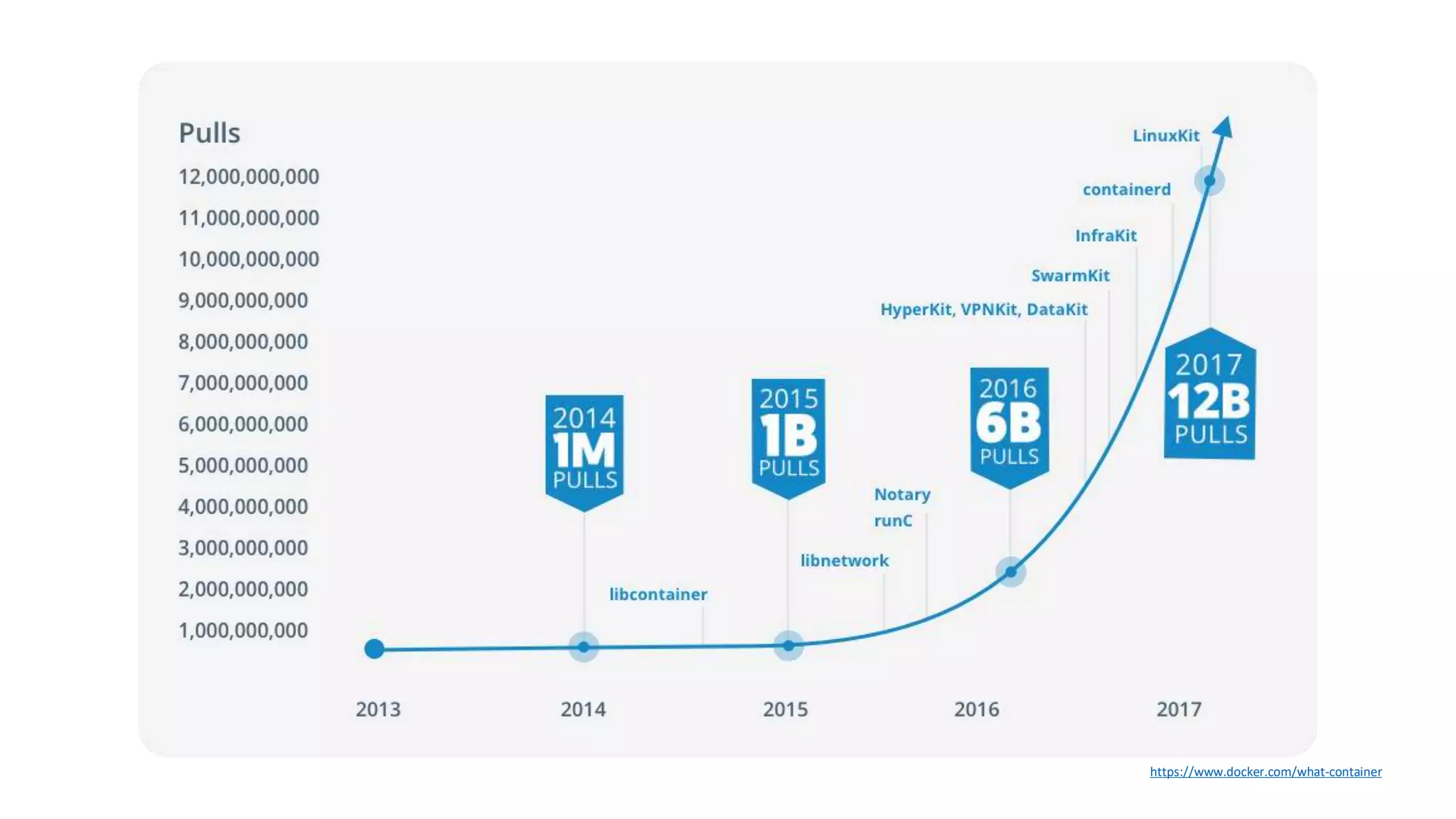
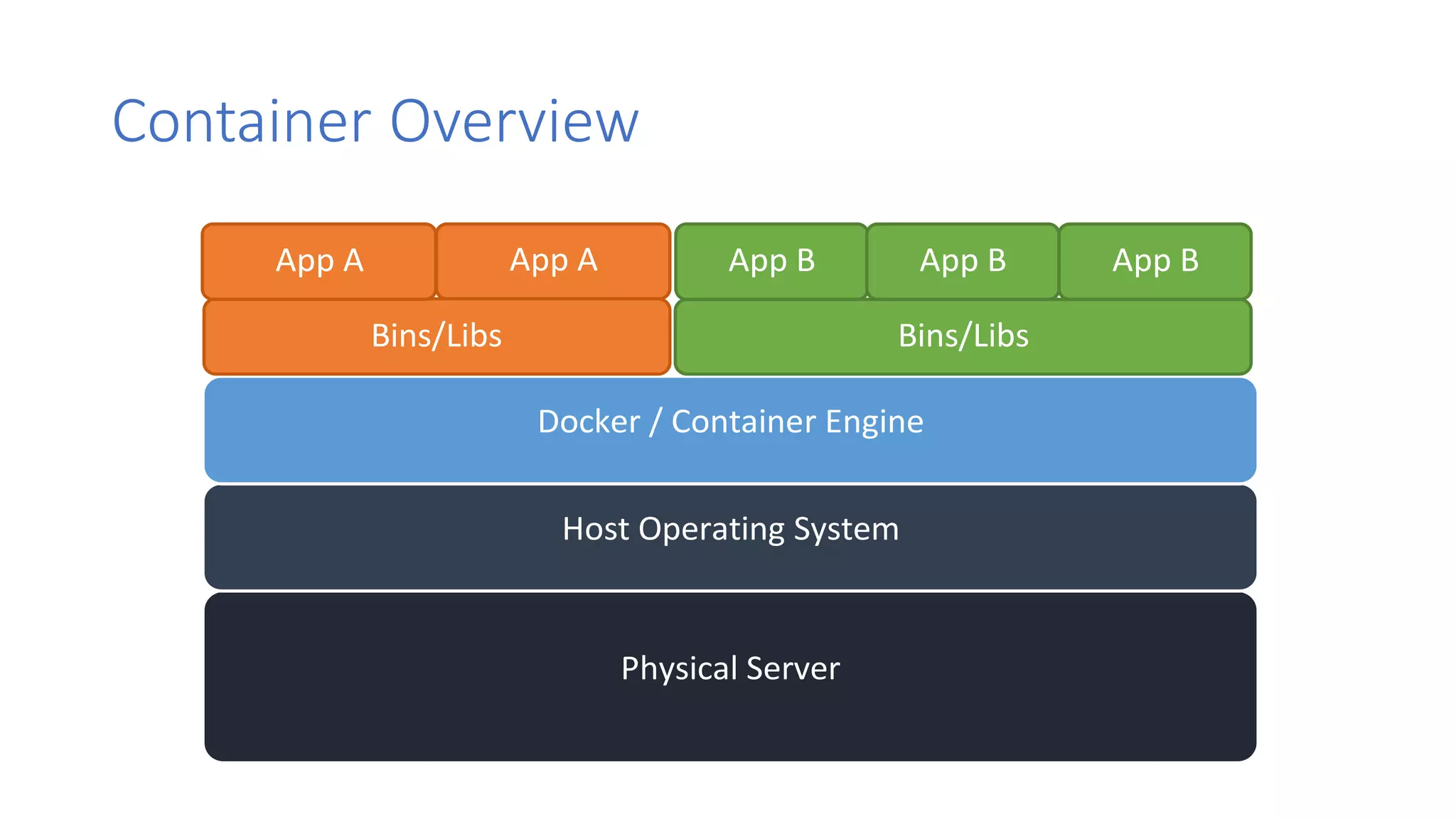
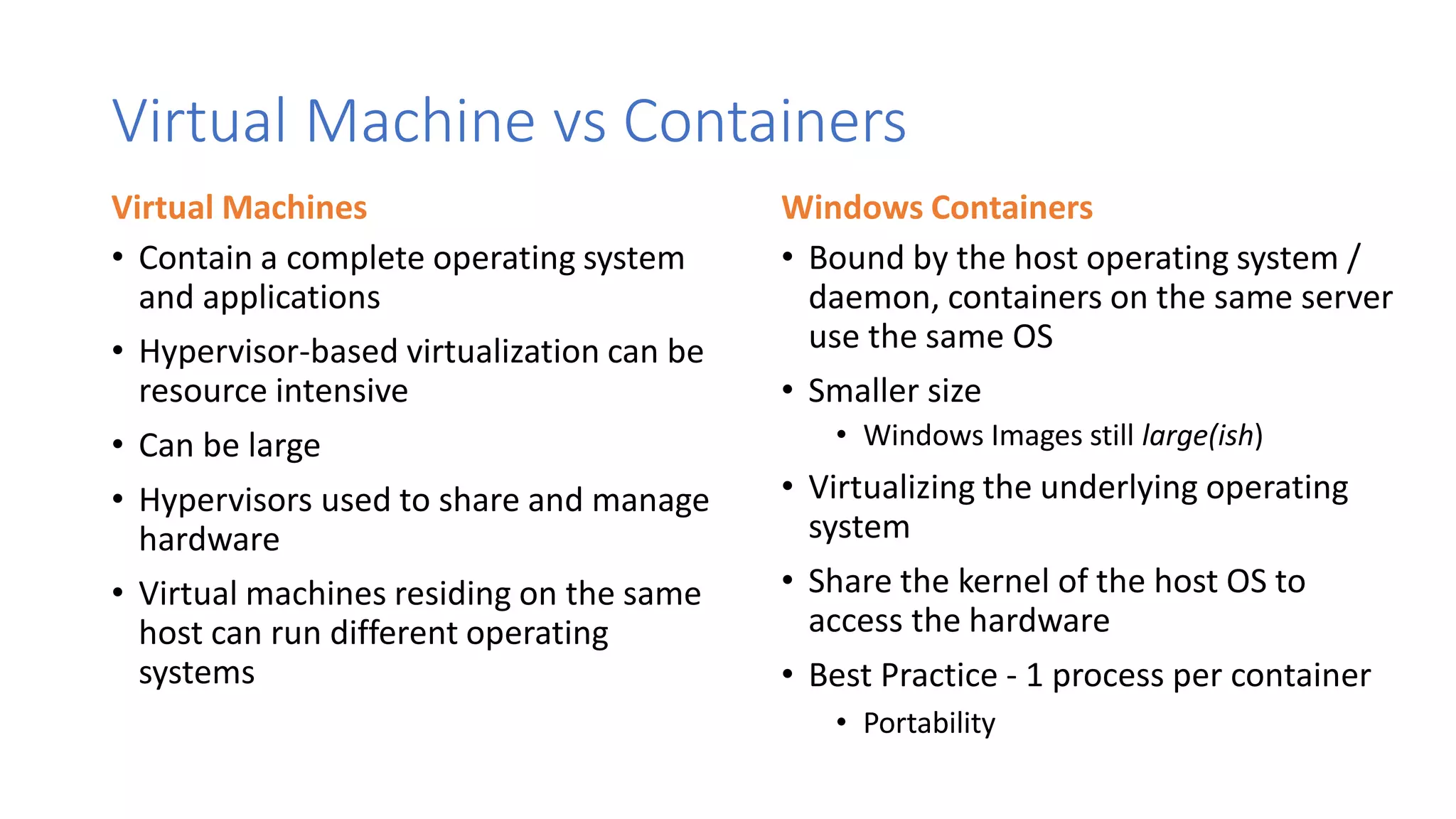
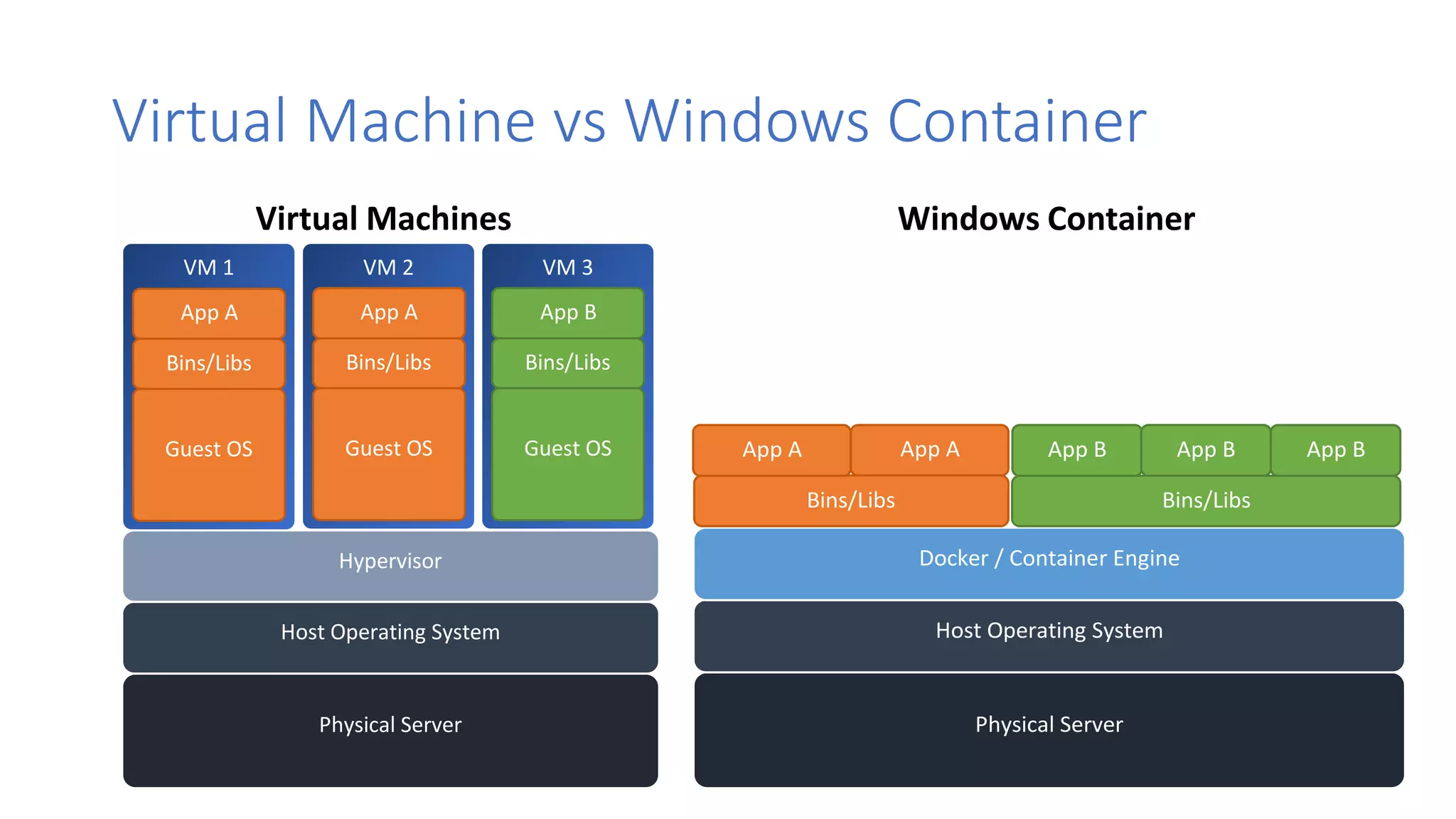
