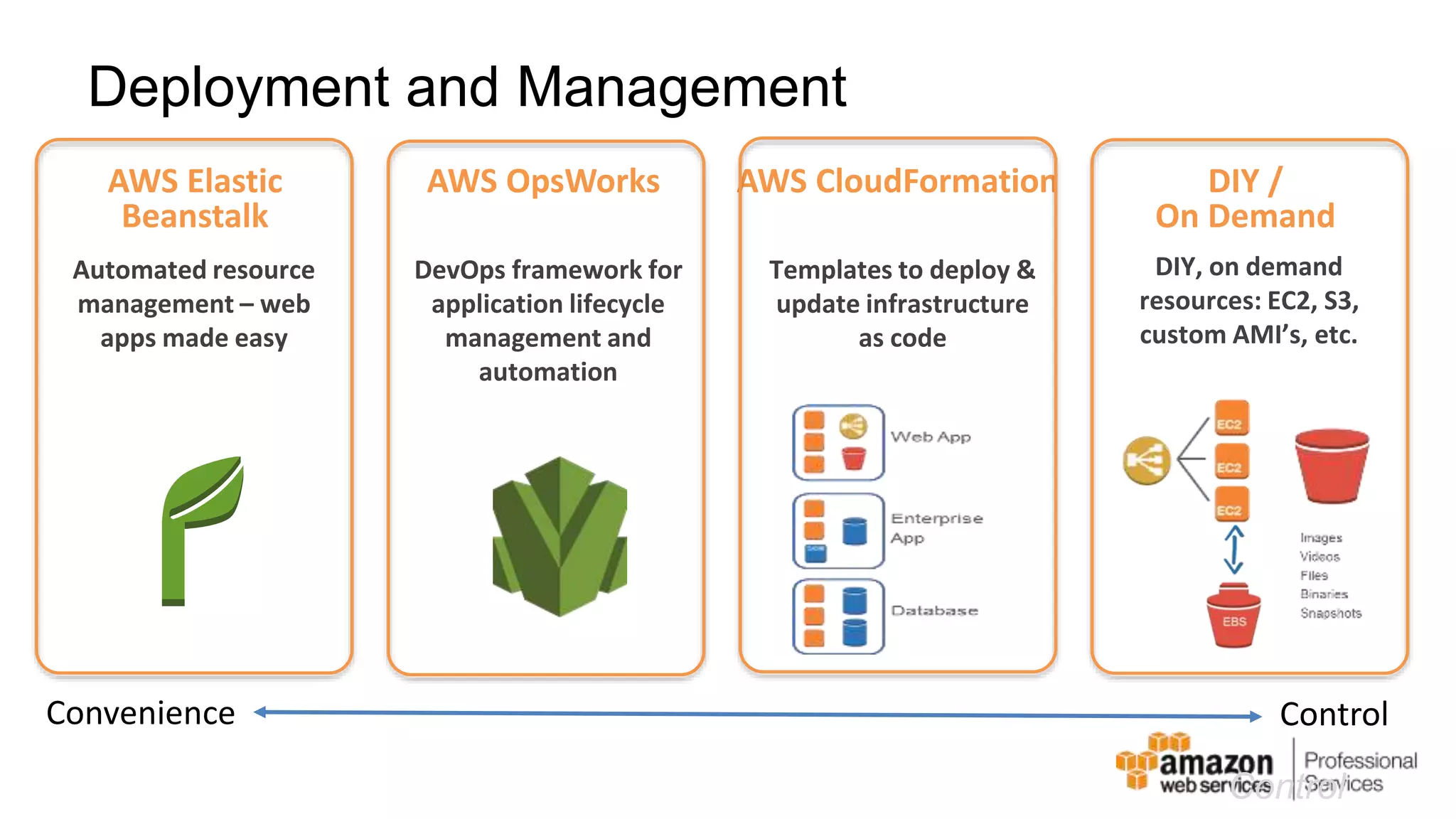
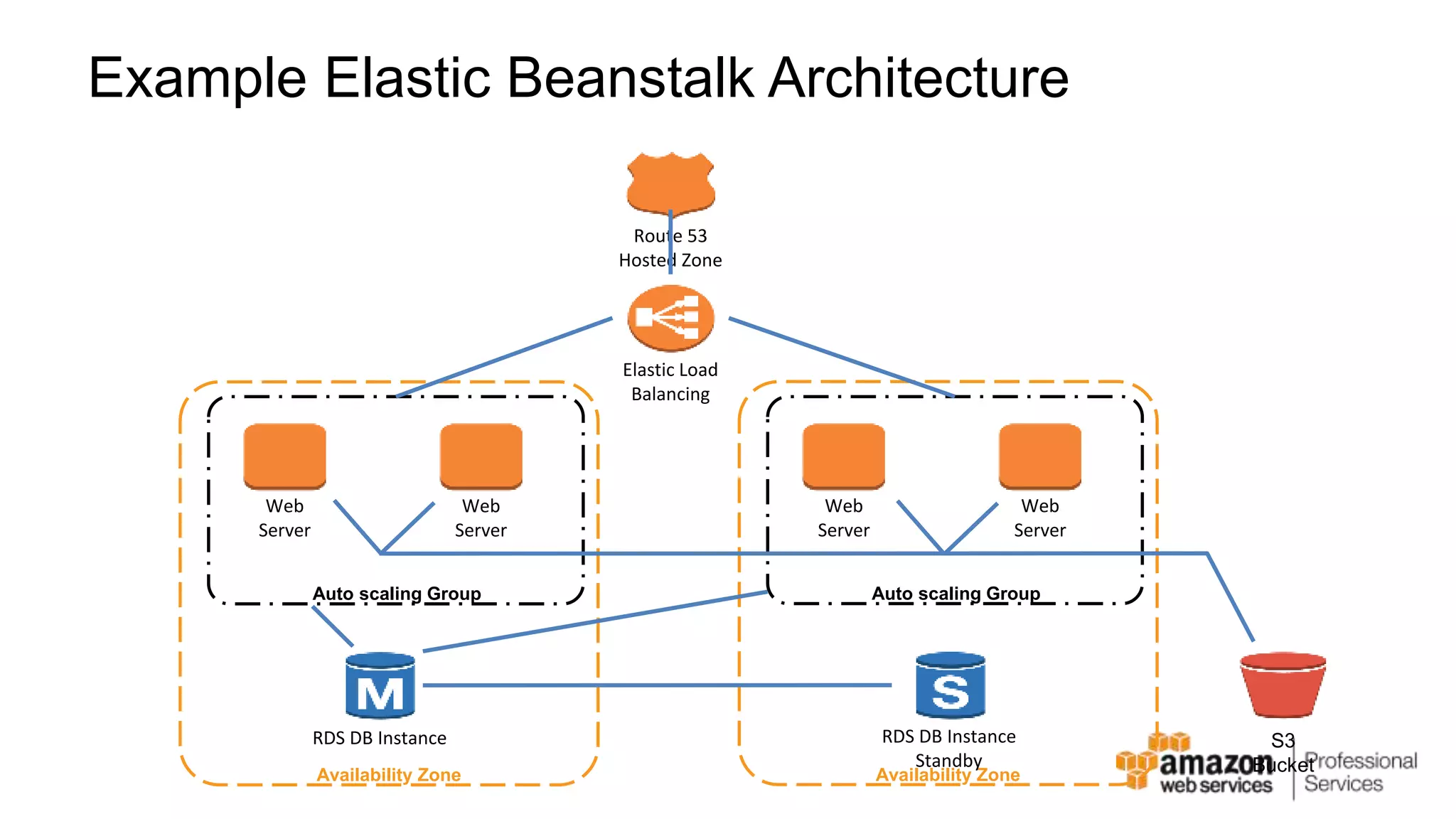
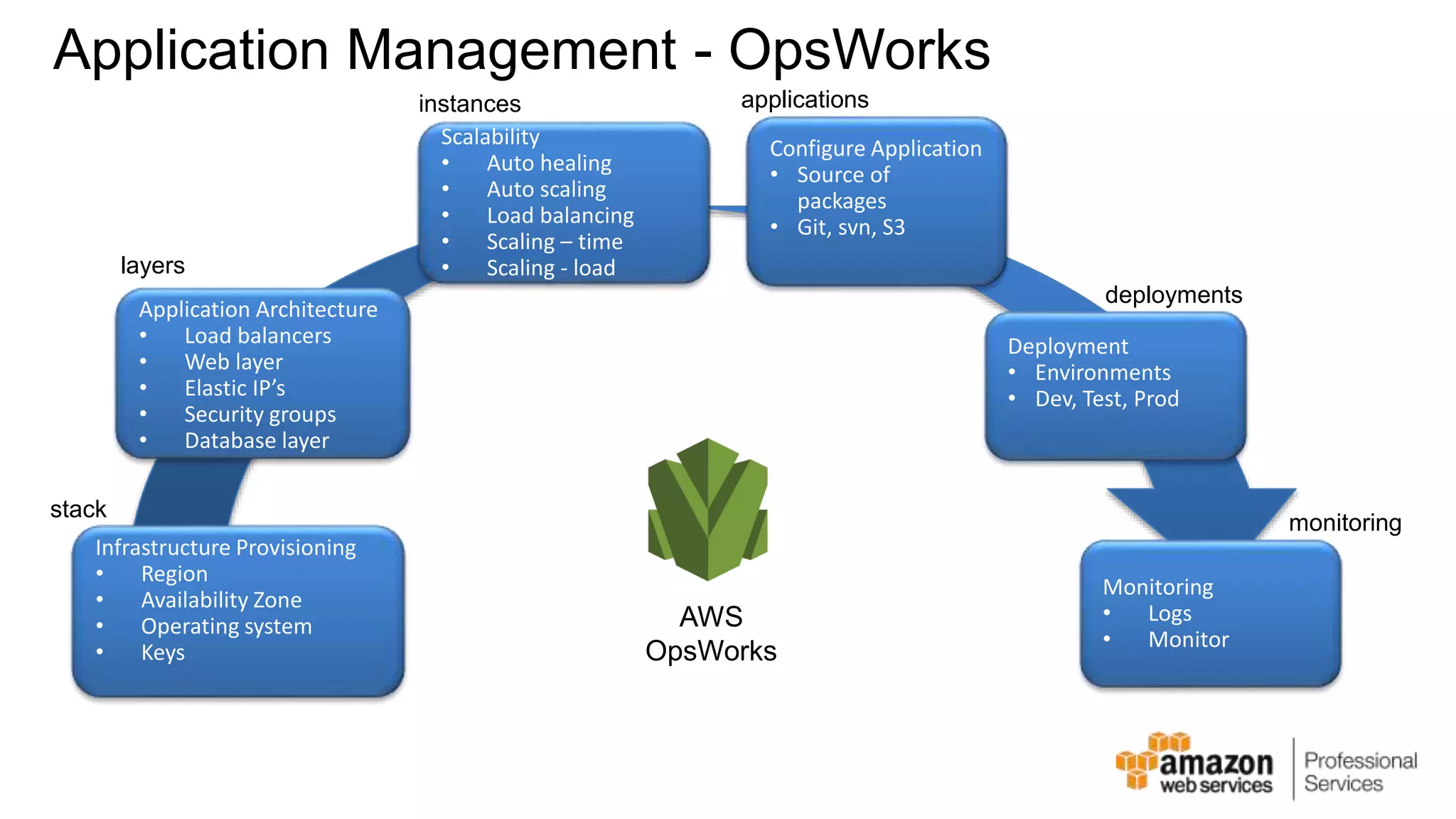
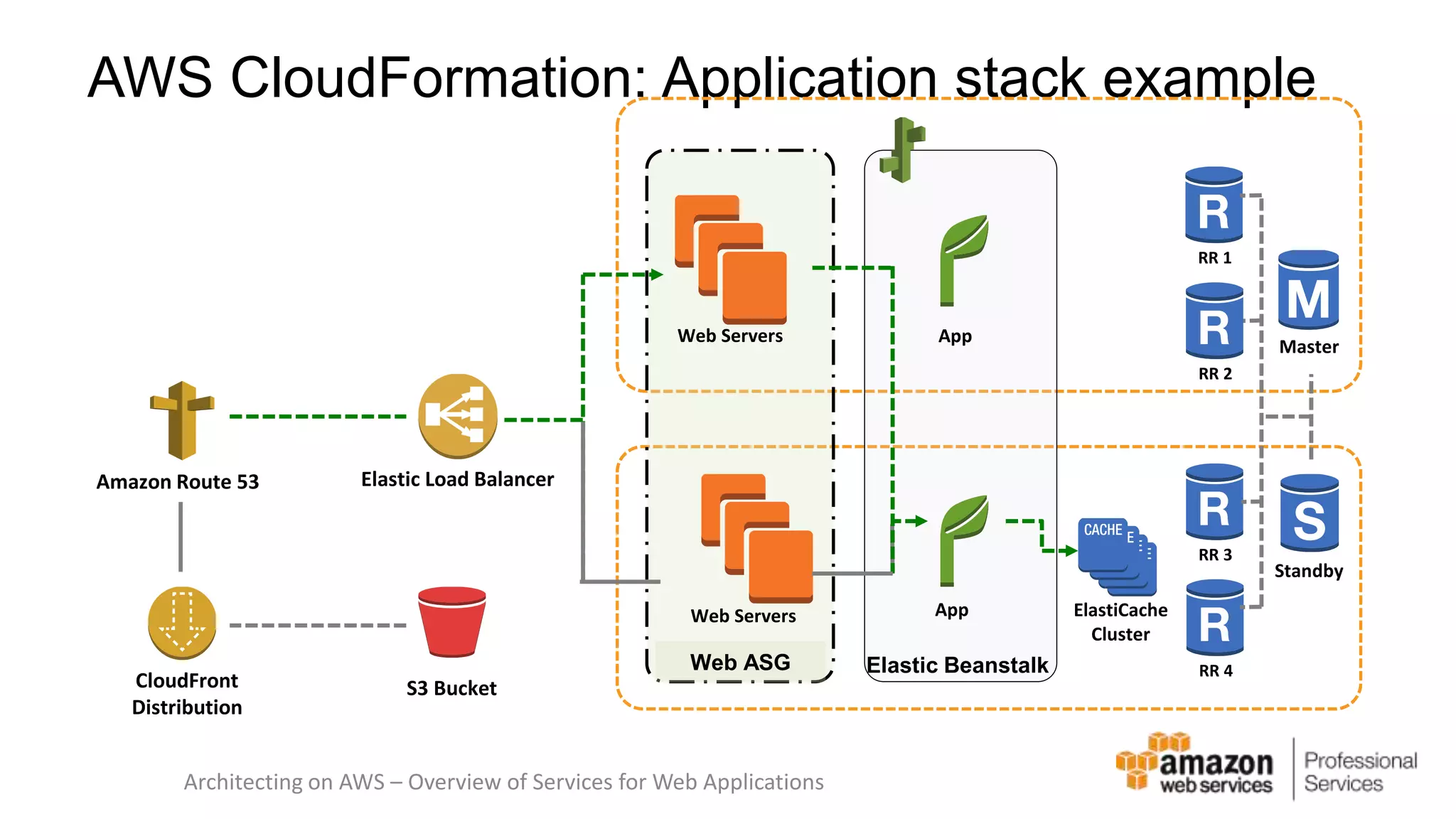
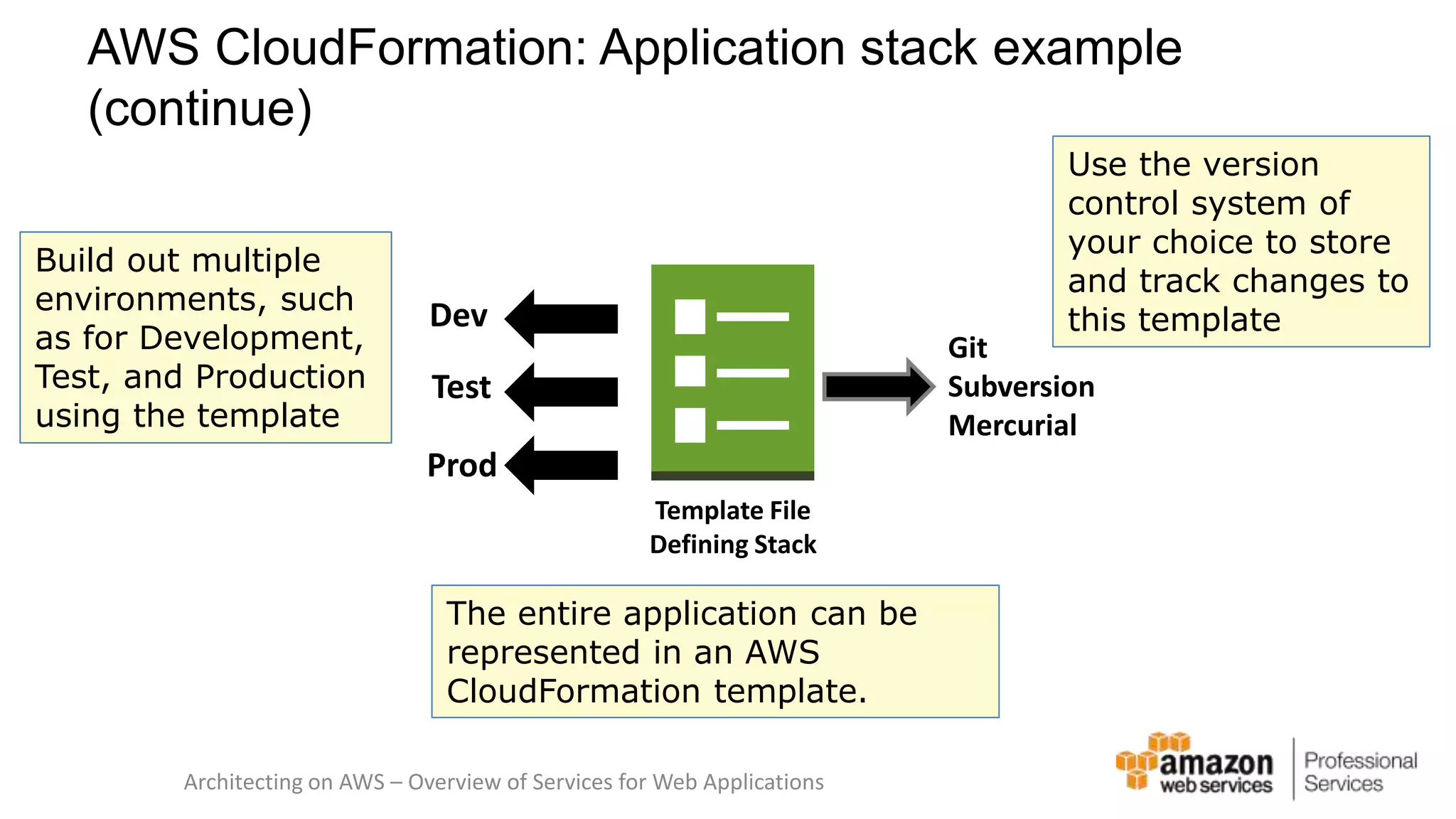
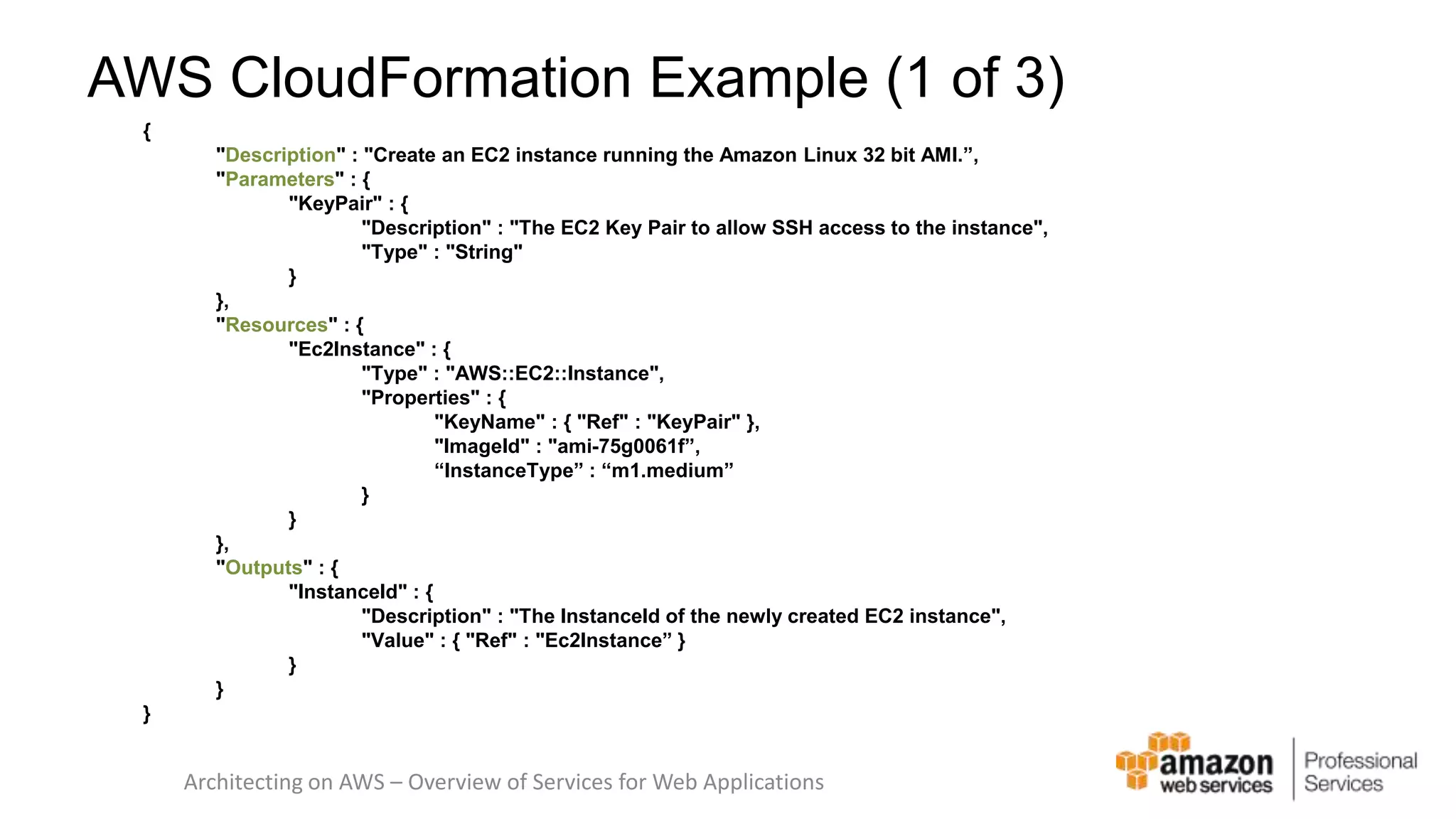
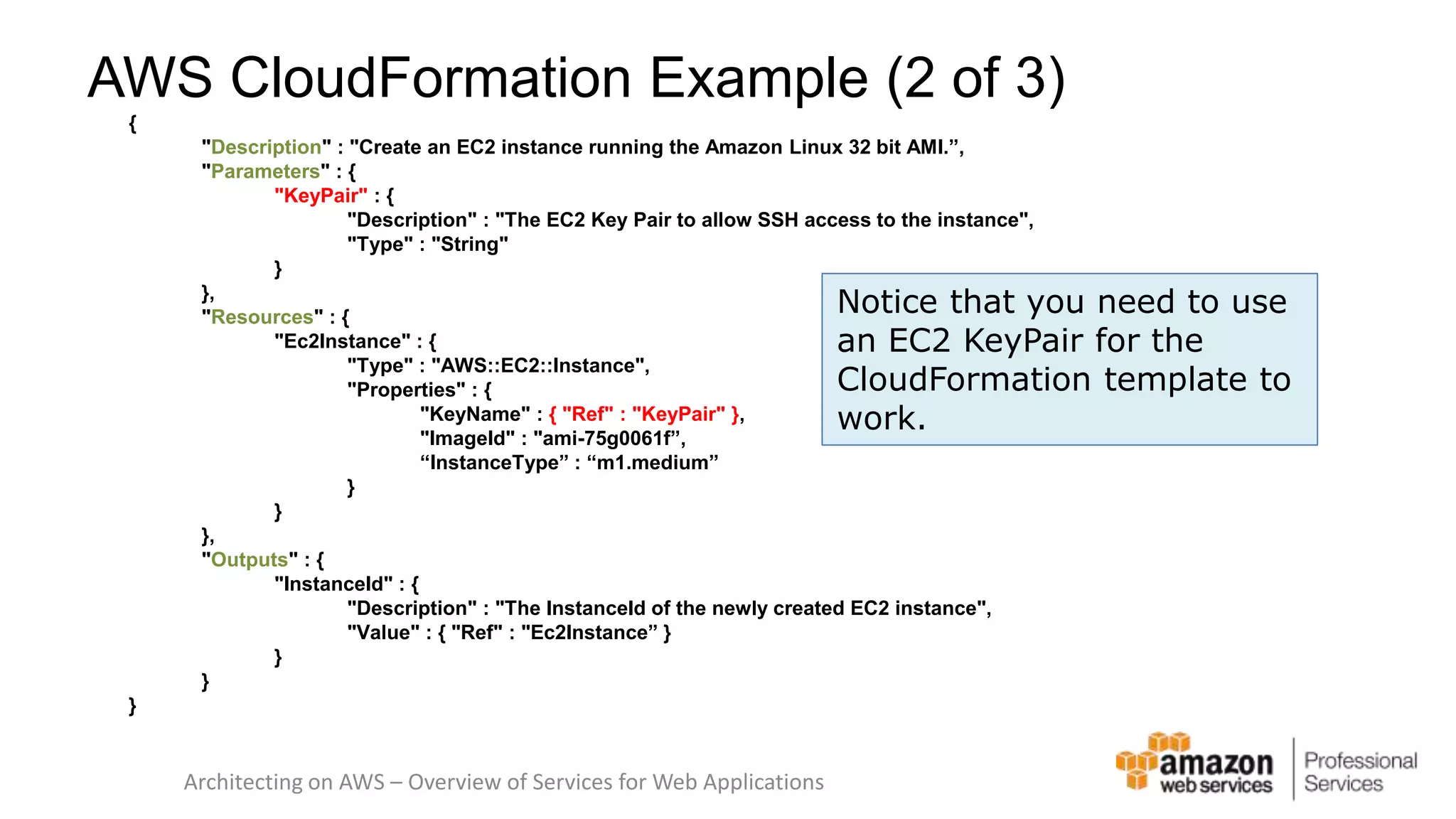
