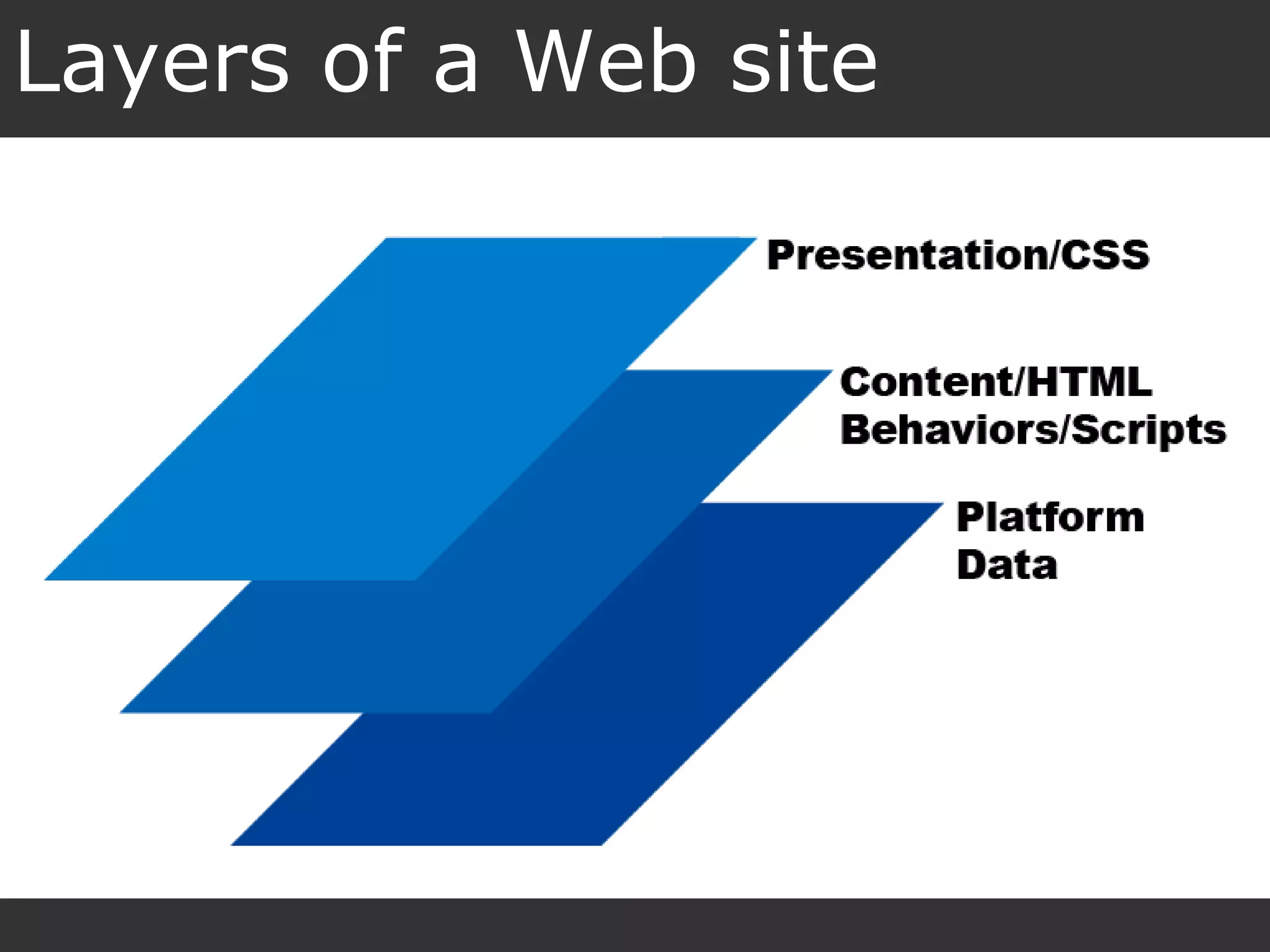
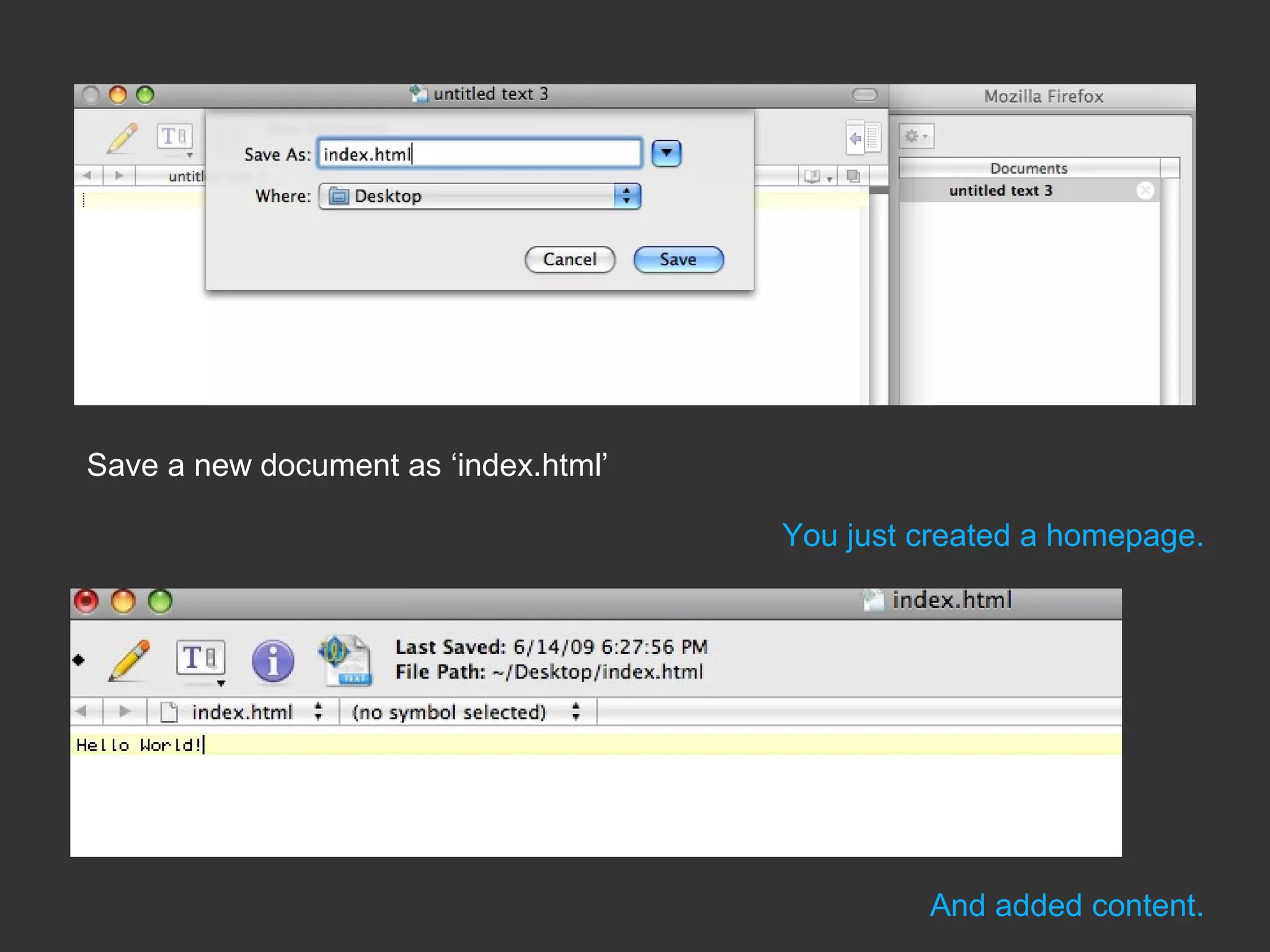
