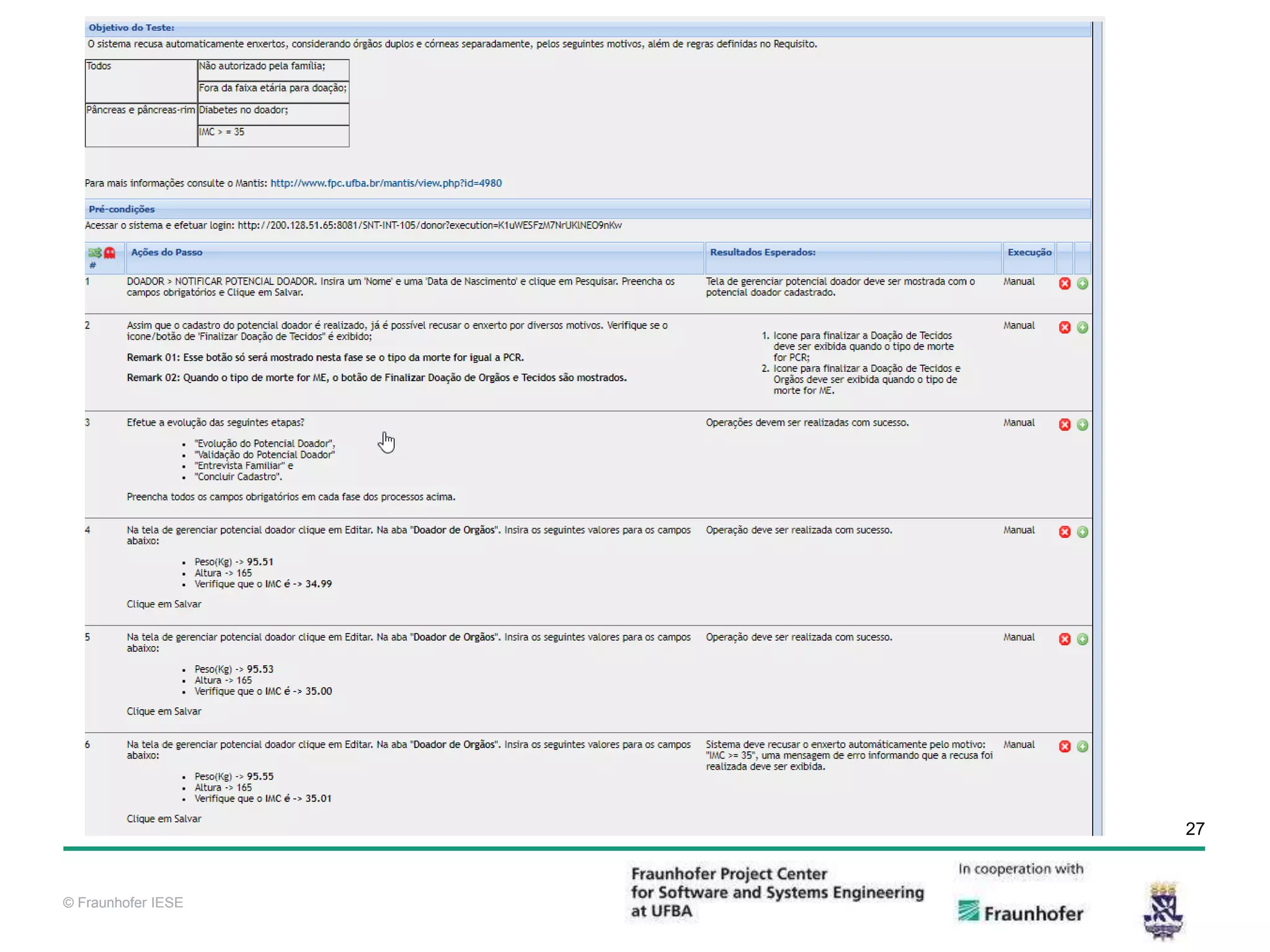
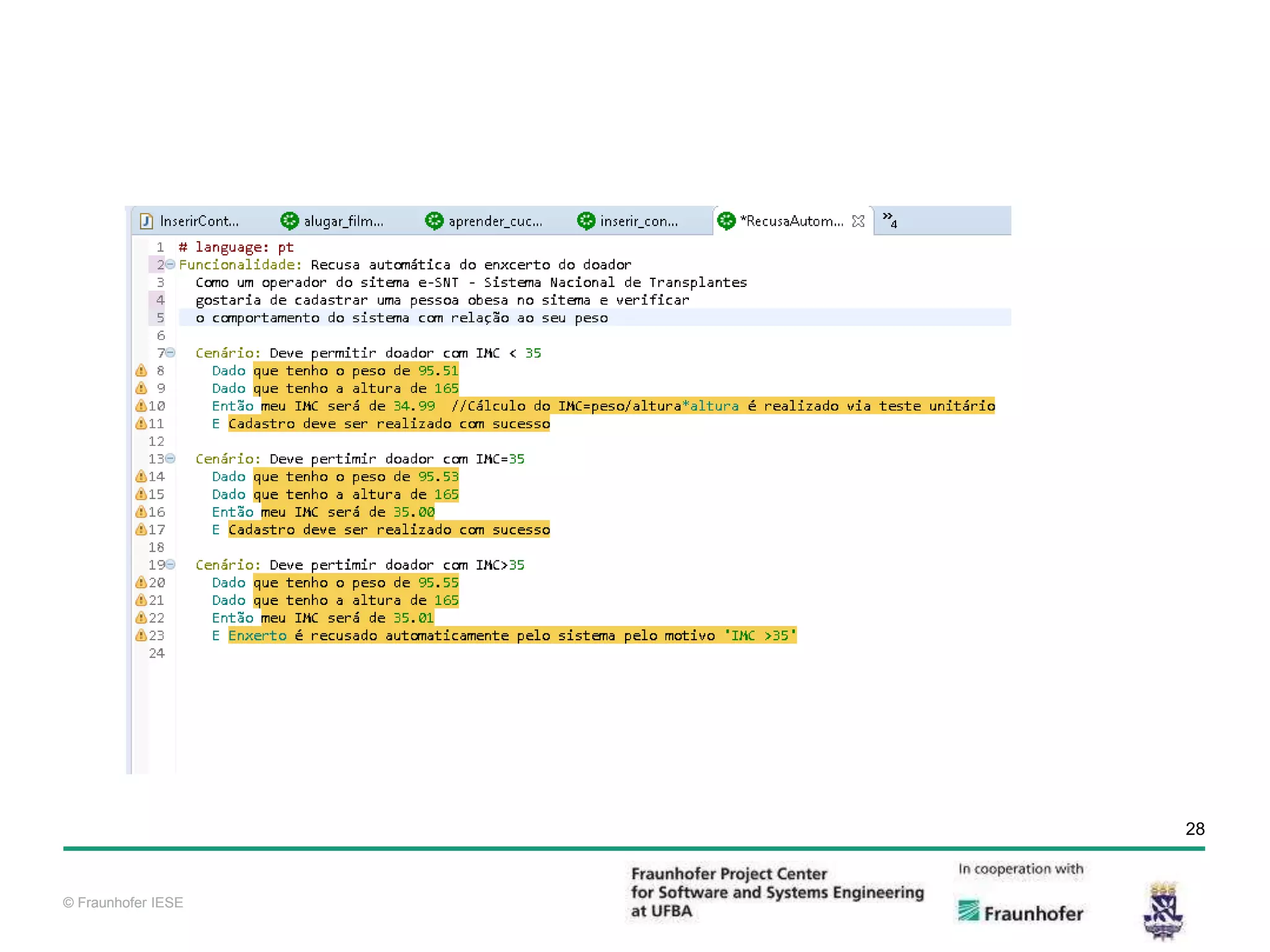
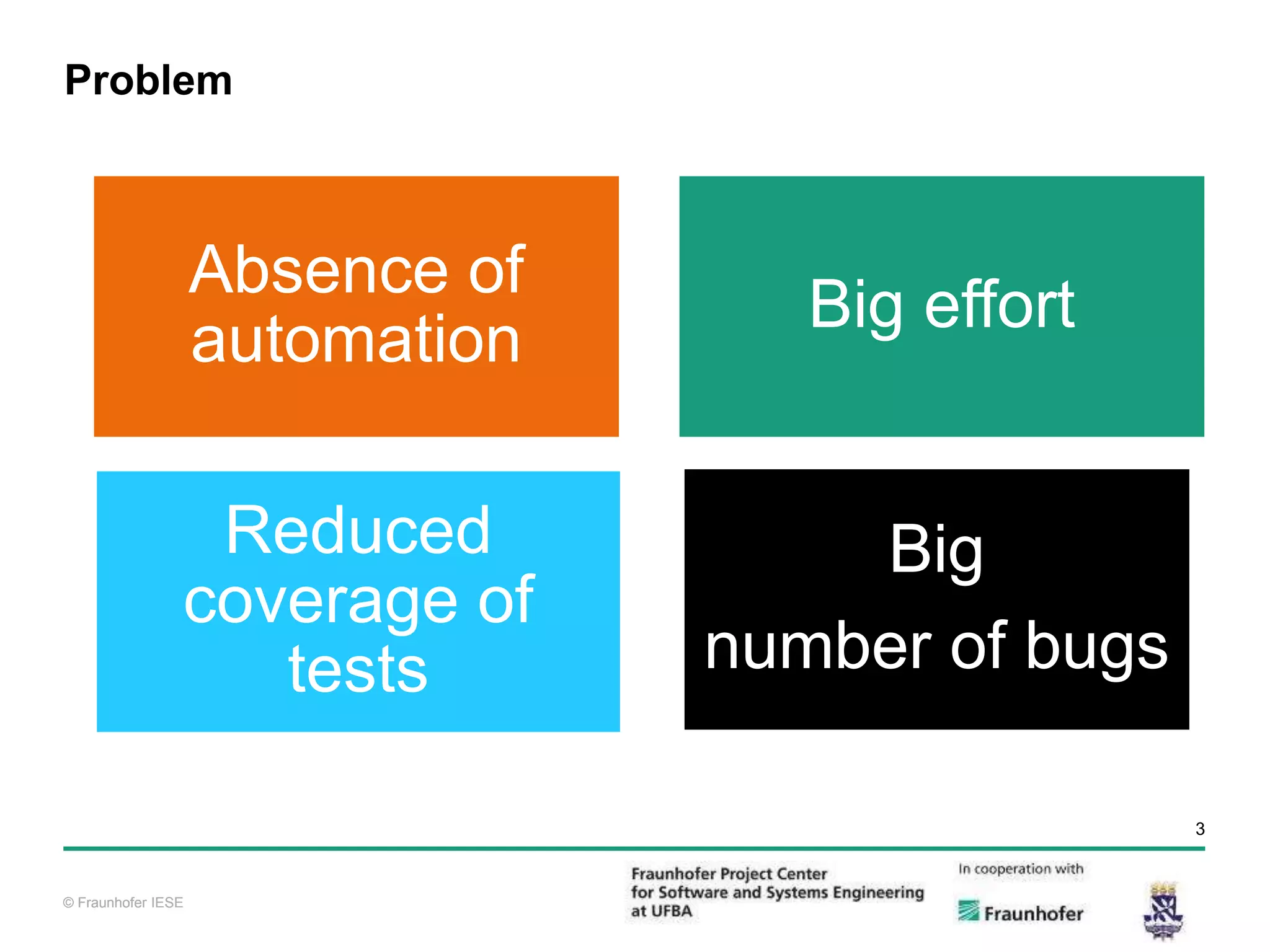
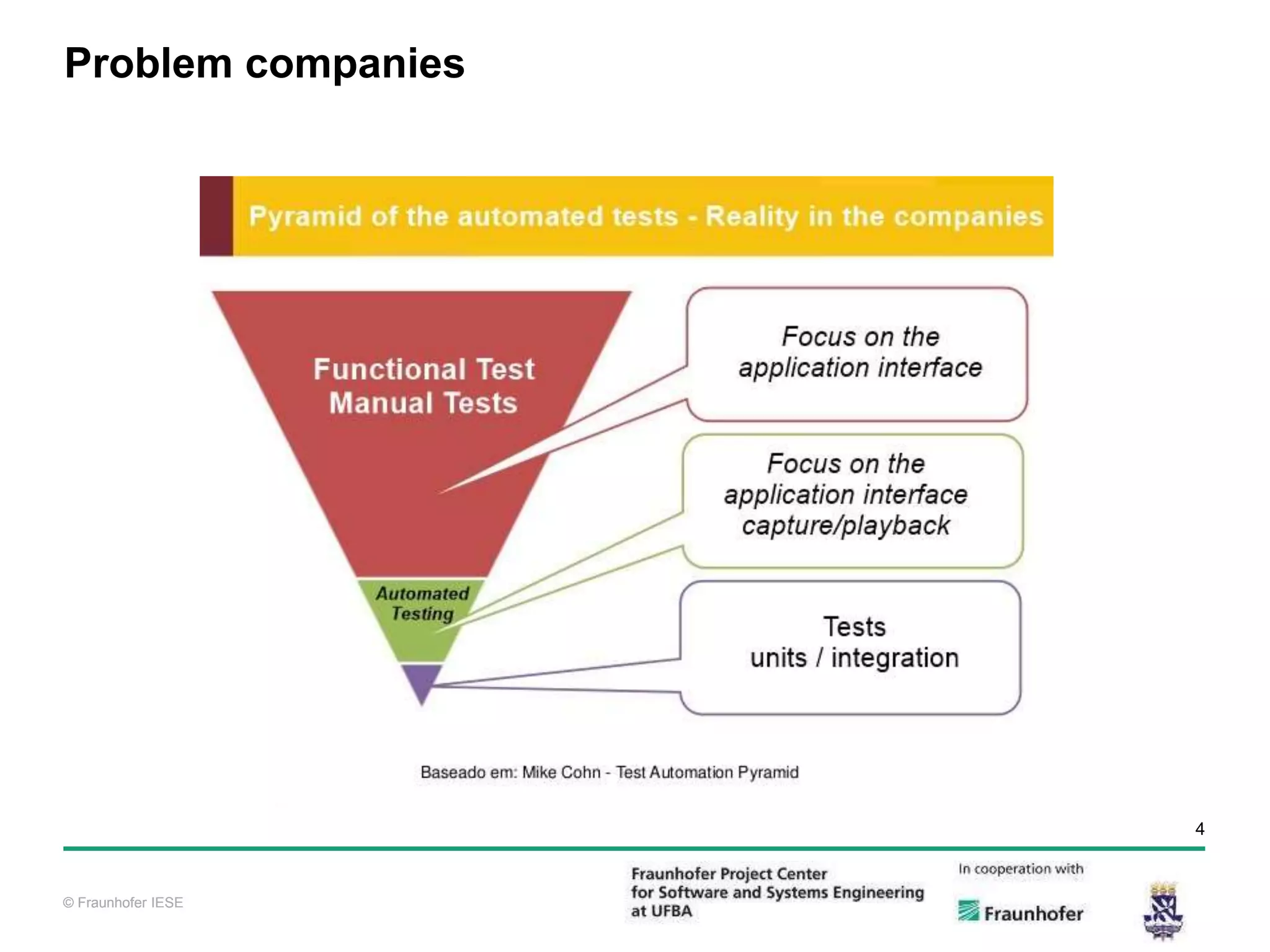
