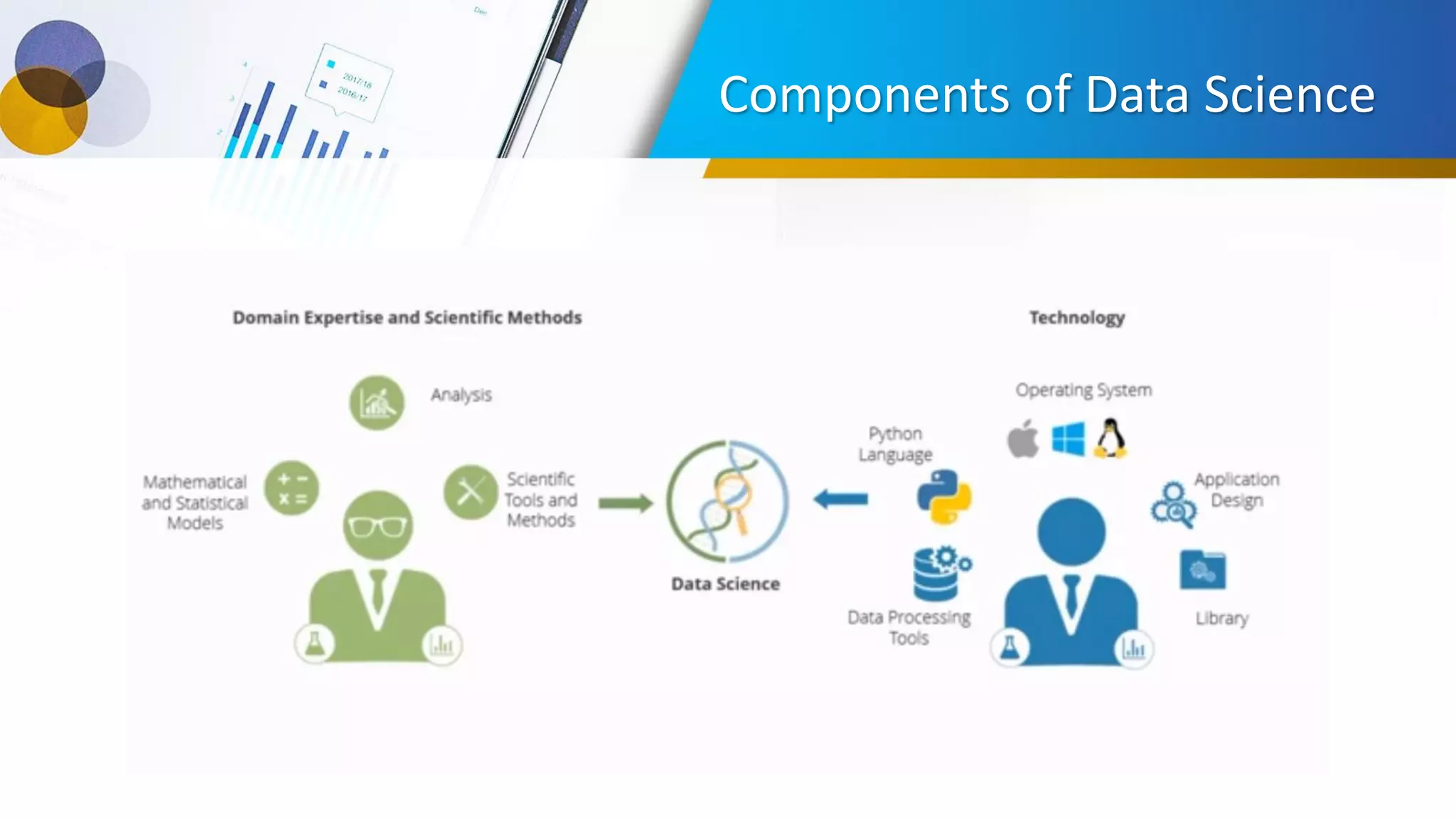
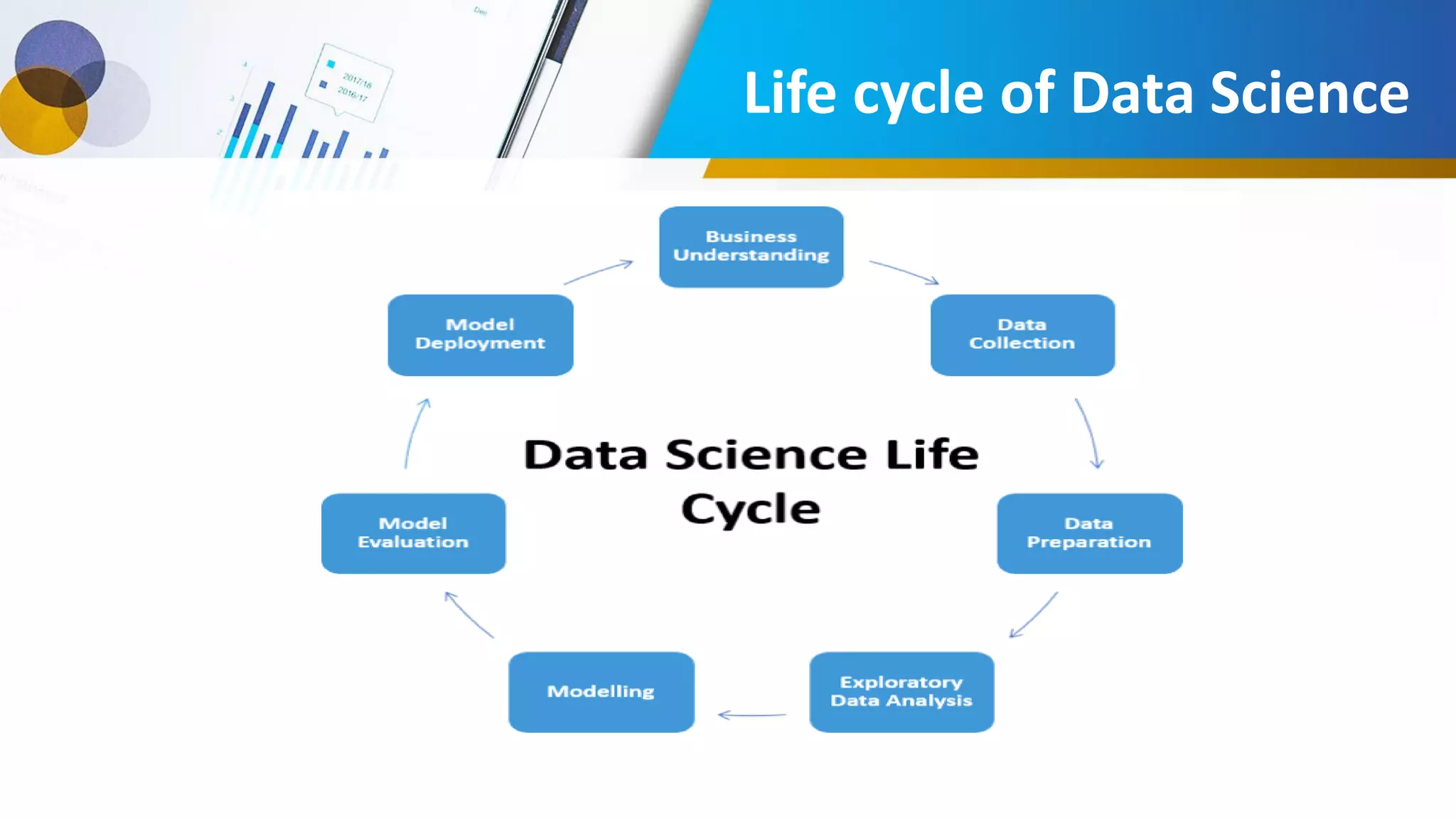
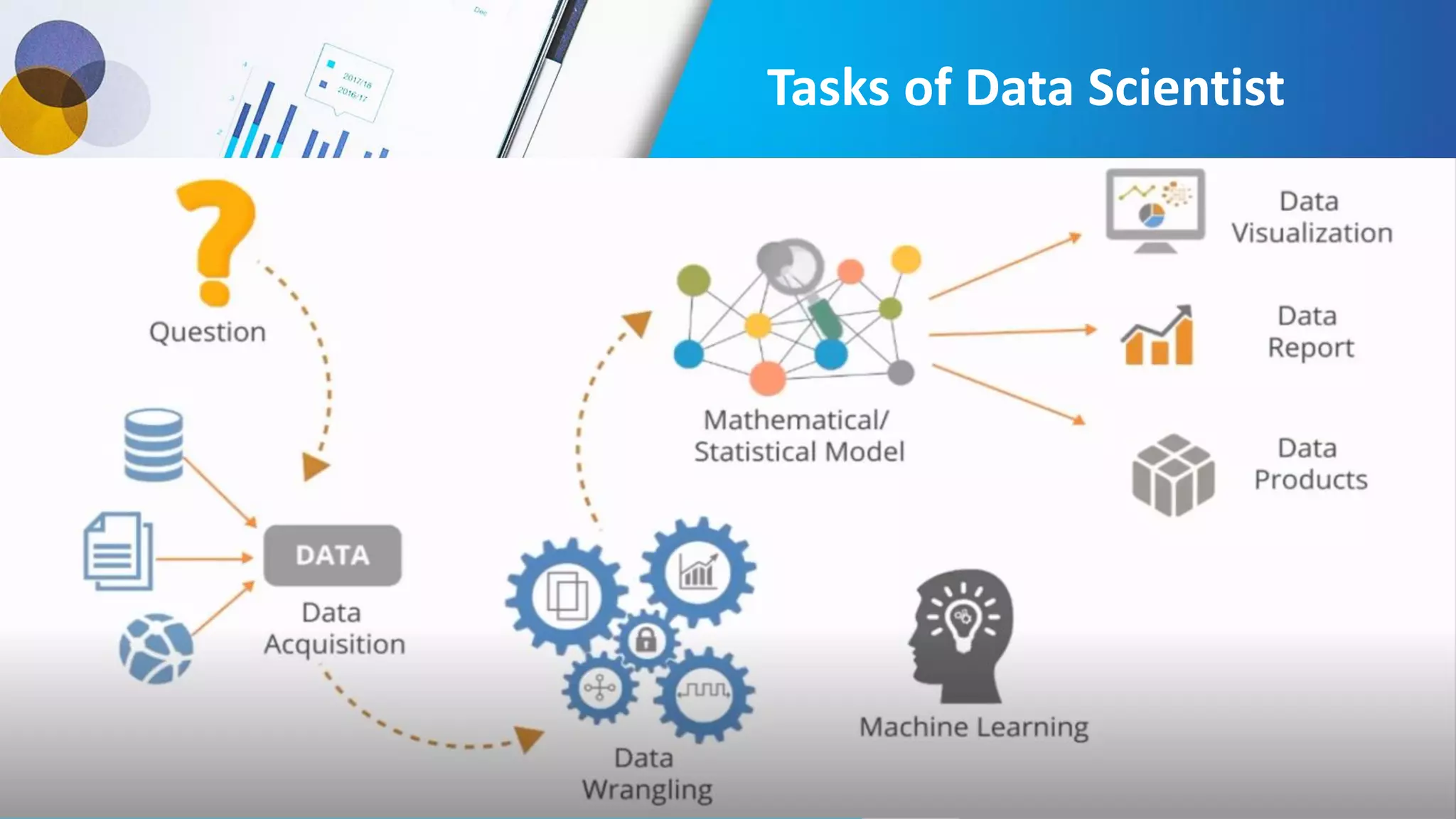