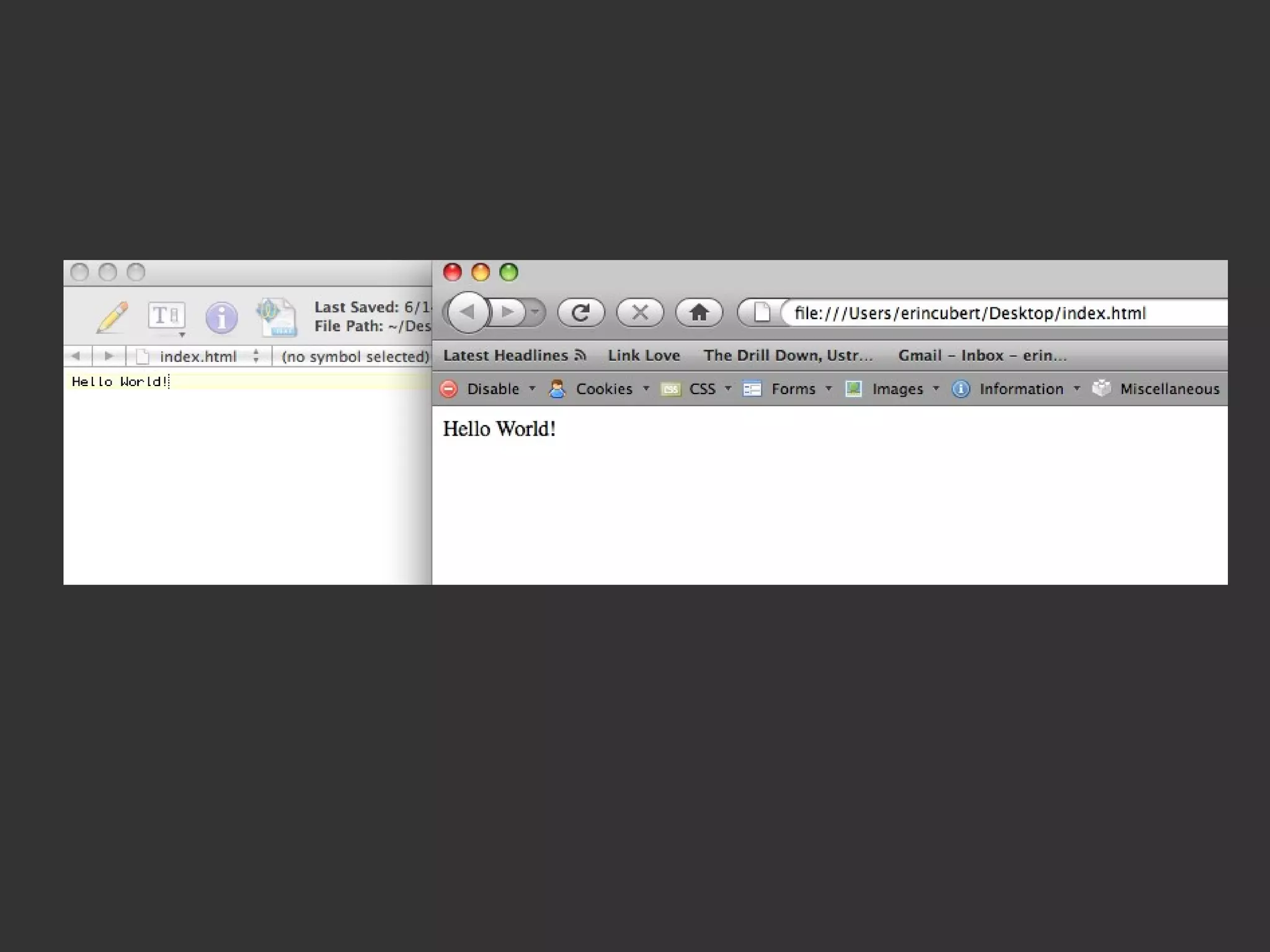
