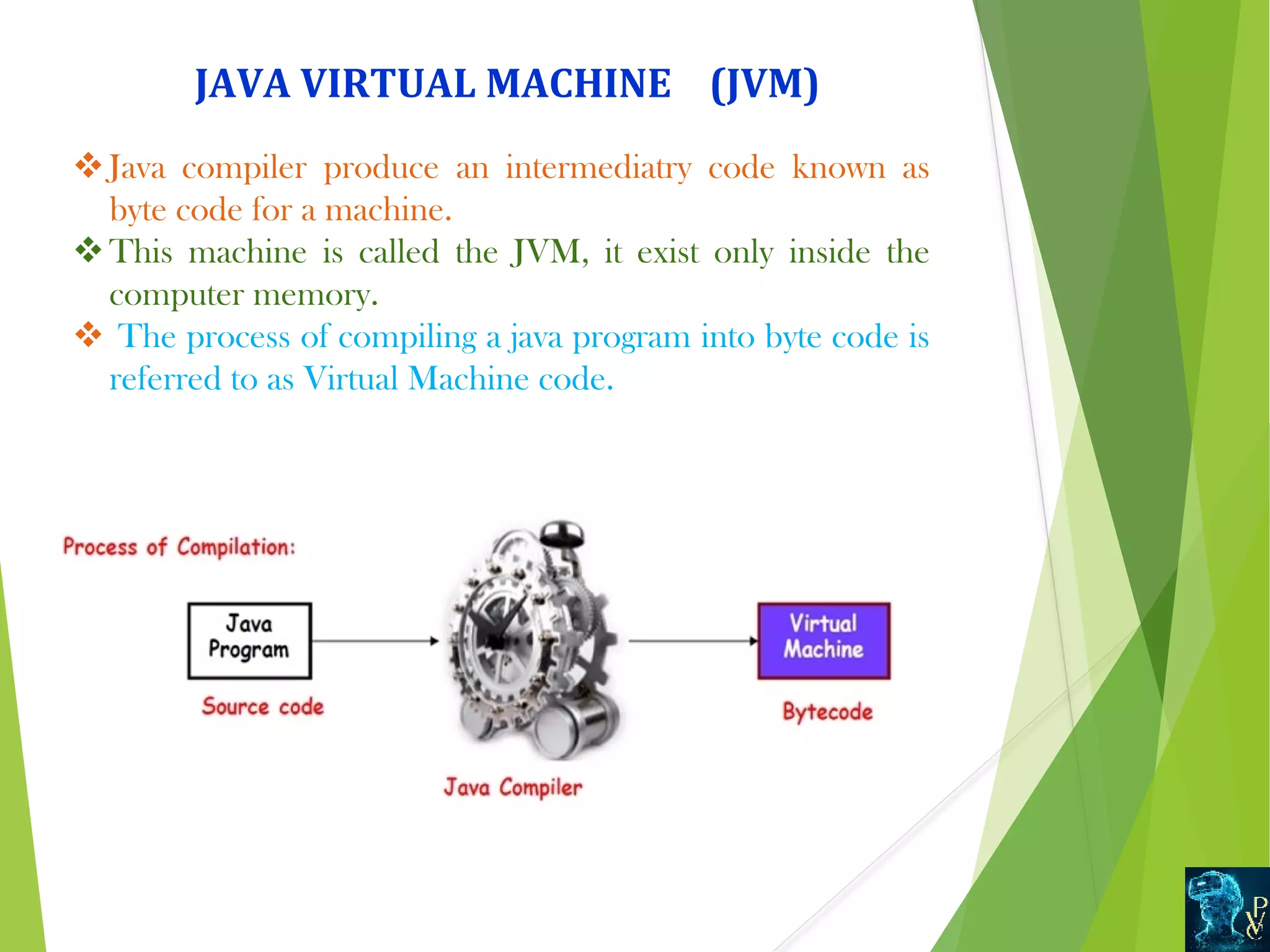
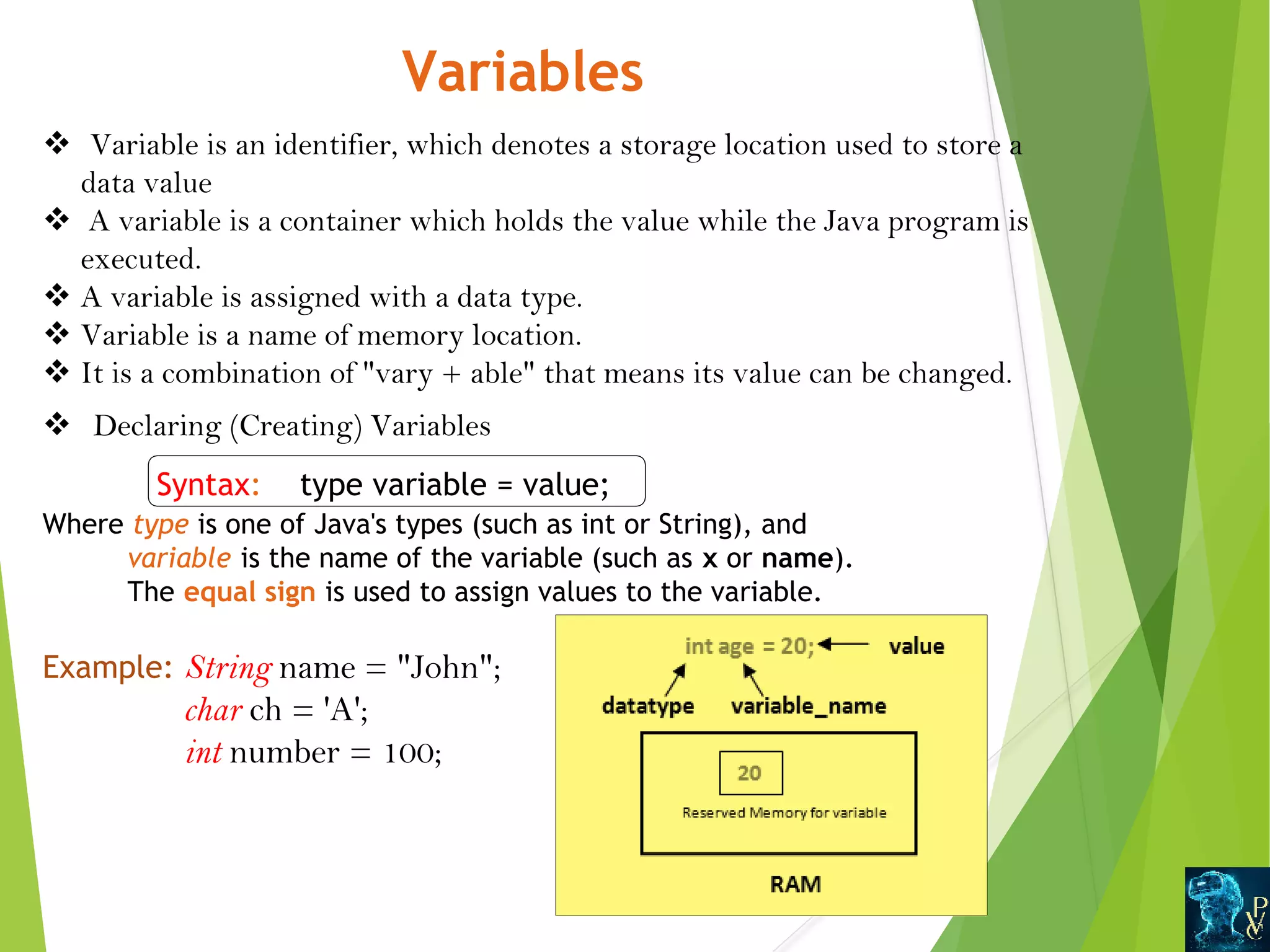
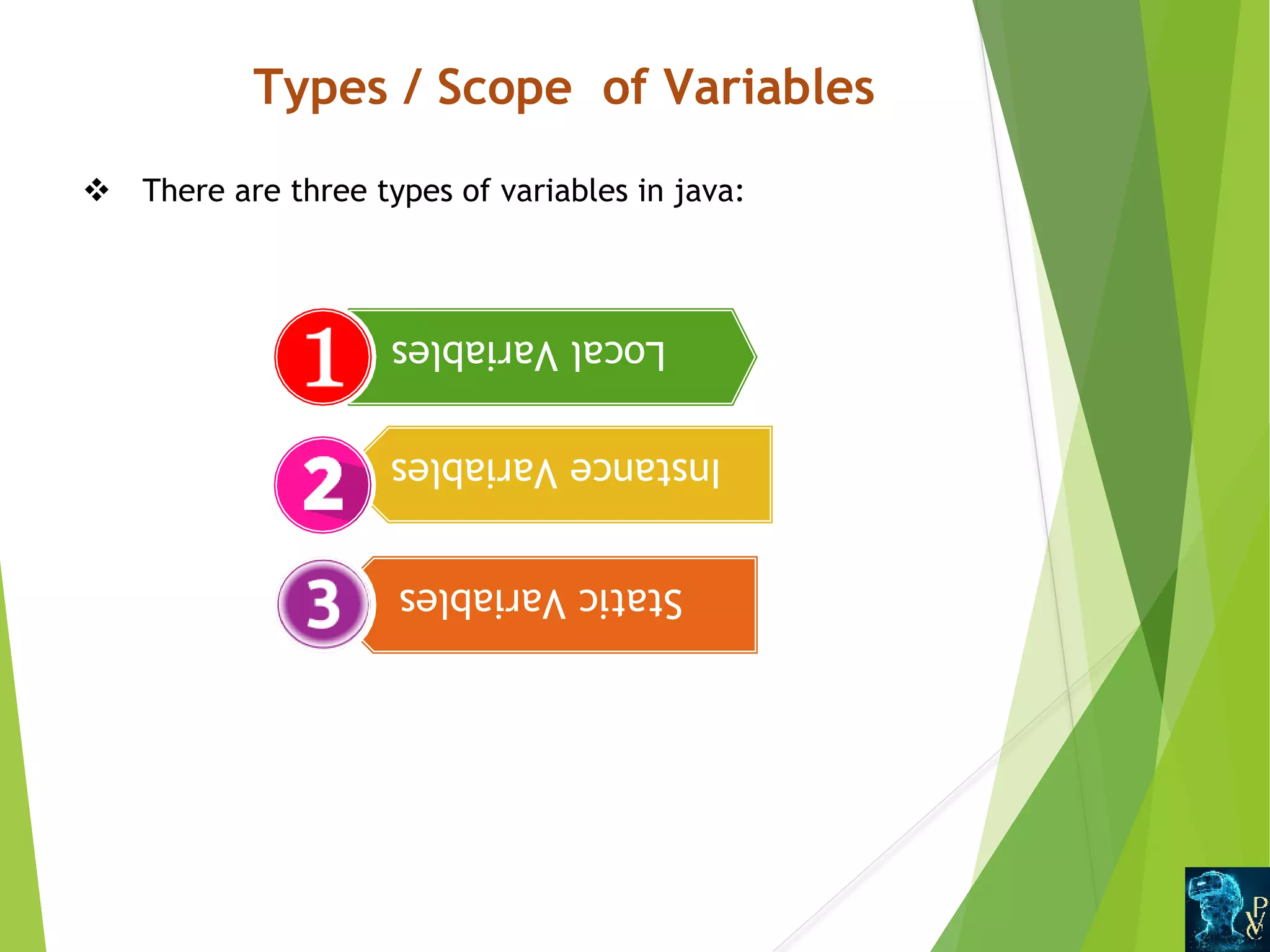