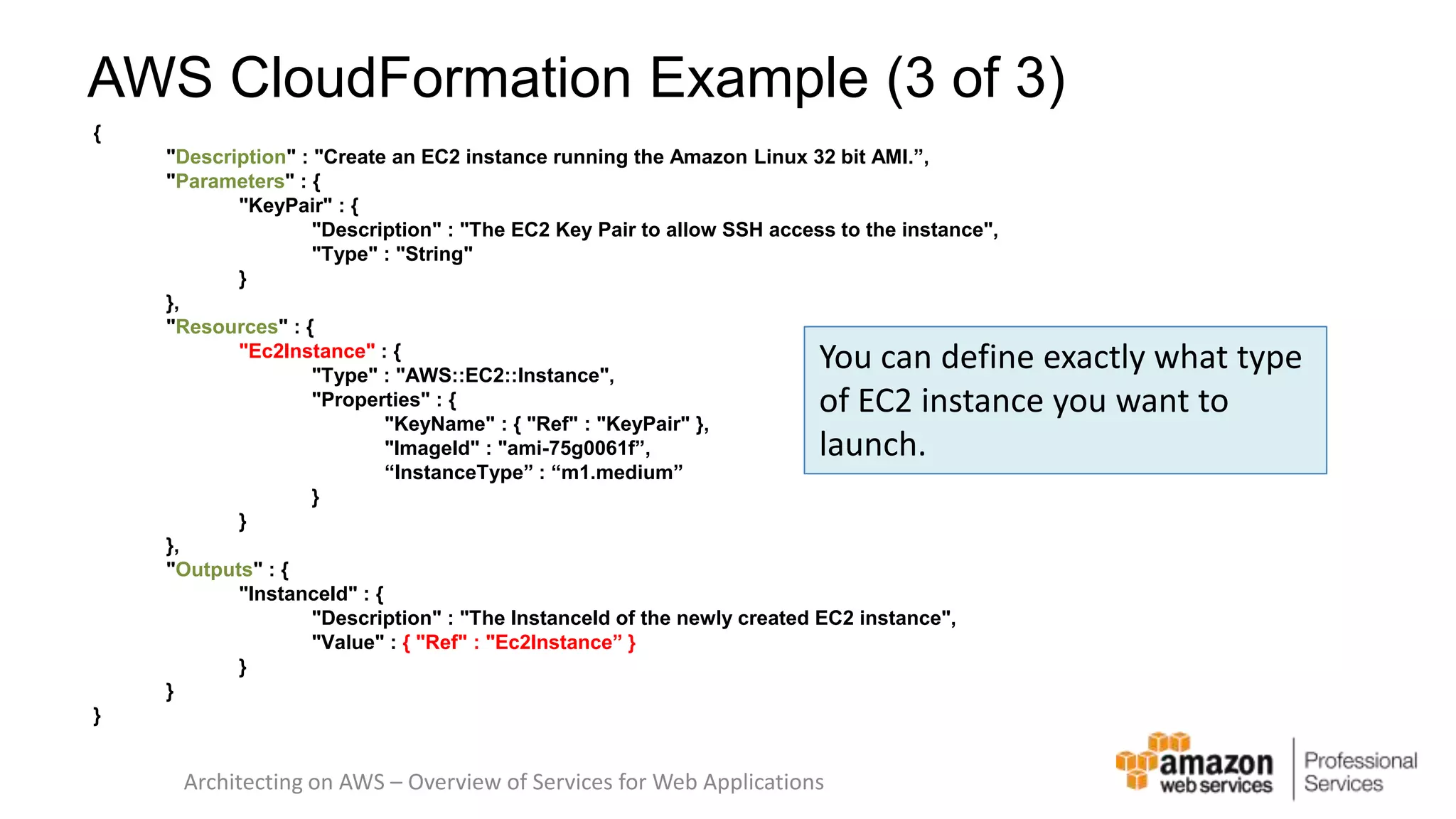
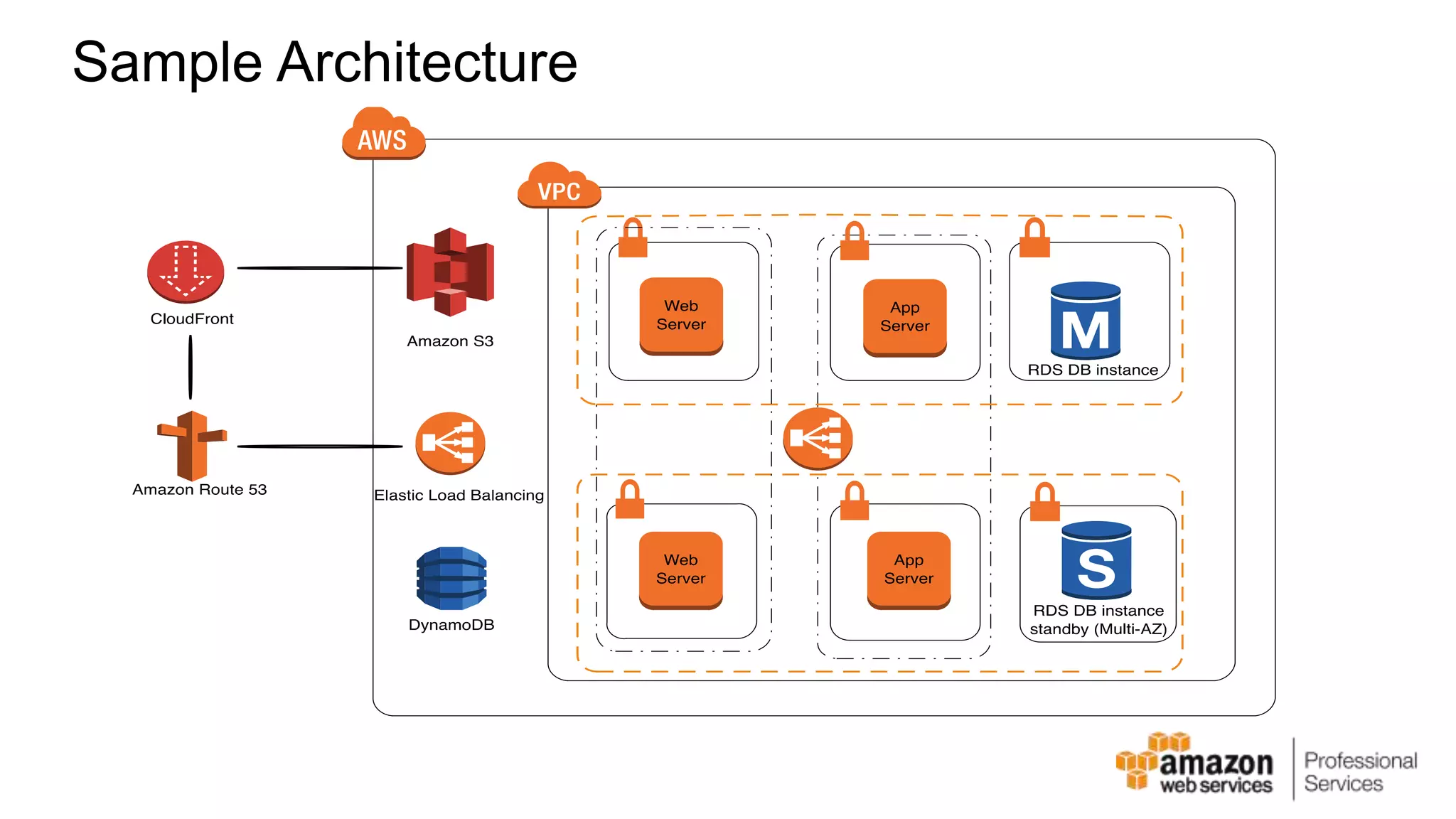
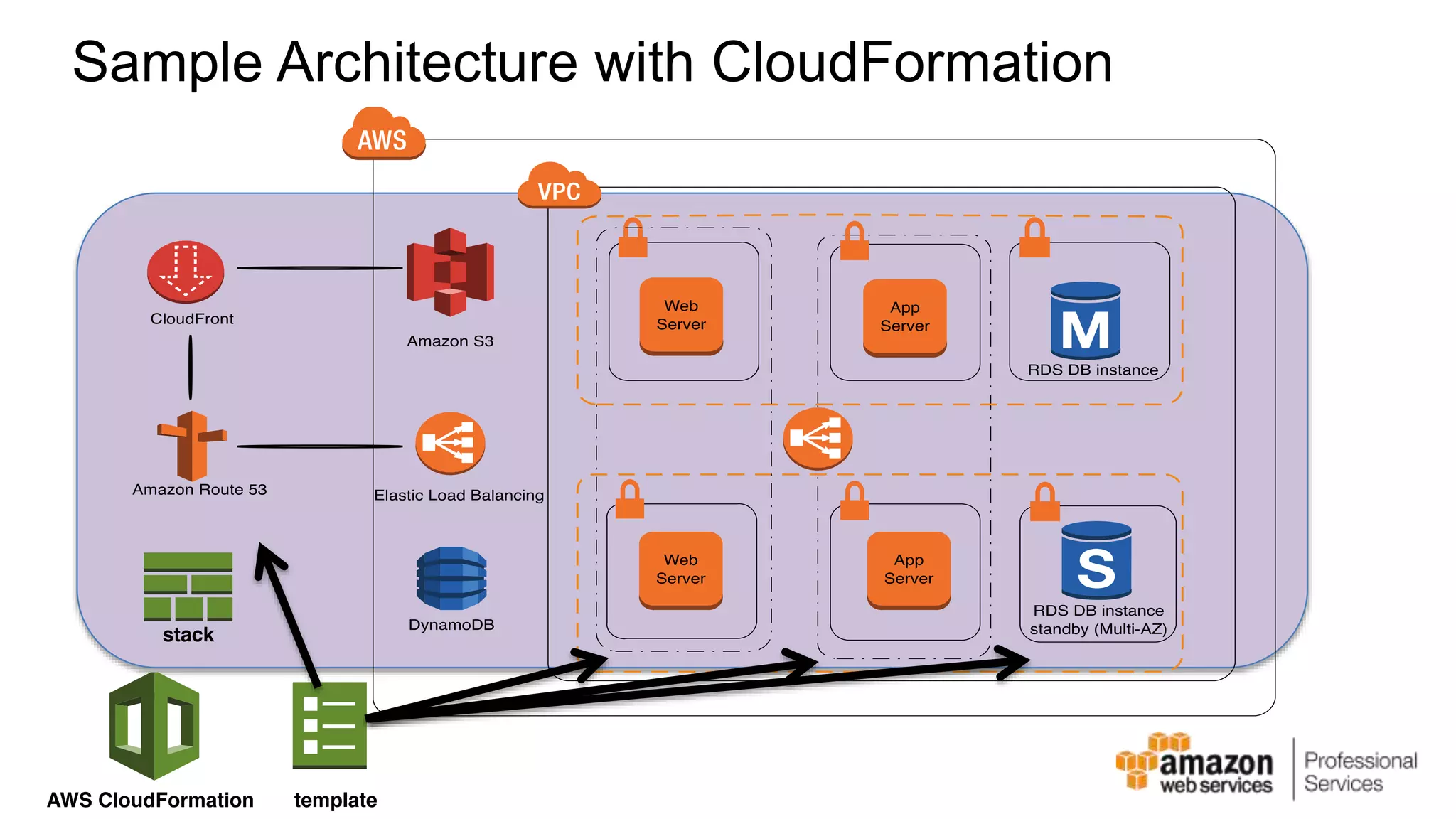
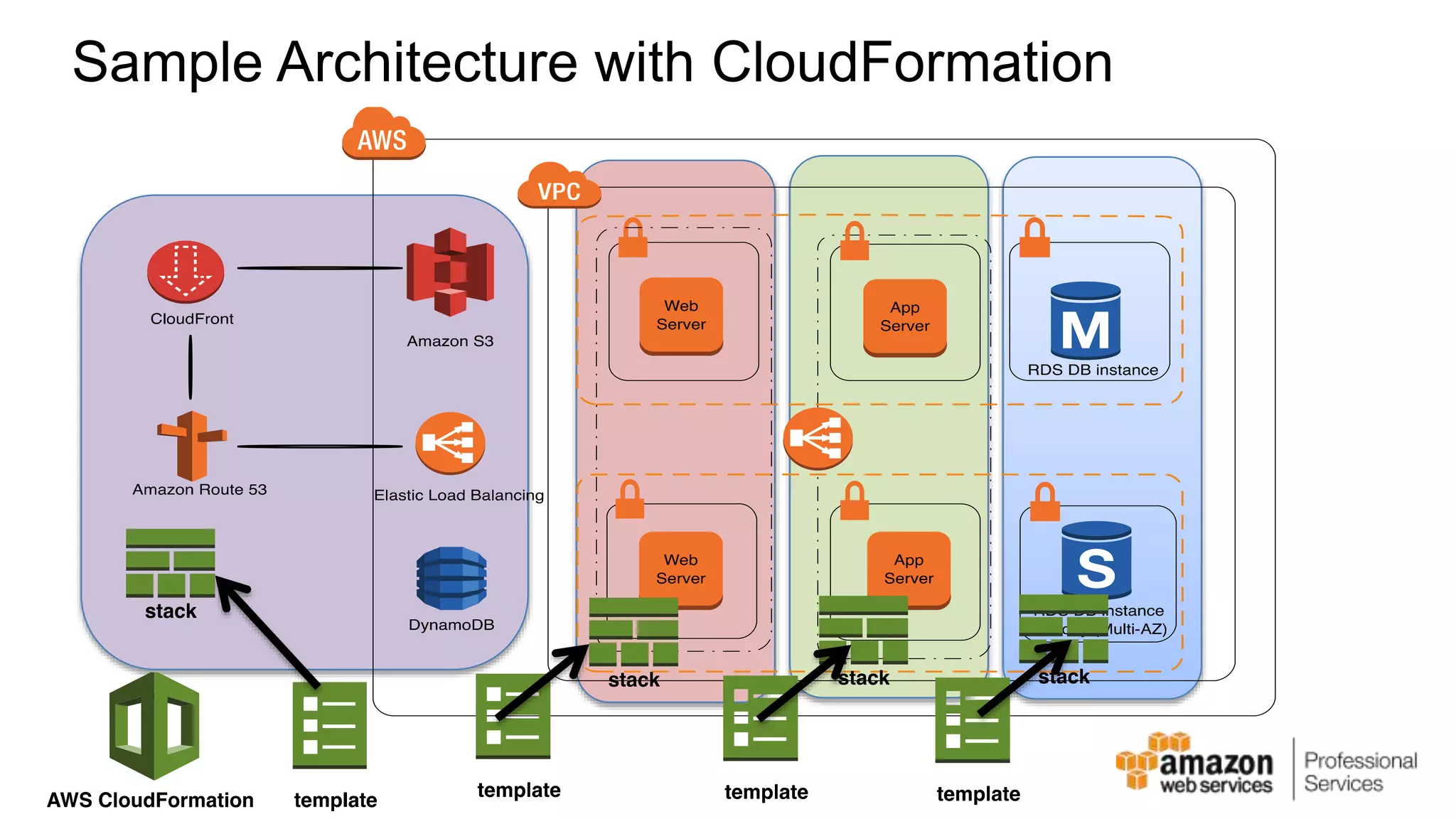
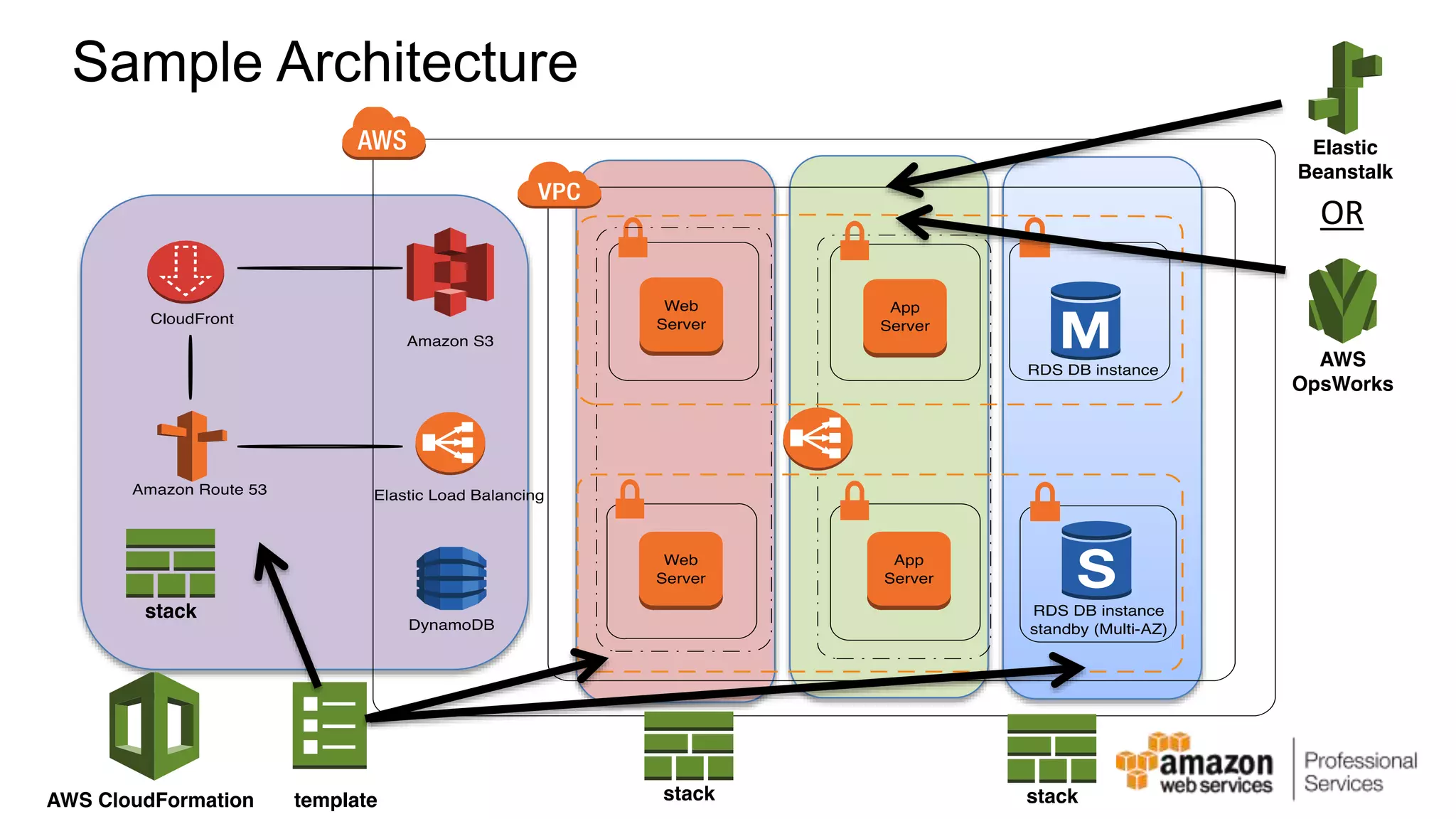
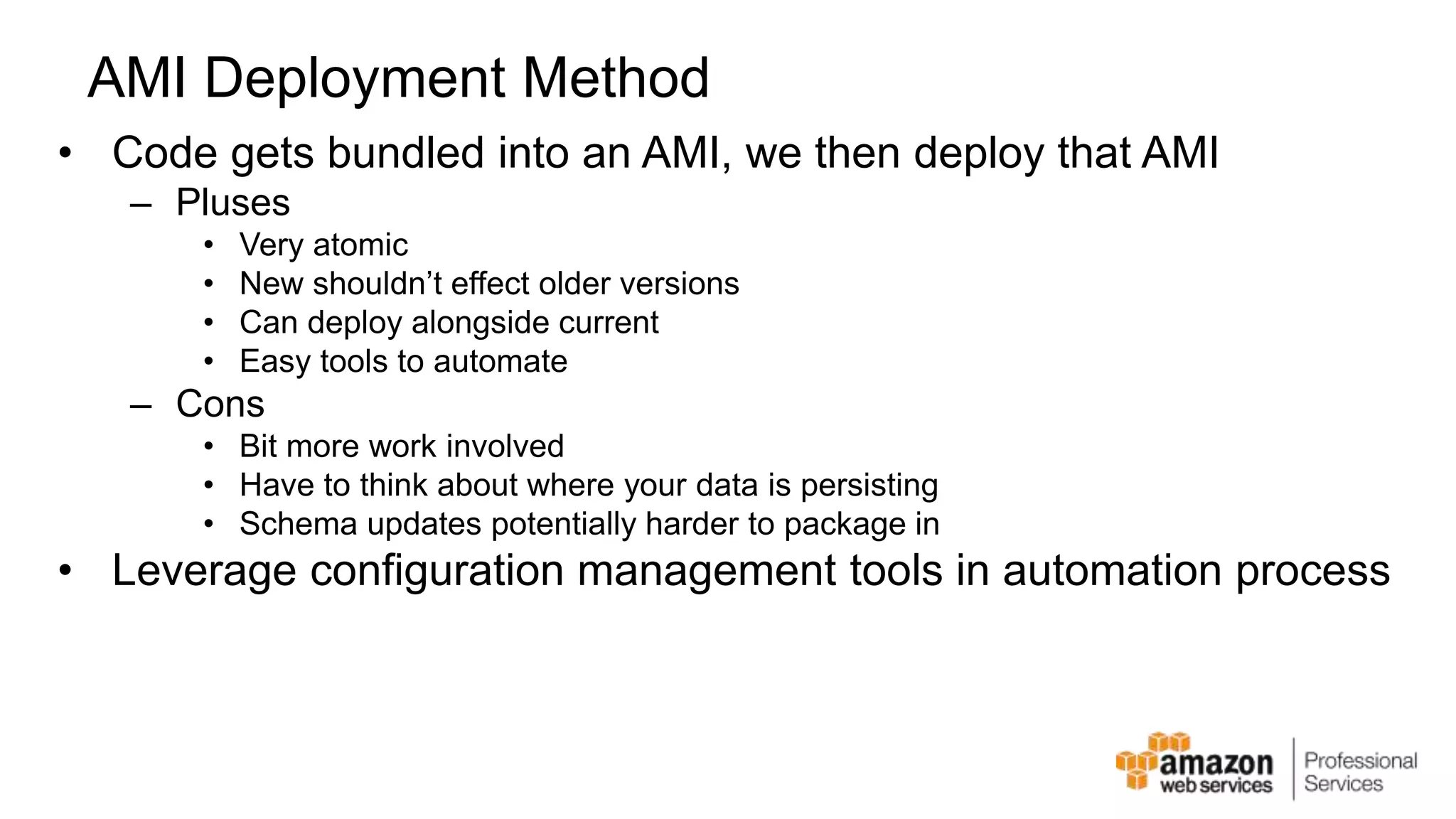
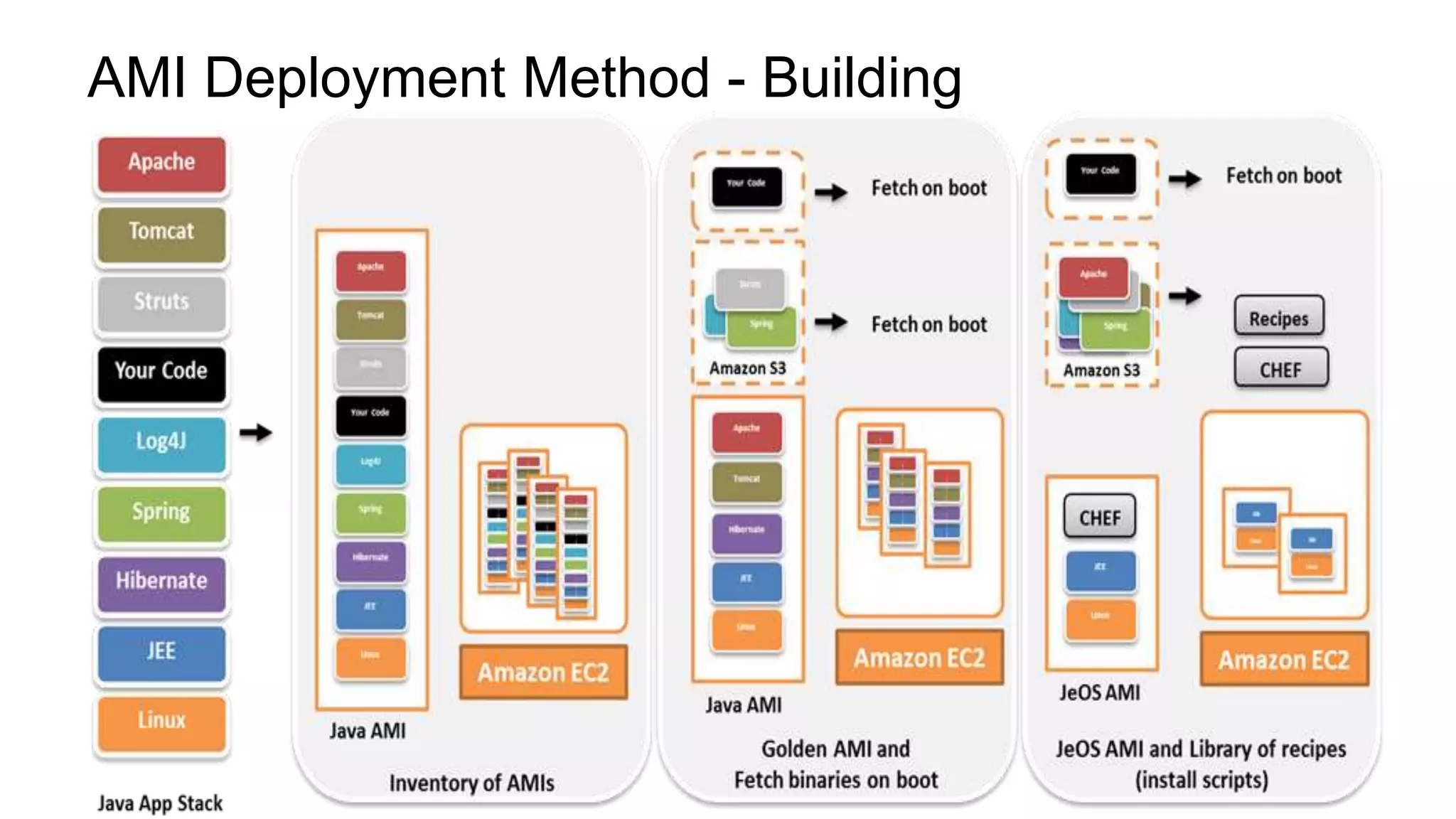
