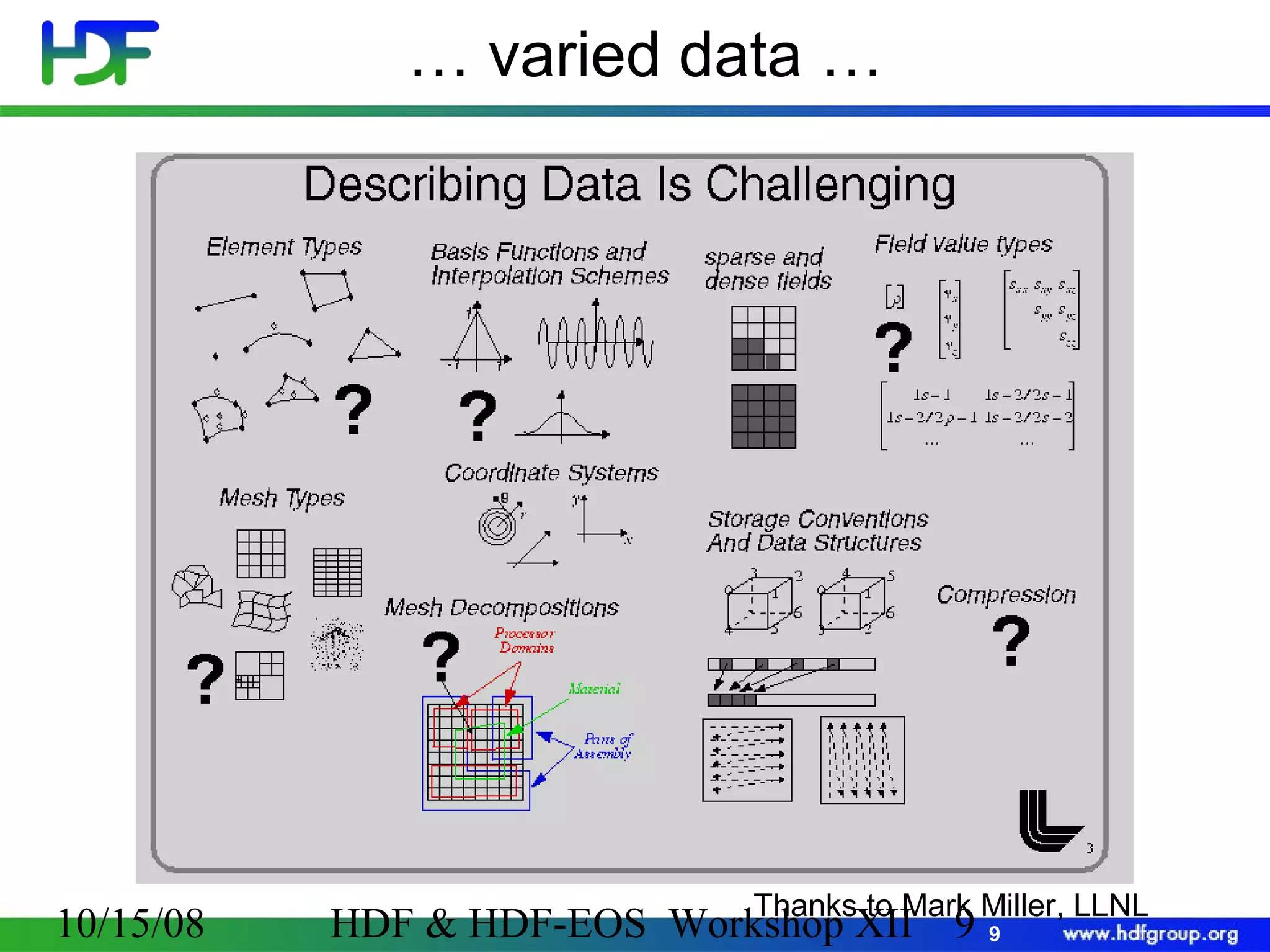
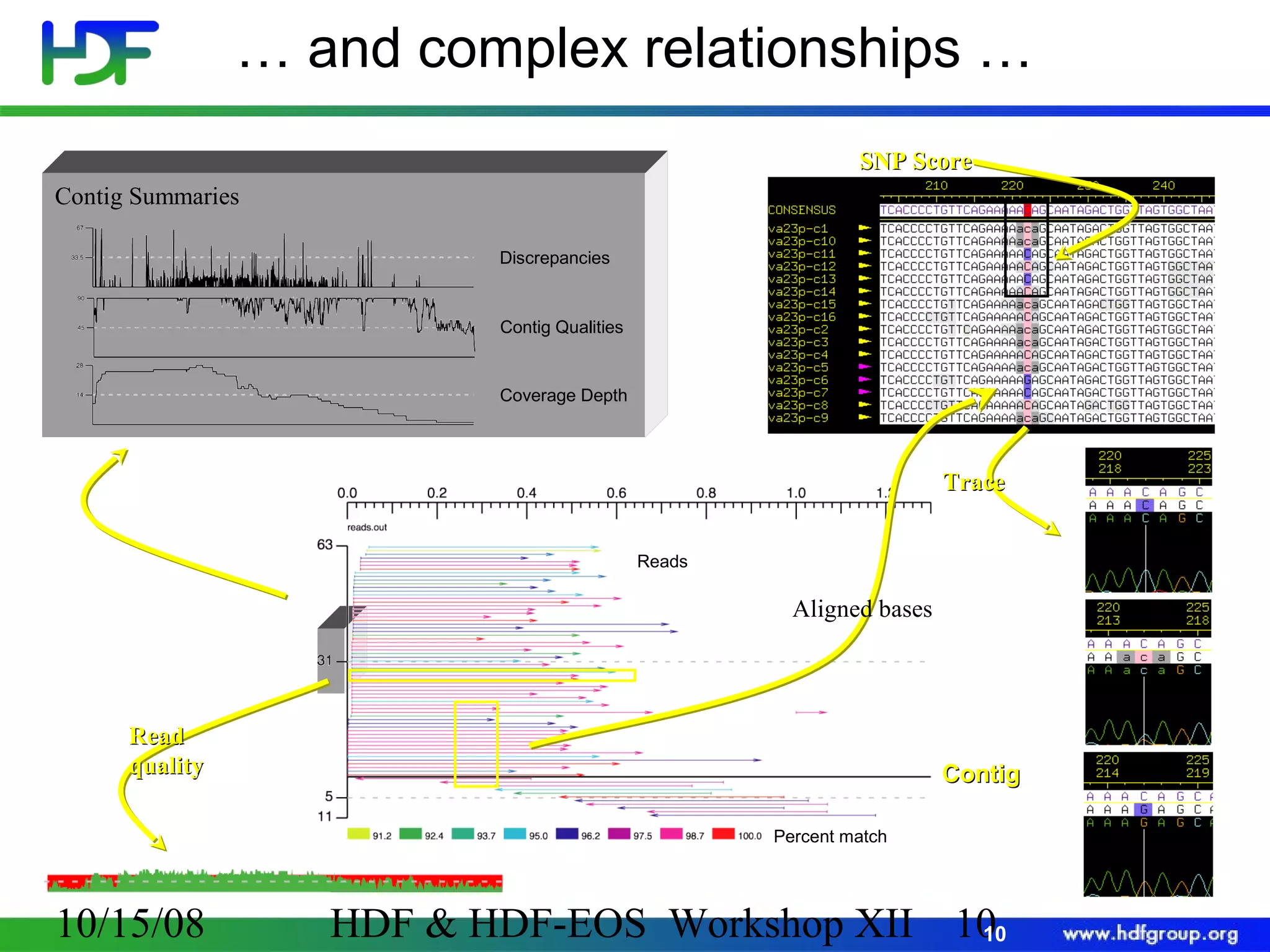
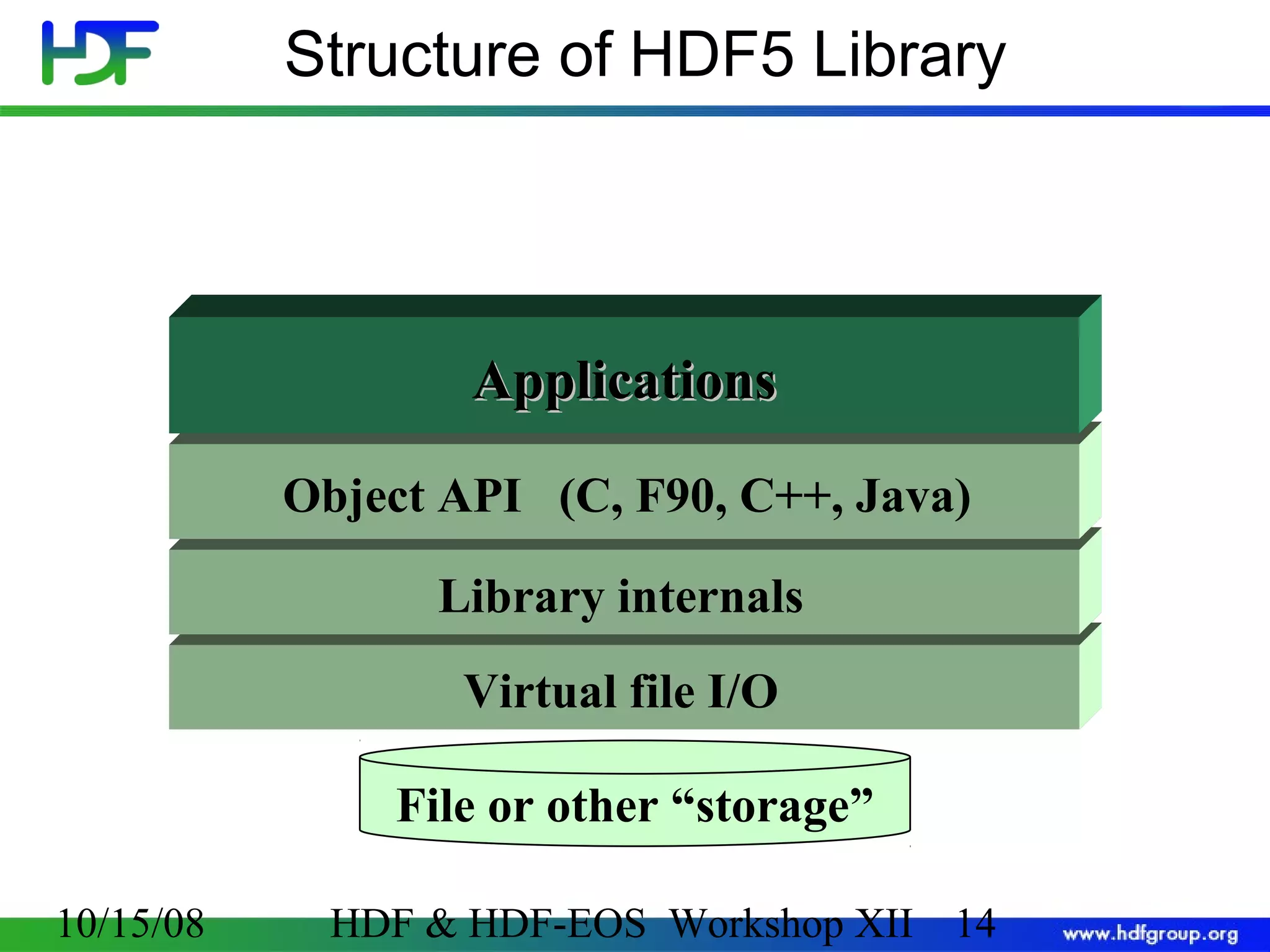
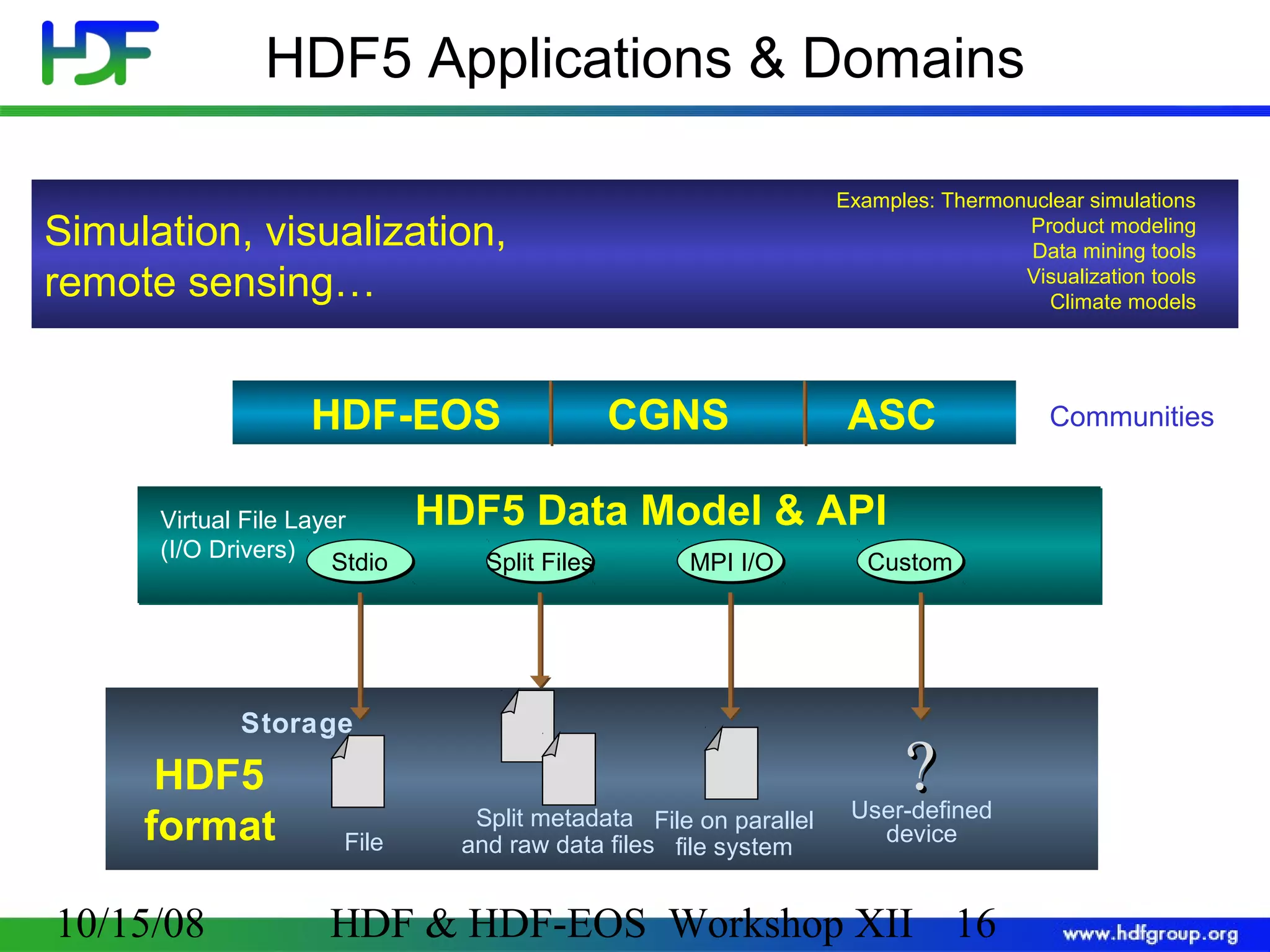
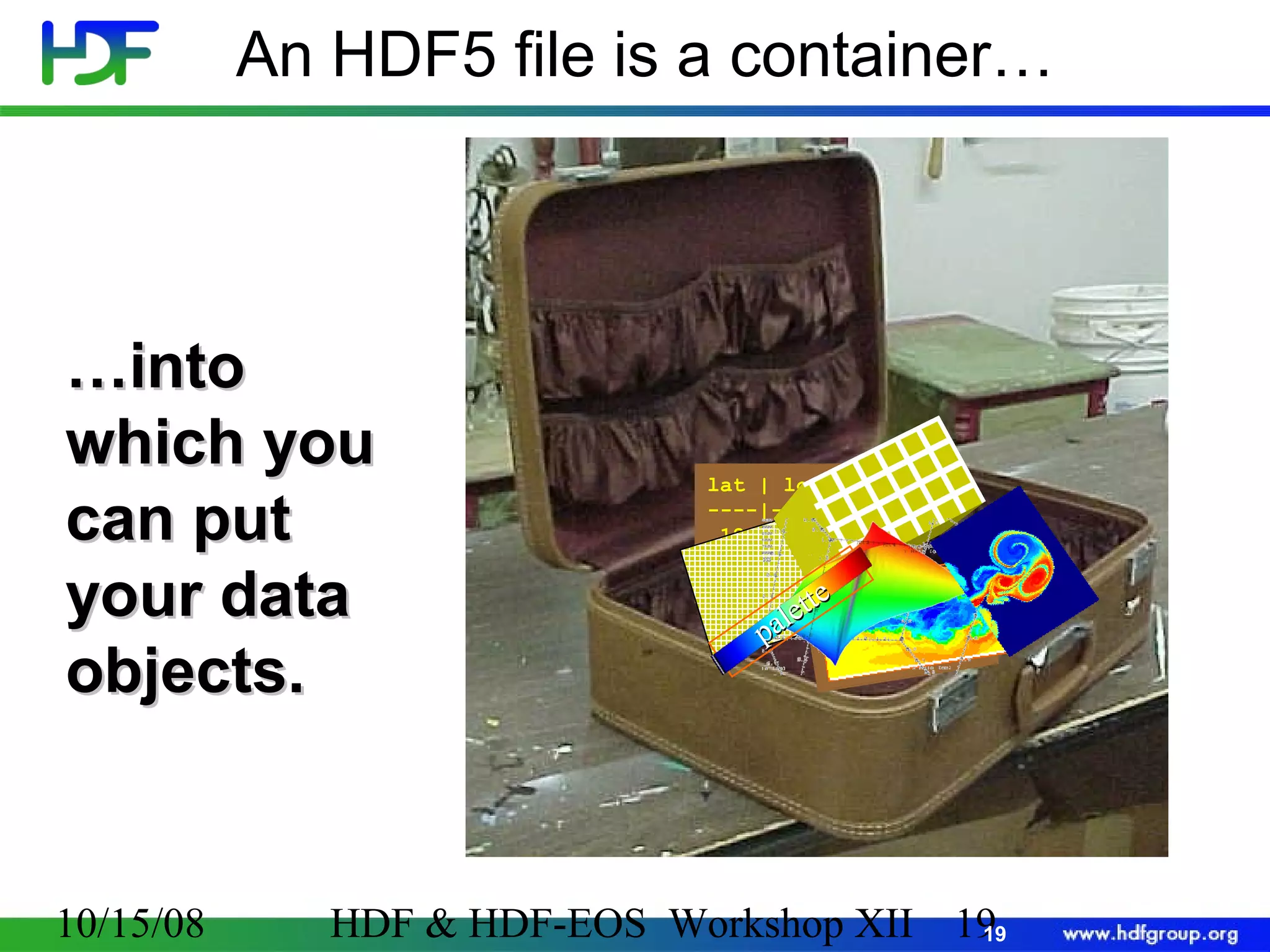
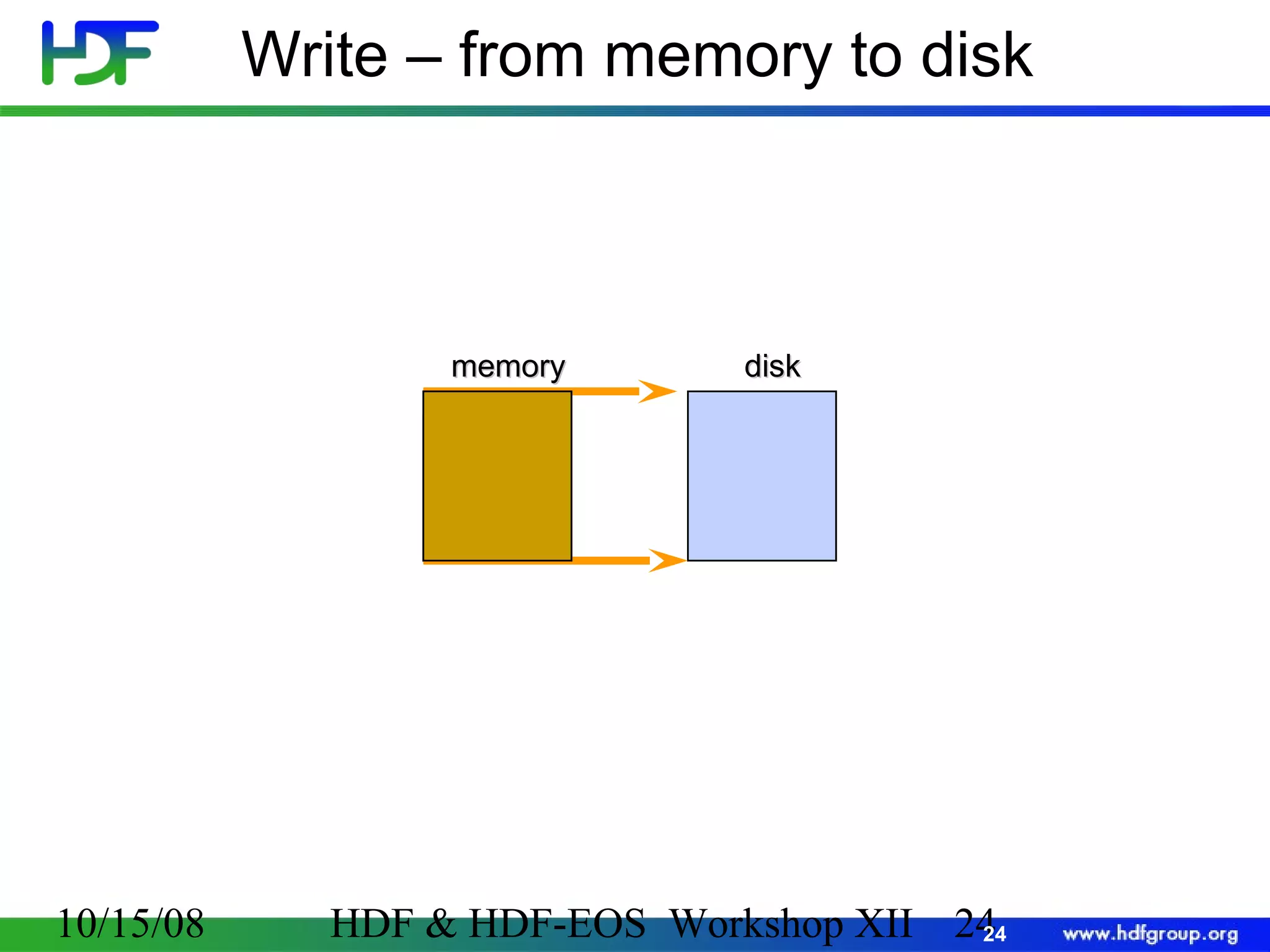