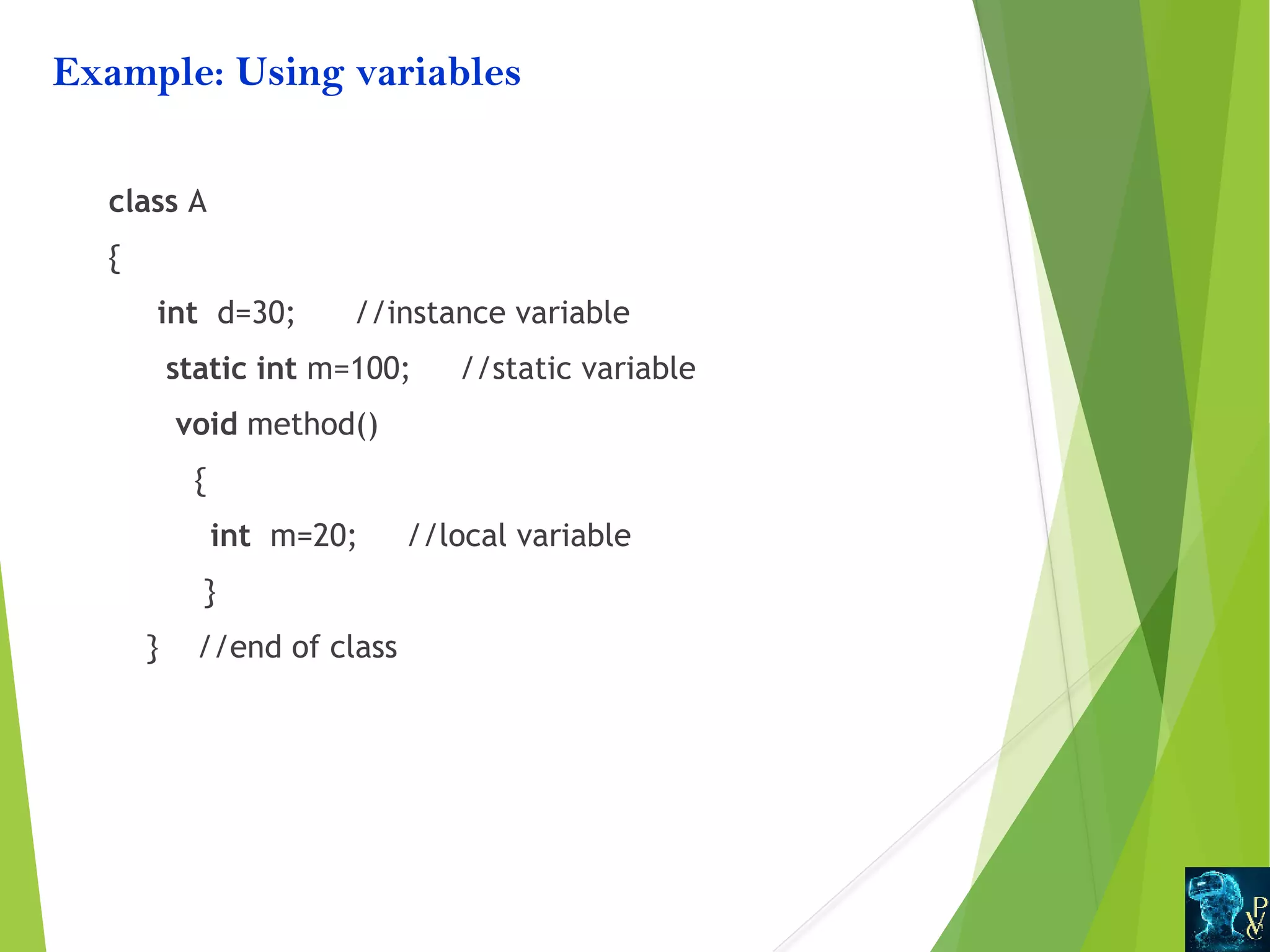
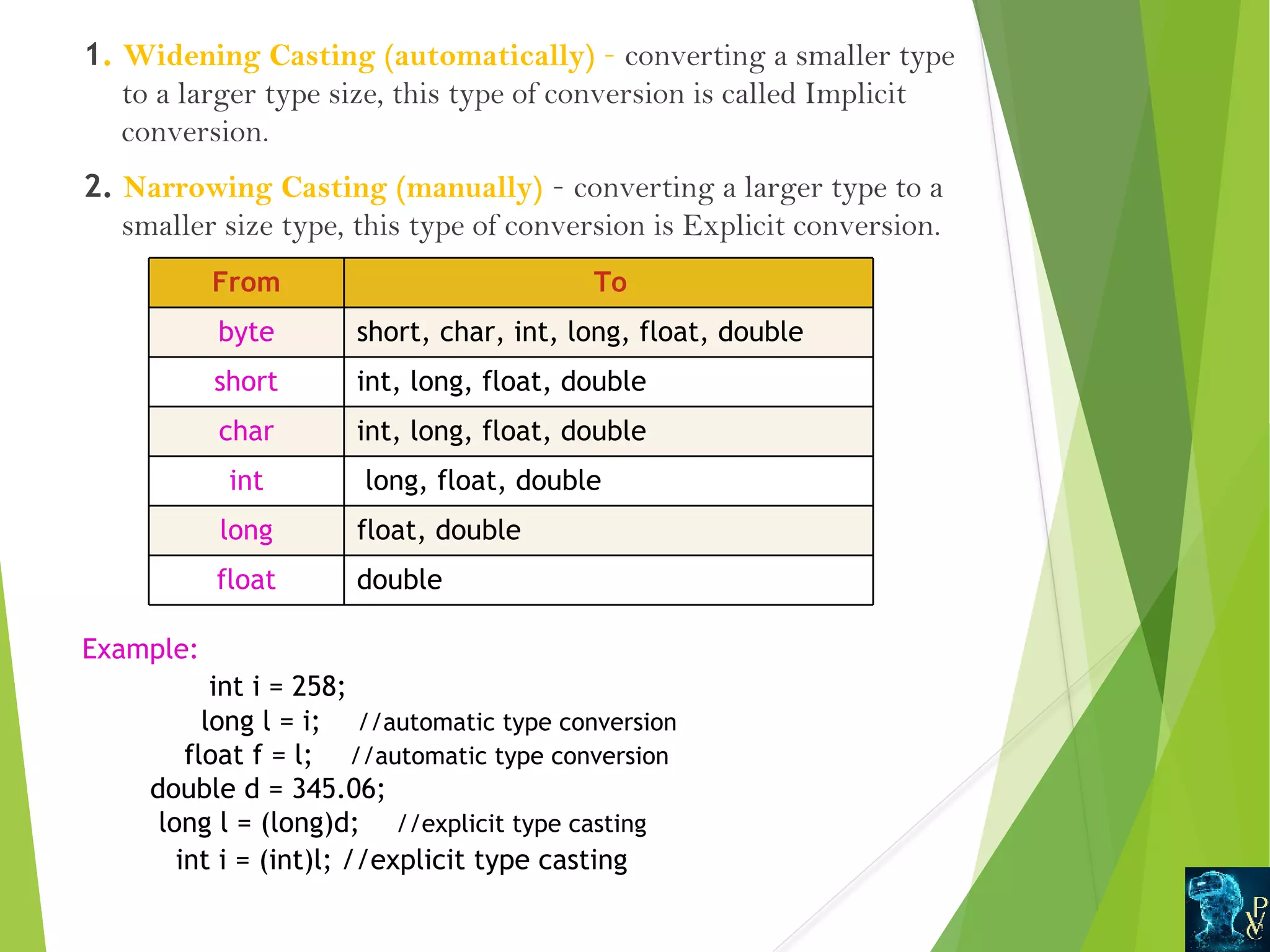
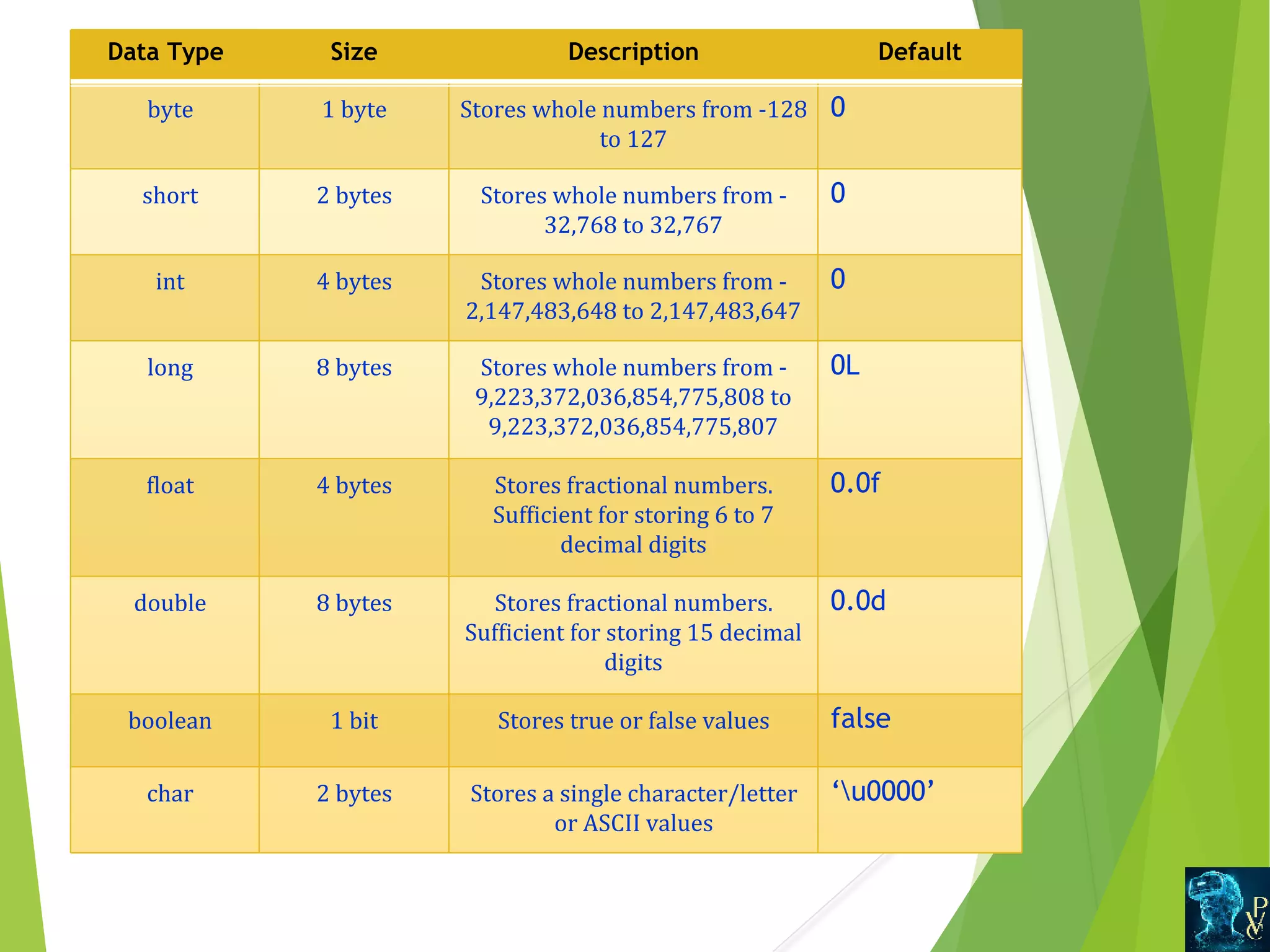