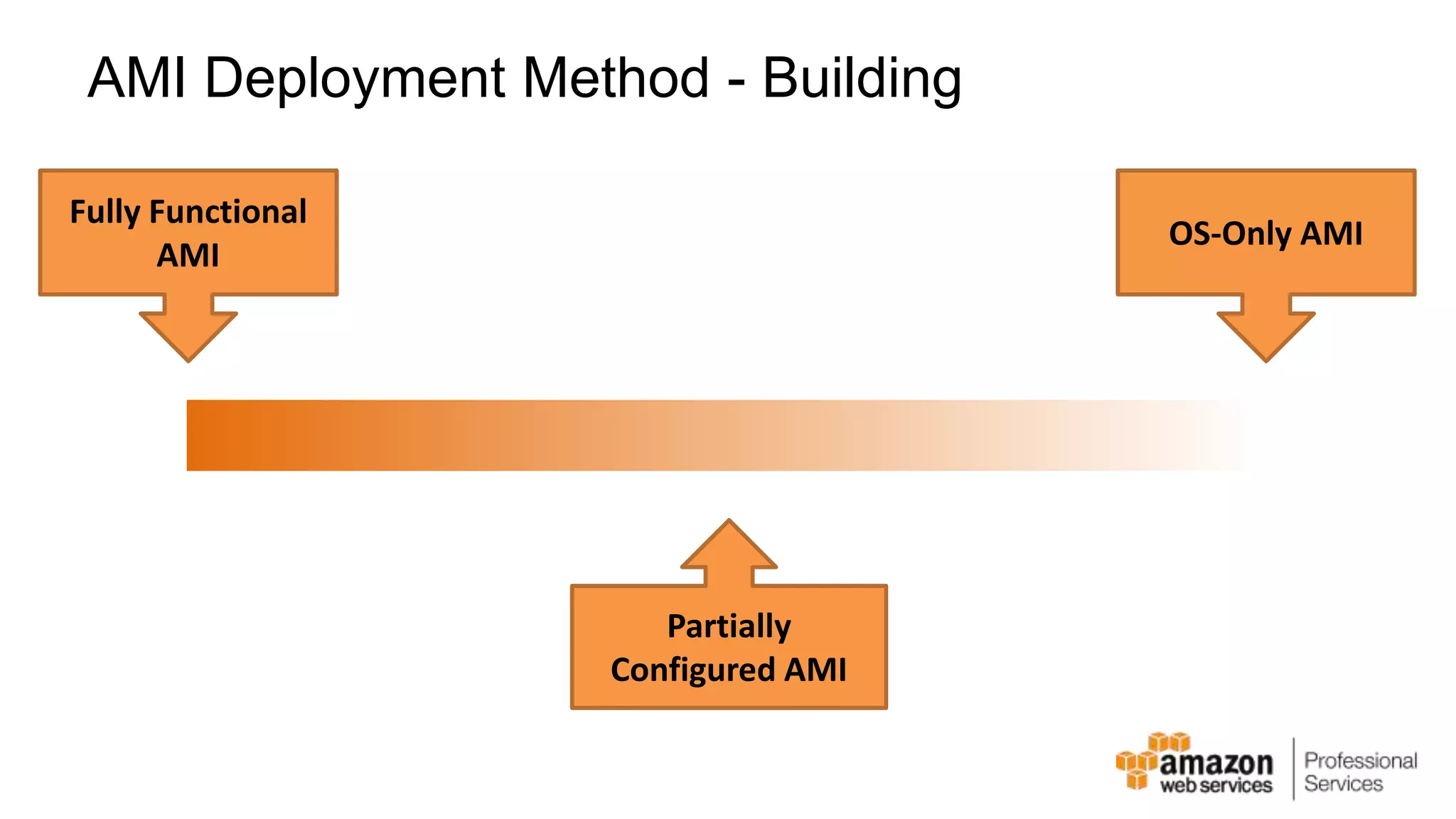
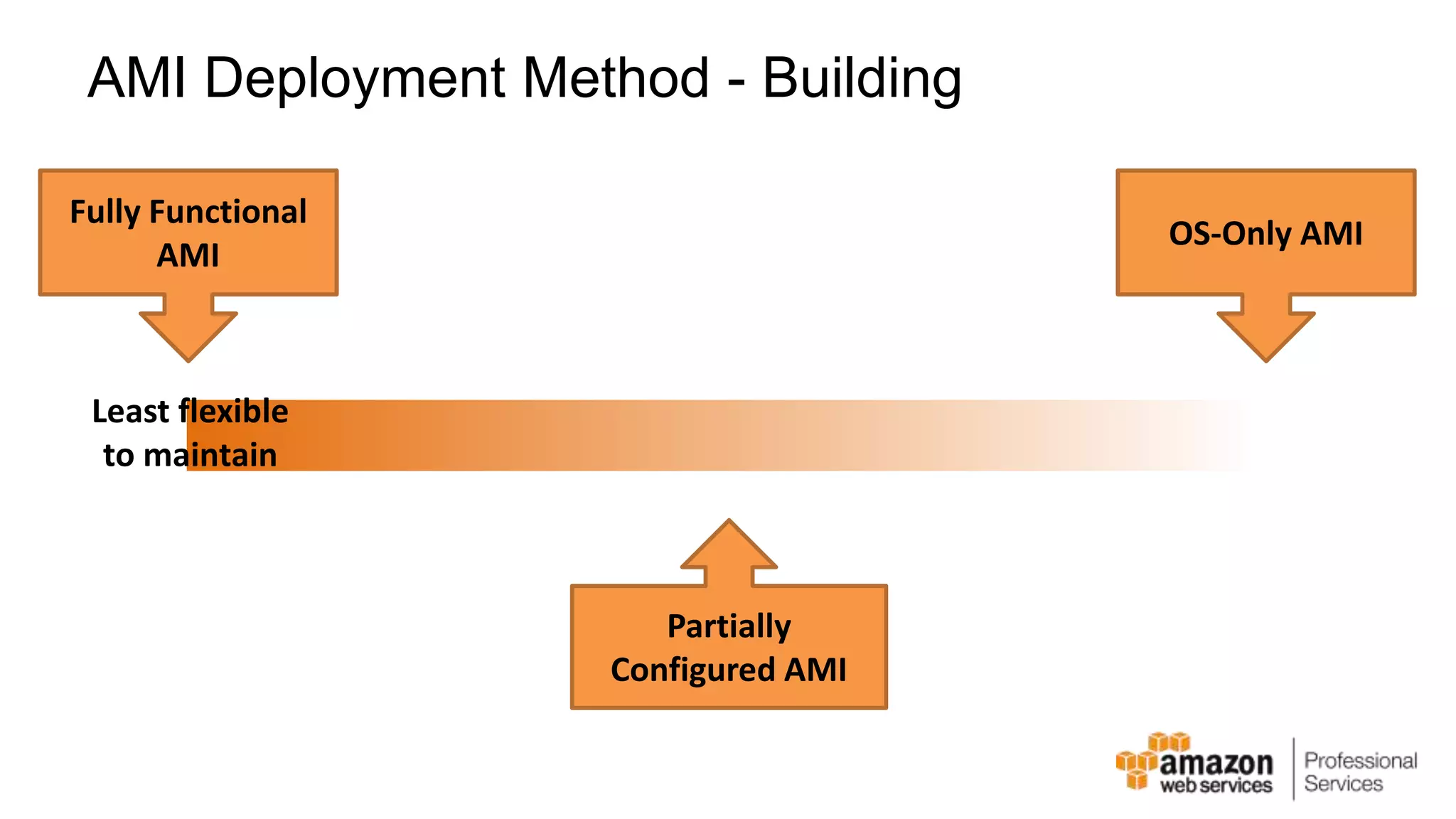
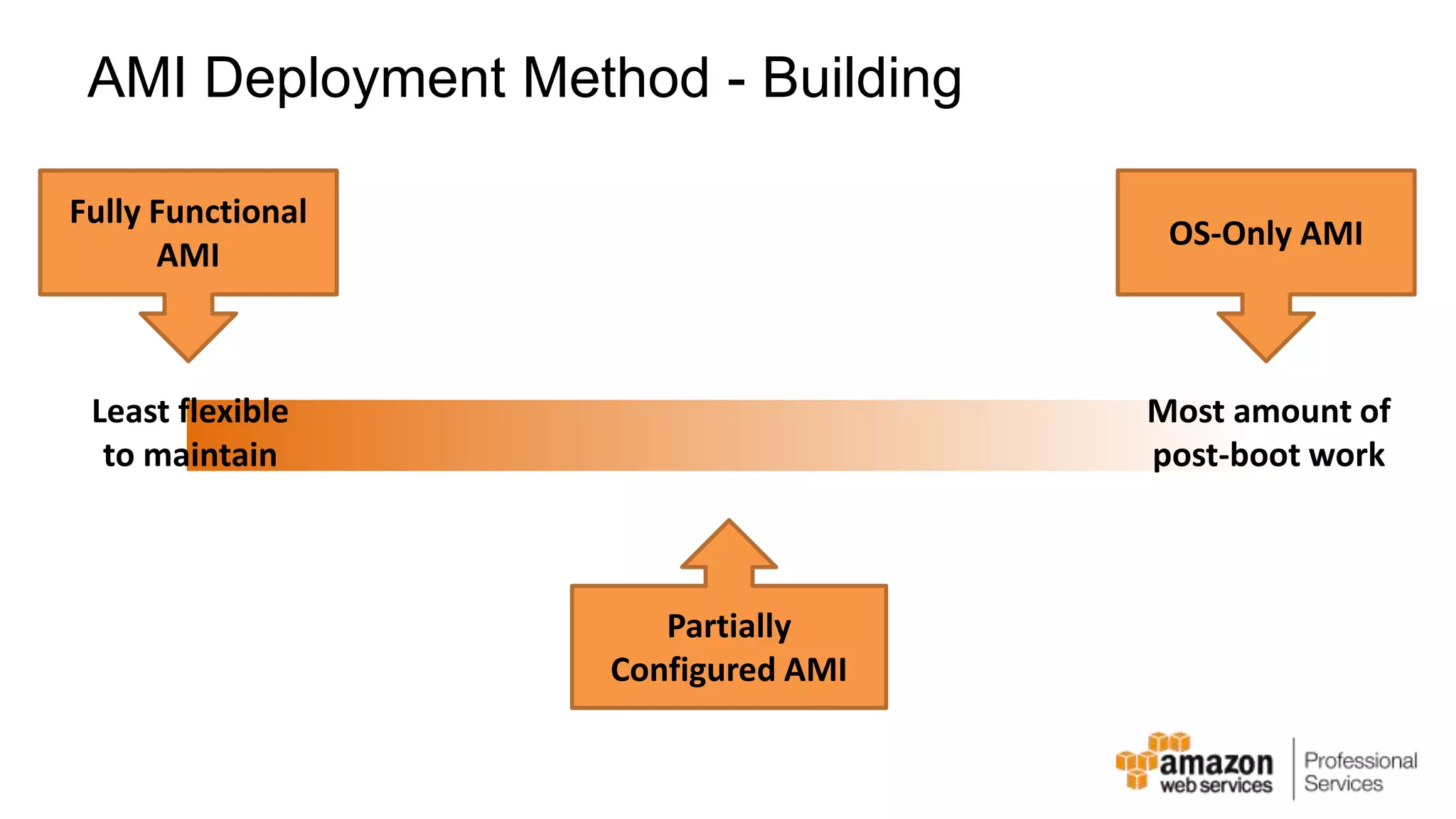
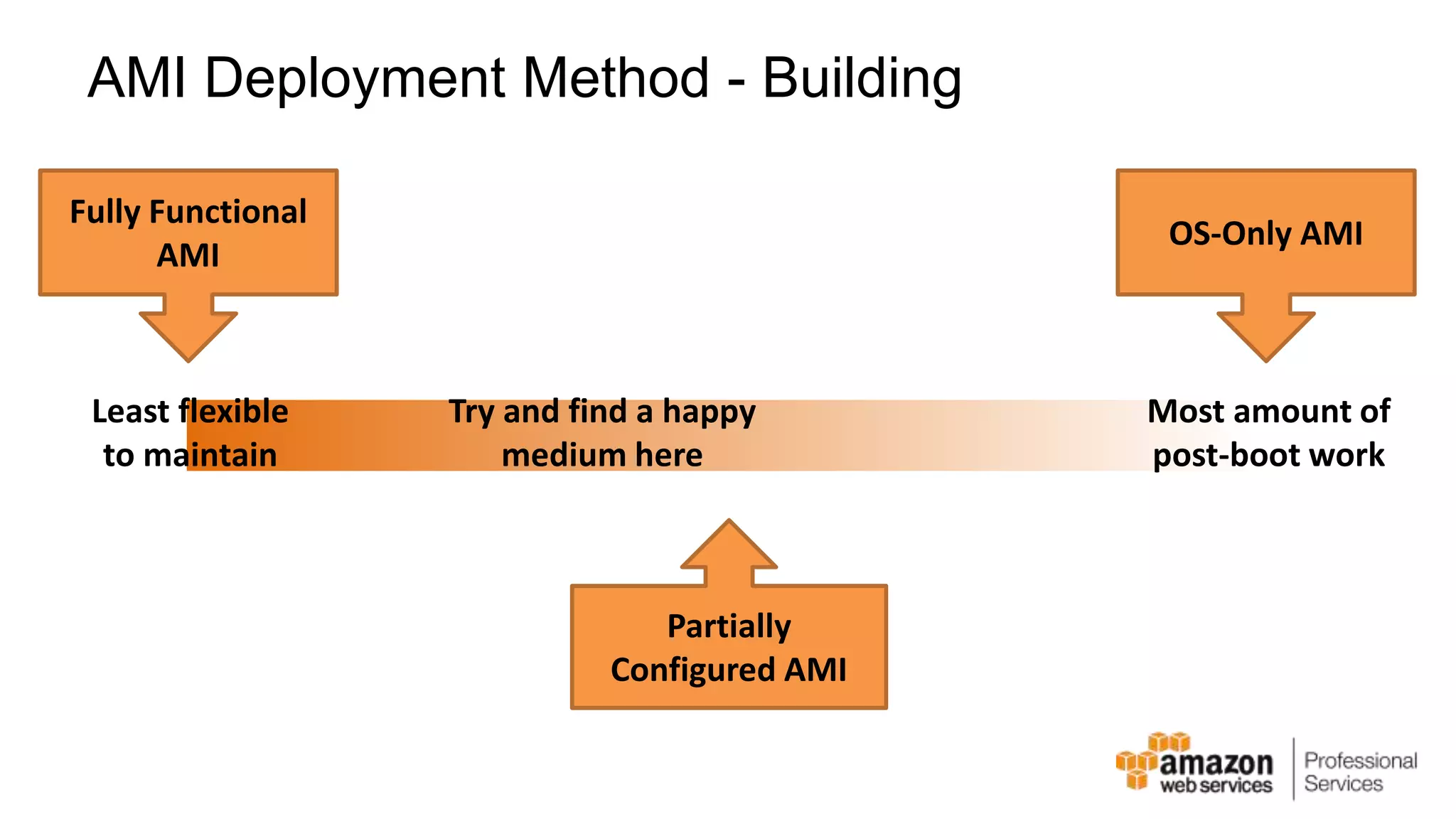
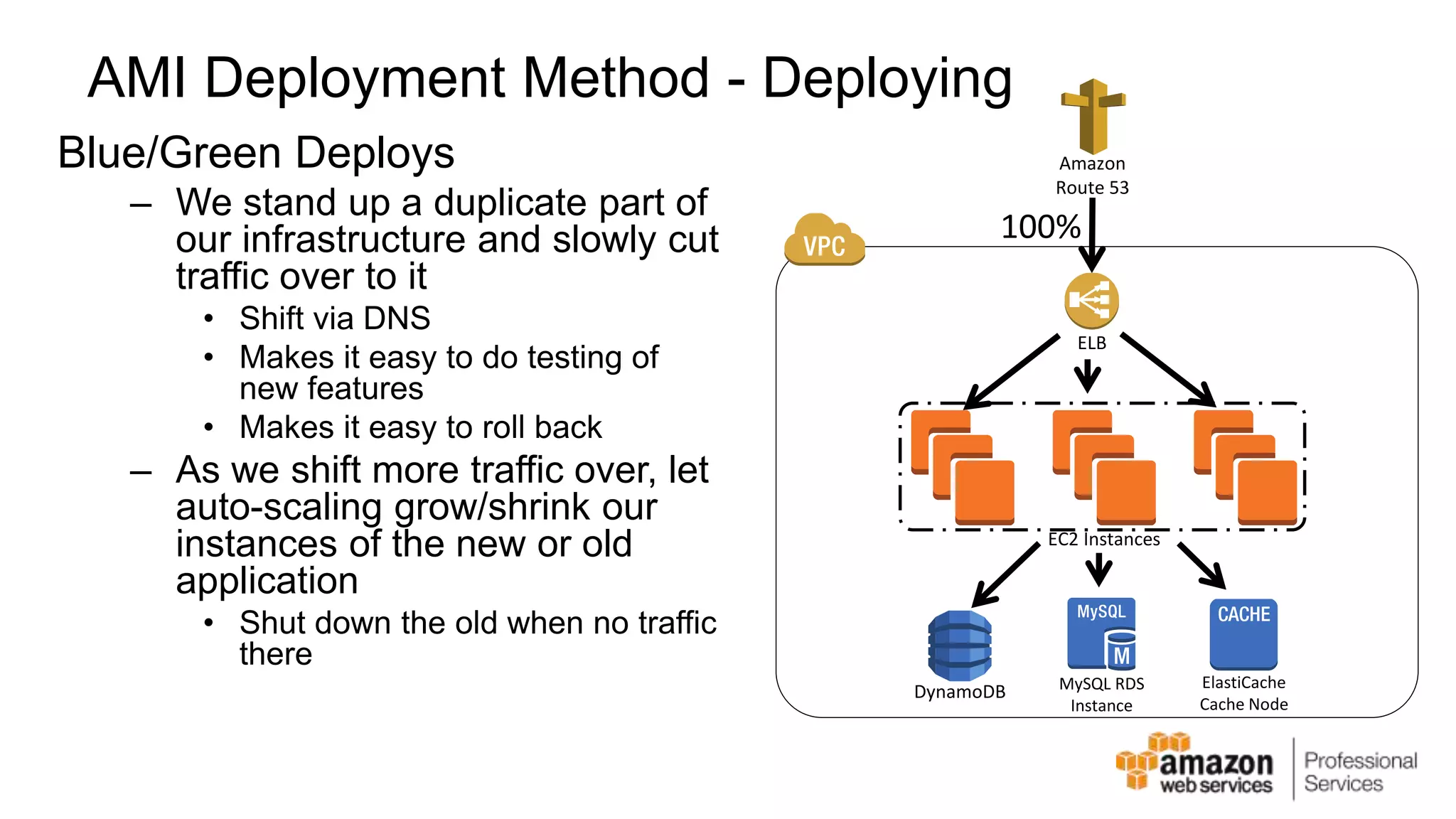
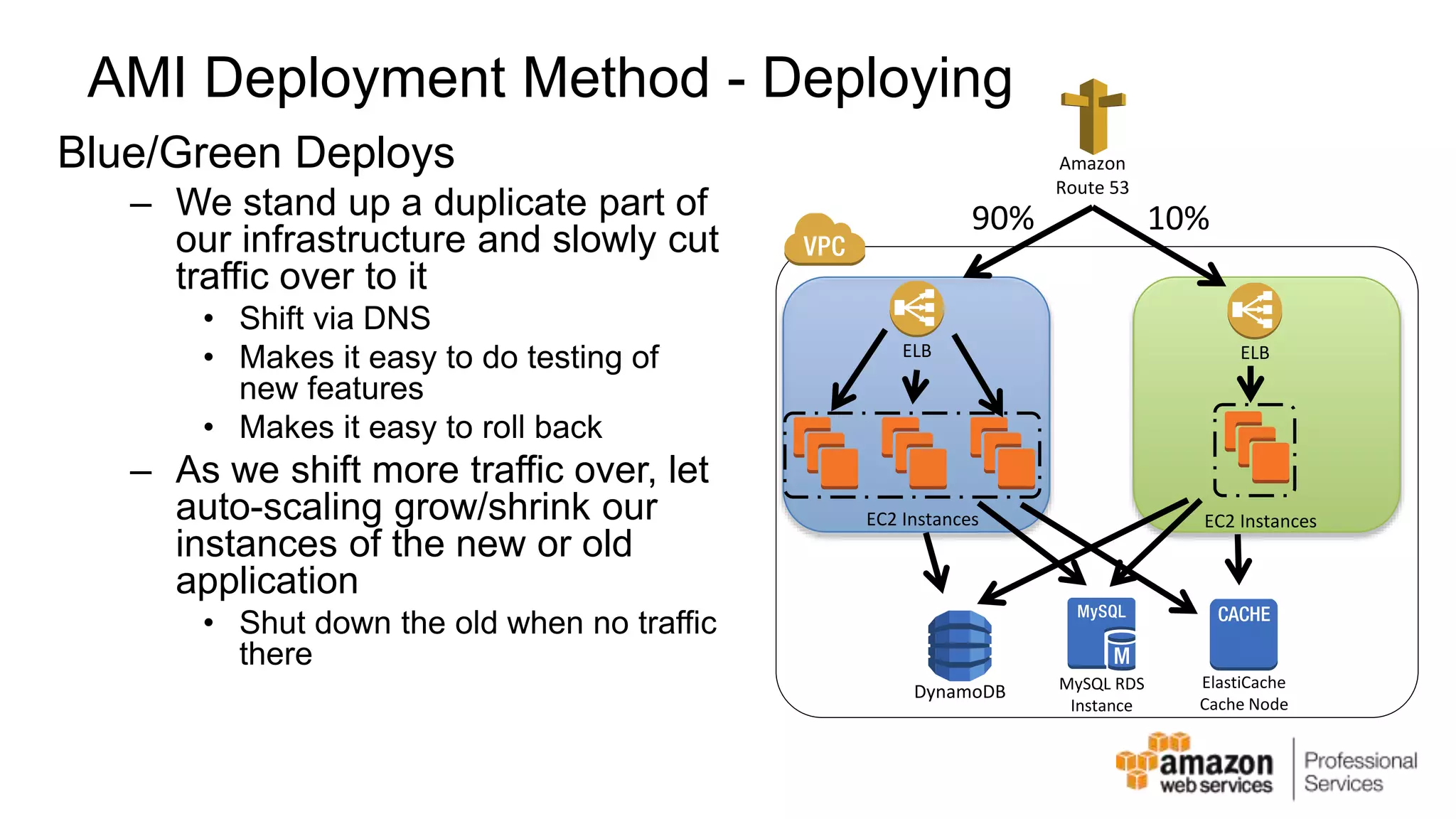
