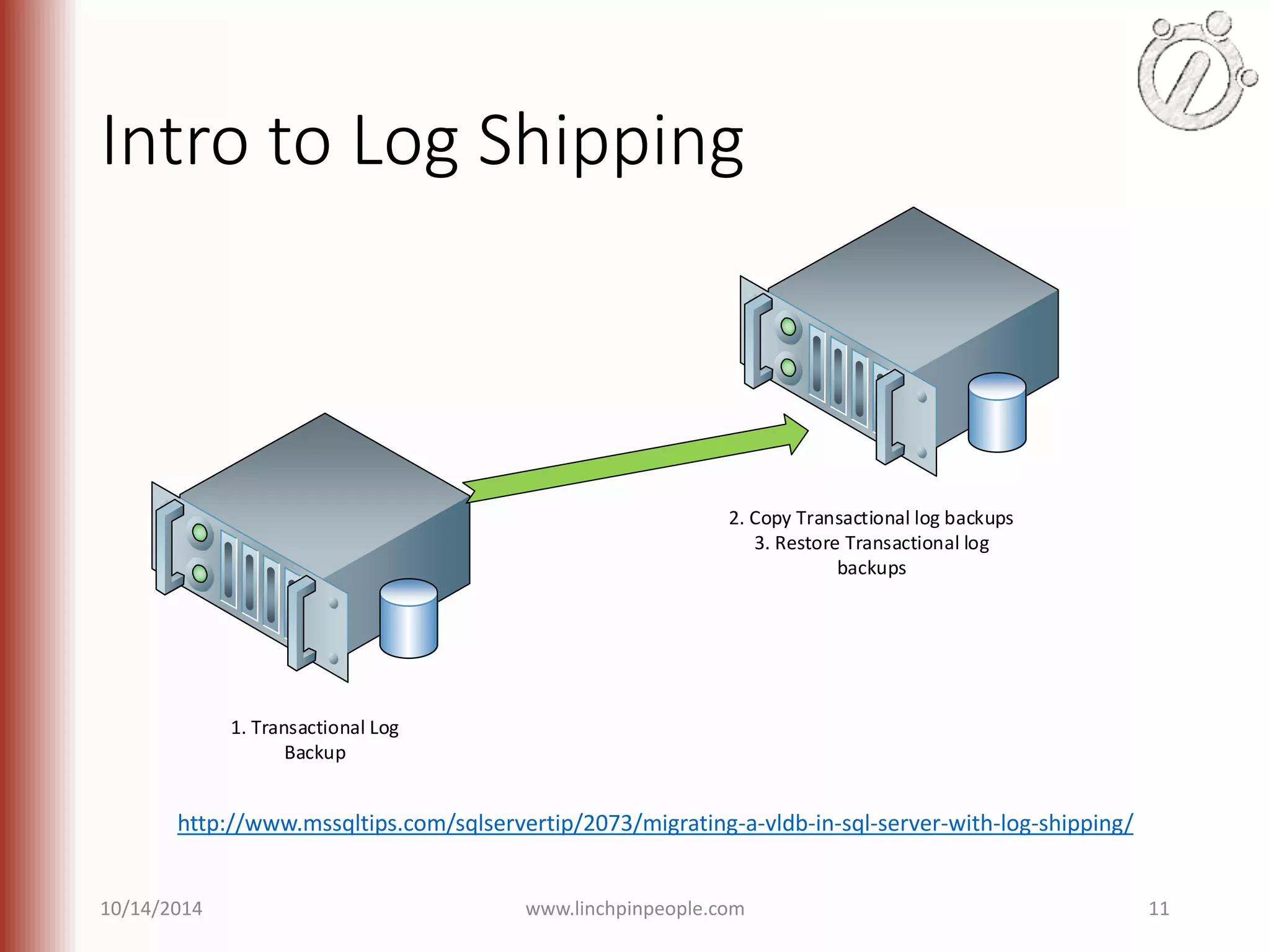
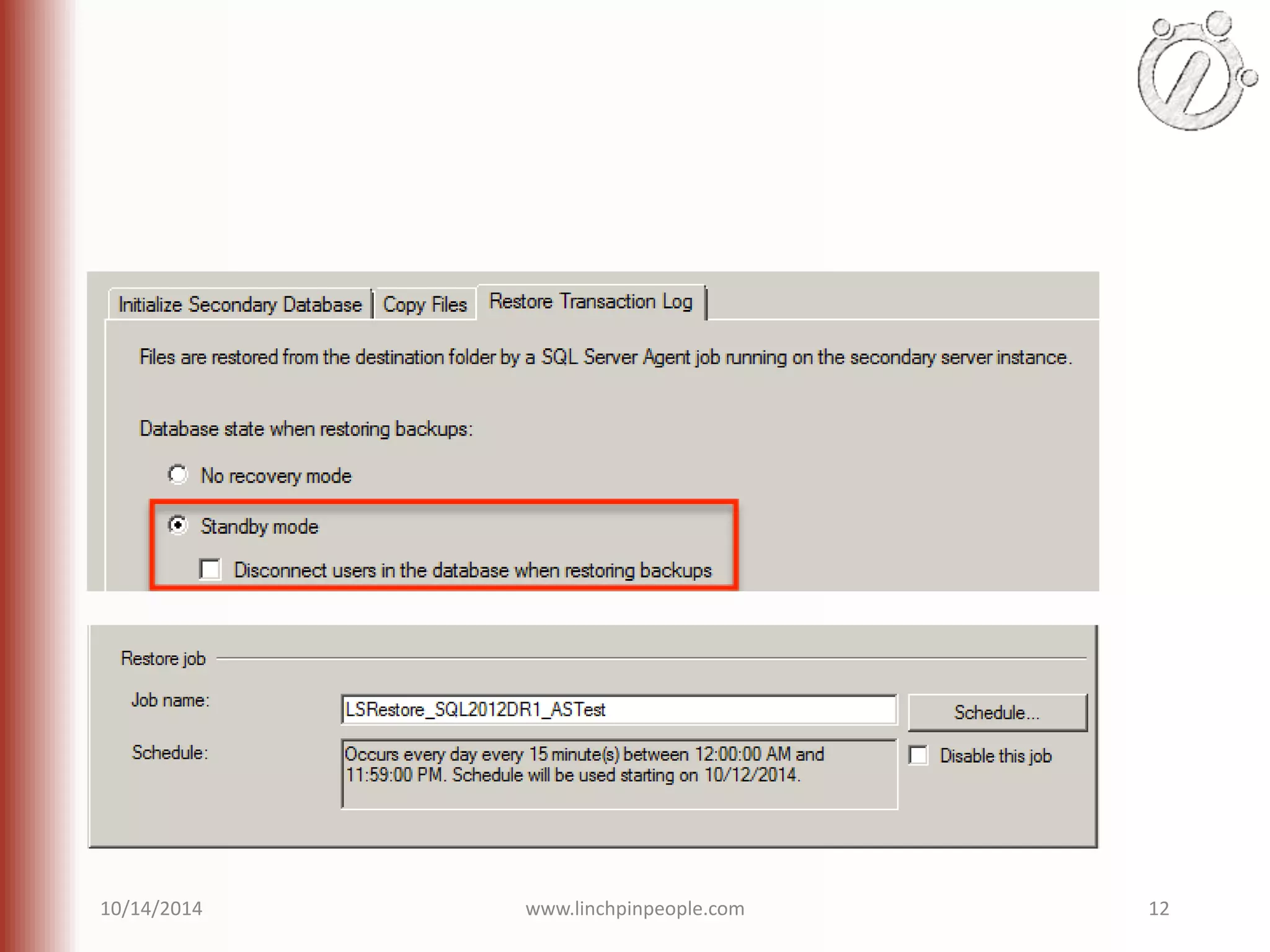
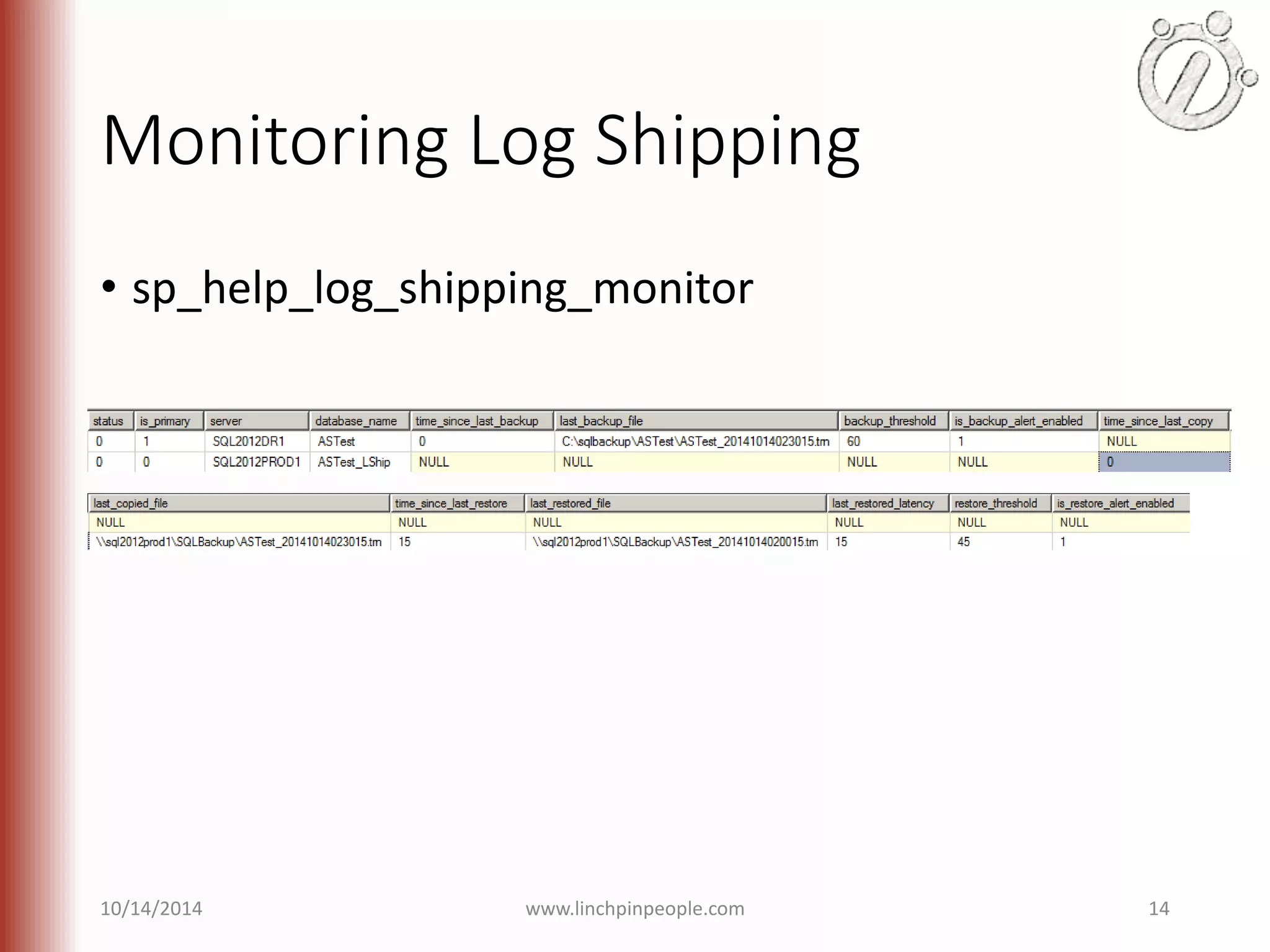
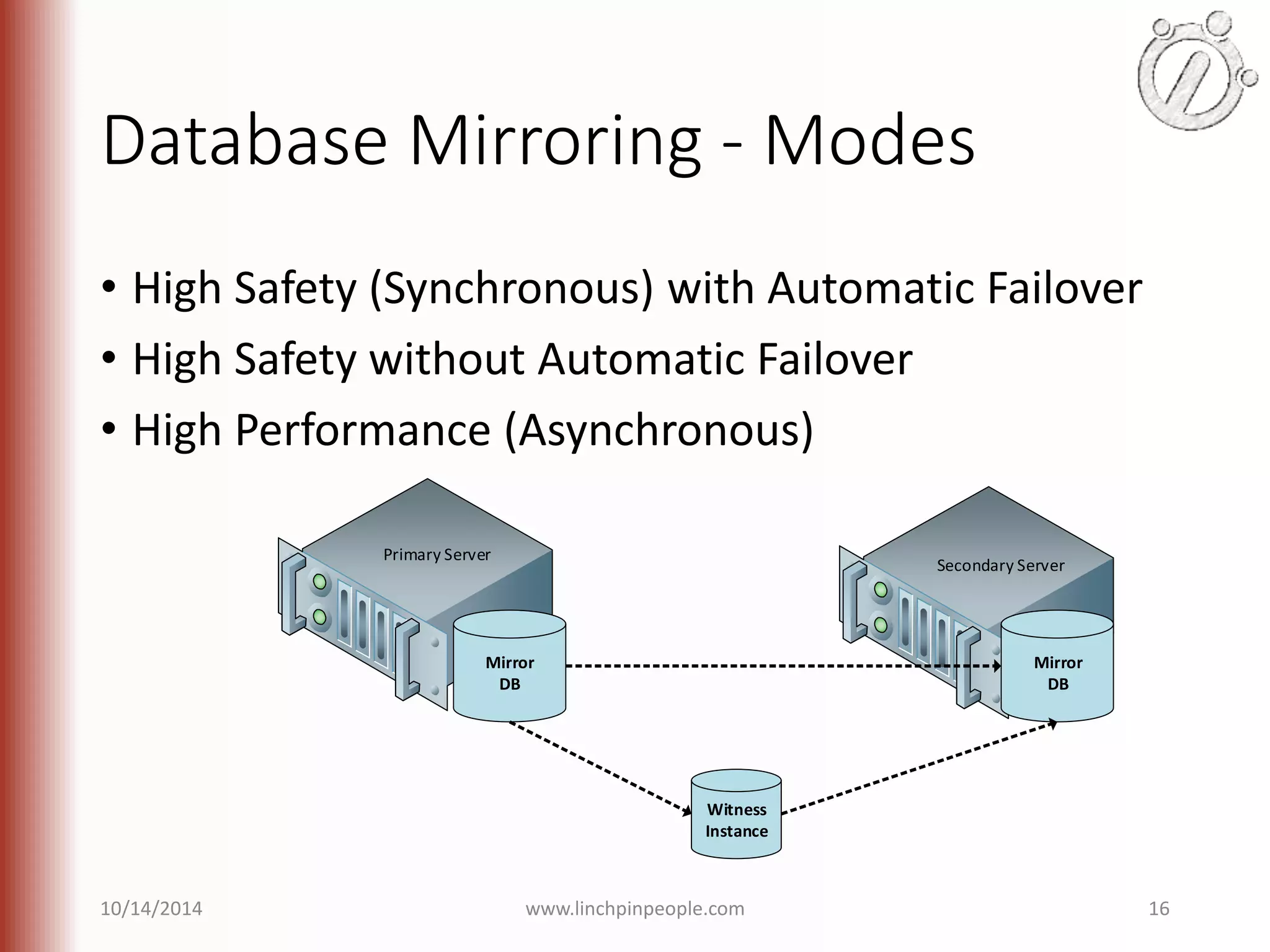
