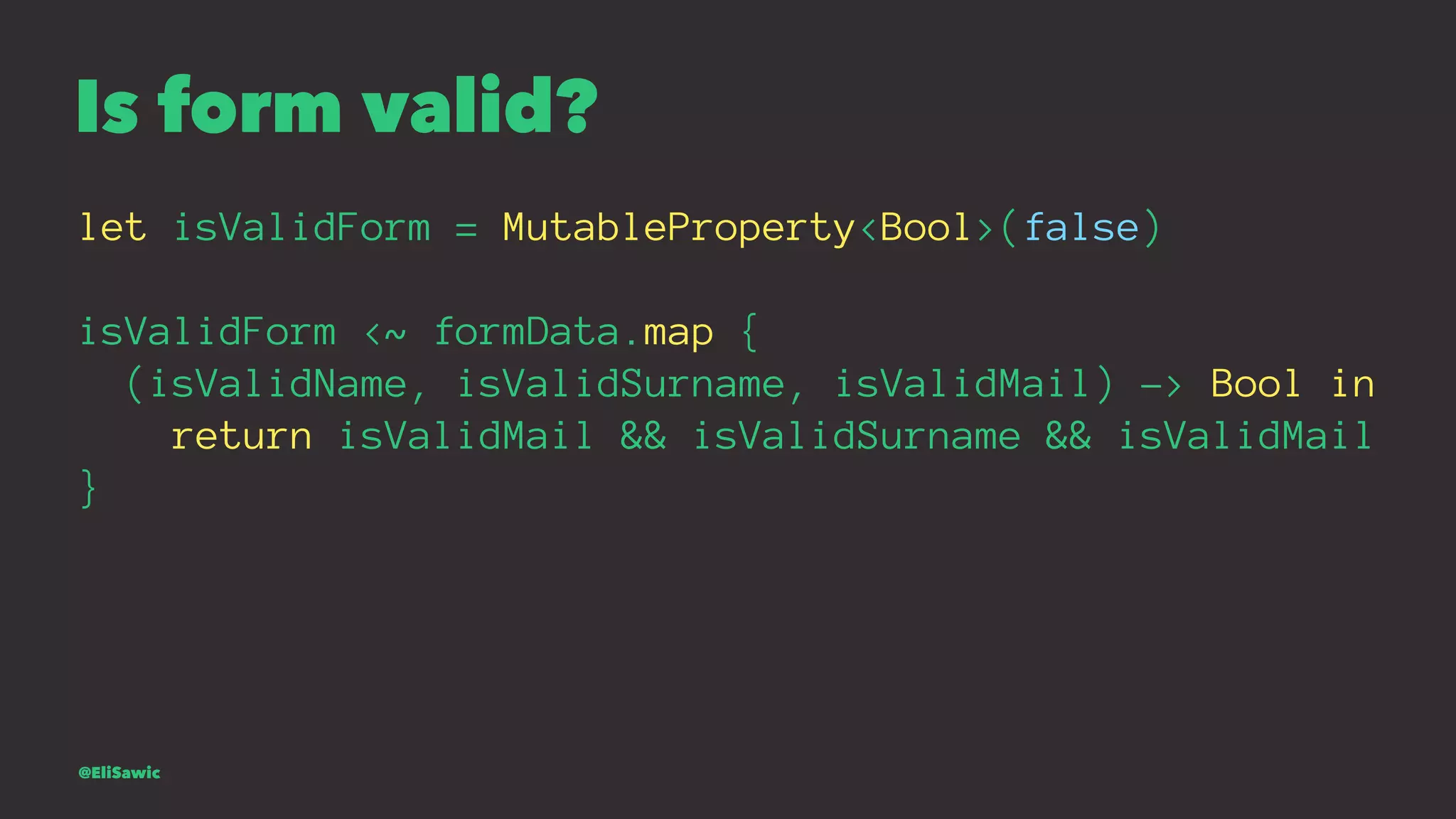
This document provides an introduction to functional reactive programming (FRP). It discusses key concepts of FRP including working with streams of asynchronous data, manipulating streams using functions like map and filter, and combining multiple streams. It also covers the ReactiveCocoa framework for FRP in iOS and OS X, including how to think in signals that represent events over time rather than mutable state. An example is provided of validating a form by combining streams of name, surname, and email validation.