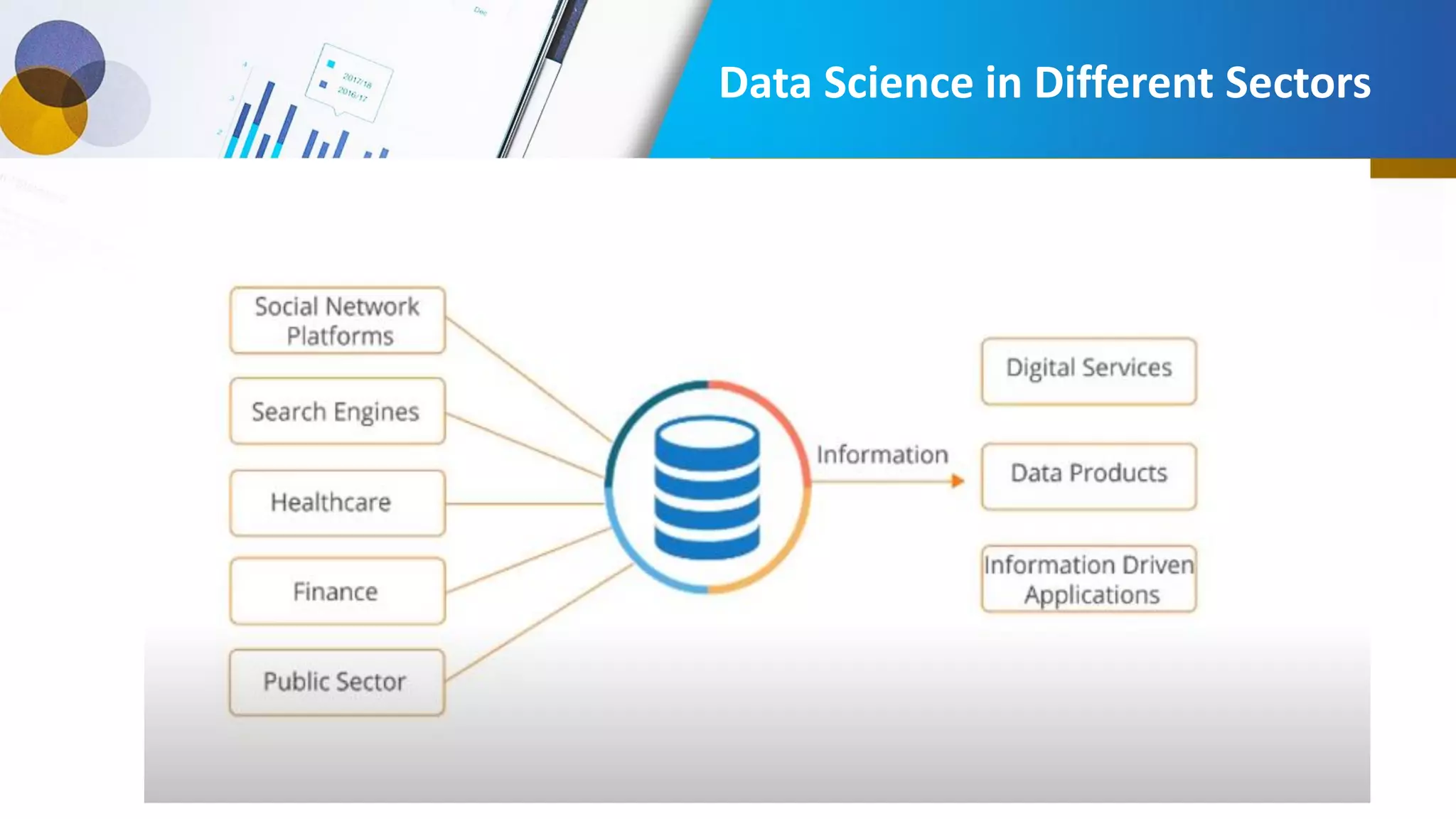
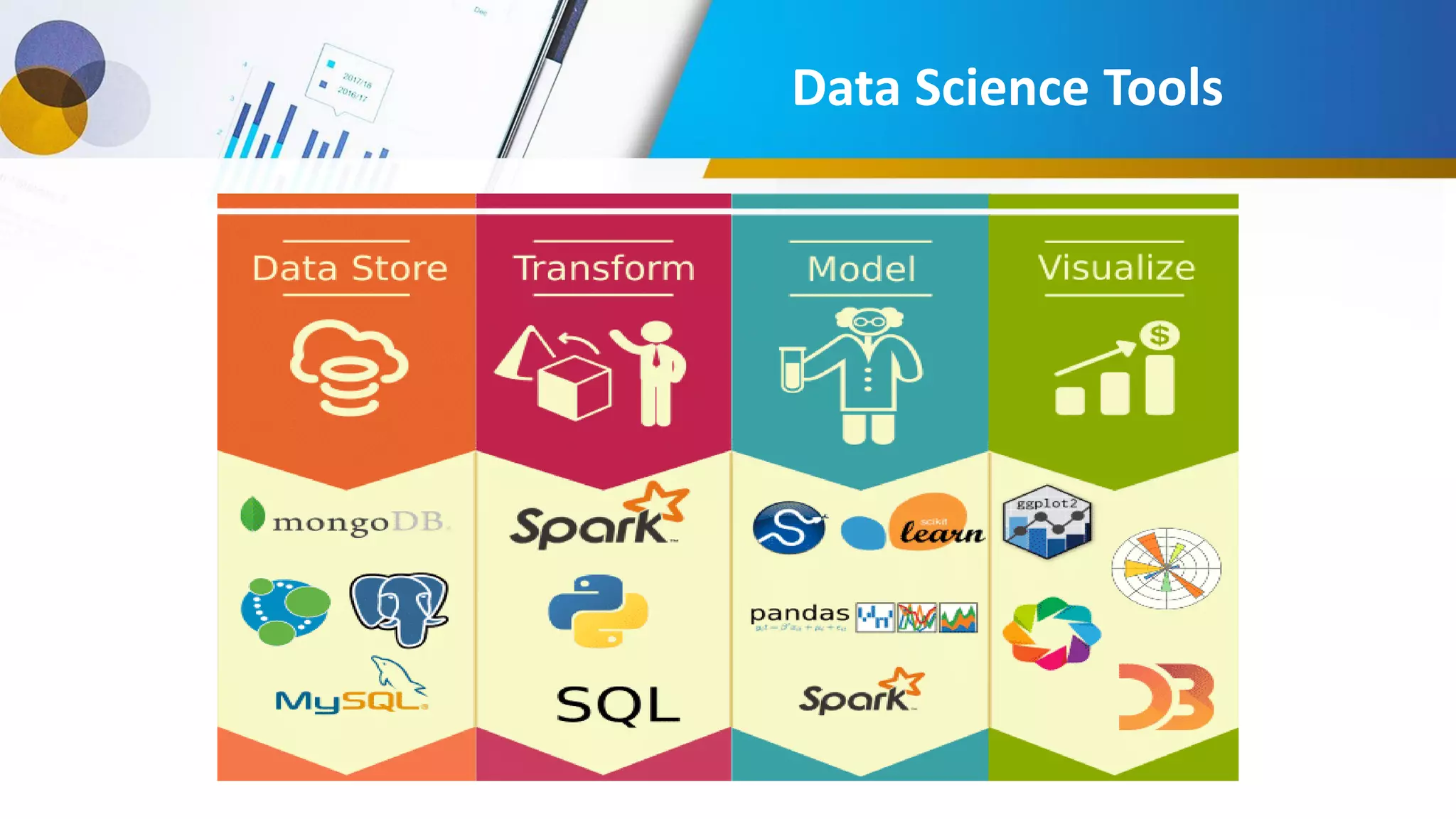