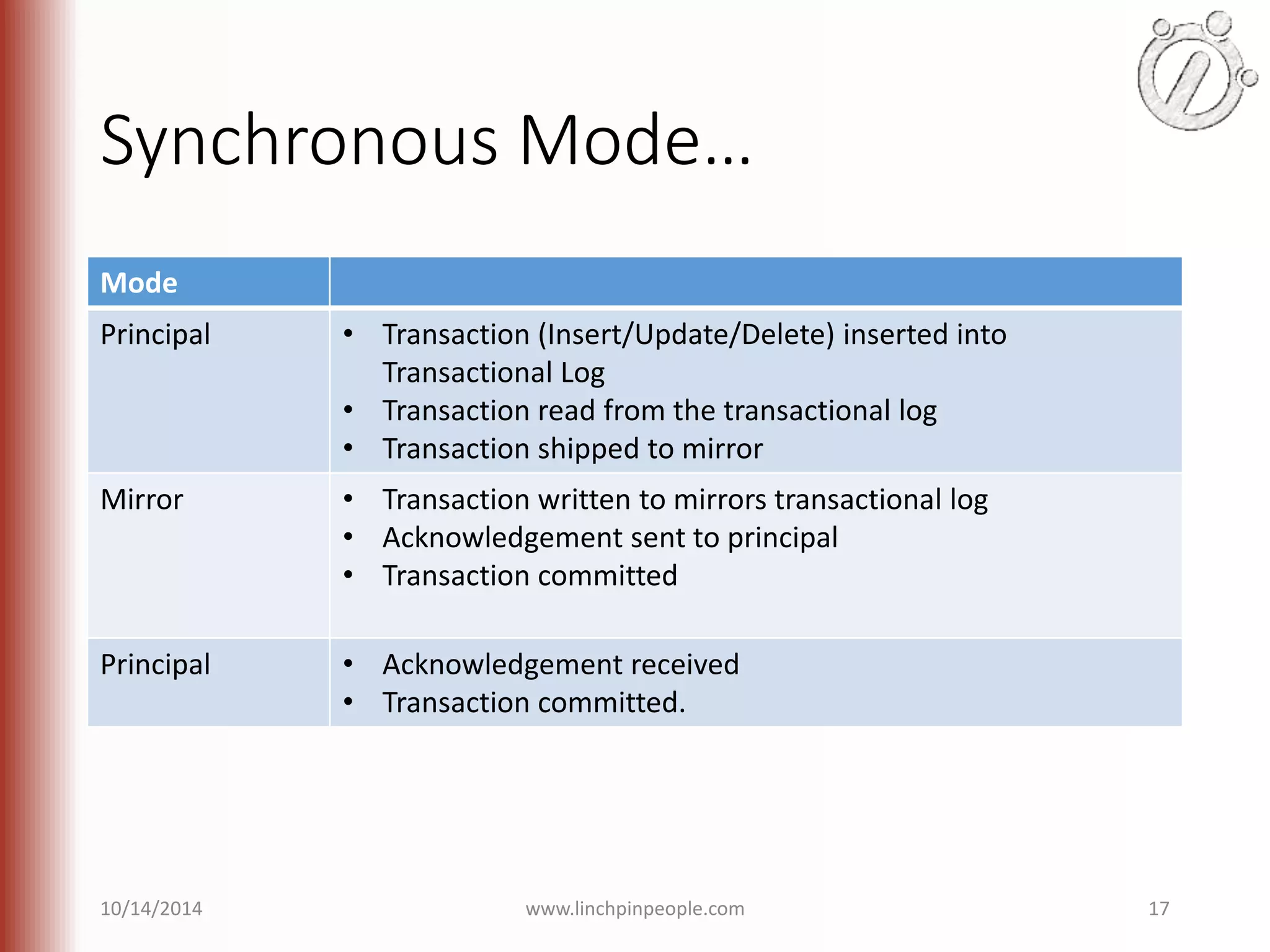
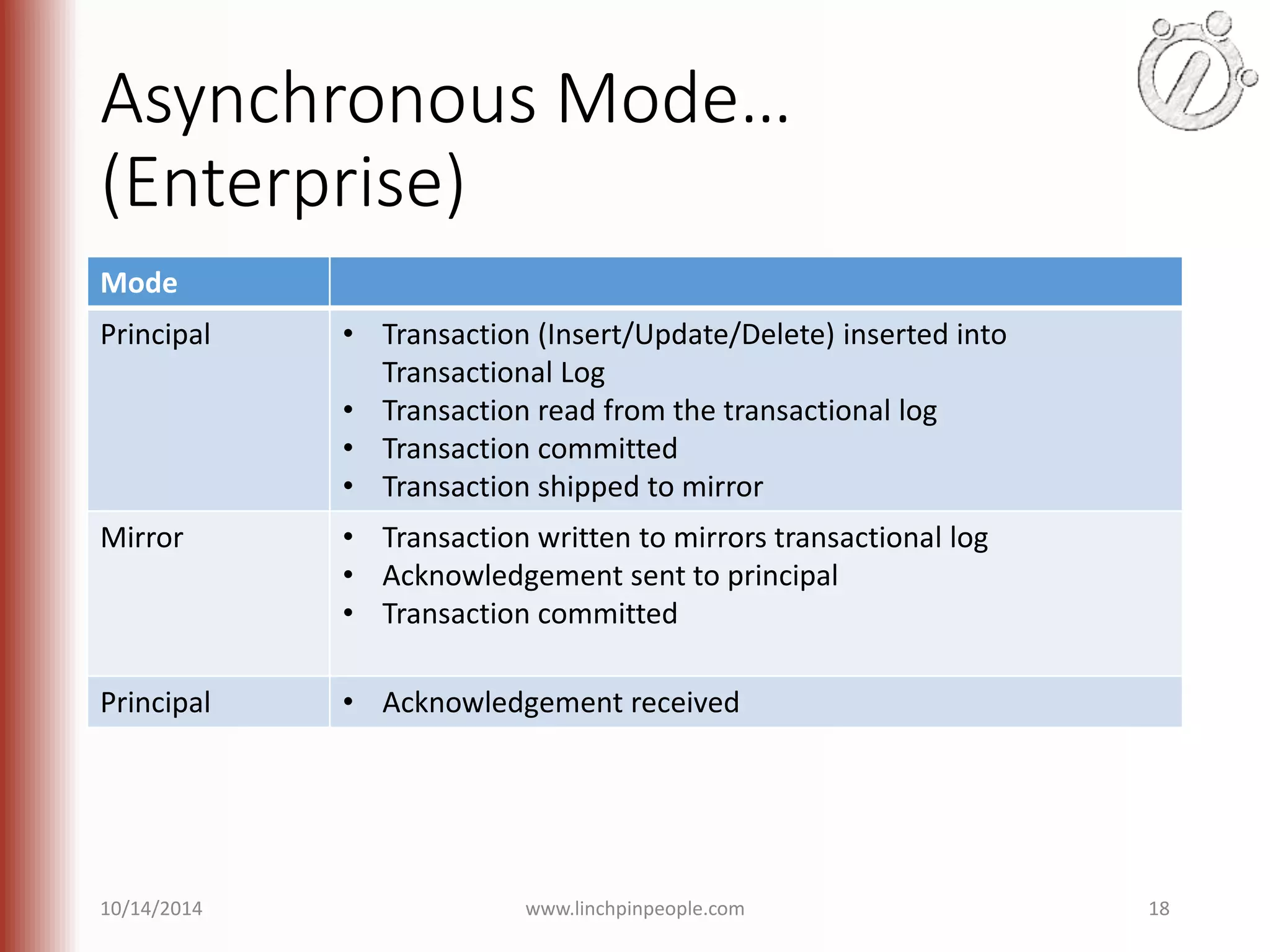
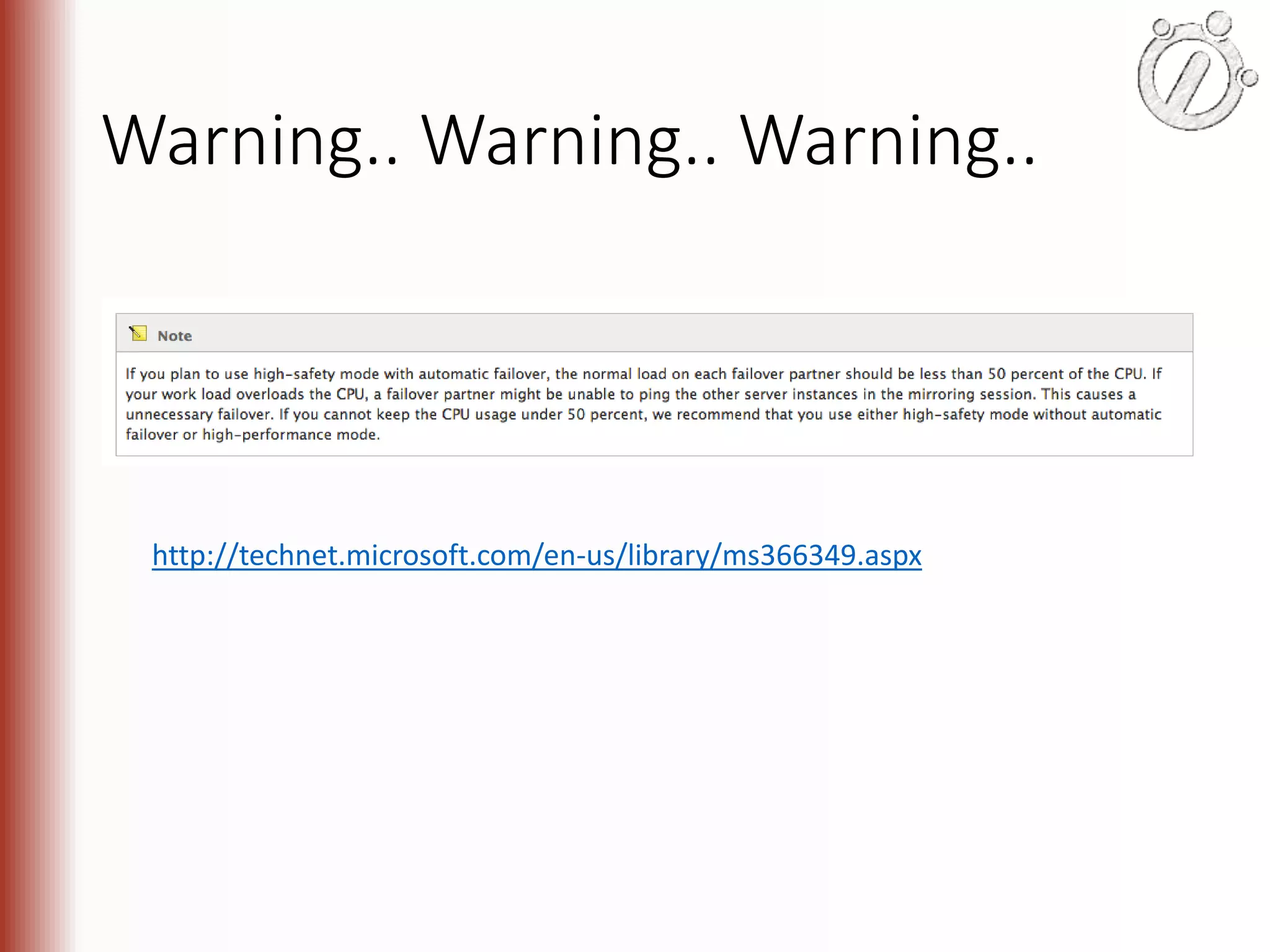
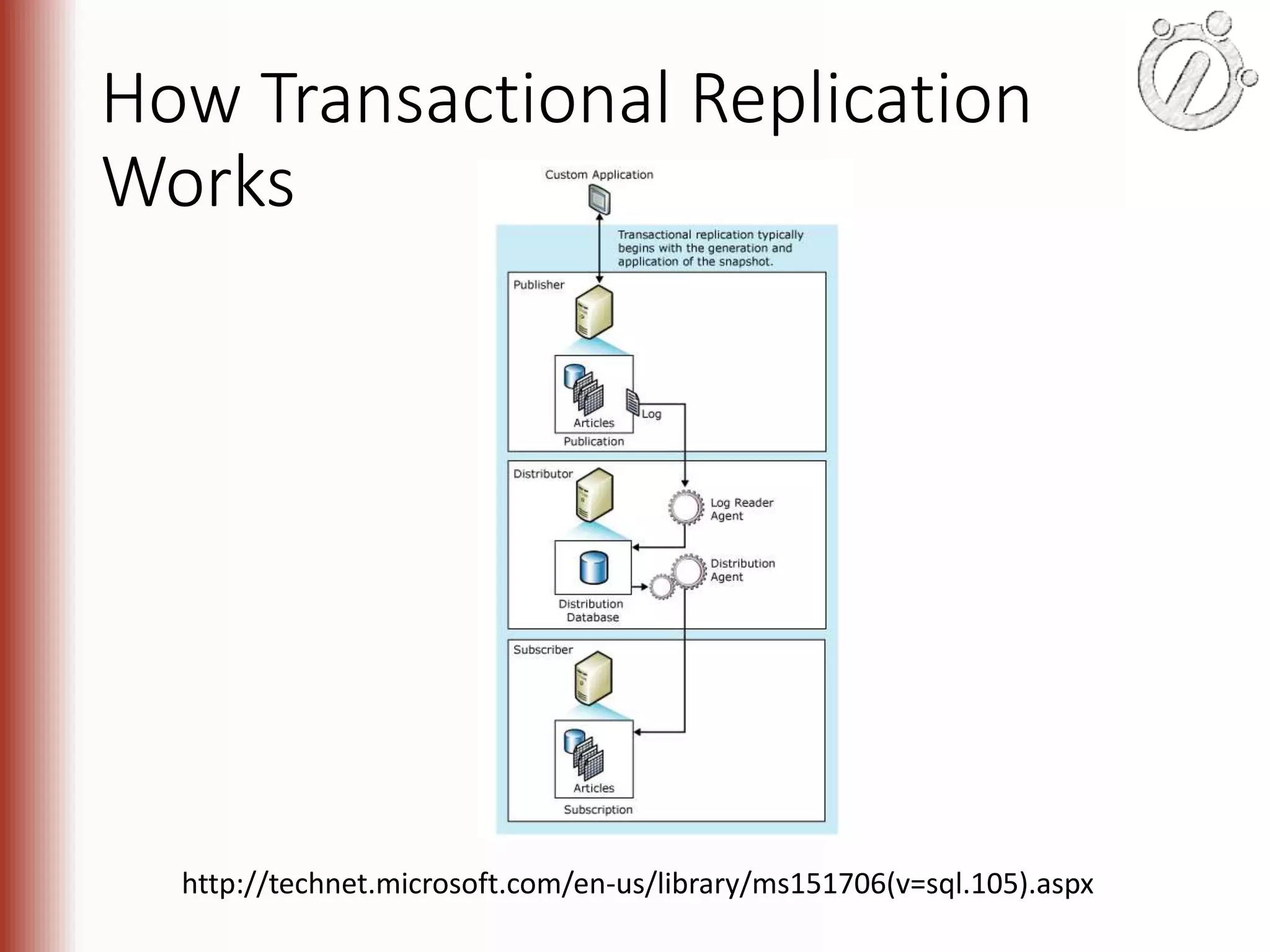