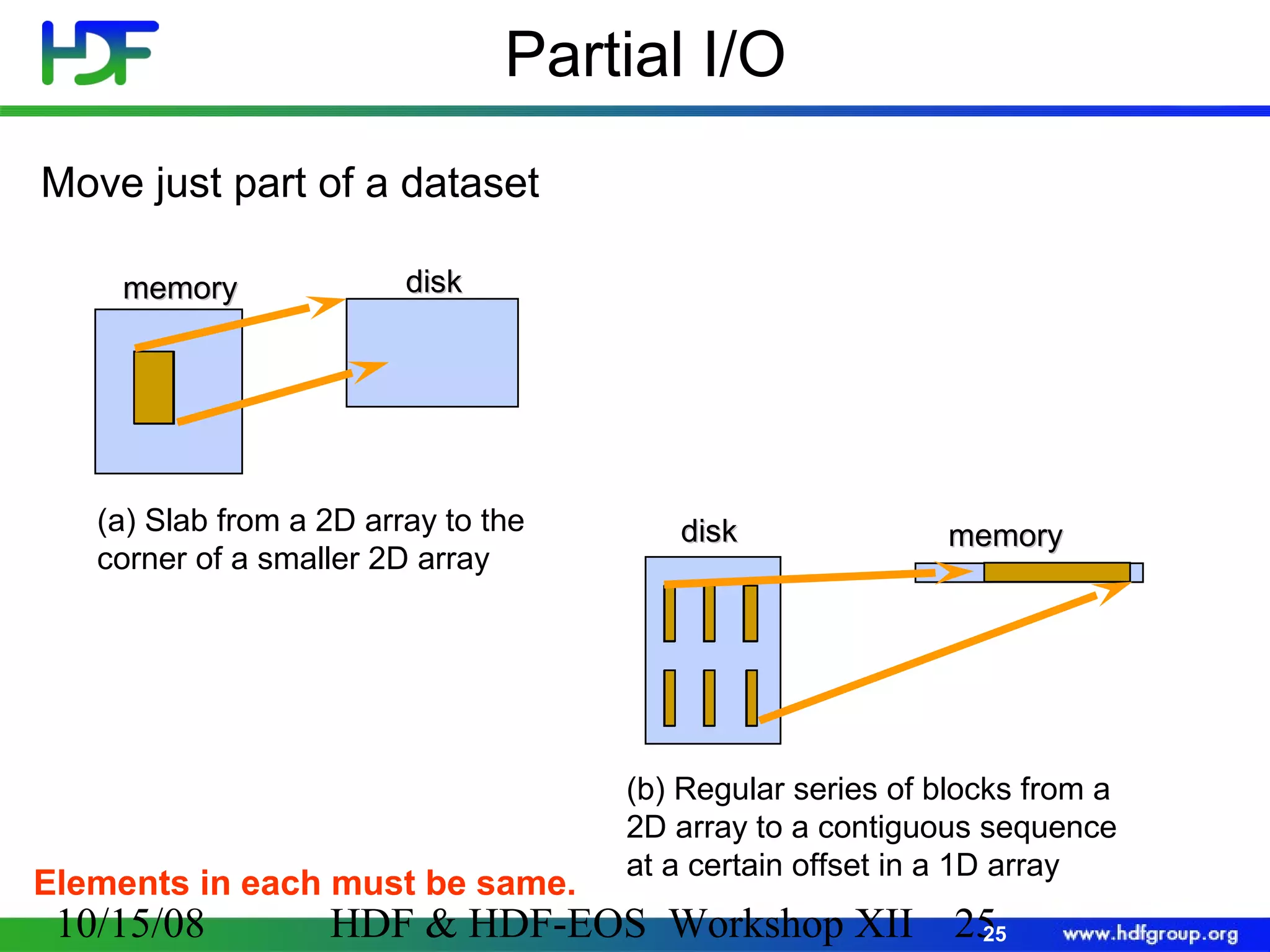
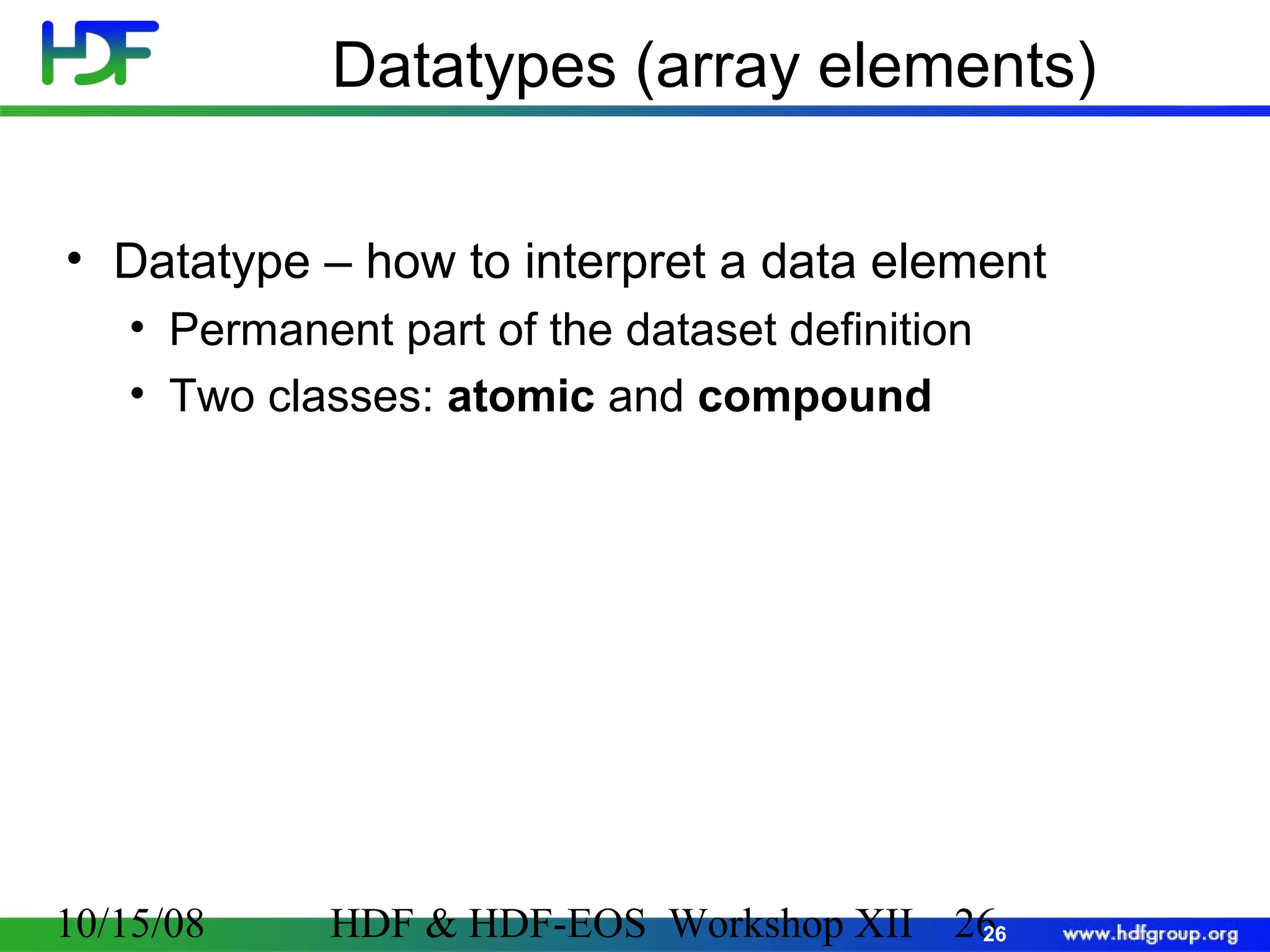
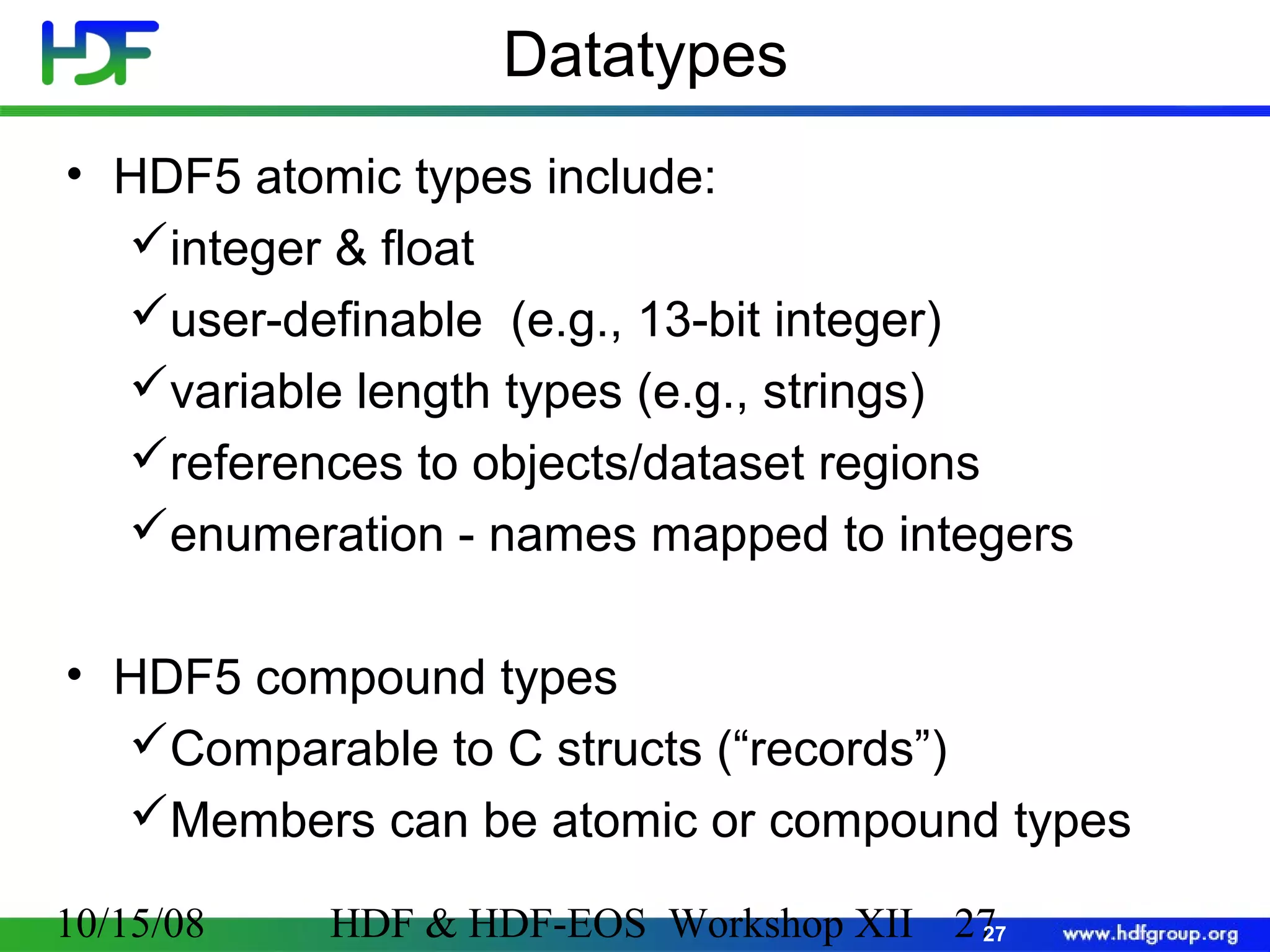
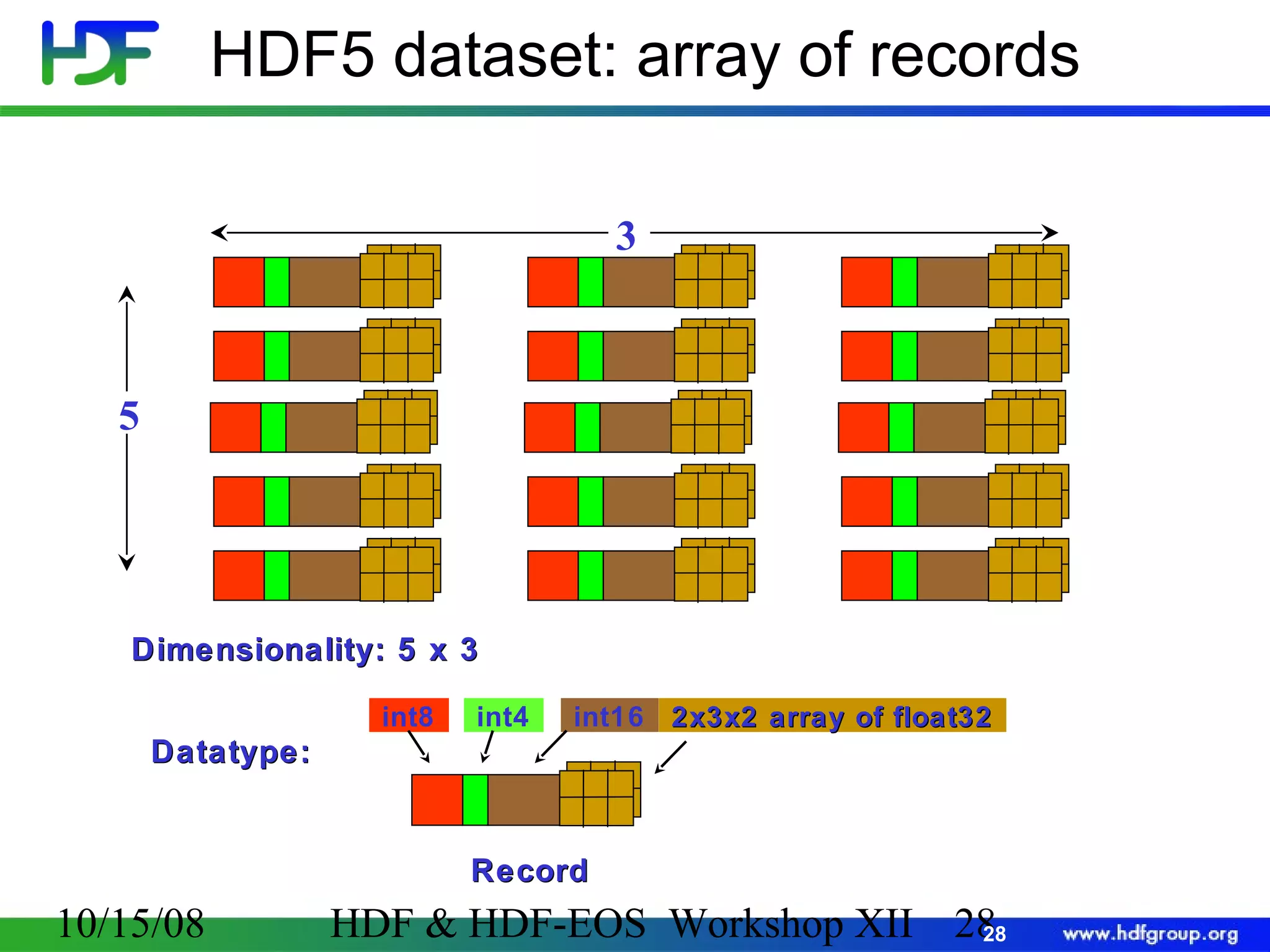
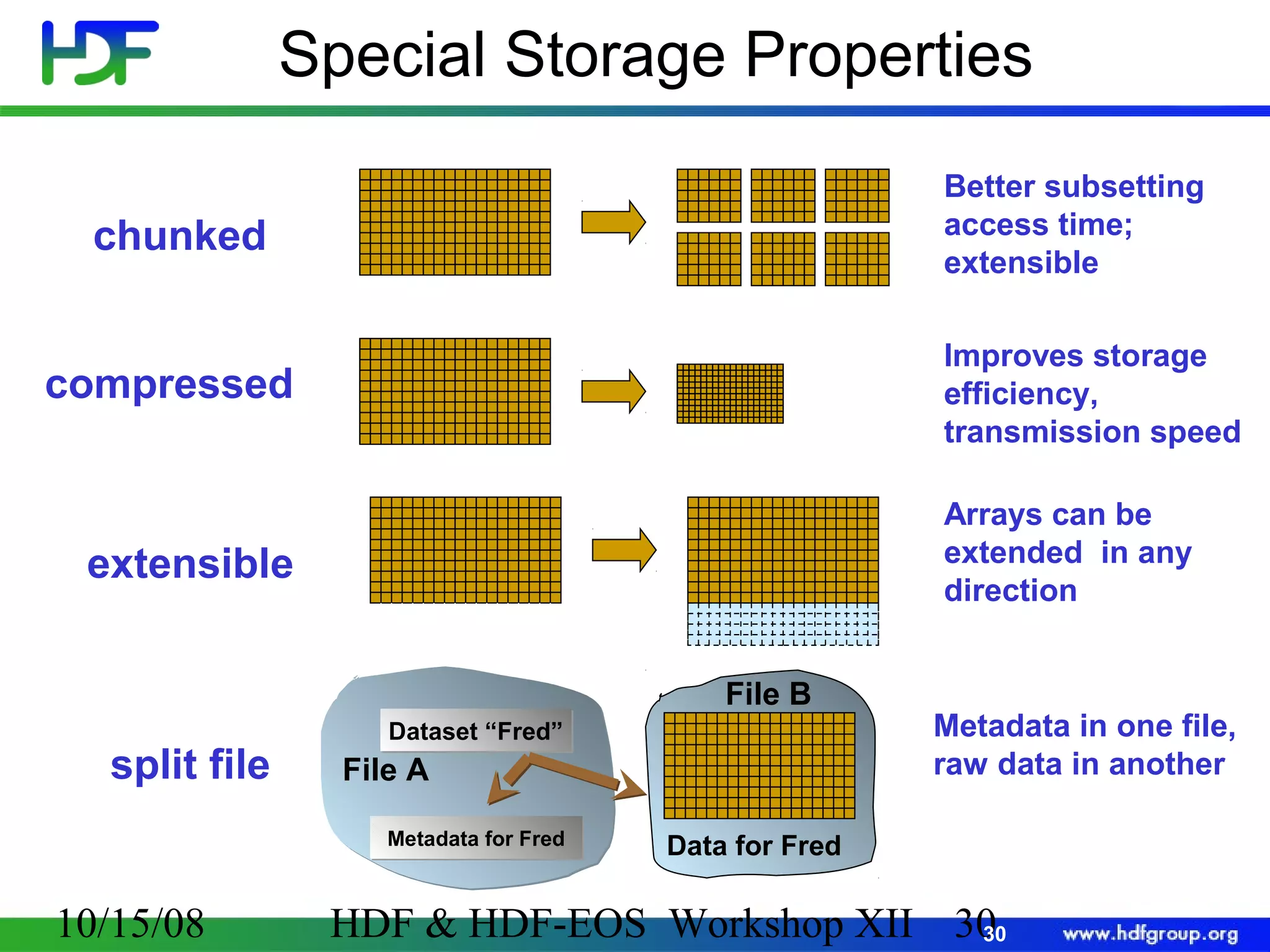
