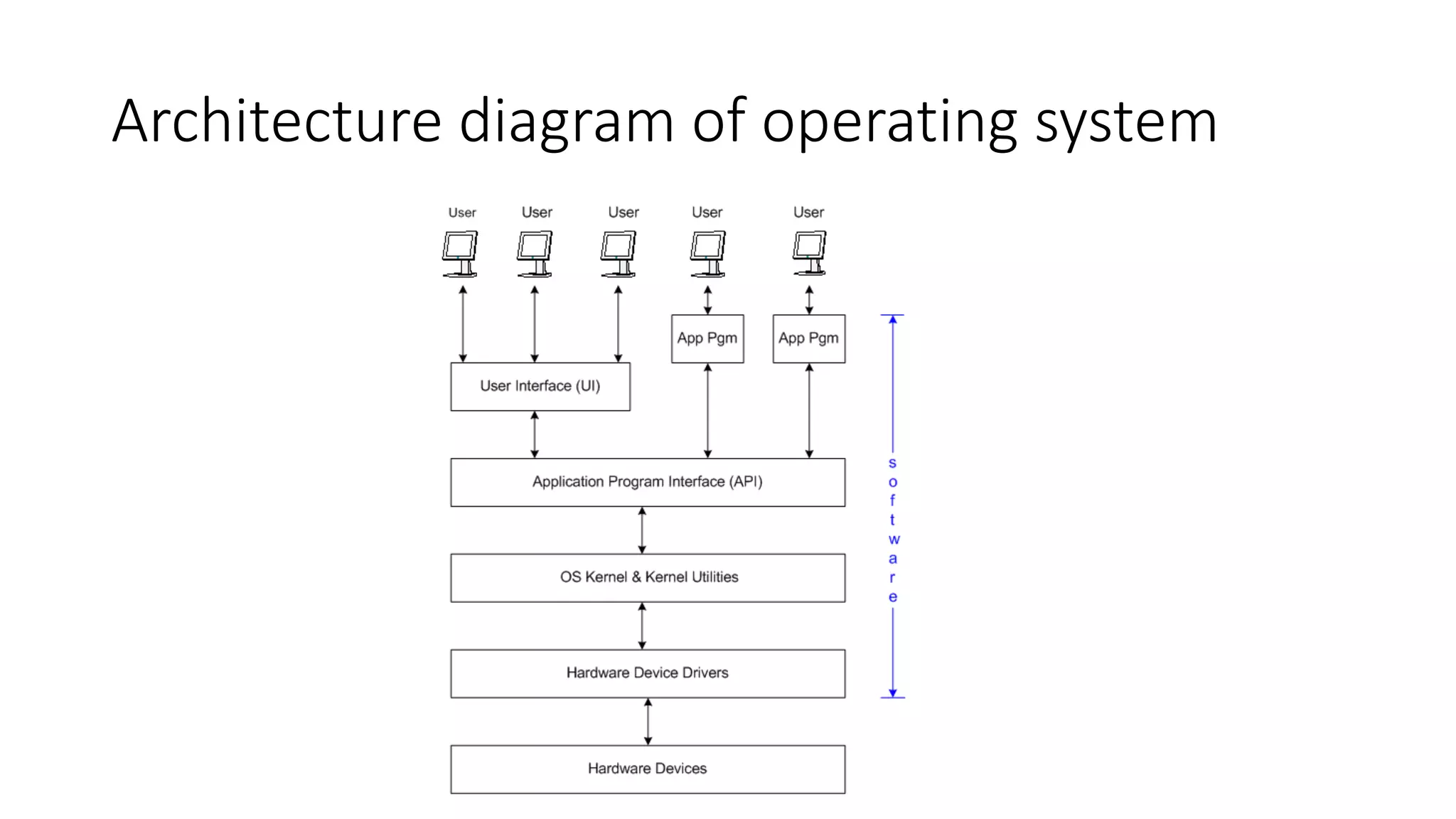
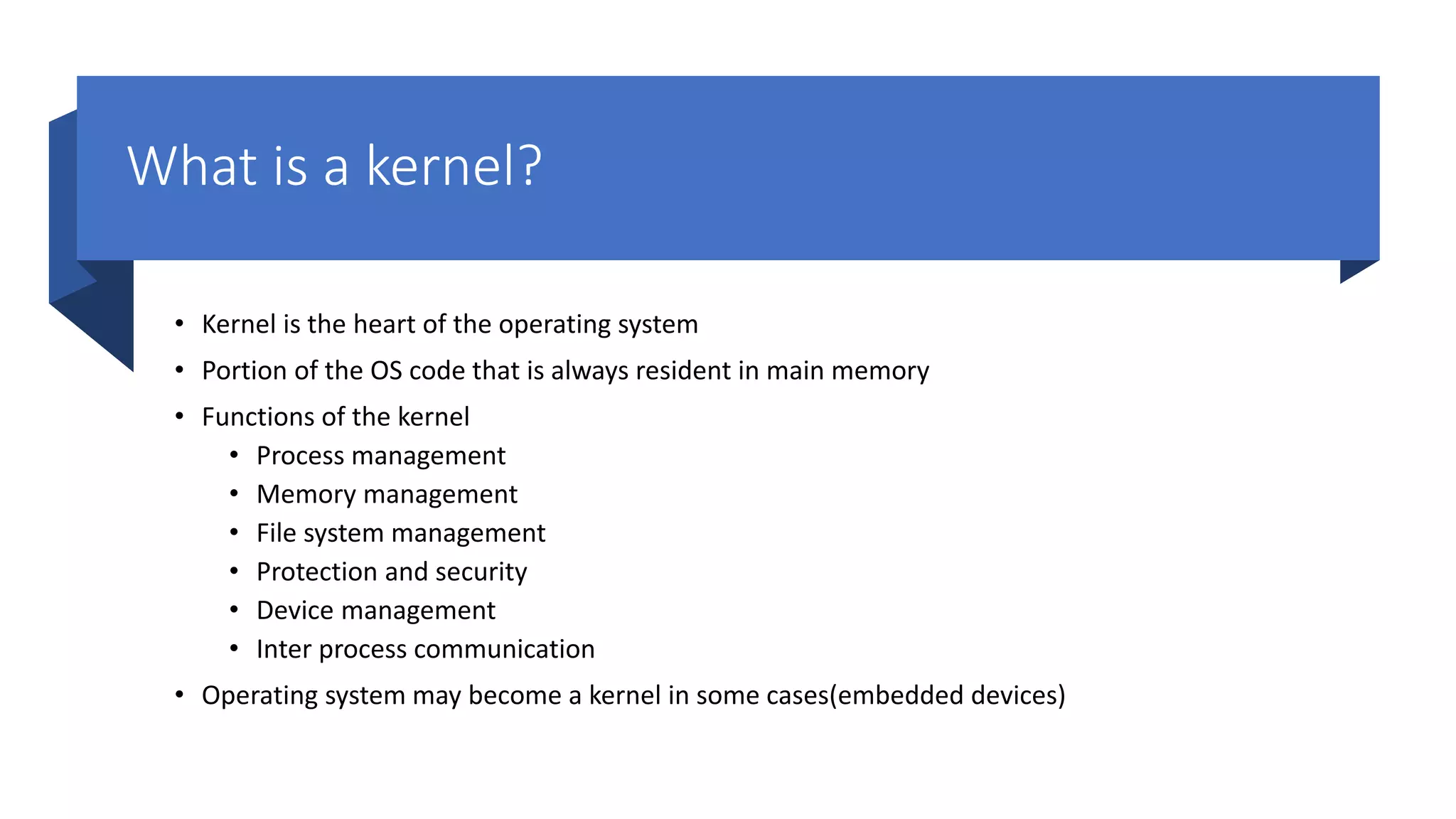
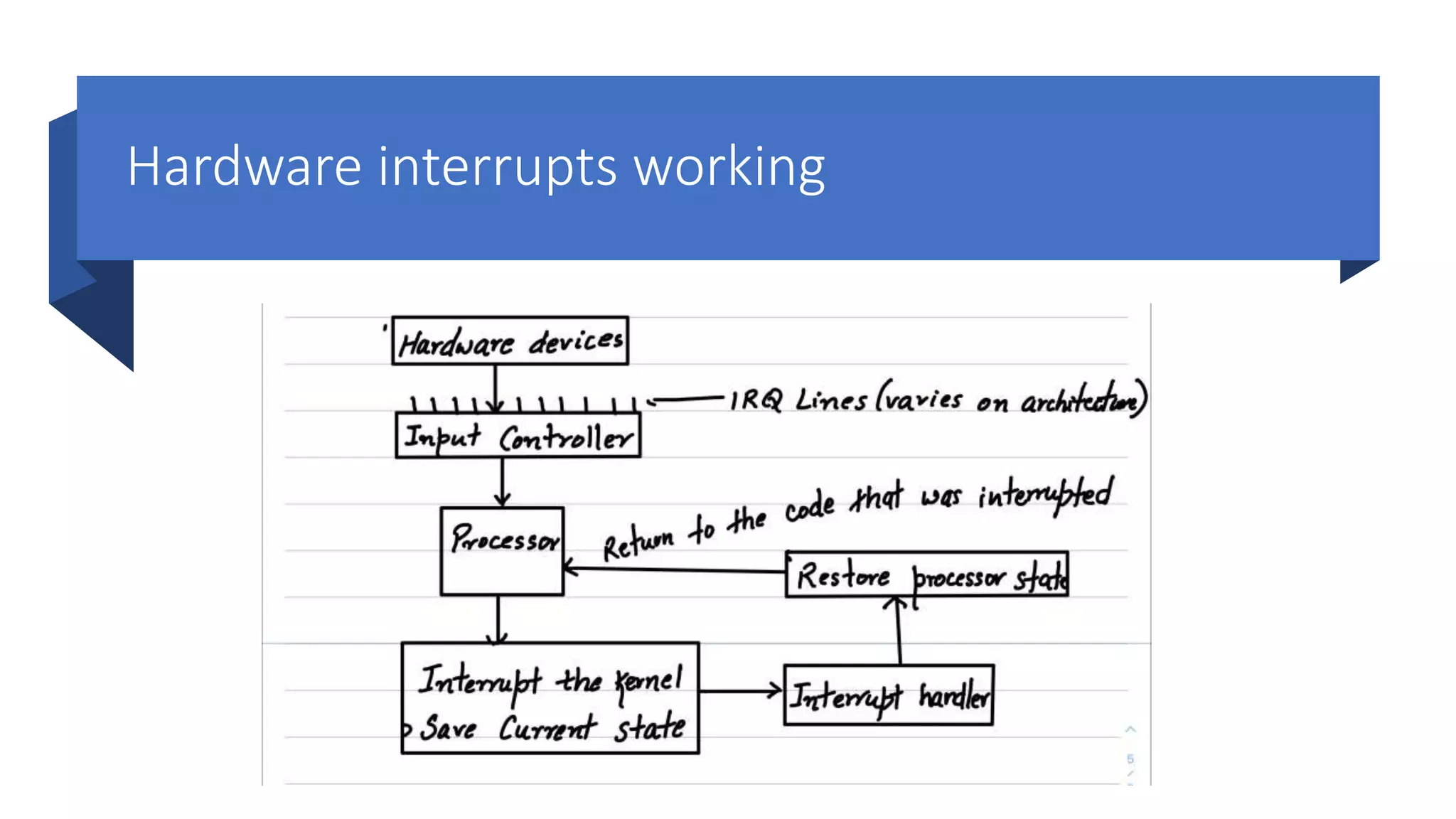
The document outlines a comprehensive introduction to operating systems, covering key topics such as operating systems interview questions, process management, memory management, and system calls. It also includes personal background information about the presenter, resources for further learning, and an invitation to join practical classes. Additional details on the structure and functions of operating systems and kernels, as well as the importance of system calls and interrupts, are provided.