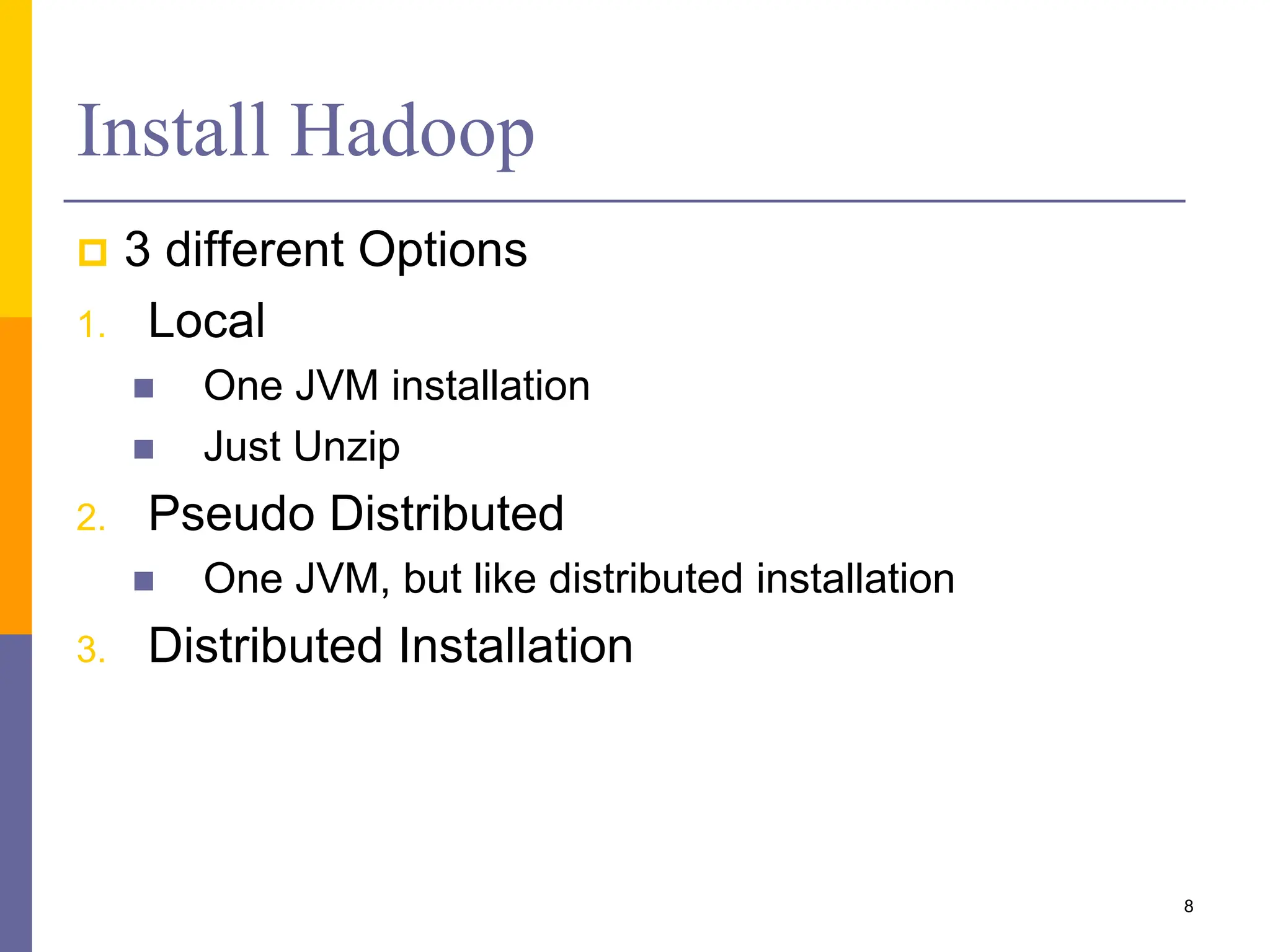
This document provides an overview of MapReduce programming with Hadoop, including descriptions of HDFS architecture, examples of common MapReduce algorithms (word count, mean, sorting, inverted index, distributed grep), and how to write MapReduce clients and customize parts of the MapReduce job like input/output formats, partitioners, and distributed caching of files.





![Example – Word Count Find words in a collection of documents & their frequency of occurrence Map(docId, text): for all terms t in text emit(t, 1); Reduce(t, values[]) int sum = 0; for all values v sum += v; emit(t, sum); 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-map-reduceprogrammingwithhadoop-240417104903-dd4f51b4/75/Introduction-to-Map-Reduce-Programming-with-Hadoop-10-2048.jpg)
![Example – Mean Compute mean value associated with same key Map(k, value): emit(k, value); Reduce(k, values[]) int sum = 0; int count = 0; for all values v sum += v; count += 1; emit(k, sum/count); 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-map-reduceprogrammingwithhadoop-240417104903-dd4f51b4/75/Introduction-to-Map-Reduce-Programming-with-Hadoop-11-2048.jpg)
![Example – Sorting How to sort an array of 1 million integers using Map reduce? Partial sorts at mapper & final sort by reducer Use of locality preserving hash function If k1 < k2 then hash(k1) < hash(k2) Map(k, v): int val = read value from v emit(val, val); Reduce(k, values[]) emit(k, k); 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-map-reduceprogrammingwithhadoop-240417104903-dd4f51b4/75/Introduction-to-Map-Reduce-Programming-with-Hadoop-12-2048.jpg)
![Example – Inverted Index Normal index is a mapping from document to terms Inverted index is mapping from terms to documents If we have a million documents, how do we build a inverted index using Map-Reduce? Map(docid, text): for all word w in text emit(w, docid) Reduce(w, docids[]) emit(w, docids[]); 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-map-reduceprogrammingwithhadoop-240417104903-dd4f51b4/75/Introduction-to-Map-Reduce-Programming-with-Hadoop-13-2048.jpg)
![Example – Distributed Grep map(k, v): Id docId = .. (read file name) If (v maps grep) emit(k, (pattern, docid)) Reduce(k, values[]) emit(k, values); 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-map-reduceprogrammingwithhadoop-240417104903-dd4f51b4/75/Introduction-to-Map-Reduce-Programming-with-Hadoop-14-2048.jpg)


![Map Reduce Client public class WordCountSample { public static class Map extends MapReduceBase implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> { private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); private Text word = new Text(); public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException {….. } } } public static class Reduce extends MapReduceBase implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values, OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException { ..} } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { JobConf conf = new JobConf(WordCountSample.class); conf.setJobName("wordcount"); conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); conf.setMapperClass(Map.class); conf.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class); conf.setReducerClass(Reduce.class); conf.setInputFormat(TextInputFormat.class); conf.setOutputFormat(TextOutputFormat.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(conf, new Path("/input")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(conf, new Path("/output/"+ System.currentTimeMillis())); JobClient.runJob(conf); } } 17 Example: http://wiki.apache.org/hadoop/WordCount](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-map-reduceprogrammingwithhadoop-240417104903-dd4f51b4/75/Introduction-to-Map-Reduce-Programming-with-Hadoop-17-2048.jpg)