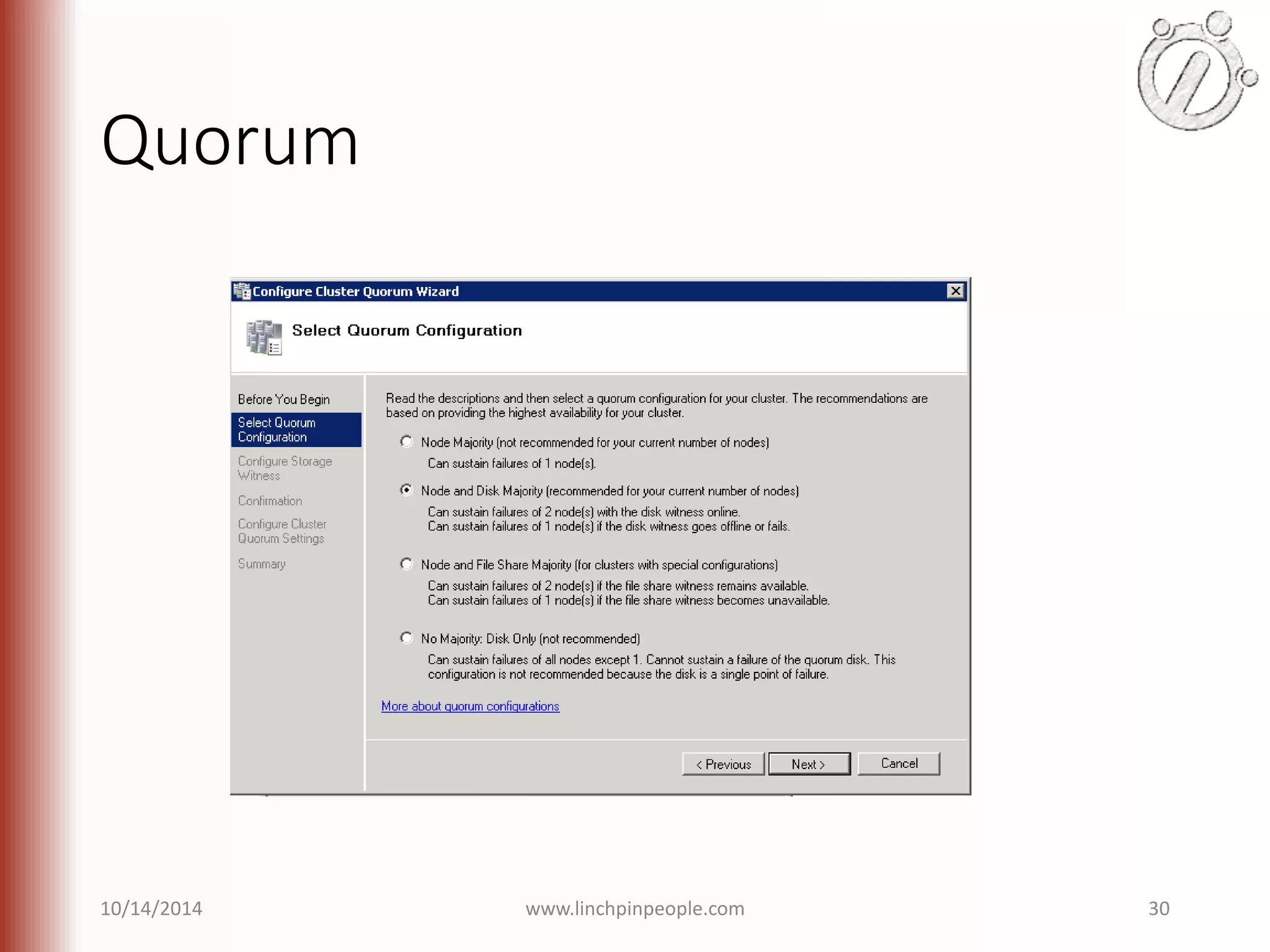
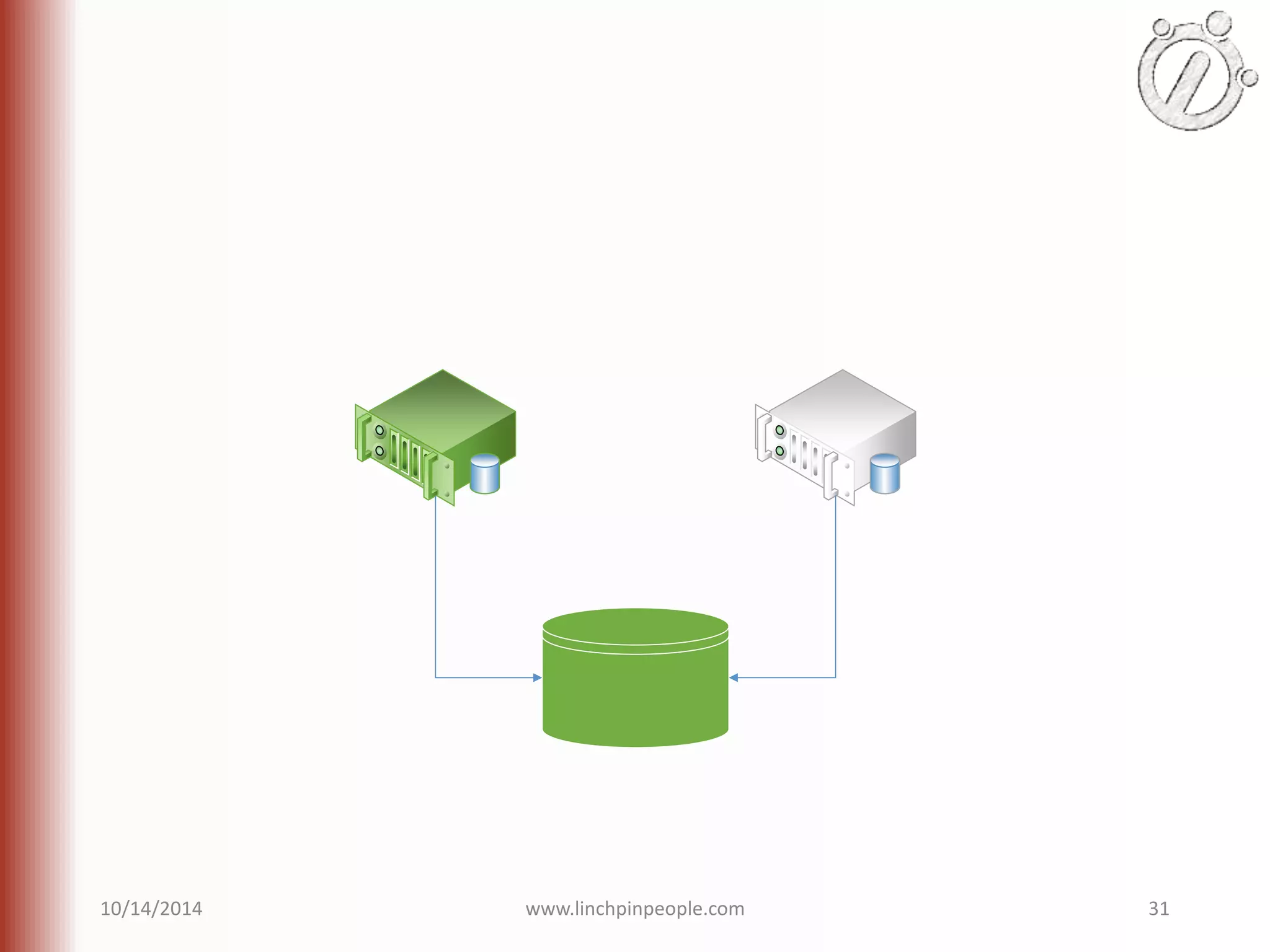
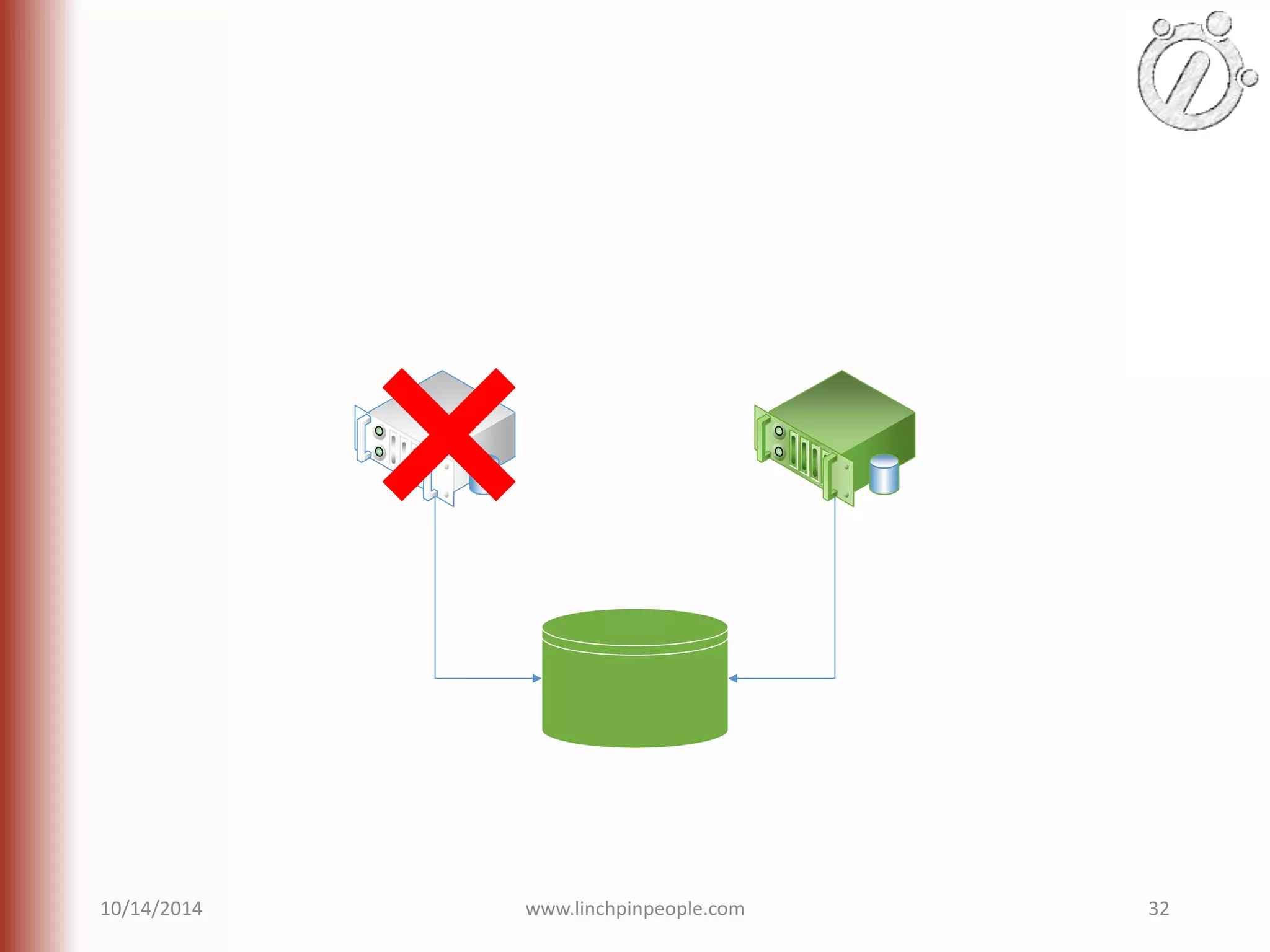
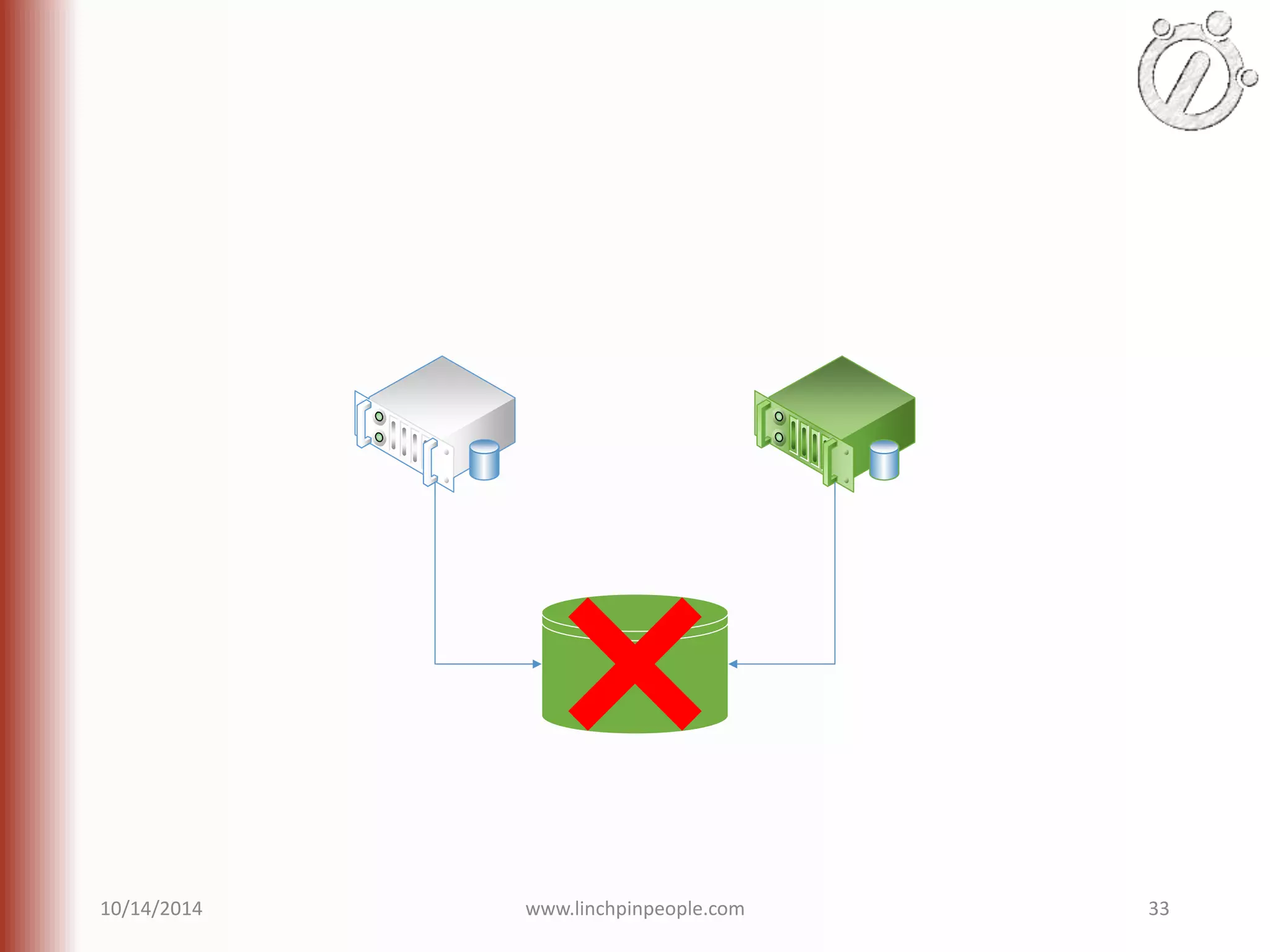