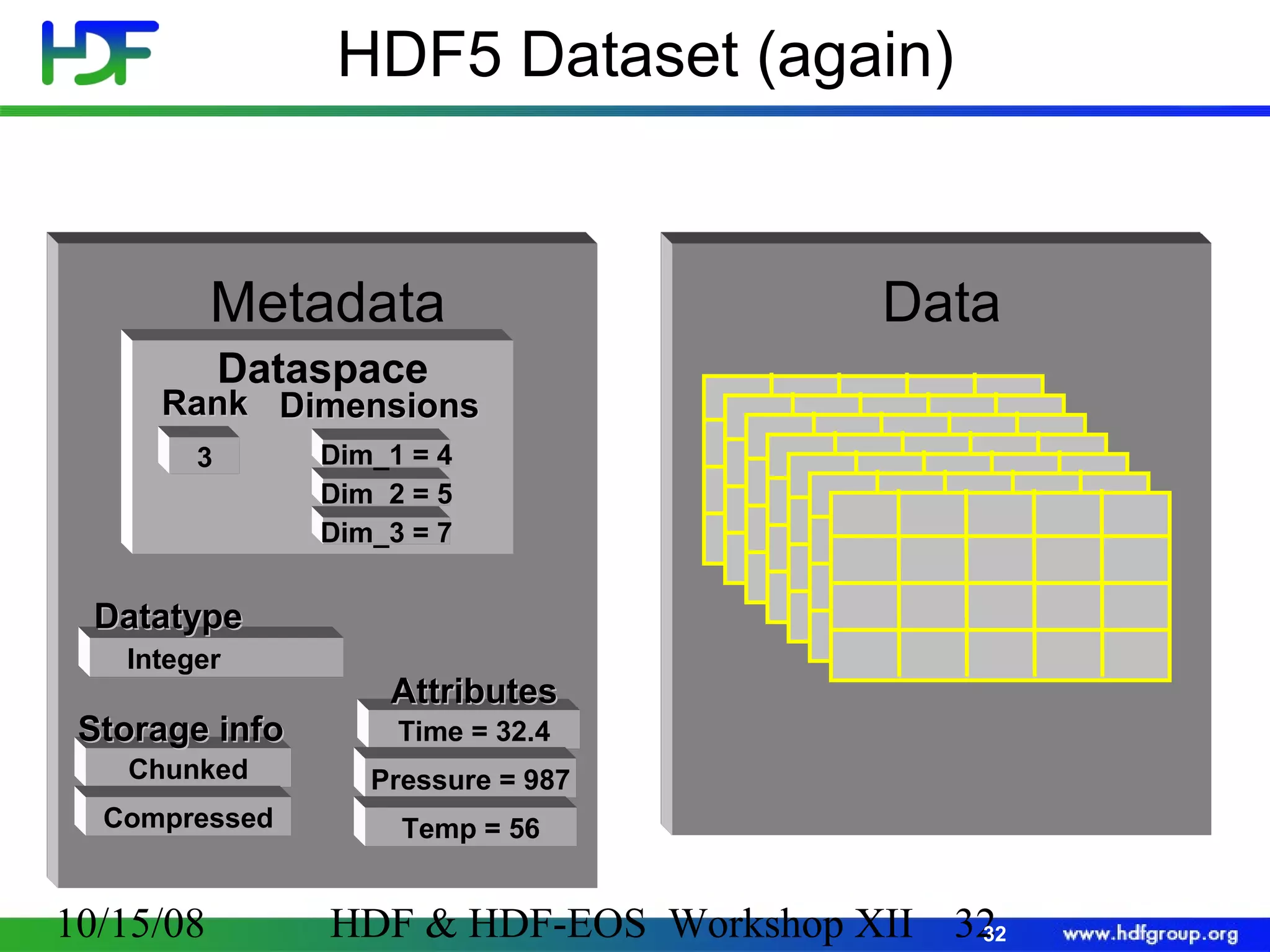
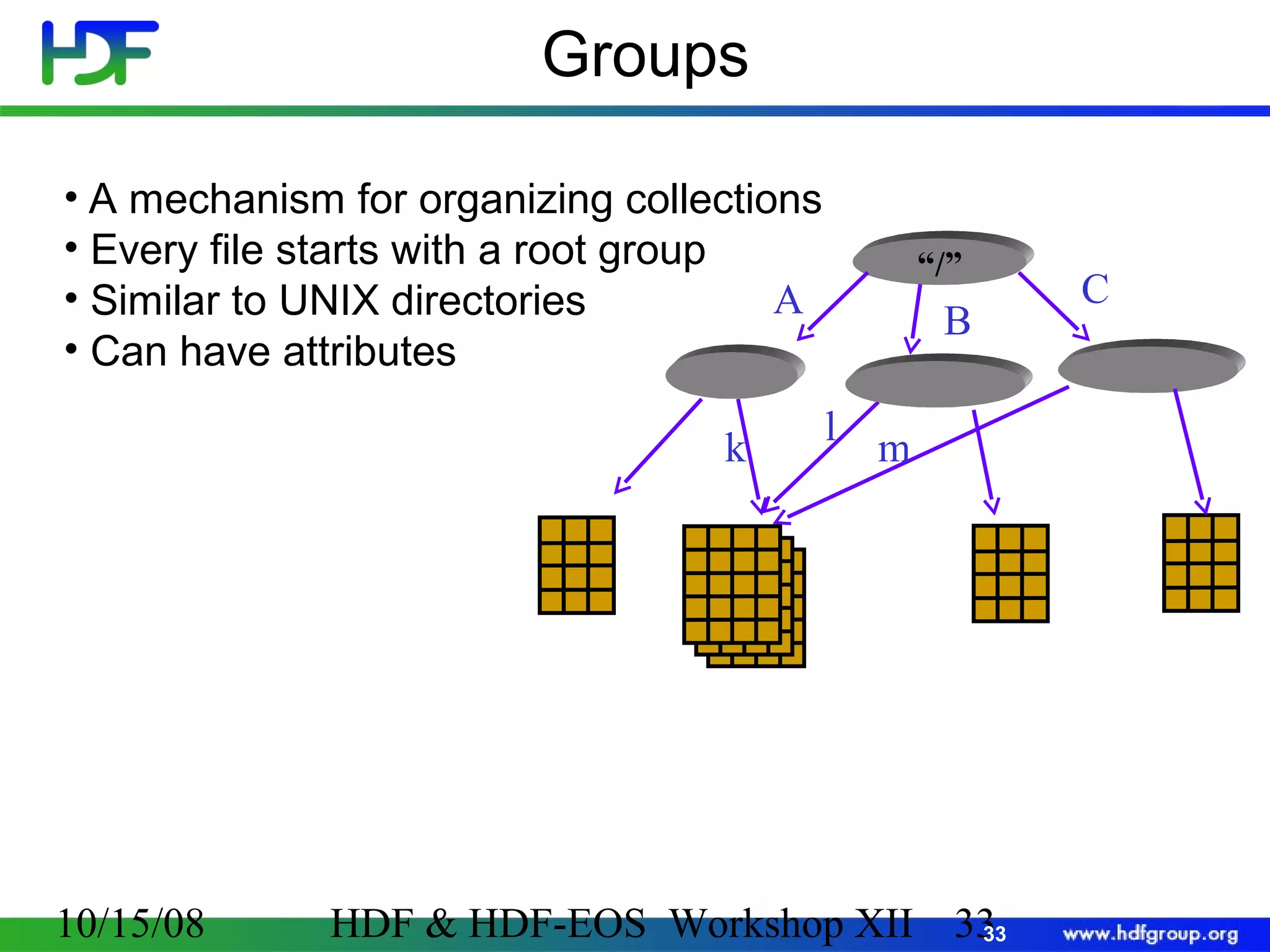
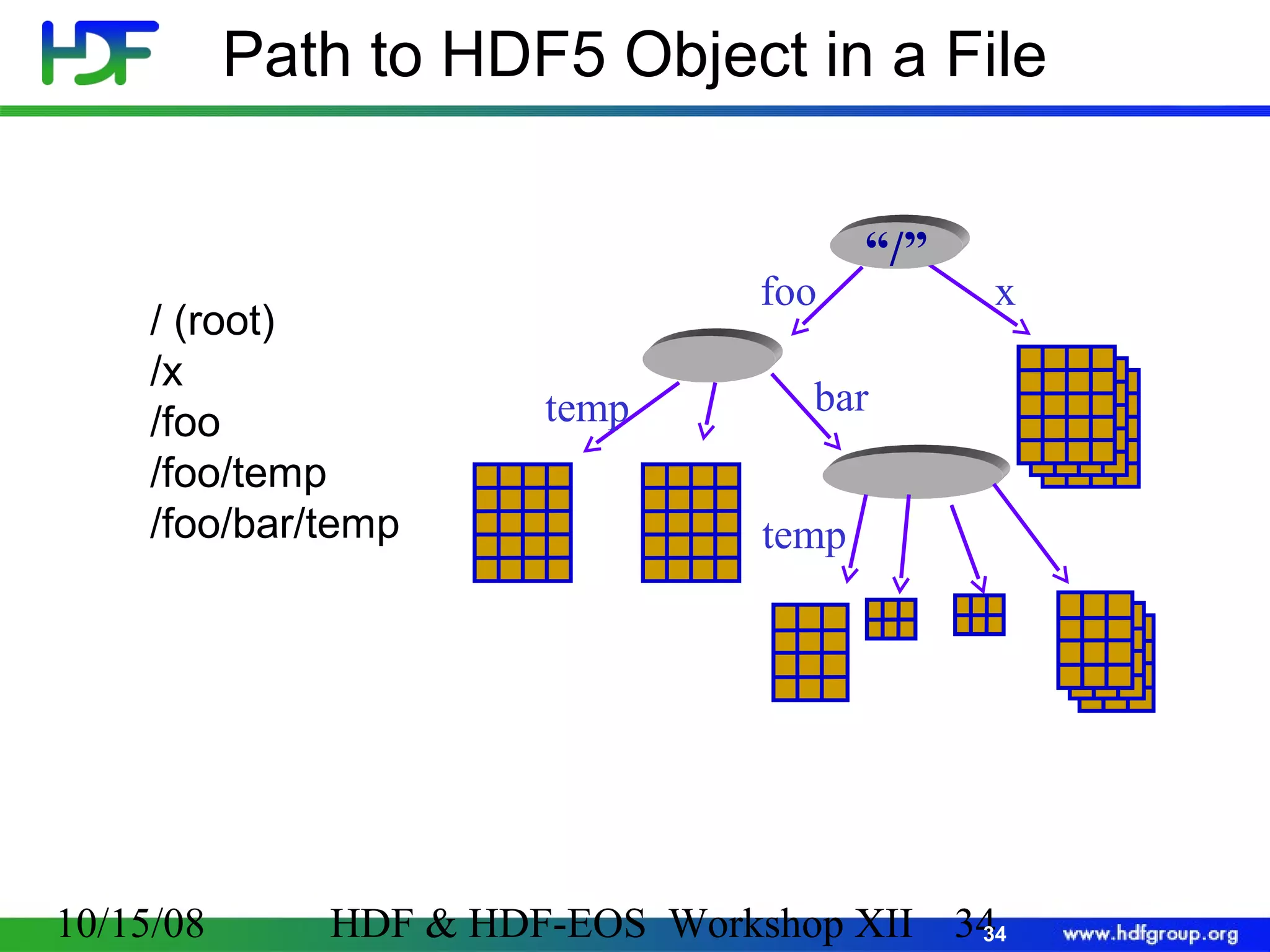
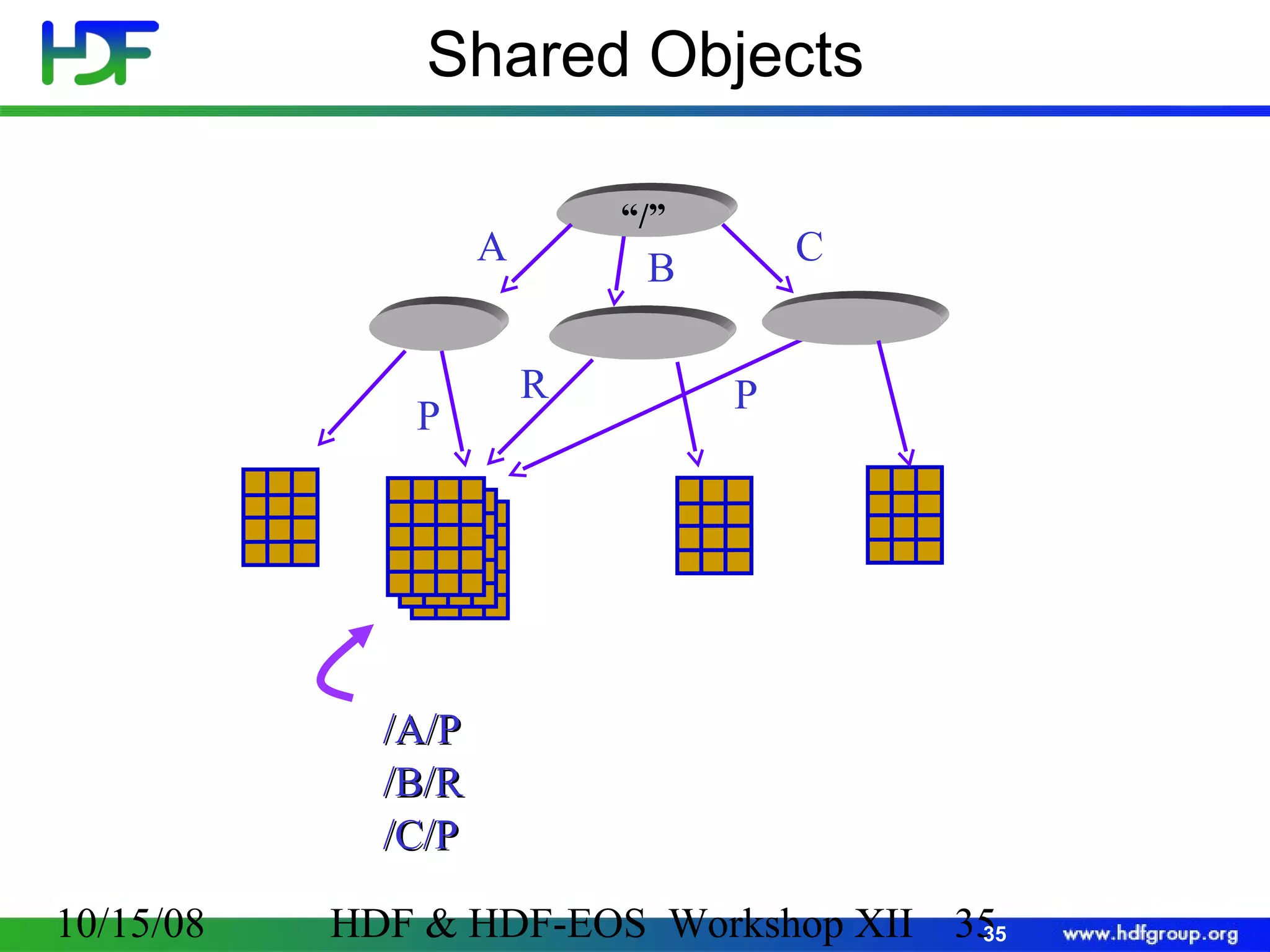
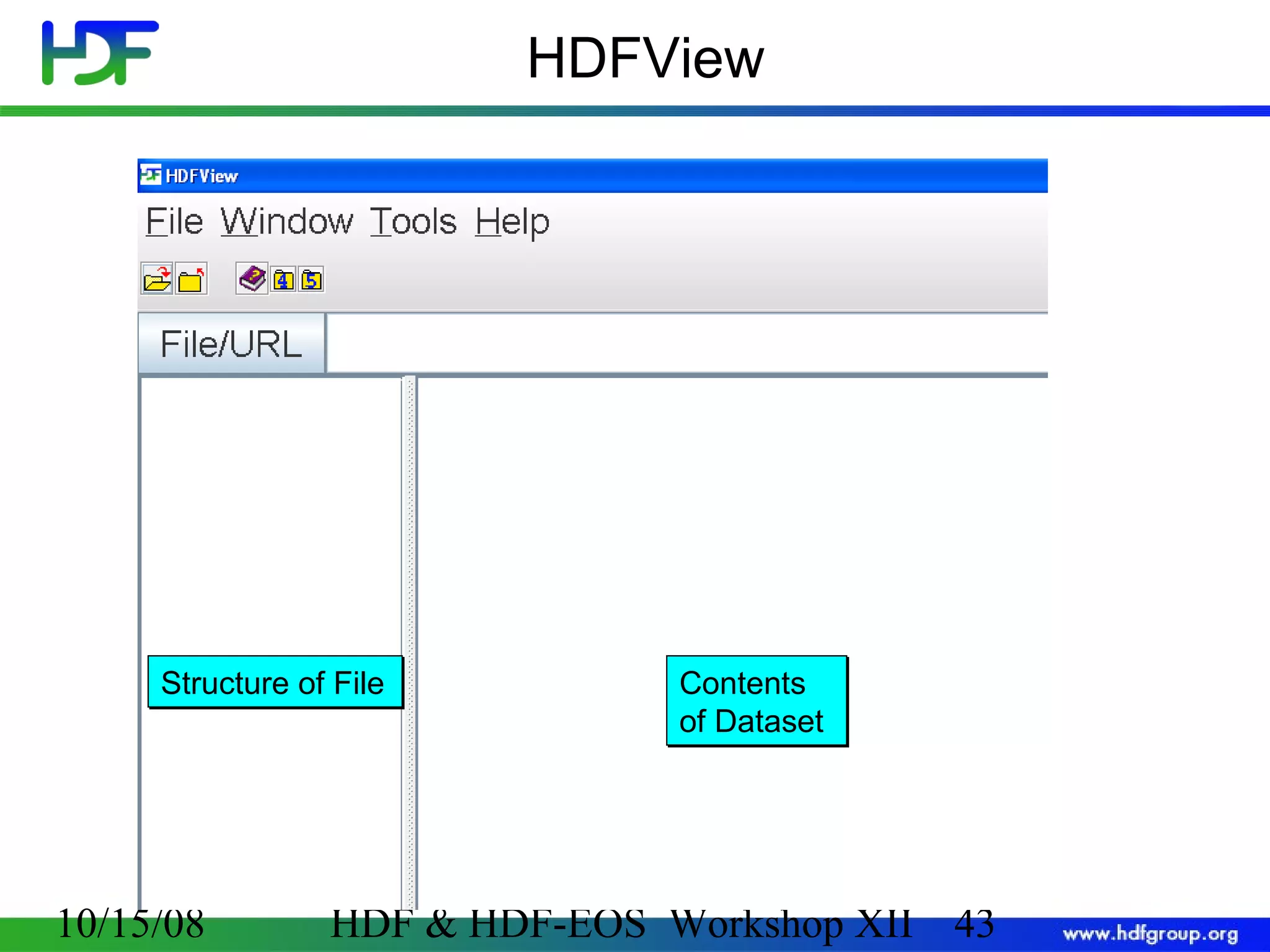
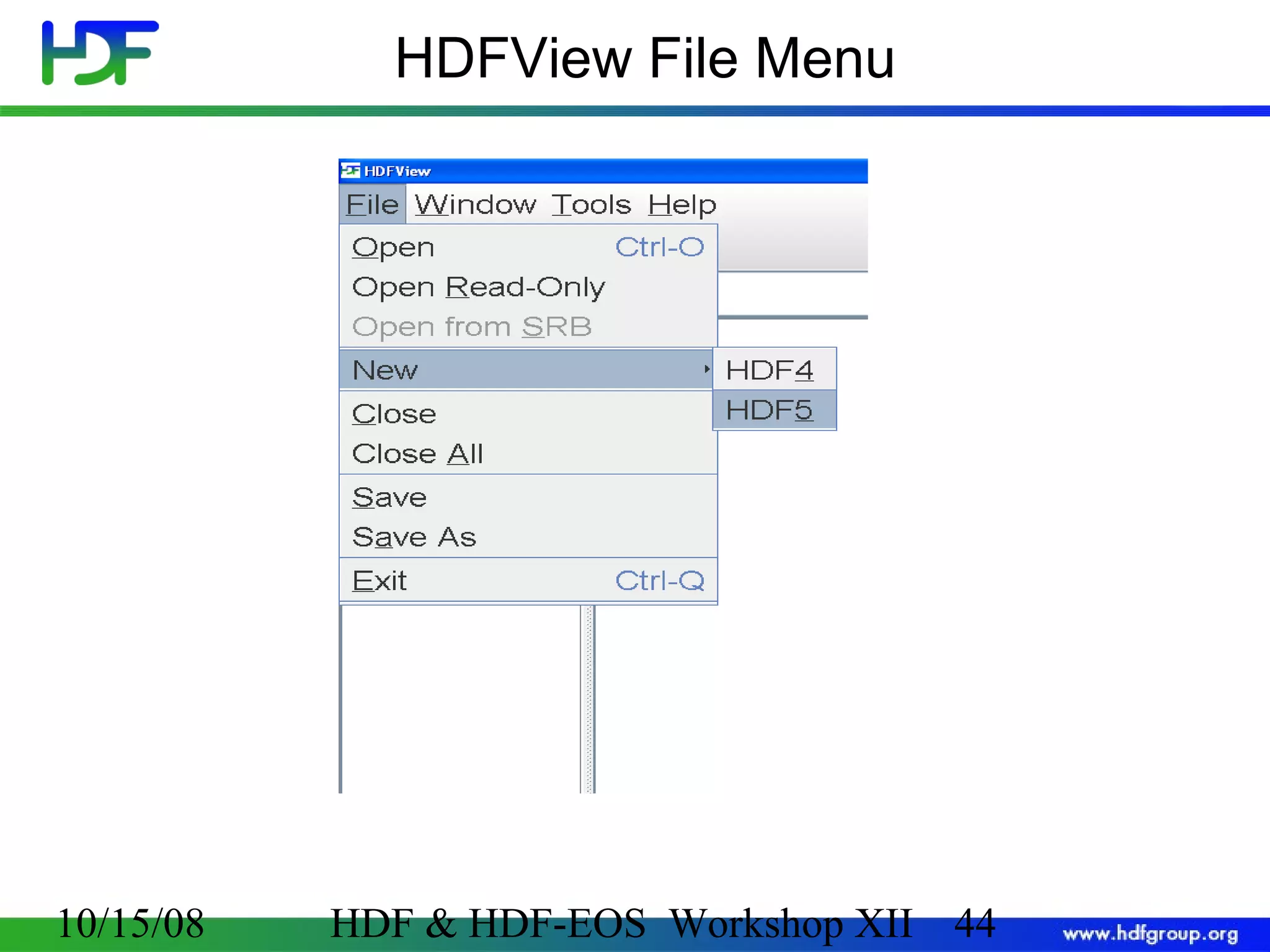
