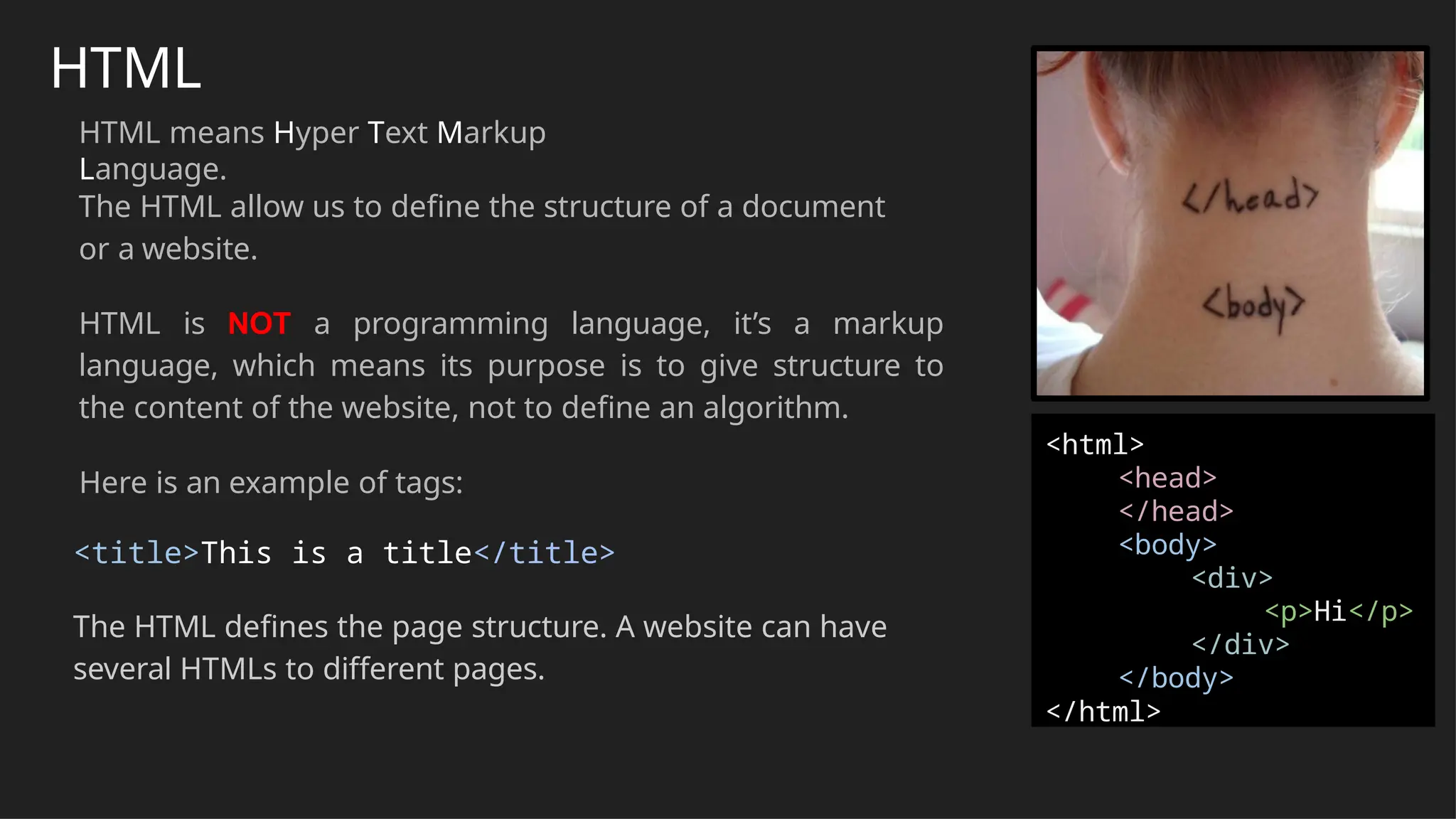
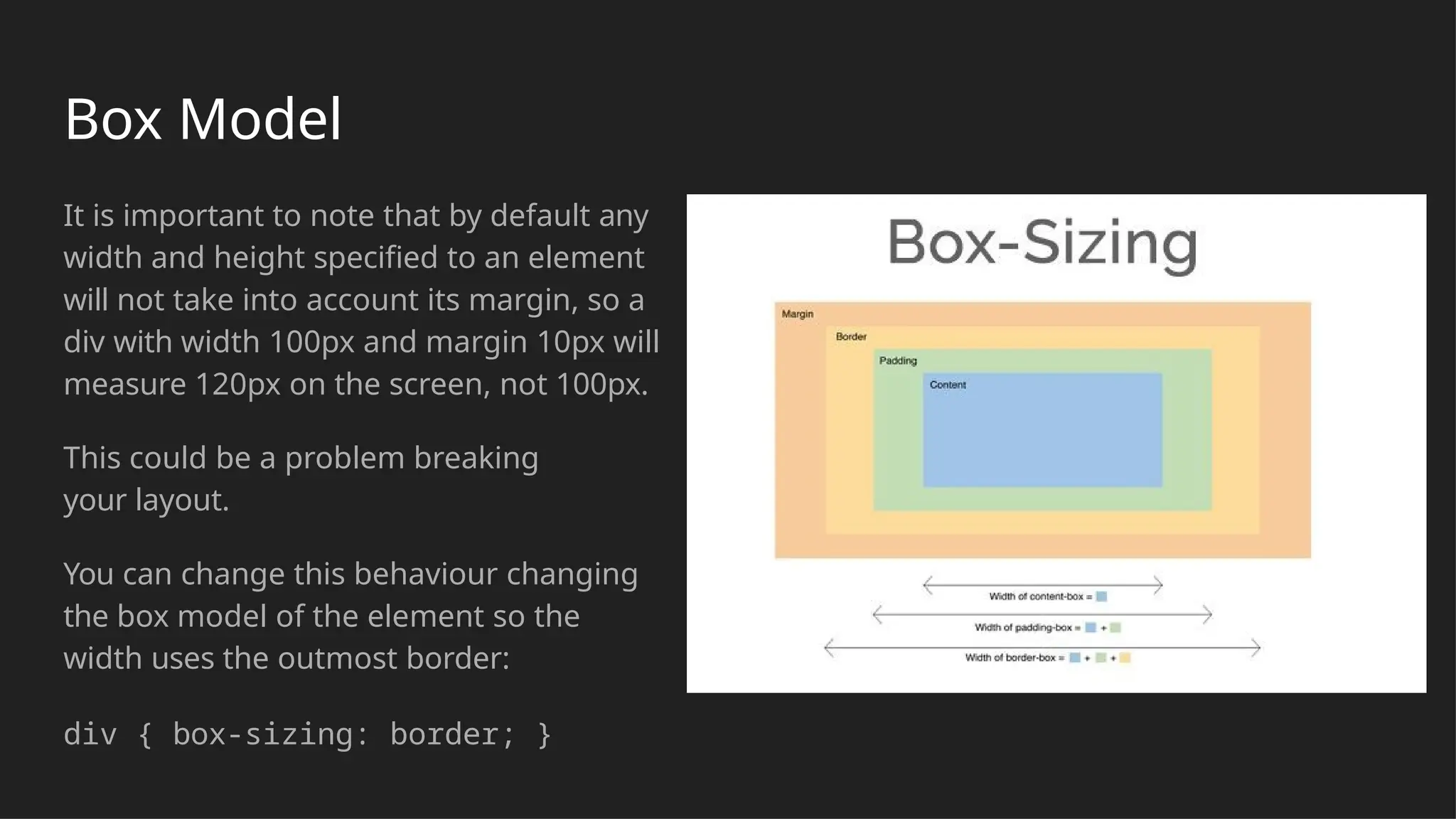
The document outlines the fundamentals of web technologies focusing on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It explains how HTML structures web content, CSS controls visual styling, and JavaScript adds interactivity, providing examples of syntax and common elements used in web development. Additionally, it discusses layout techniques, including the flexbox model, and shows an example of a website structure combining these technologies.














![Javascript: Syntax Very similar to C++ or Java but much simpler. var my_number = 10; //this is a comment var my_string = "hello"; var my_array = [10,20,"name",true]; var my_object = { name: "javi", city: "Barcelona" }; function say( str ) { for(var i = 0; i < 10; ++i) console.log(" say: " + str );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontohtmlcssjavascriptbydeepu-241109051639-3a731db4/75/Introduction-to-HTML-CSS-Javascript-by-Deepu-pptx-17-2048.jpg)