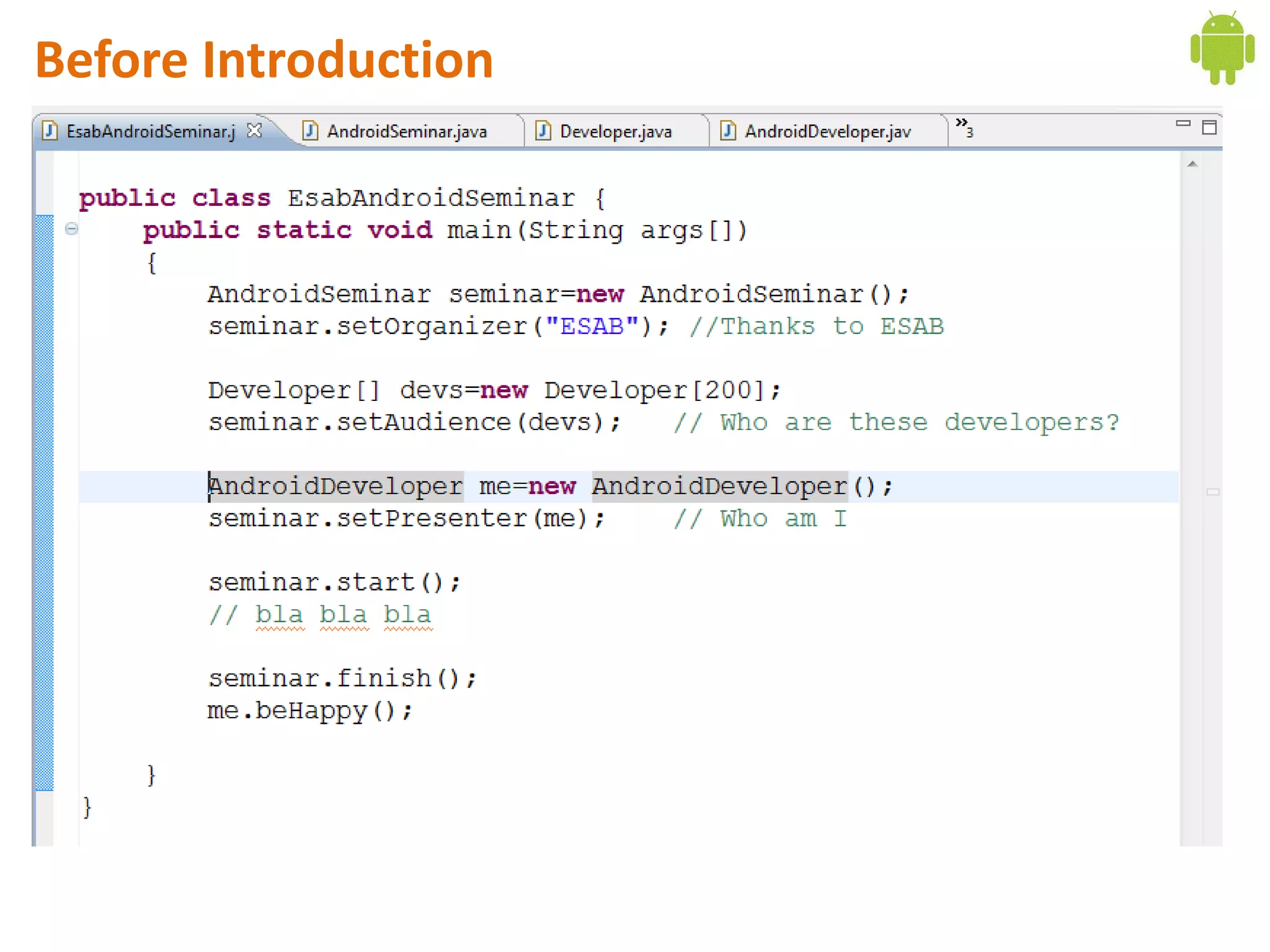
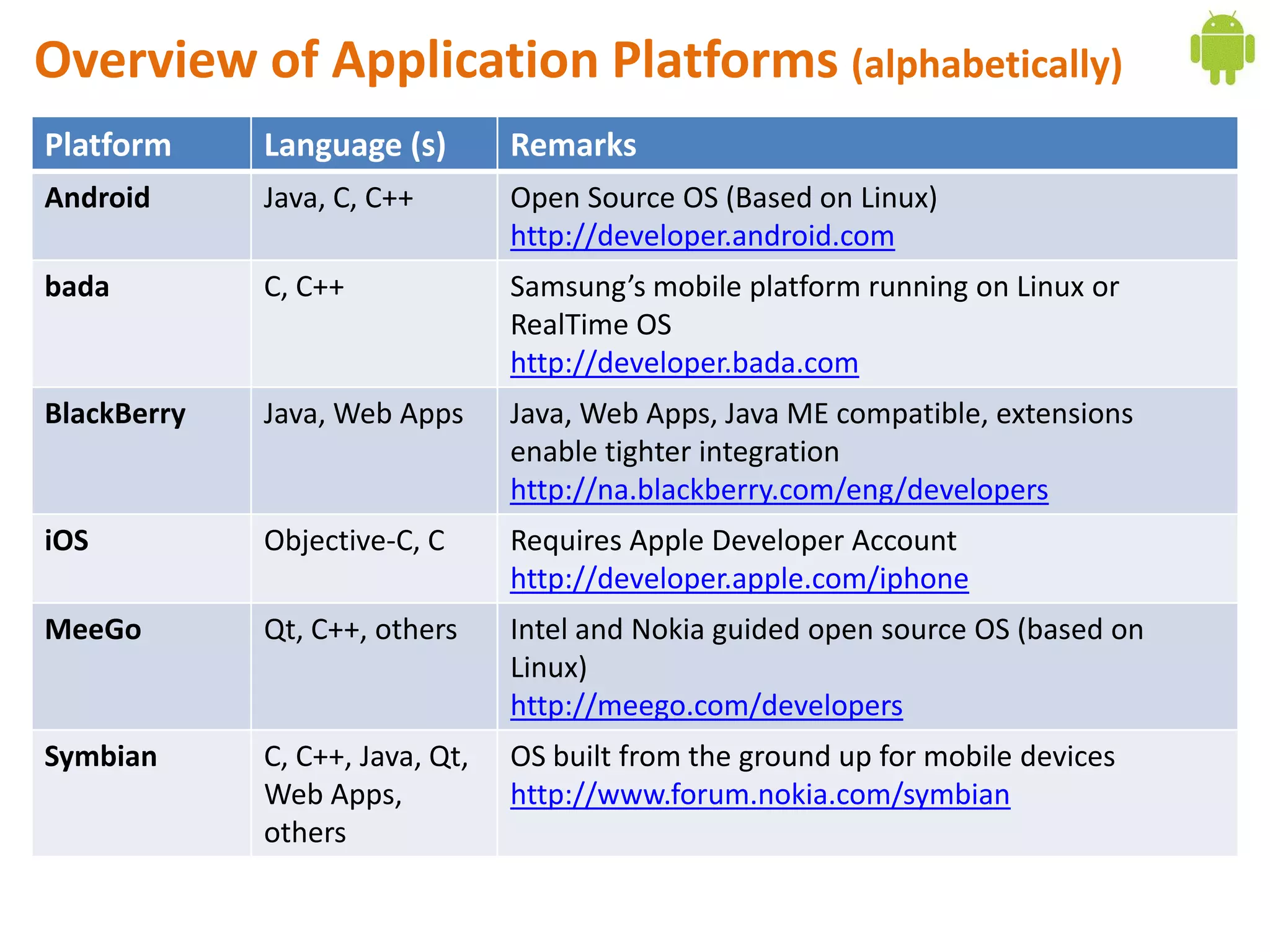
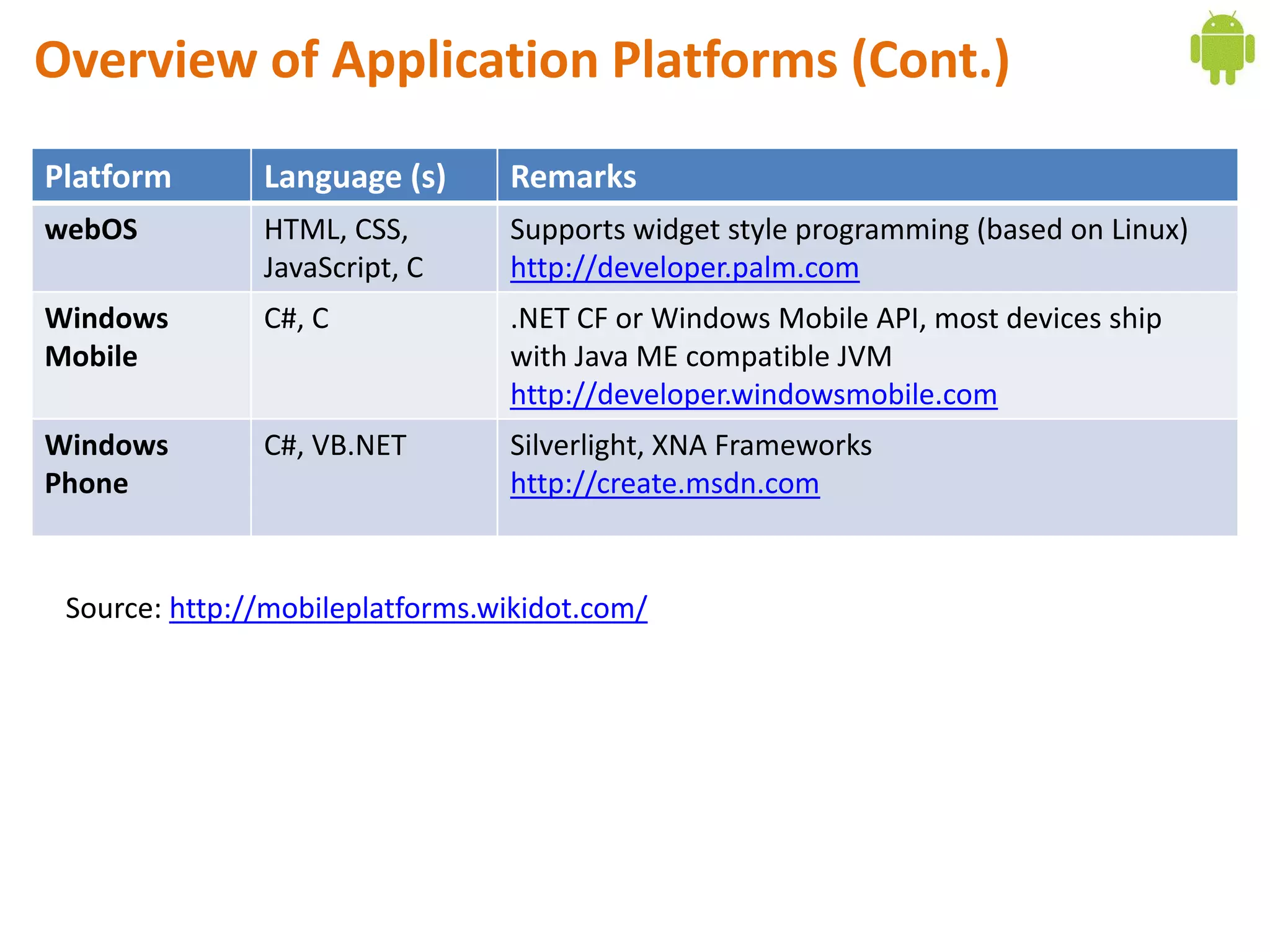
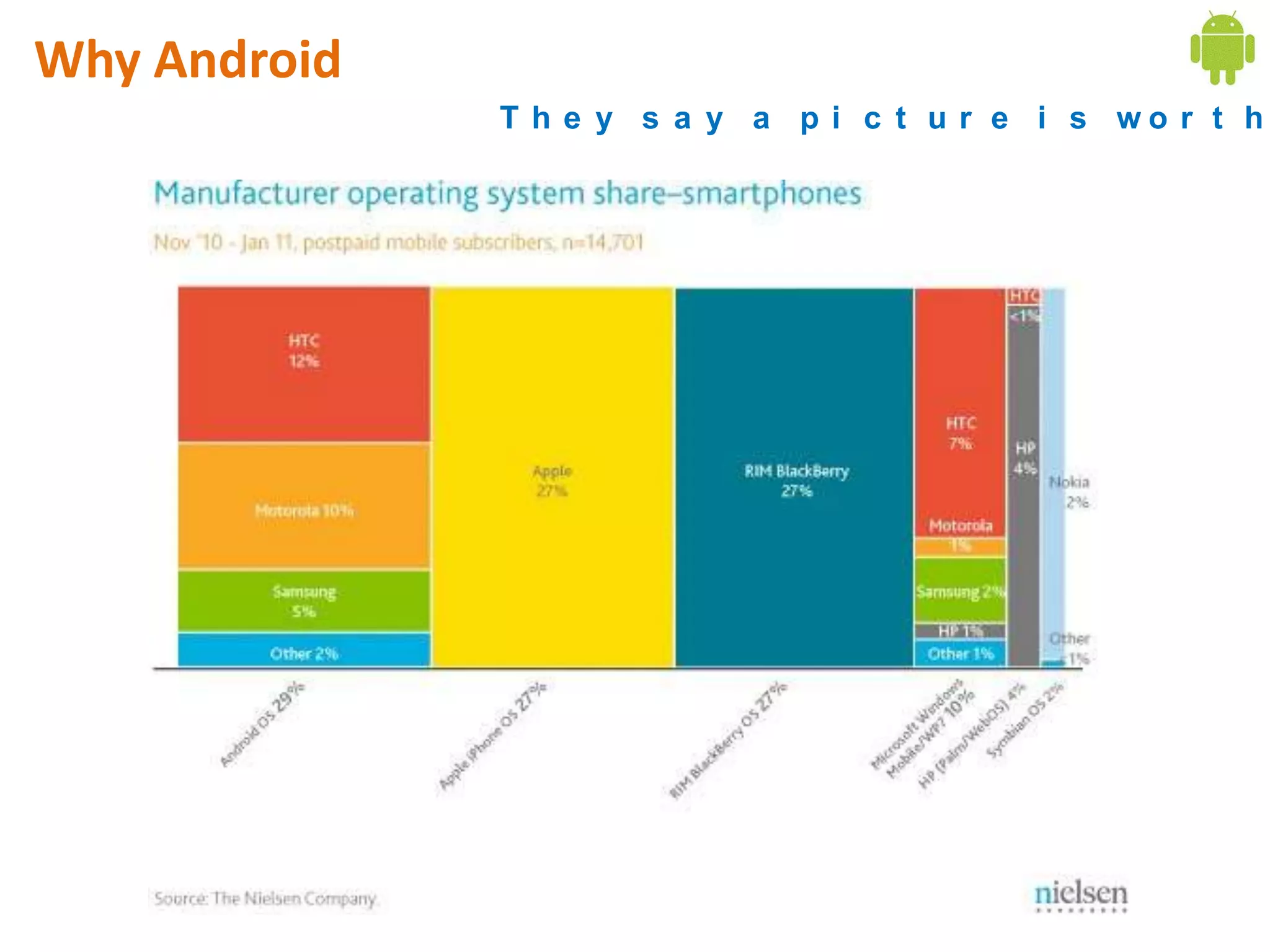
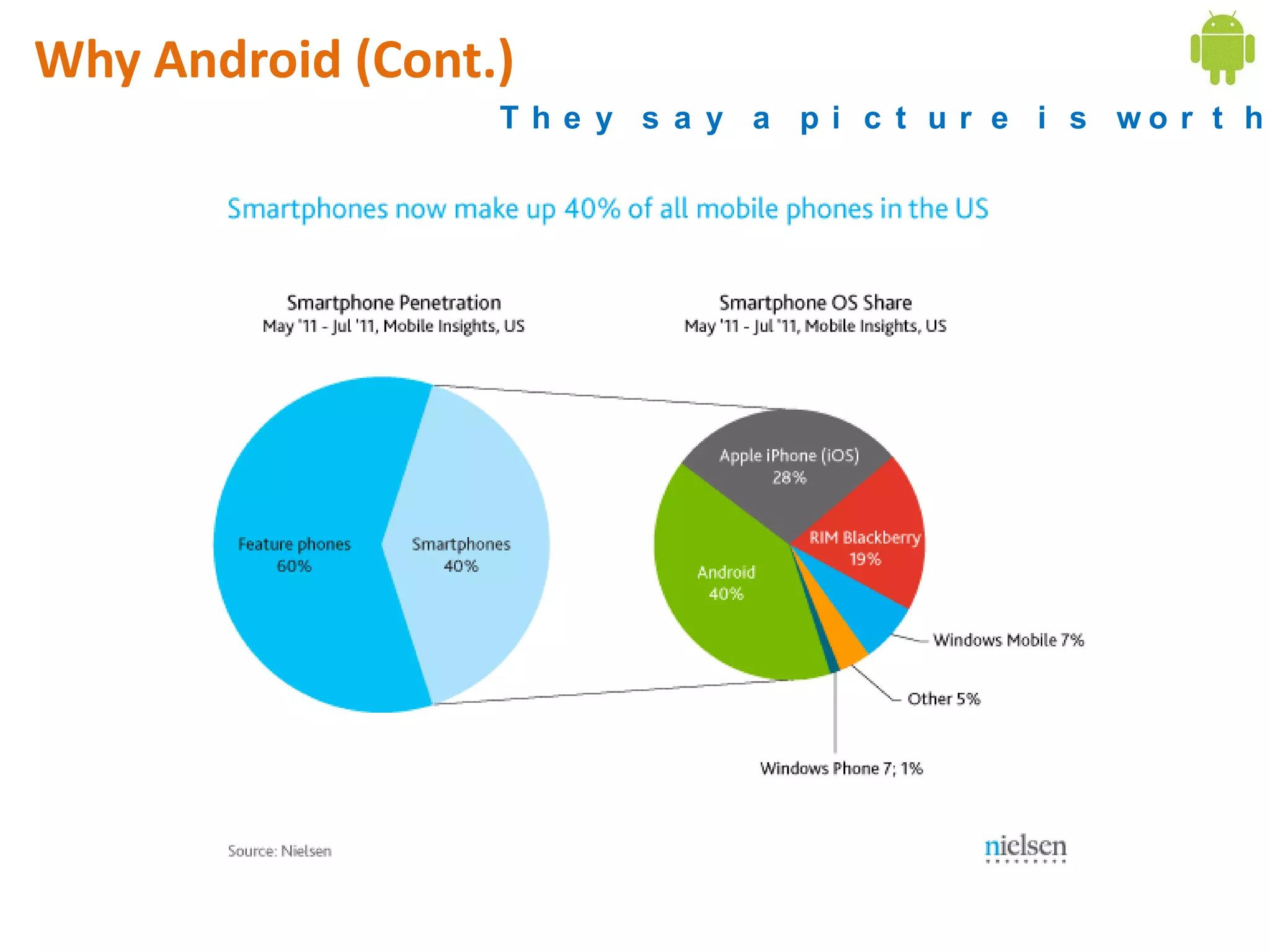
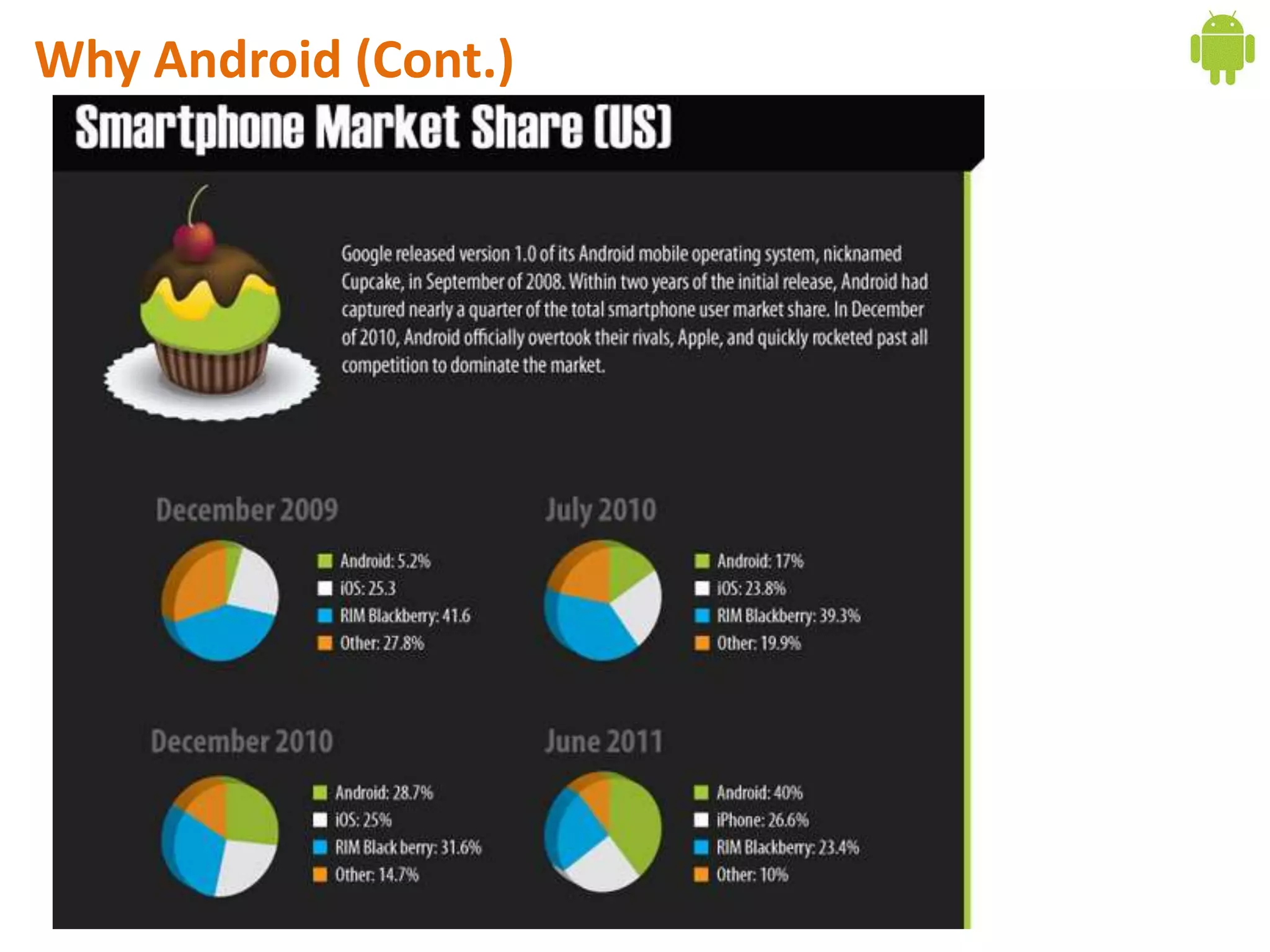
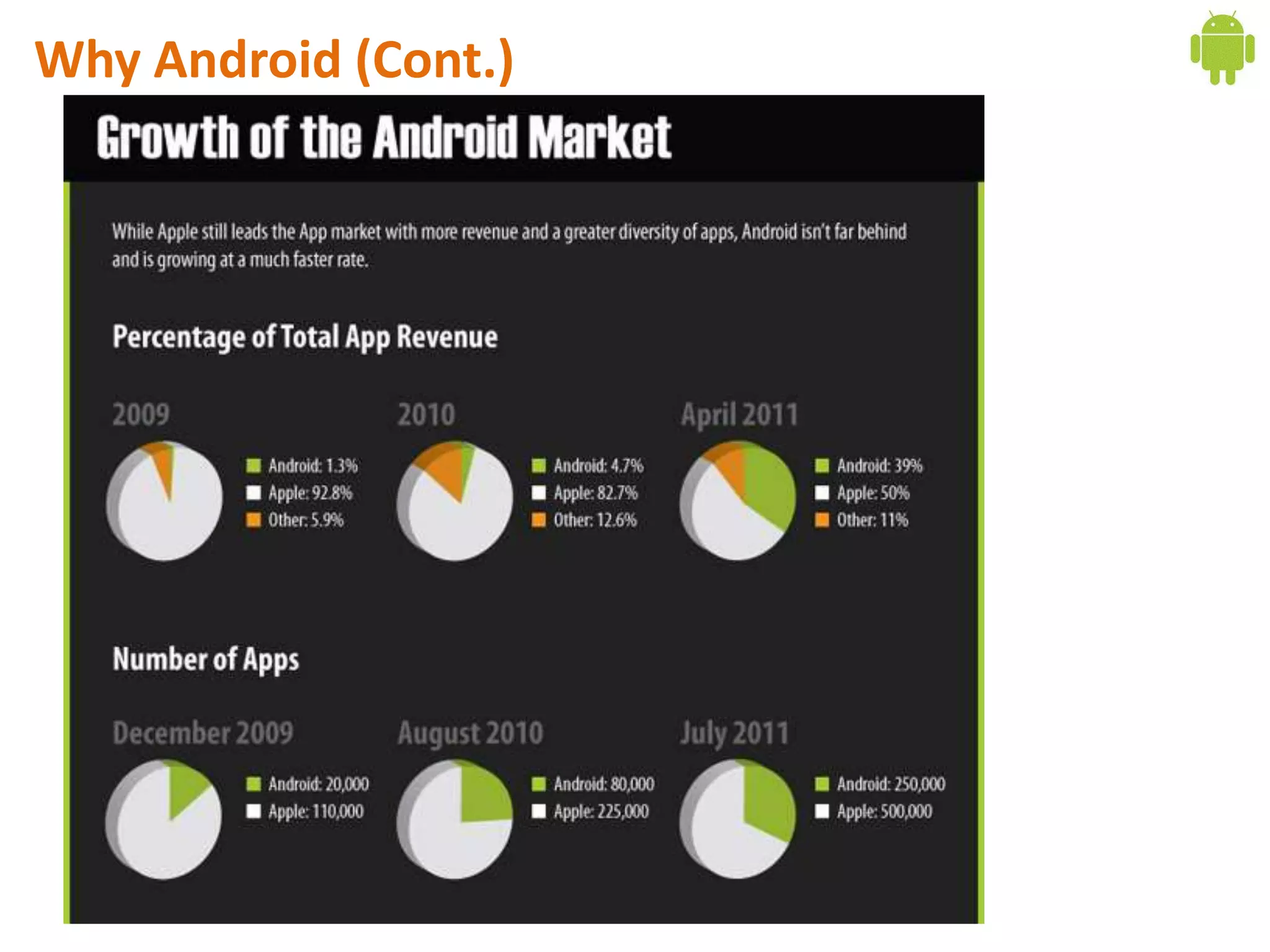
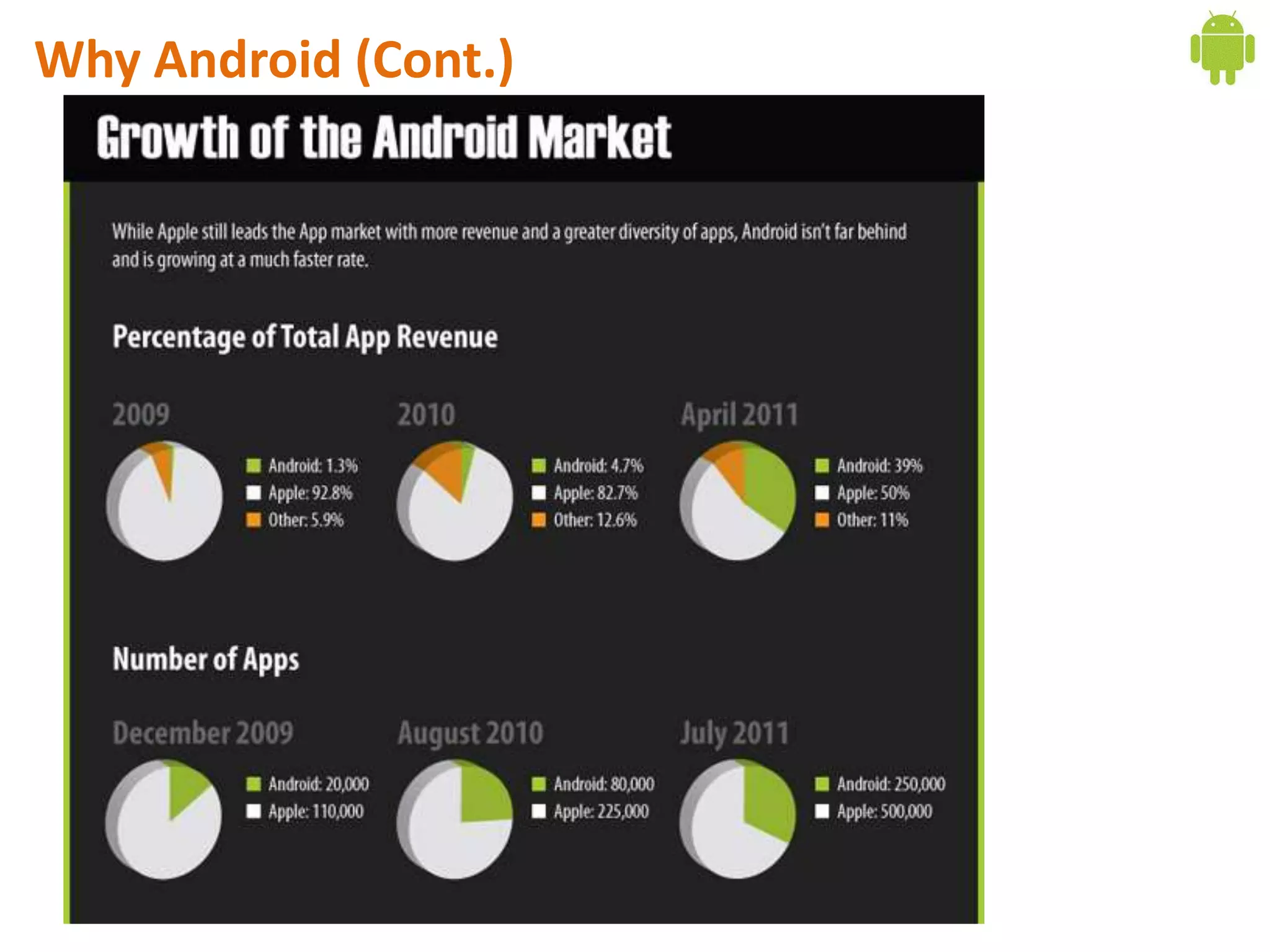