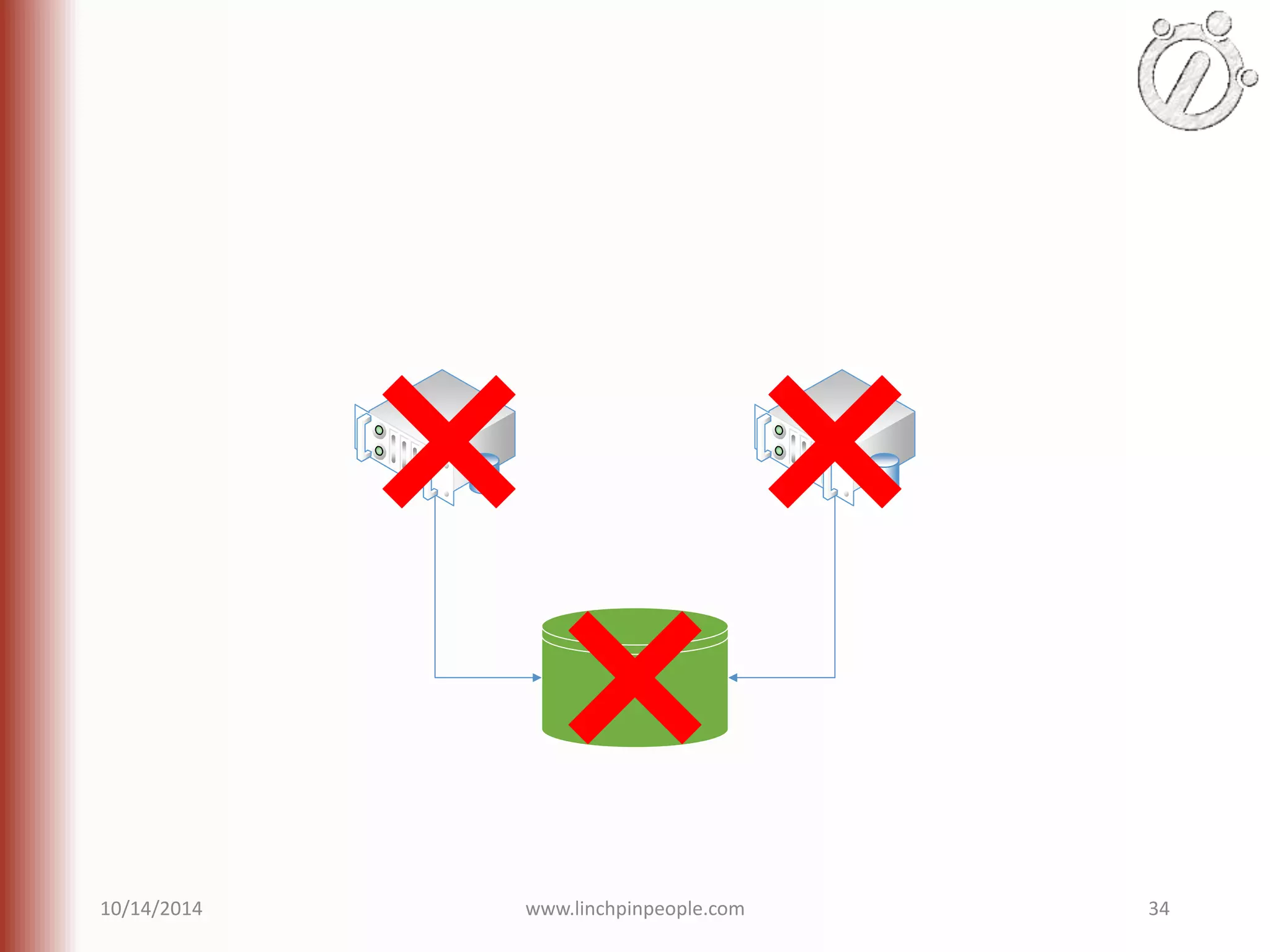
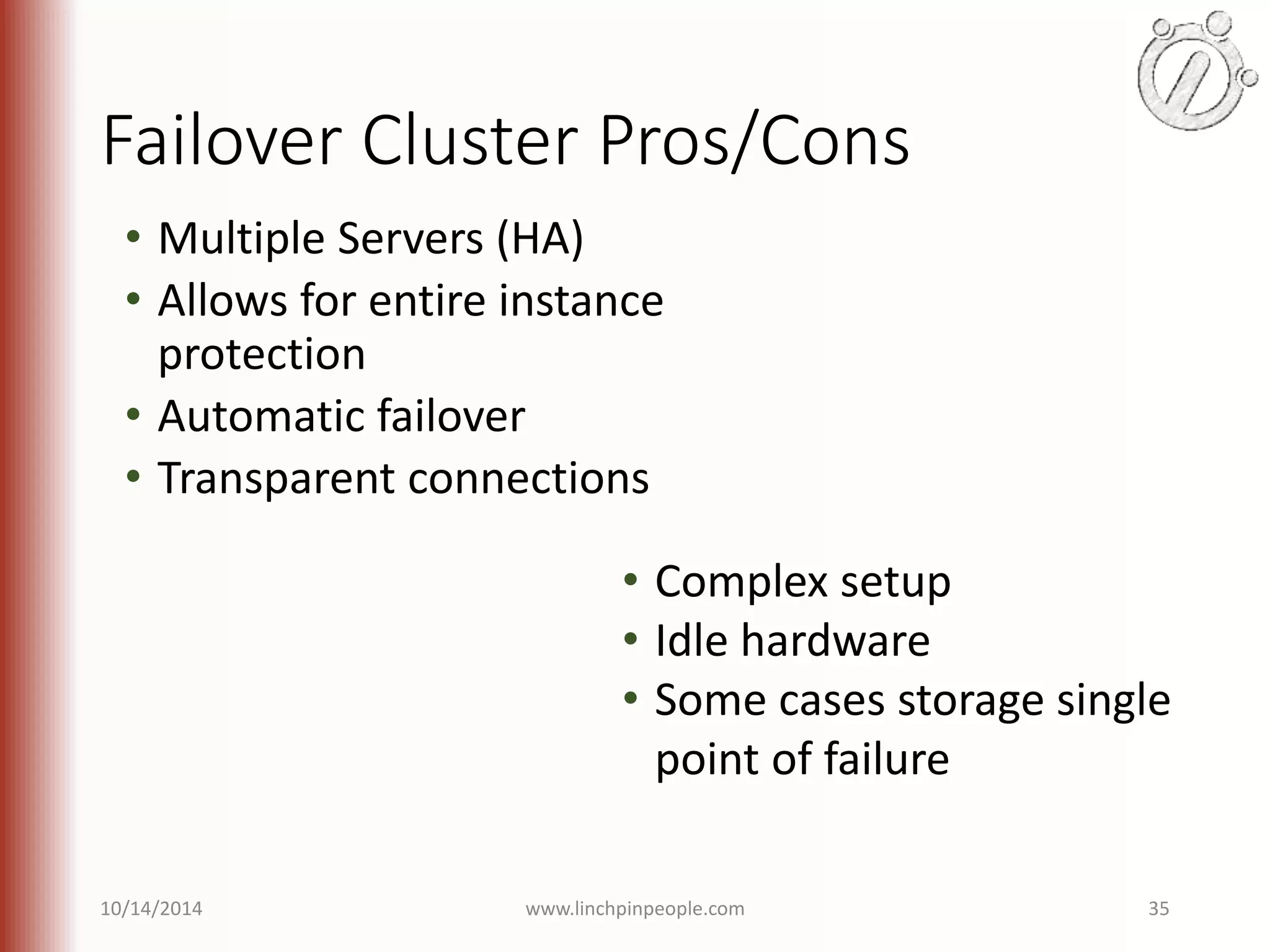
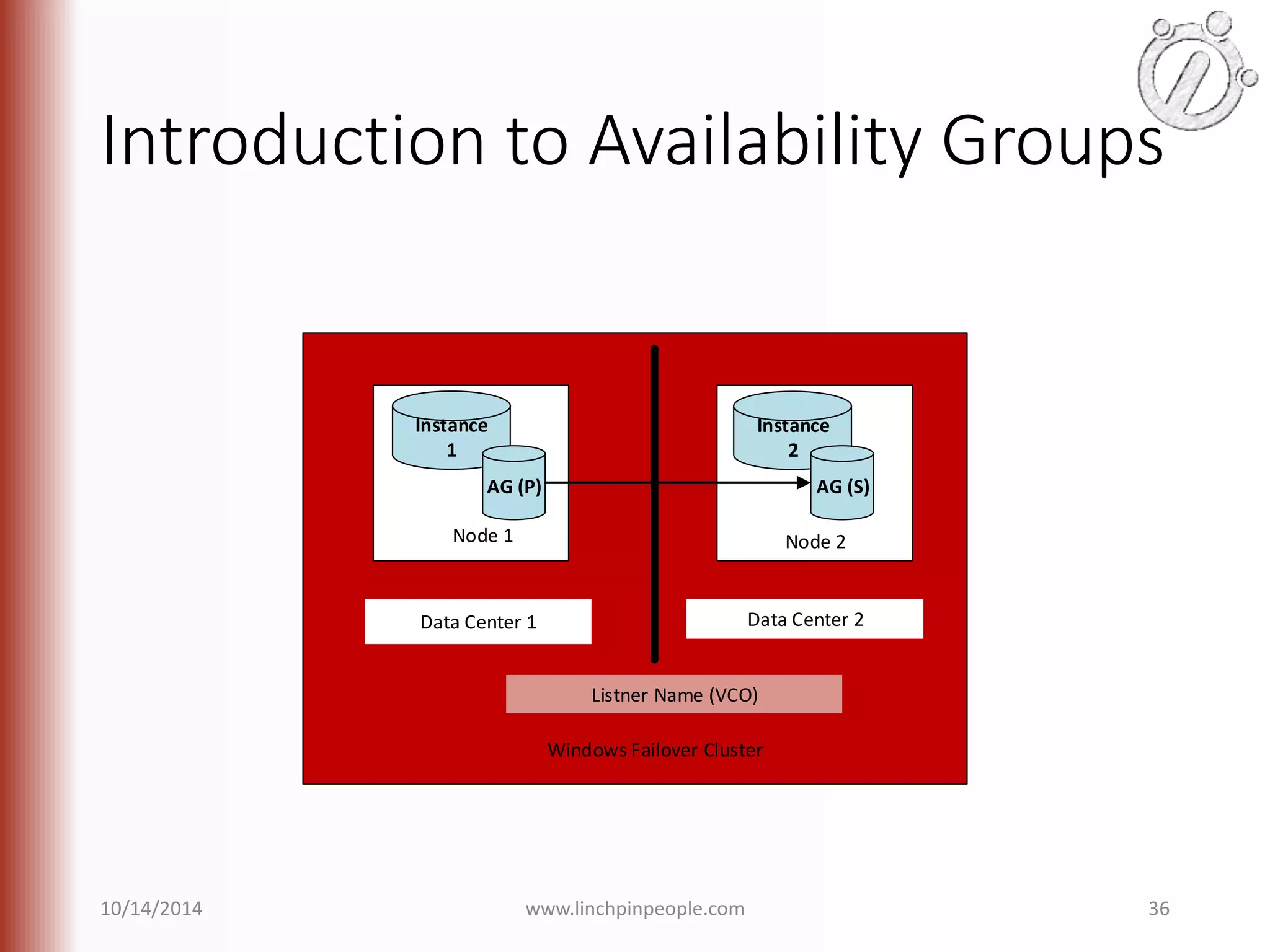
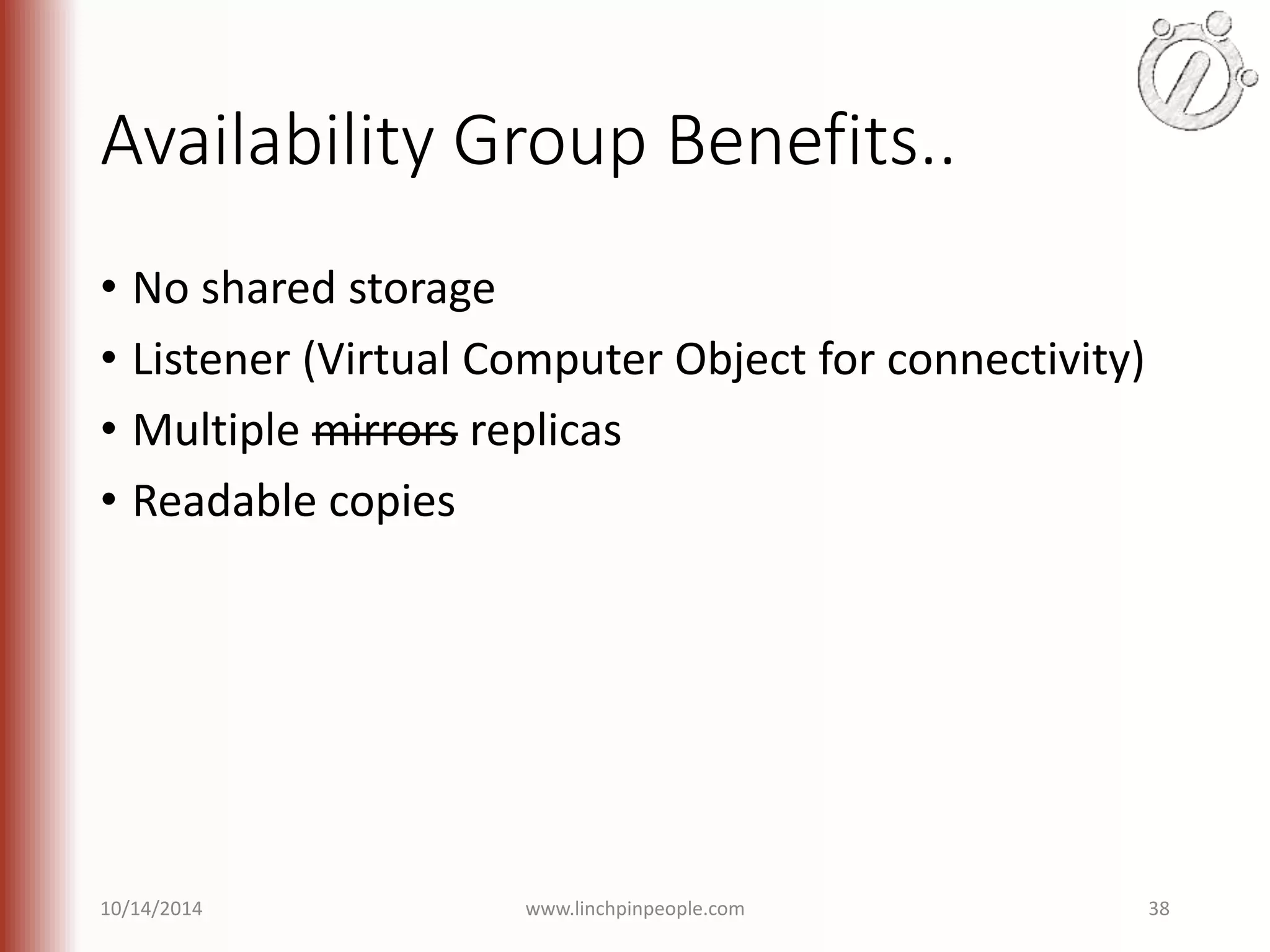