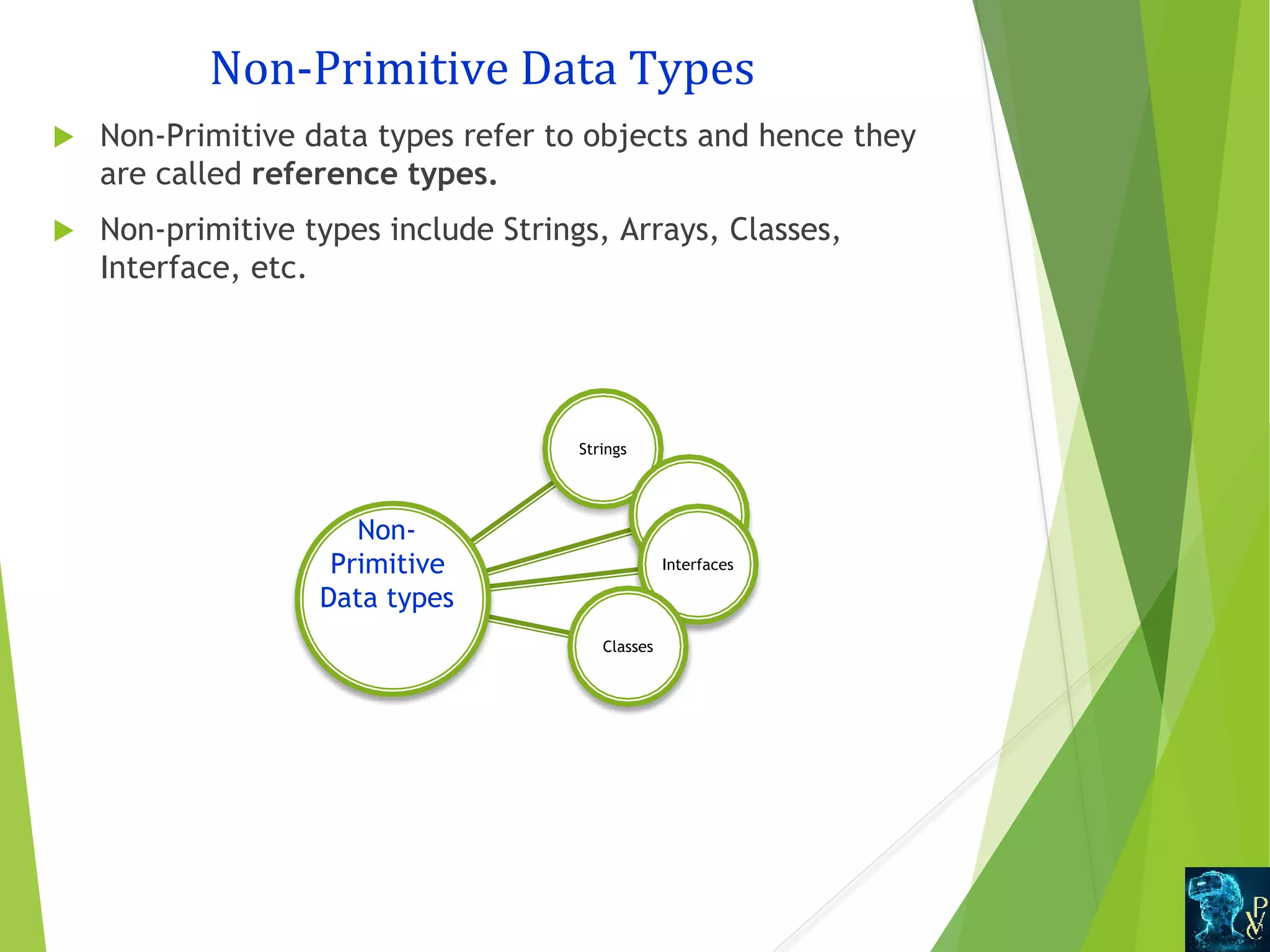
This document discusses Java data types and variables. It defines variables as containers that hold data values and notes there are three types: local, instance, and static. Local variables are declared within methods while instance variables are declared in a class but outside methods. Static variables can be accessed by the class name. The document also outlines Java's primitive data types like int and double, and non-primitive types like Strings and Arrays. It explains type casting between primitive types and differences between primitive and non-primitive data types.