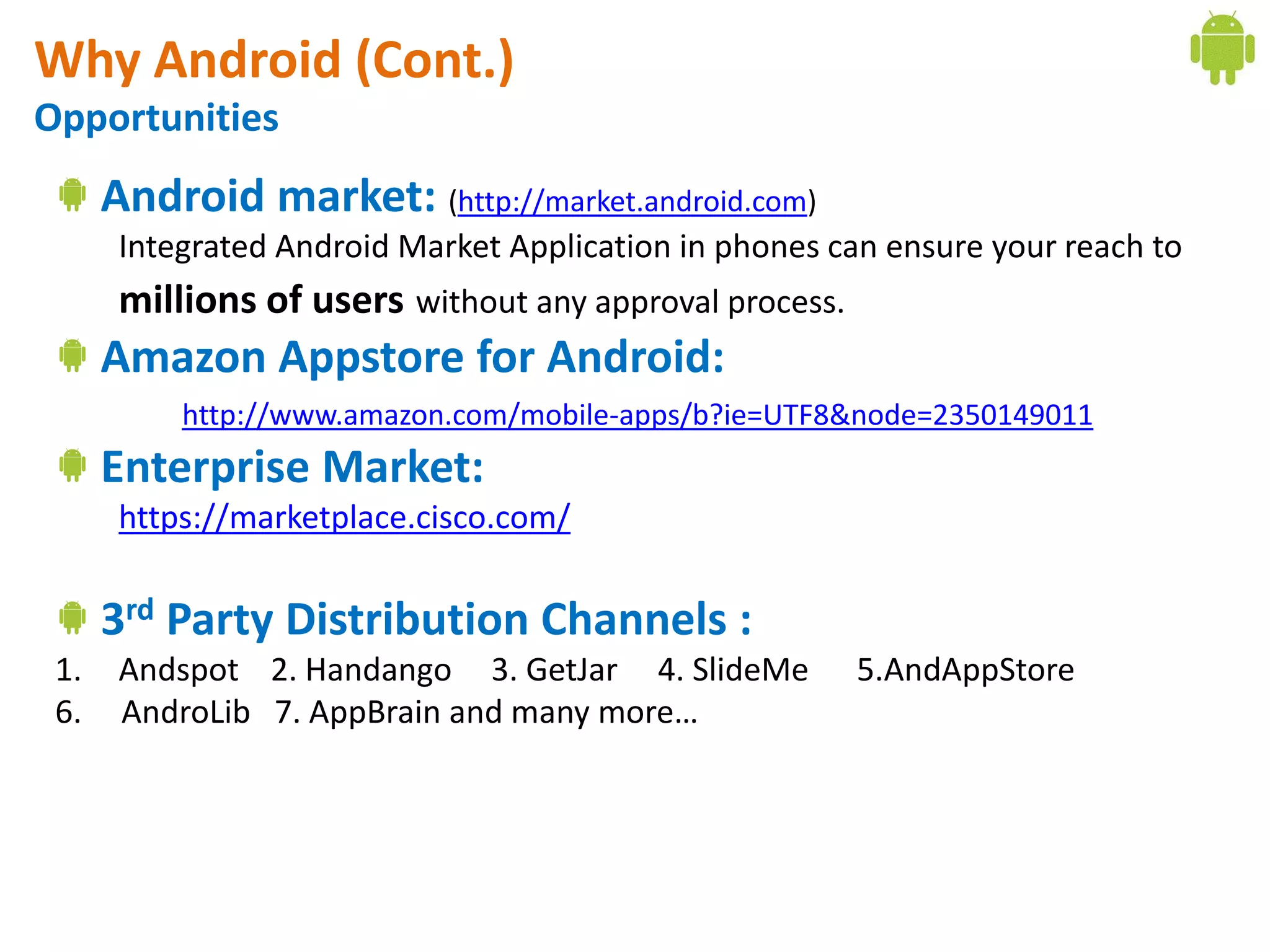
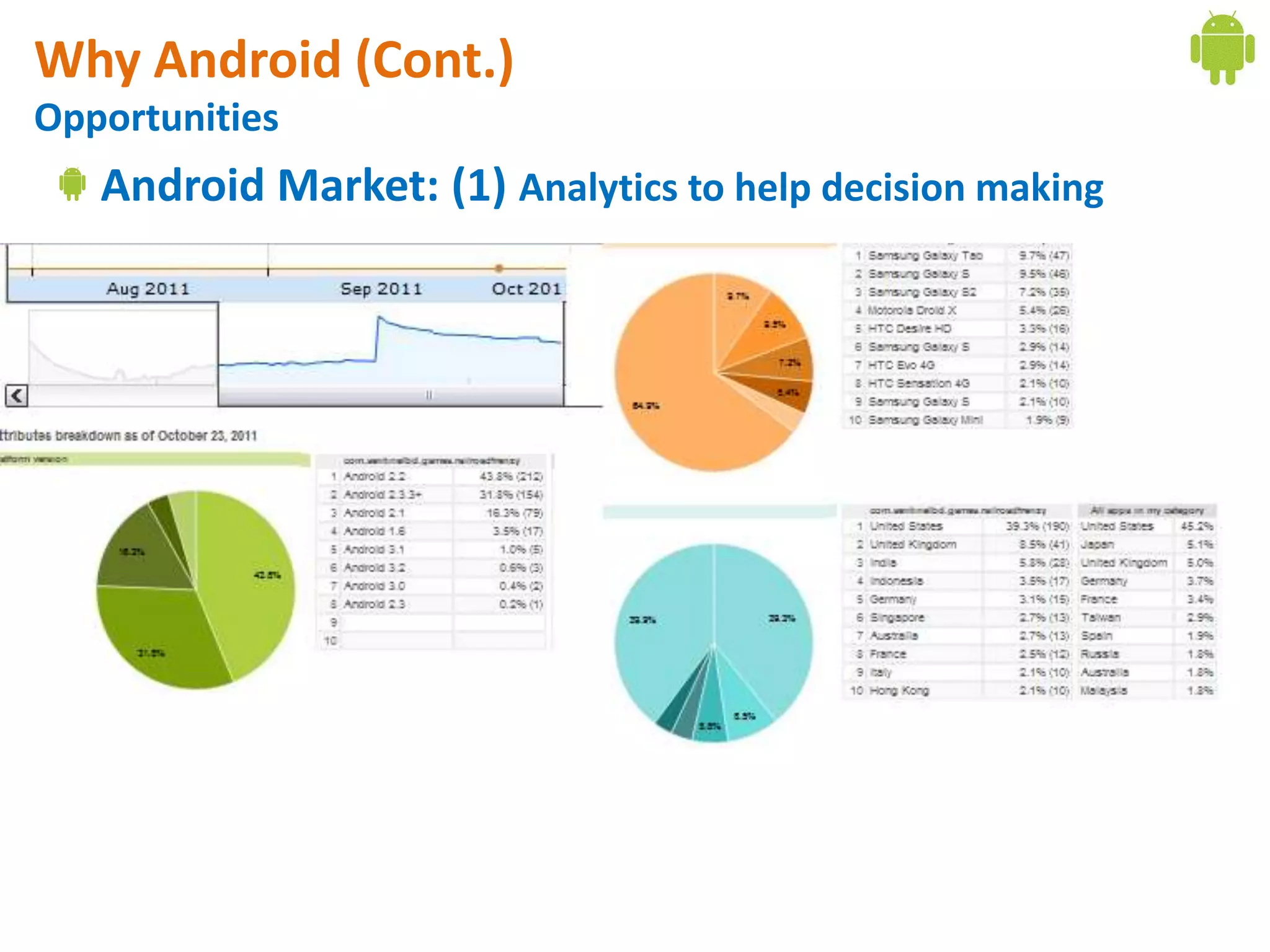
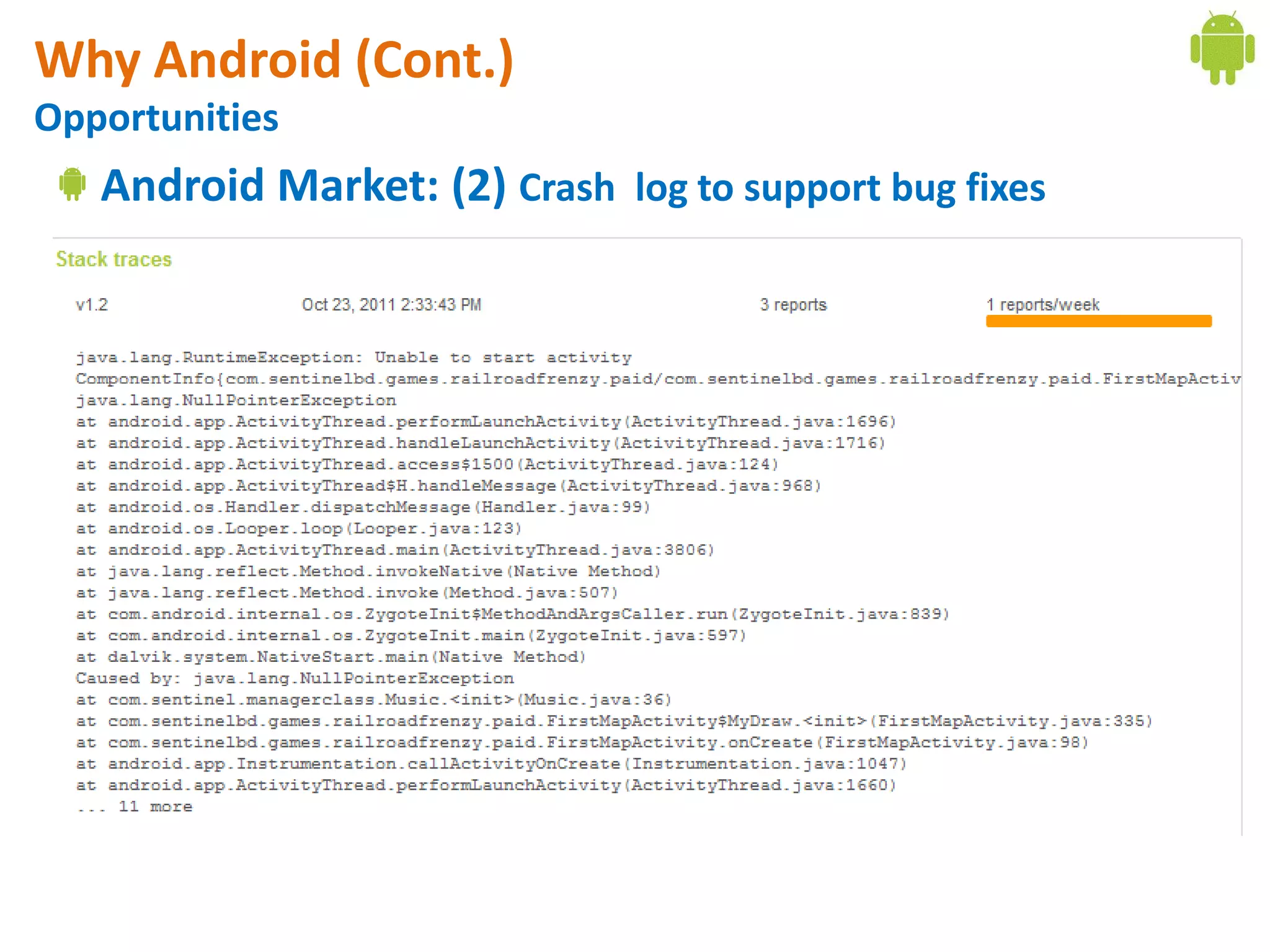
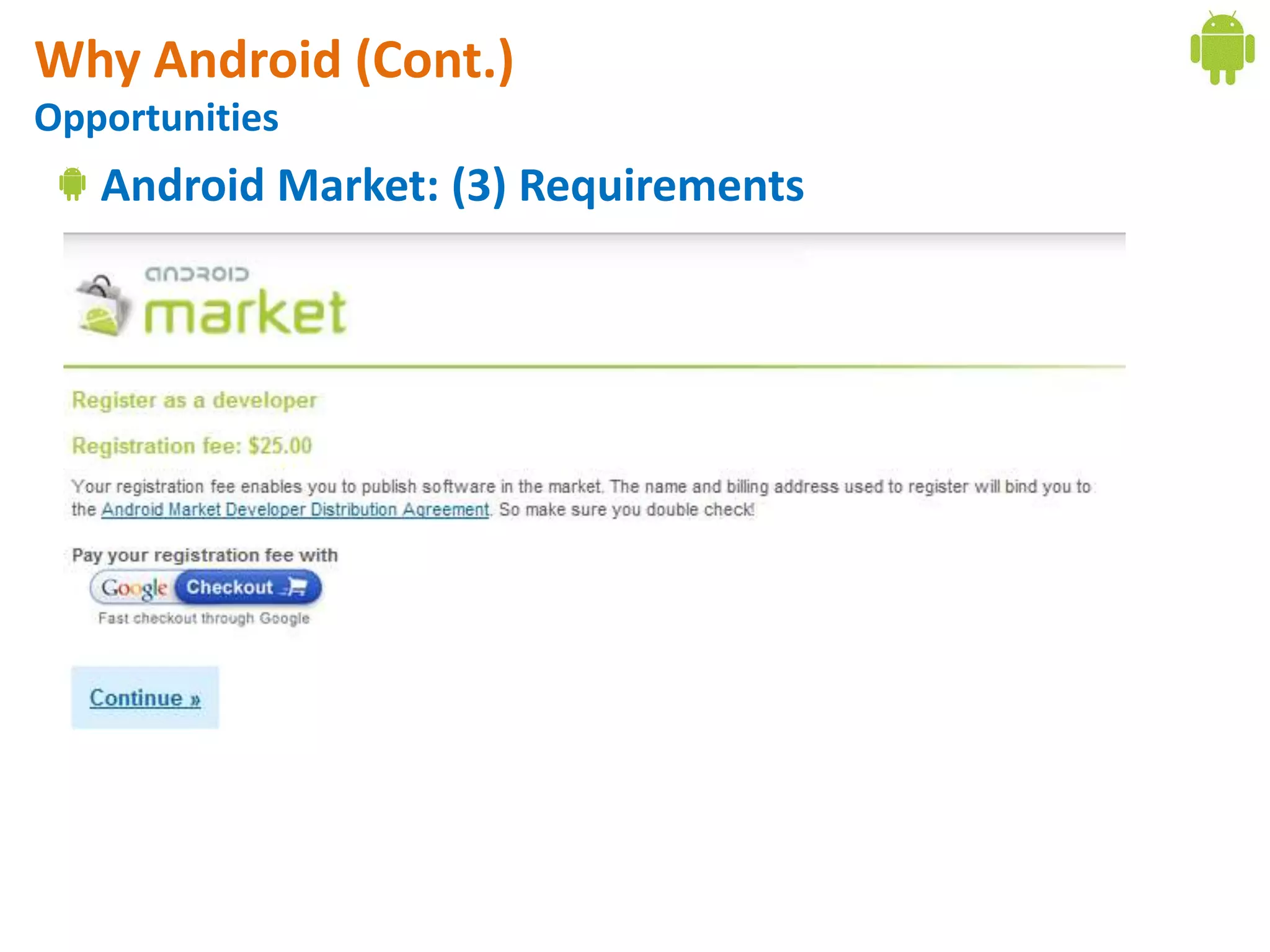
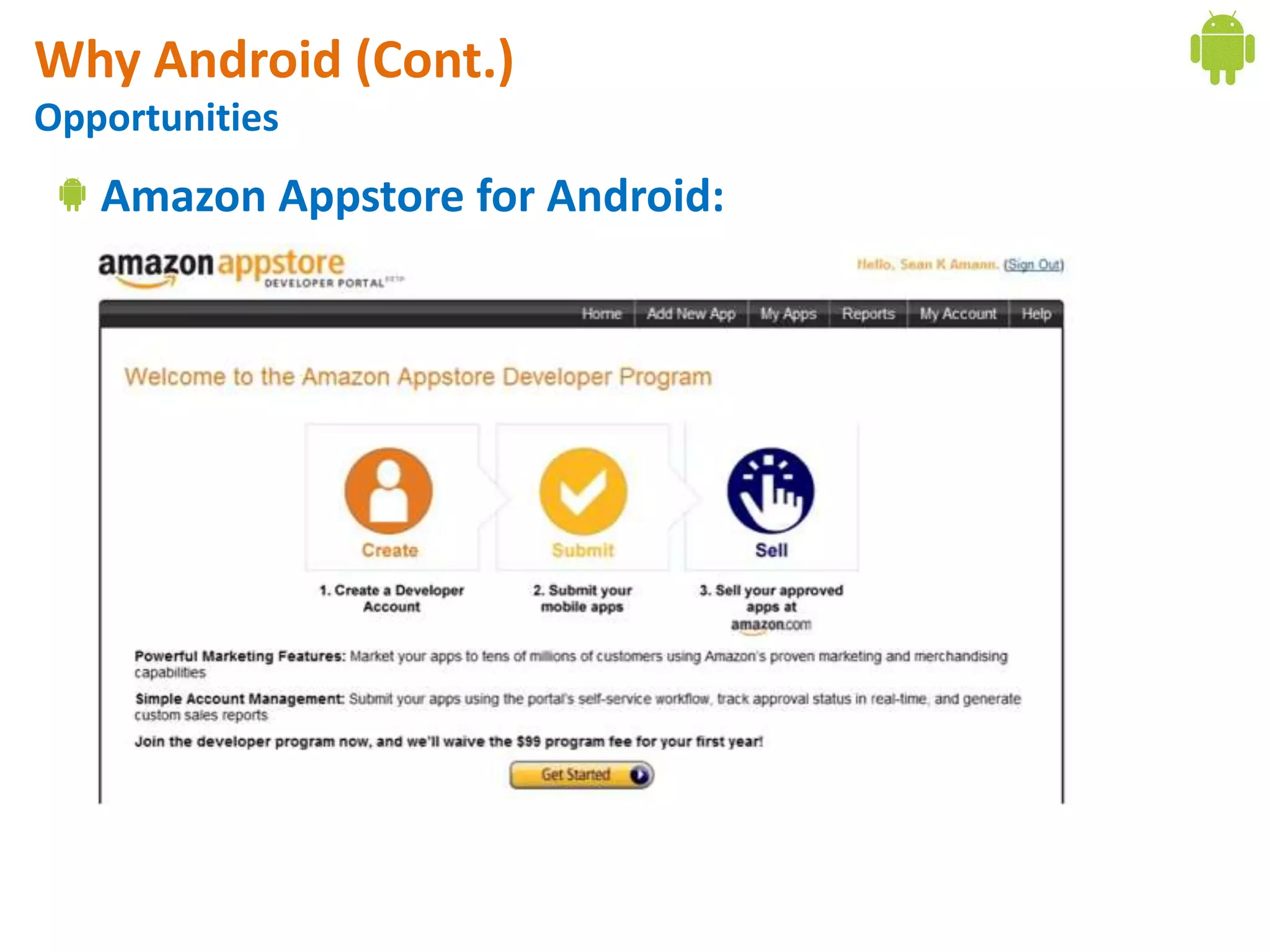
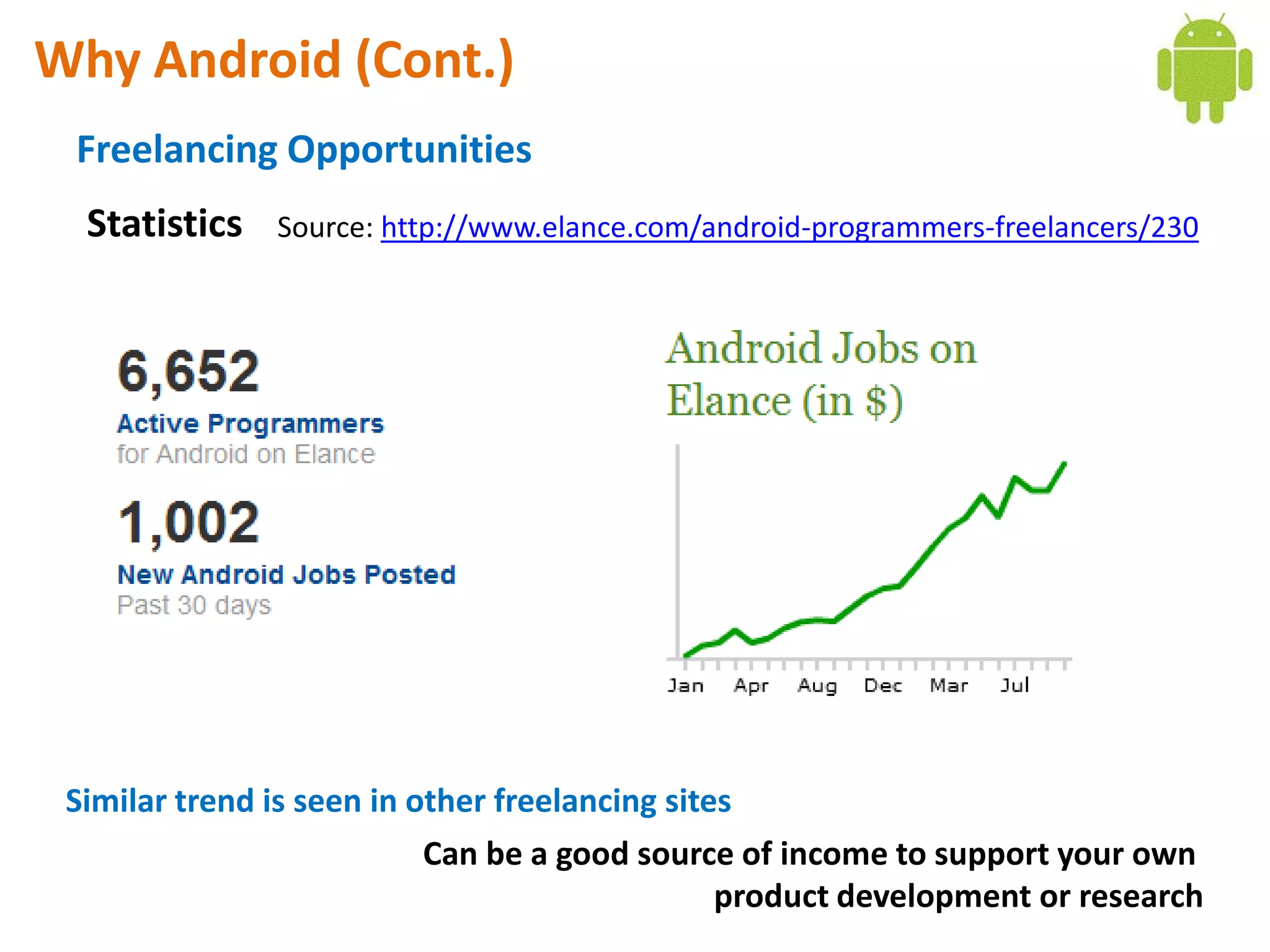
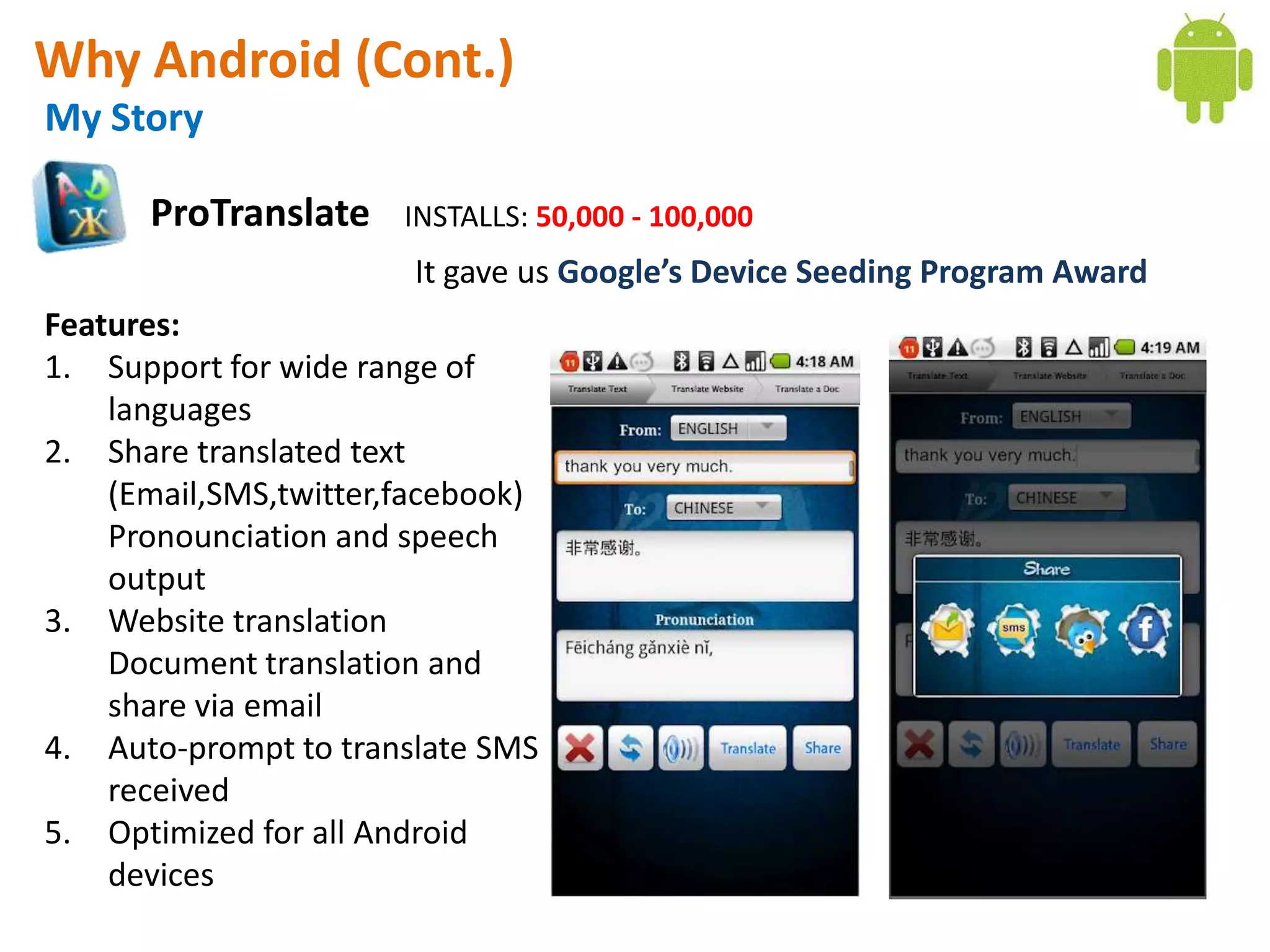
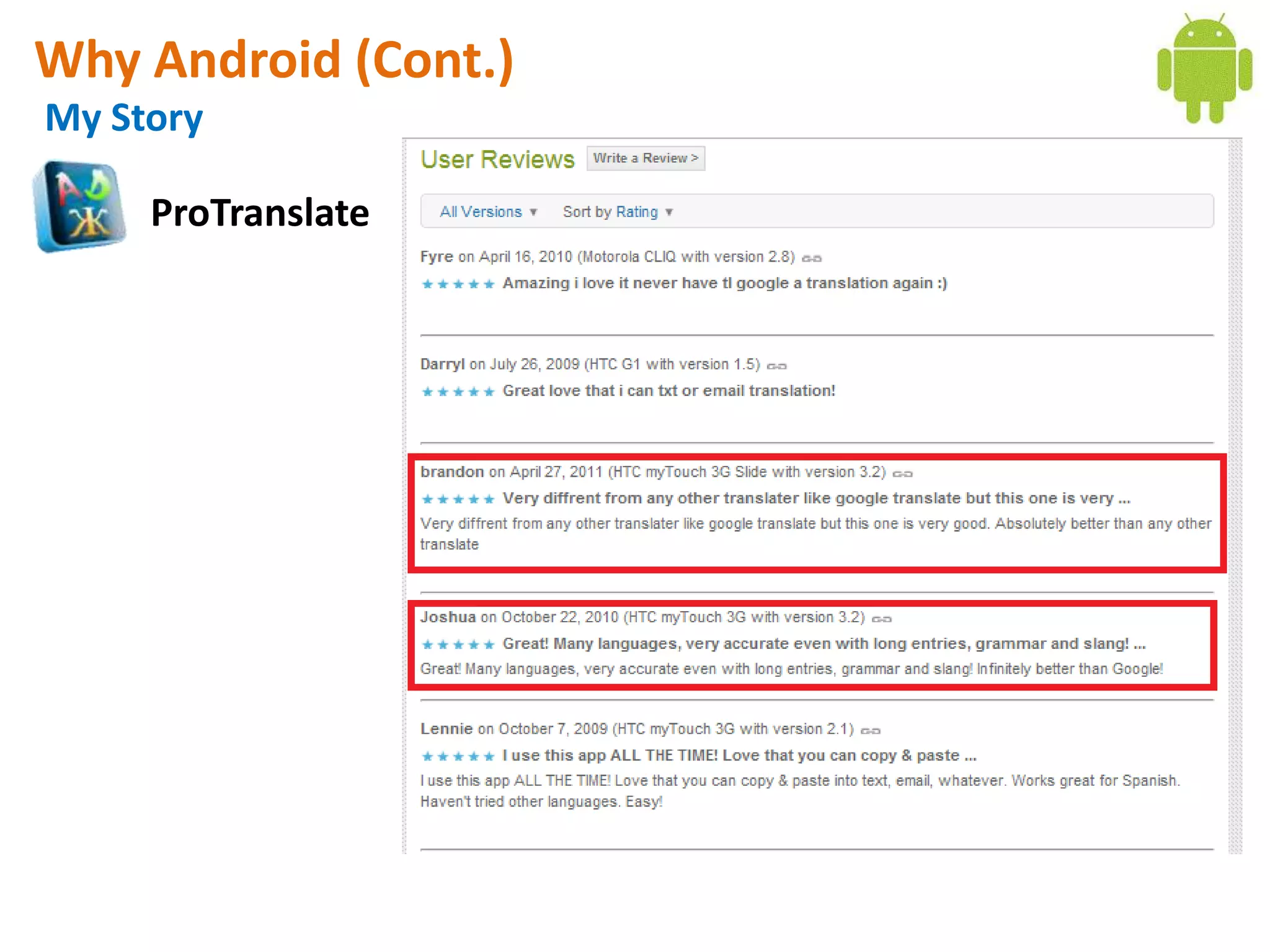