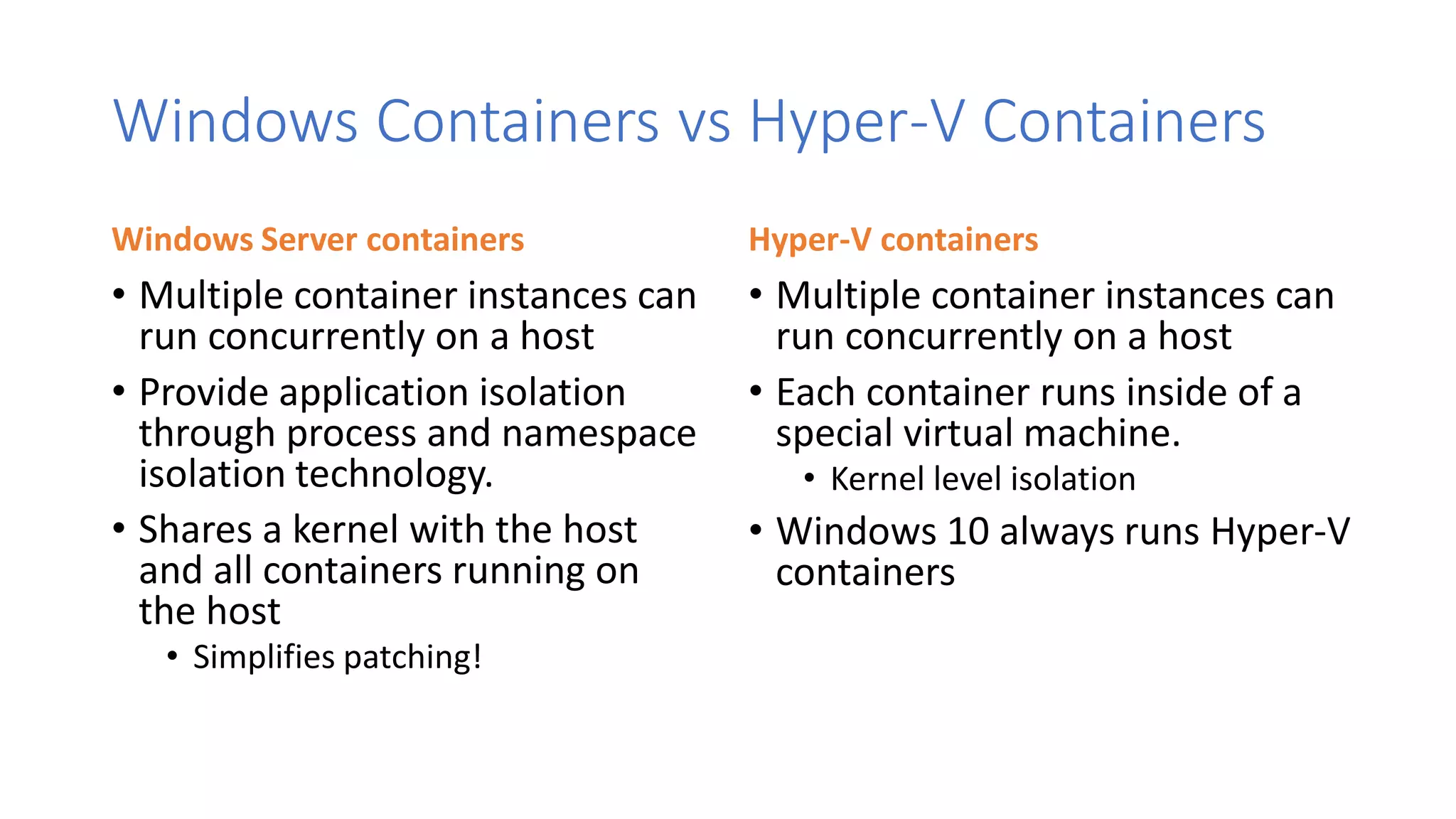
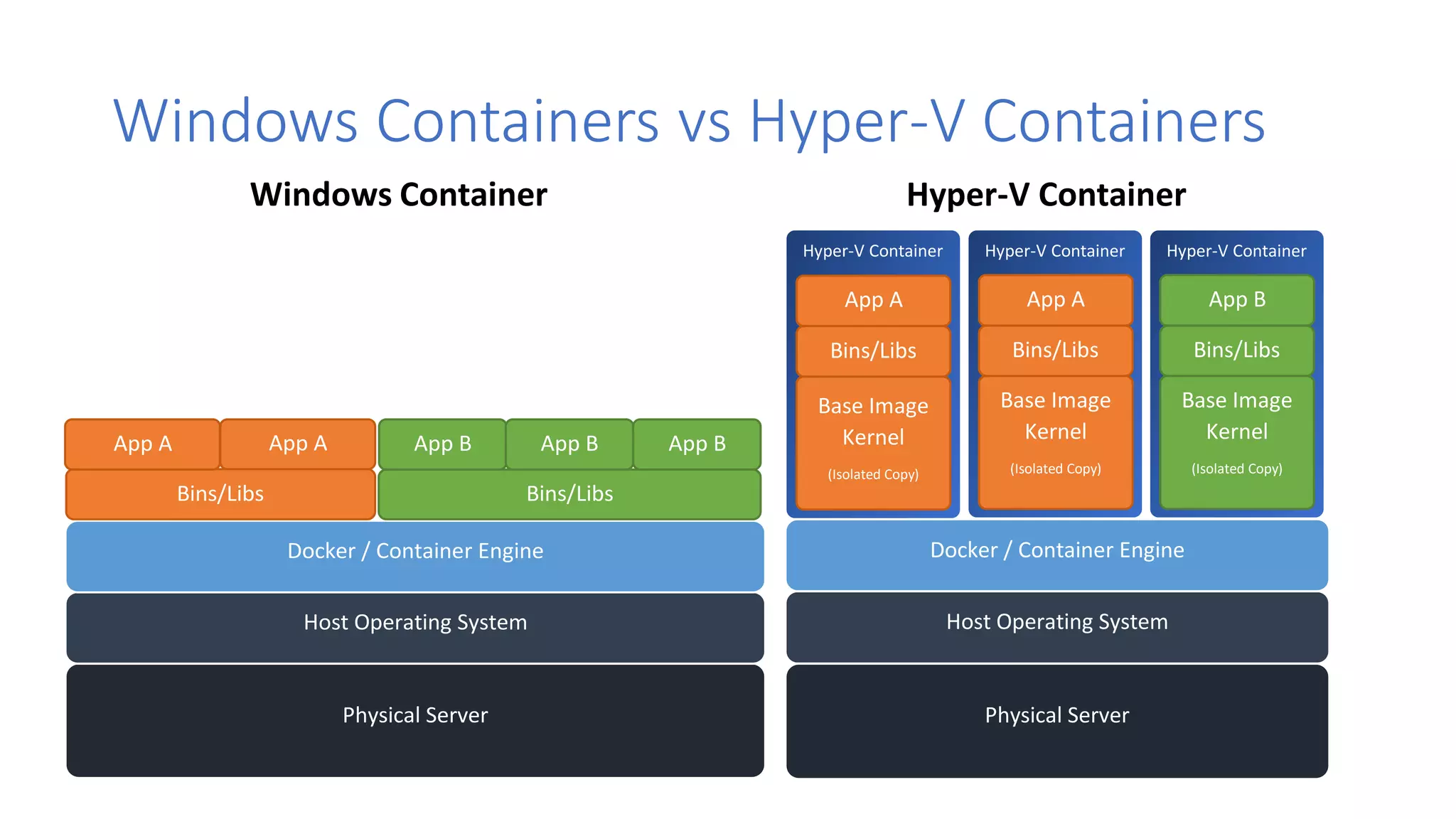
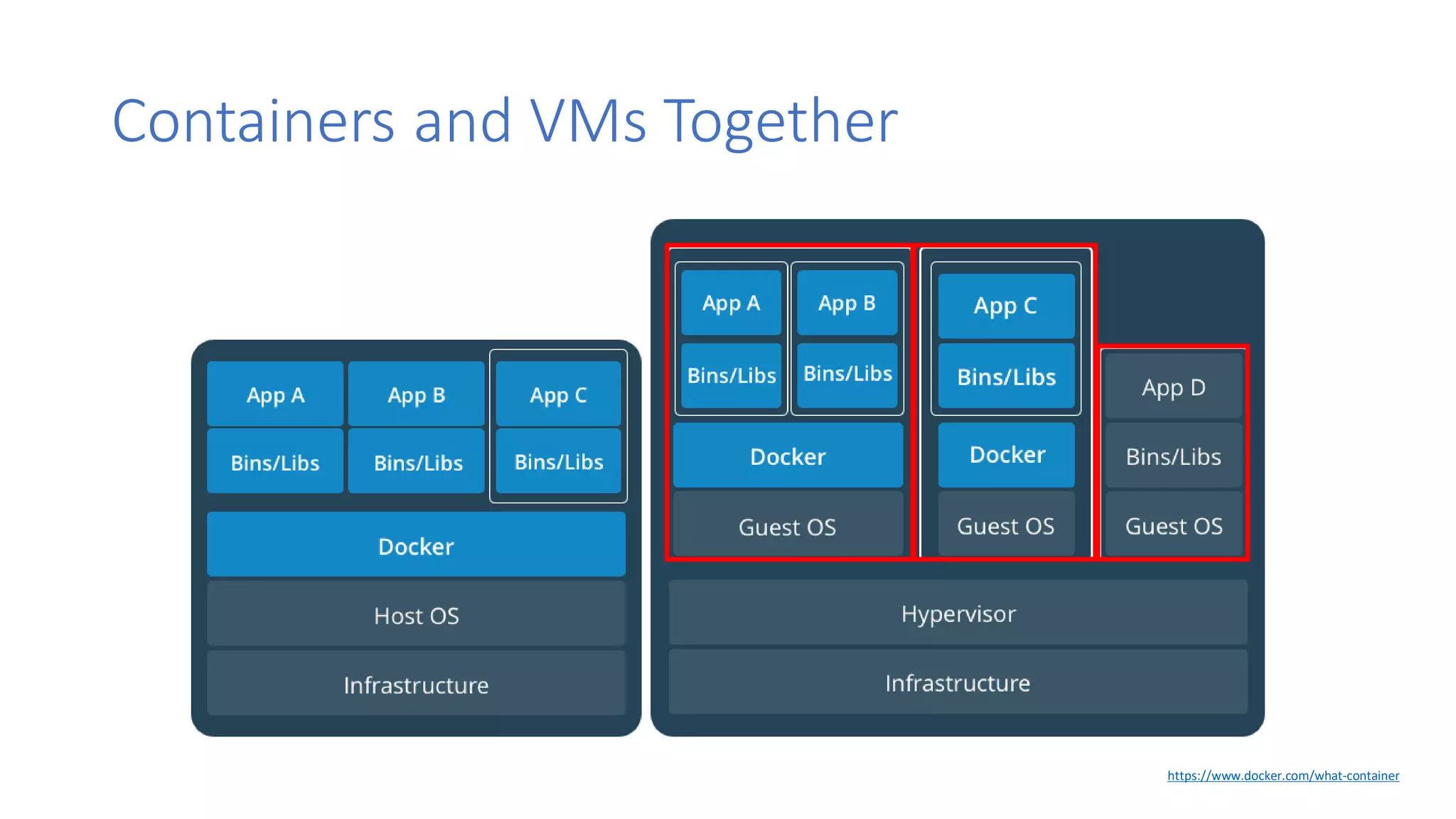