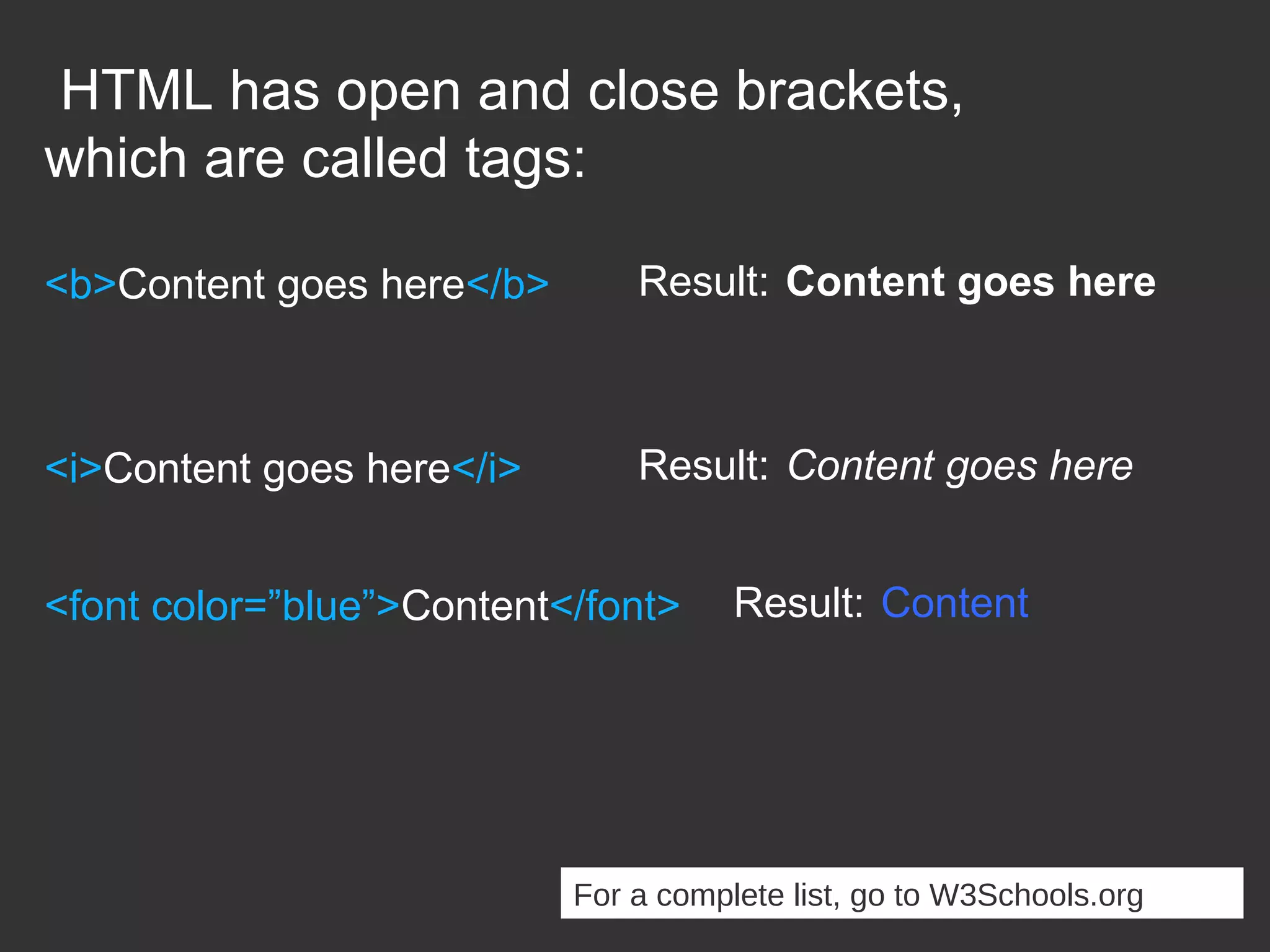
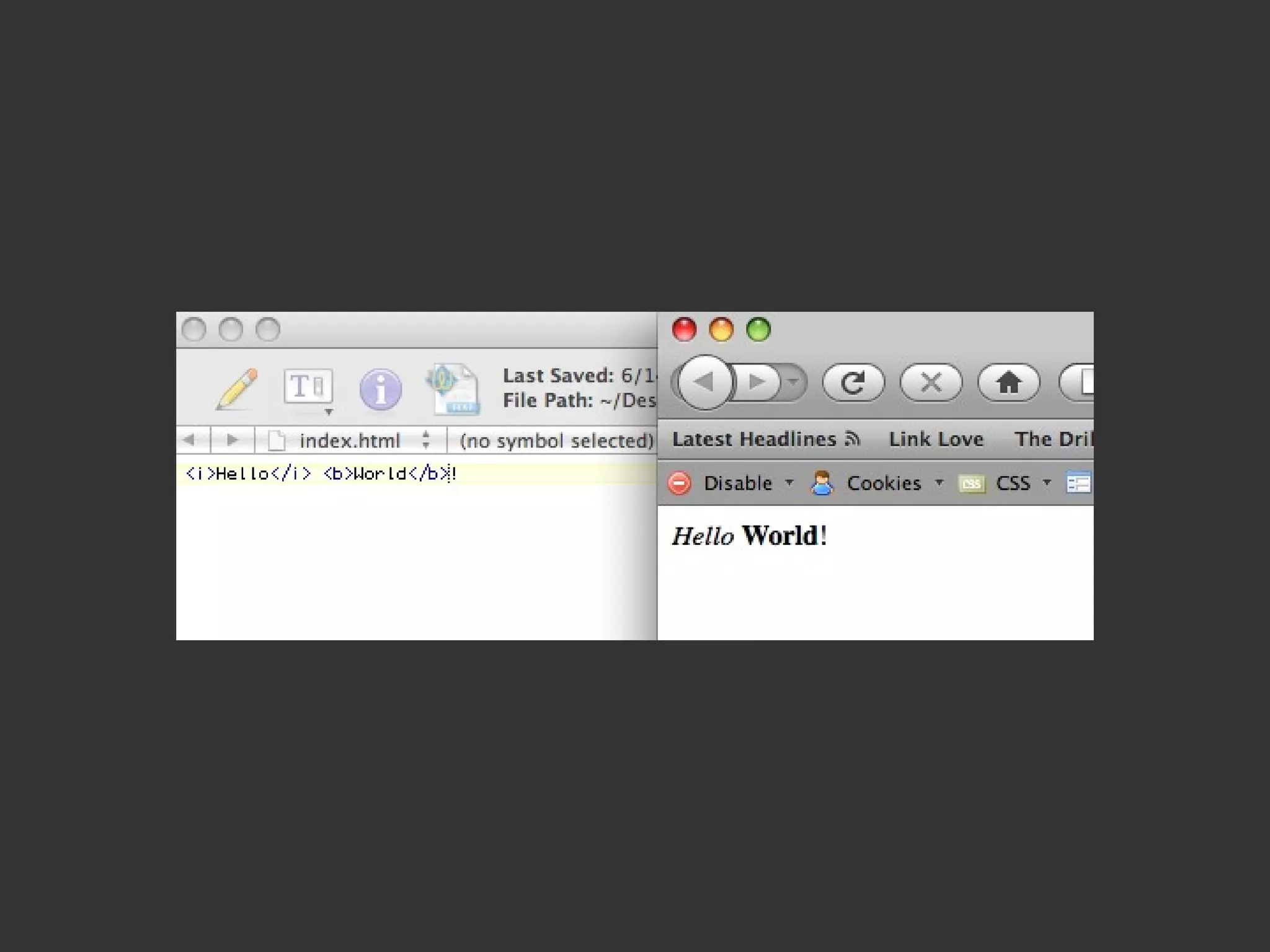