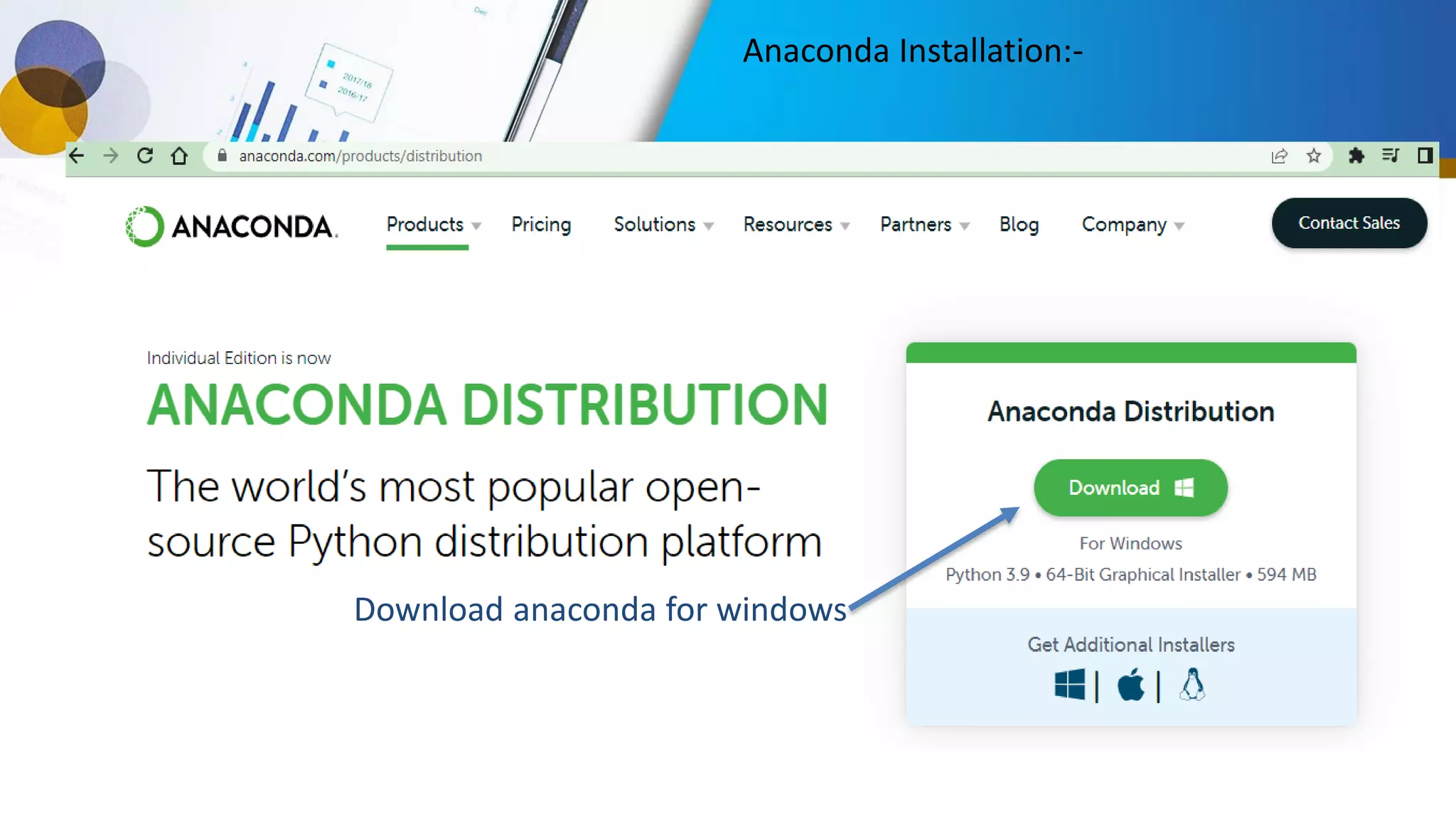
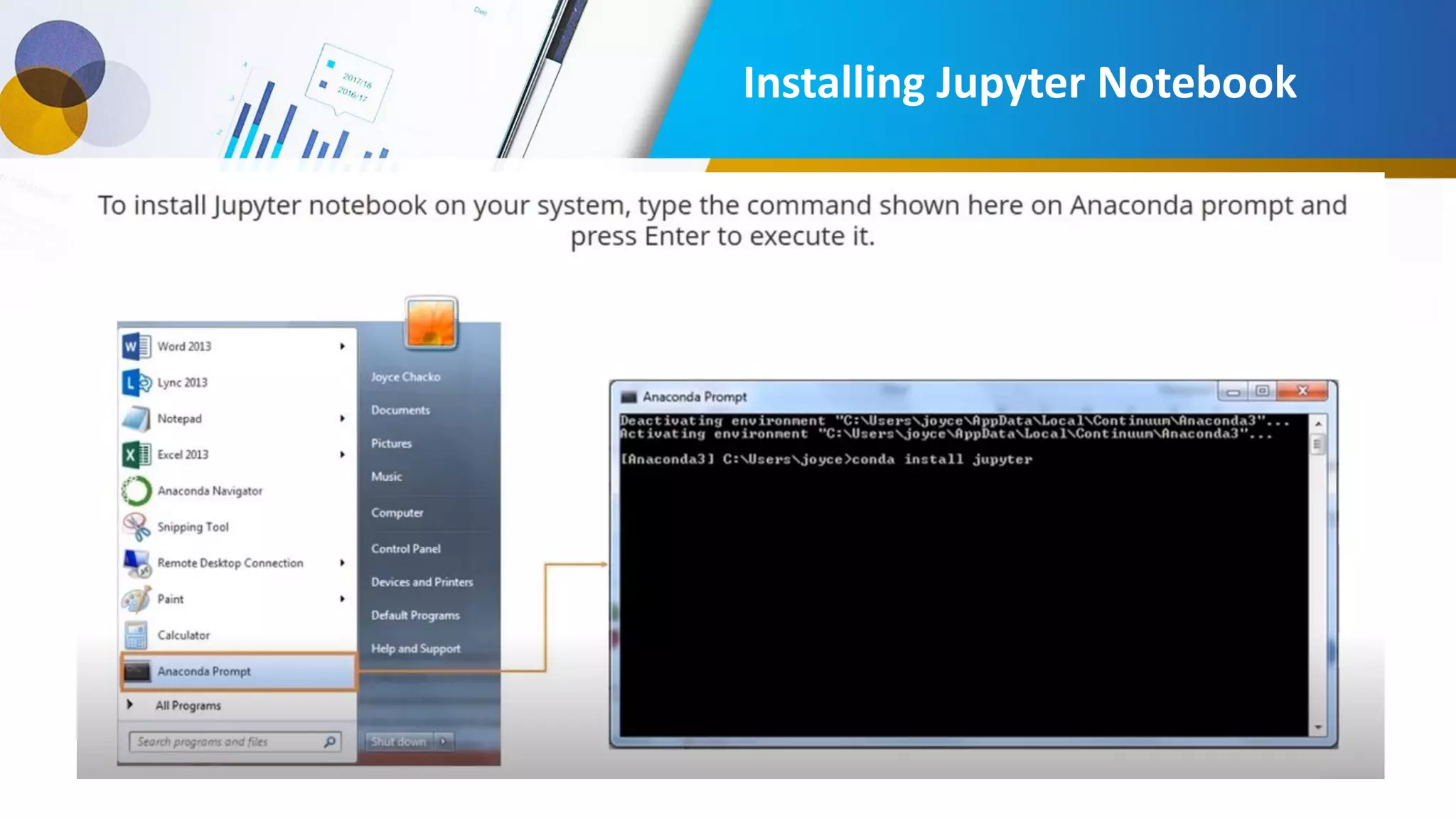
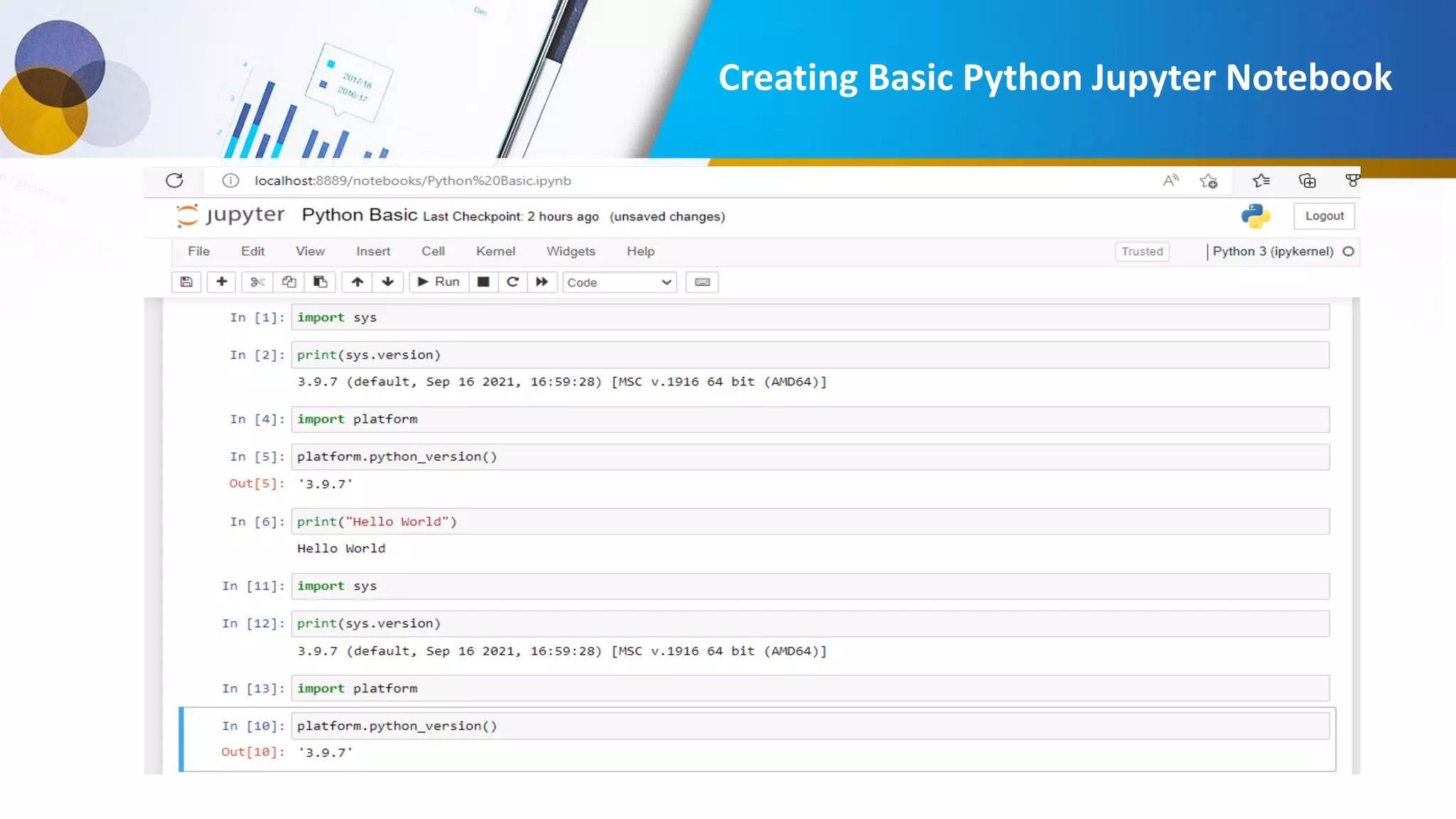