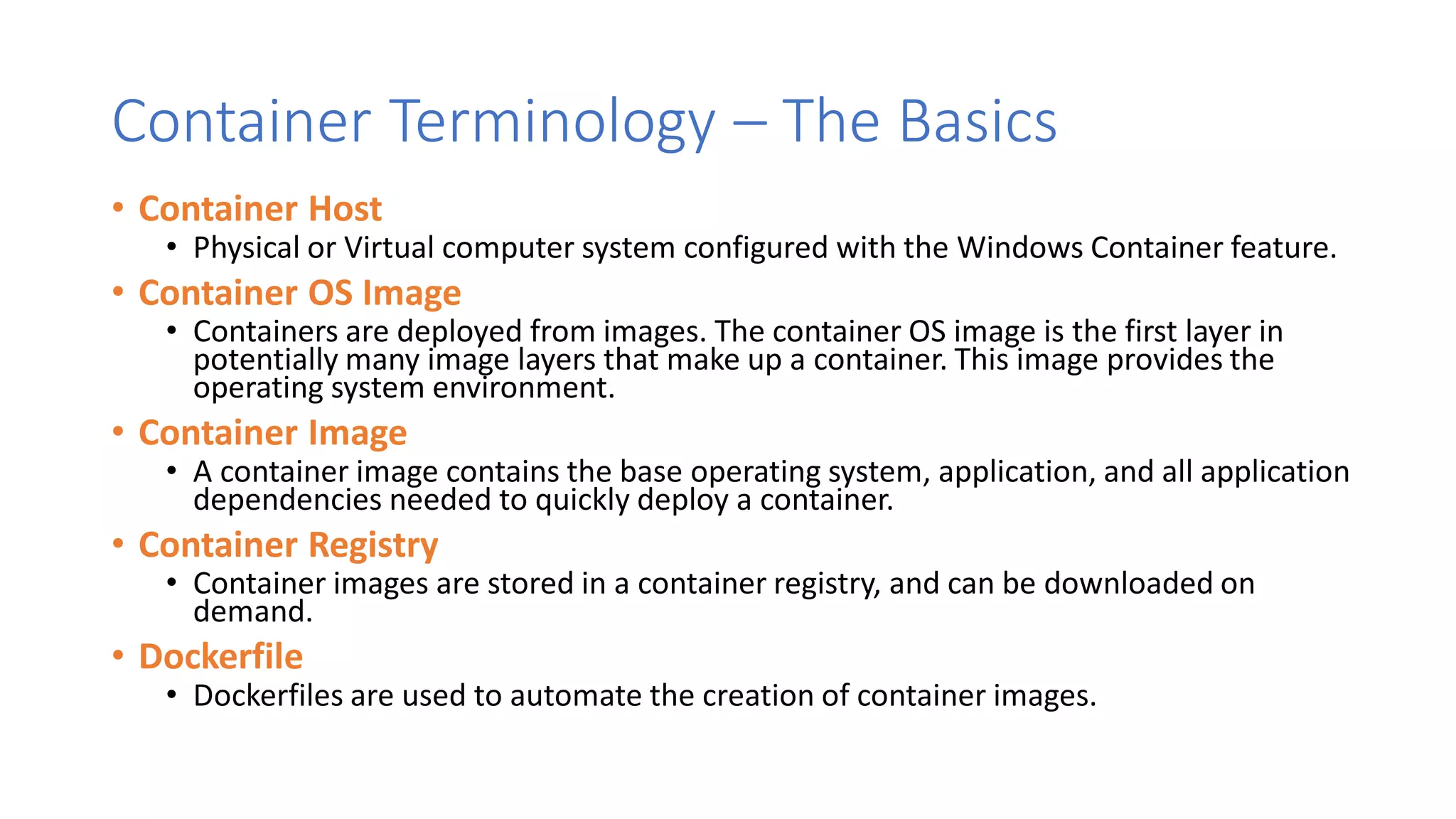
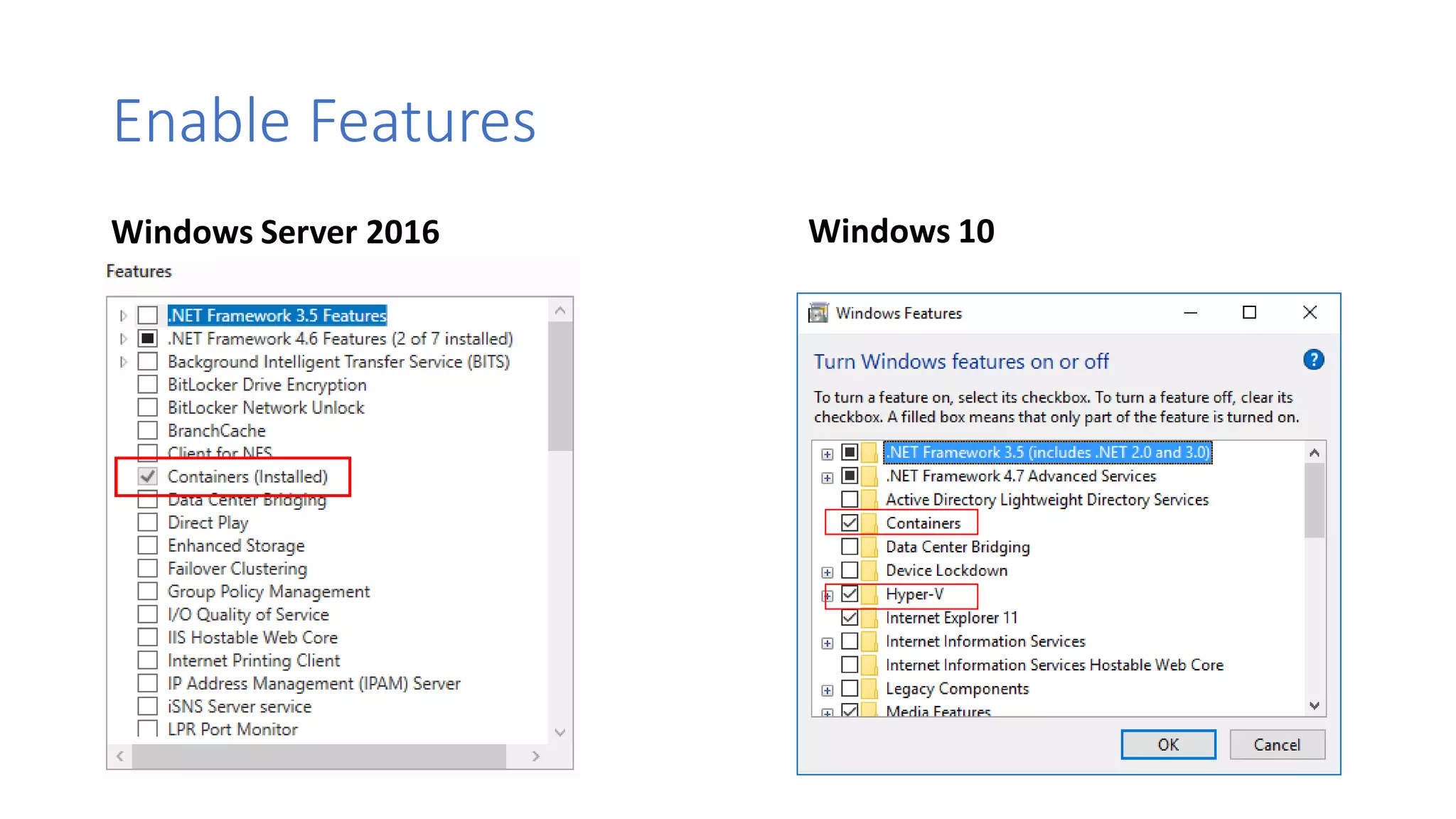
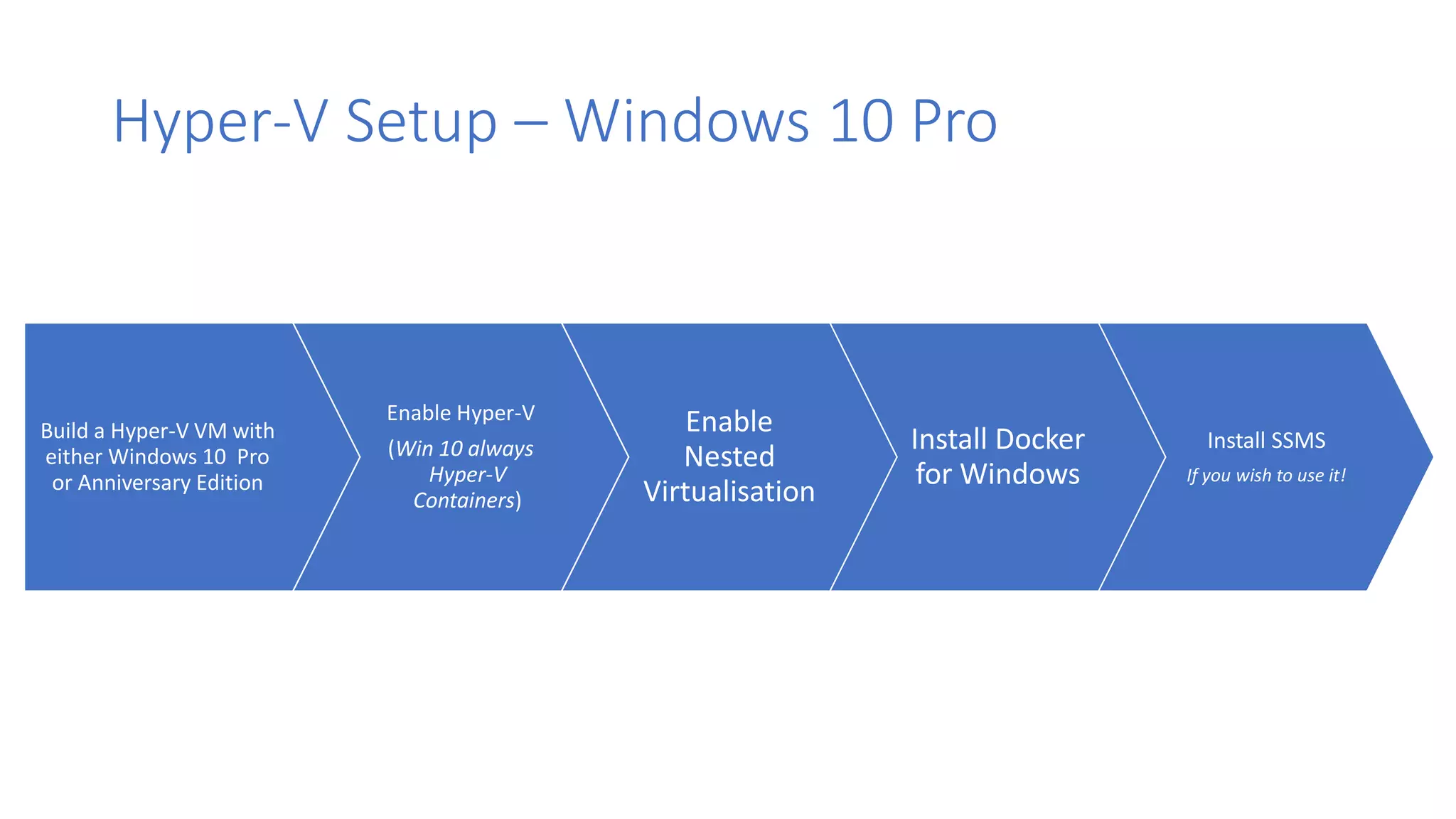
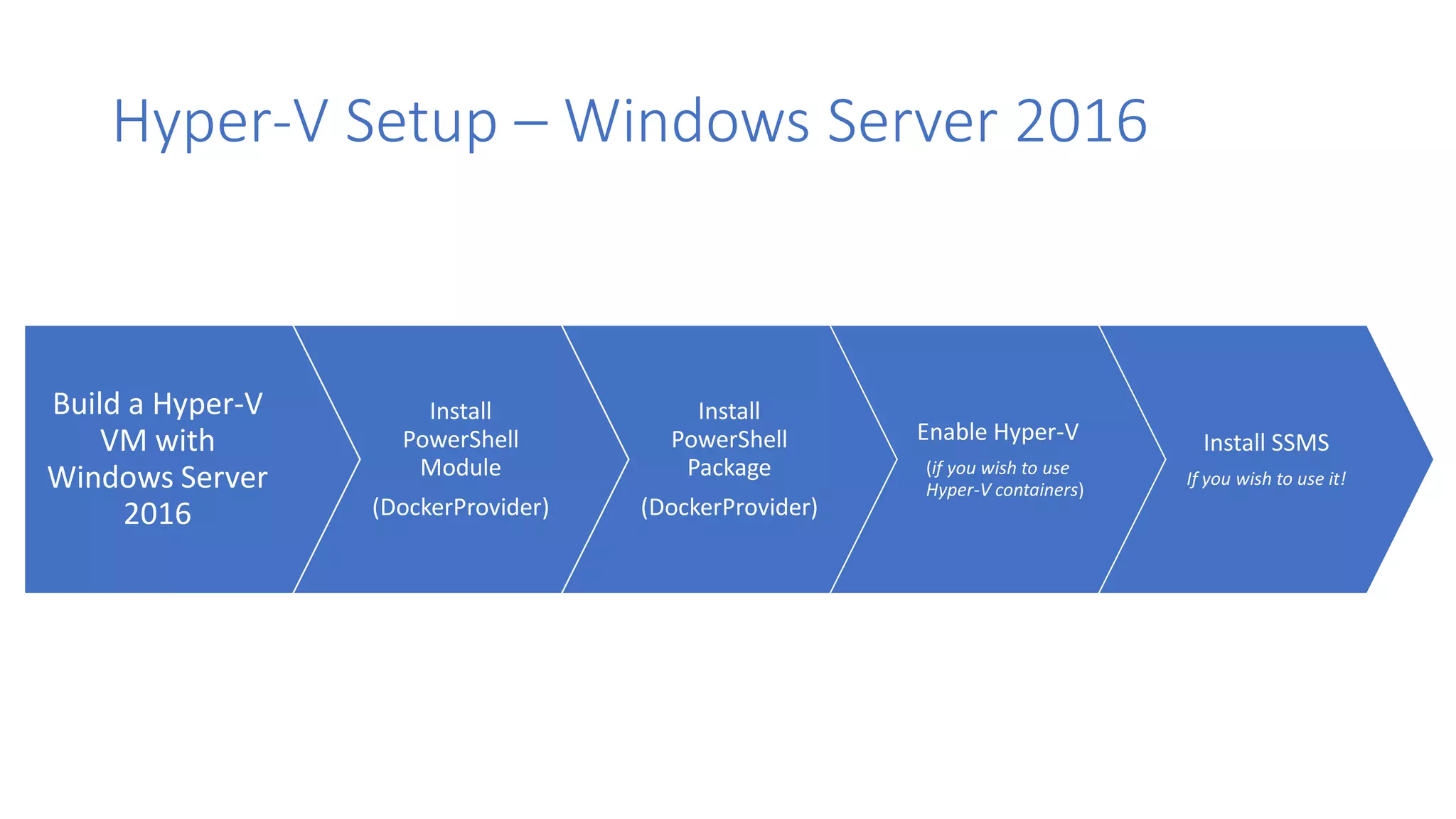