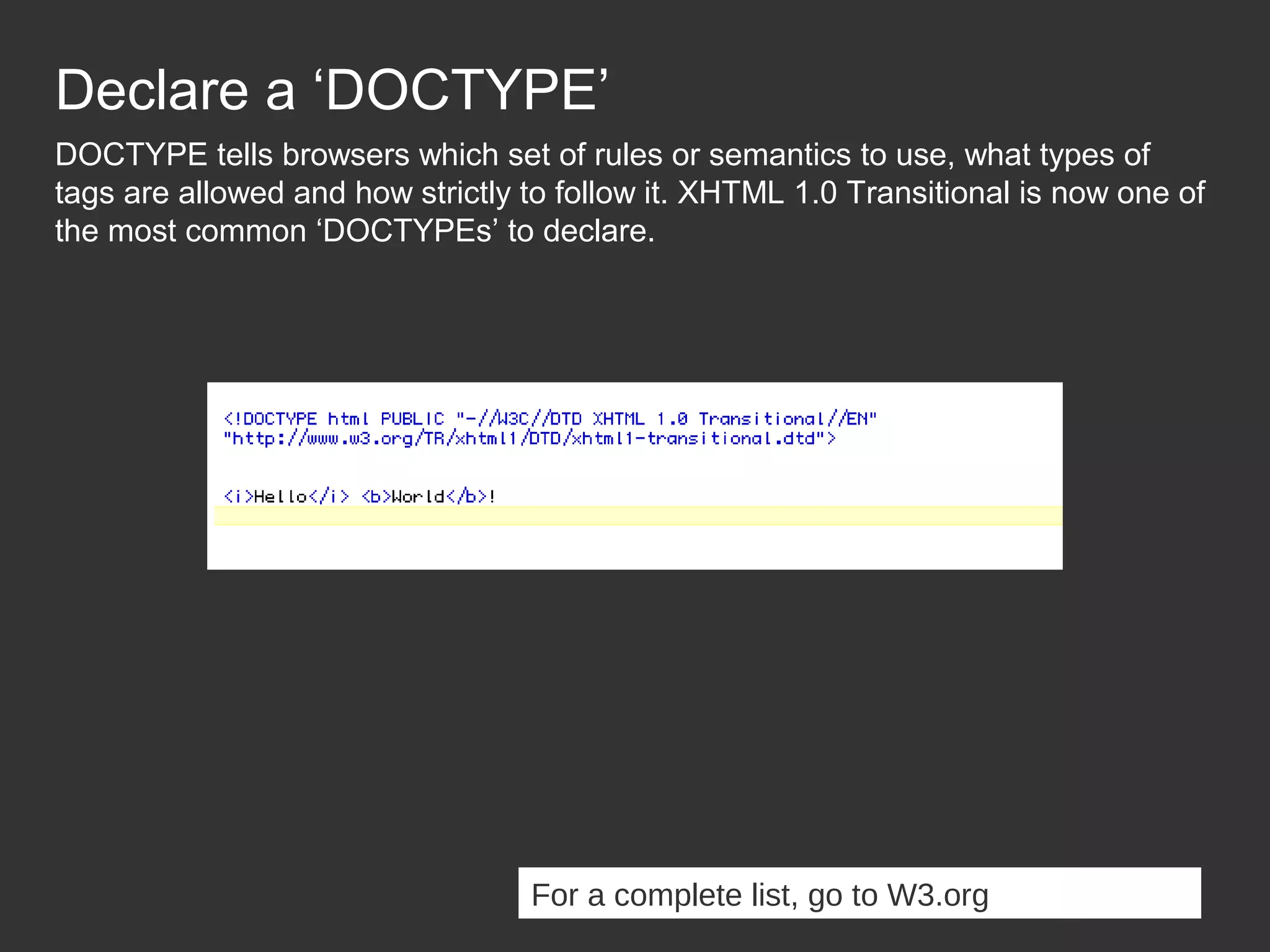