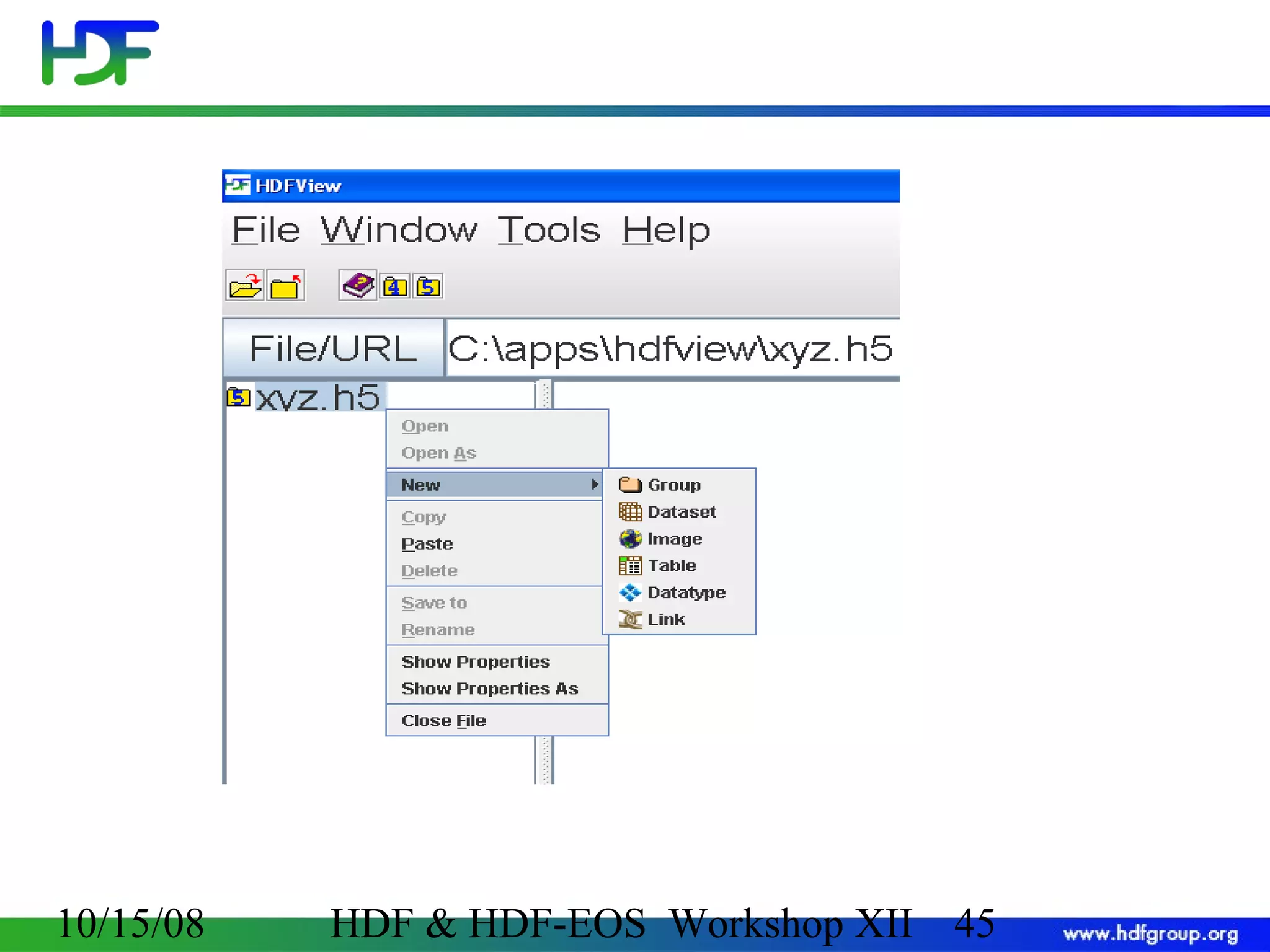
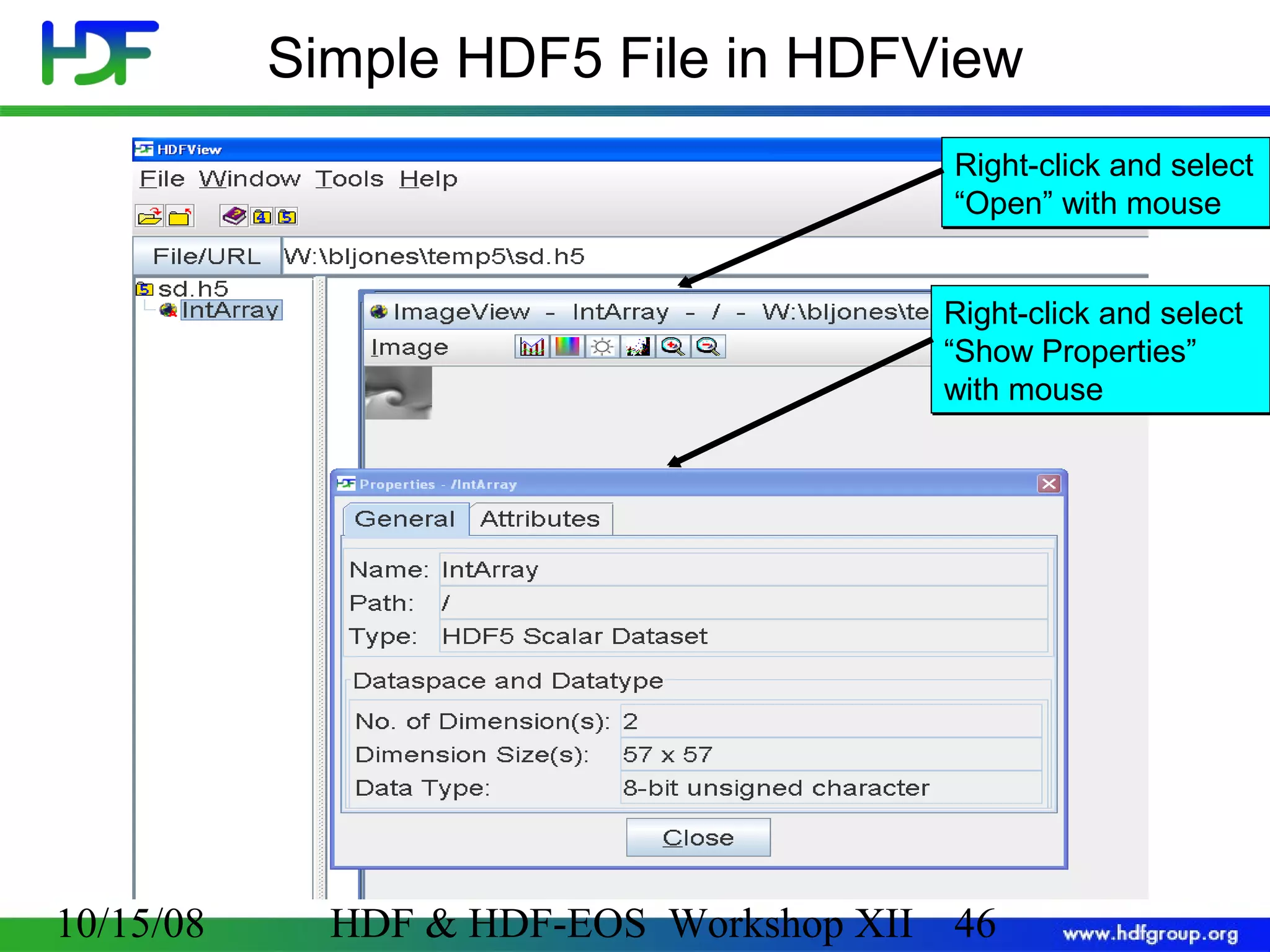
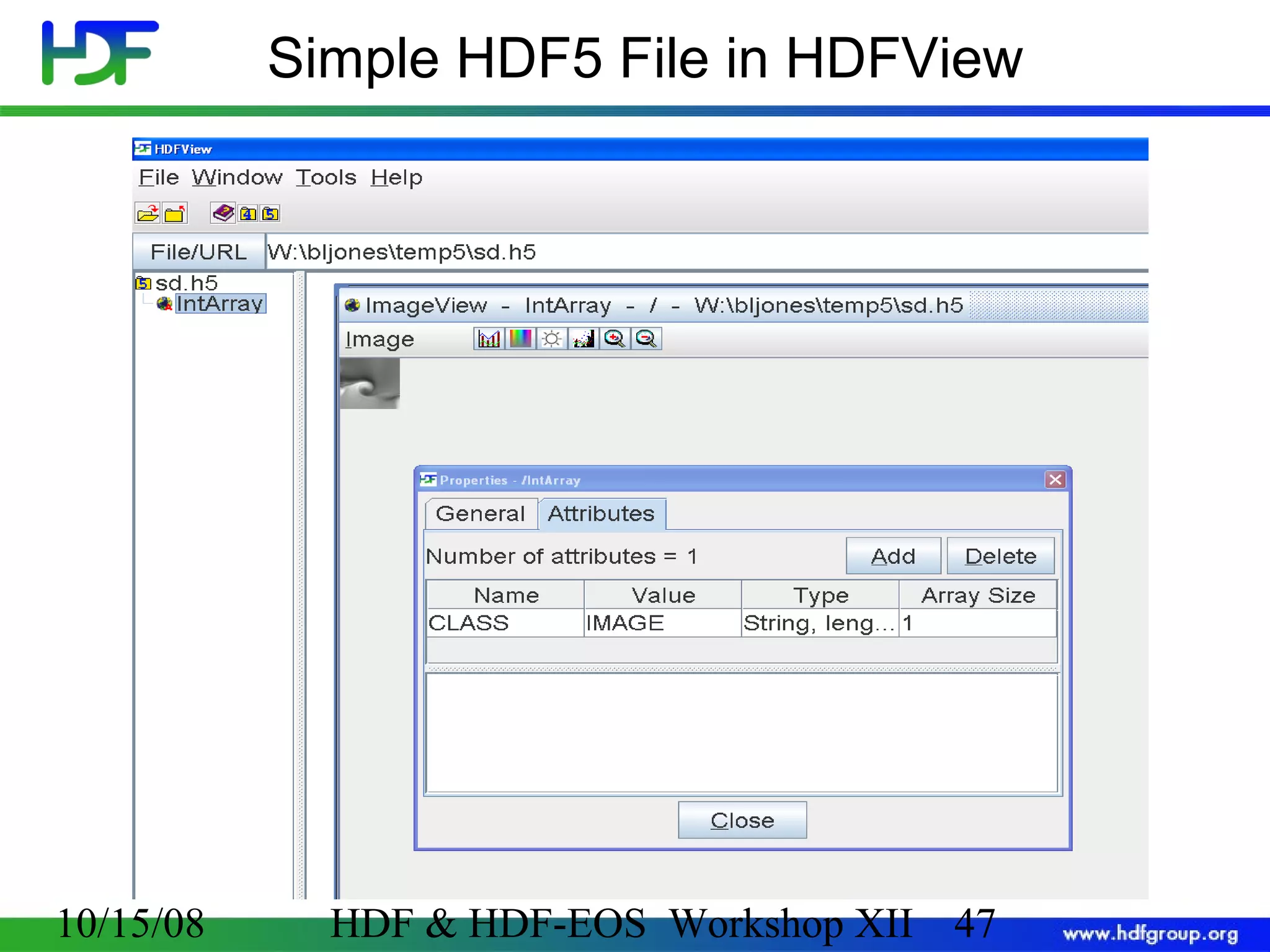
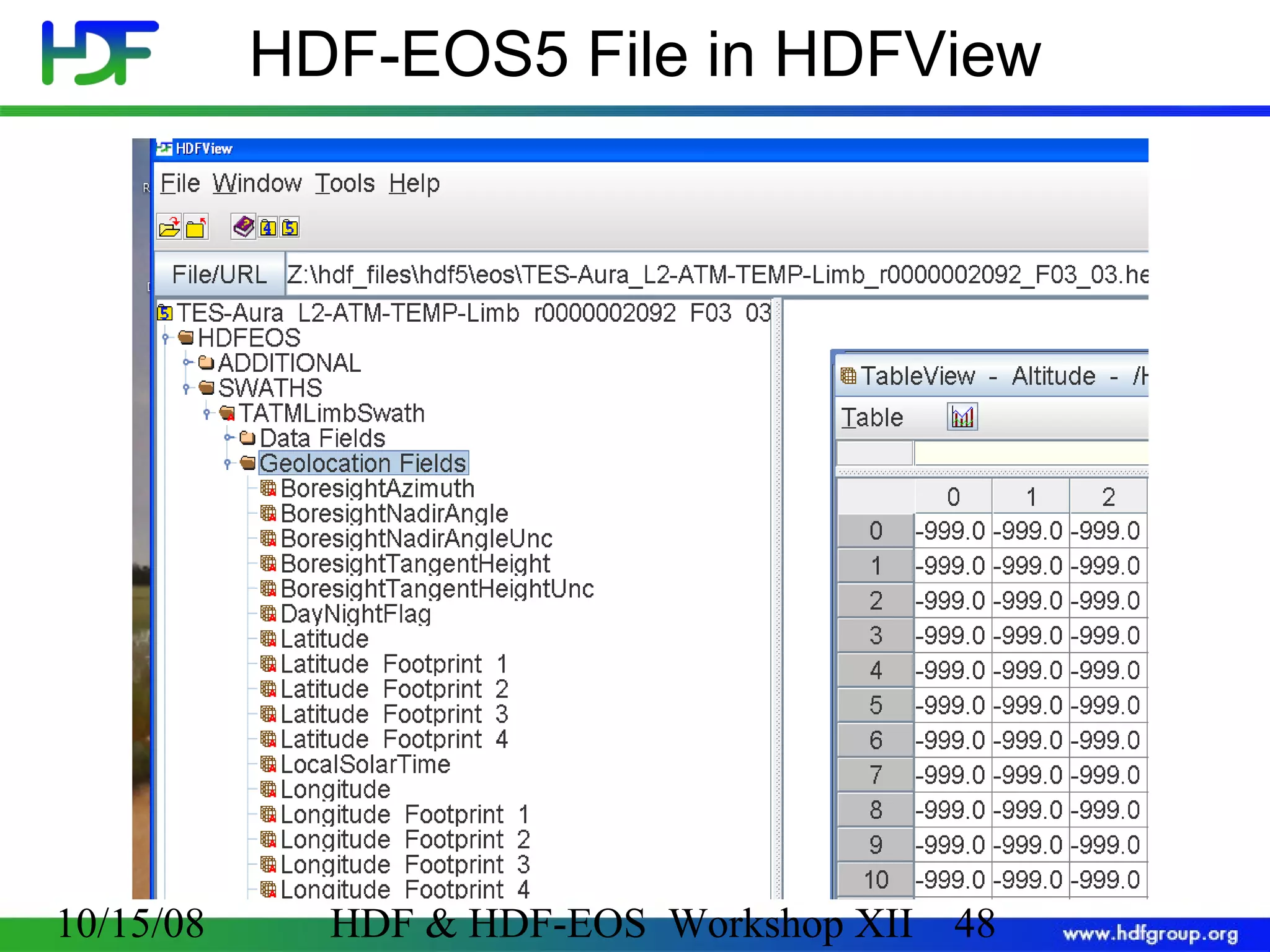
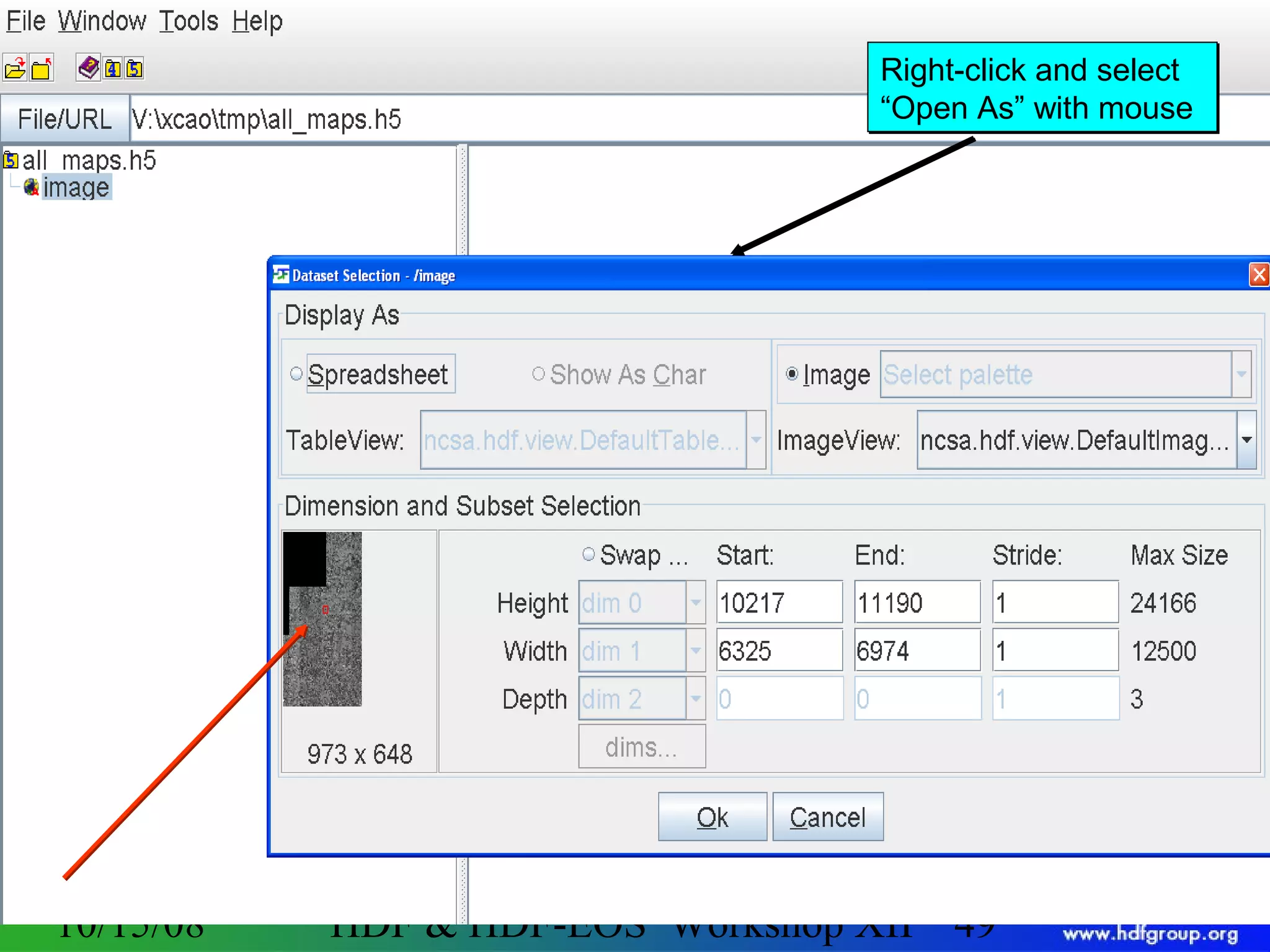
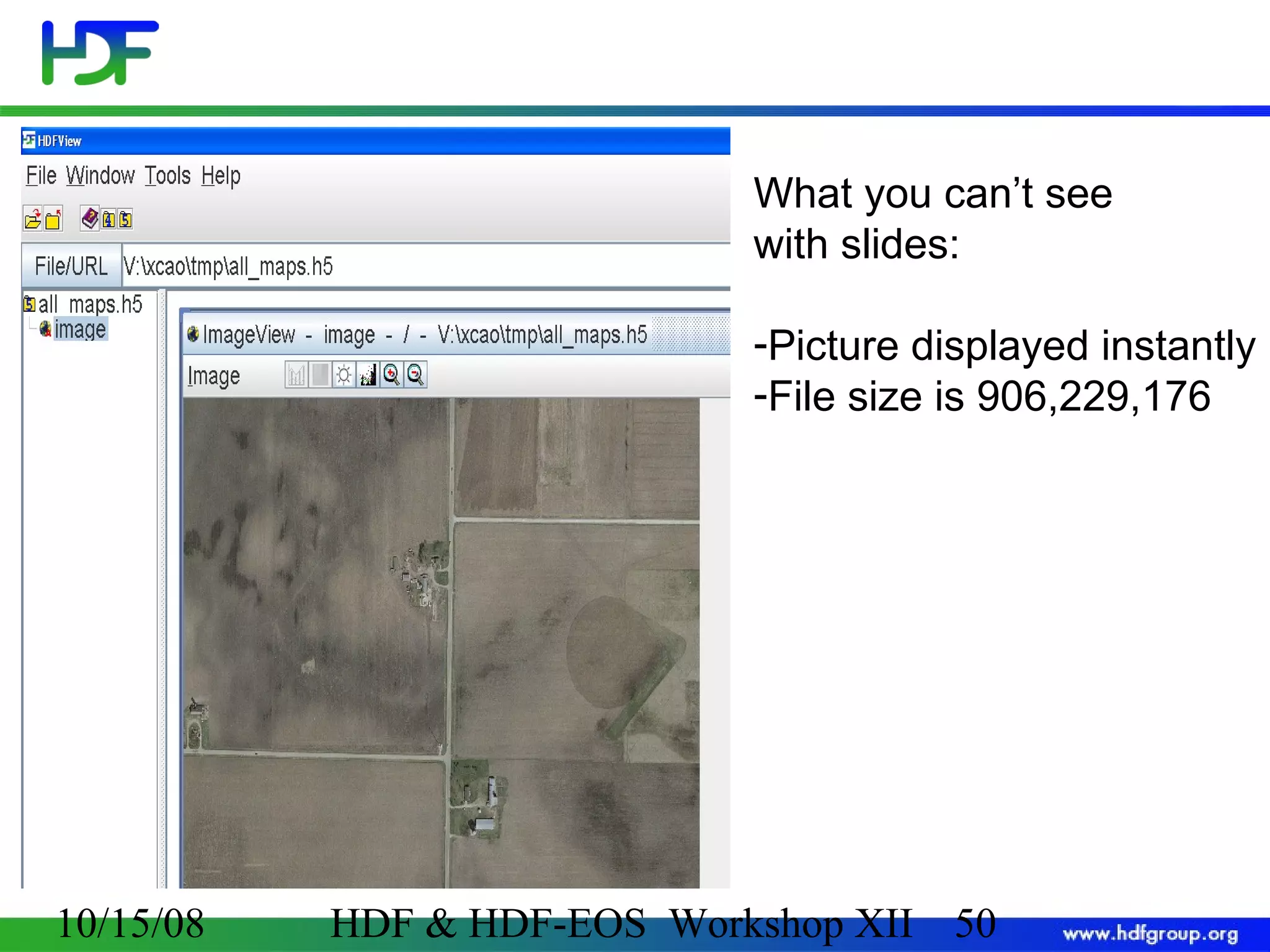
The document is an introduction to HDF5, outlining its history, structure, and use cases, particularly in managing large and complex data sets. It covers HDF5's data model, programming interface, and tools for accessing and manipulating data, highlighting its efficiency and versatility across various computing environments. Additionally, it provides examples of operations supported by the API and resources for accessing further information about HDF5.