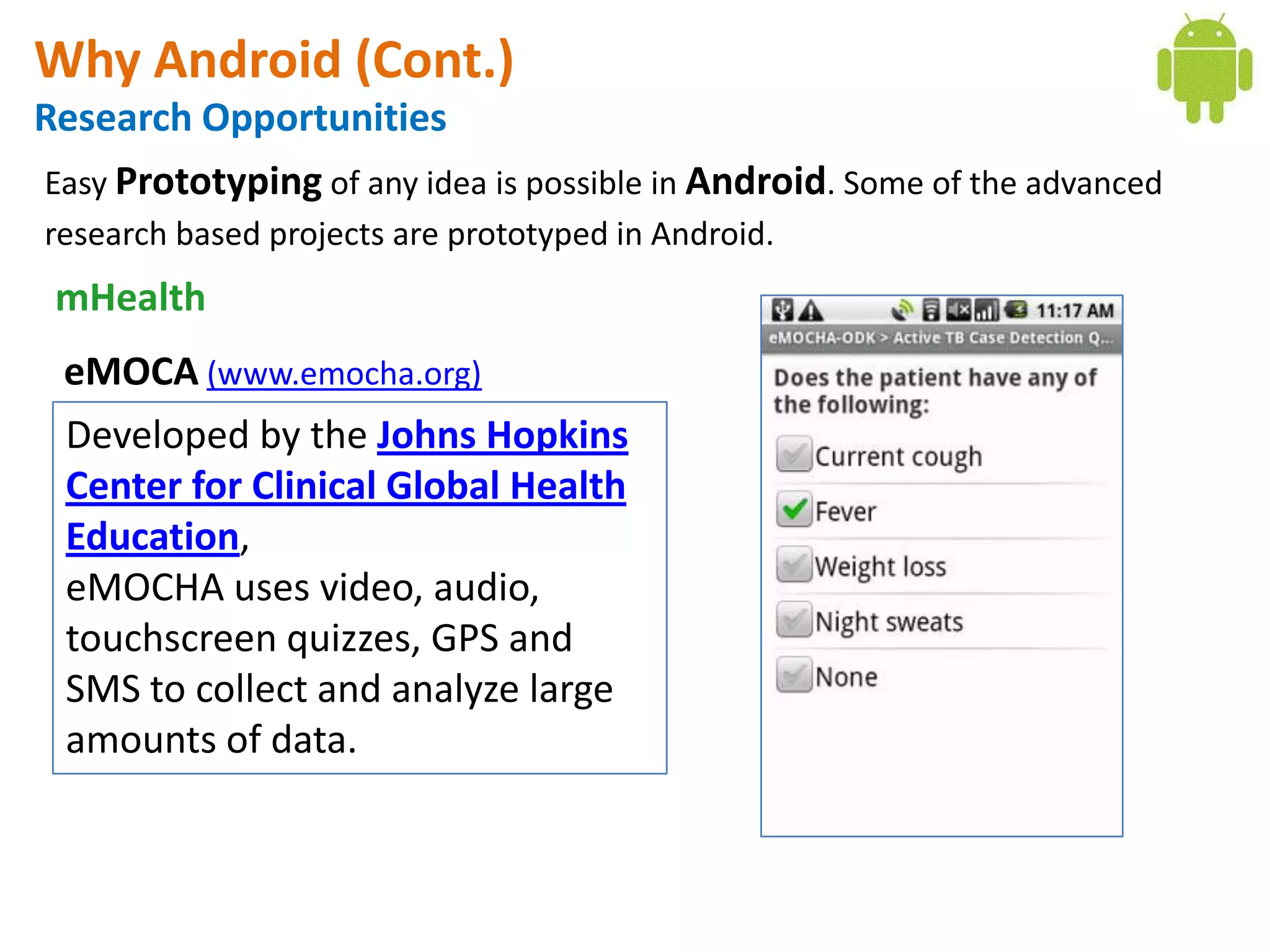
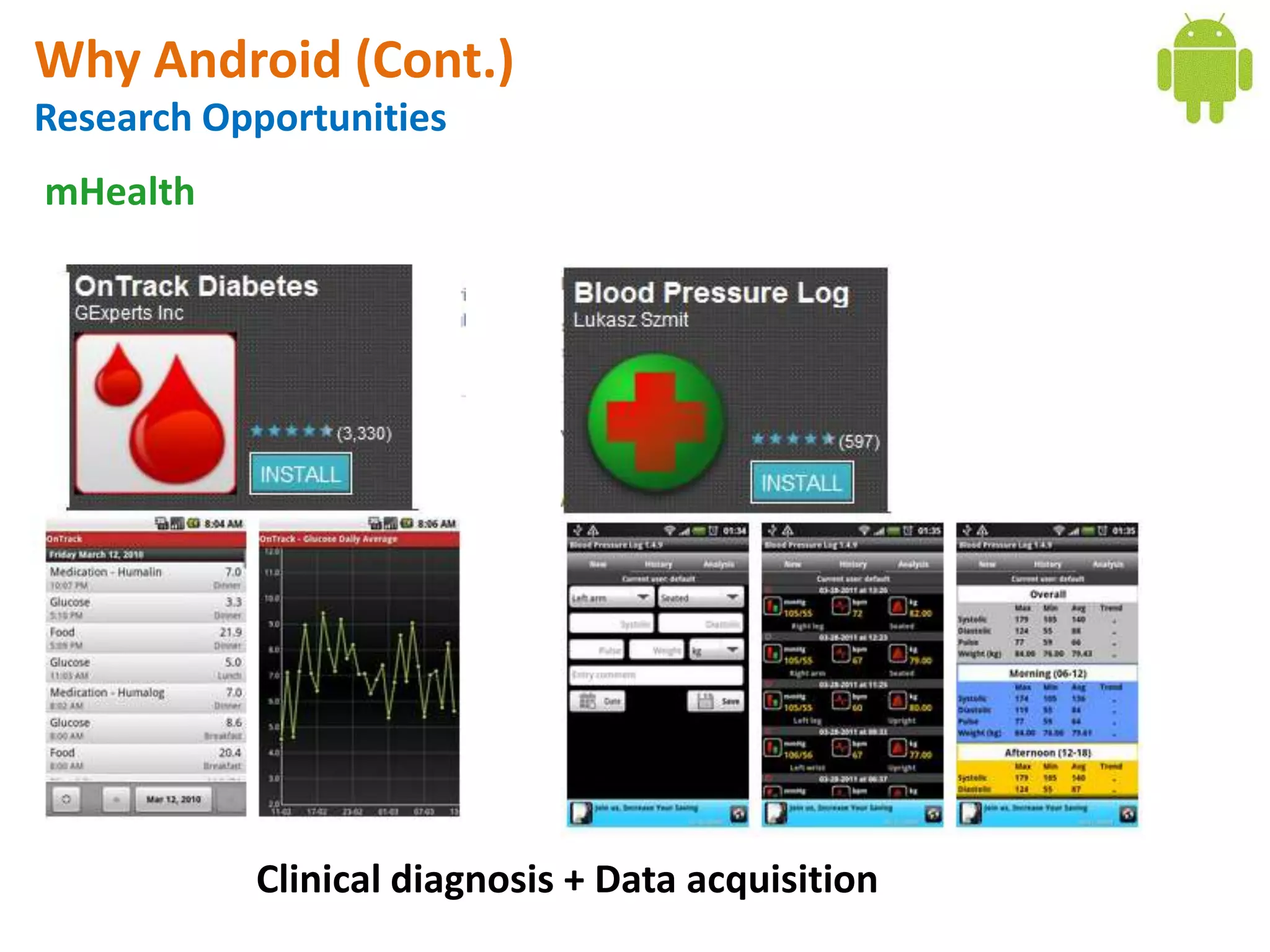
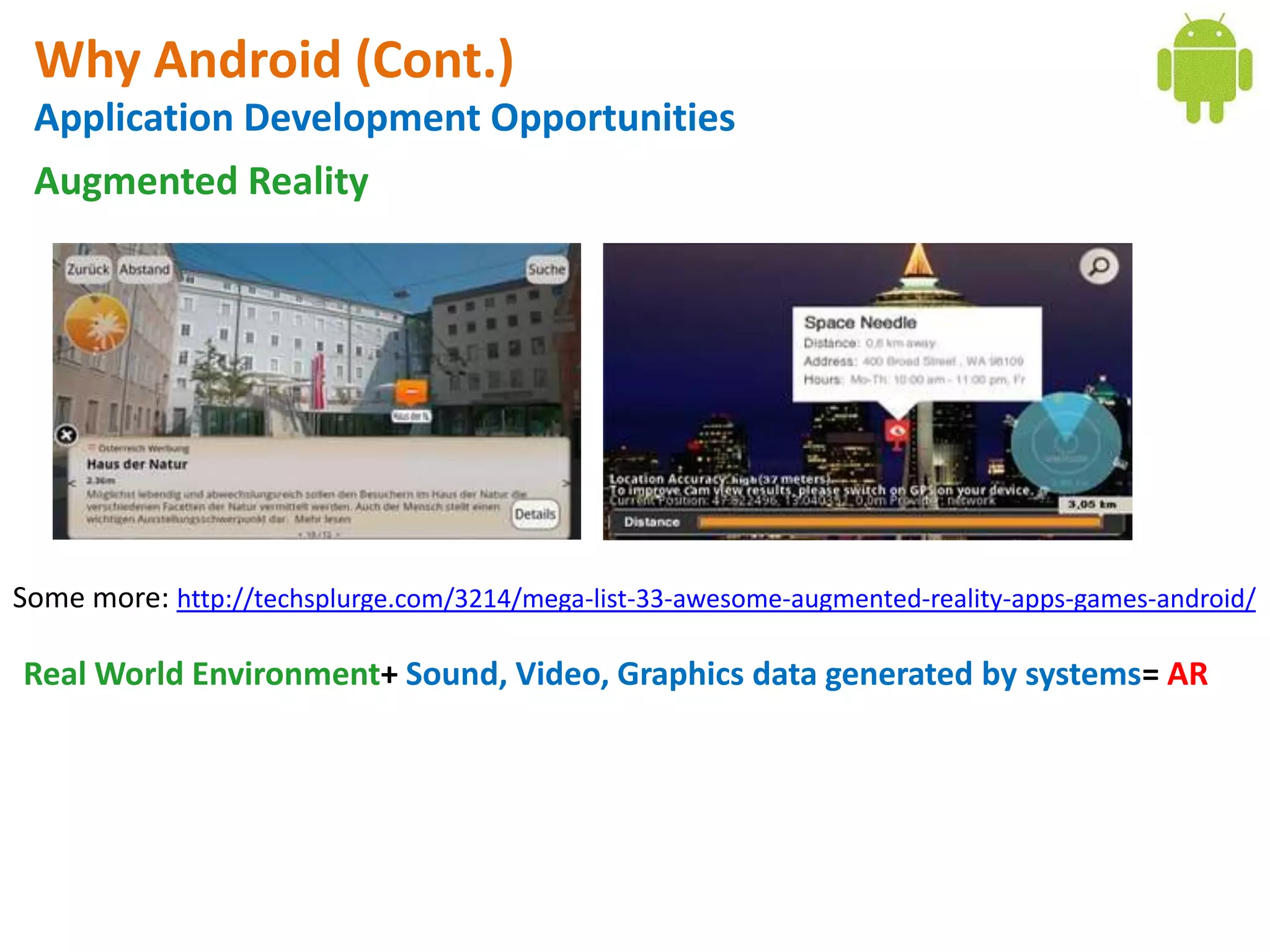
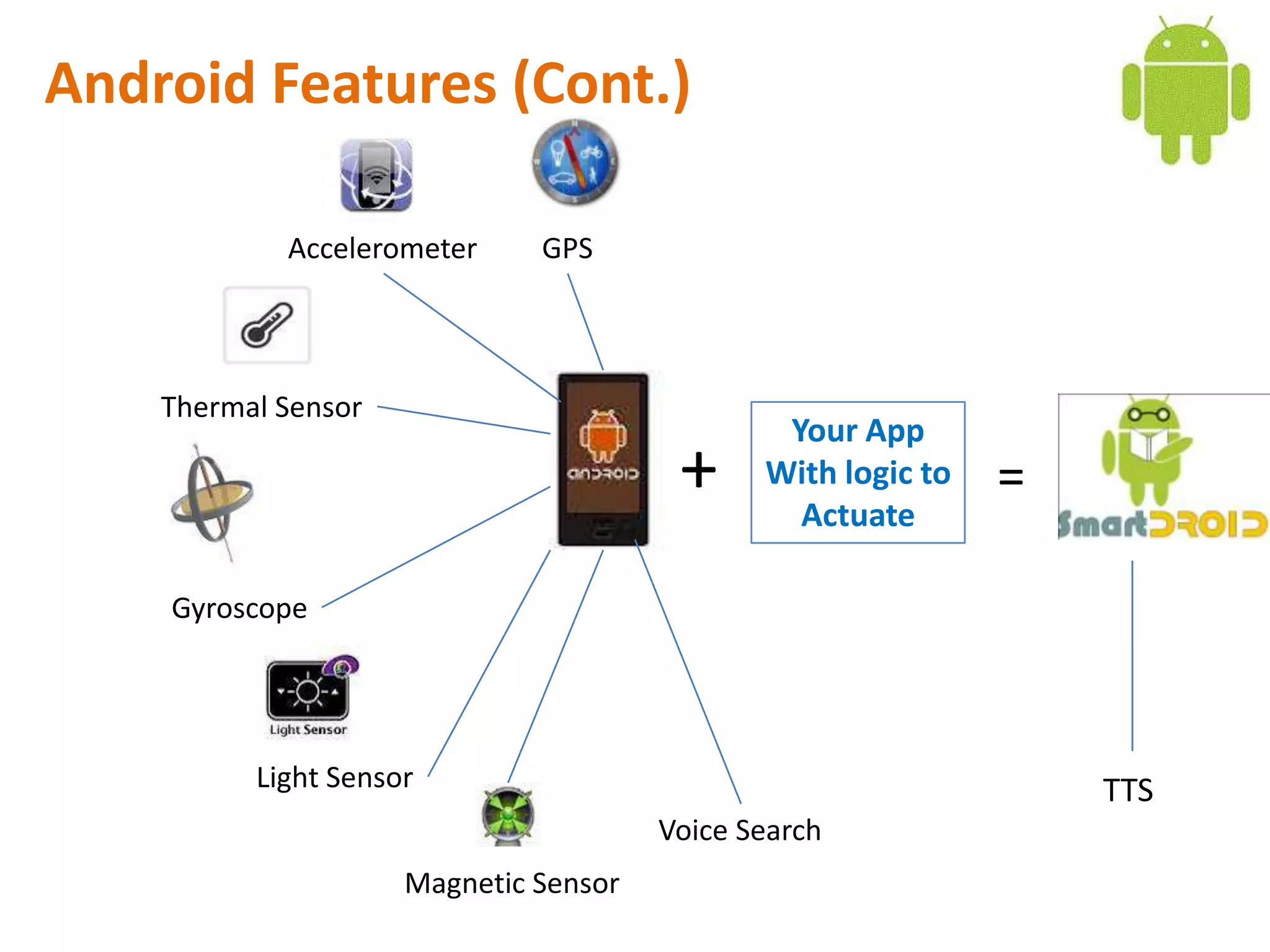
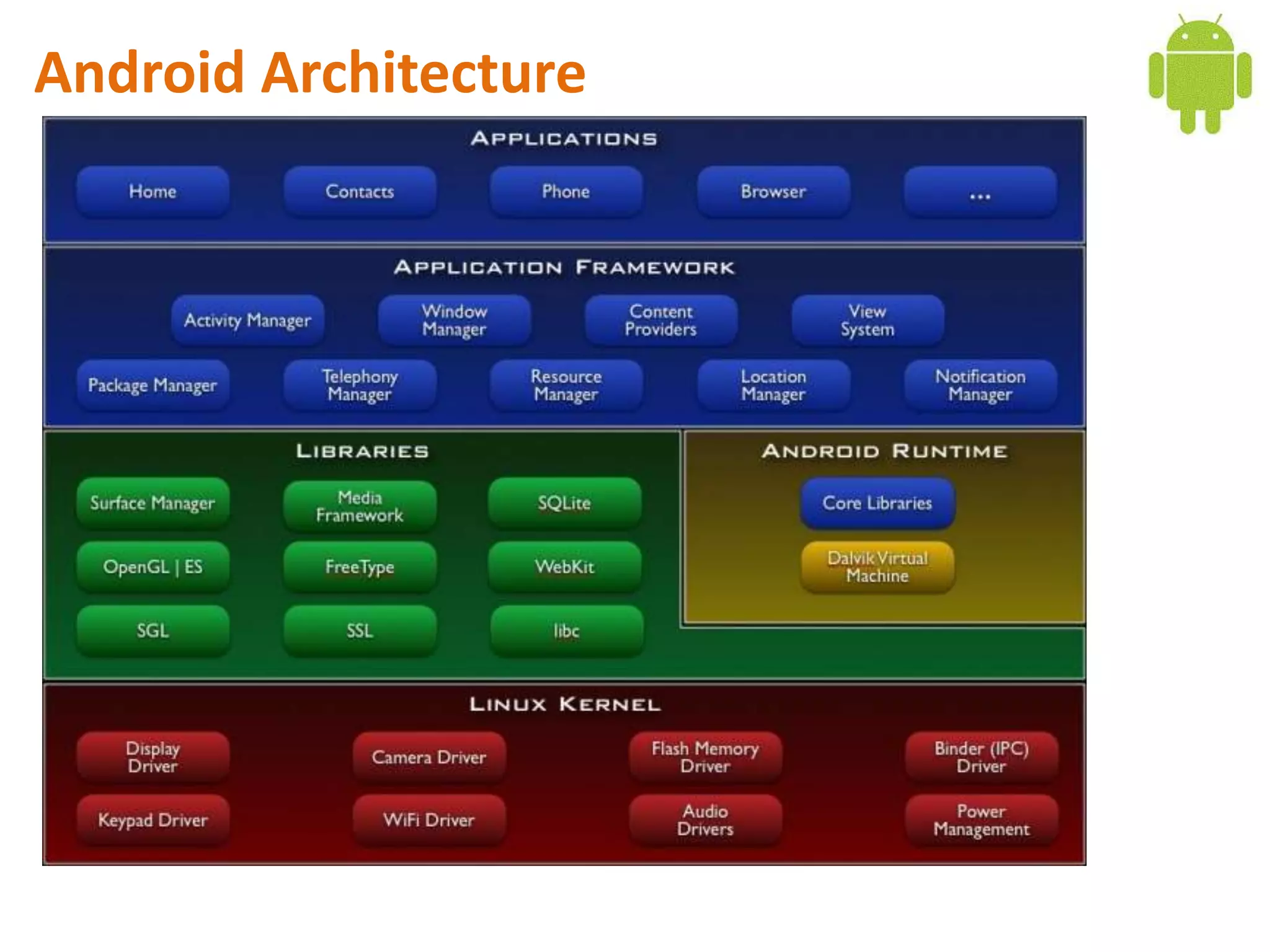
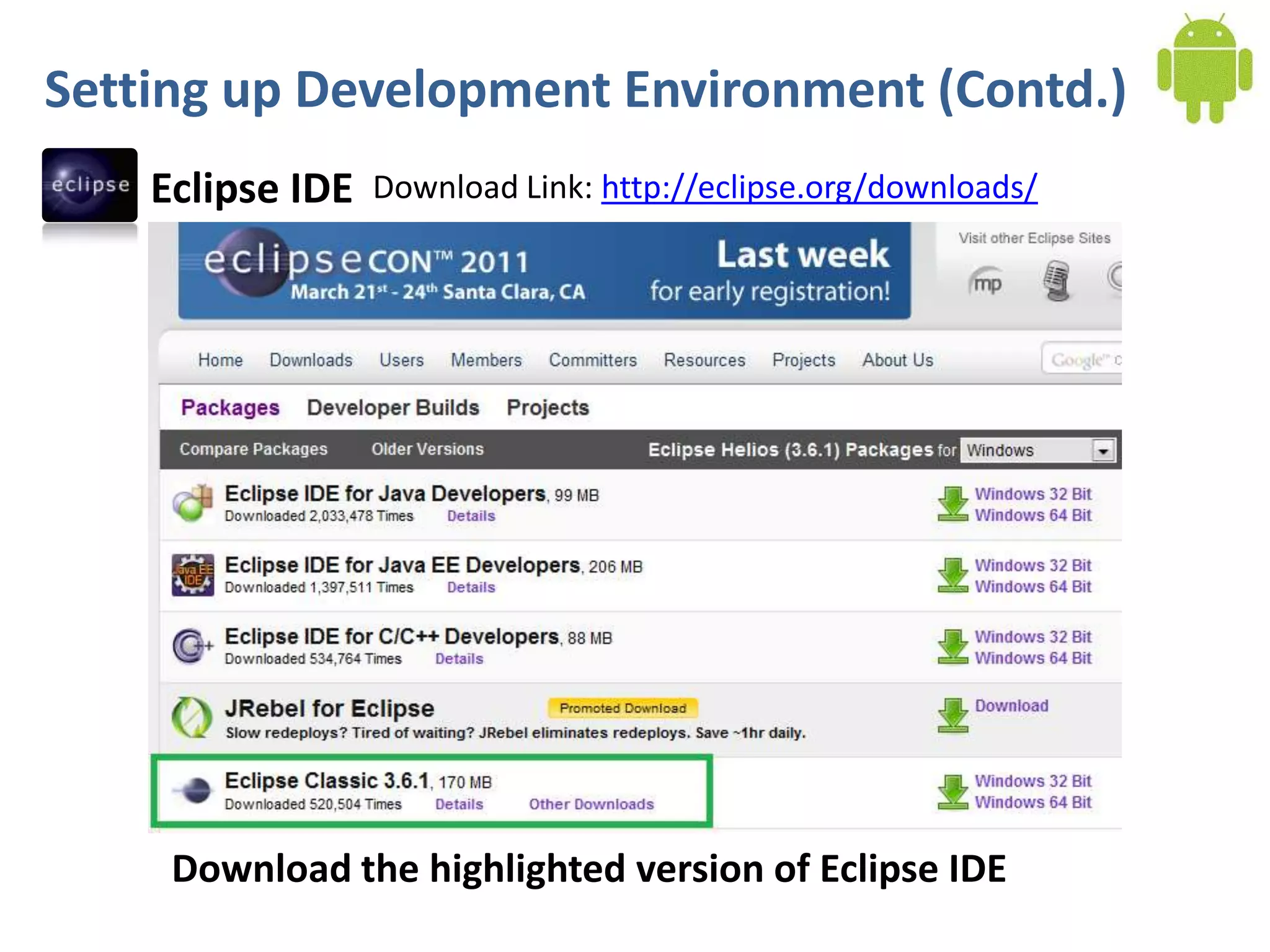
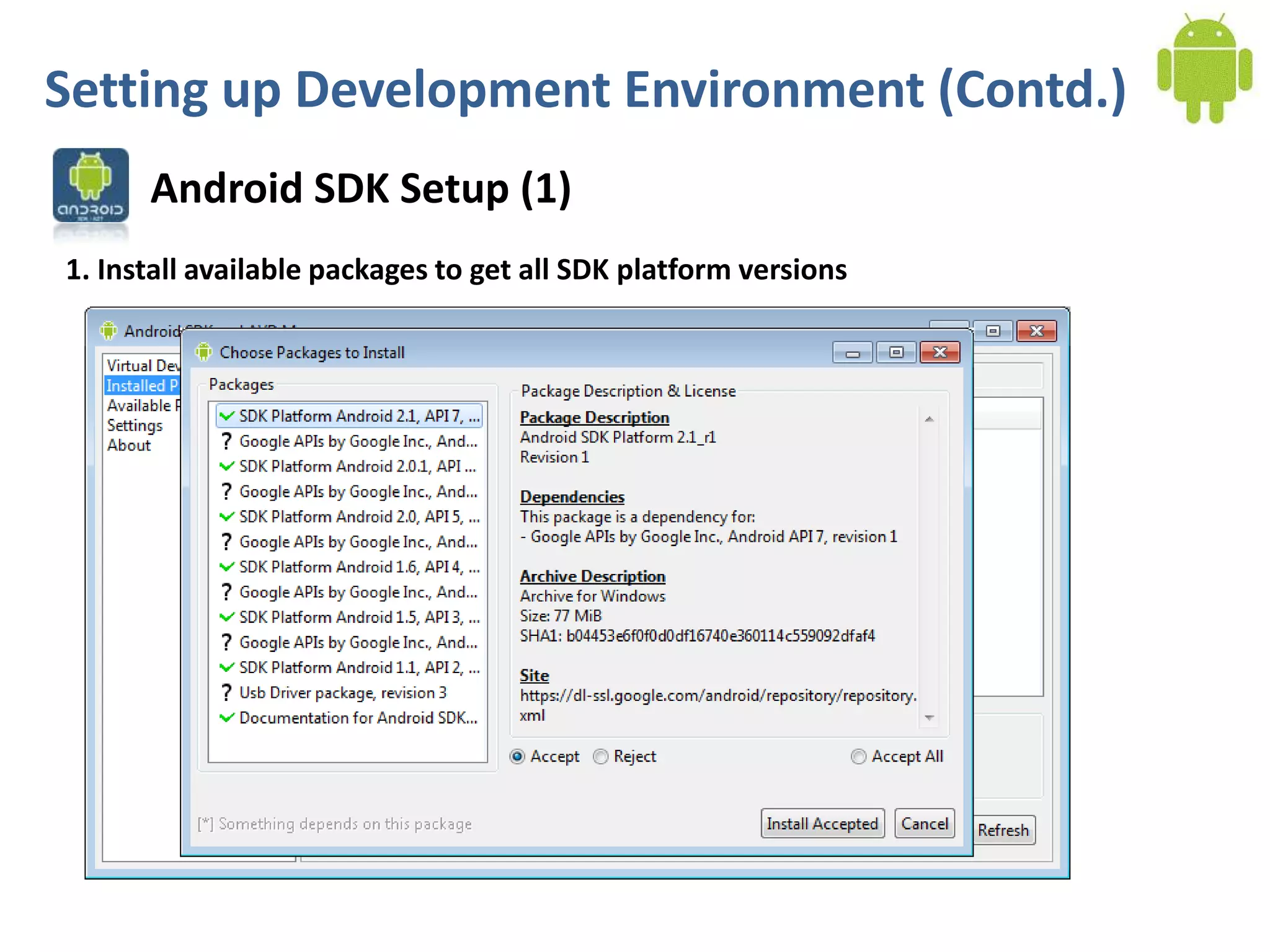
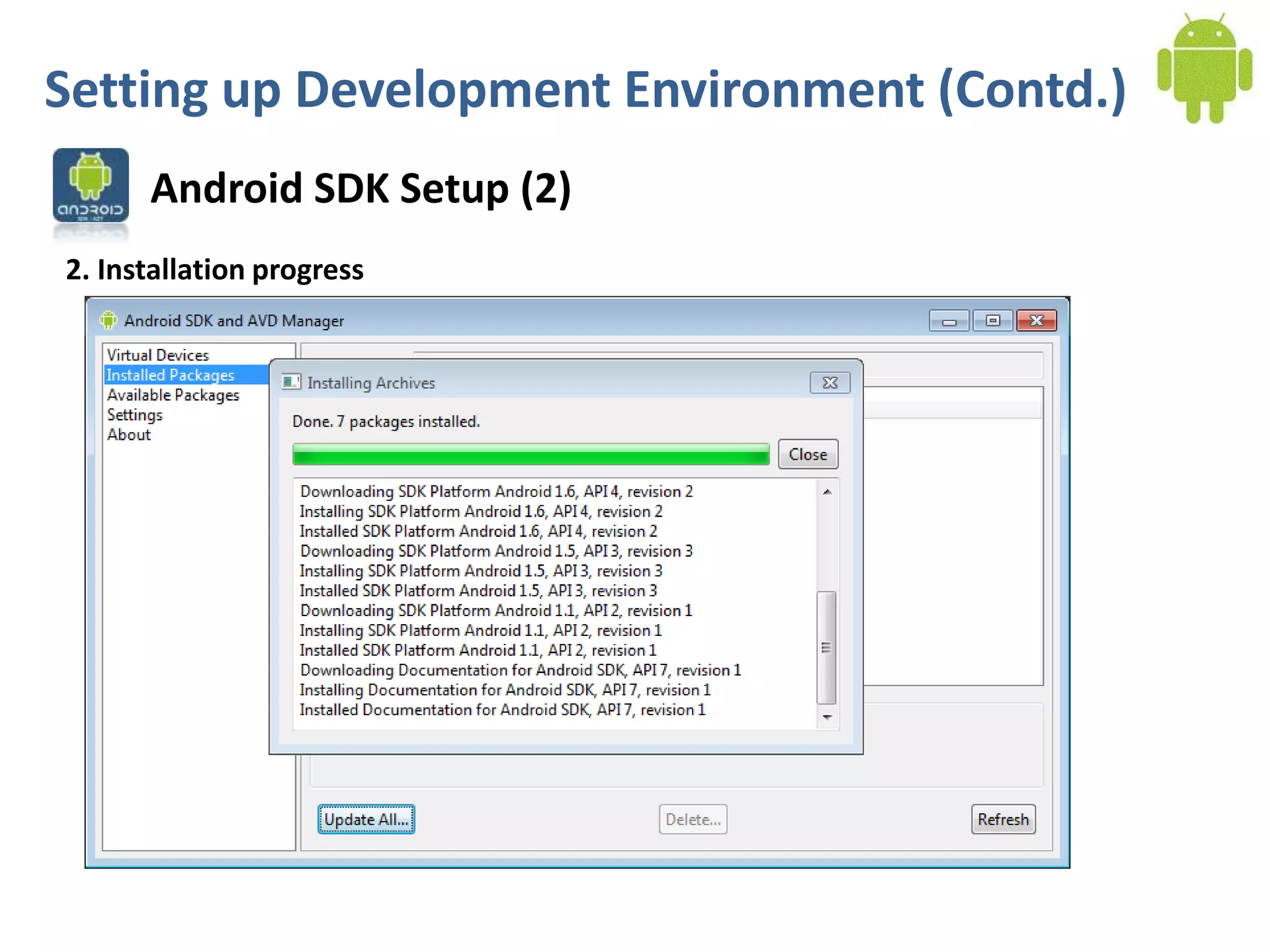