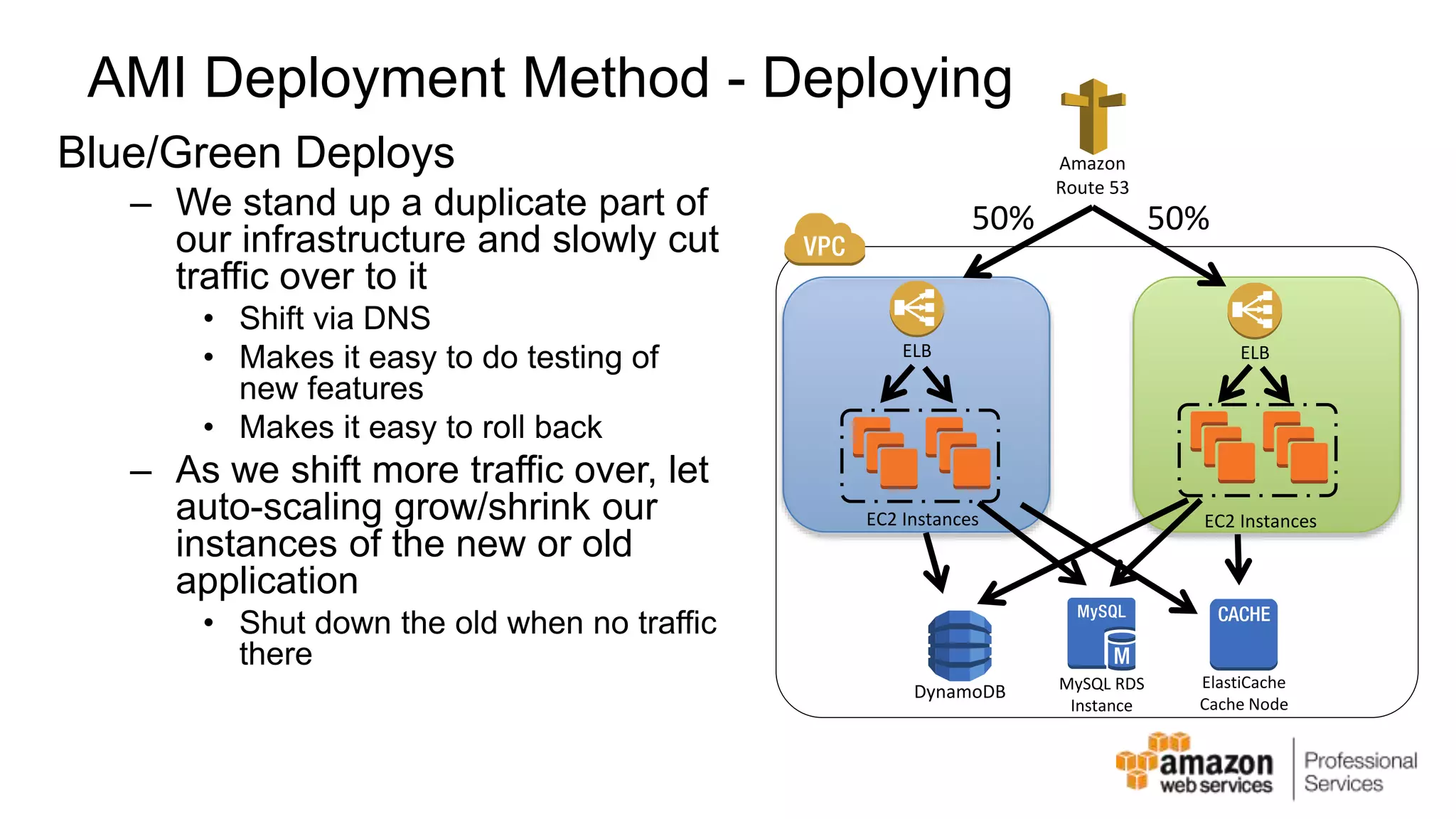
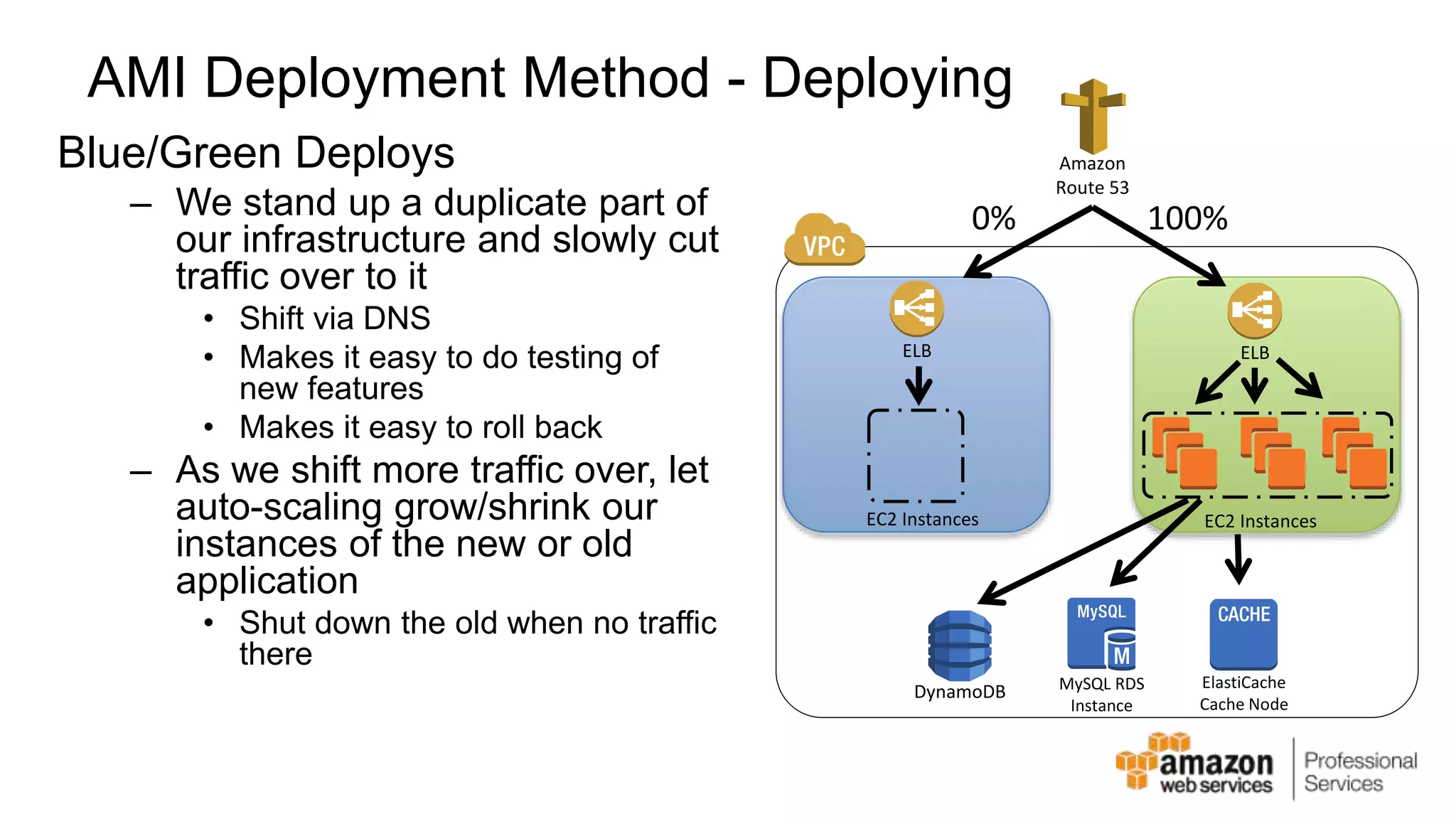
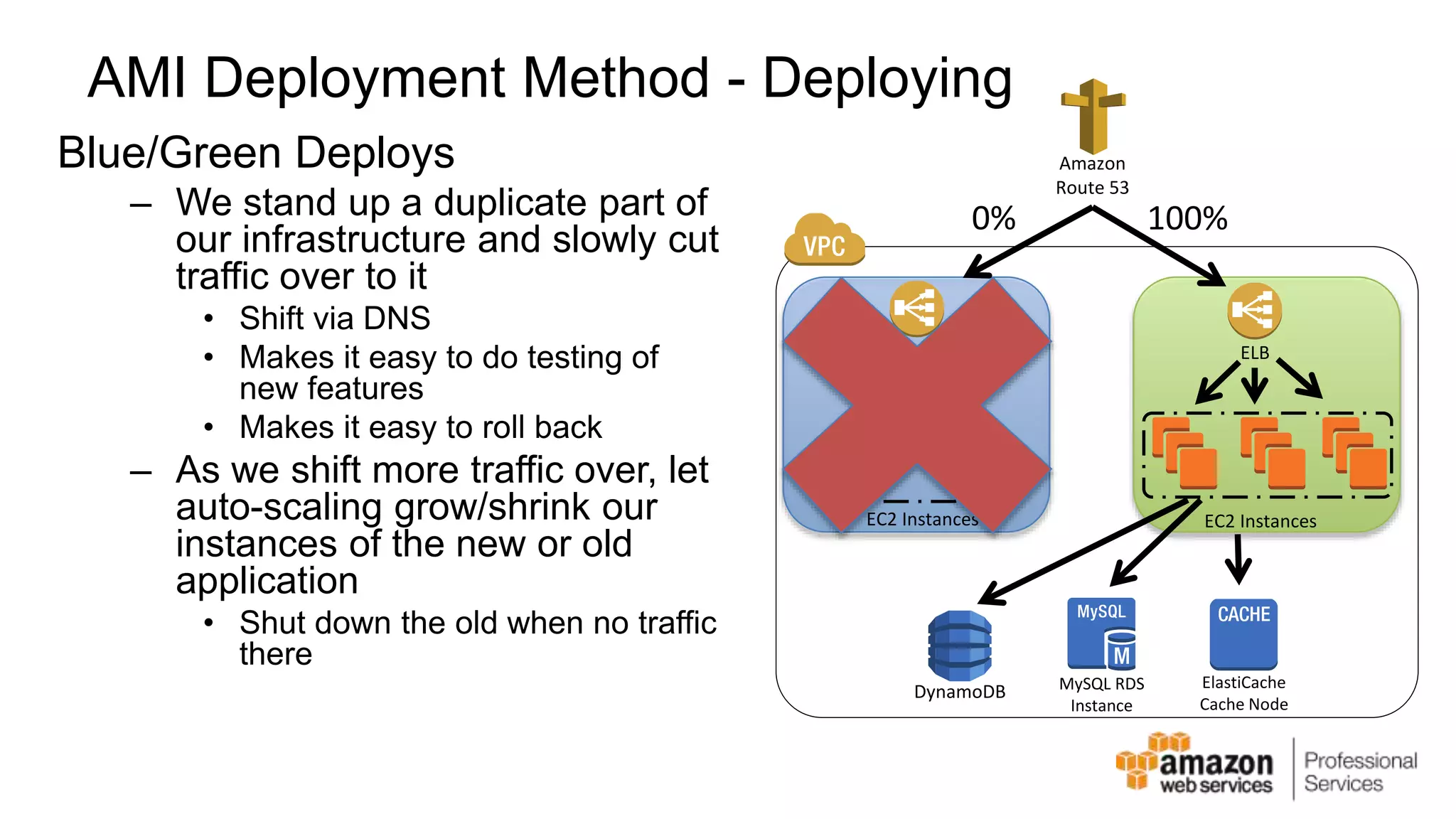
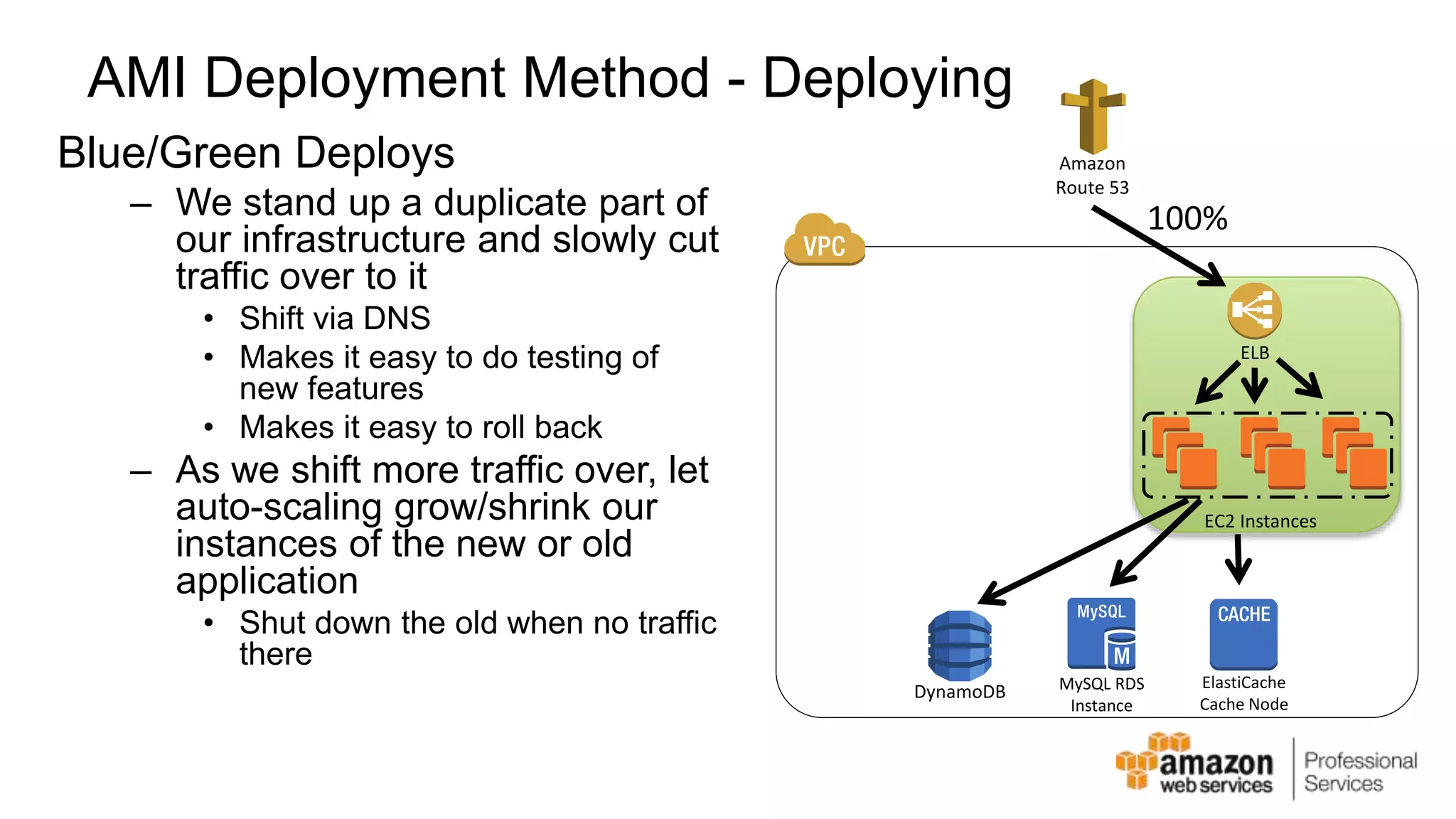
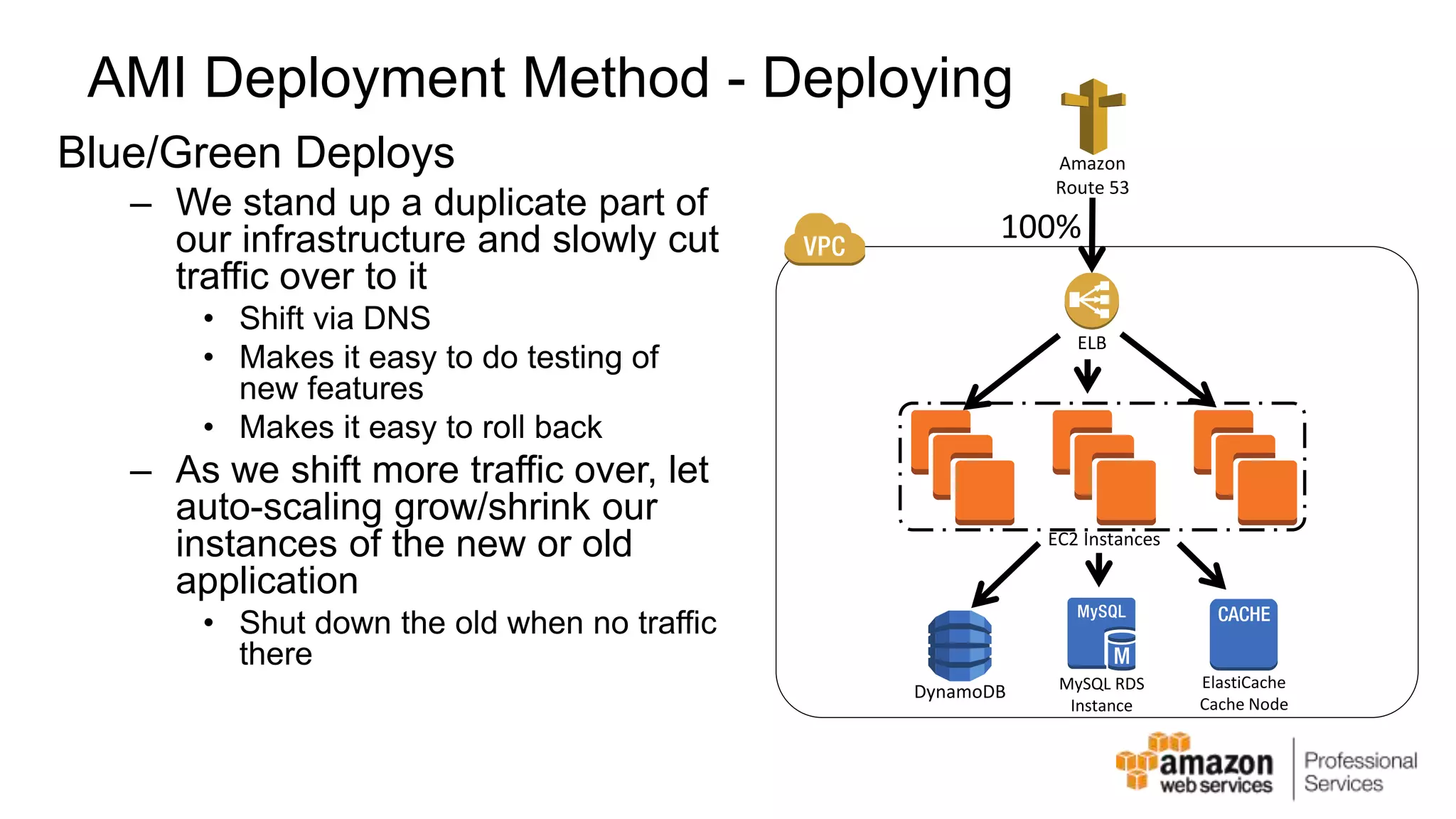
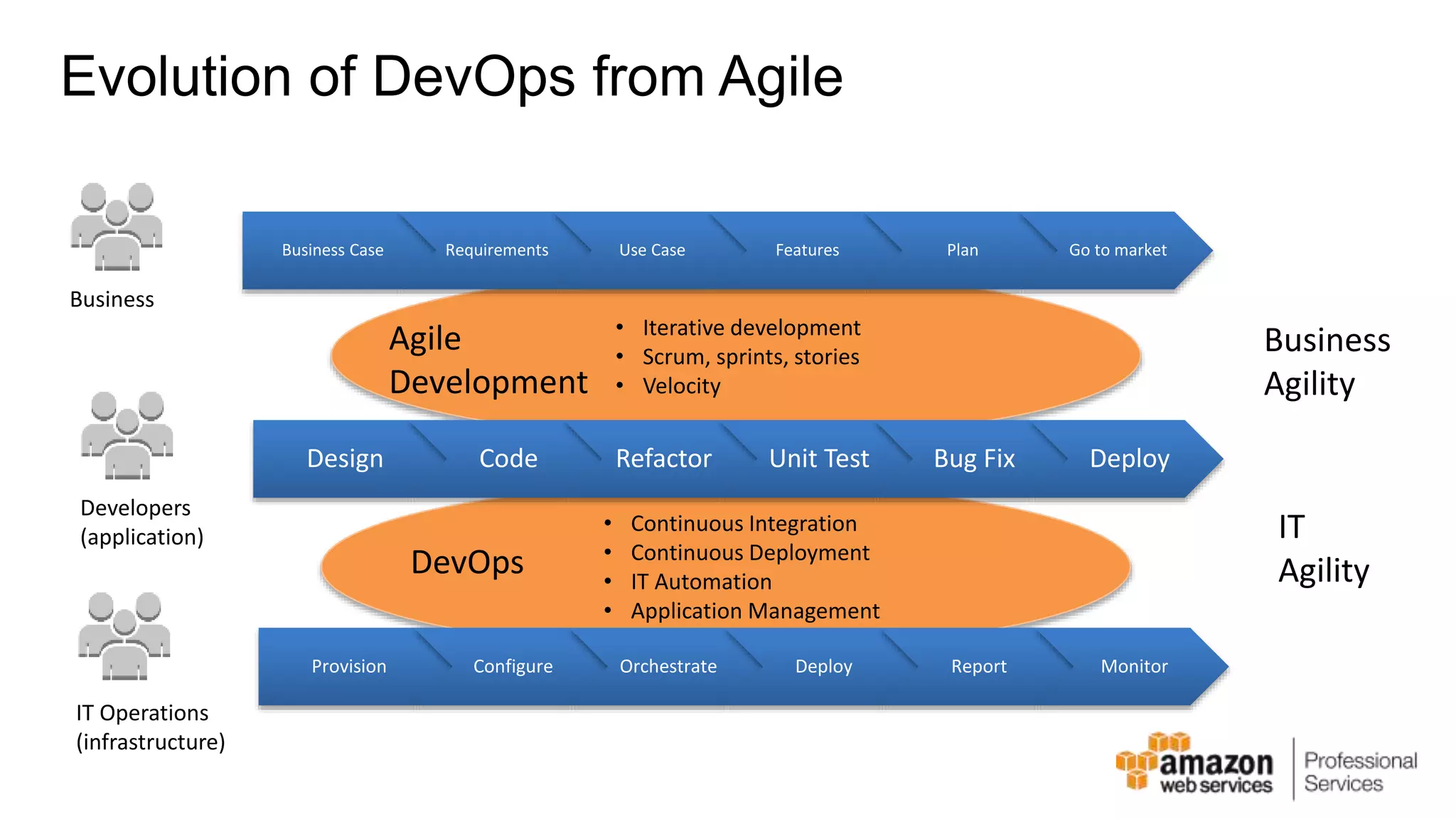
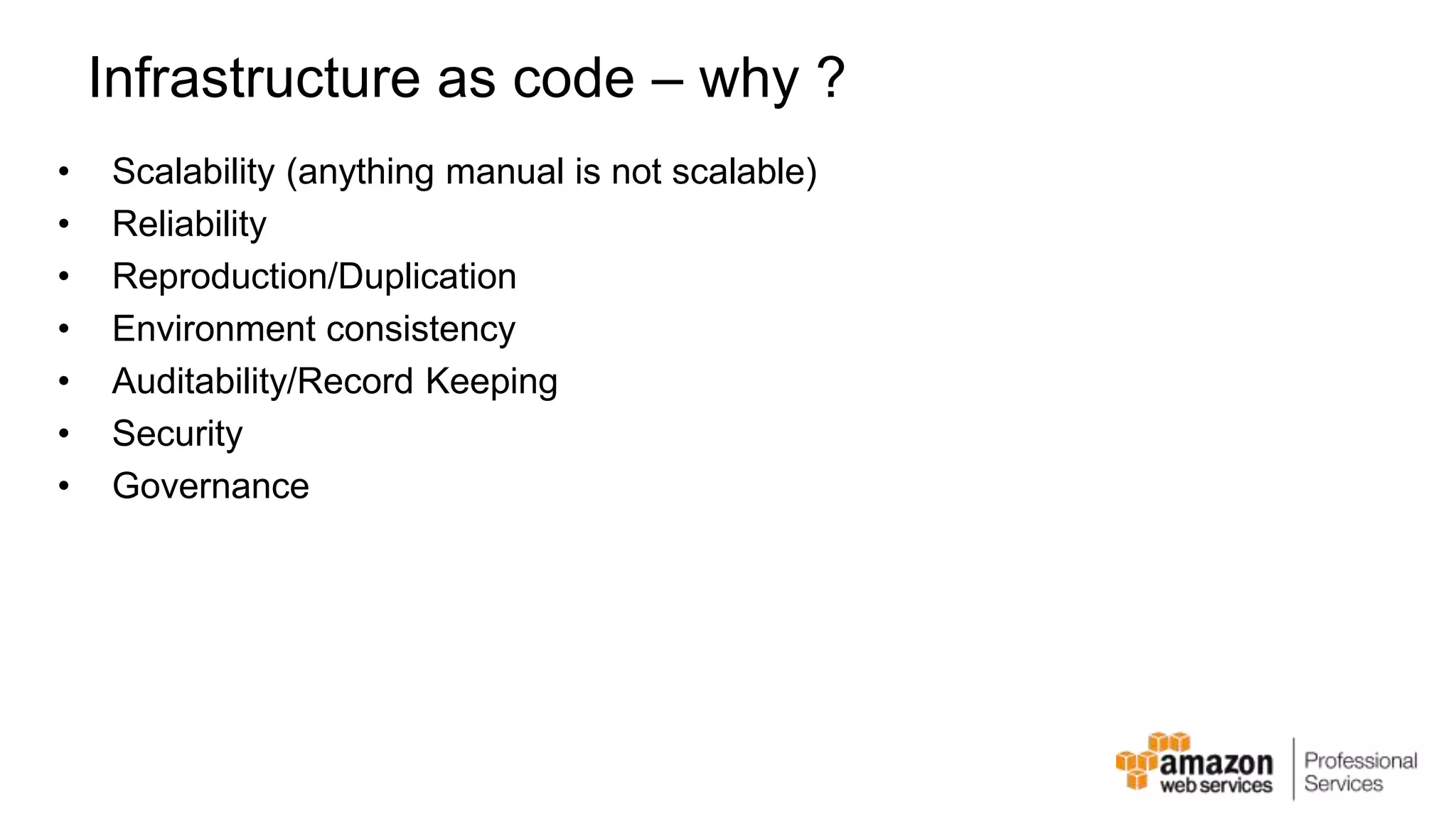
The document provides an introduction to DevOps principles and practices specifically on AWS, including infrastructure as code, continuous integration, and deployment techniques. It outlines key services like CloudFormation, Elastic Beanstalk, and OpsWorks, emphasizing automation and effective collaboration between development and IT operations. Additionally, it discusses deployment models such as blue/green deployment, infrastructure provisioning, and resource management using AWS technologies.





![Here’s some infrastructure as Code "WebServer": { "Type": "AWS::EC2::Instance", "Metadata" : { "AWS::CloudFormation::Init" : { "config" : { "packages" : { "yum" : { "httpd" : [], "php" : [], "php-mysql" : [], "php-gd" : [], "php-xml" : [], "php-mbstring" : [], "mysql" : [] } }, "sources" : { "/var/www/html" : "http://ftp.drupal.org/files/projects/drupal-7.8.tar.gz", "/home/ec2-user" : "http://ftp.drupal.org/files/projects/drush-7.x-4.5.tar.gz" }, AWS CloudFormation template](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-devops-on-aws-141124165930-conversion-gate01/75/Introduction-to-DevOps-on-AWS-8-2048.jpg)