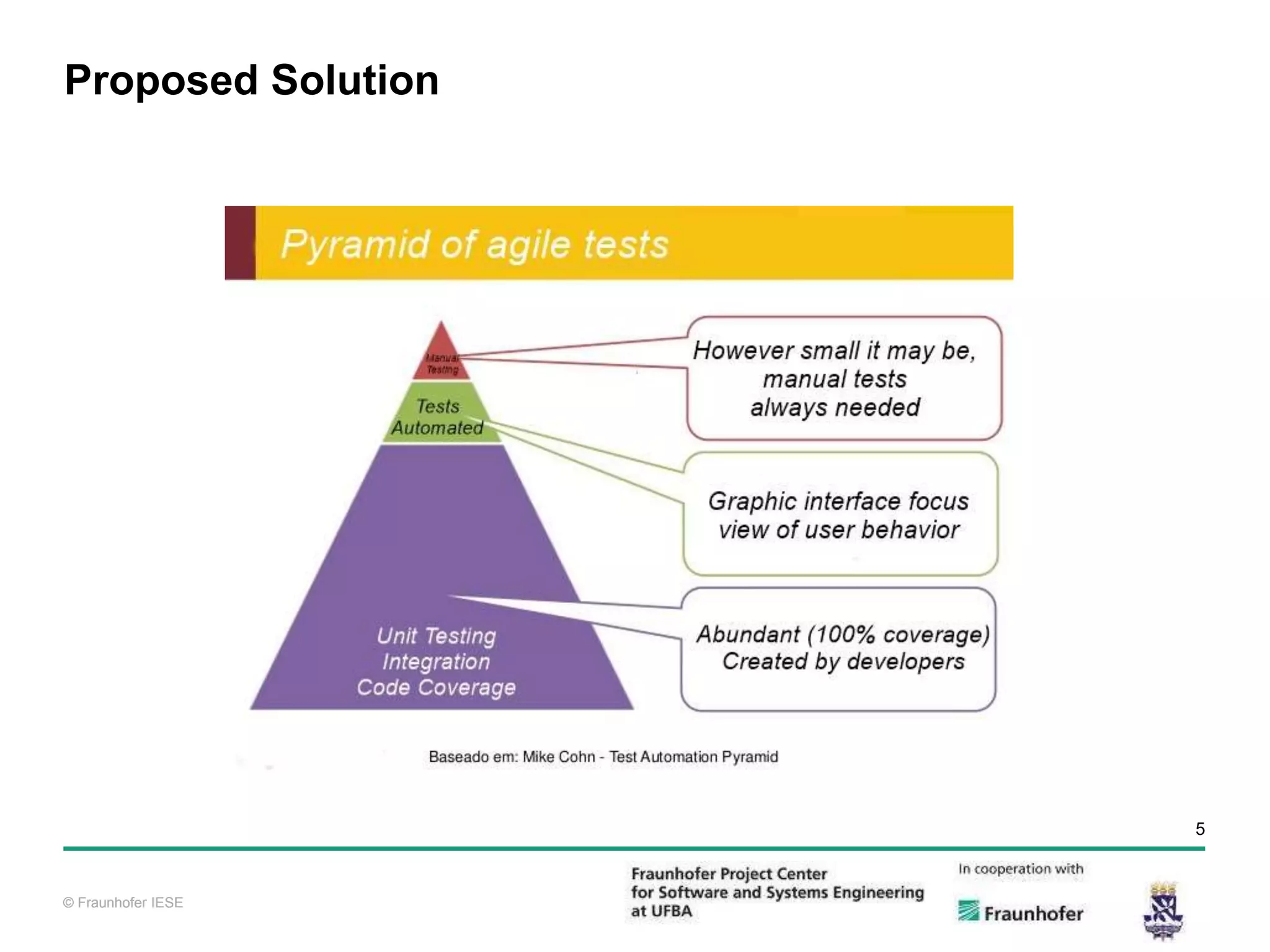
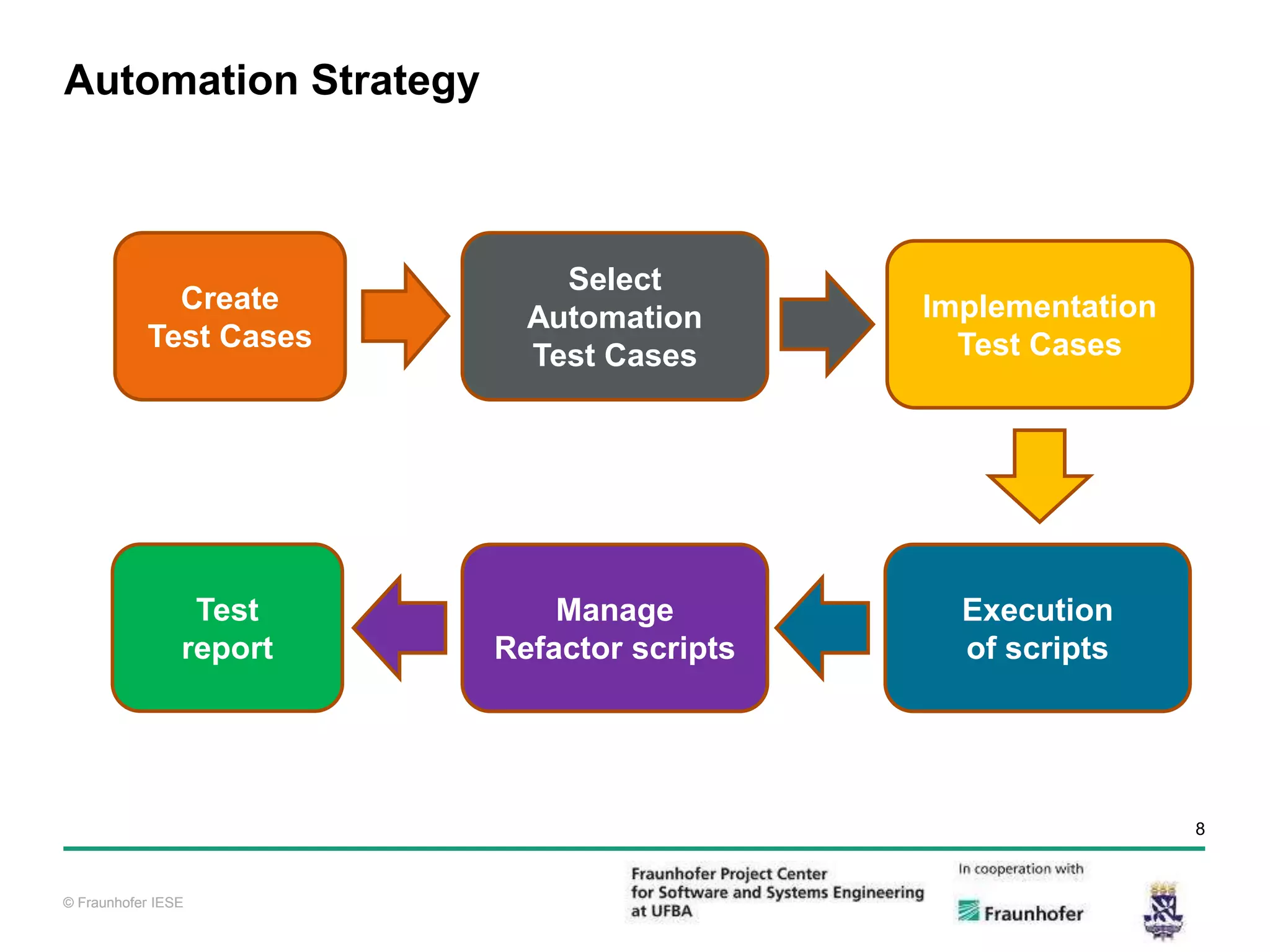
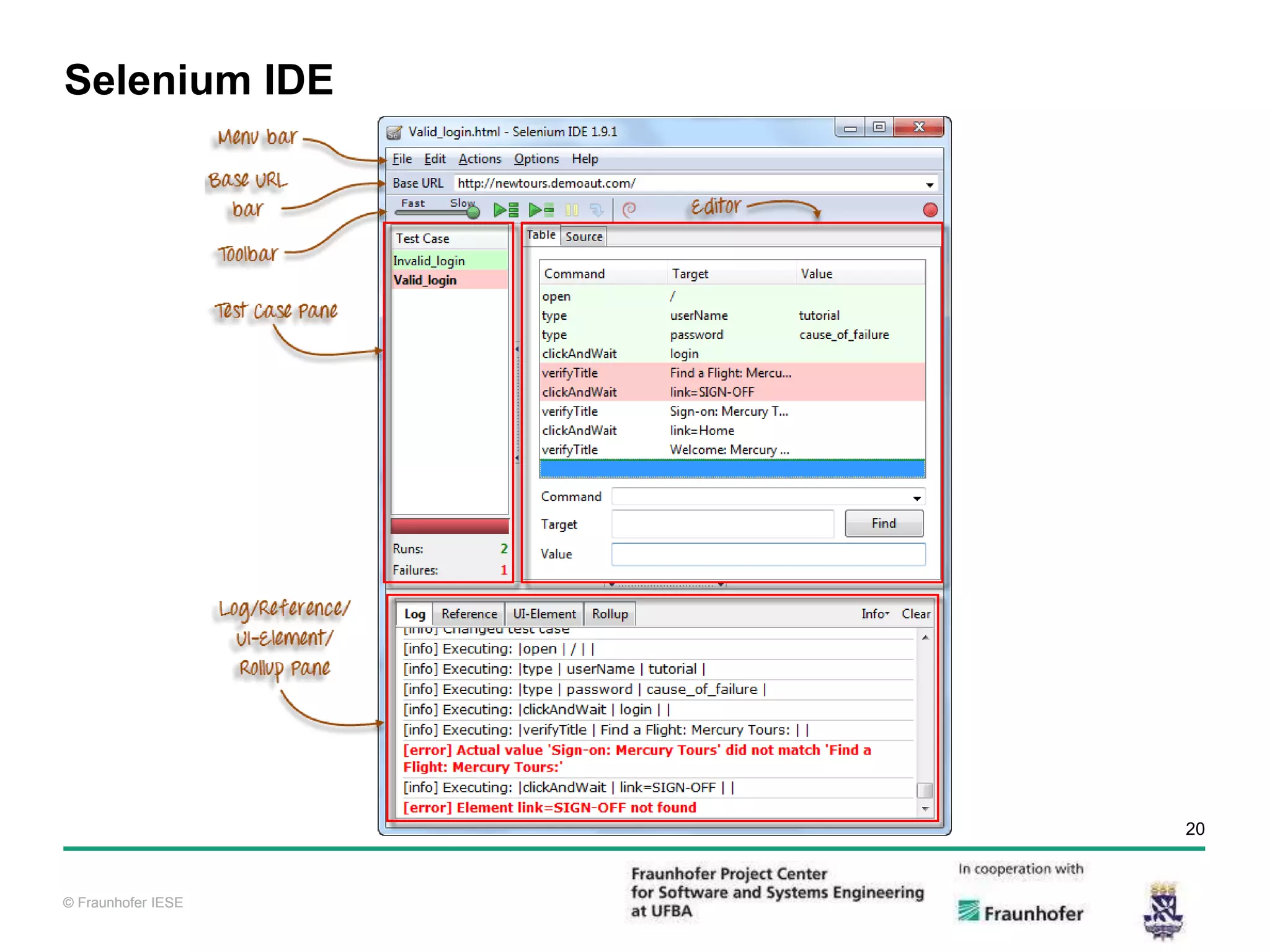
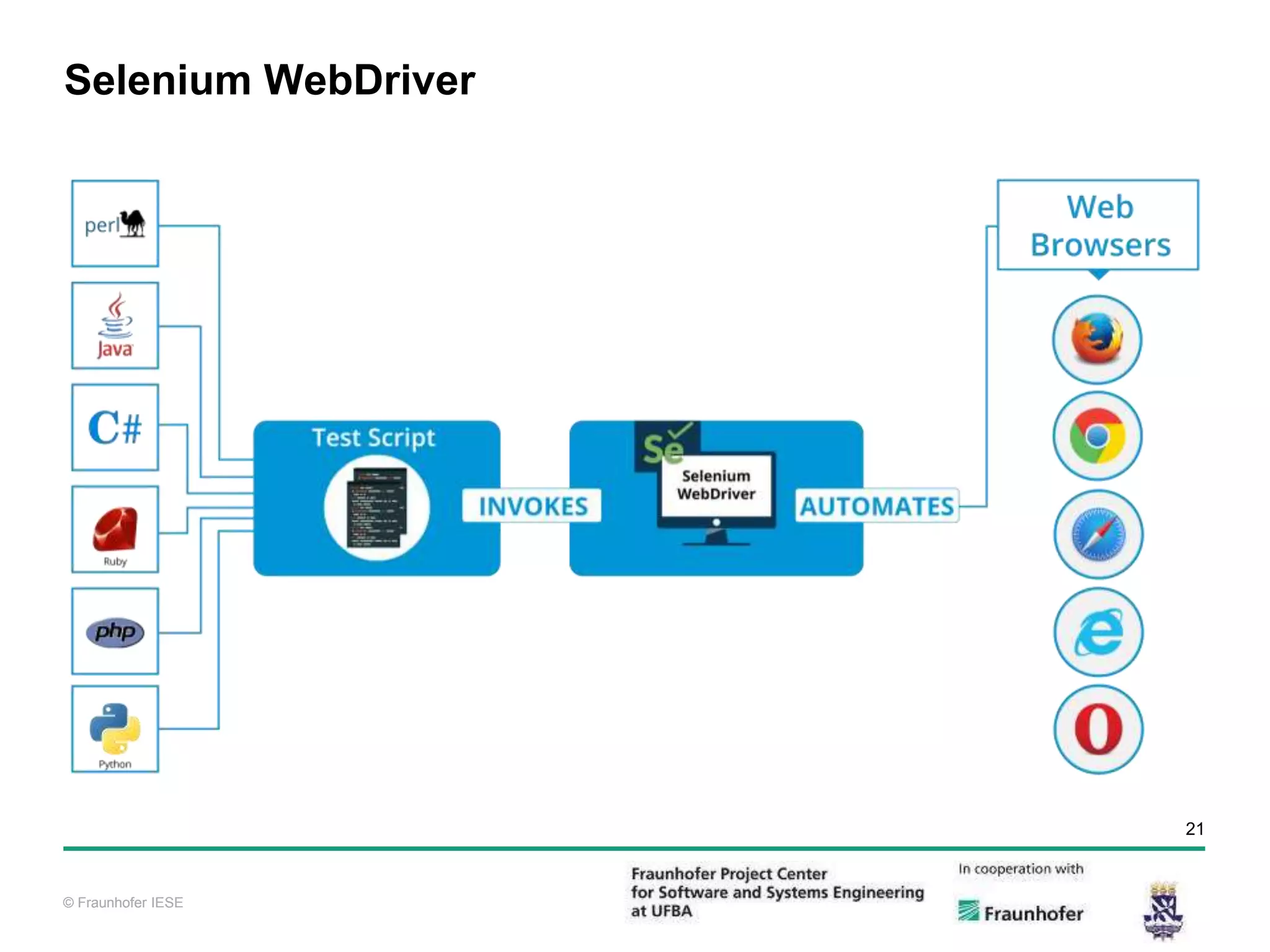
The document discusses functional test automation using Cucumber and Selenium. It introduces behavioral-driven development (BDD) and the problems with a lack of automation like reduced test coverage and bugs. It then describes Cucumber as a tool that uses BDD to write acceptance tests and Selenium as a tool for automating interactions with web browsers. The document provides details on how Cucumber and Selenium work and how to identify page elements before demonstrating how to automate a test.








![© Fraunhofer IESE 25 © Fraunhofer IESE Identifying Elements in Browser + detail Identification by ID Ex. <Input type = "text" id = "name" /> • Identification by NAME Ex. <Textarea name = "name"> </ textarea> • CSS Identification Ex. <Button class = "btn btn-medium btn-save" /> • XPath identification Ex. // input [@ name = "cpf"] • DOM dom=document.getElementById('loginForm') (3) dom=document.forms['loginForm'] (3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontothefunctionaltestautomationwithcucumberandselenium-180525202453/75/Introduction-to-the-functional-test-automation-with-cucumber-and-selenium-25-2048.jpg)