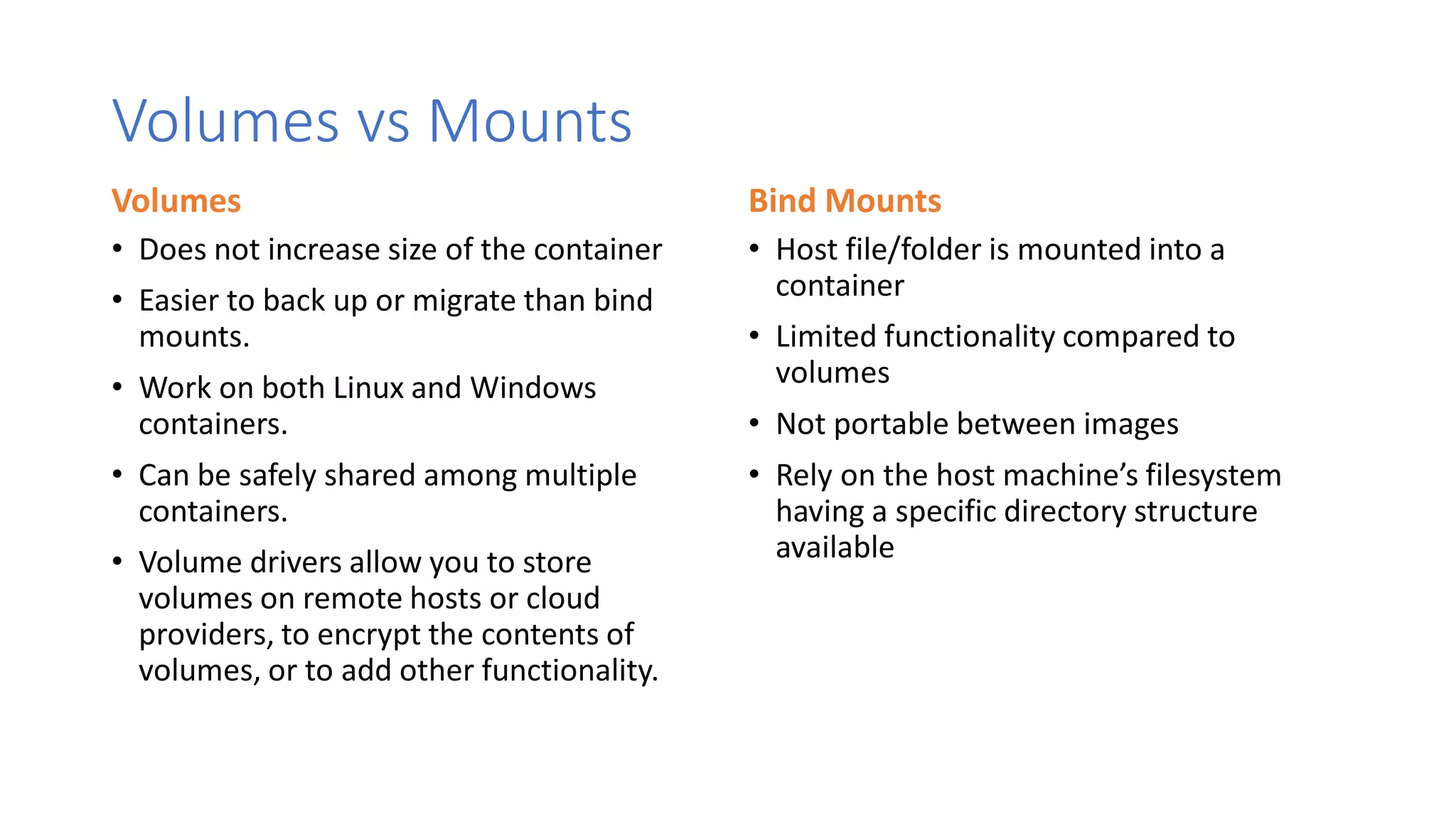
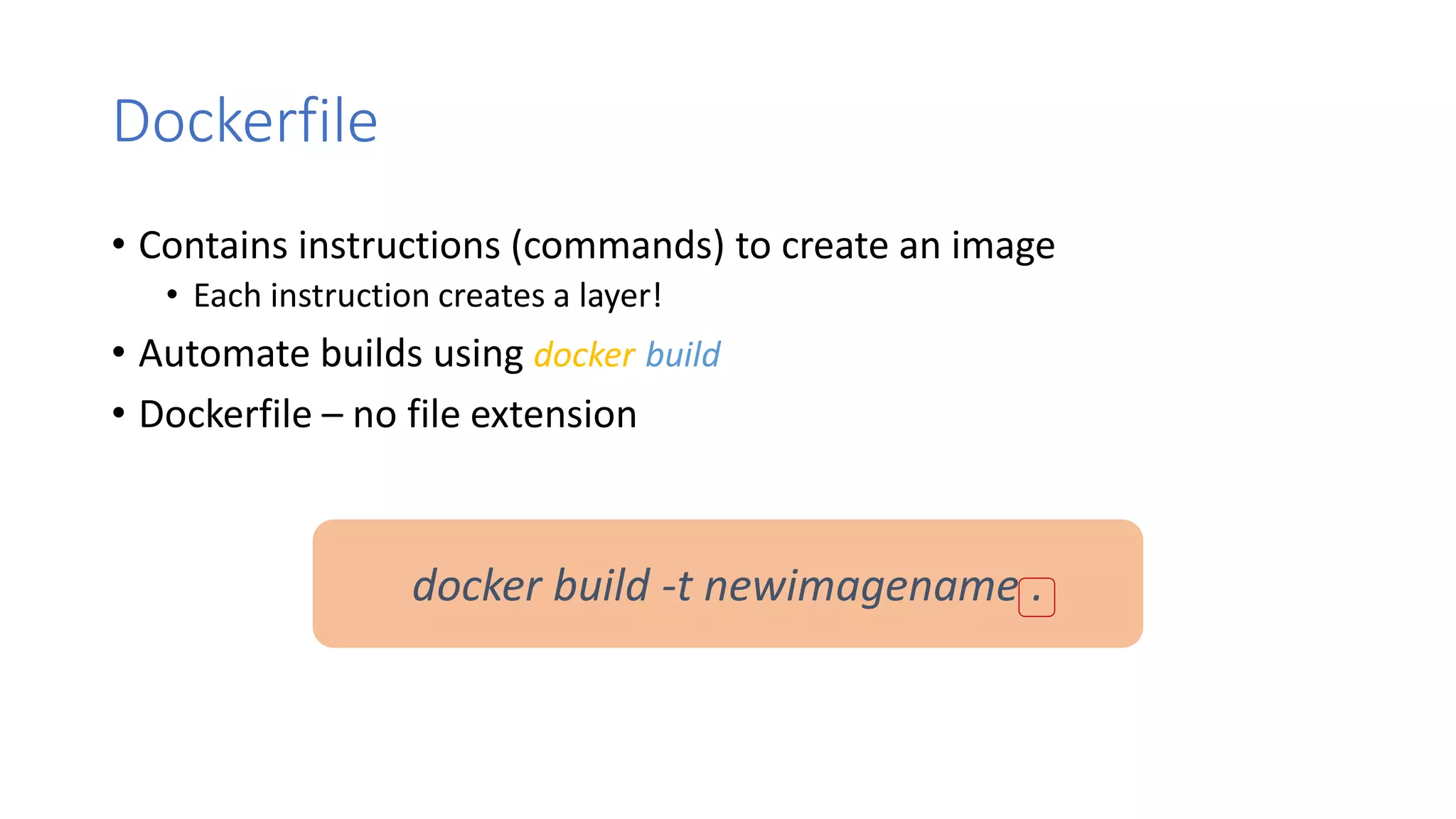
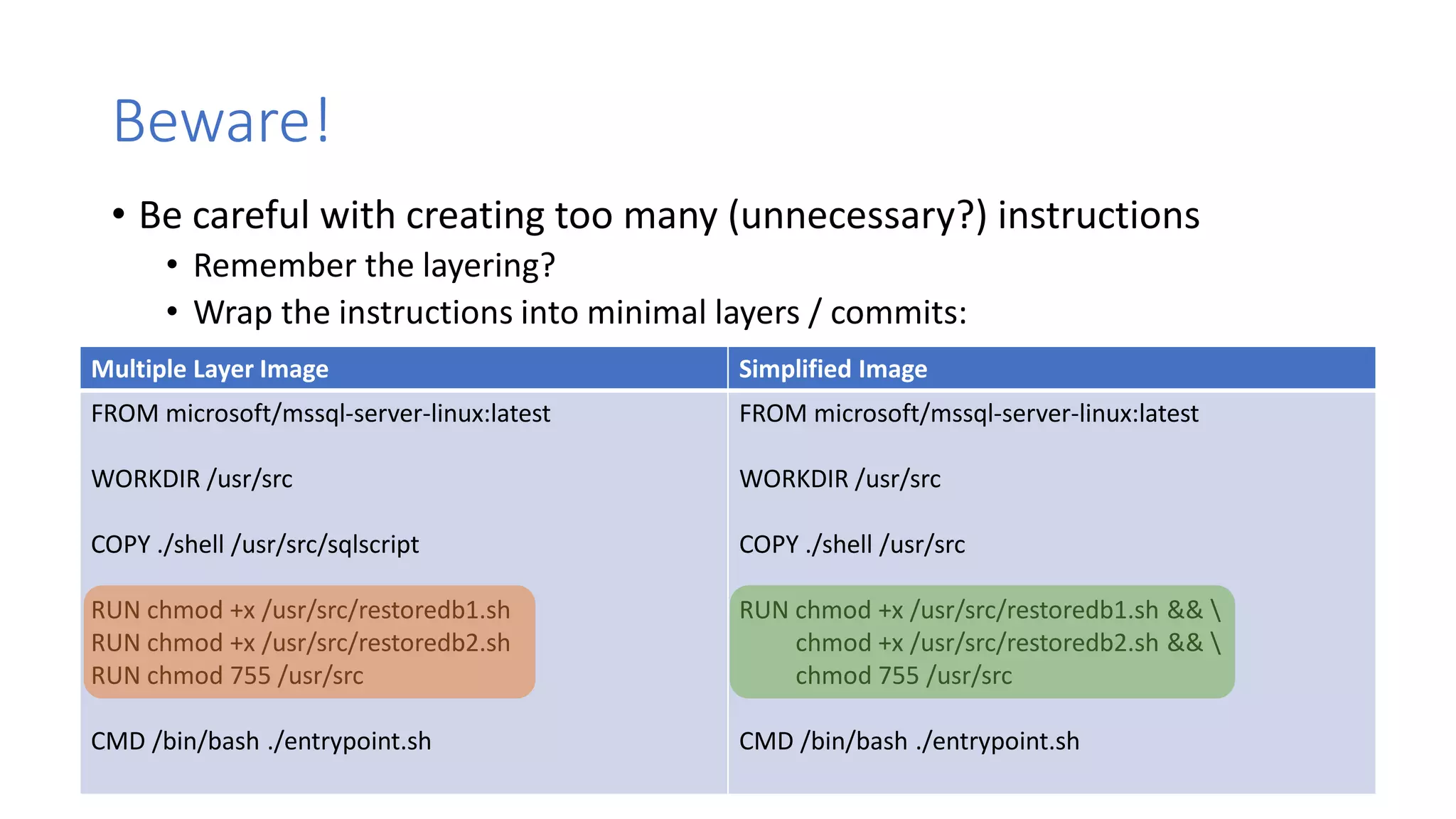
