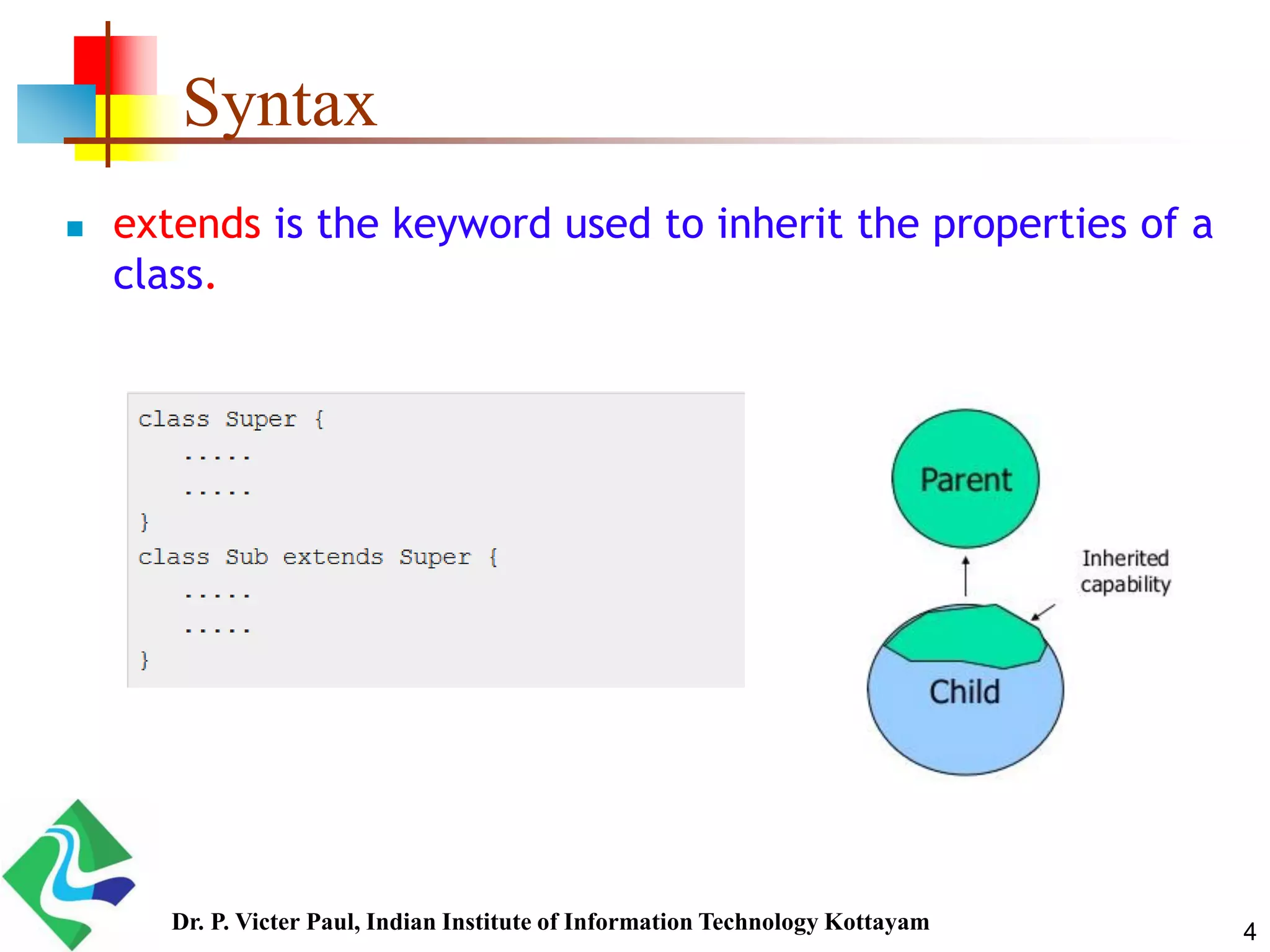
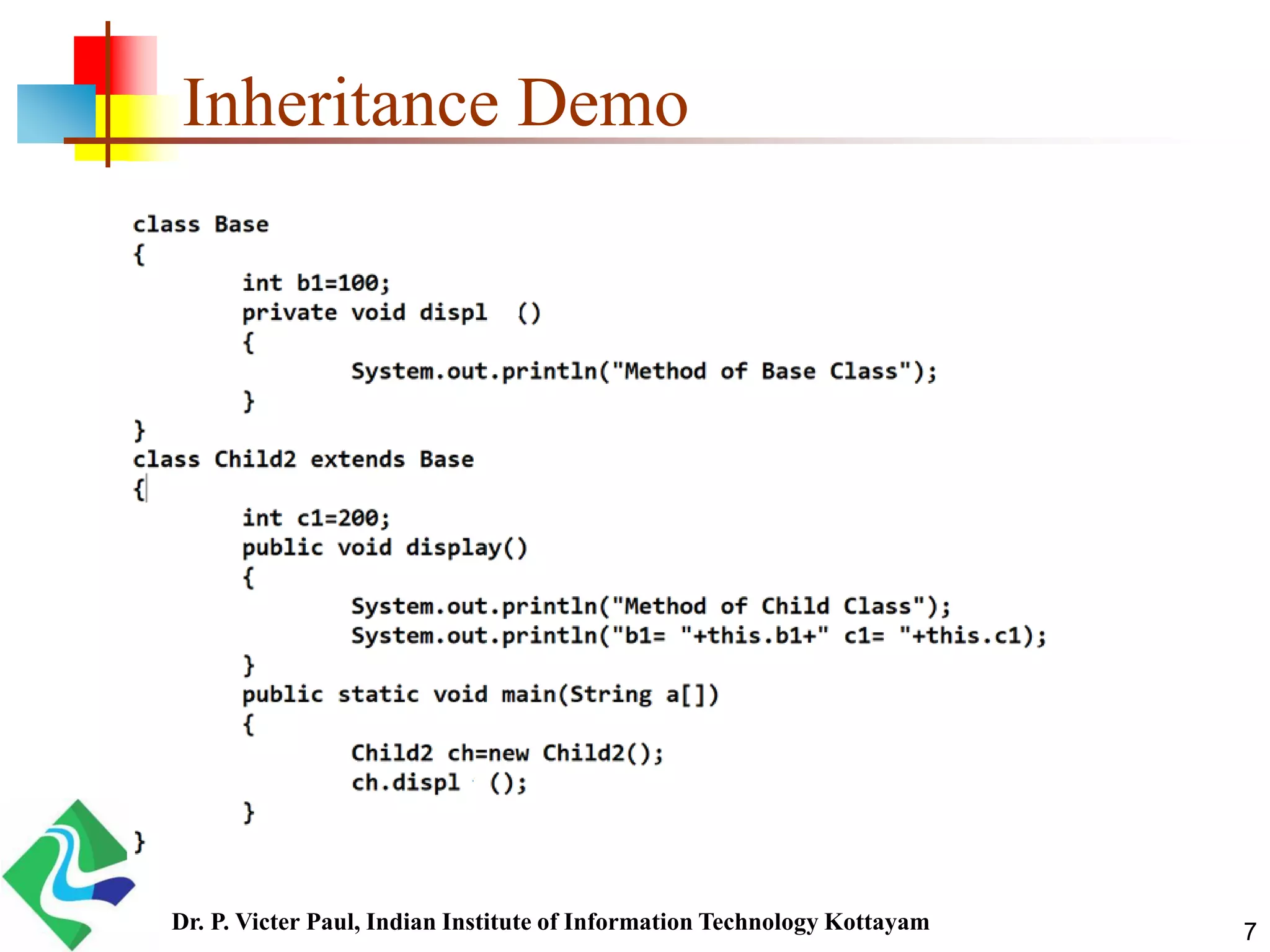