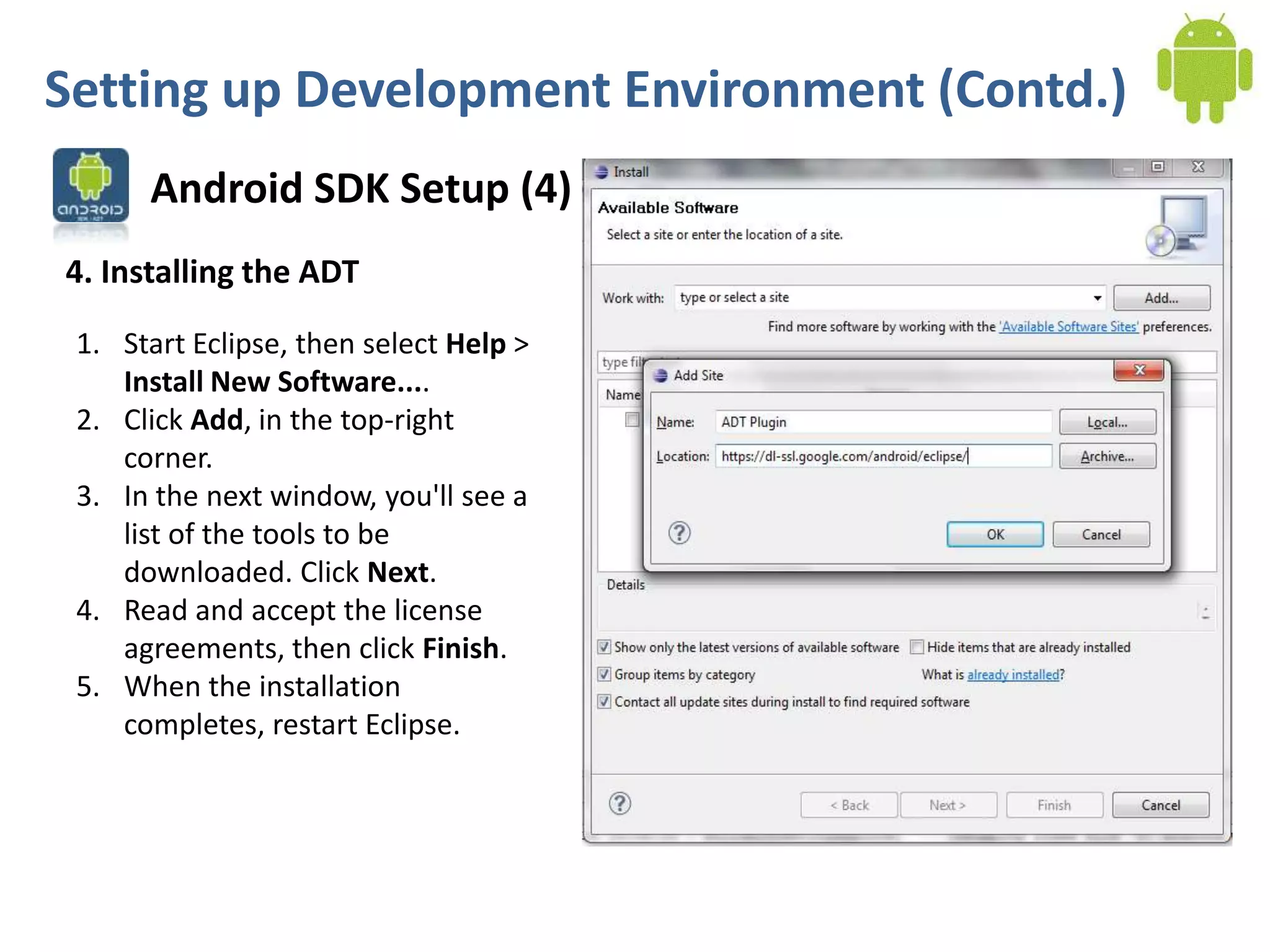
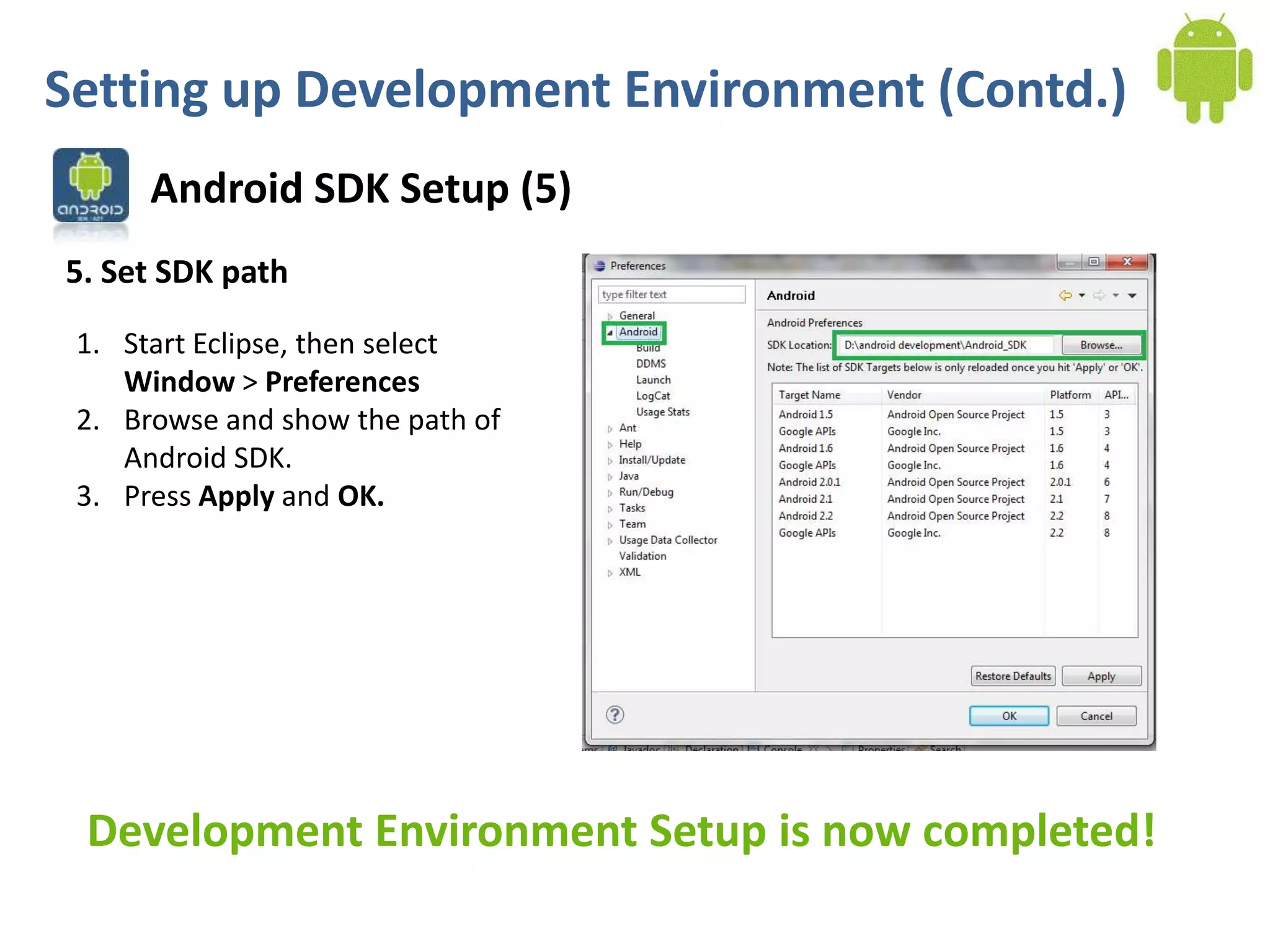
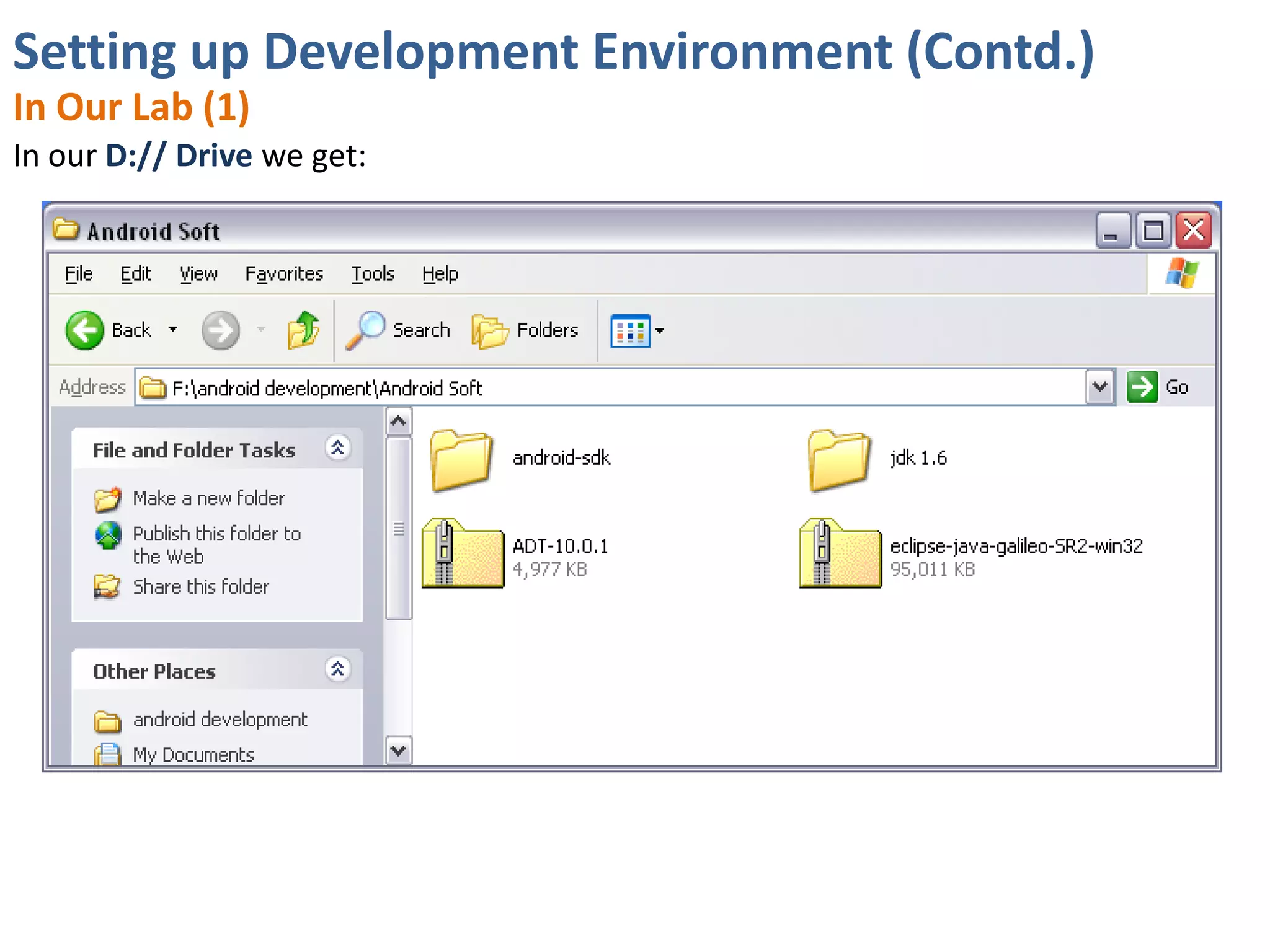
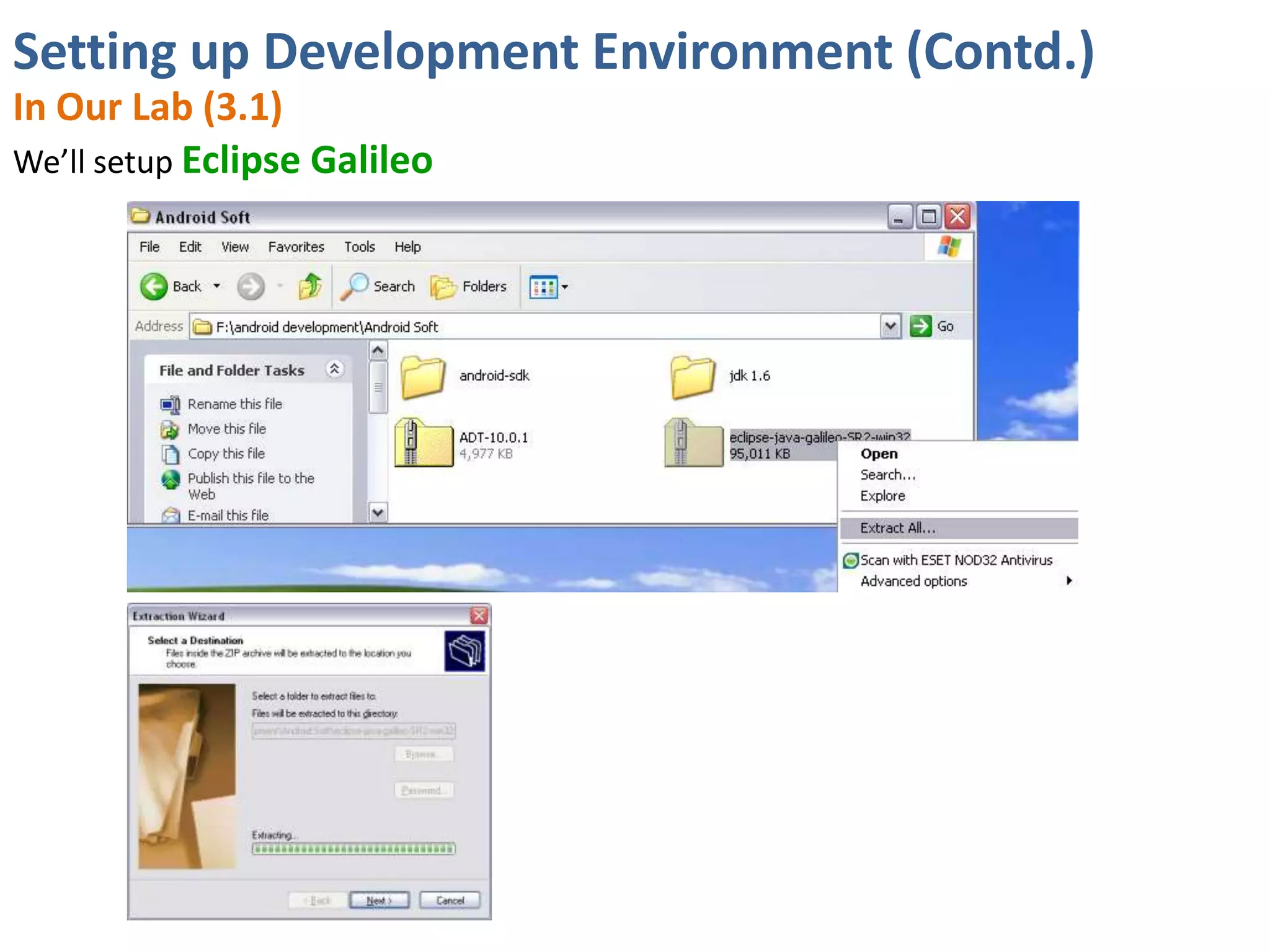
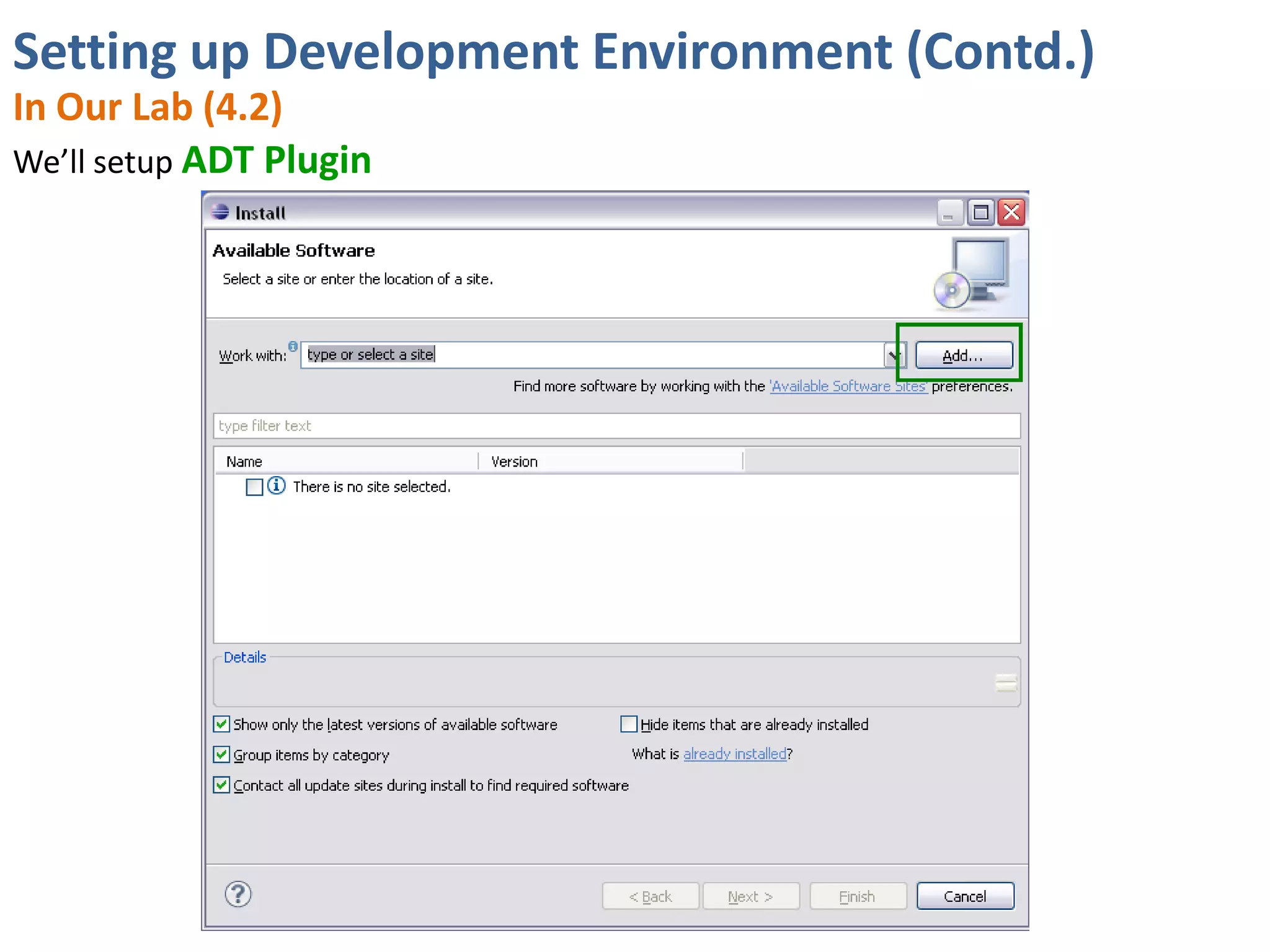
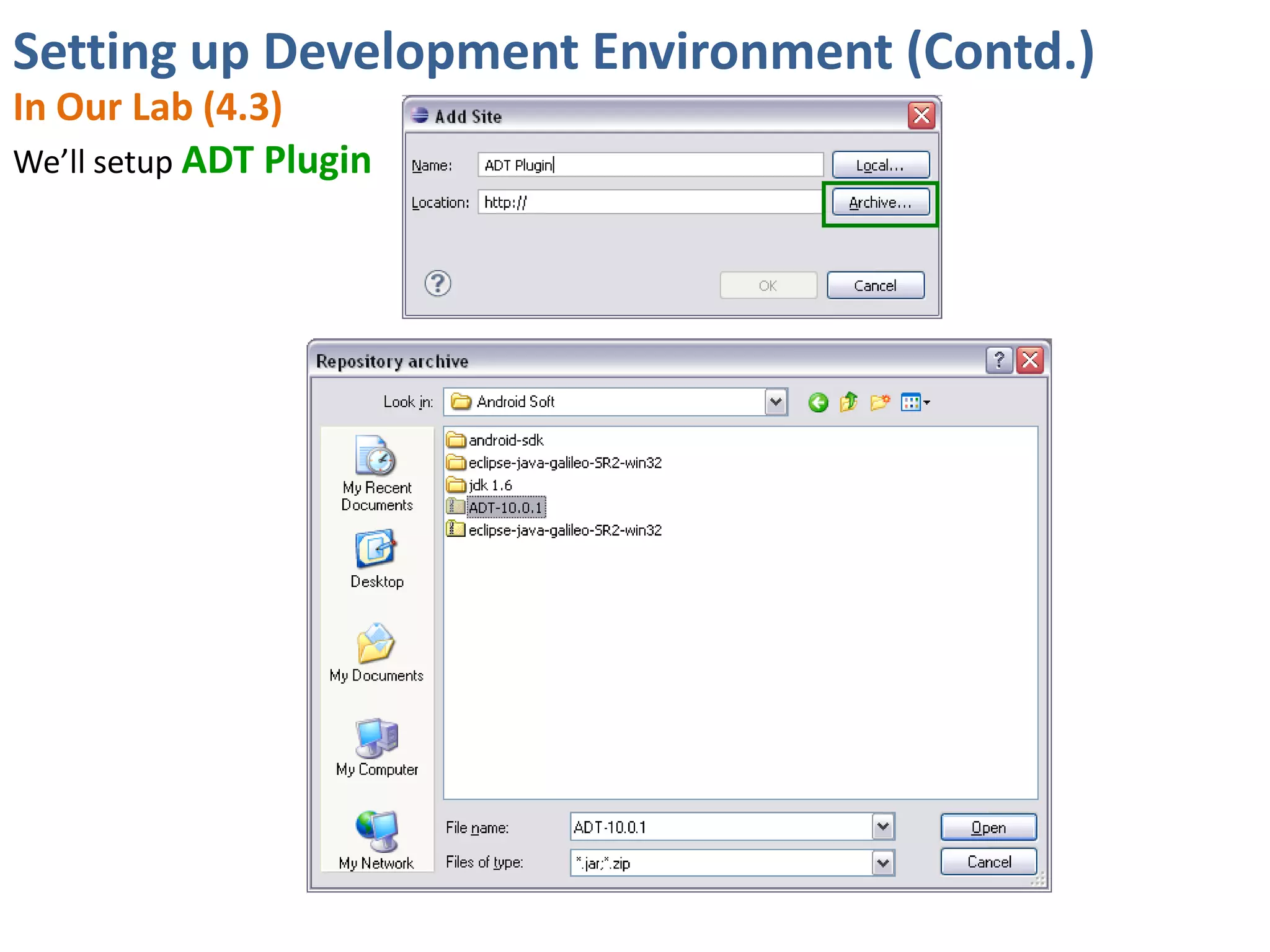
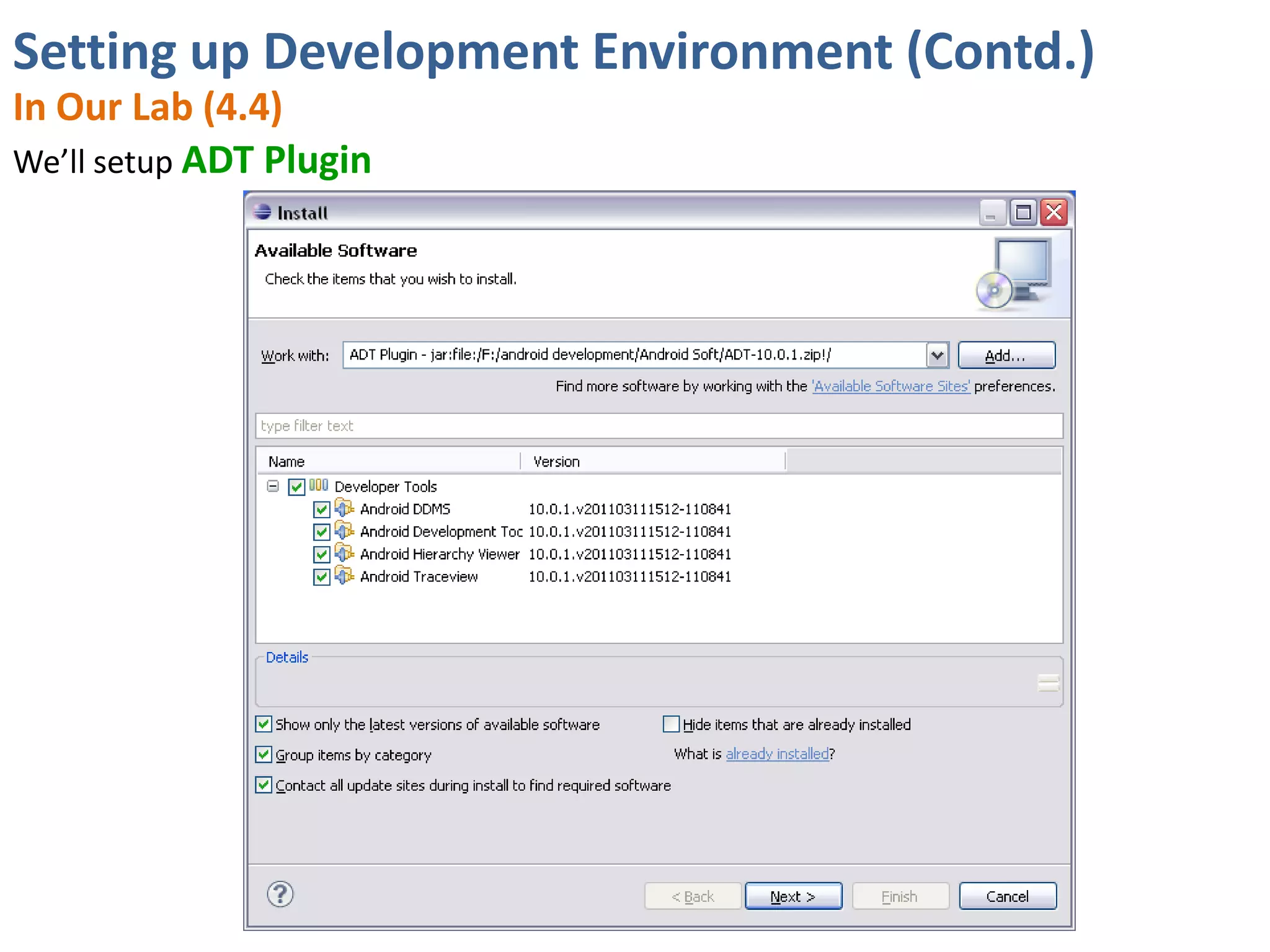
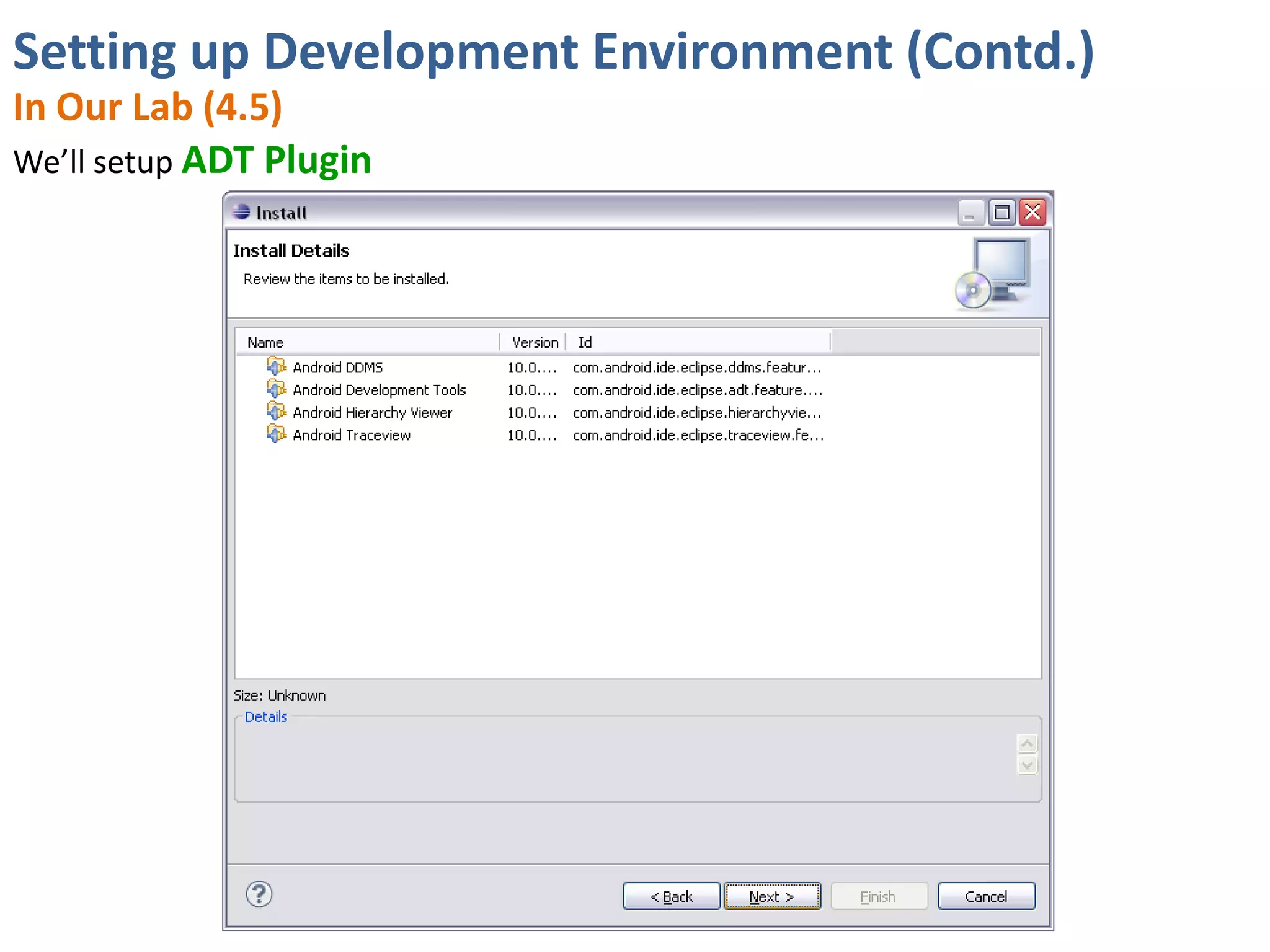