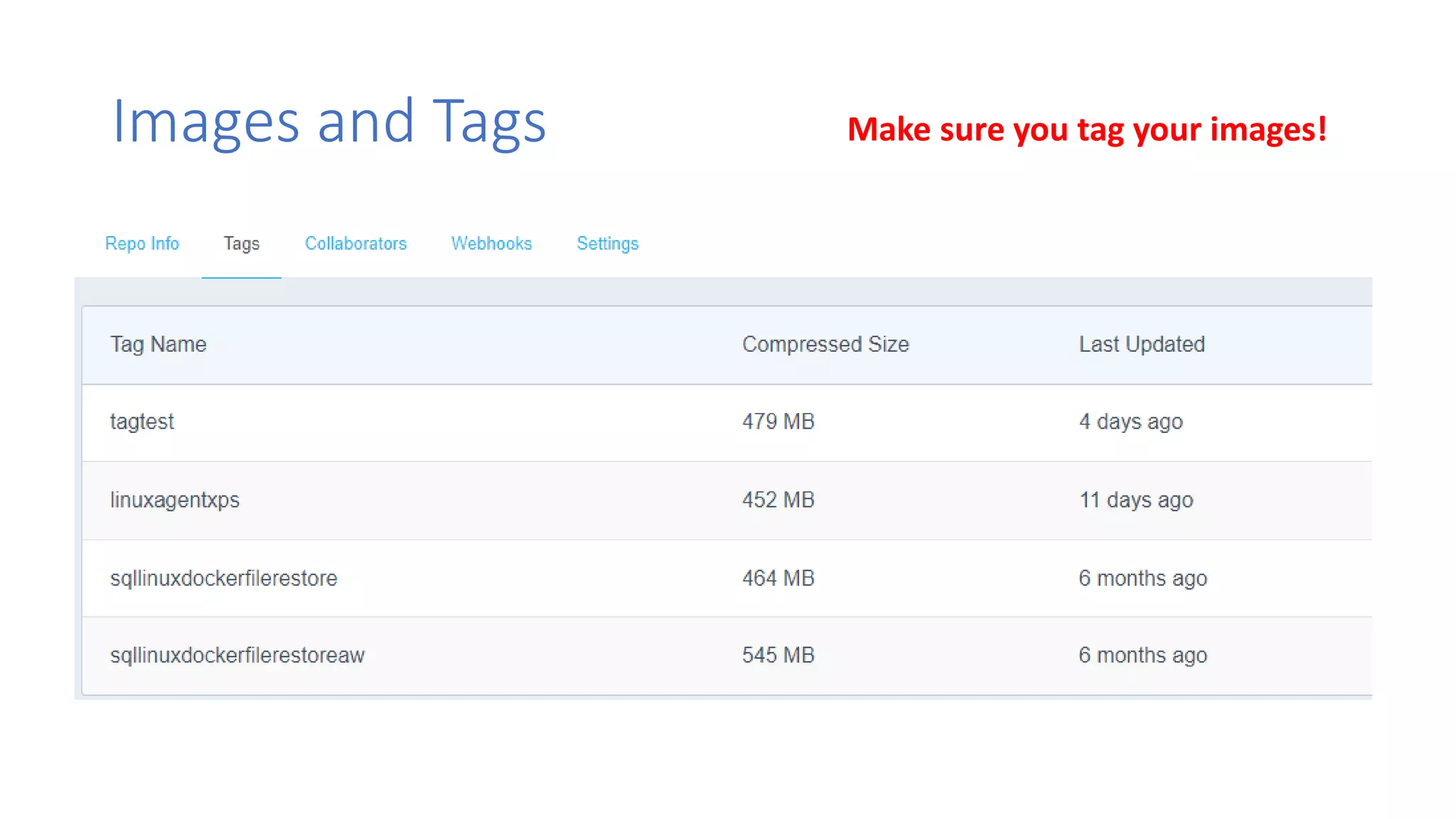
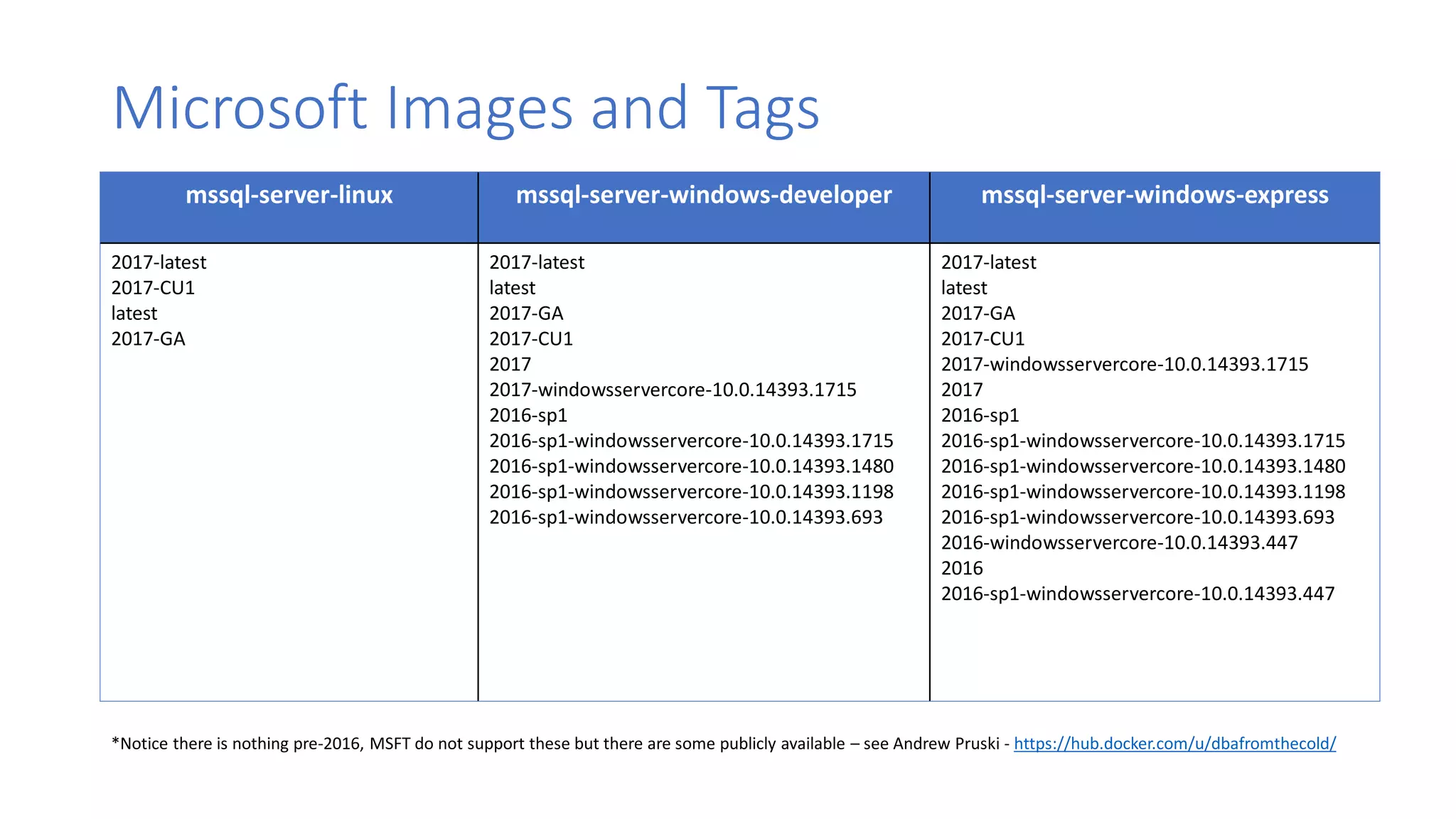
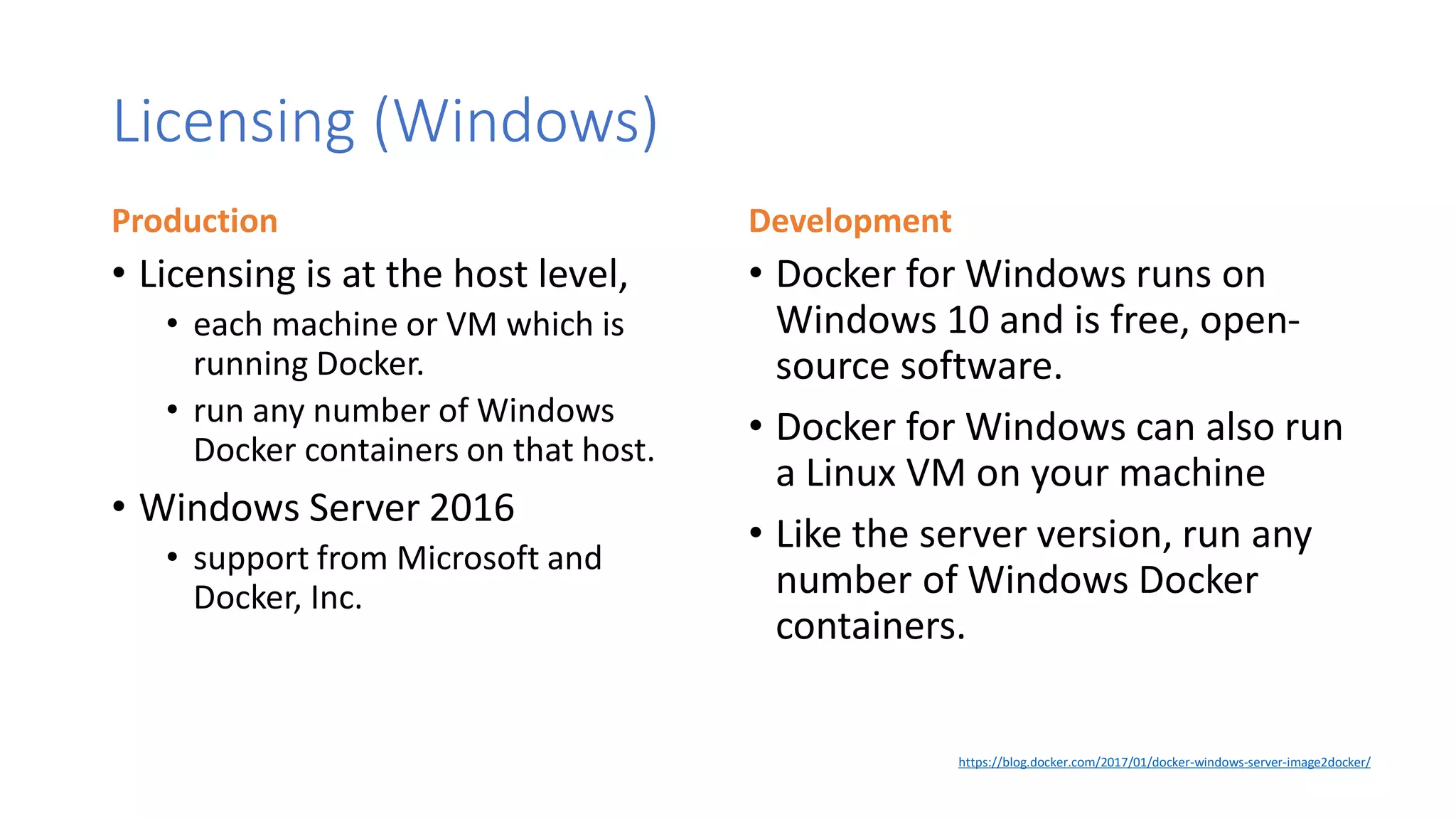
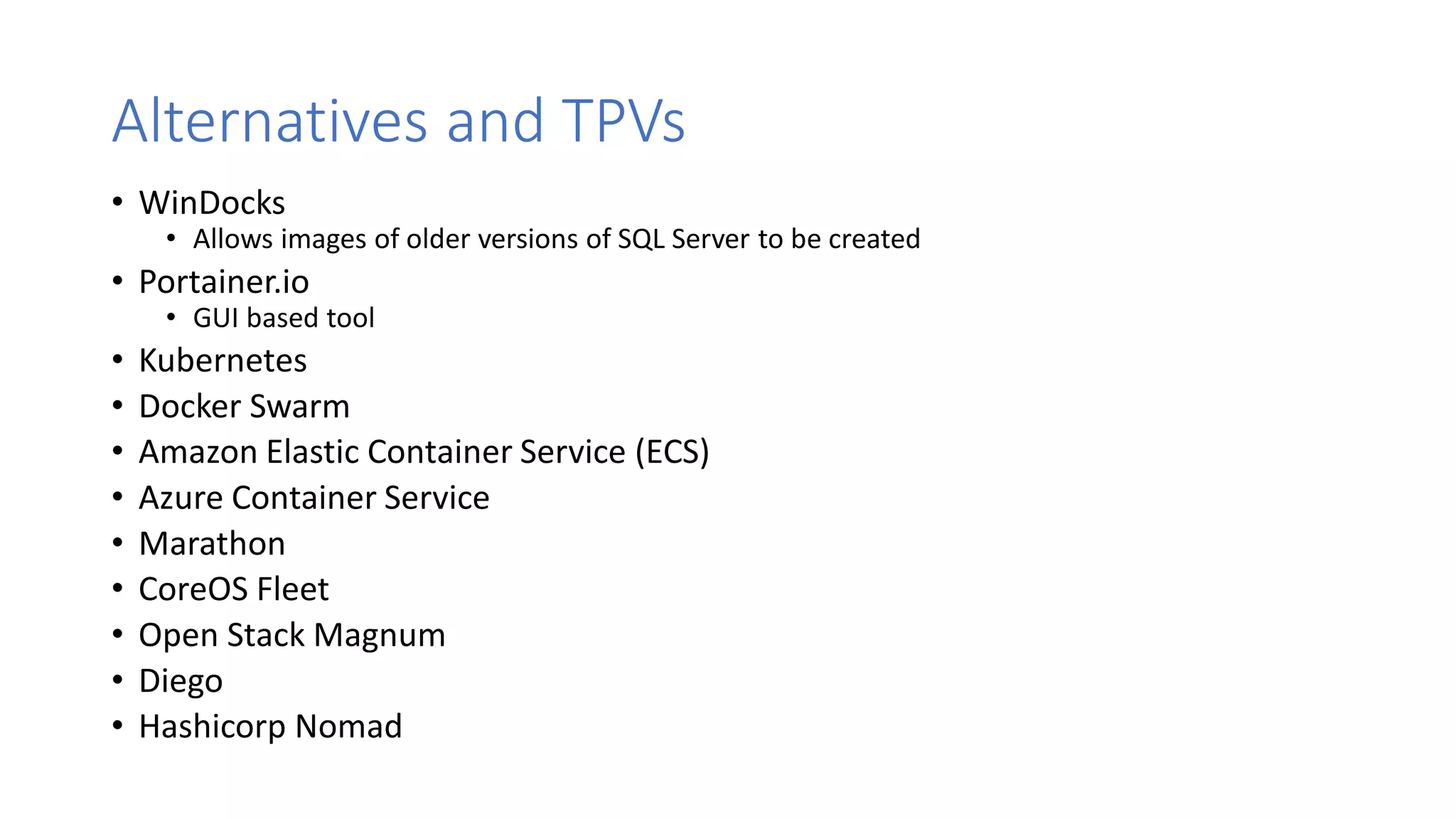
Containers provide lightweight virtualization that packages applications and dependencies together. The document introduces containers and Docker, discusses the differences between containers and virtual machines, and covers key Docker concepts like images, Dockerfiles, Docker Hub, and running SQL Server in containers. It also addresses container setup, licensing, and performance considerations for using containers with SQL Server.