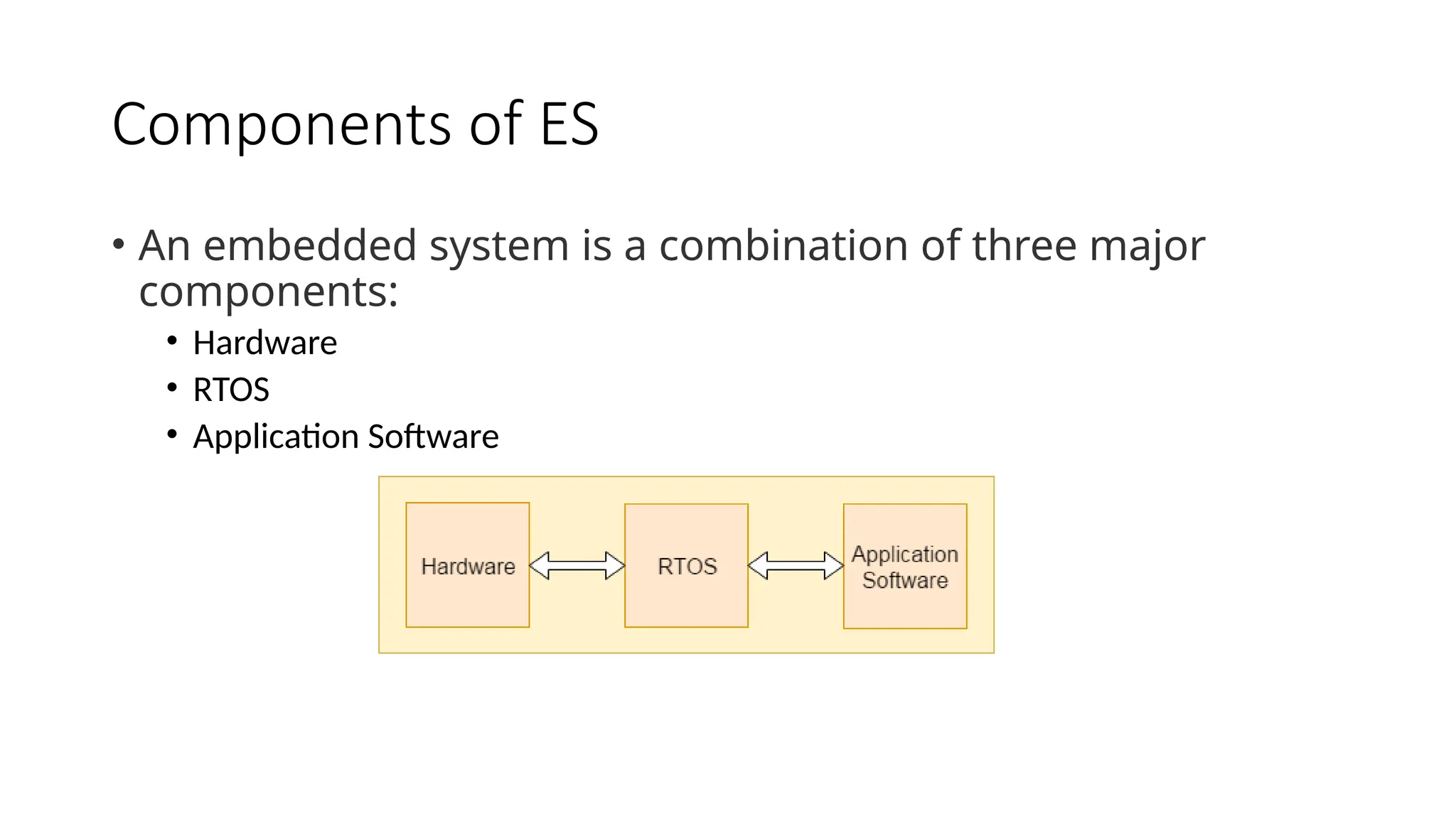
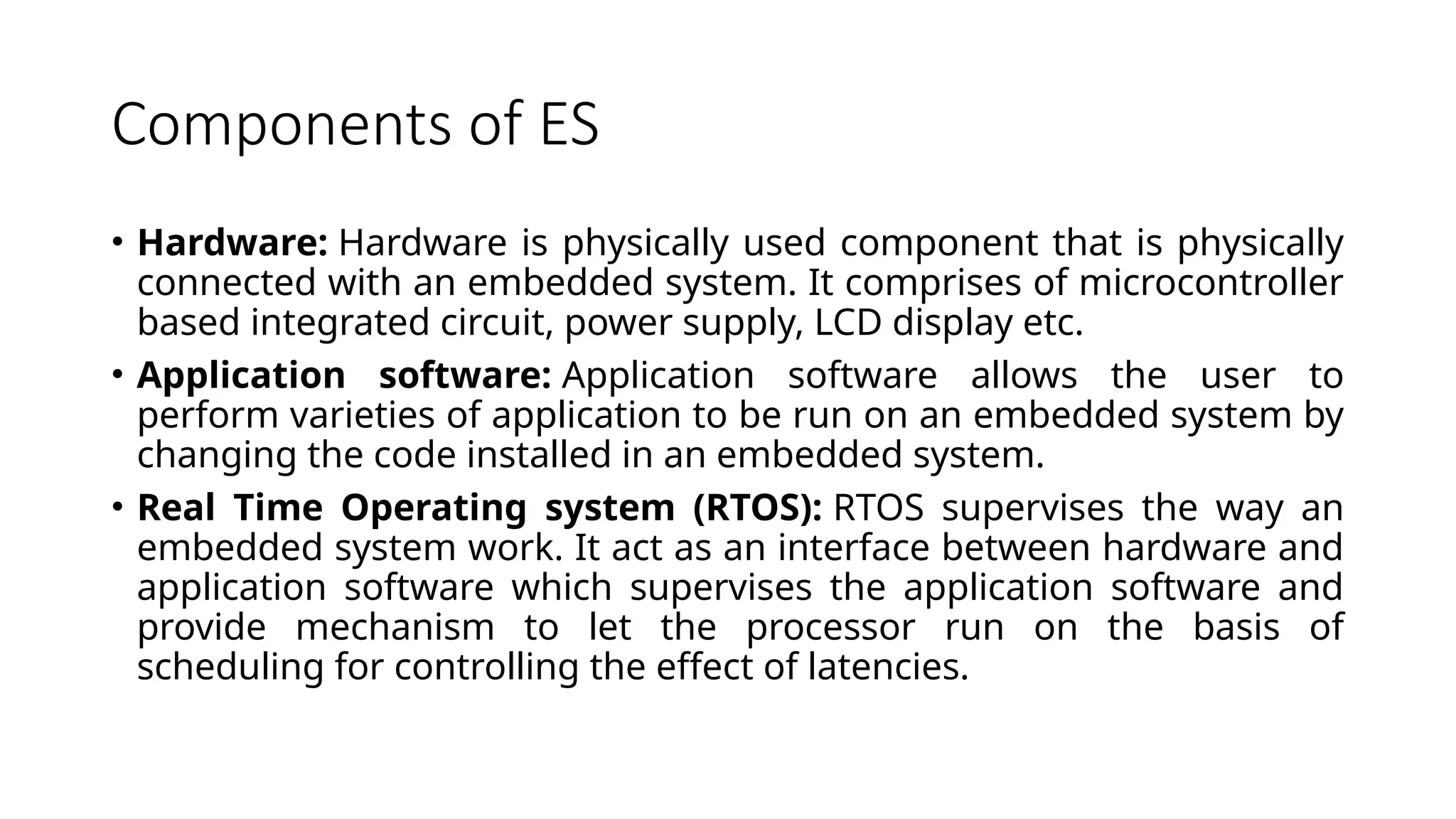
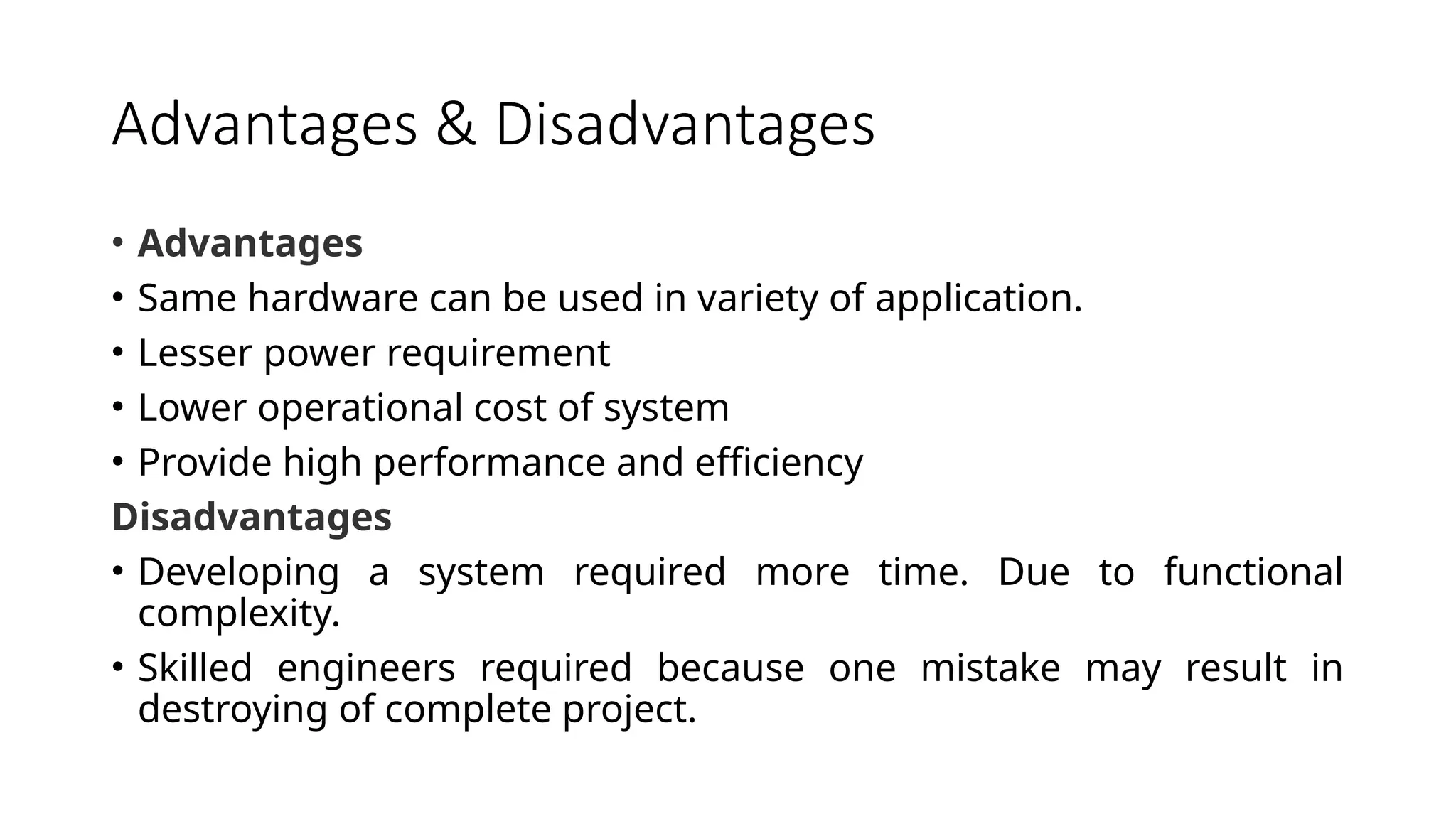
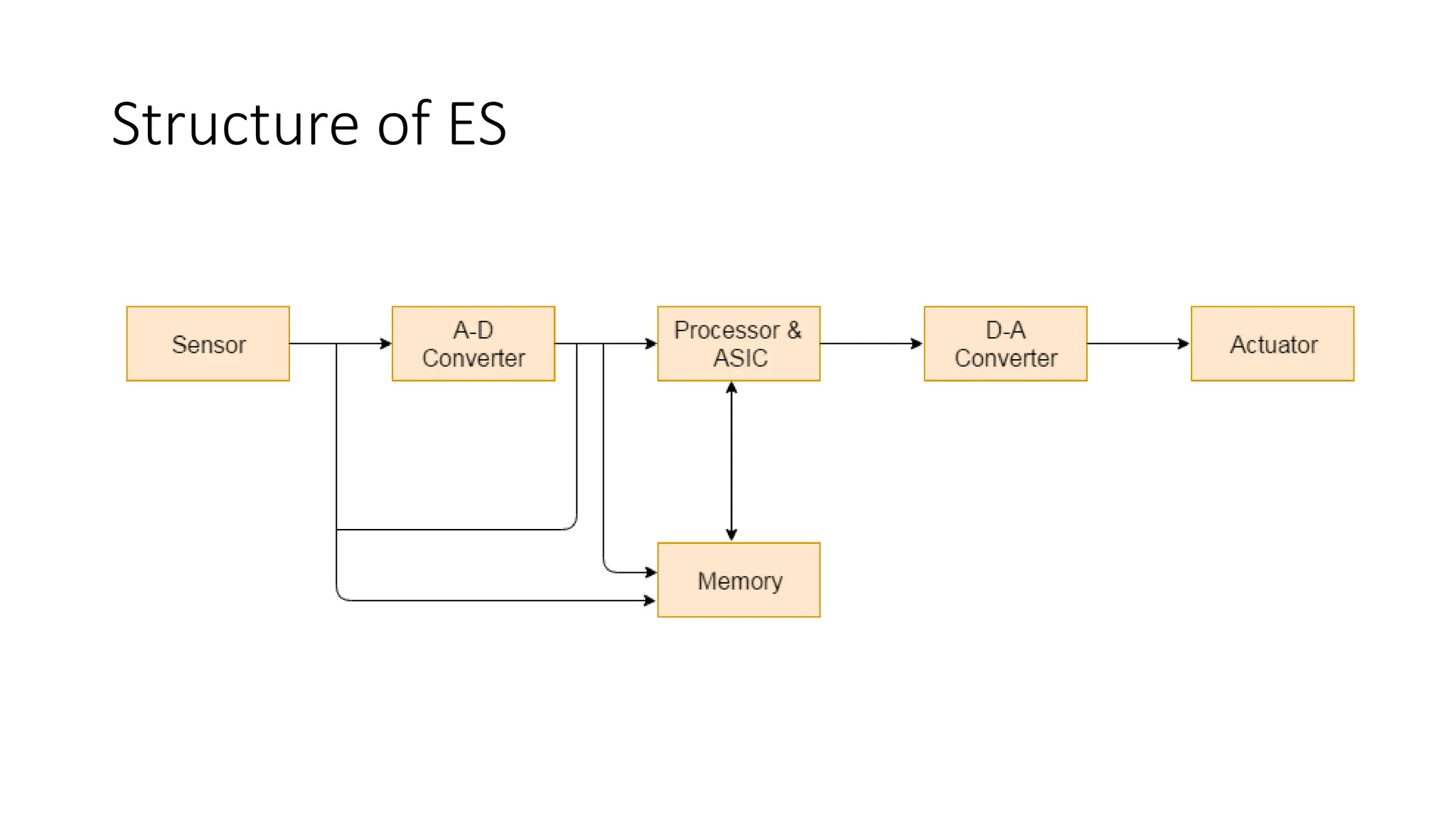
An embedded system (ES) is a hardware and software combination tailored for specific tasks, featuring components like microcontrollers, real-time operating systems (RTOS), and application software. ES can be part of larger systems, allowing for programmability and fixed functions, and it includes various elements like sensors, processors, and converters to perform real-time operations efficiently. Key considerations in designing ES include hardware selection, power consumption, cost, and system requirements.