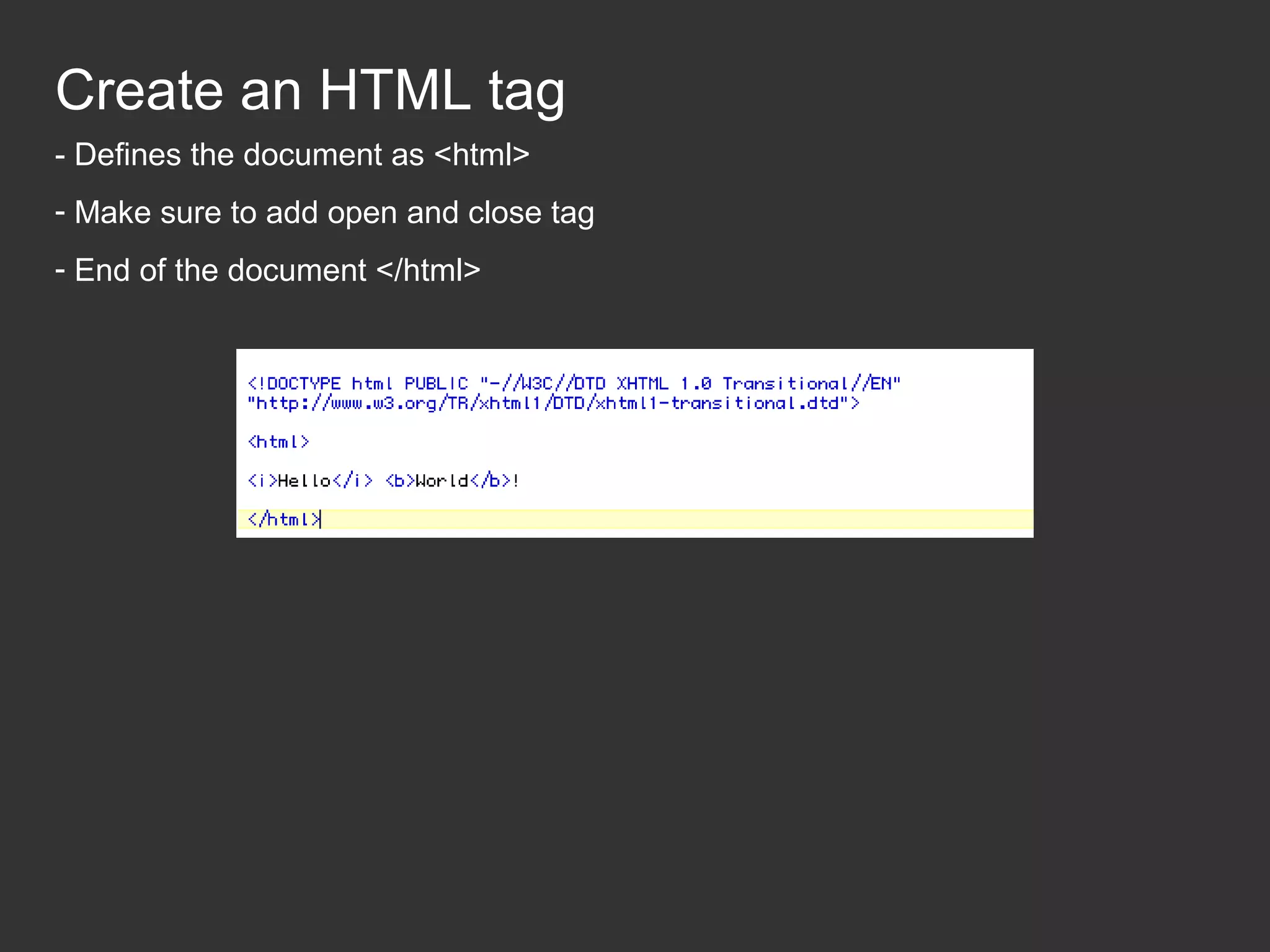
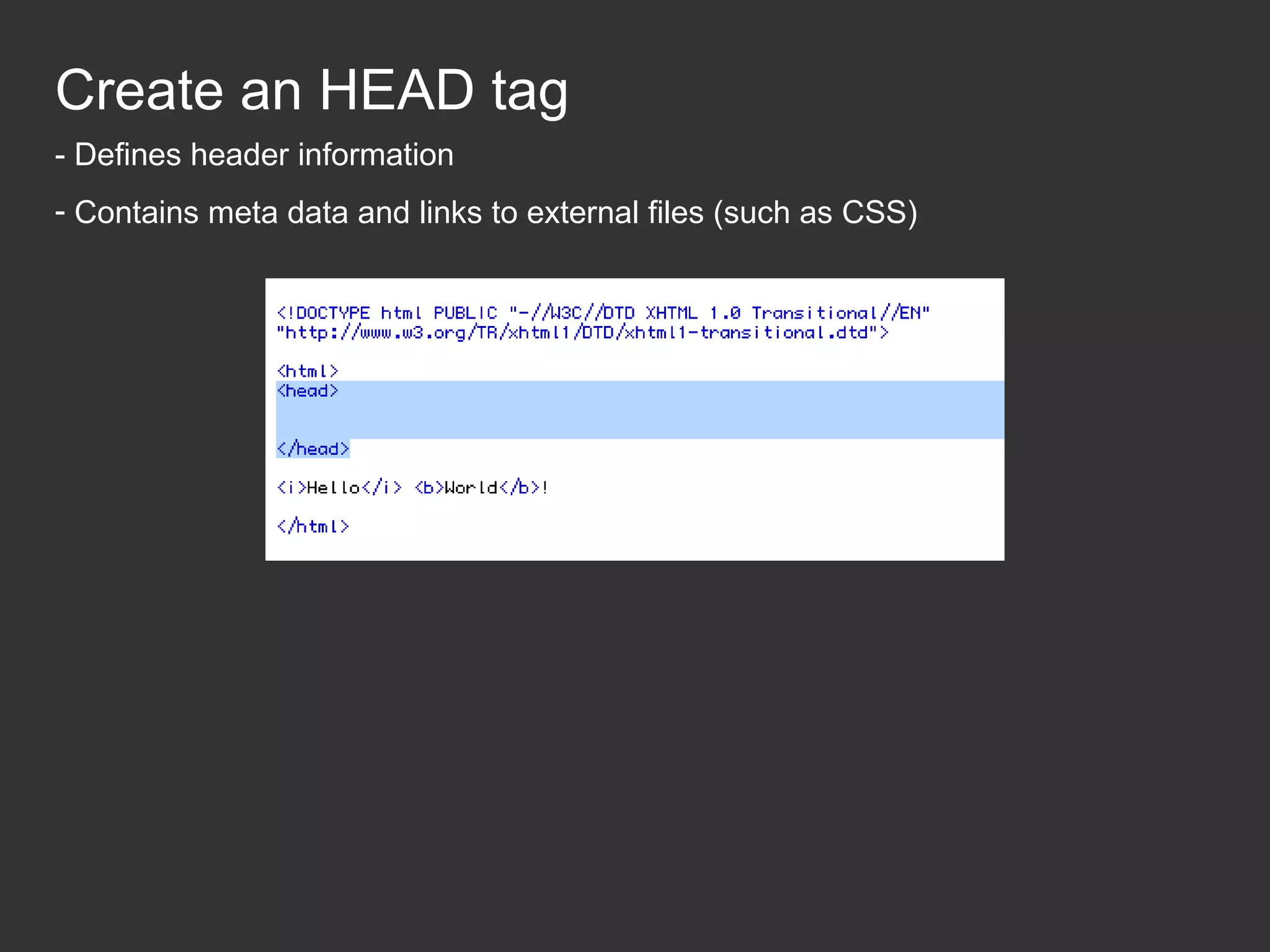