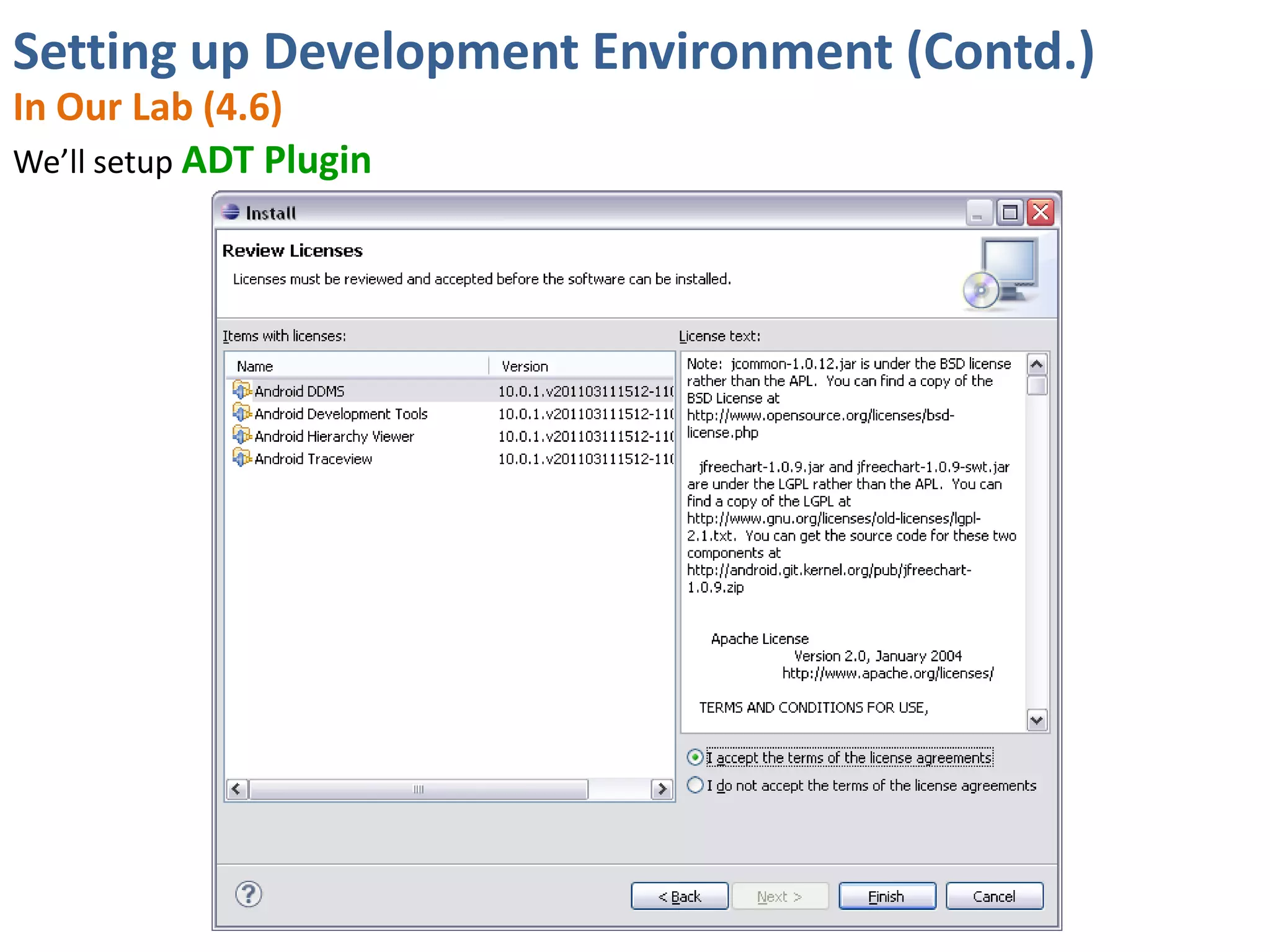
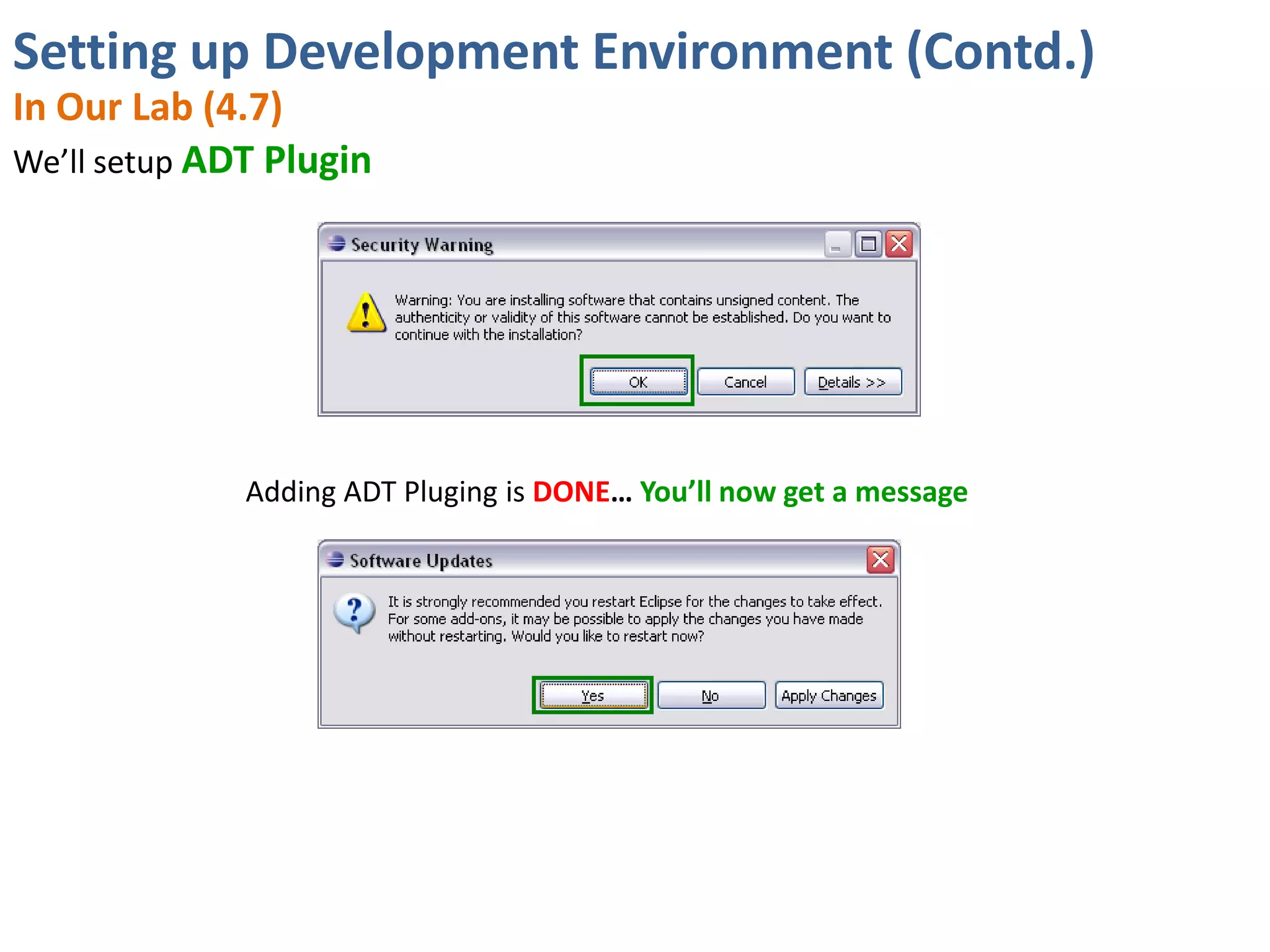
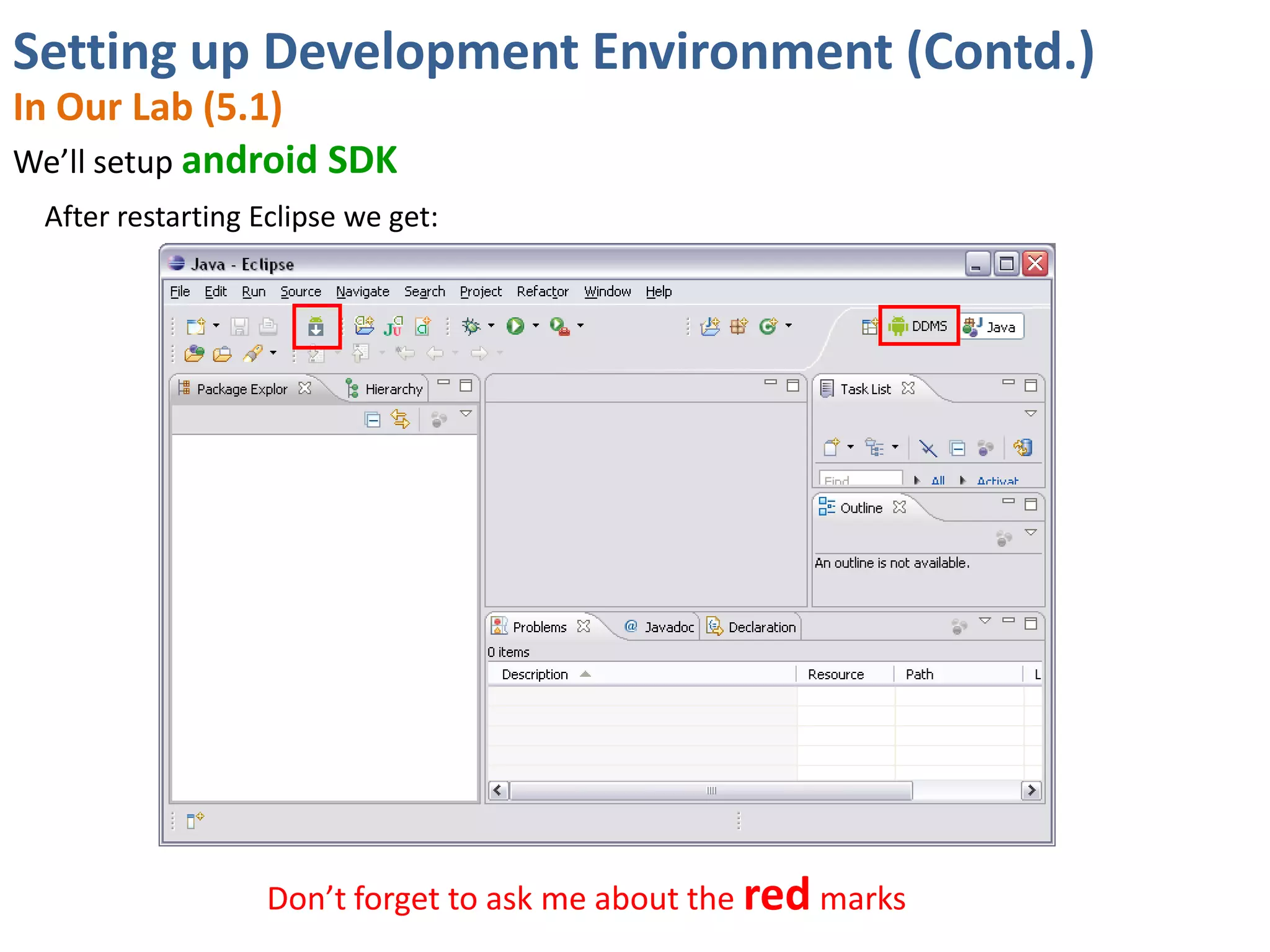
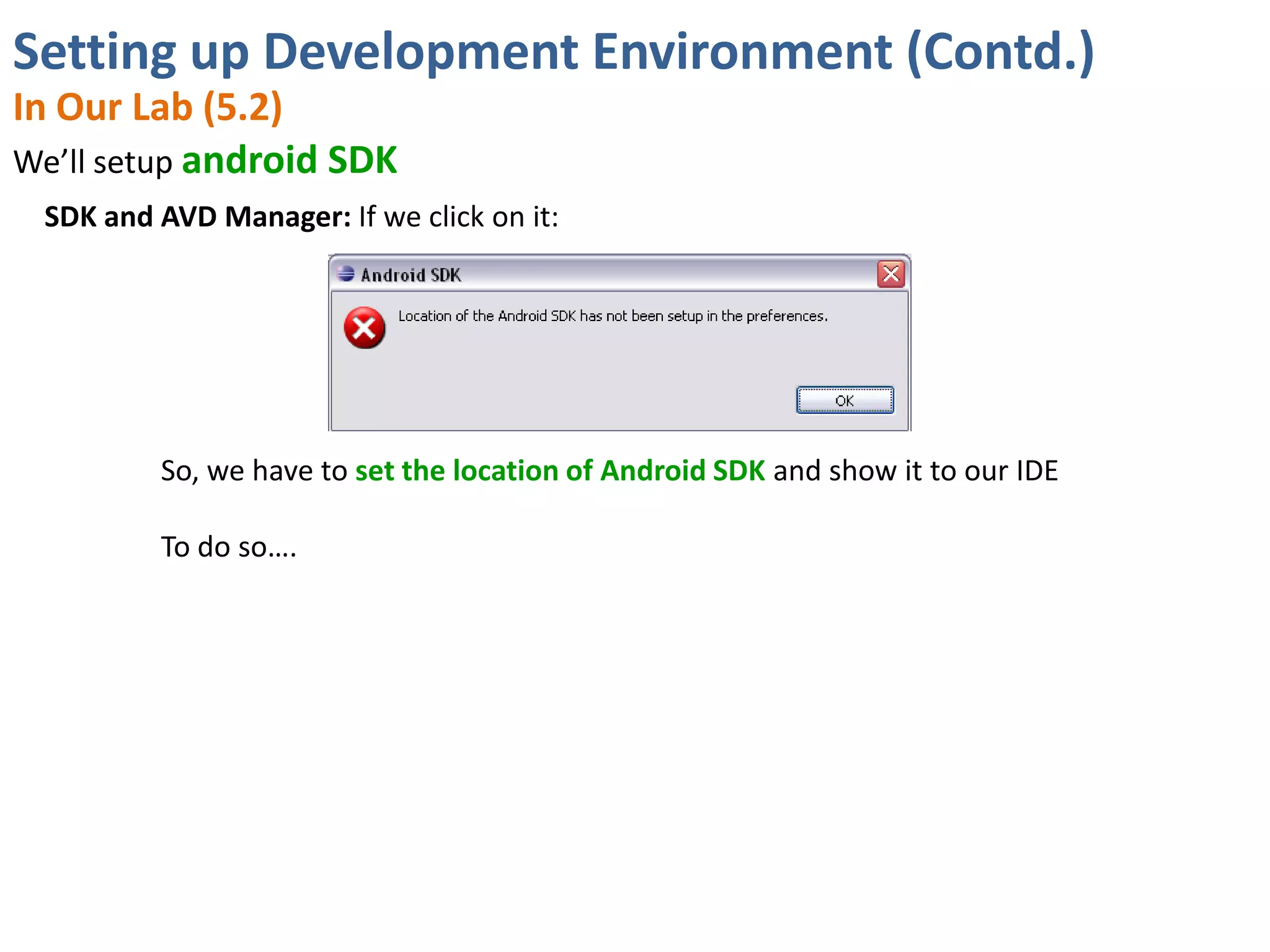
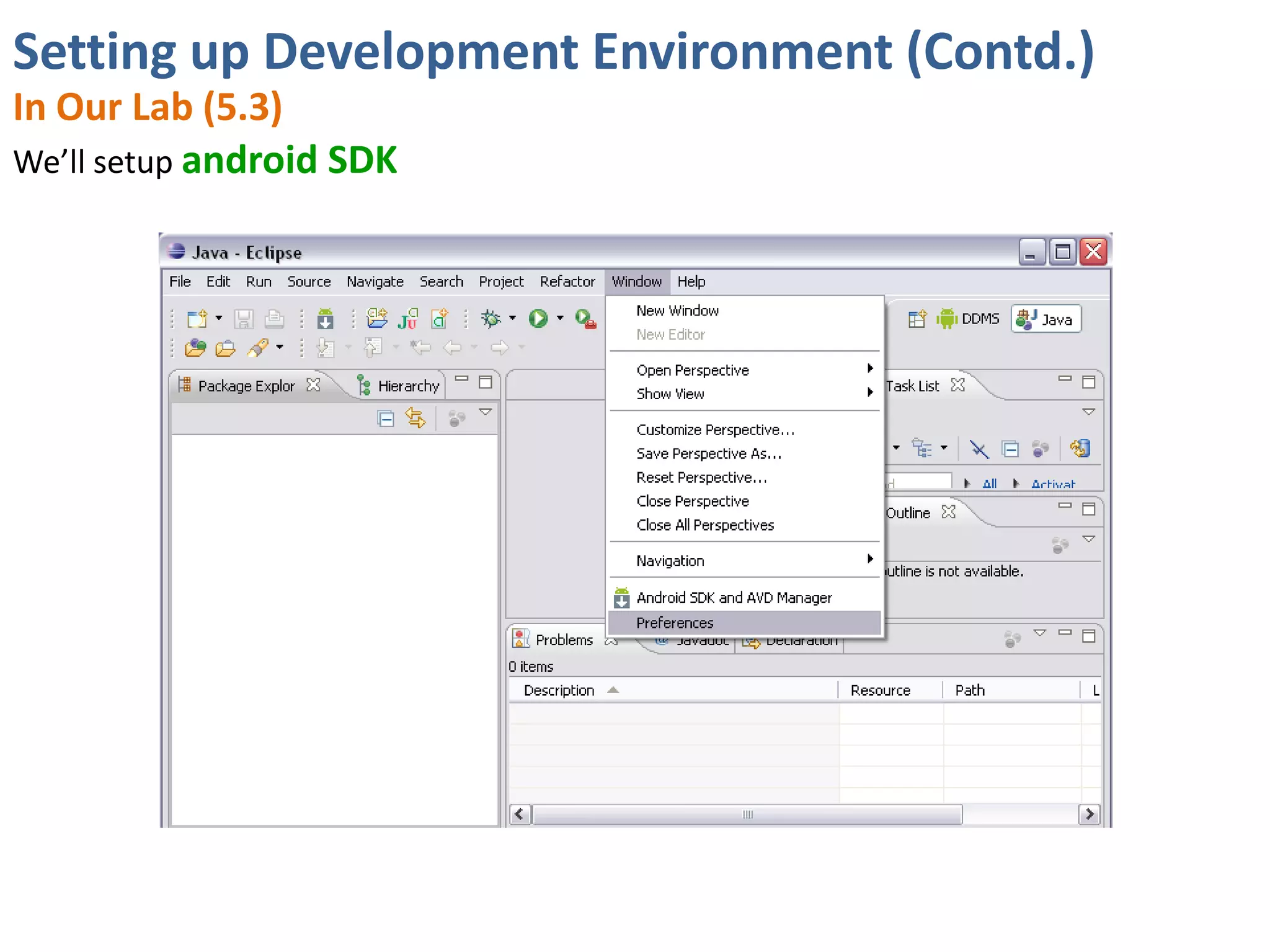
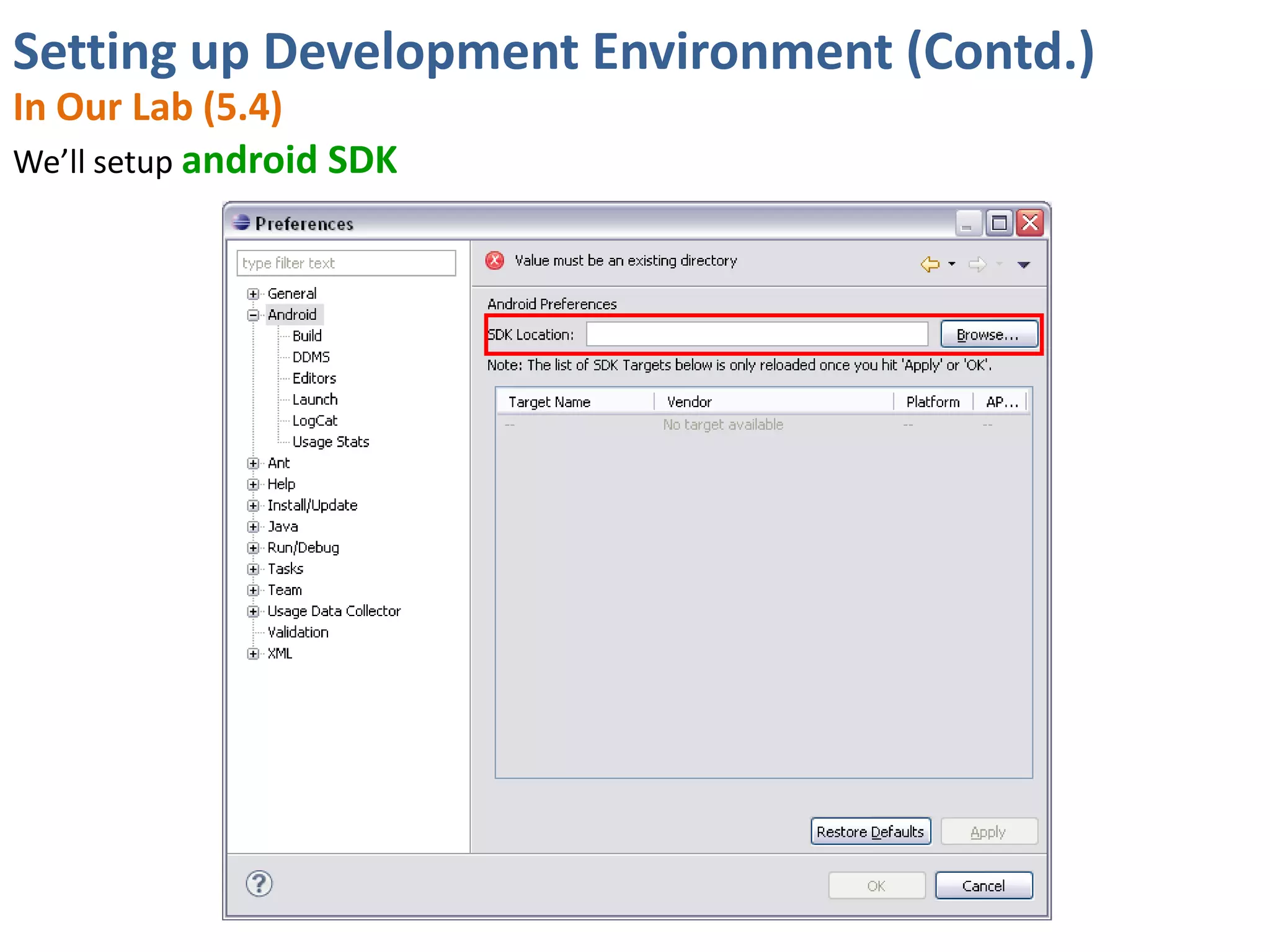
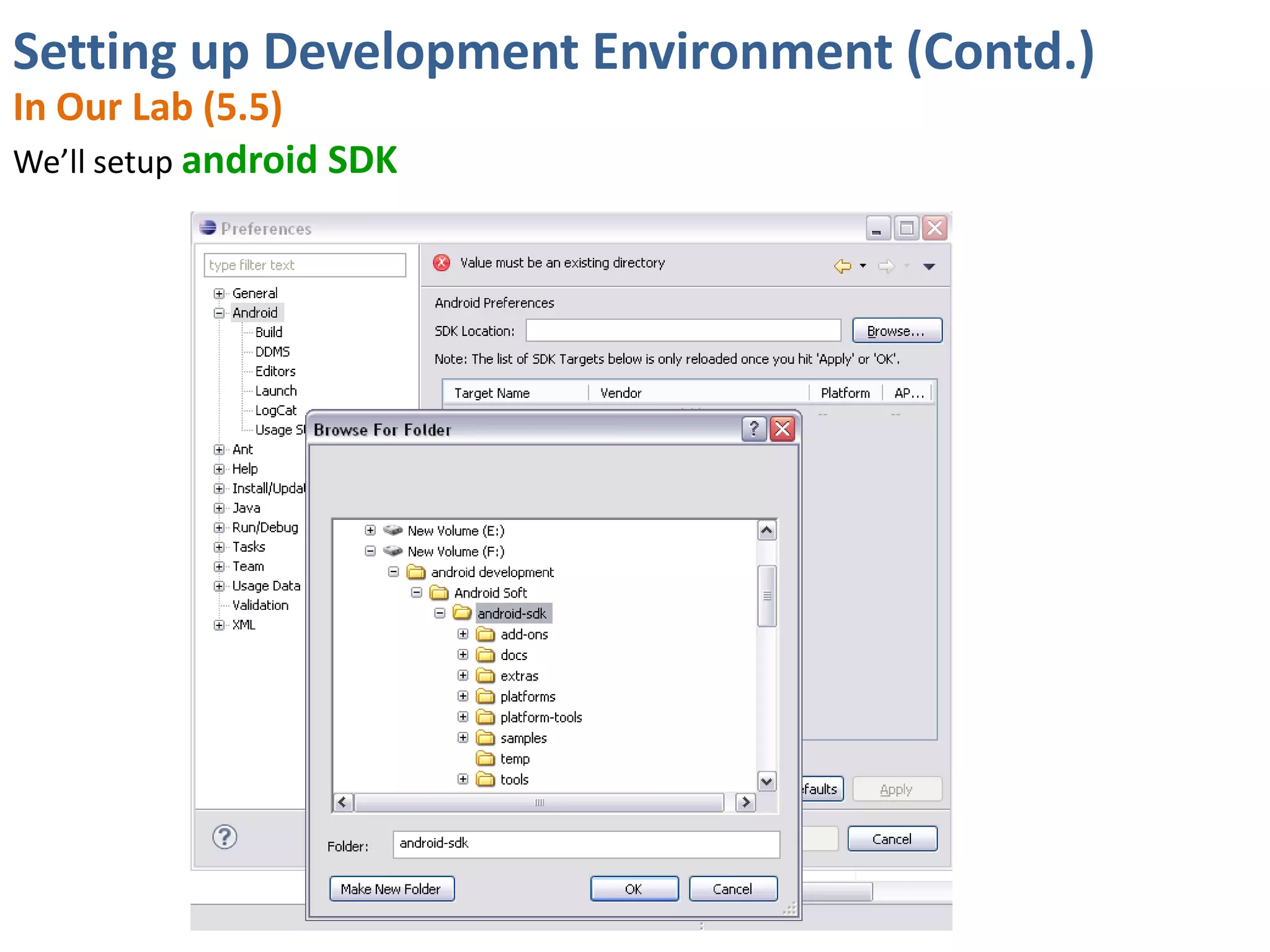
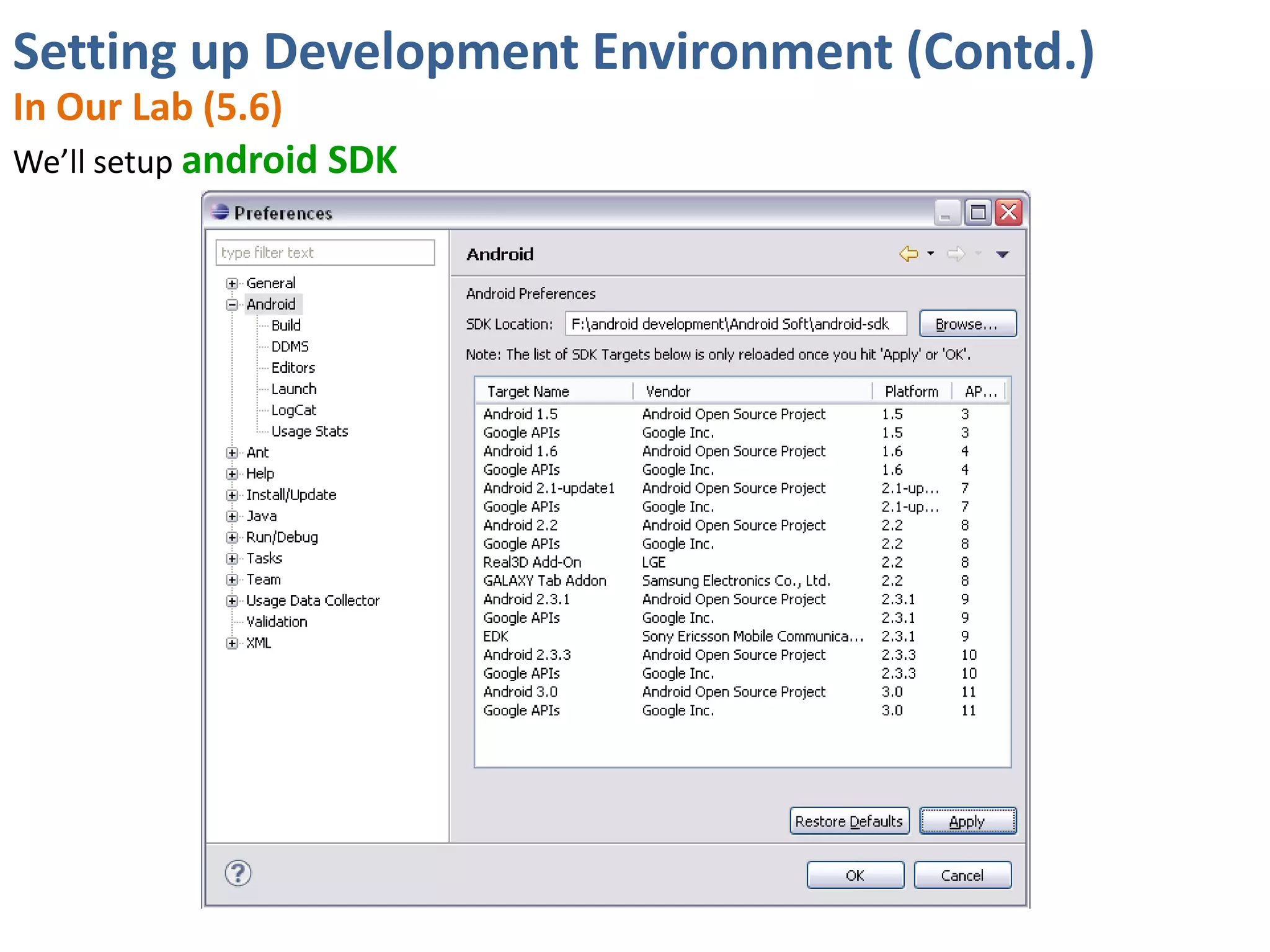