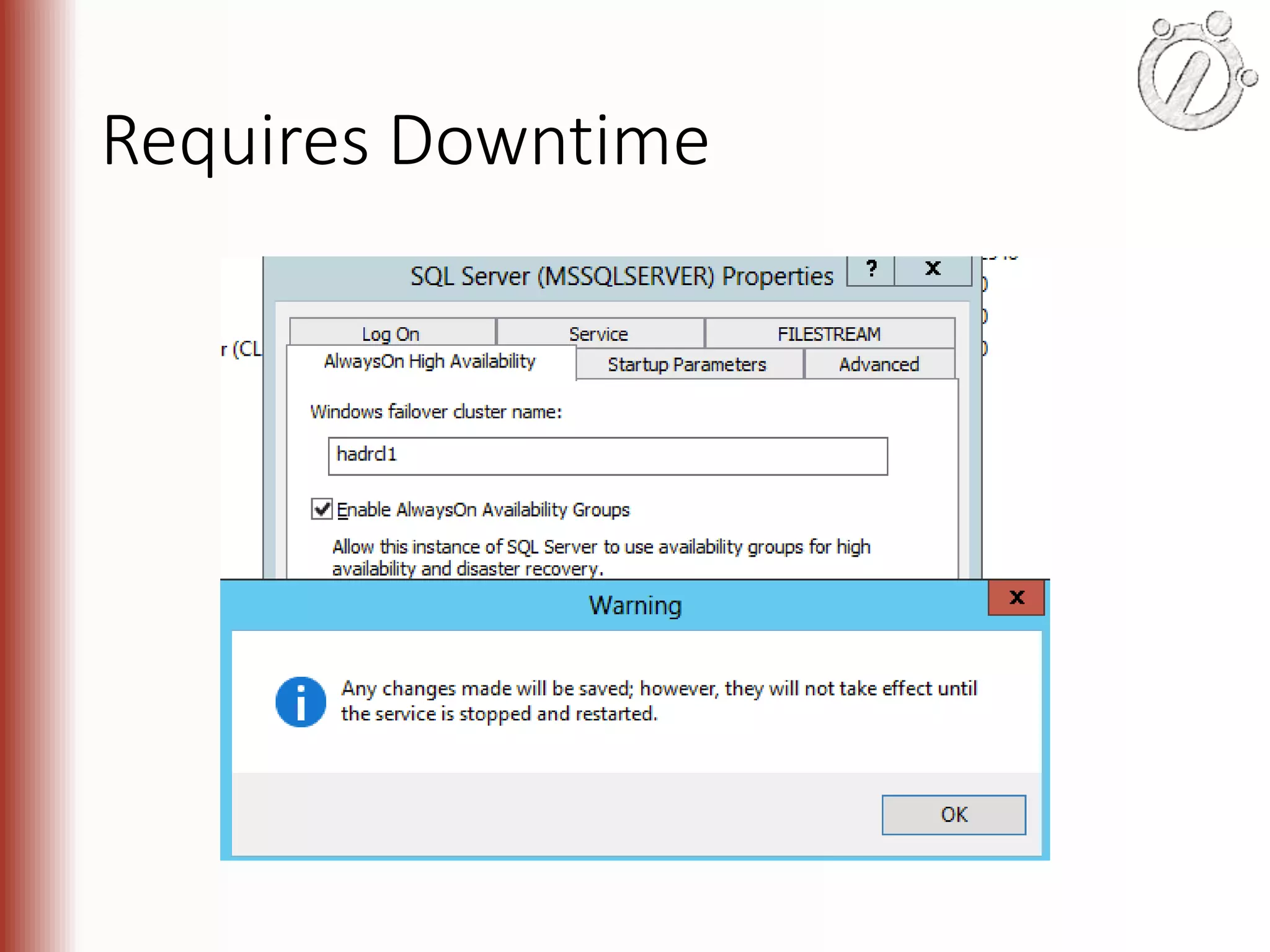
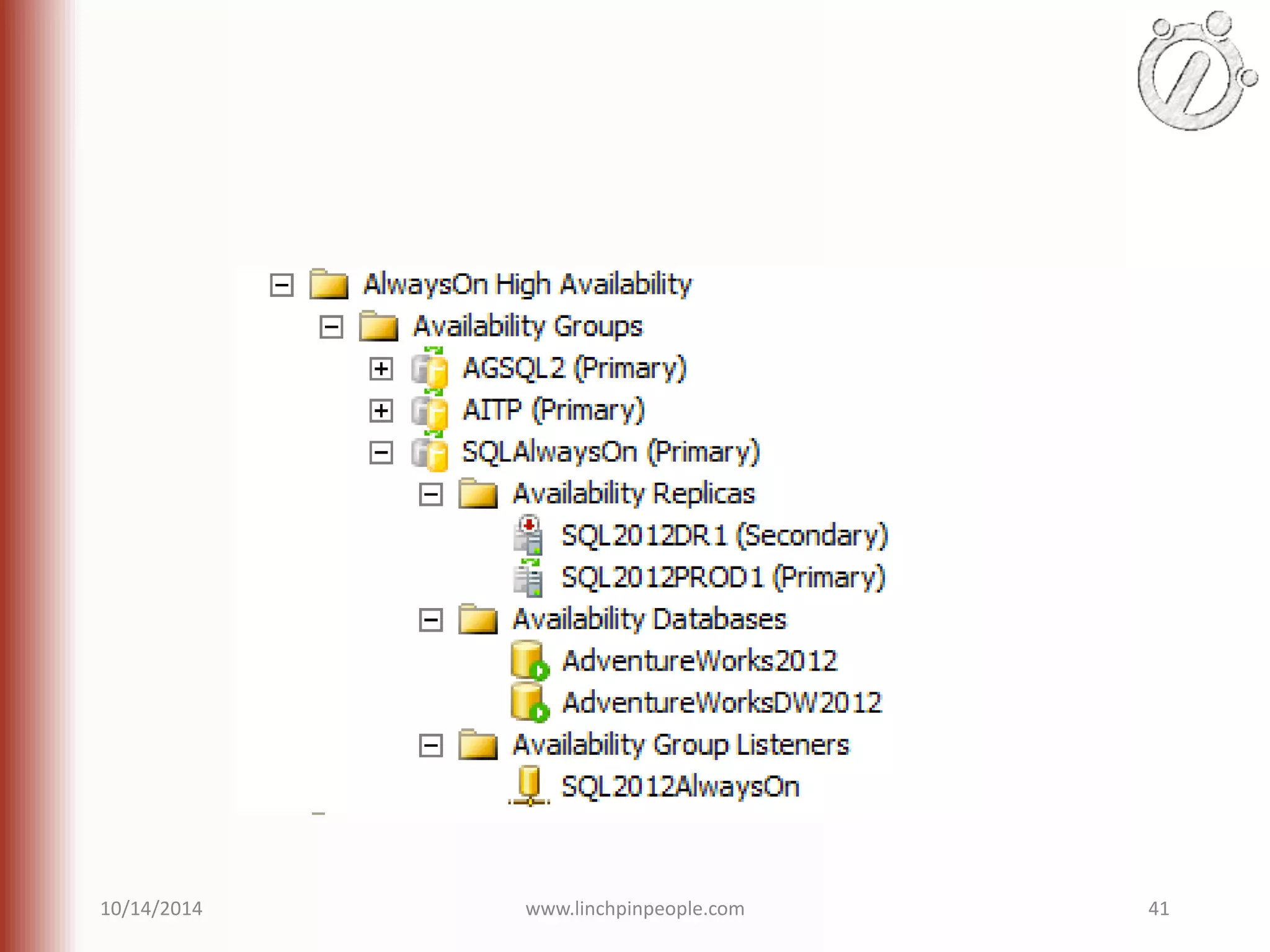
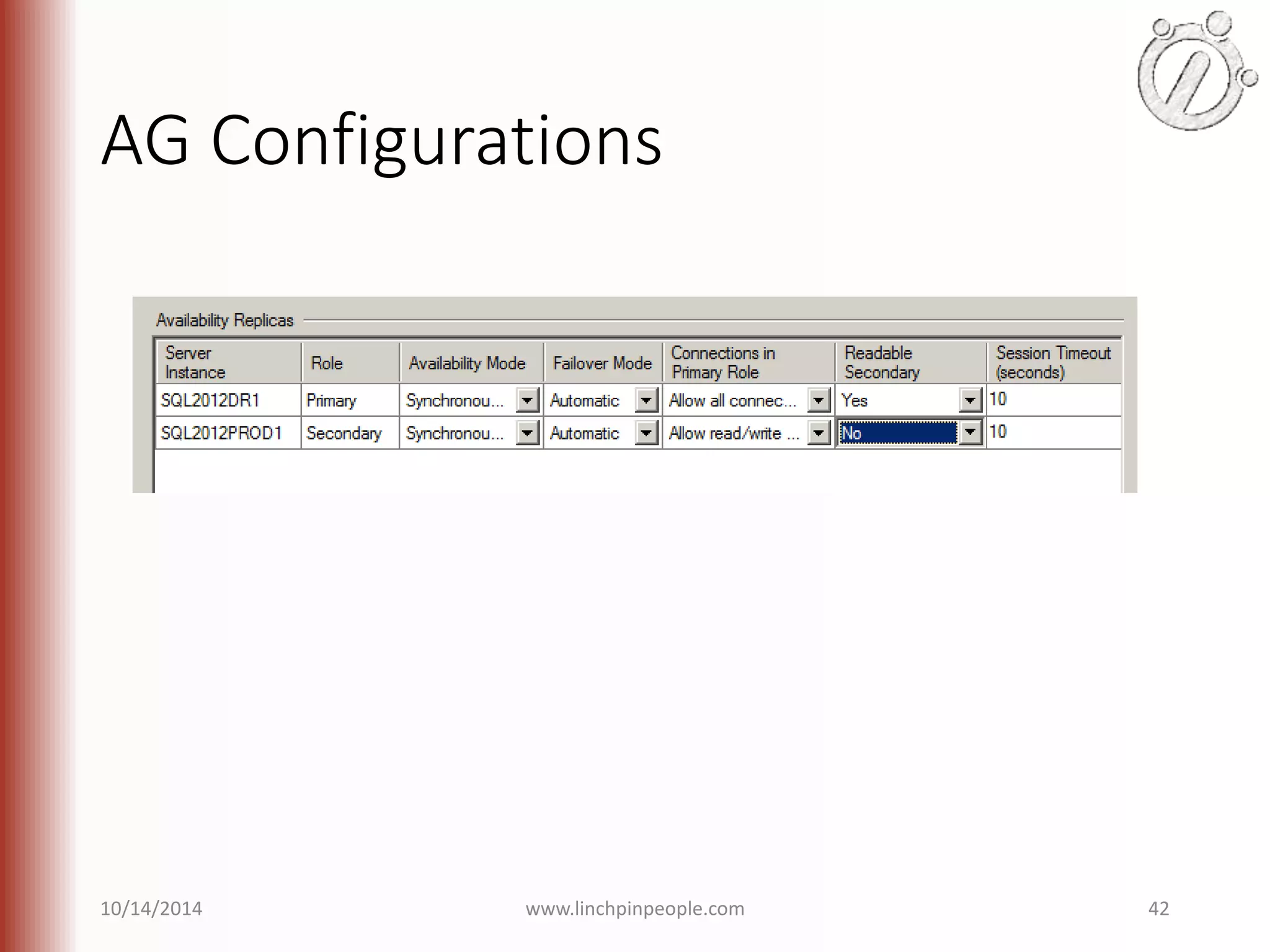
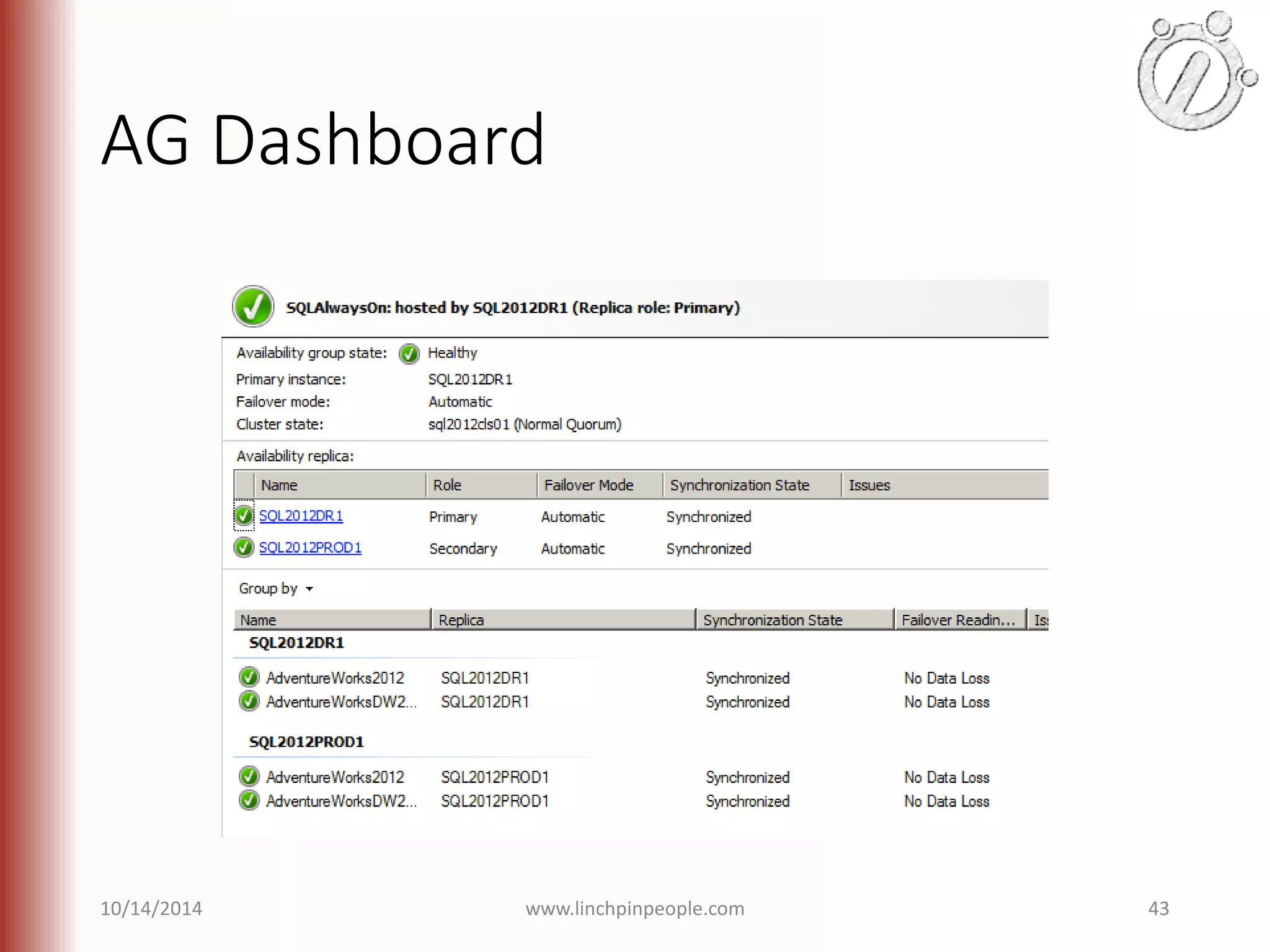
The document provides an overview of high availability (HA) and disaster recovery (DR) solutions in SQL Server, outlining various options such as log shipping, database mirroring, replication, failover cluster instances, and AlwaysOn availability groups. It covers definitions, functionalities, and pros and cons of each method, emphasizing the importance of reducing downtime and ensuring data protection. The content is aimed at improving business operations through effective database management strategies.