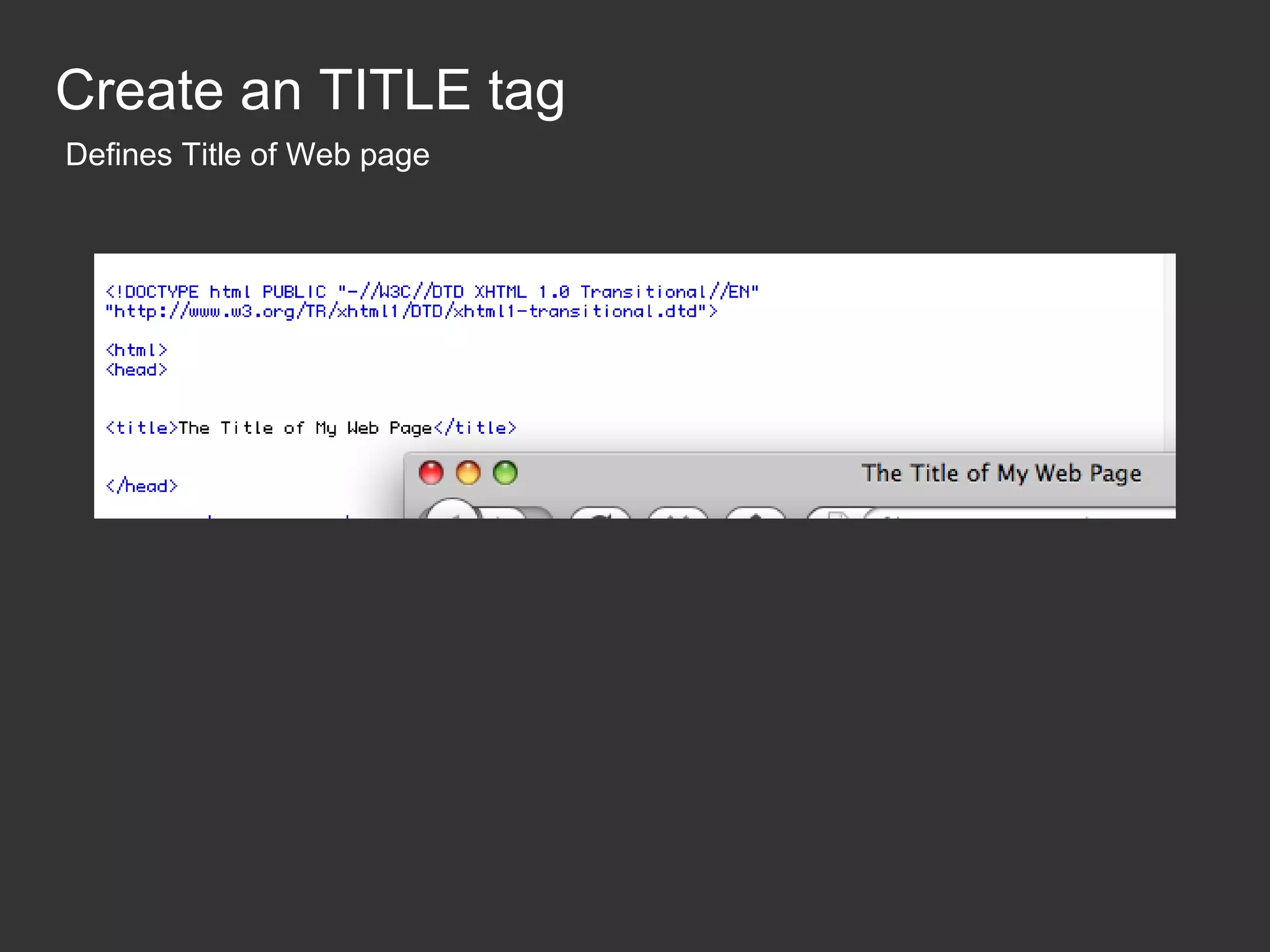
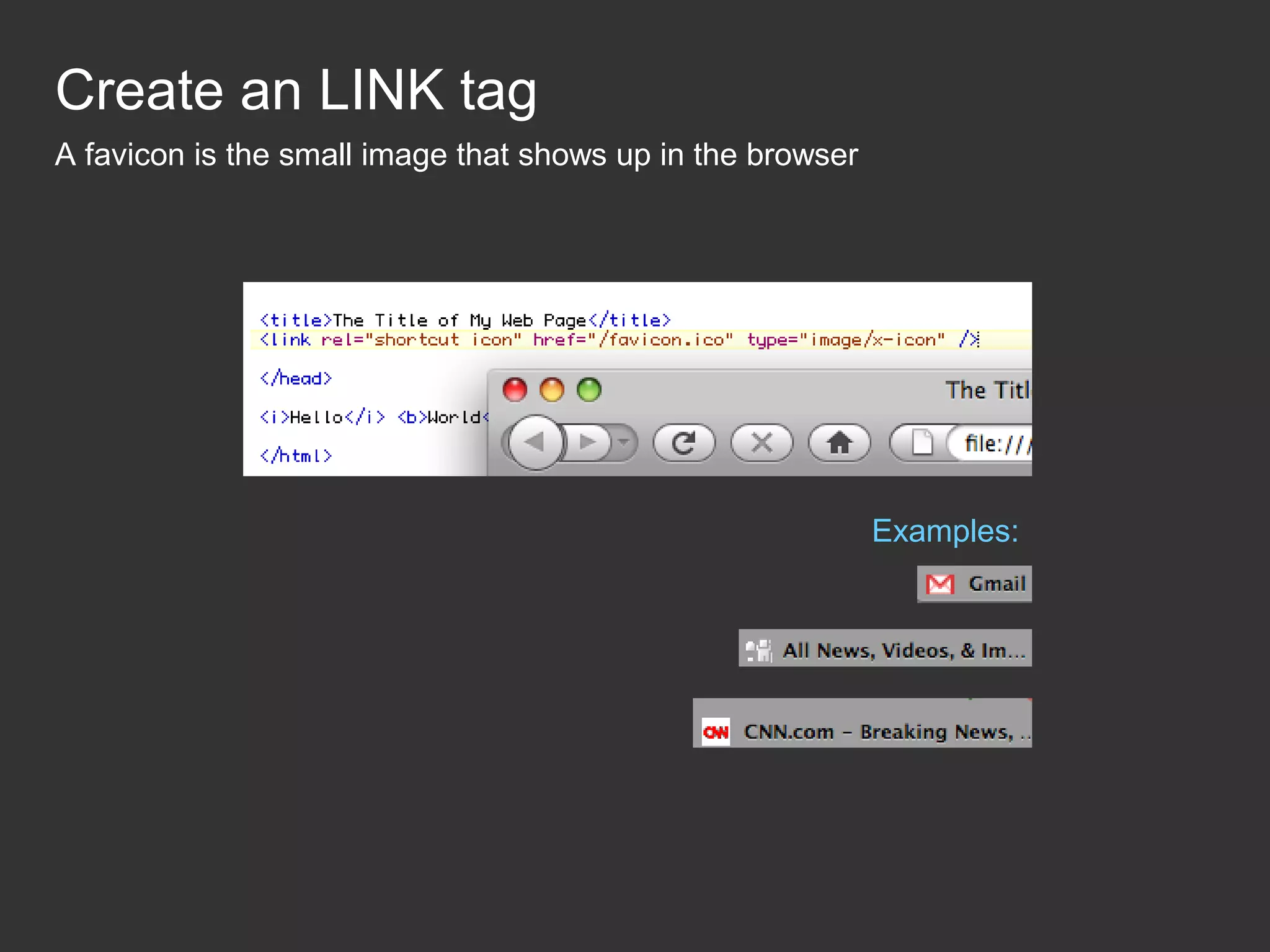
