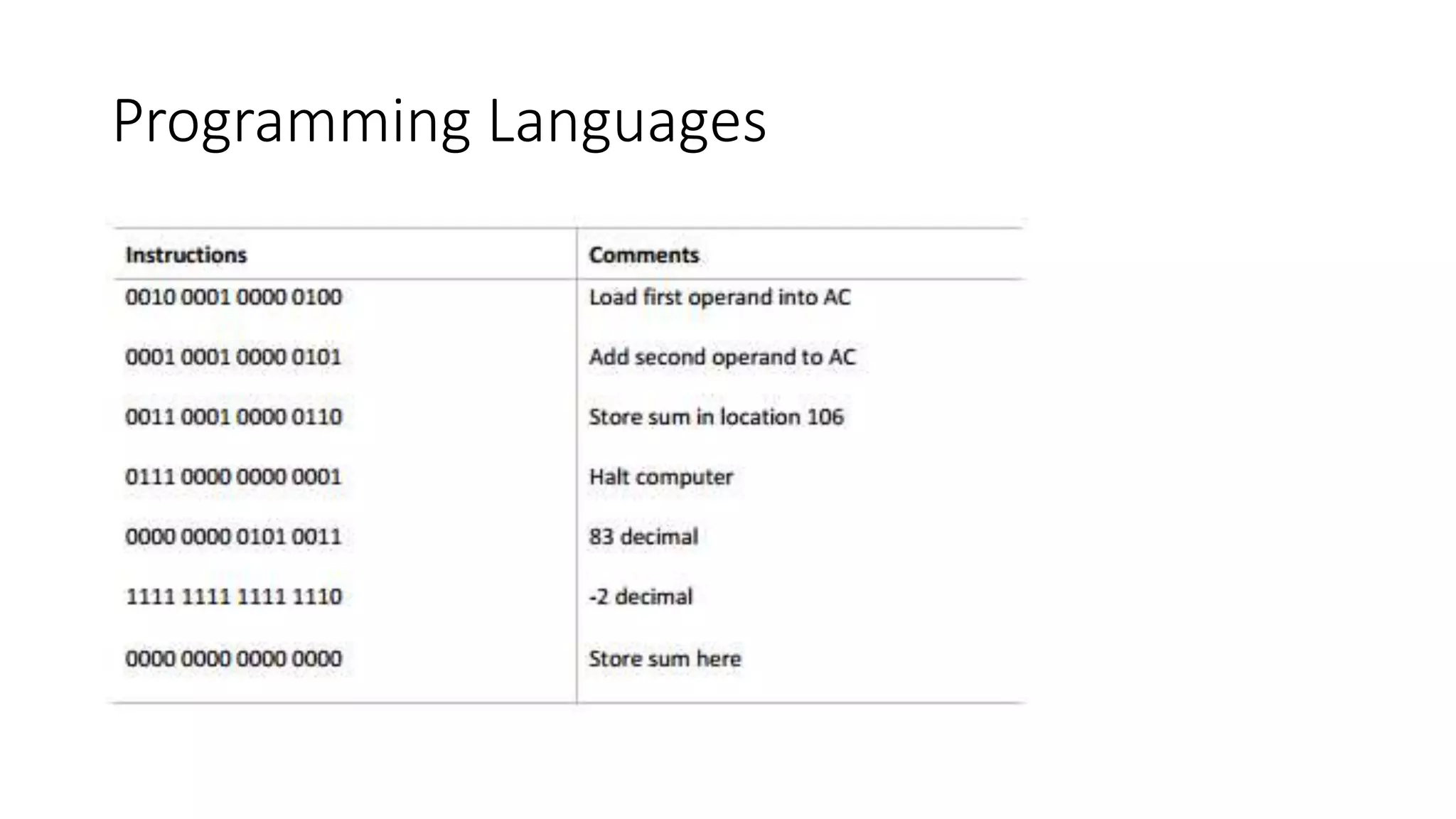
This document provides an introduction and overview of programming languages. It discusses the different types of programming languages including machine languages, assembly languages, and high-level languages. It also outlines the components of programming languages, such as syntax and semantics. Finally, it categorizes programming languages into structured programming languages, modular programming languages, and object-oriented programming languages.