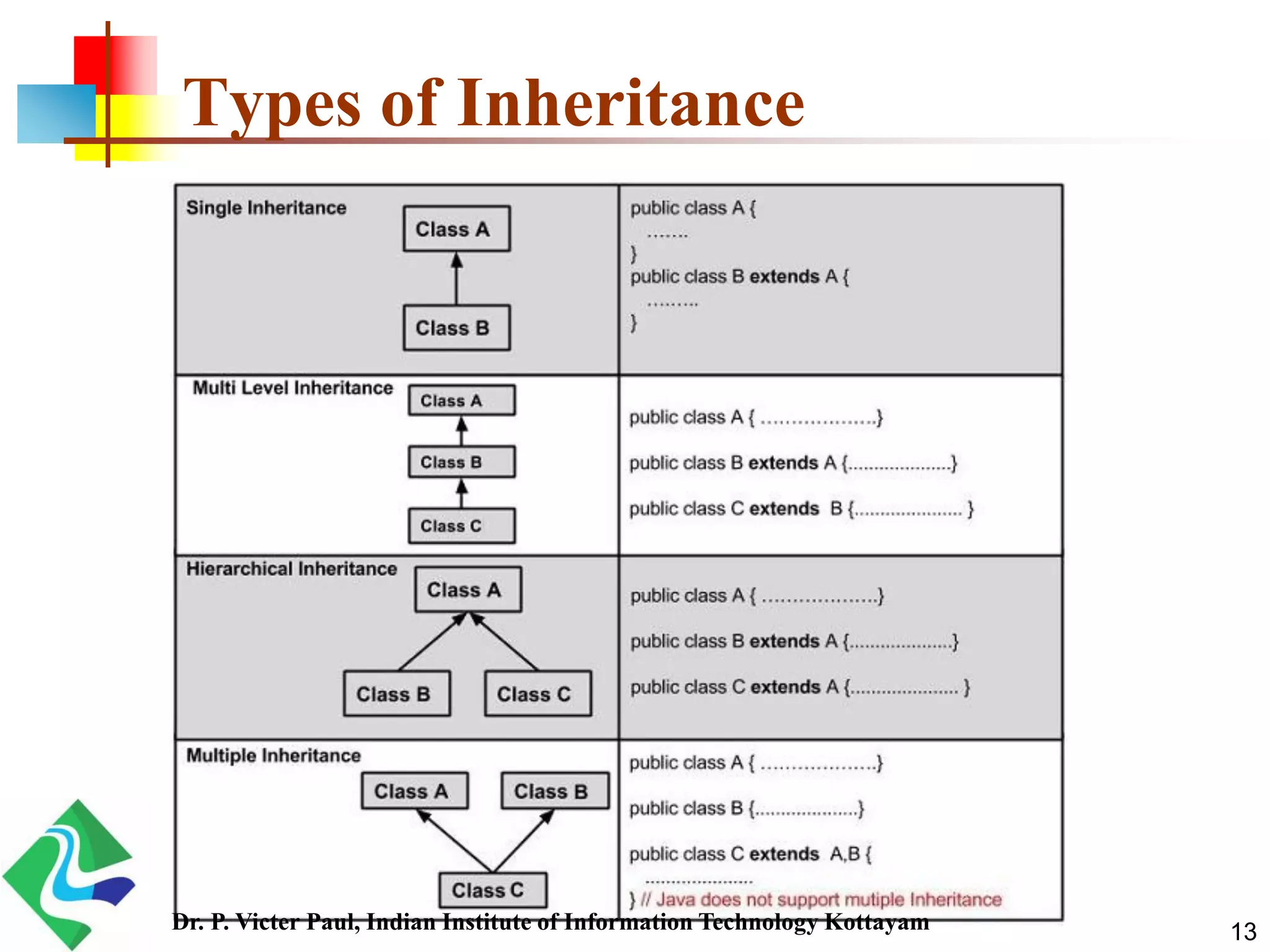
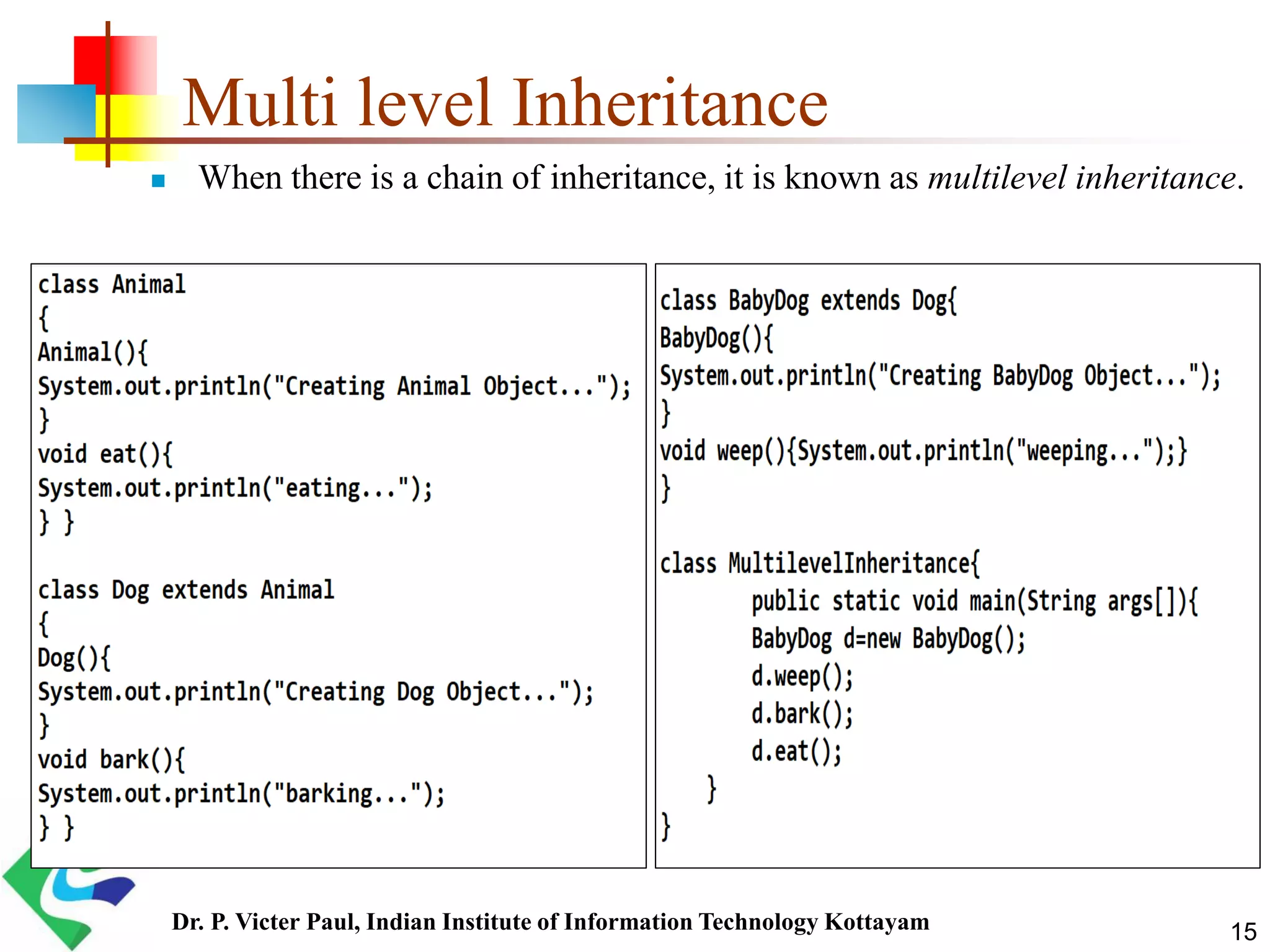