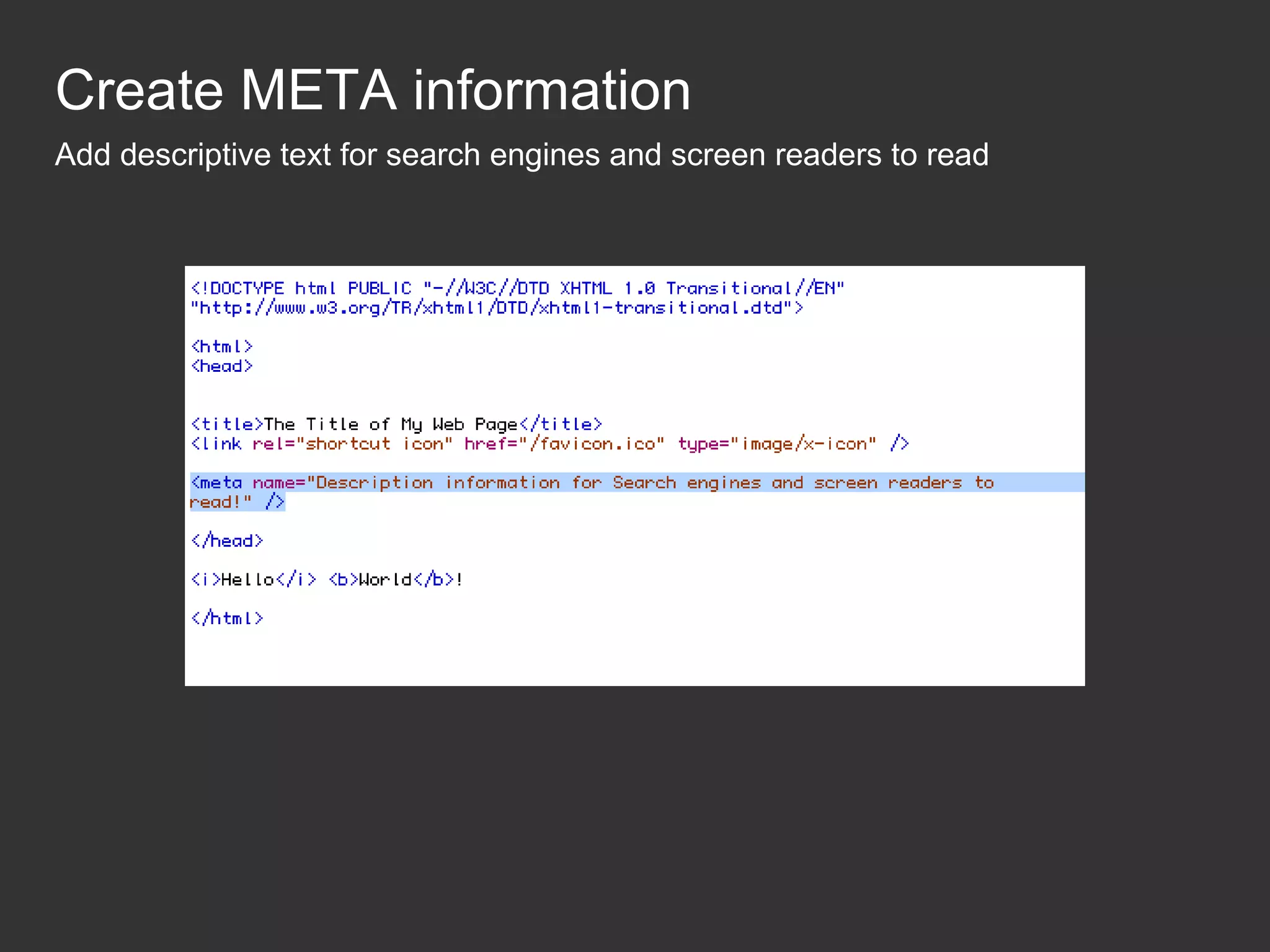