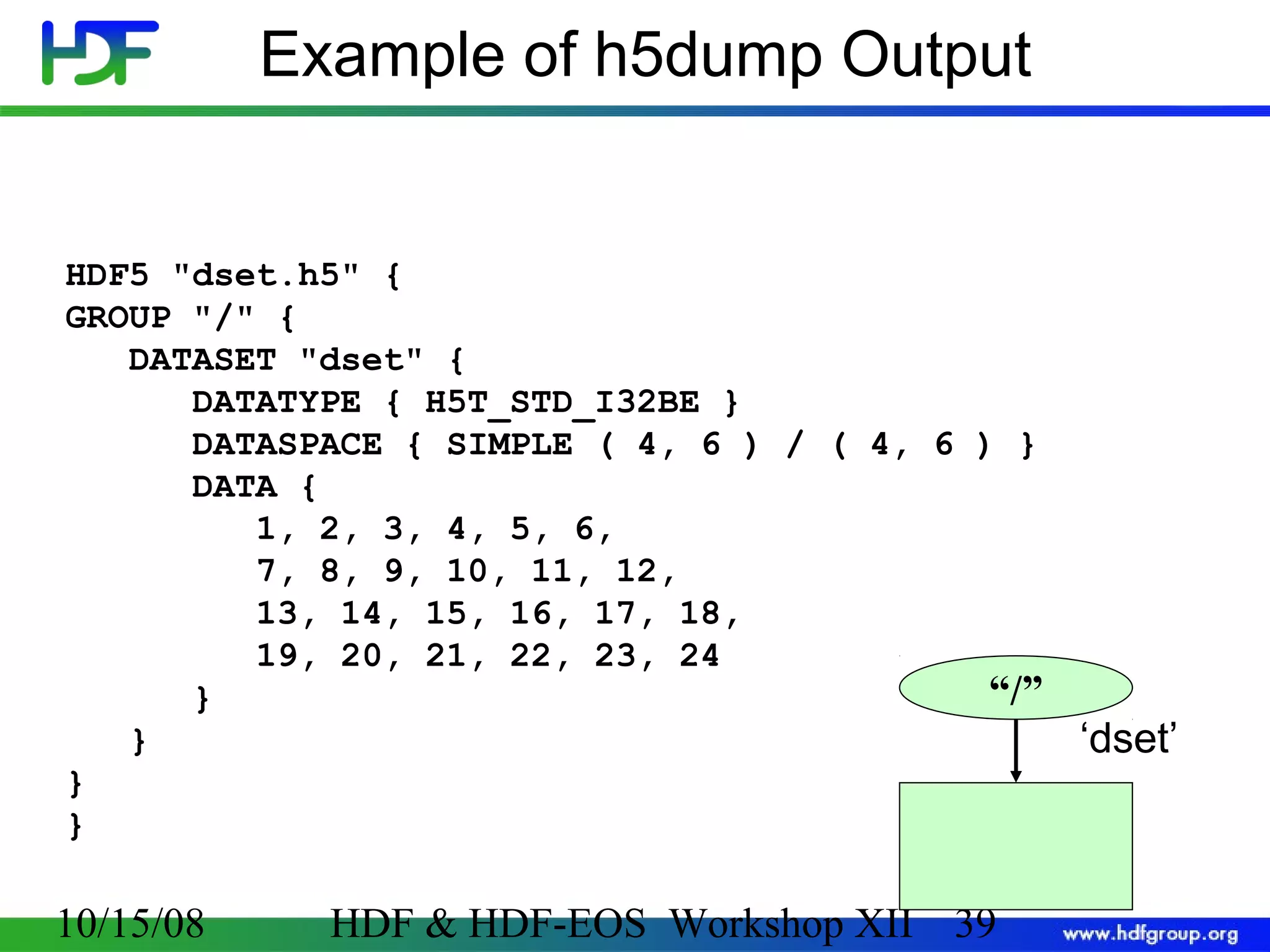
![H5dump Command-line Utility To View HDF5 File h5dump [--header] [-a ] [-d <names>] [-g <names>] [-l <names>] [-t <names>] [-p] <file> --header Display header only; no data is displayed. -a <names> Display the specified attribute(s). -d <names> Display the specified dataset(s). -g <names> Display the specified group(s) and all the members. -l <names> Displays the value(s) of the specified soft link(s). -t <names> Display the specified named datatype(s). -p Display properties. <names> is one or more appropriate object names. 10/15/08 HDF & HDF-EOS Workshop XII 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bxj-140217133918-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-HDF5-38-2048.jpg)


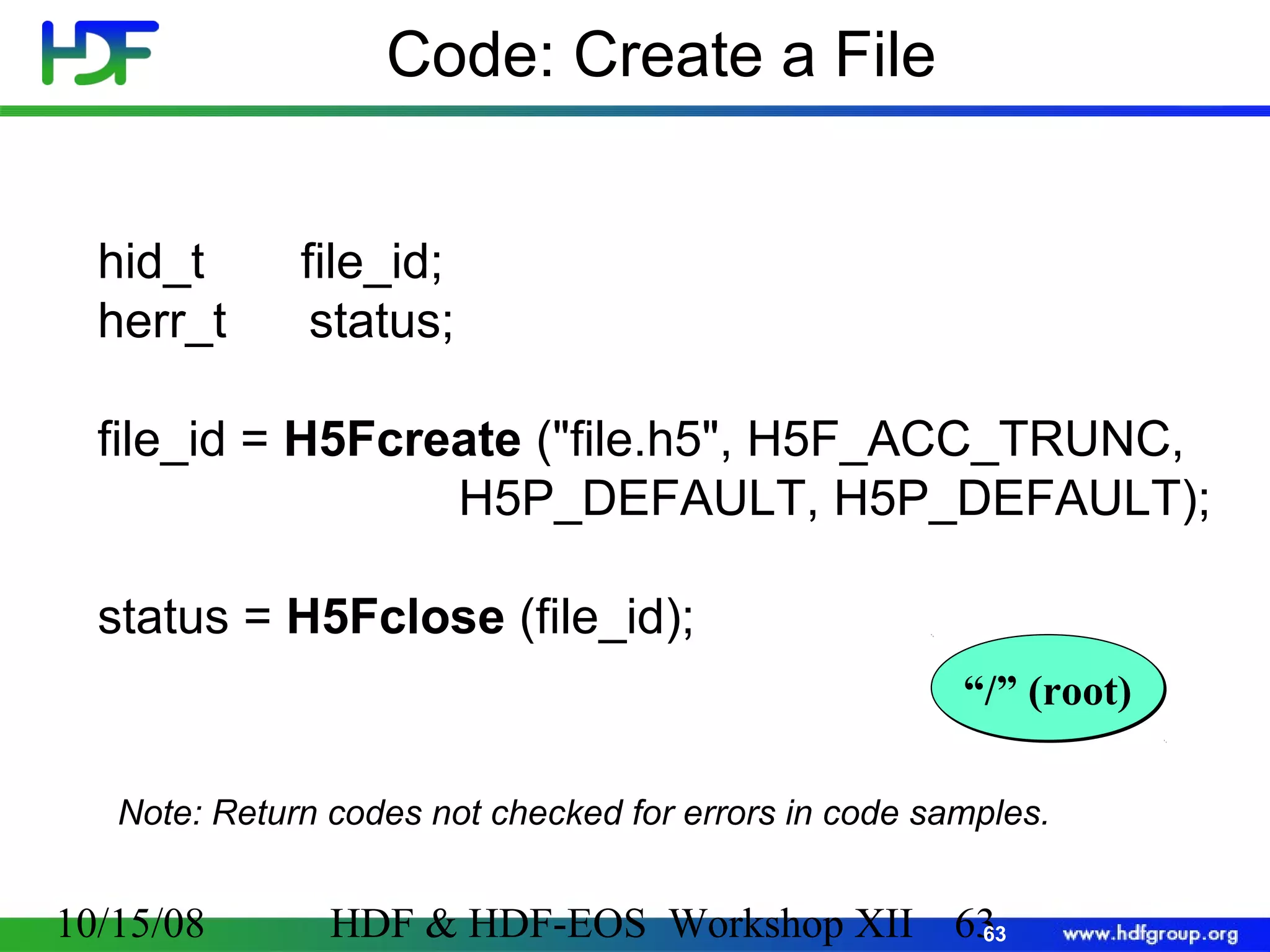
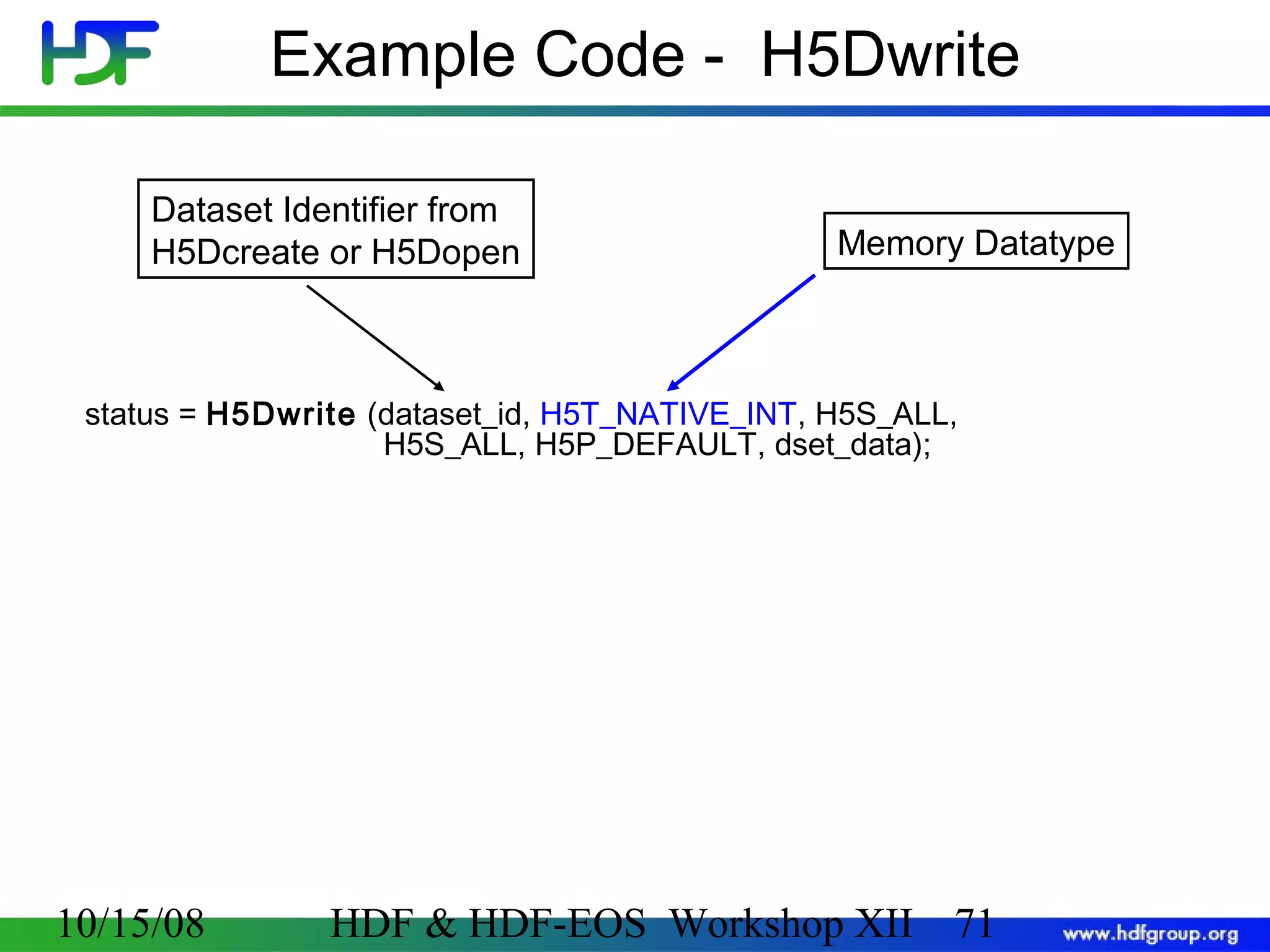
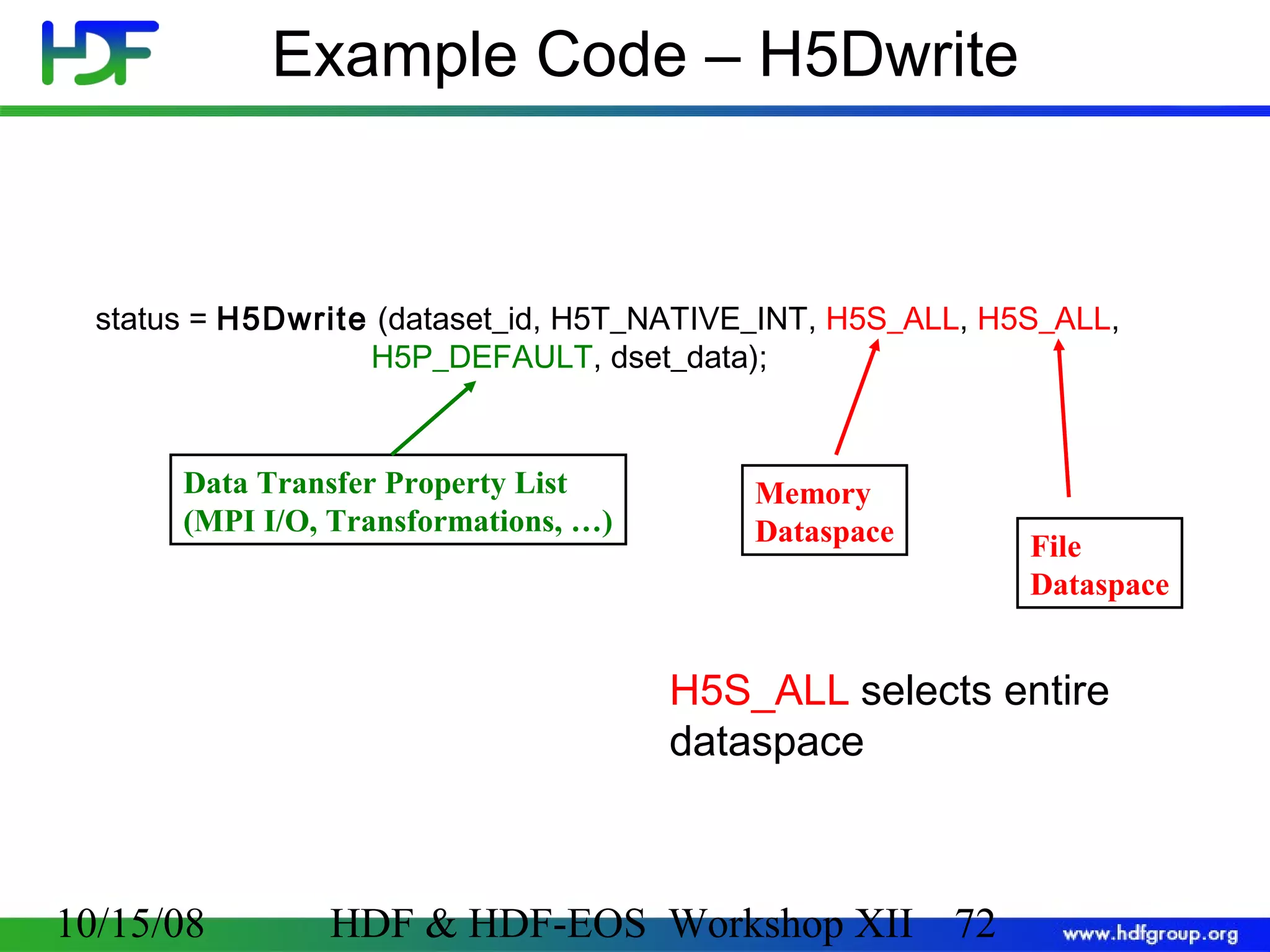
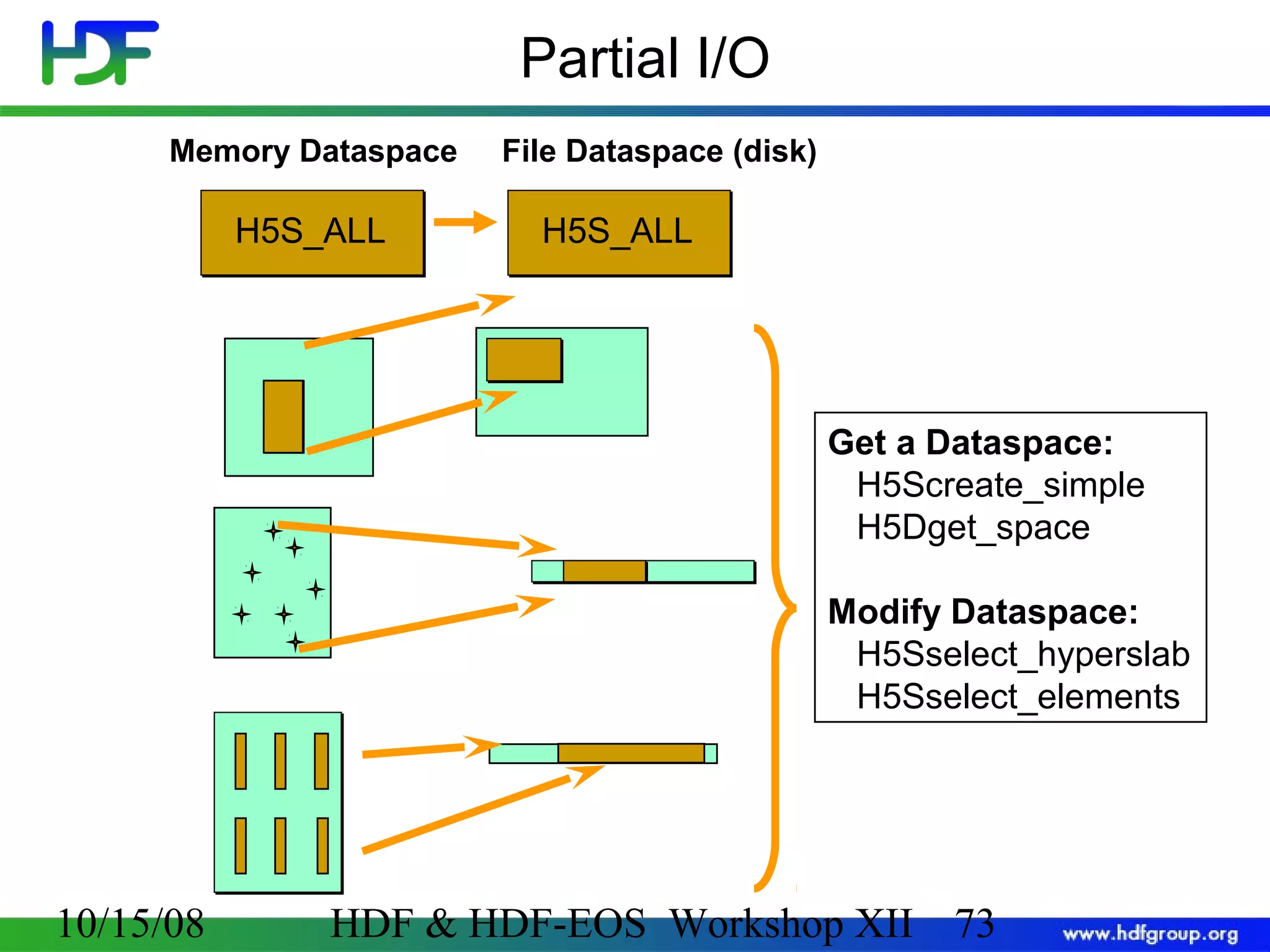