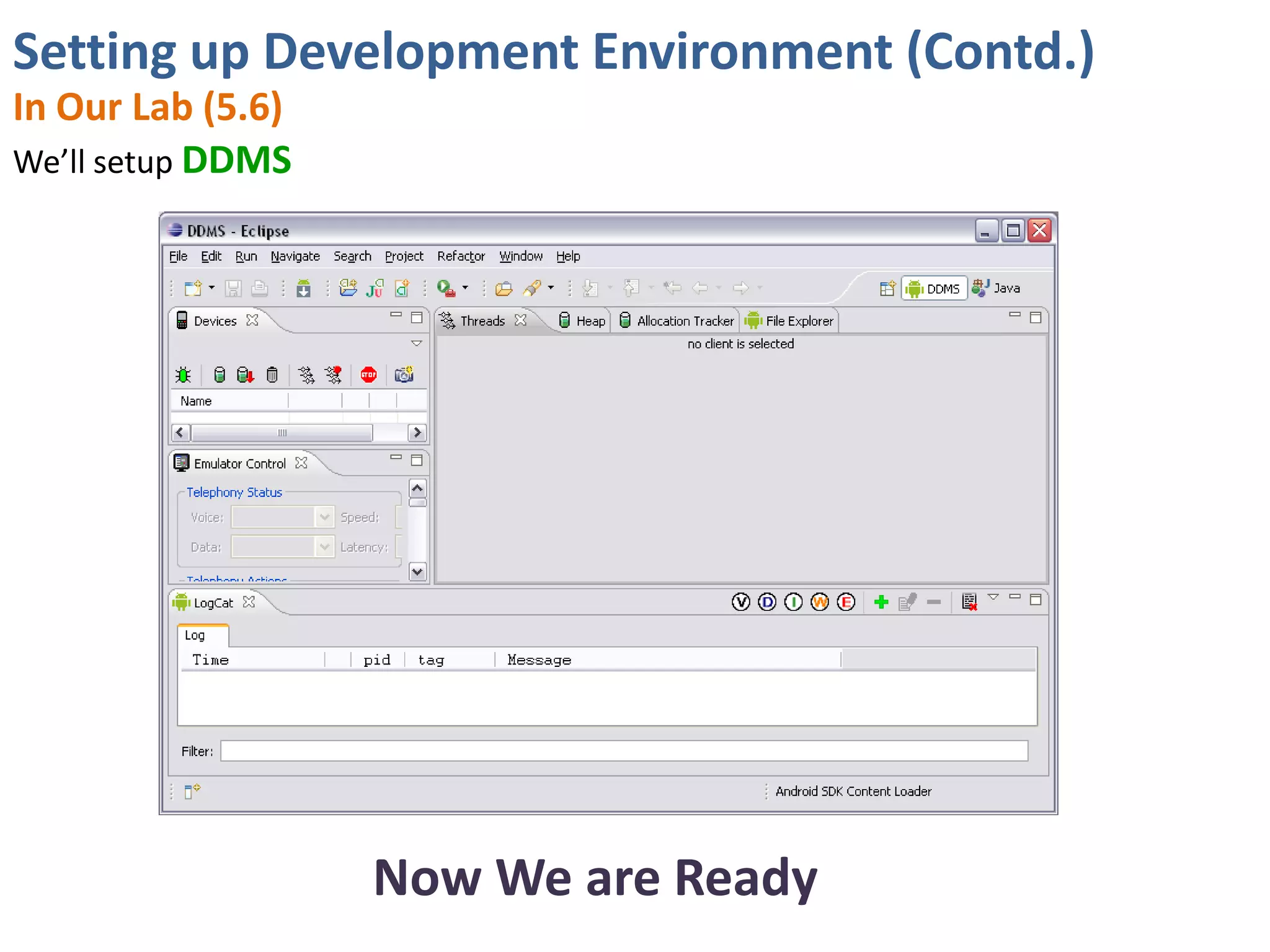
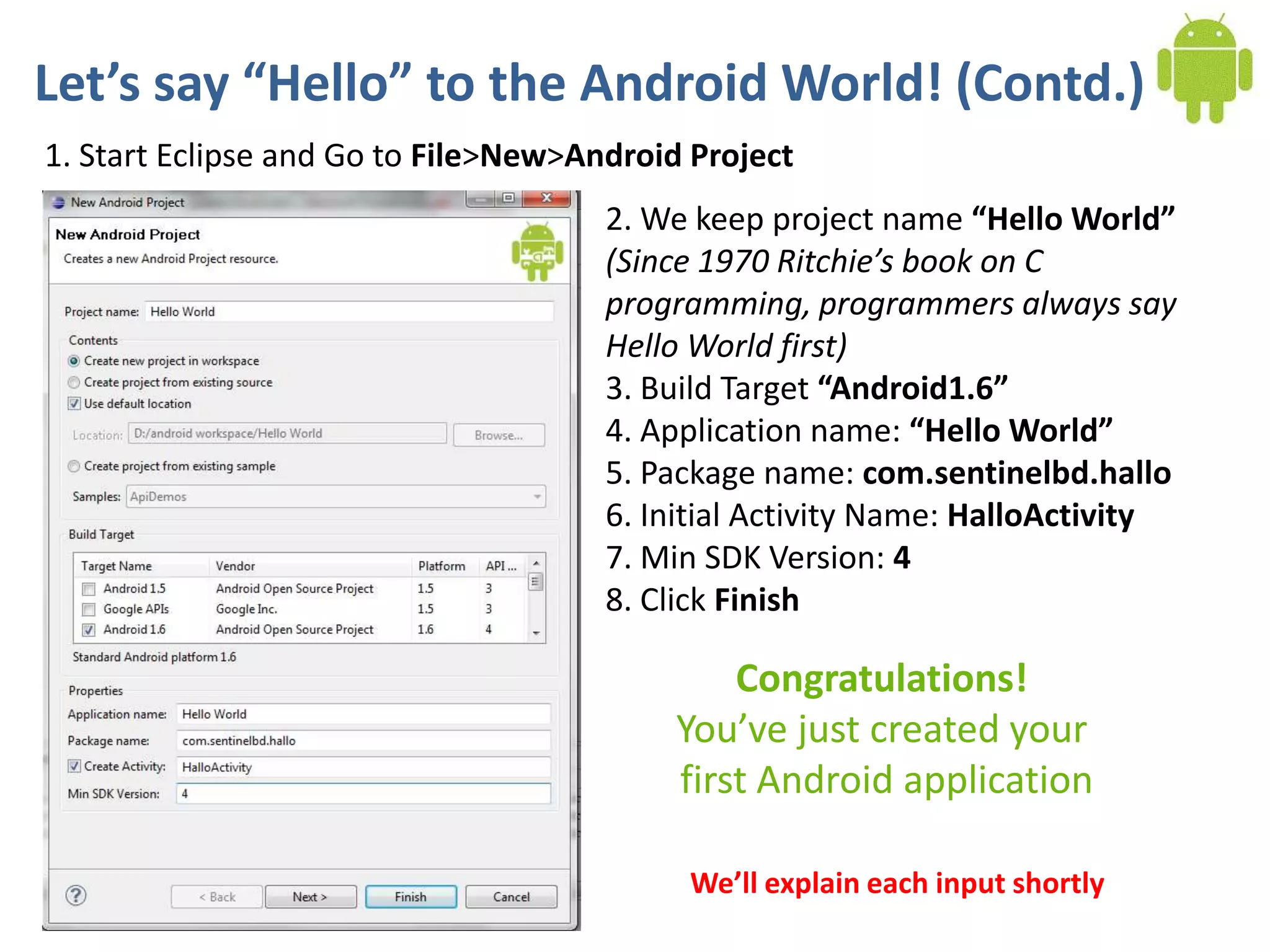
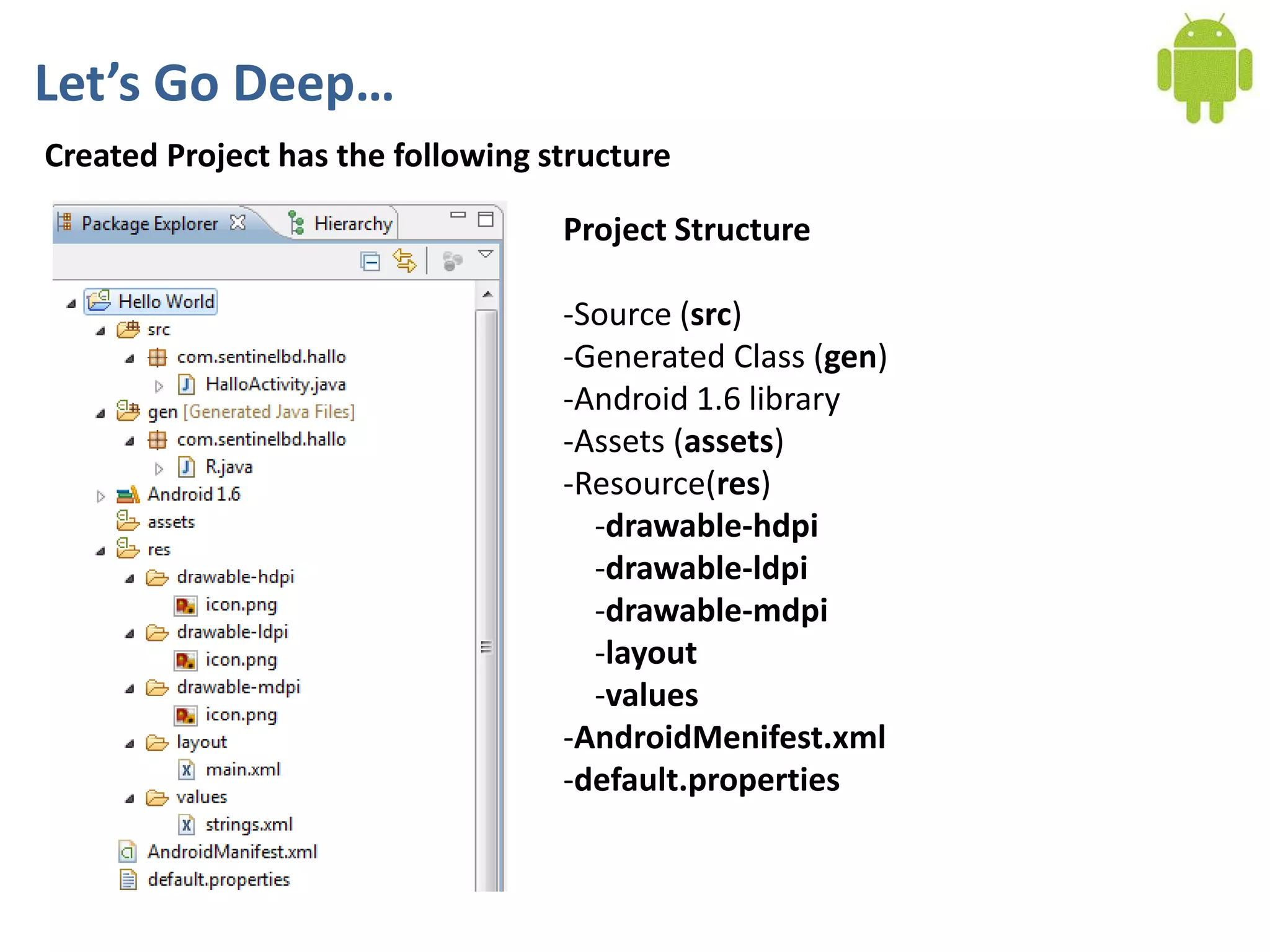
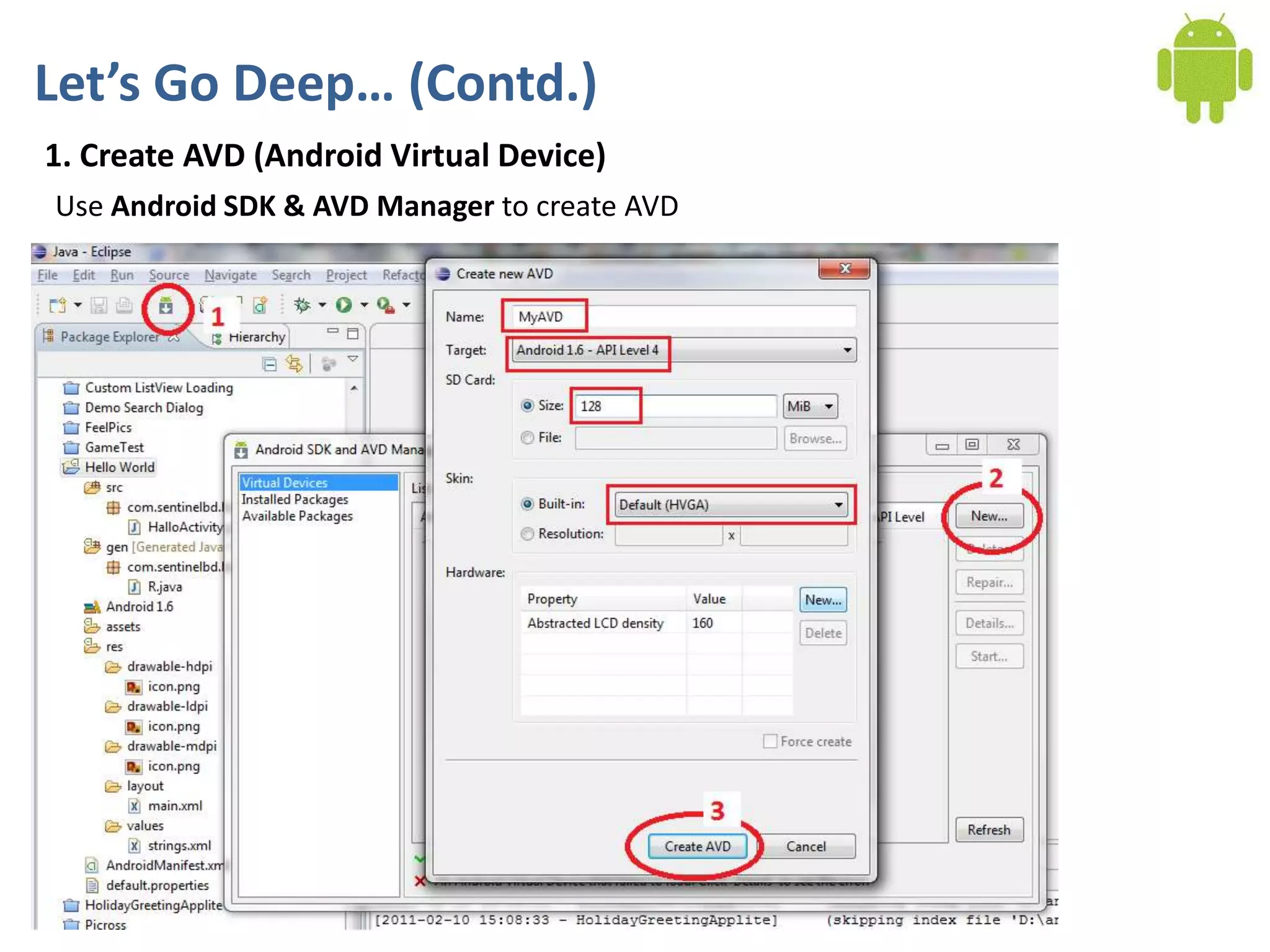
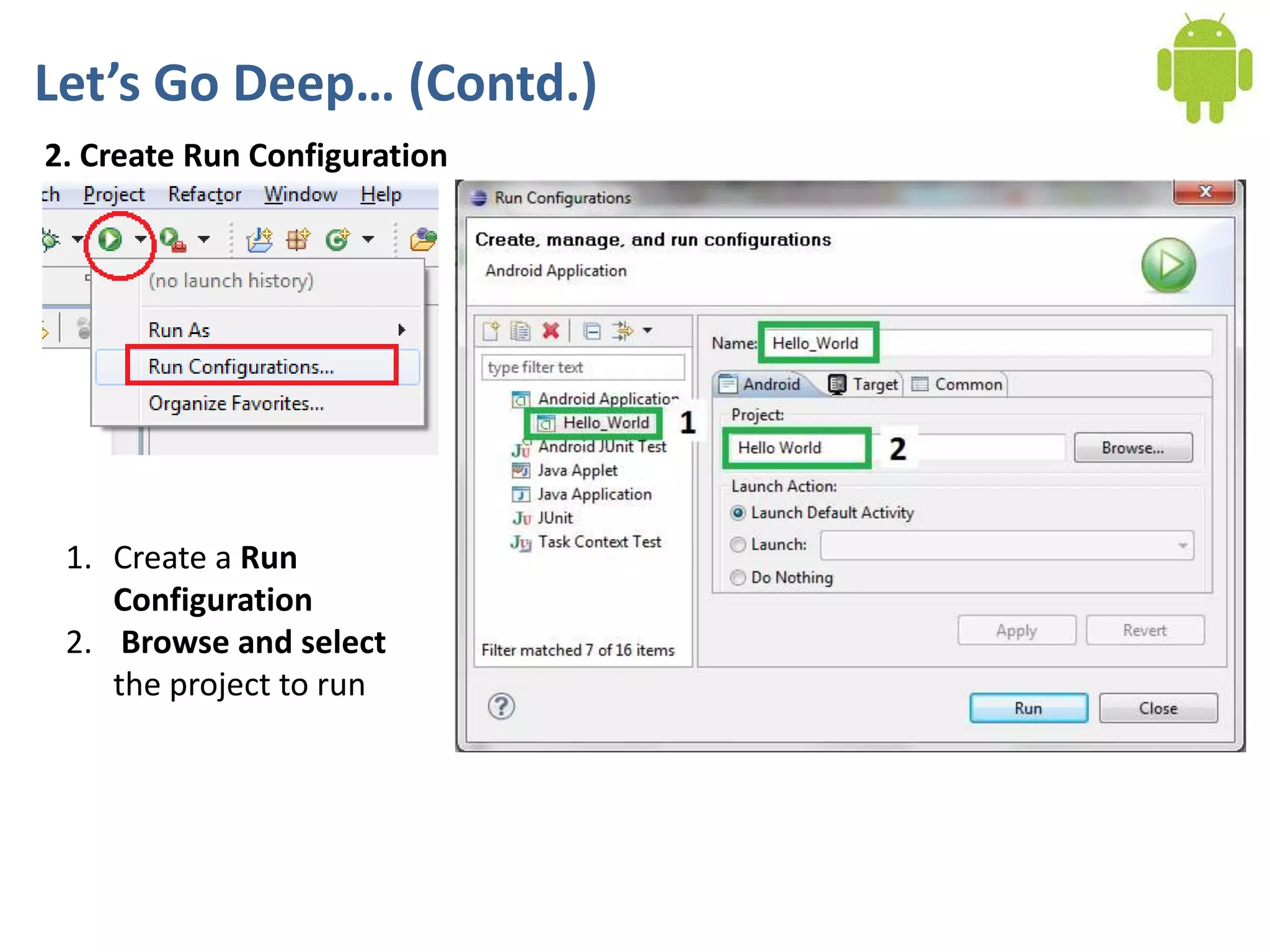
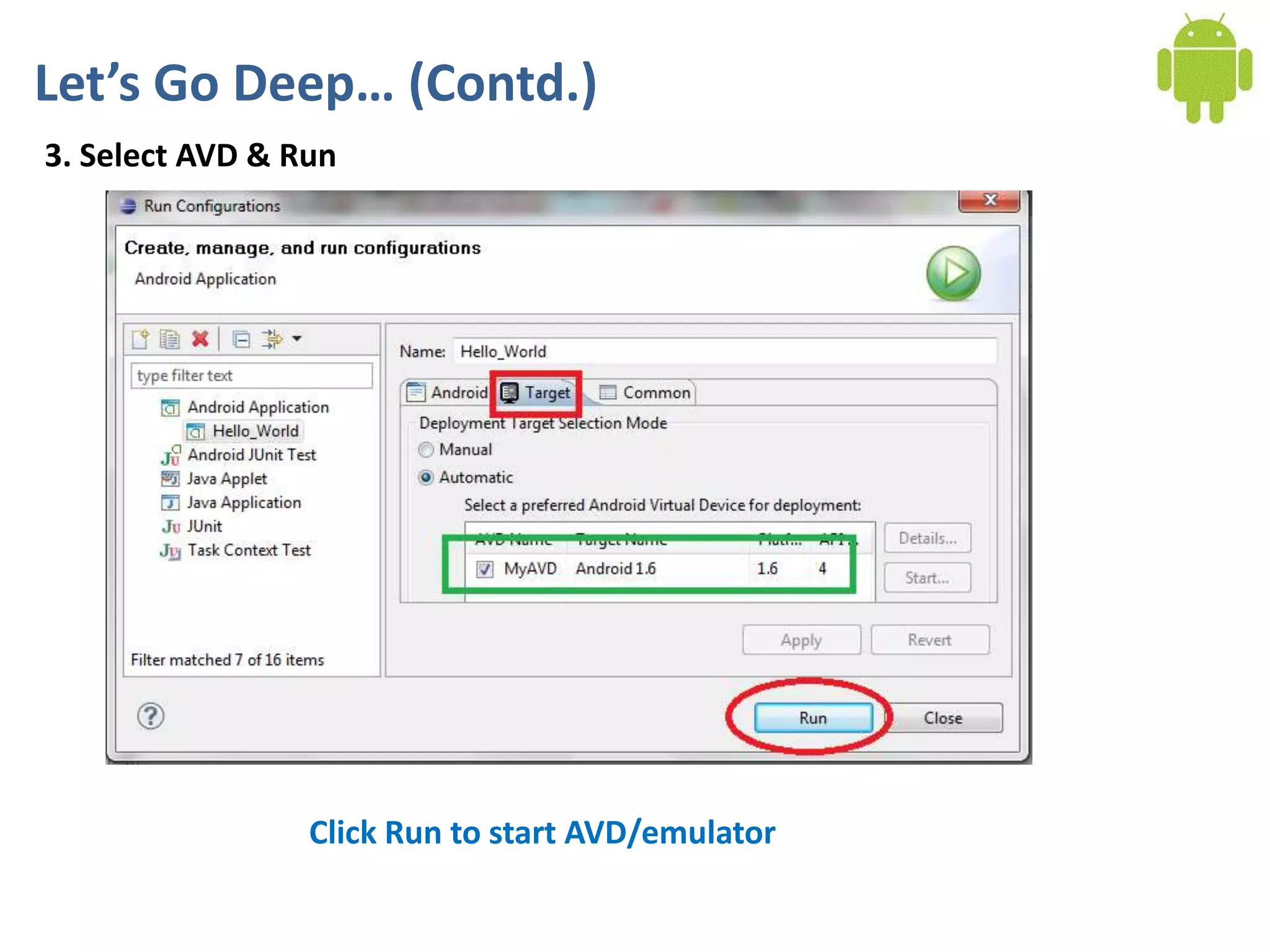
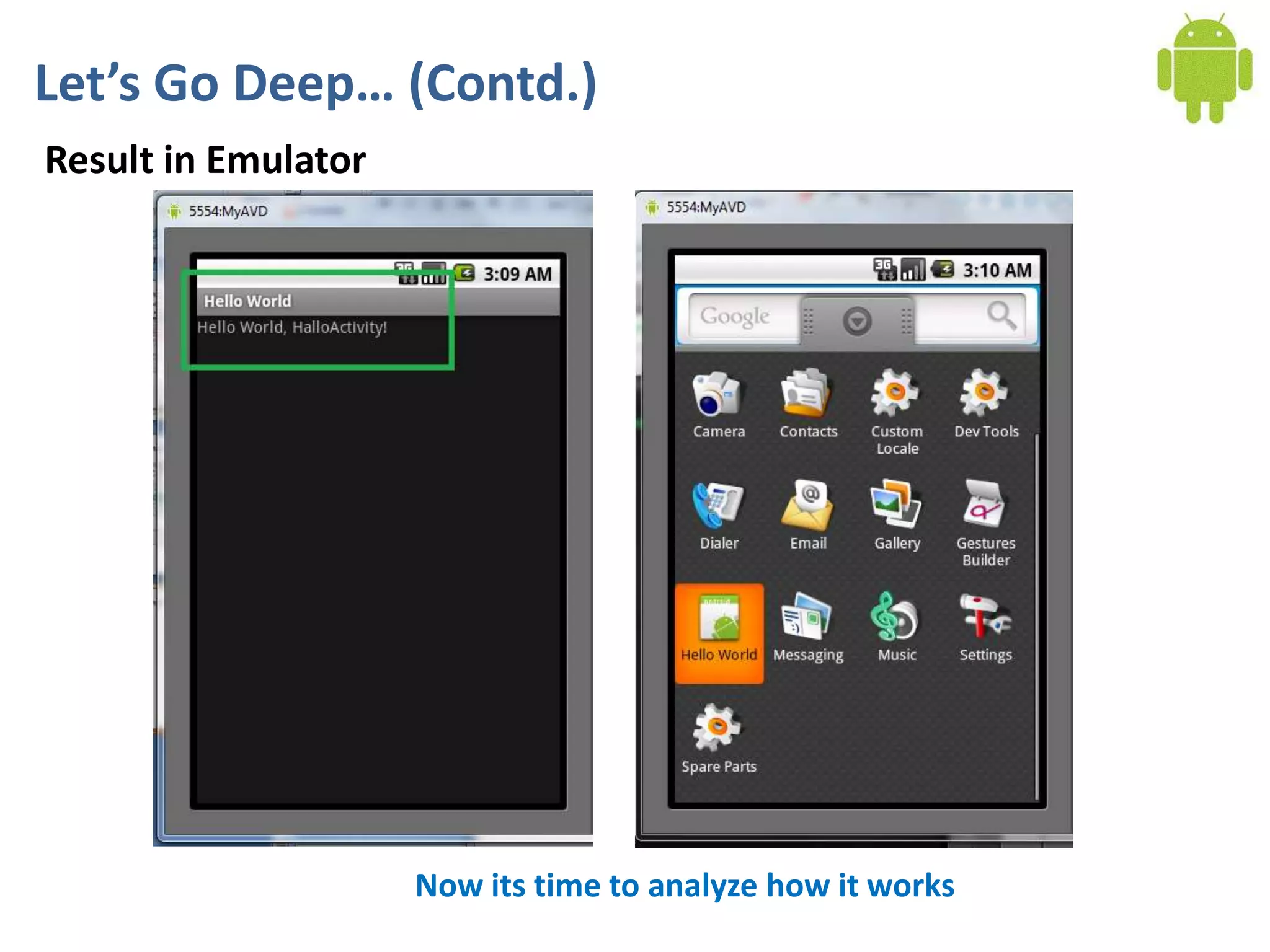
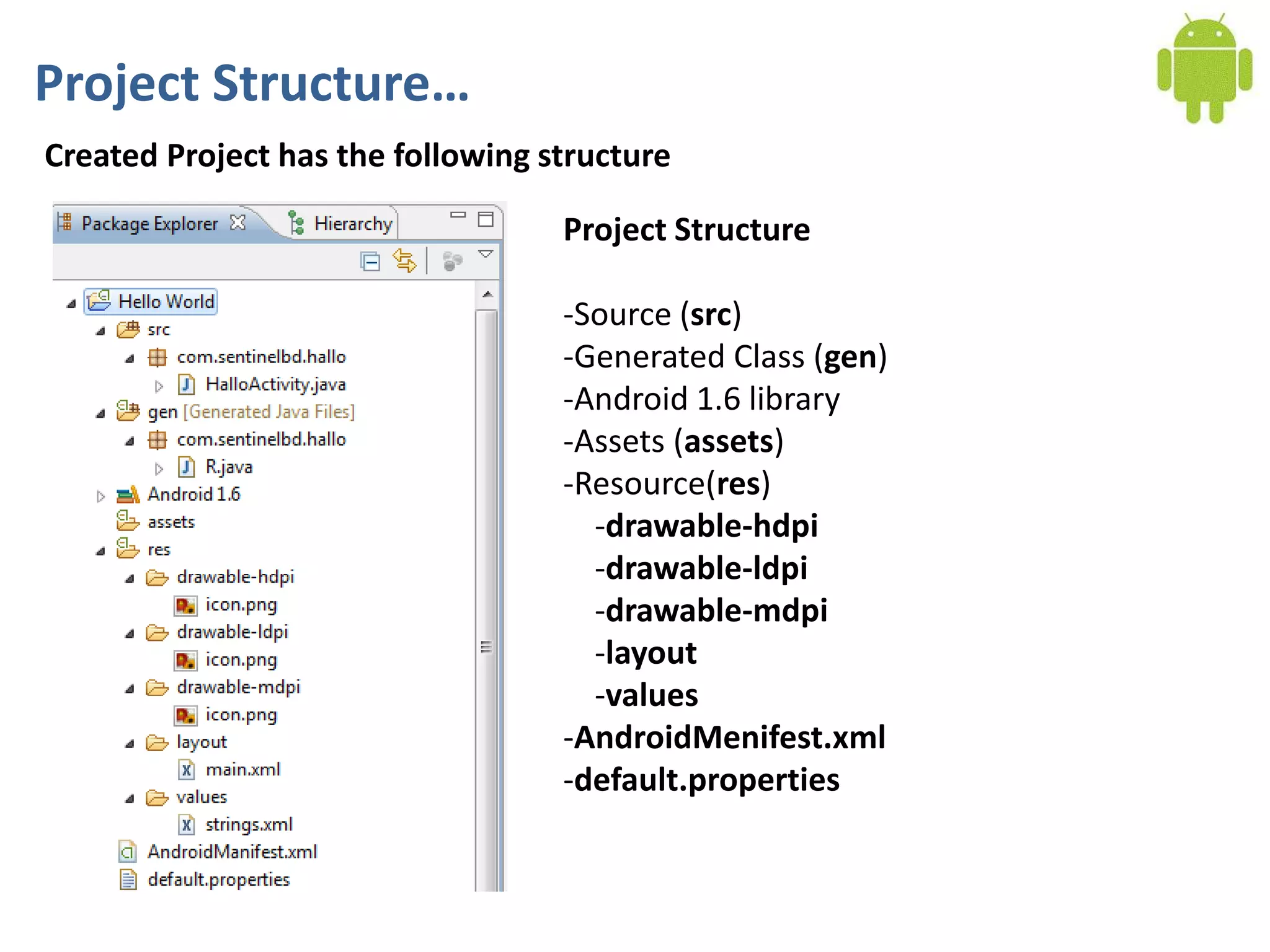
