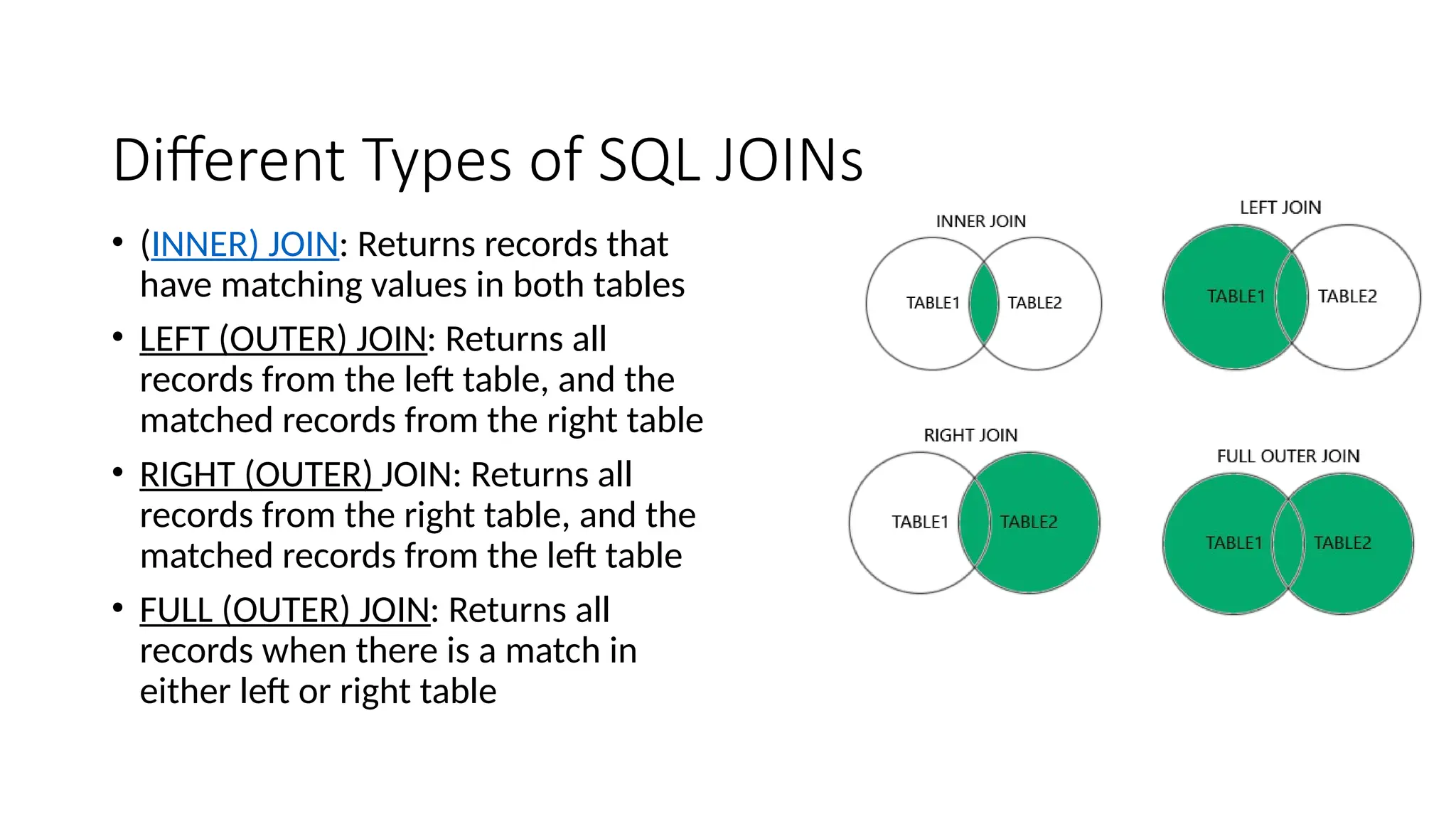
The document provides an introduction to SQL (Structured Query Language), detailing its commands and capabilities for managing databases, including data definition, manipulation, control, and transaction management. It explains various SQL commands such as DDL for defining database structures, DML for processing data, DCL for managing access permissions, and TCL for handling transactions. Additionally, it covers SQL aggregate functions, joins, and other important clauses to enhance data queries.