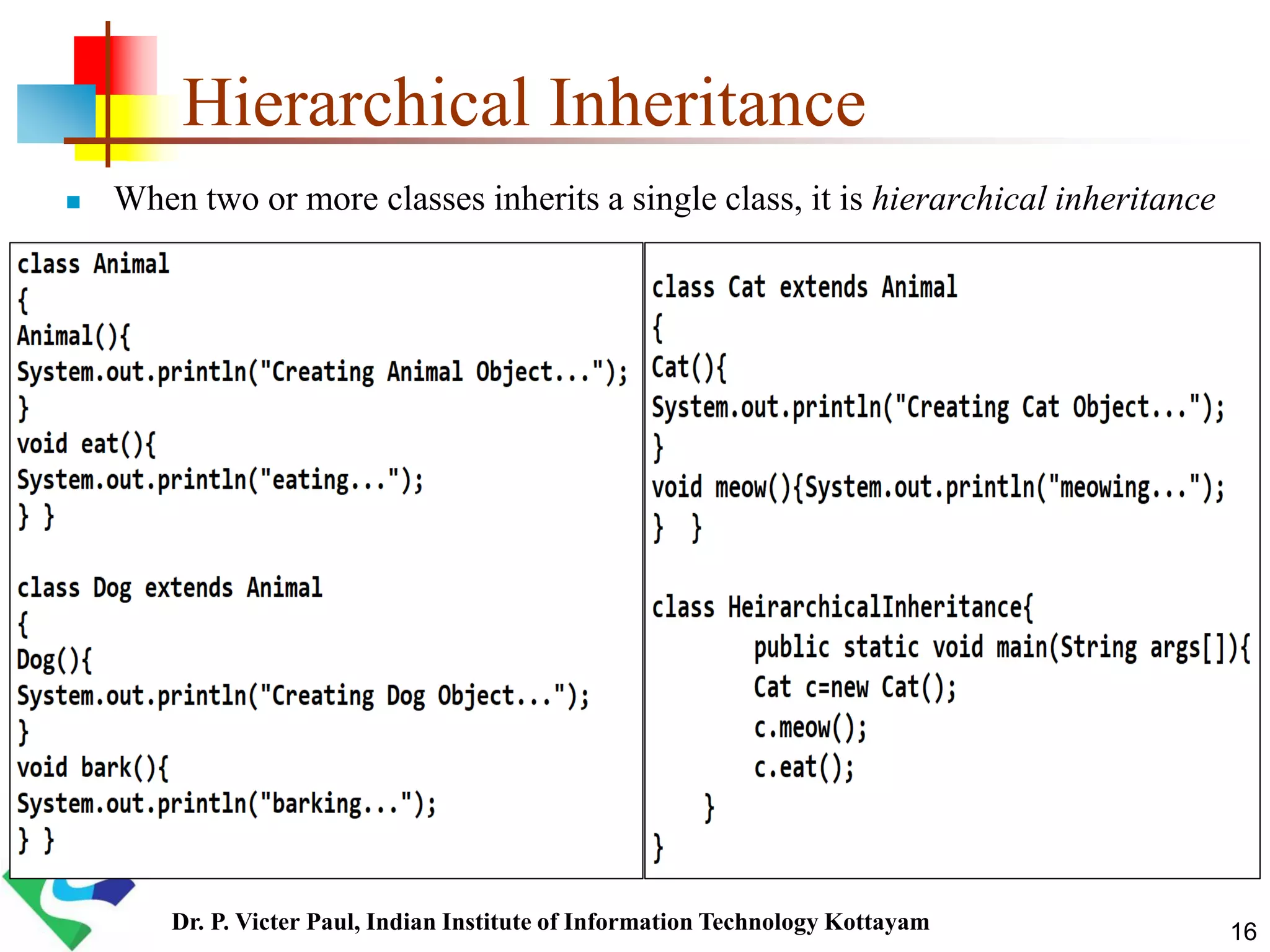
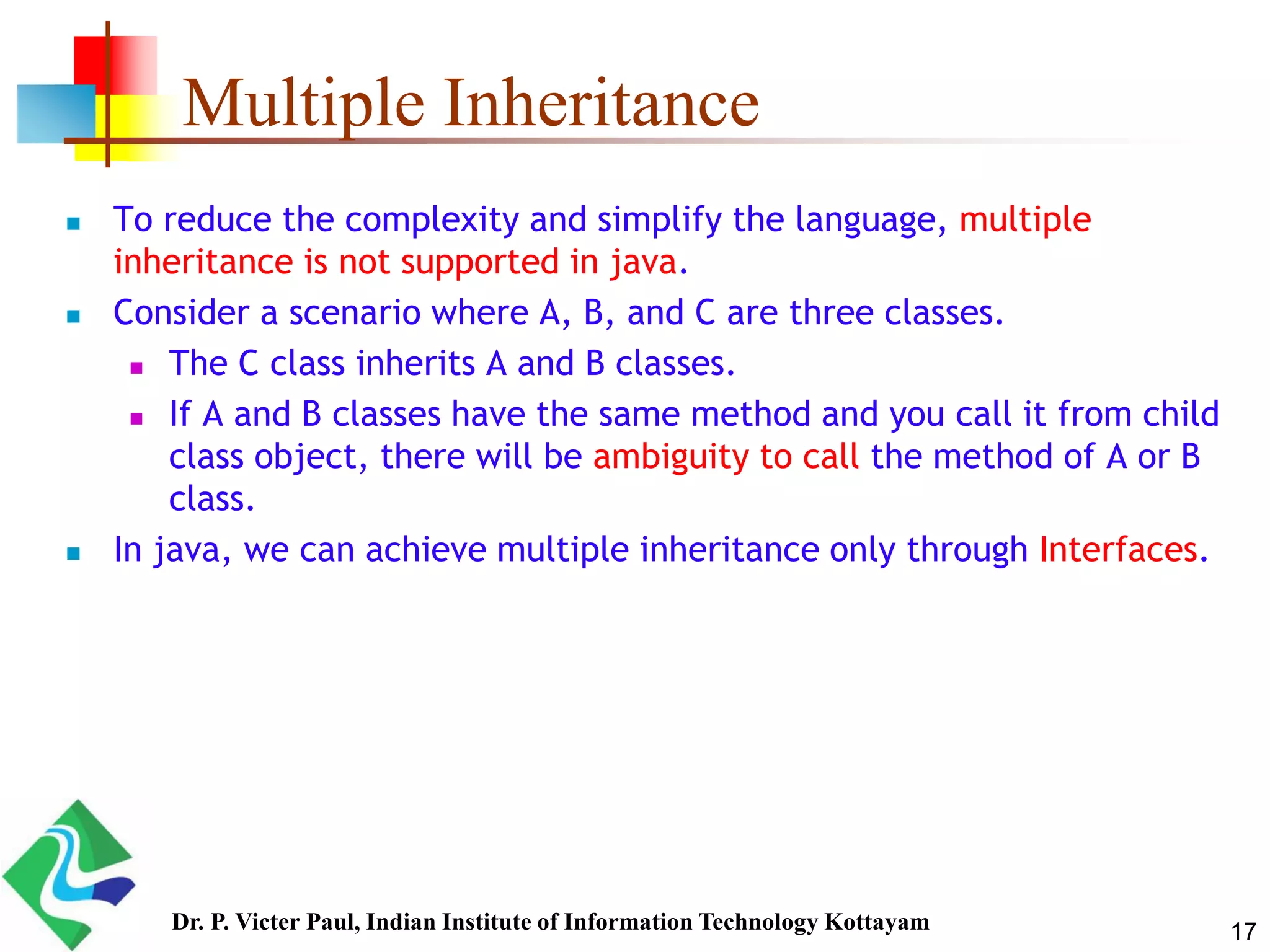
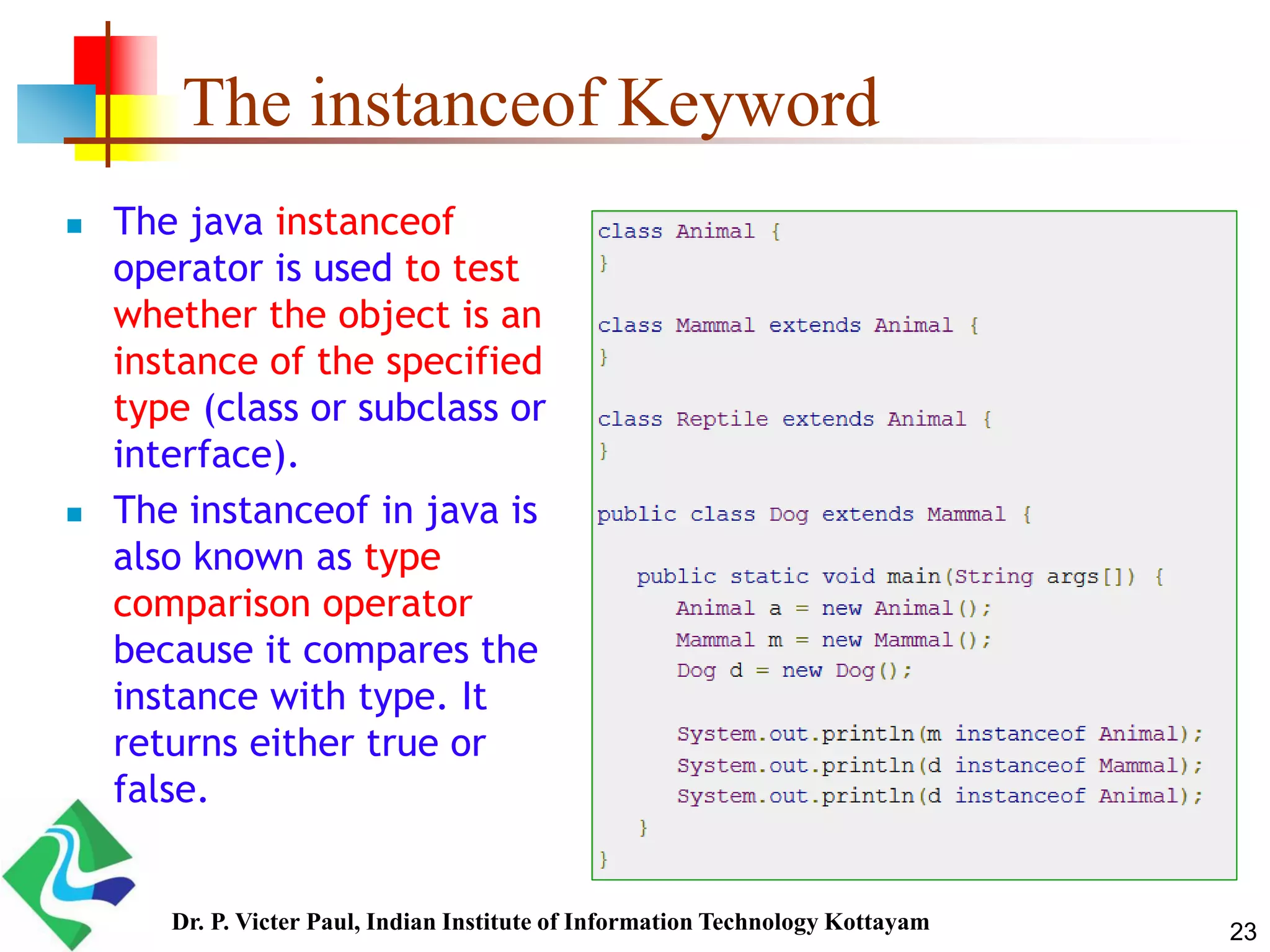
Inheritance allows one class to acquire properties of another class. The subclass inherits all properties of the superclass such as methods and fields. The subclass can also define its own unique properties in addition to what it inherits. Inheritance enables code reuse and is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming.