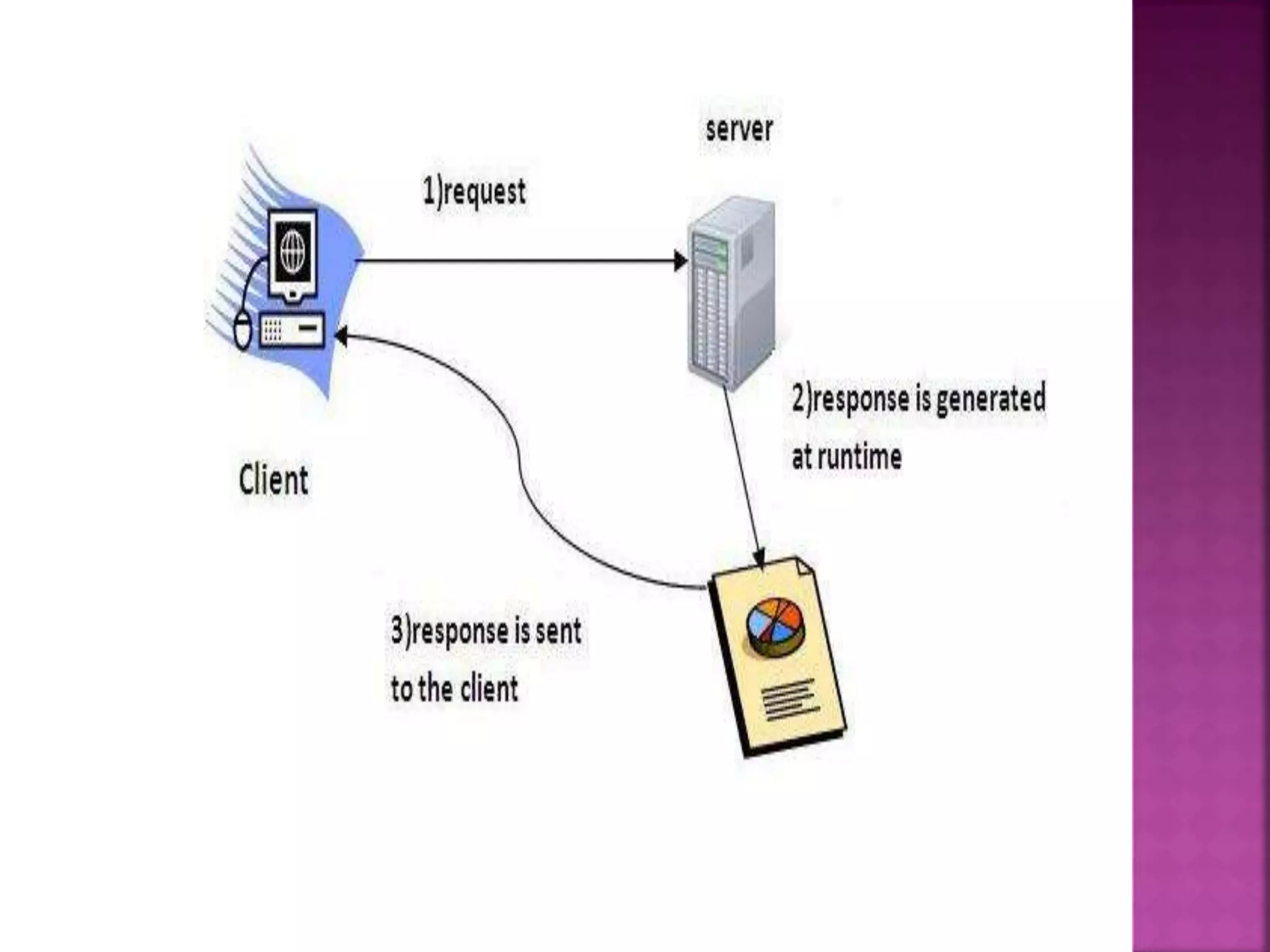
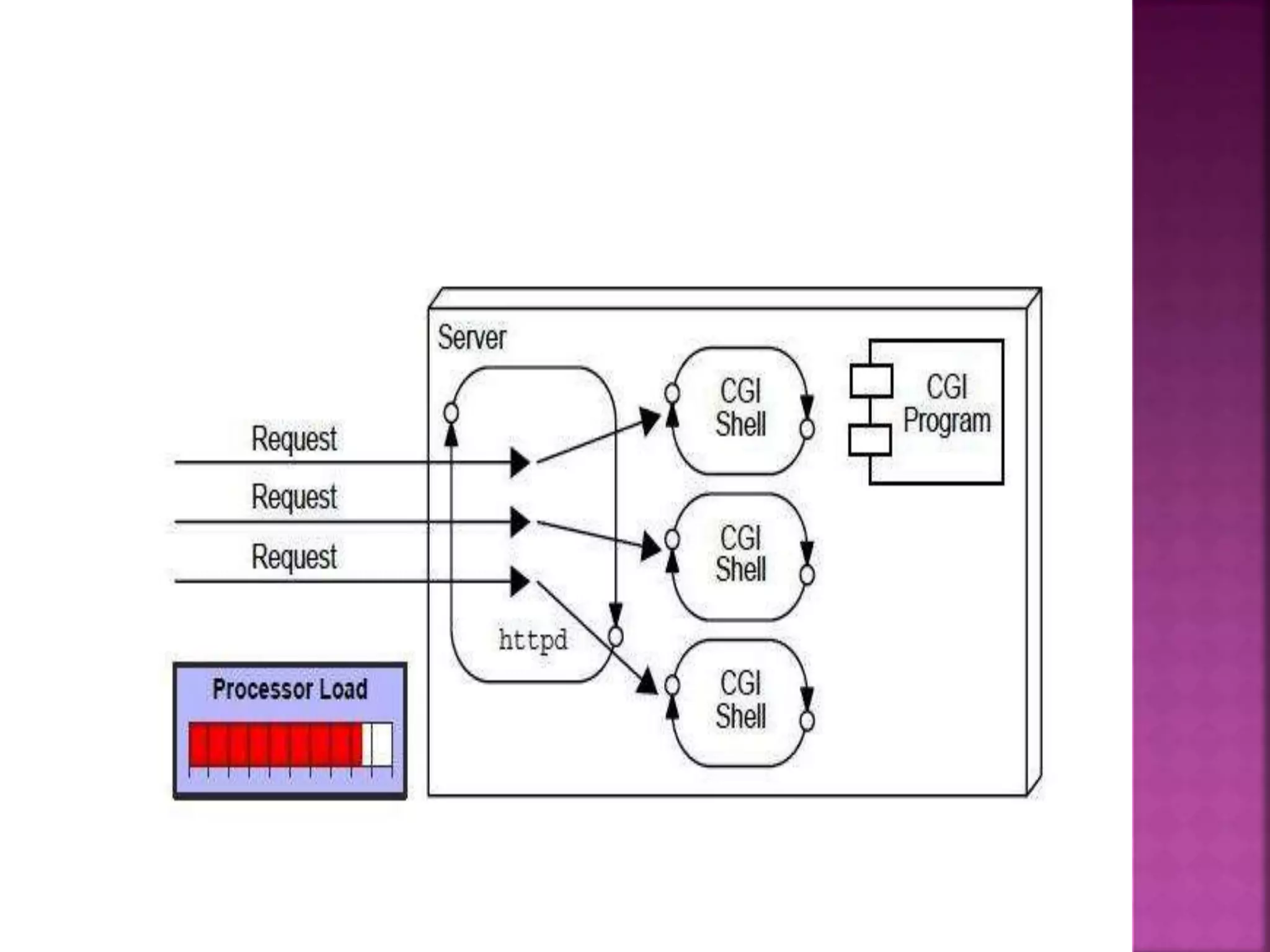
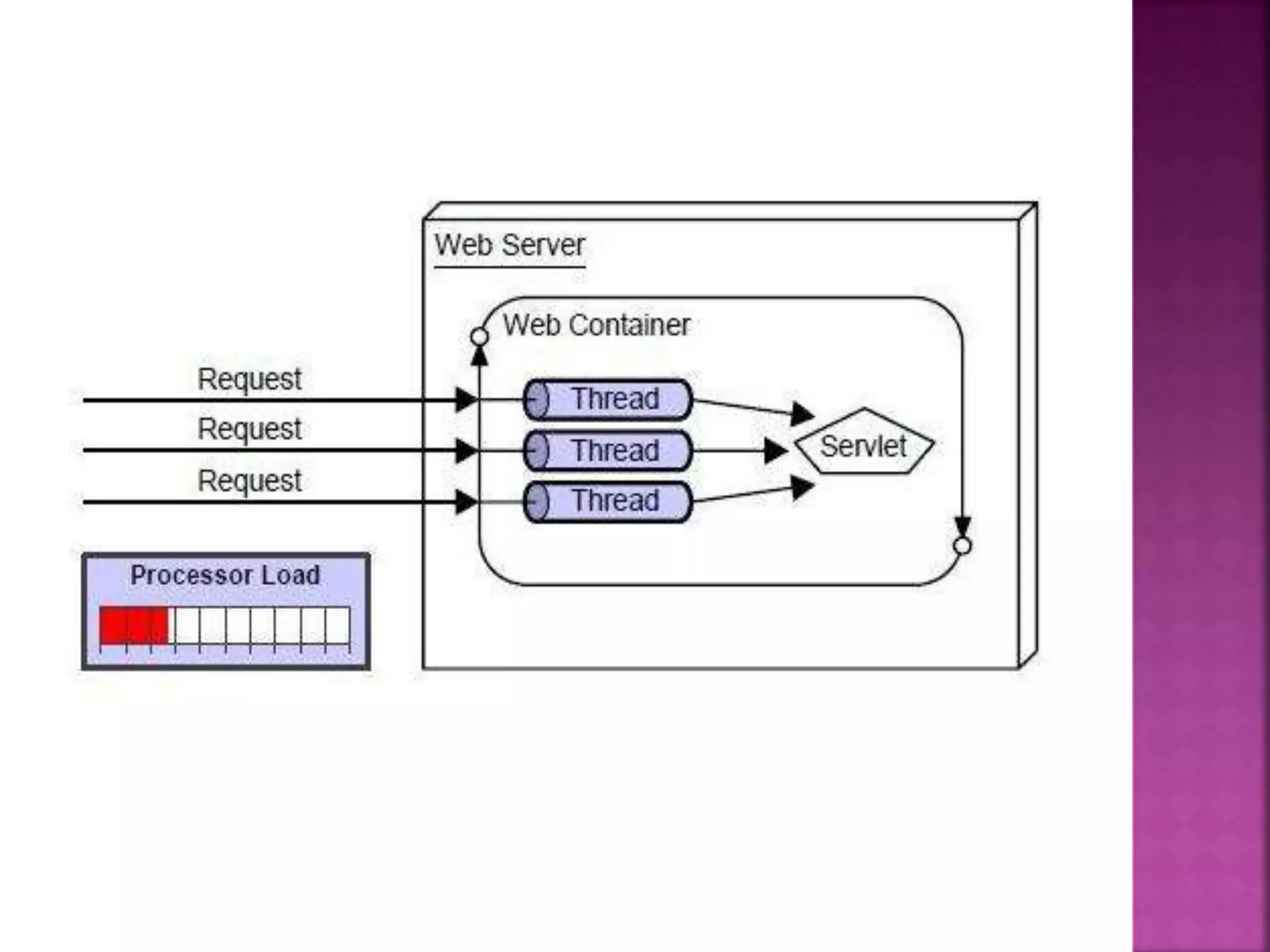
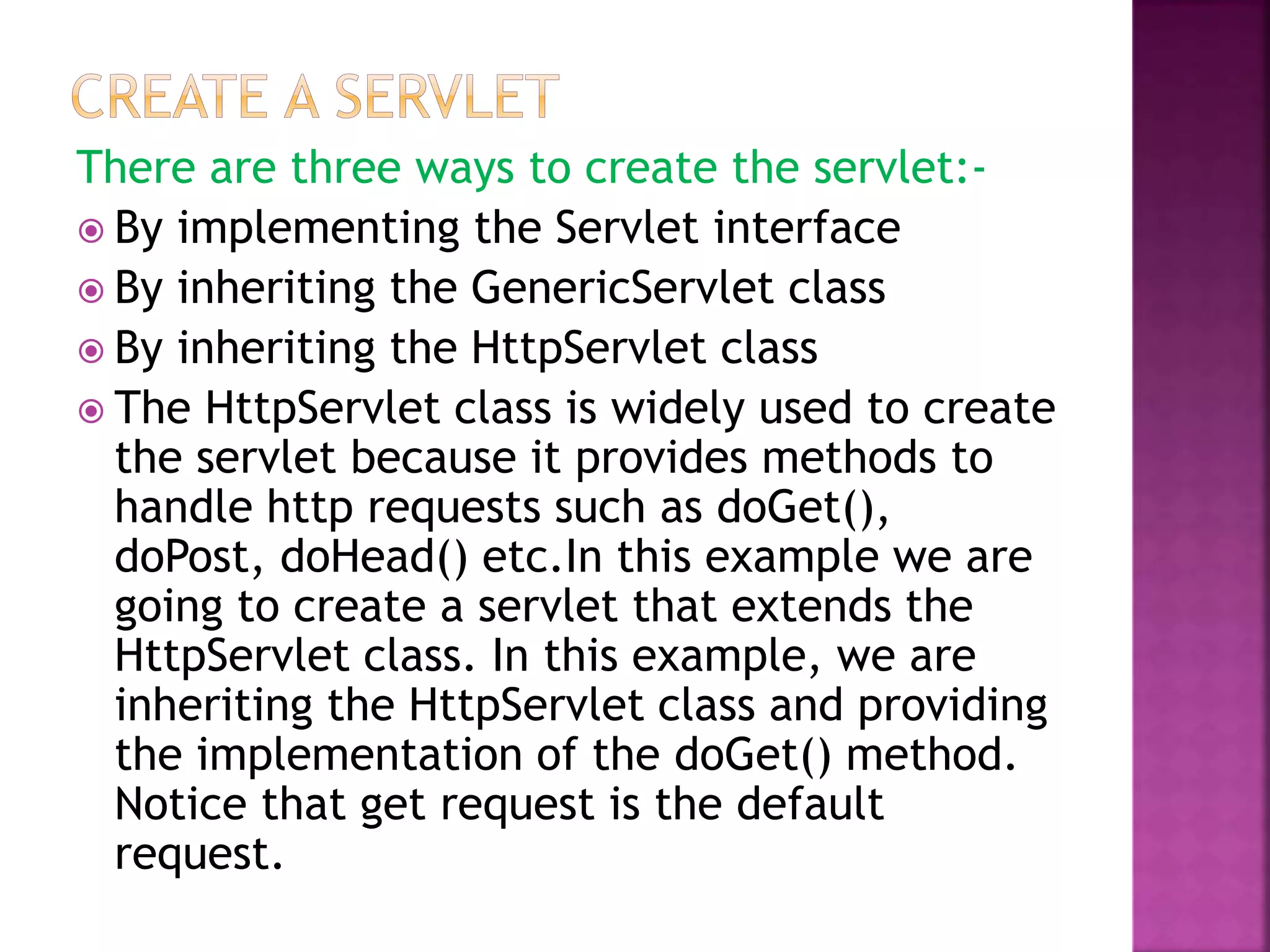
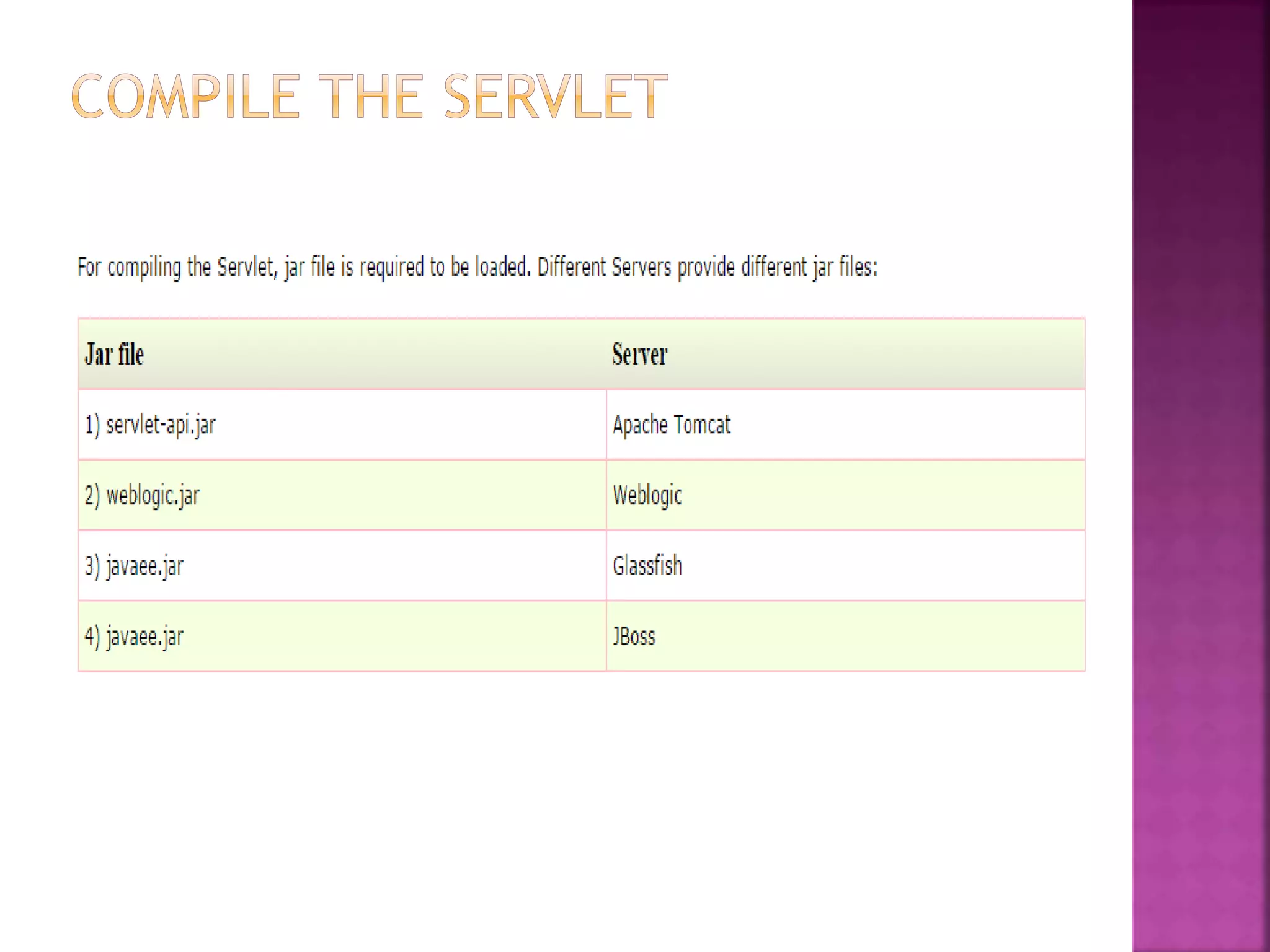
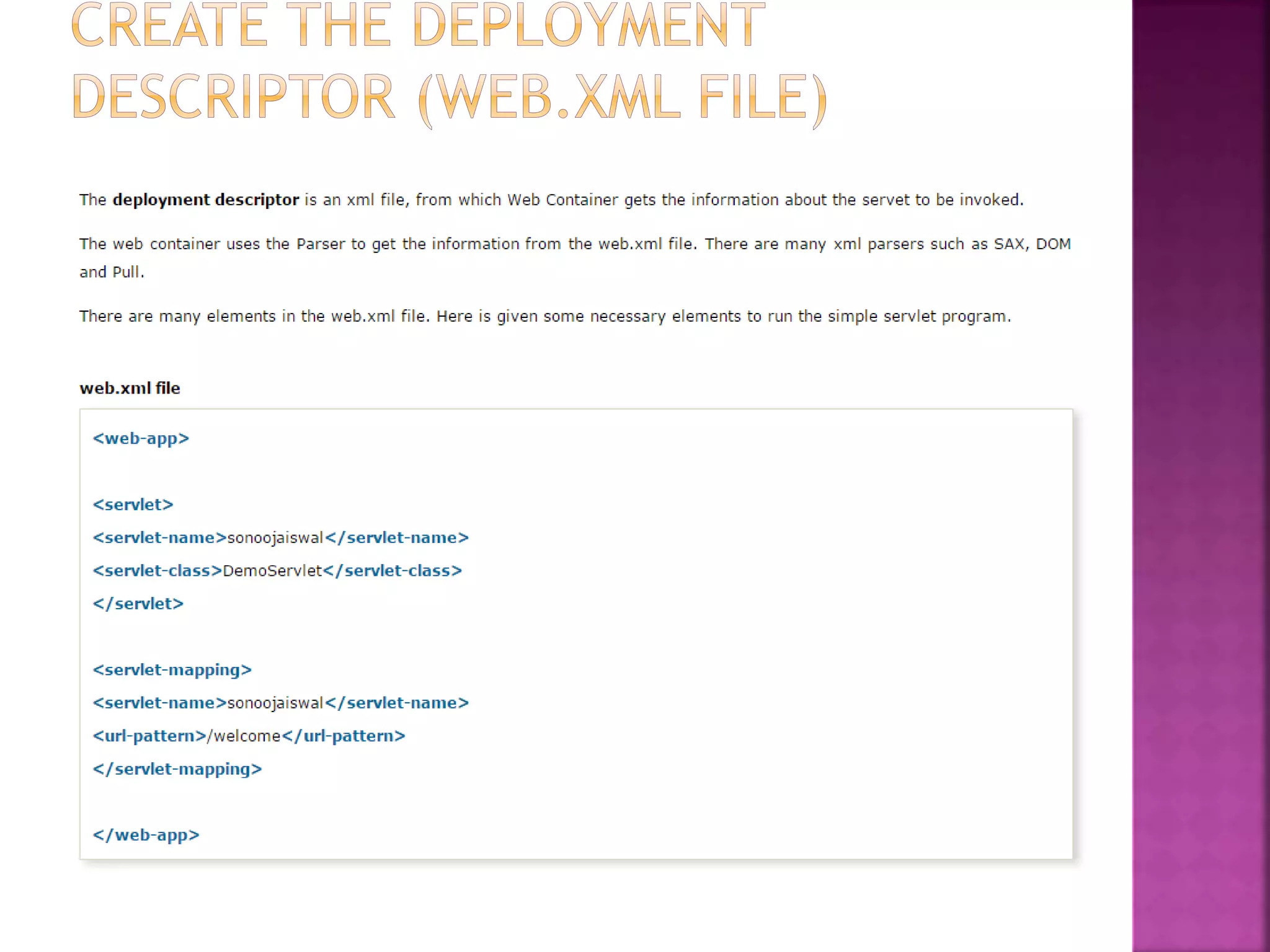
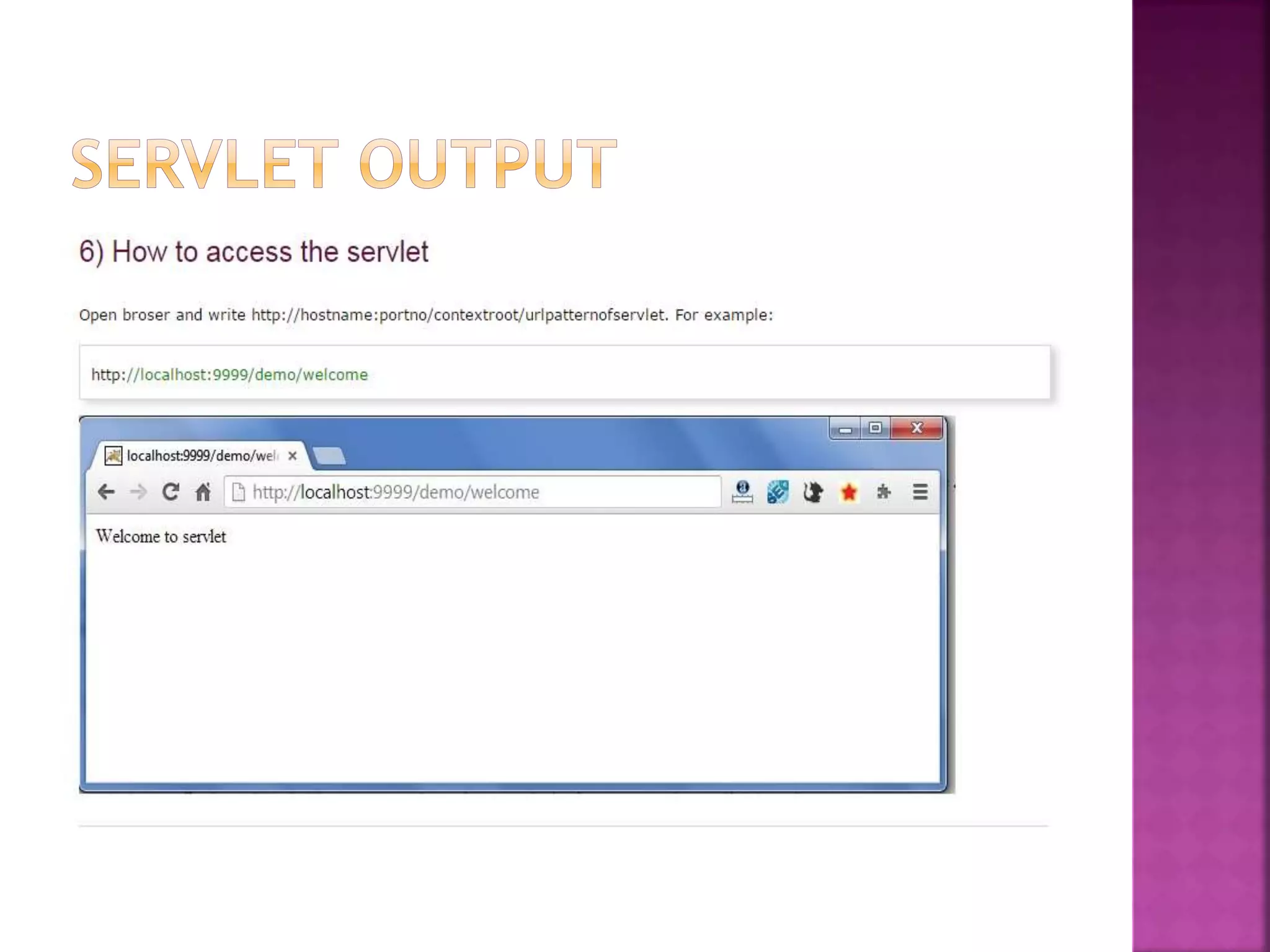
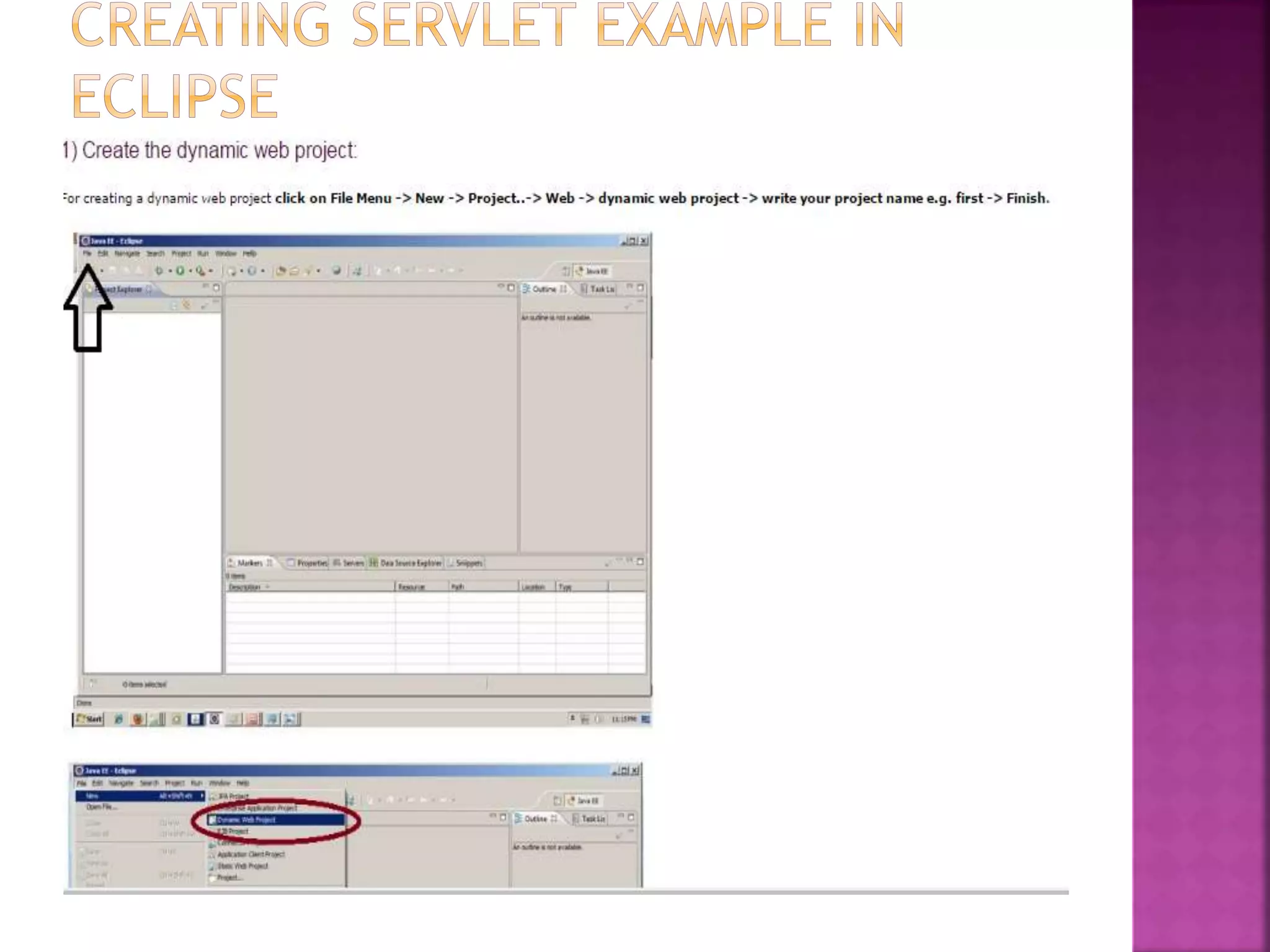
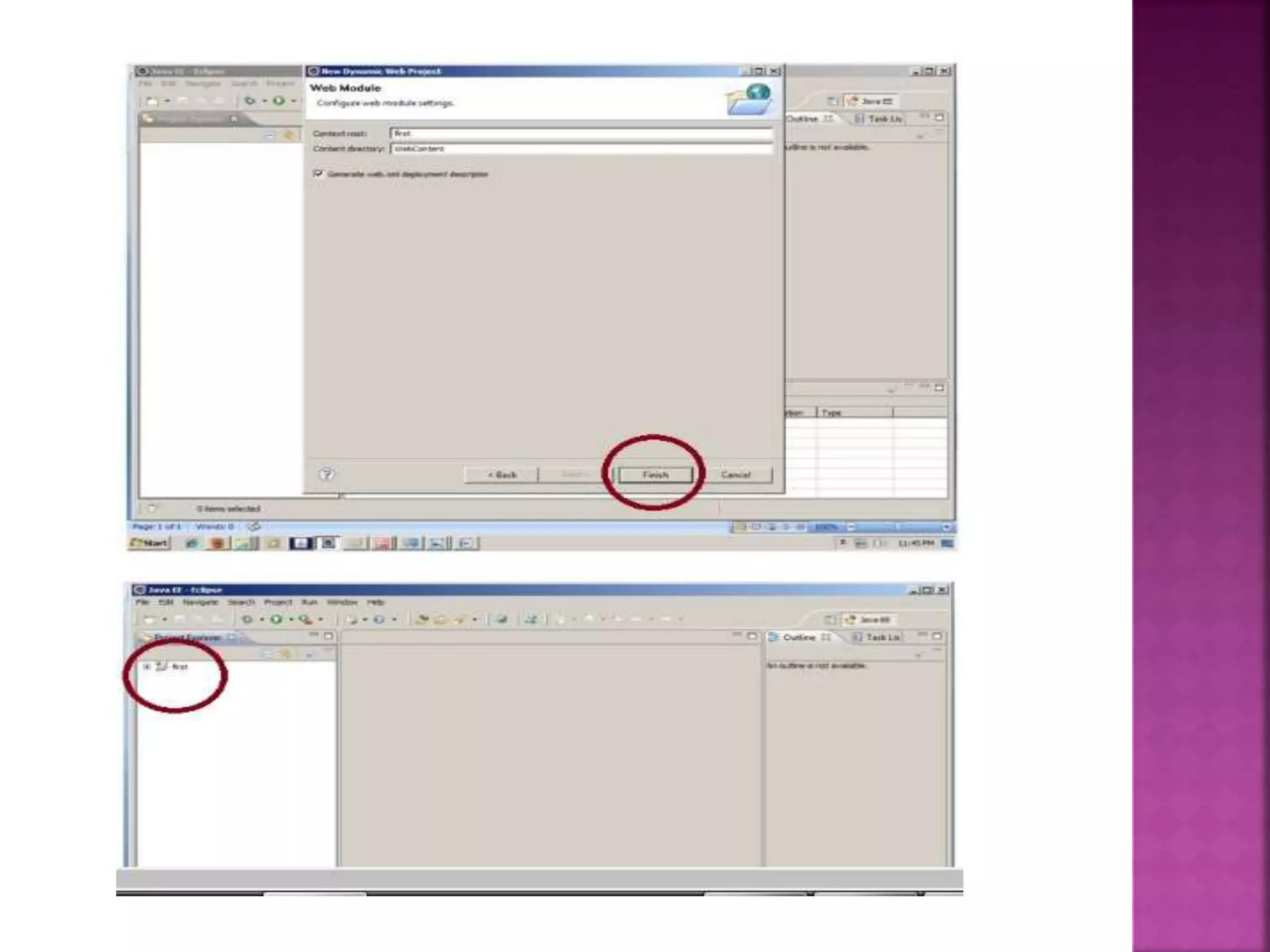
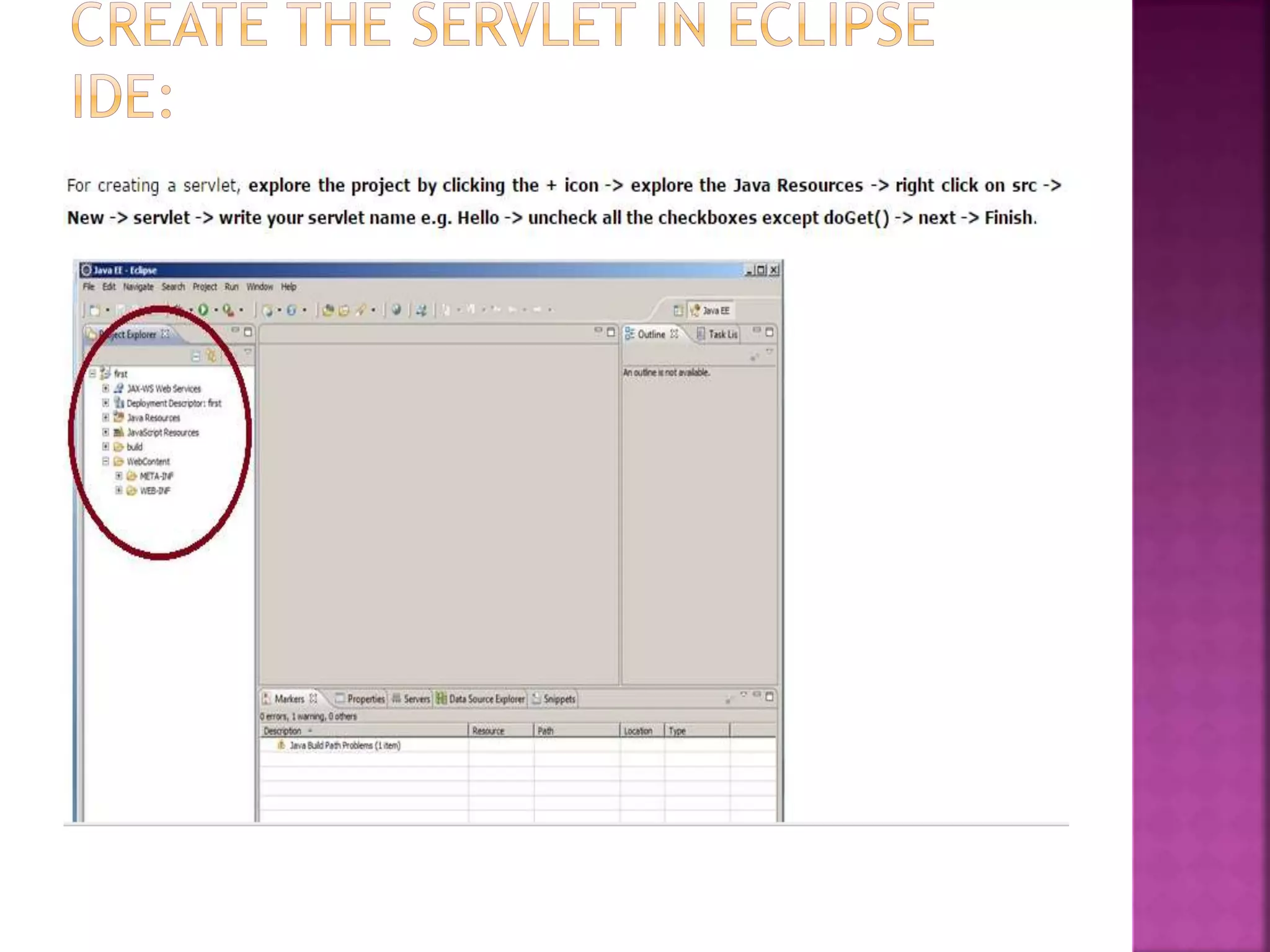
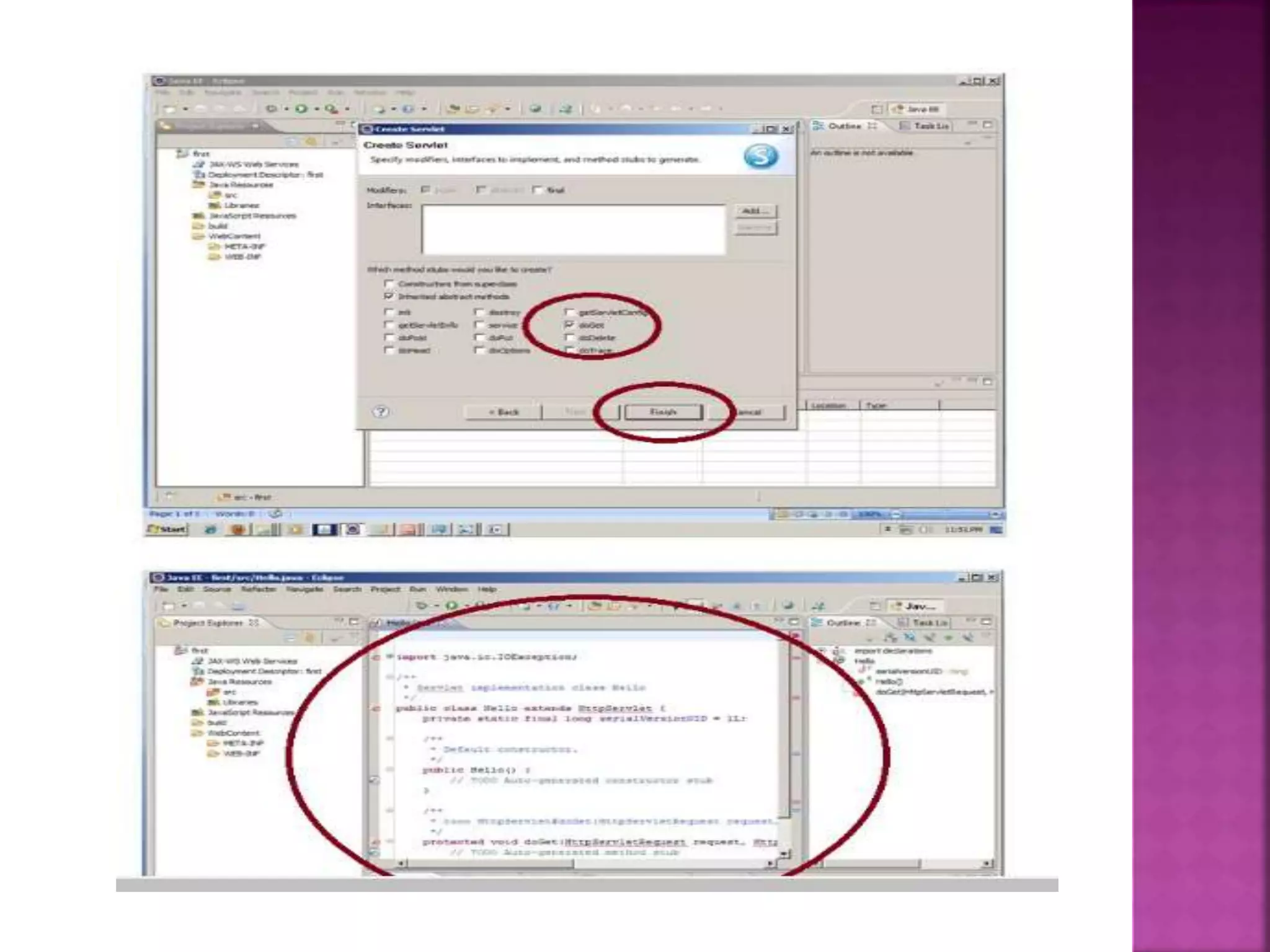
The document discusses servlet technology and how it is used to create dynamic web applications. Some key points: - Servlet technology allows creating web applications that reside on the server-side and generate dynamic web pages. - Servlets are more robust and scalable than previous CGI technology due to being implemented in Java. - The servlet API defines interfaces like Servlet, GenericServlet, HttpServlet, ServletRequest, and ServletResponse that are used to build servlets.