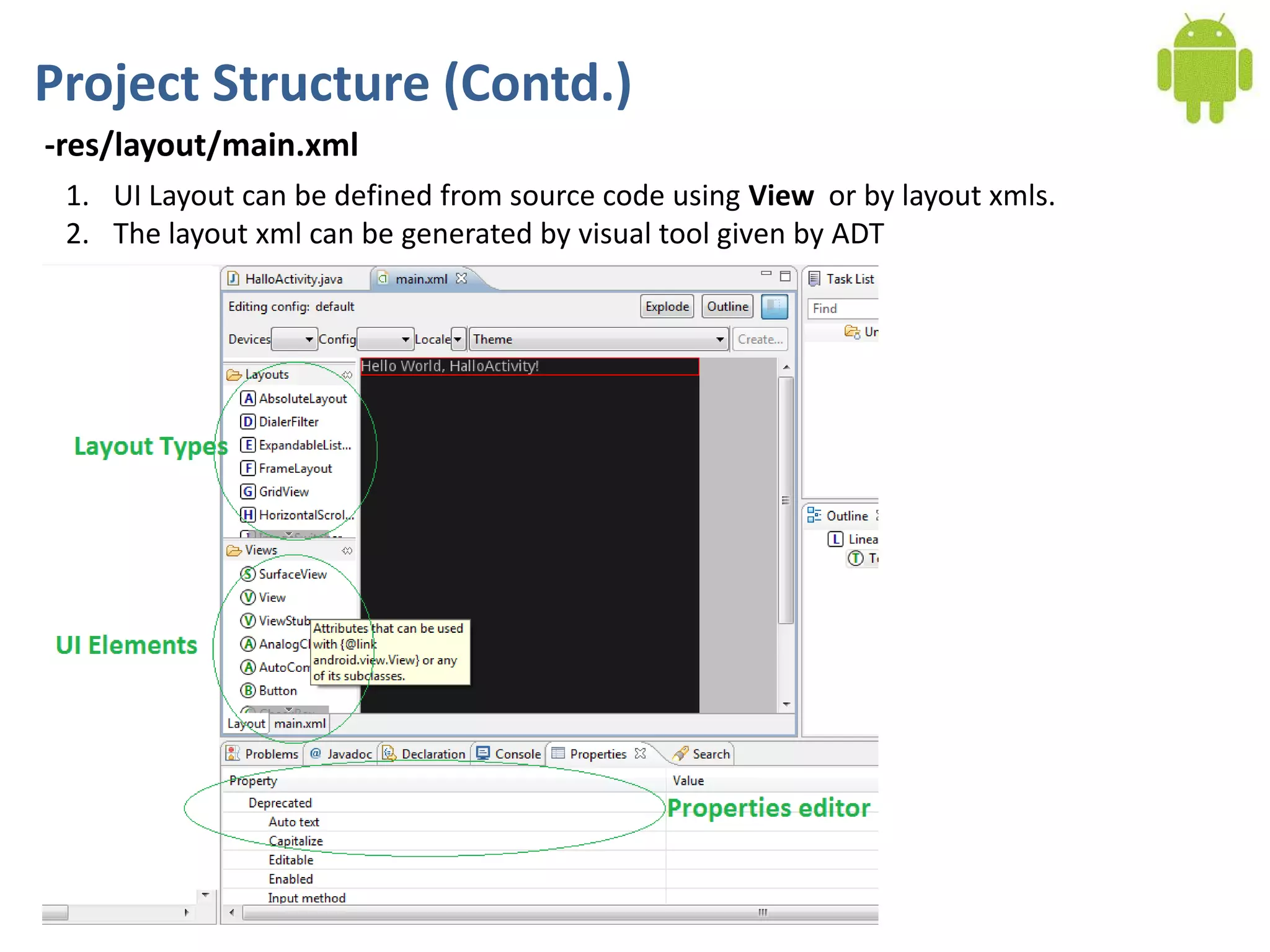
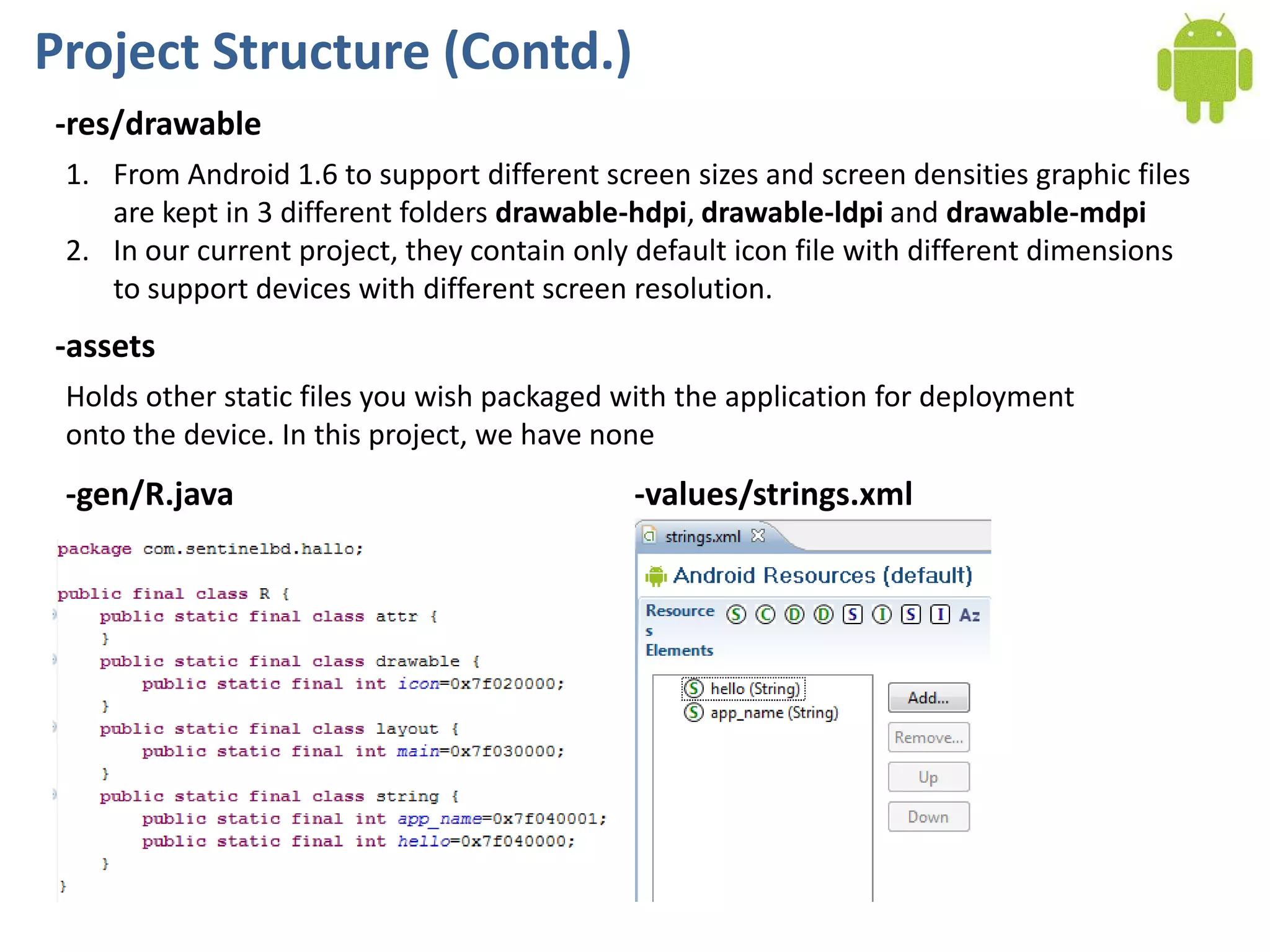
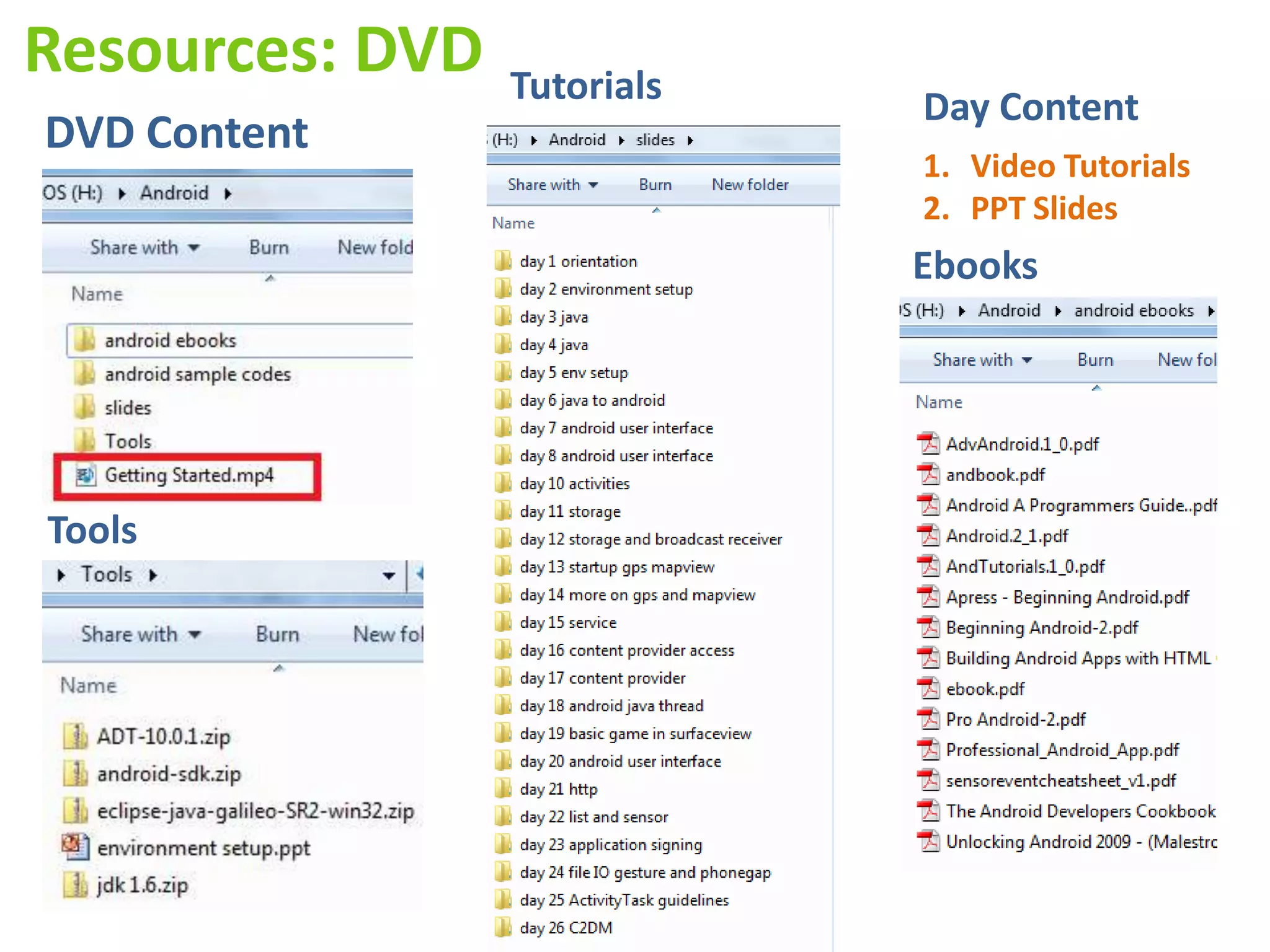
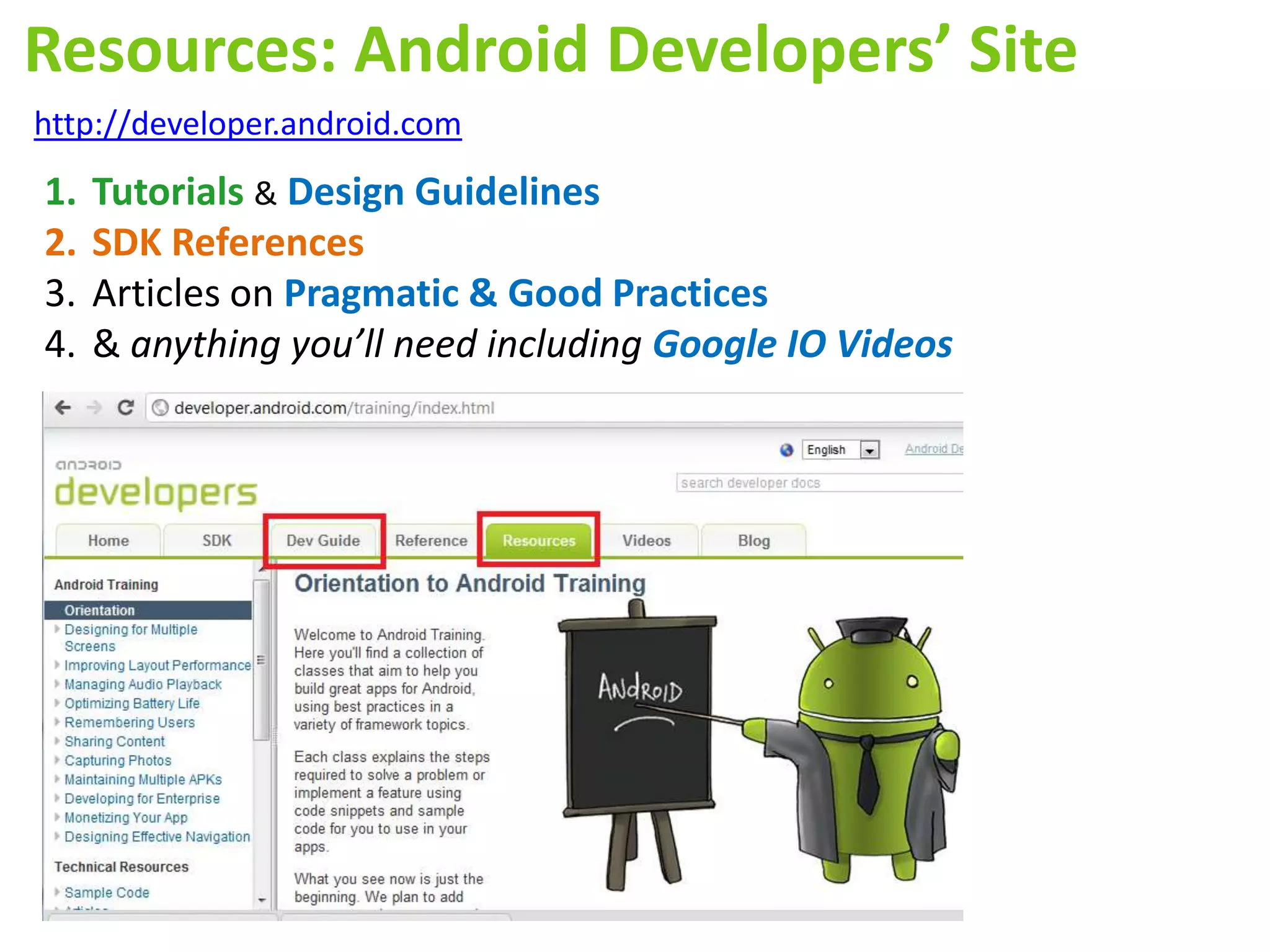
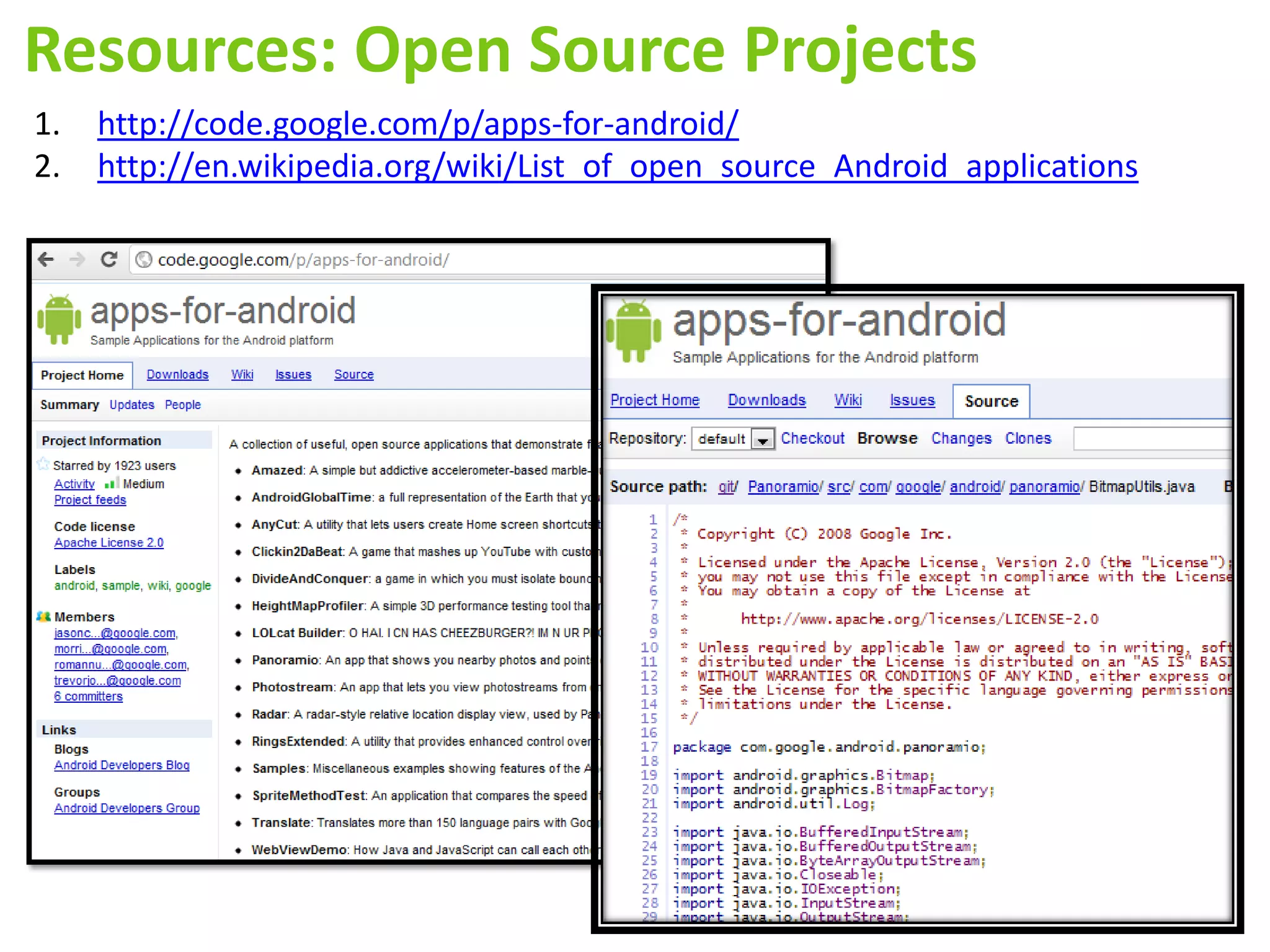
Android application development seminar focused on getting started. The document provided an overview of mobile and smartphone applications and platforms like Android, discussed why developers should learn the Android platform due to its open source nature, vast opportunities for distribution and business advantages over other platforms. It suggested holding workshops and training programs going forward to help novice developers learn.