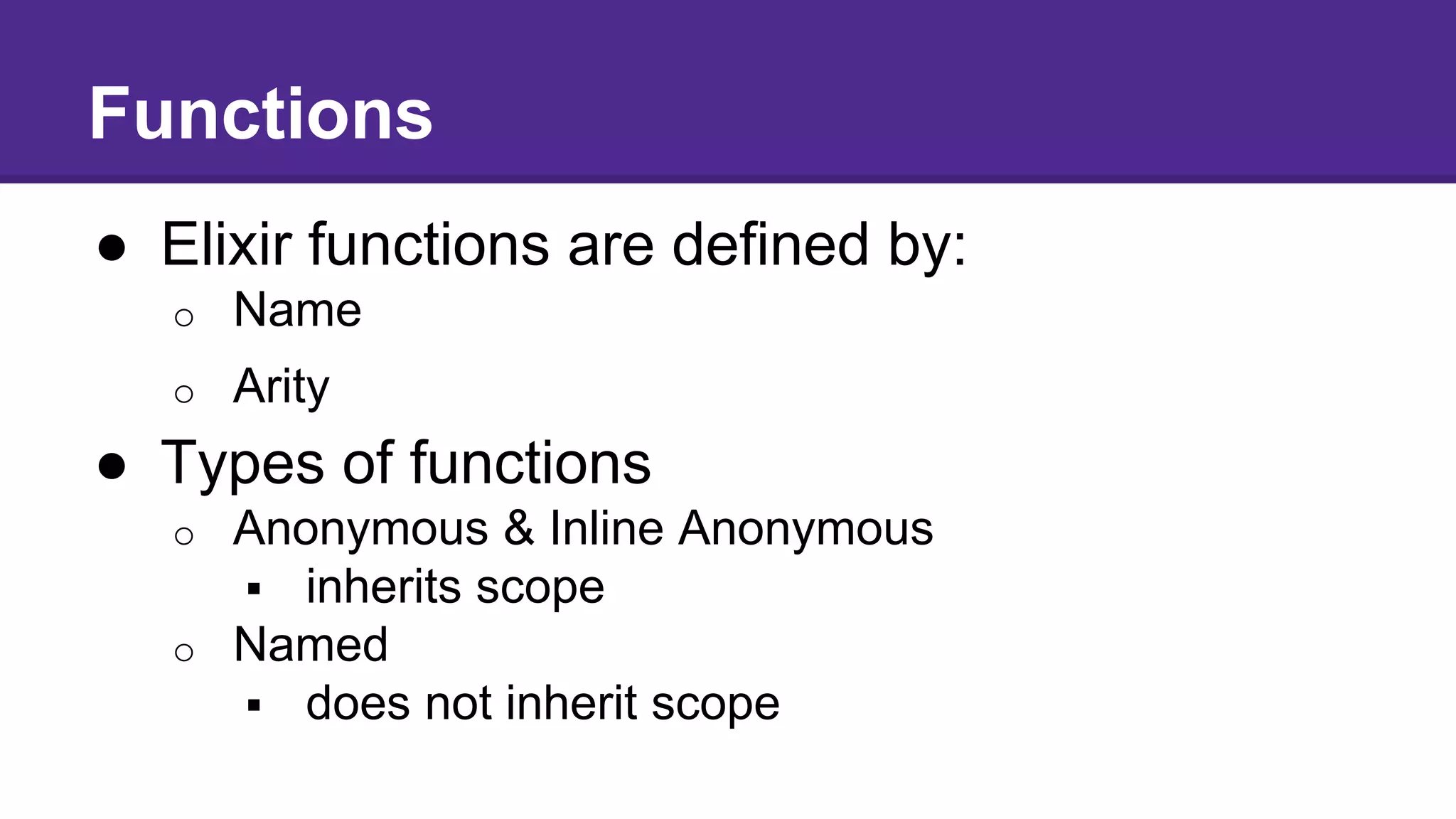
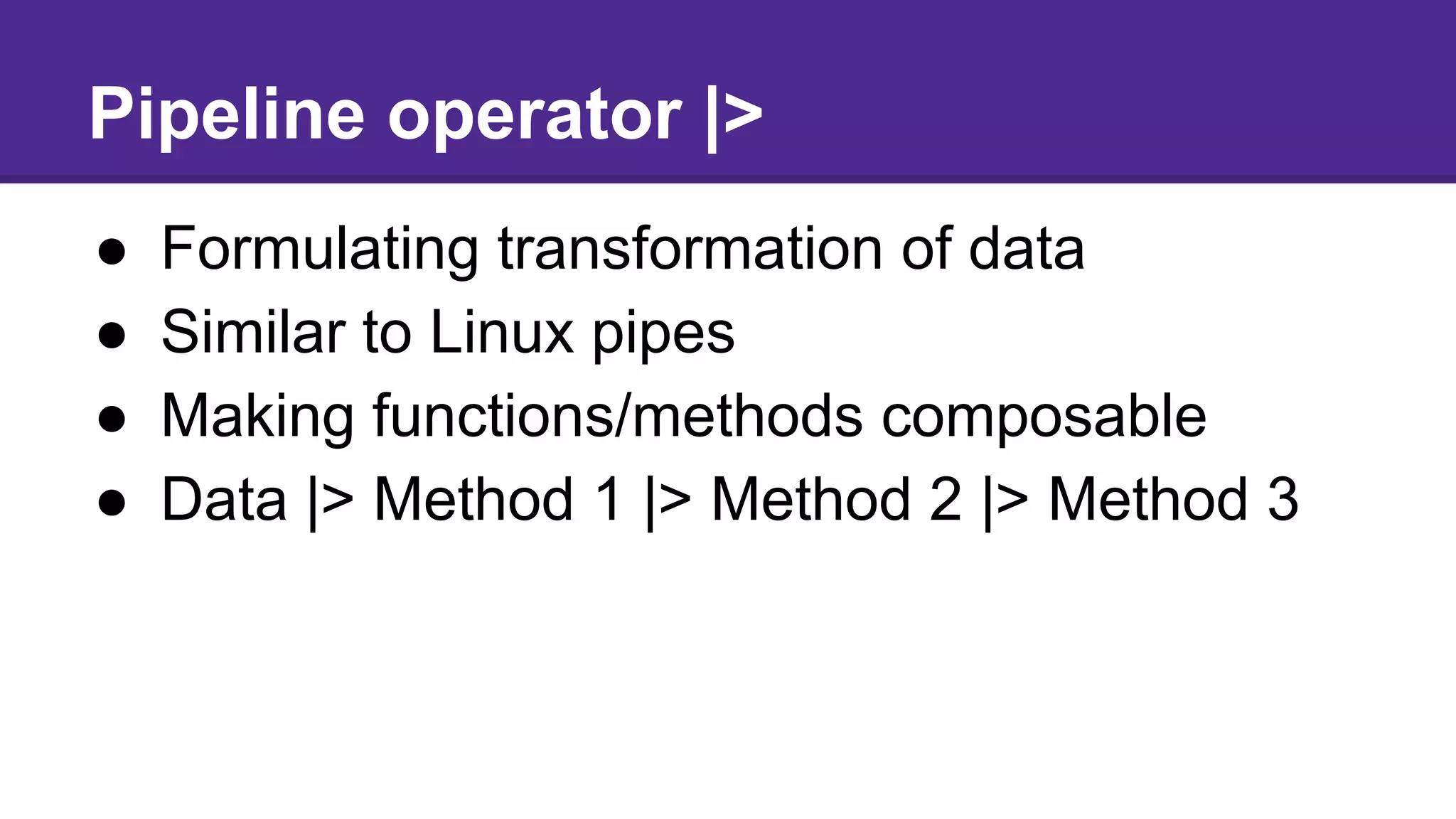
This document introduces functional programming with Elixir. It discusses how functional programming is an alternative paradigm to object-oriented programming, with concepts like pure functions, immutable data, and functions as first-class citizens. Elixir is a functional language that runs on the Erlang VM, allowing it to easily build concurrent, distributed, and fault-tolerant systems. It provides many benefits over Erlang like better tooling and syntax. The document outlines Elixir's core concepts like modules, functions, pattern matching, and the pipeline operator and provides examples of how to work with Elixir's basic datatypes.