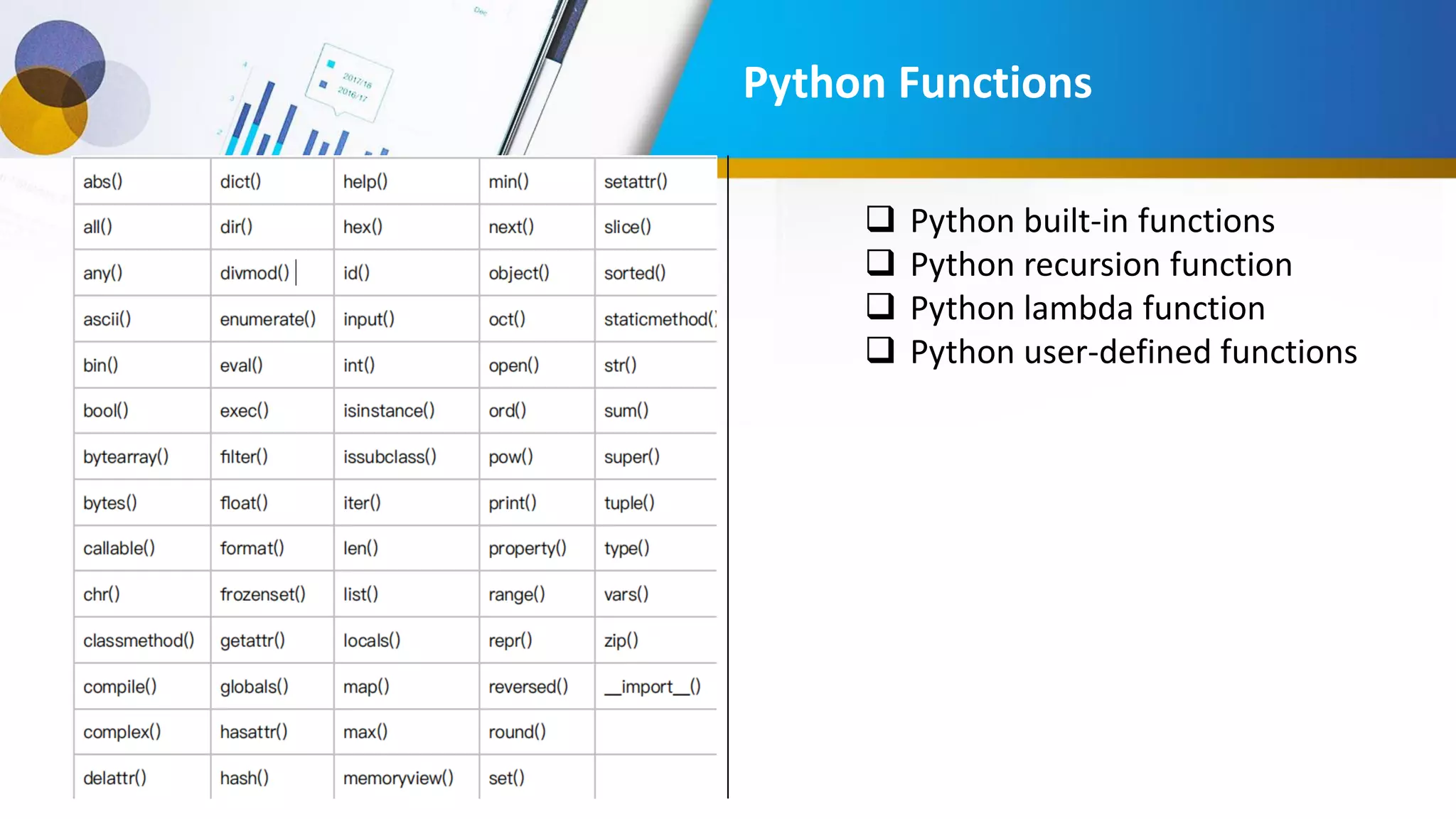
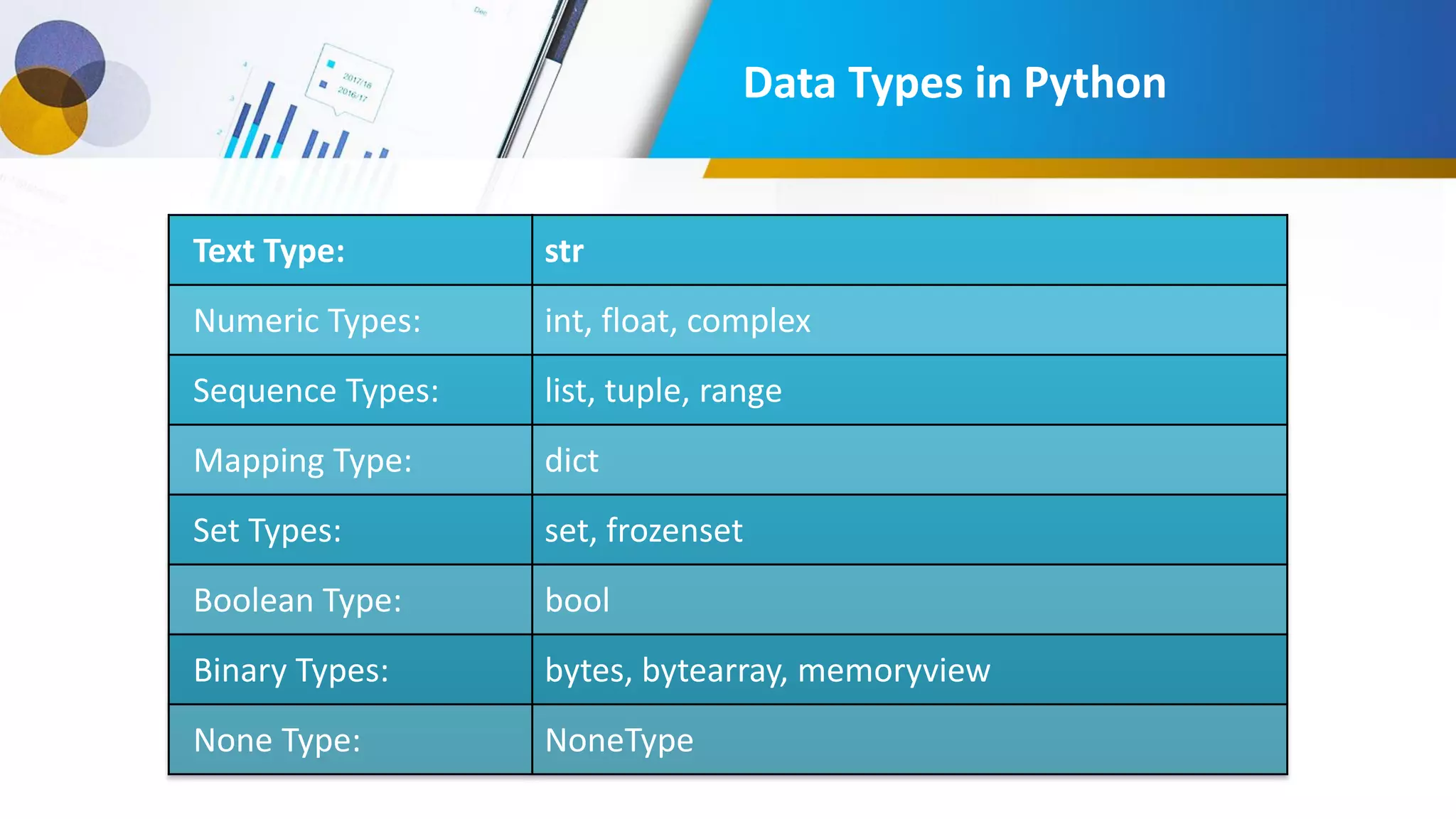
This document provides an introduction to data science, including what it is, its components and uses. It discusses the life cycle and tasks of a data scientist. It also covers Python as a programming language for data science, how to install Anaconda and Jupyter Notebook, basic Python concepts like data types, functions and statements. Key tools like Anaconda and Jupyter Notebook are introduced for working with Python for data analysis and visualization.