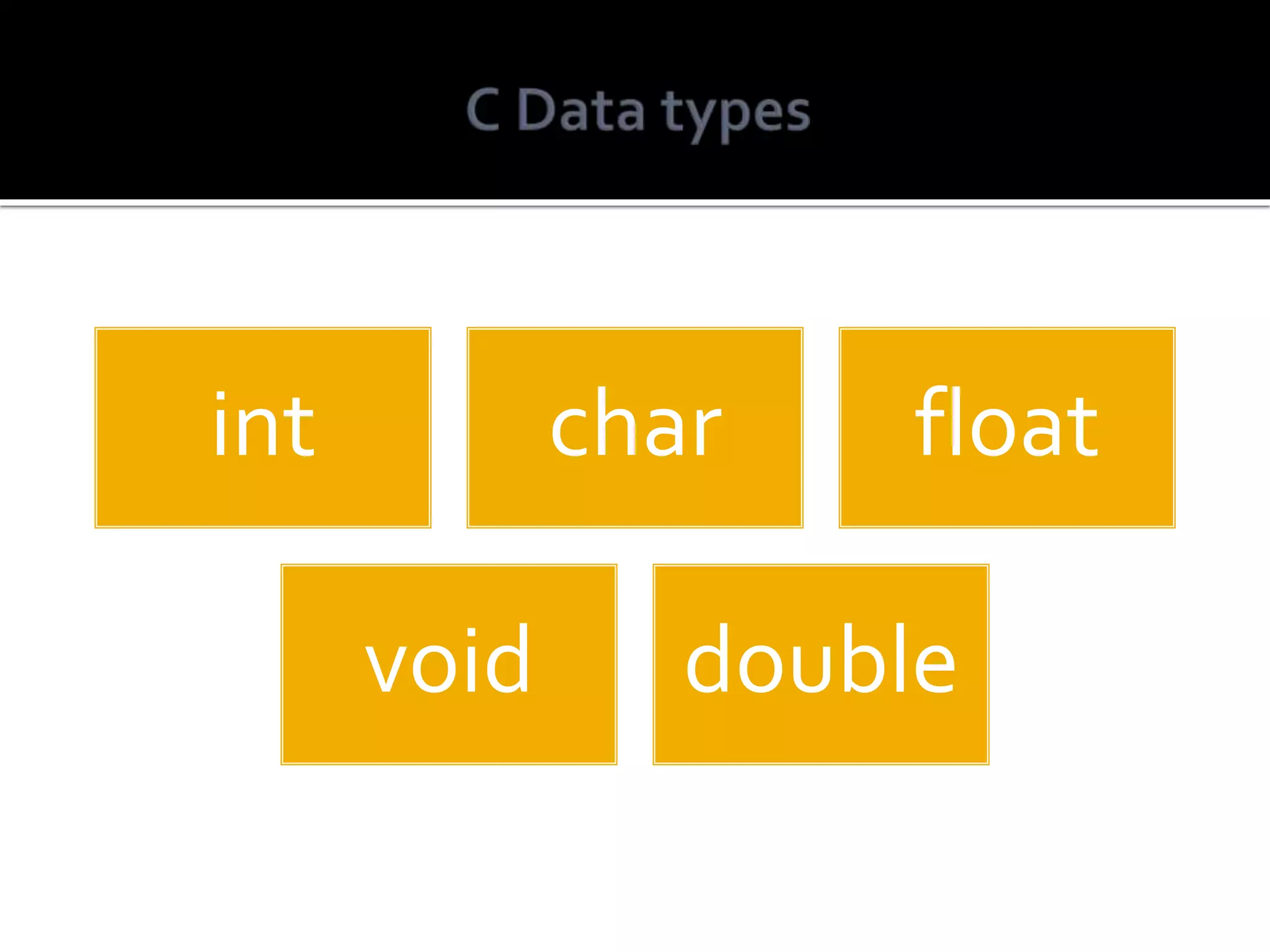
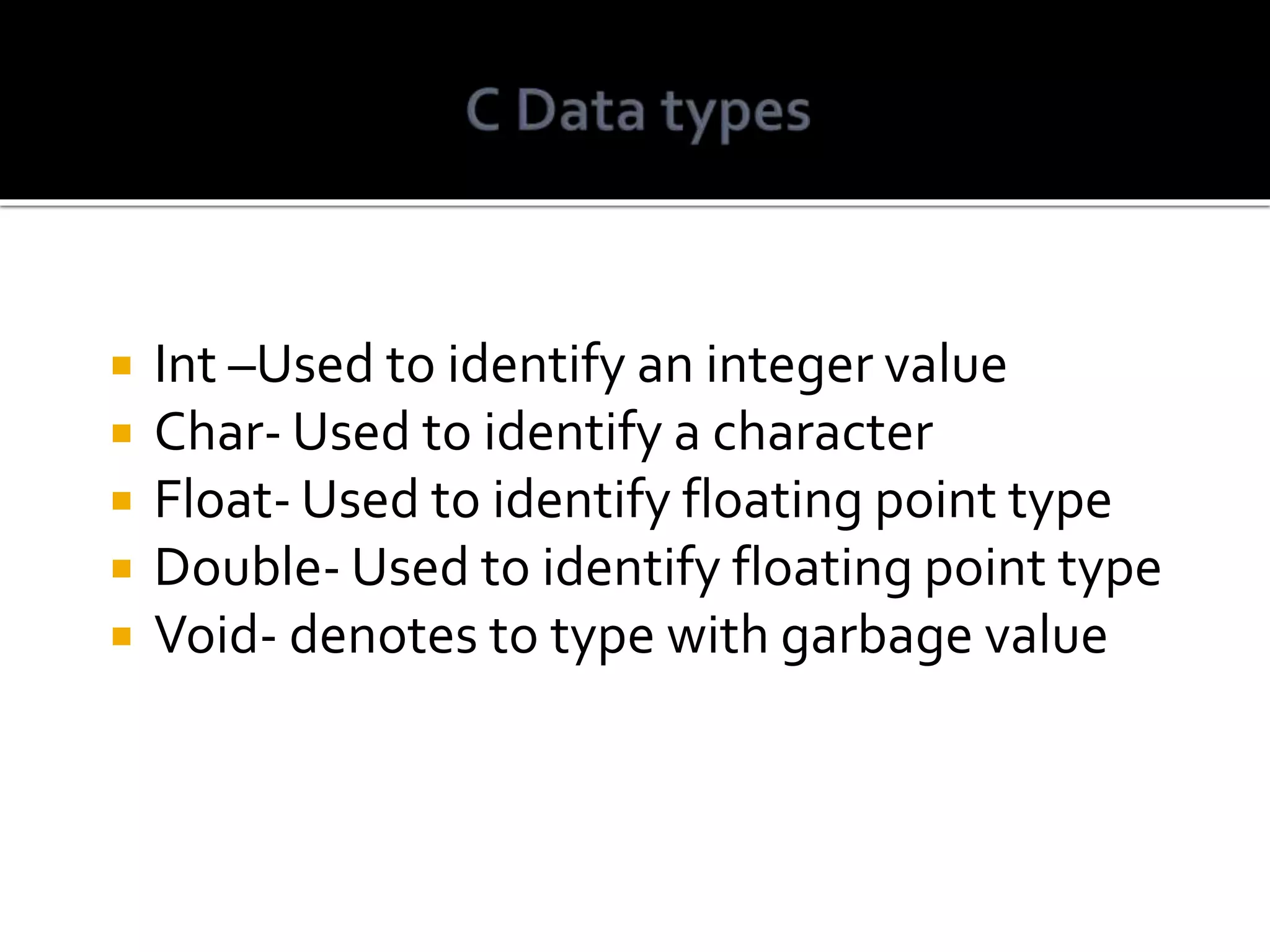
C is a general purpose, procedural programming language developed in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs. It is a high-level language that provides low-level capabilities and efficiency. C code can be compiled for different computer architectures, making it portable. It is a structured language commonly used to develop system applications and remains one of the most widely used programming languages.