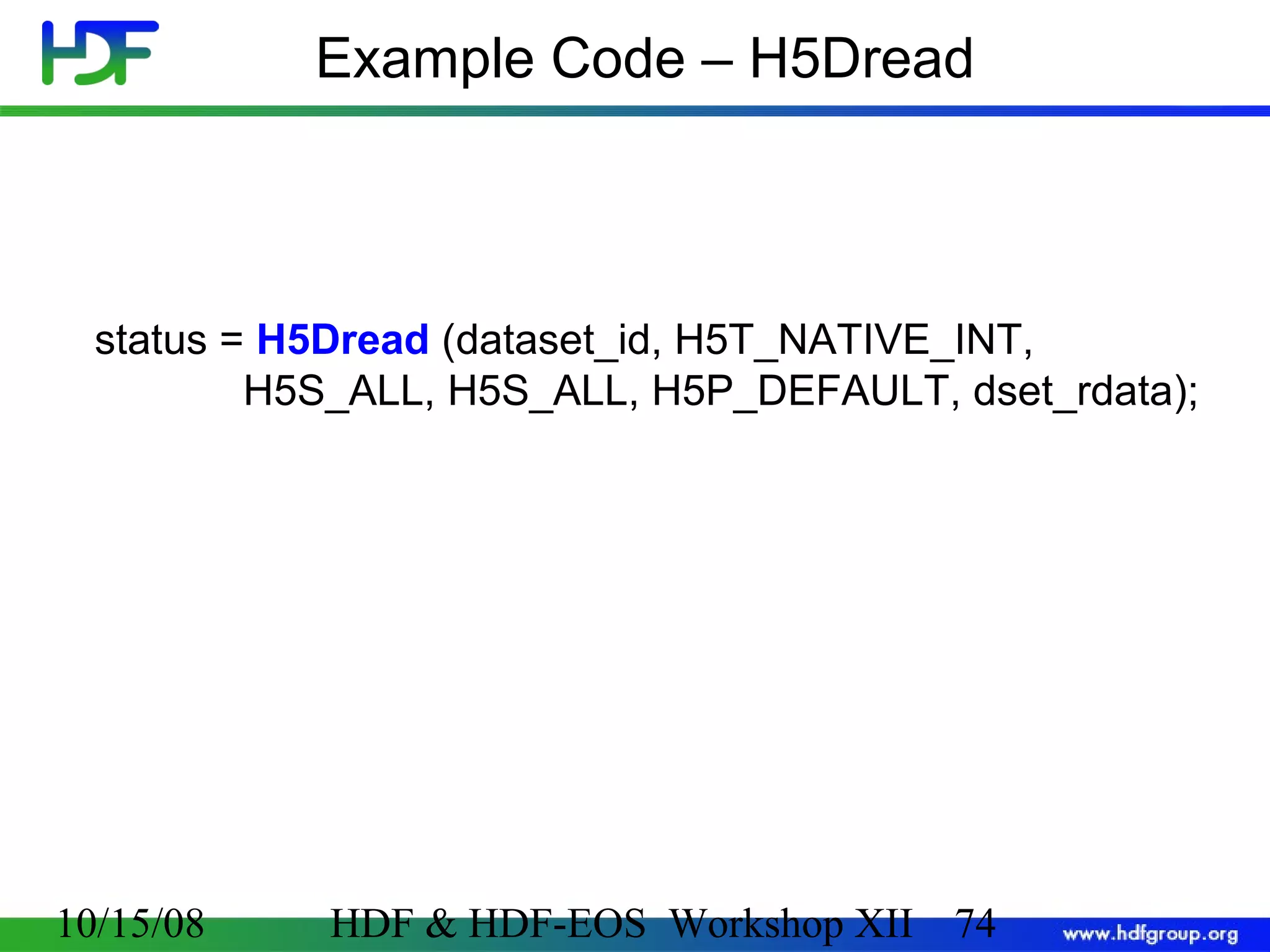
![Code: Create a Dataset 1 2 3 hid_t hsize_t herr_t file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id; dims[2]; status; 4 file_id = H5Fcreate (”file.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); Create a 5 dataspace= 4; dims[0] 6 7 rank dims[1] = 6; dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL); Create a dataset 8 current dims pathname datatype dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,”A",H5T_STD_I32BE, dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT); dataspace Terminate access to dataset, dataspace, file 9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id); 10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id); 11 status = H5Fclose (file_id); 10/15/08 property list (default) HDF & HDF-EOS Workshop XII 70 70](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bxj-140217133918-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-HDF5-70-2048.jpg)