![Imperative let array = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] var evenNumbers = [Int]() for element in array { if element % 2 == 0 { evenNumbers.append(element) } } @EliSawic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontofrp19-161120213443/75/Introduction-To-Functional-Reactive-Programming-Poznan-20-2048.jpg)

![Declarative let array = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] let evenNumbers = array.filter { $0 % 2 == 0 } @EliSawic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontofrp19-161120213443/75/Introduction-To-Functional-Reactive-Programming-Poznan-22-2048.jpg)



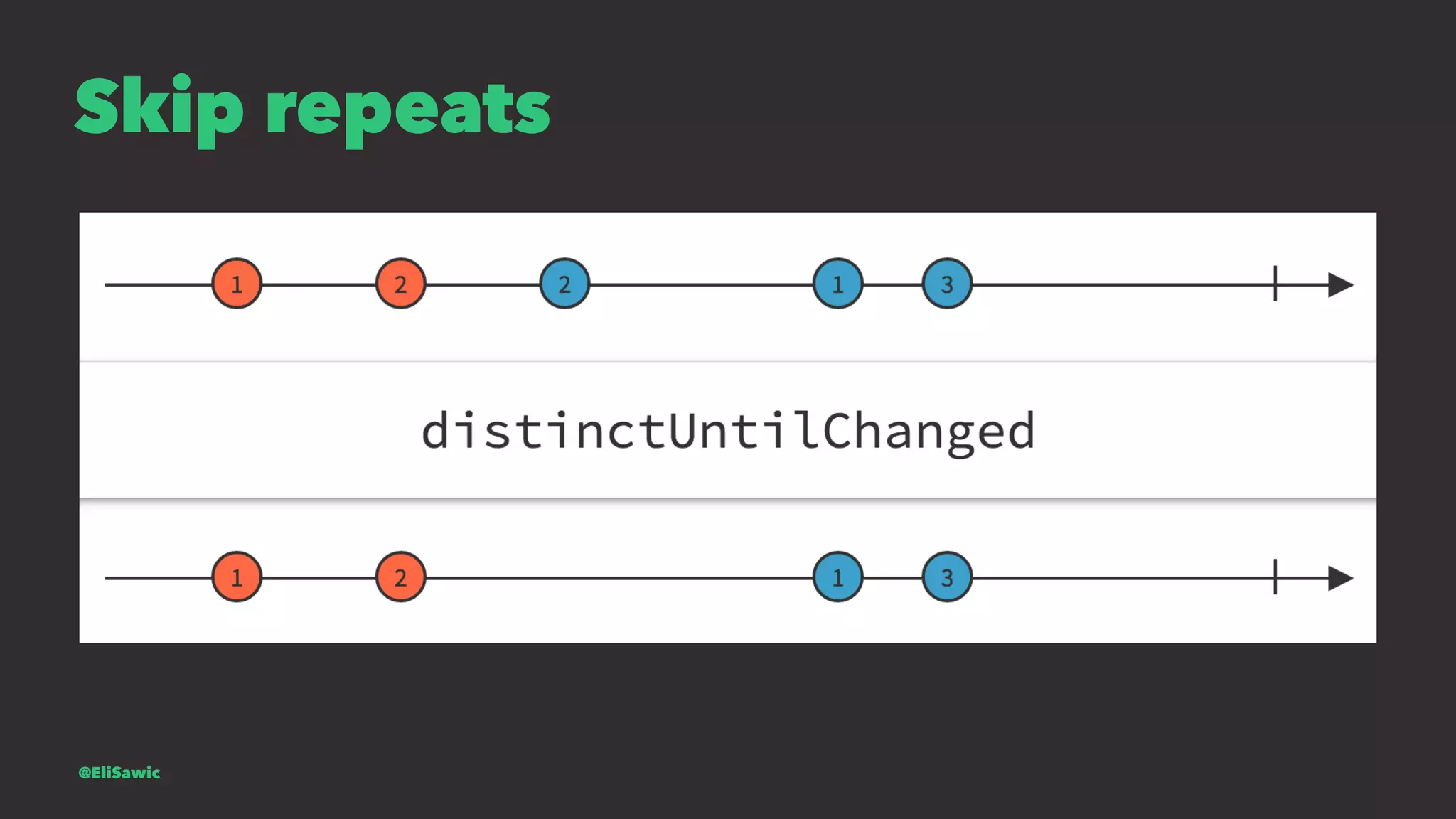

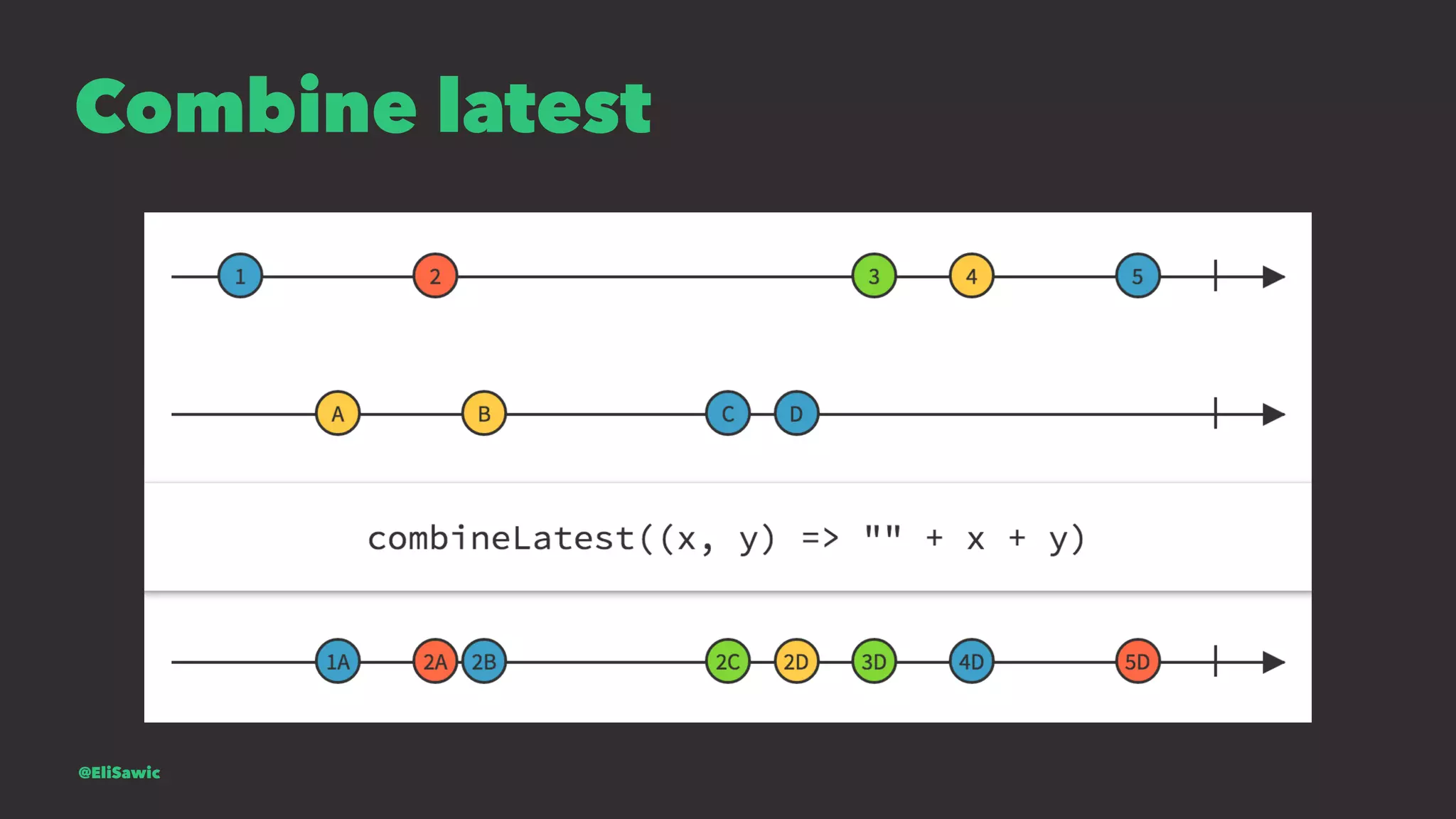
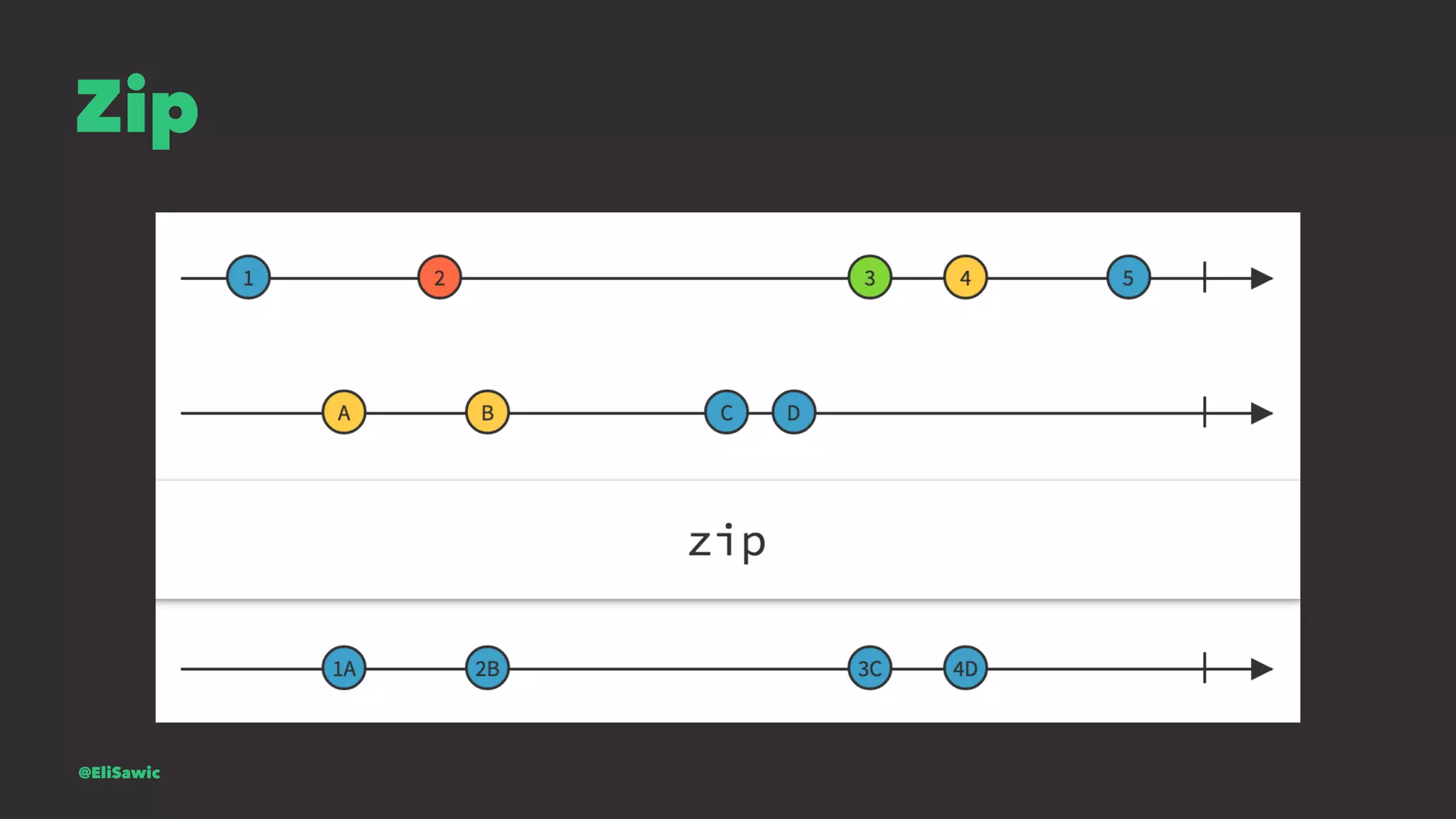
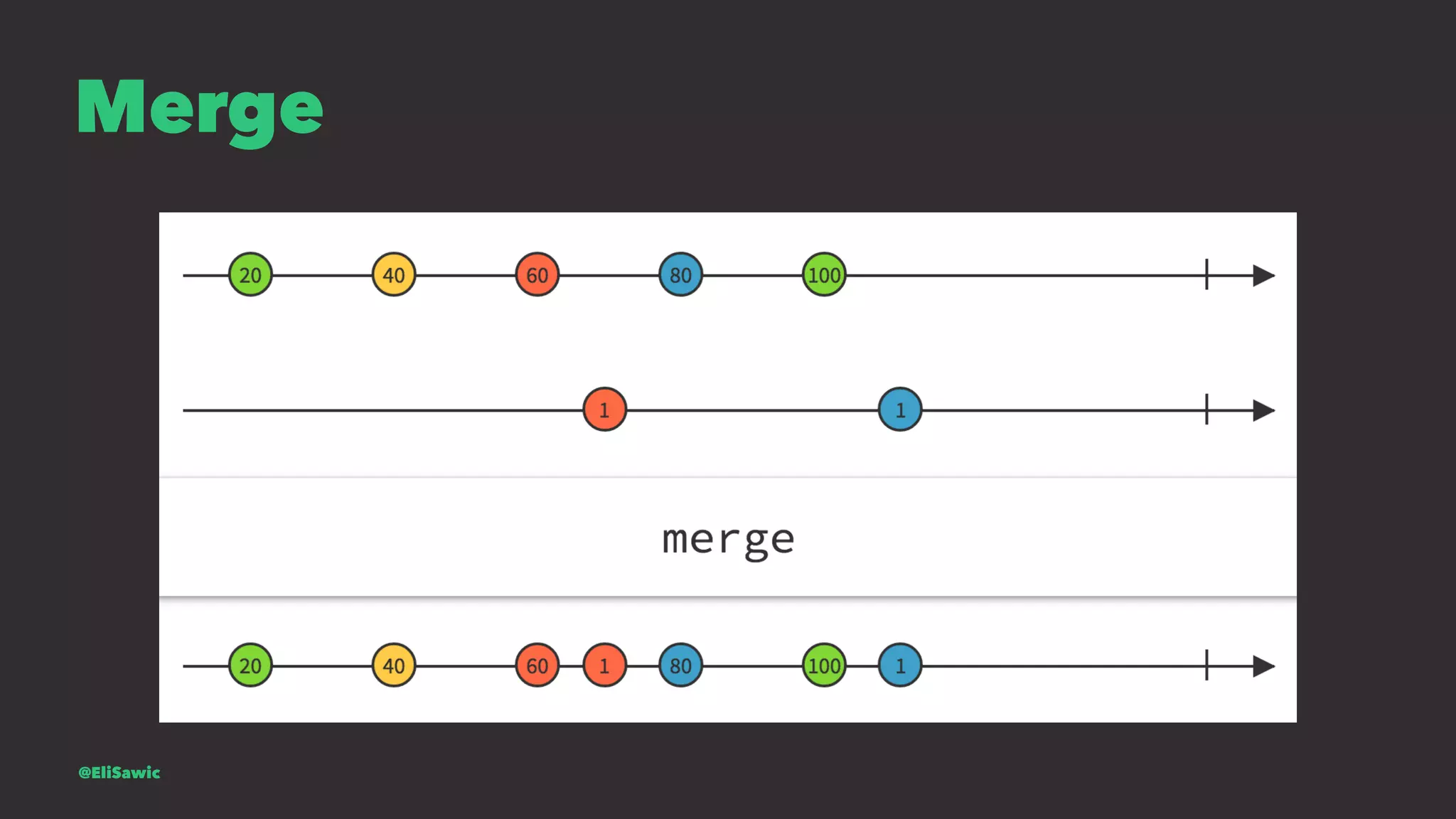








































![Is mail valid? let isValidMail = mailSignal.map { (mail) -> Bool in let emailRegEx = "[A-Z0-9a-z._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+.[A-Za-z]{2,}" let emailTest = NSPredicate(format:"SELF MATCHES %@", emailRegEx) return emailTest.evaluateWithObject(mail) } @EliSawic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontofrp19-161120213443/75/Introduction-To-Functional-Reactive-Programming-Poznan-77-2048.jpg)