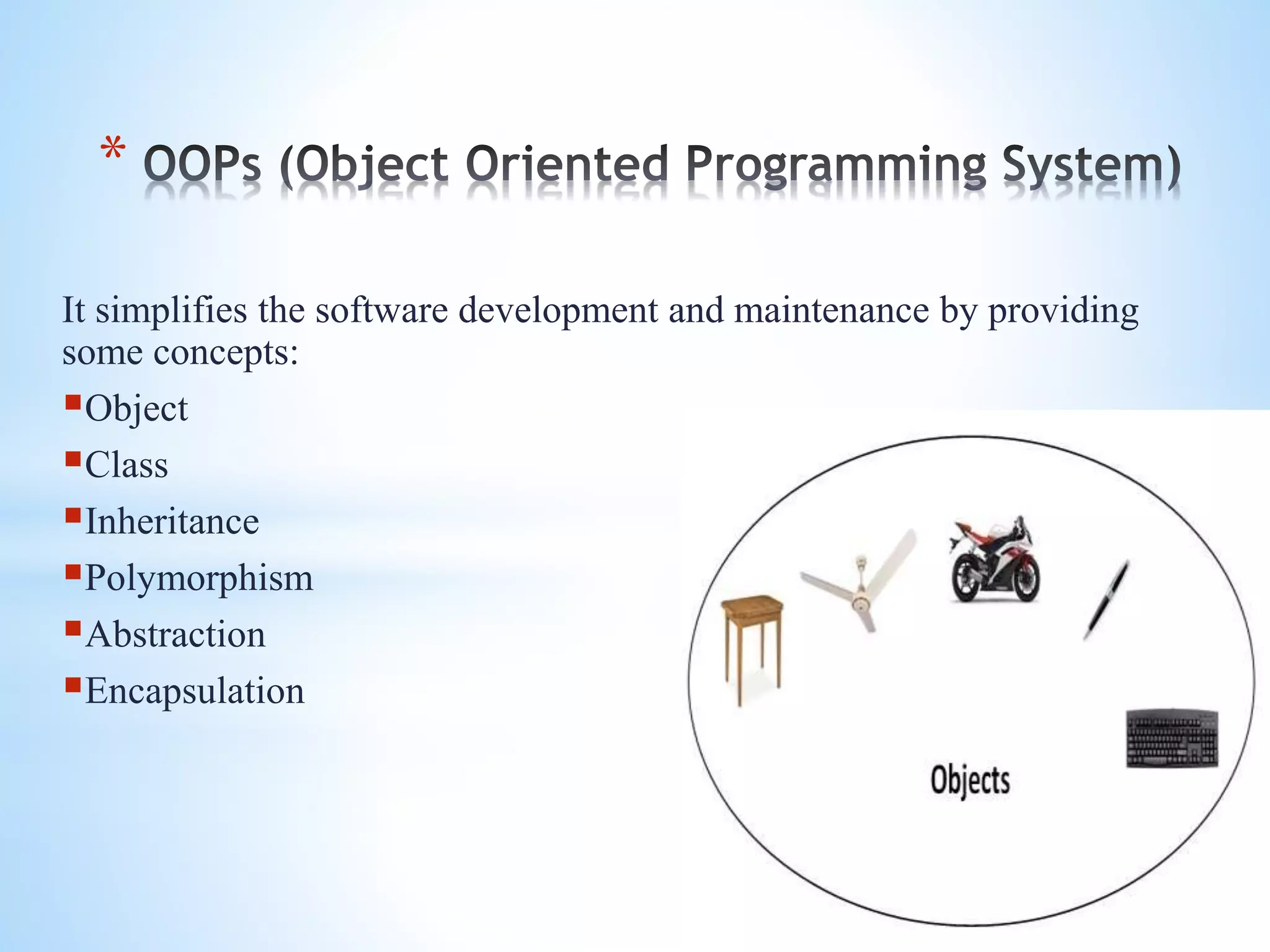
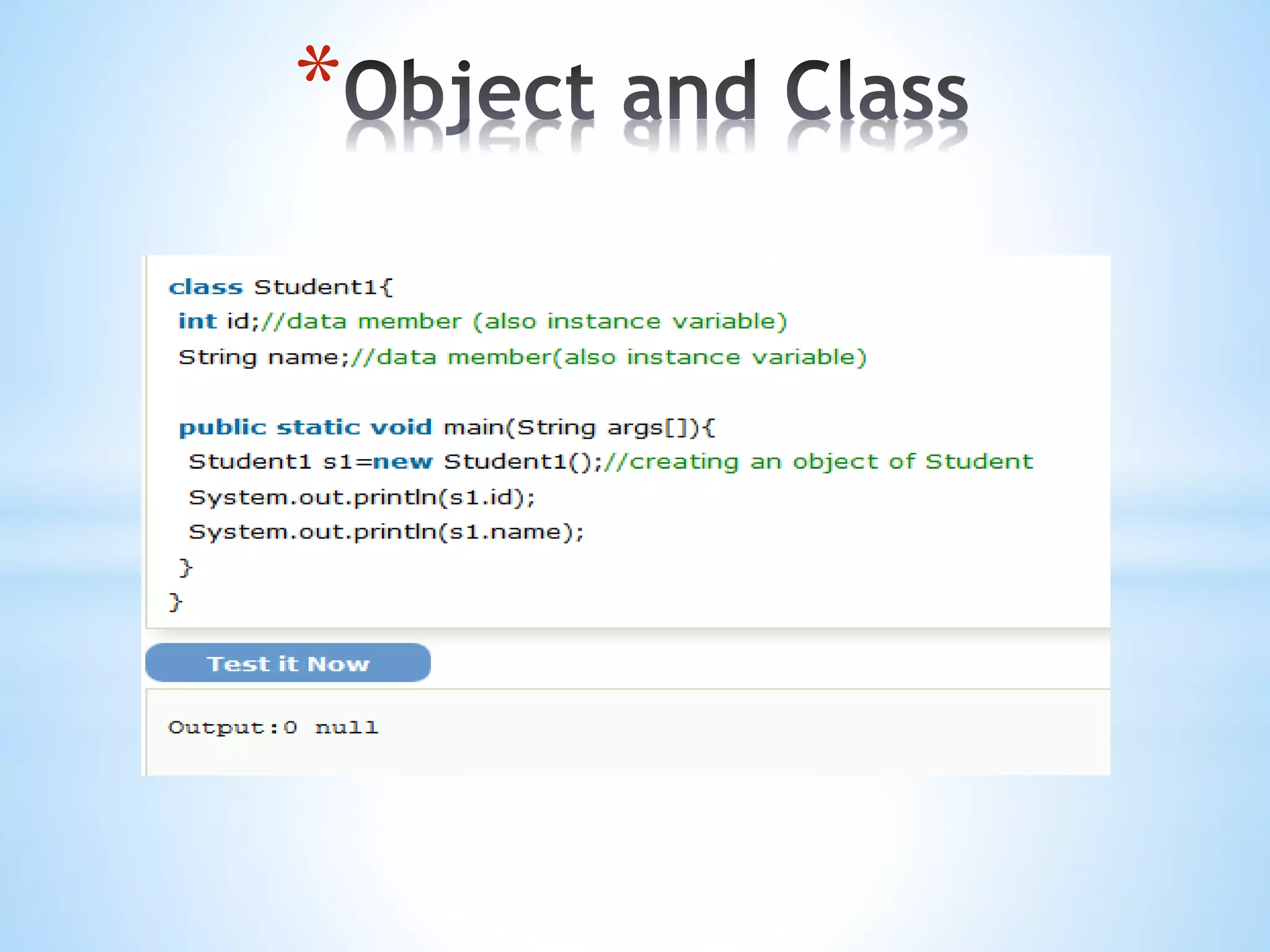
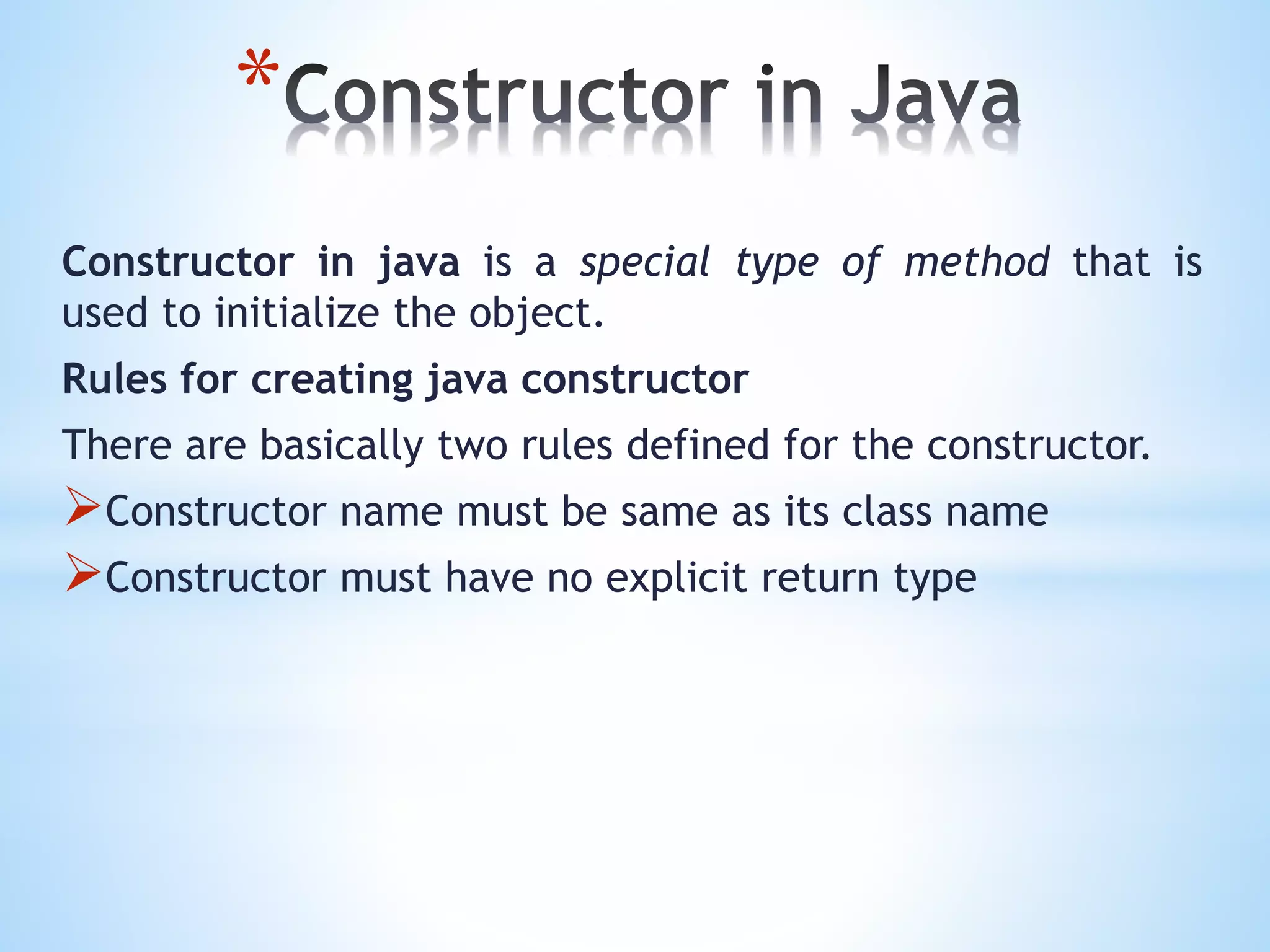
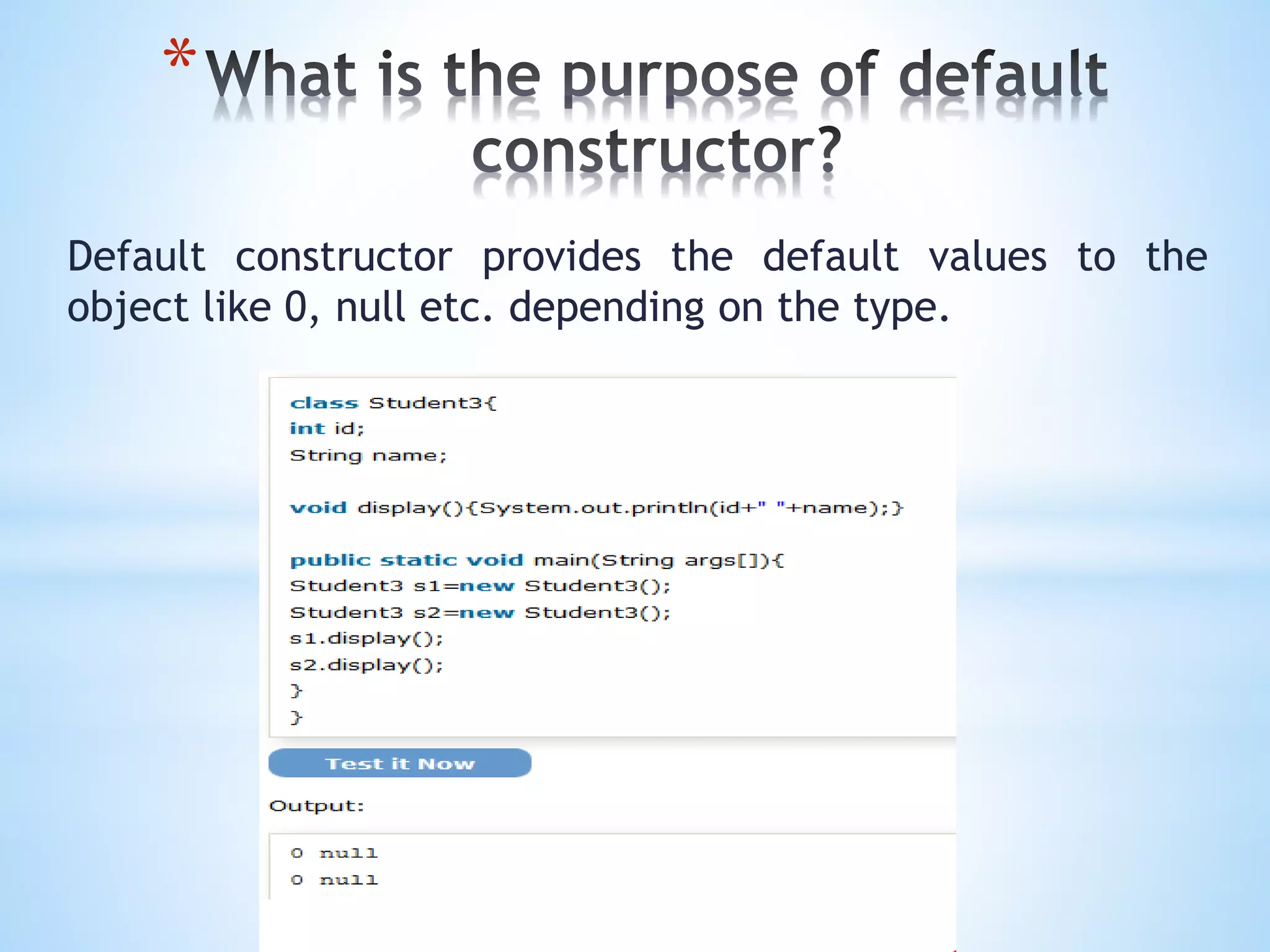
The document discusses key concepts in Object Oriented Programming including objects, classes, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. It defines each concept and provides examples. Objects have state, behavior, and identity. A class is a template for creating objects that share common properties. Inheritance allows an object to acquire properties of a parent object. Polymorphism allows one task to be performed in different ways. Abstraction hides internal details and shows functionality. Encapsulation binds code and data into a single unit.