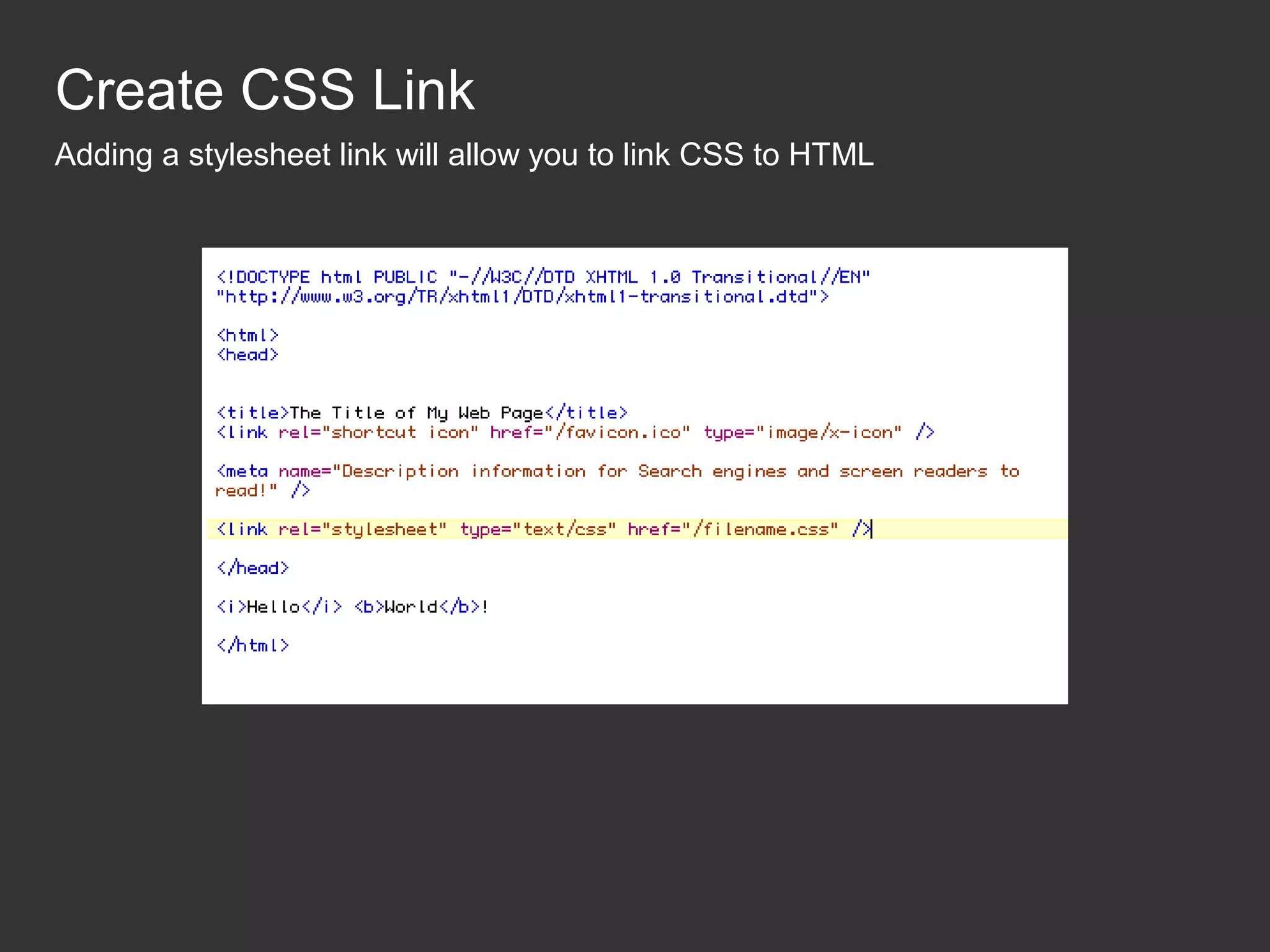
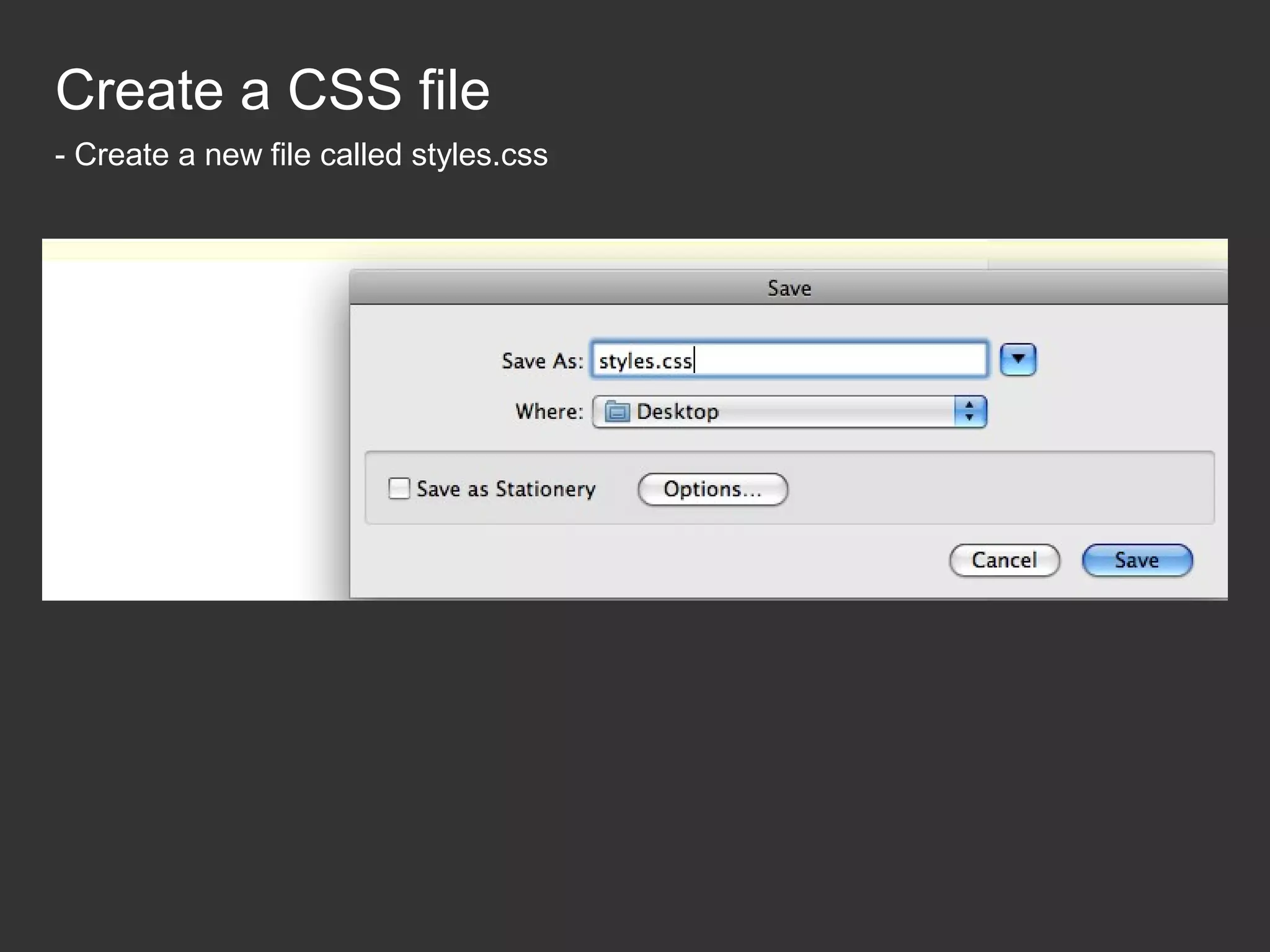
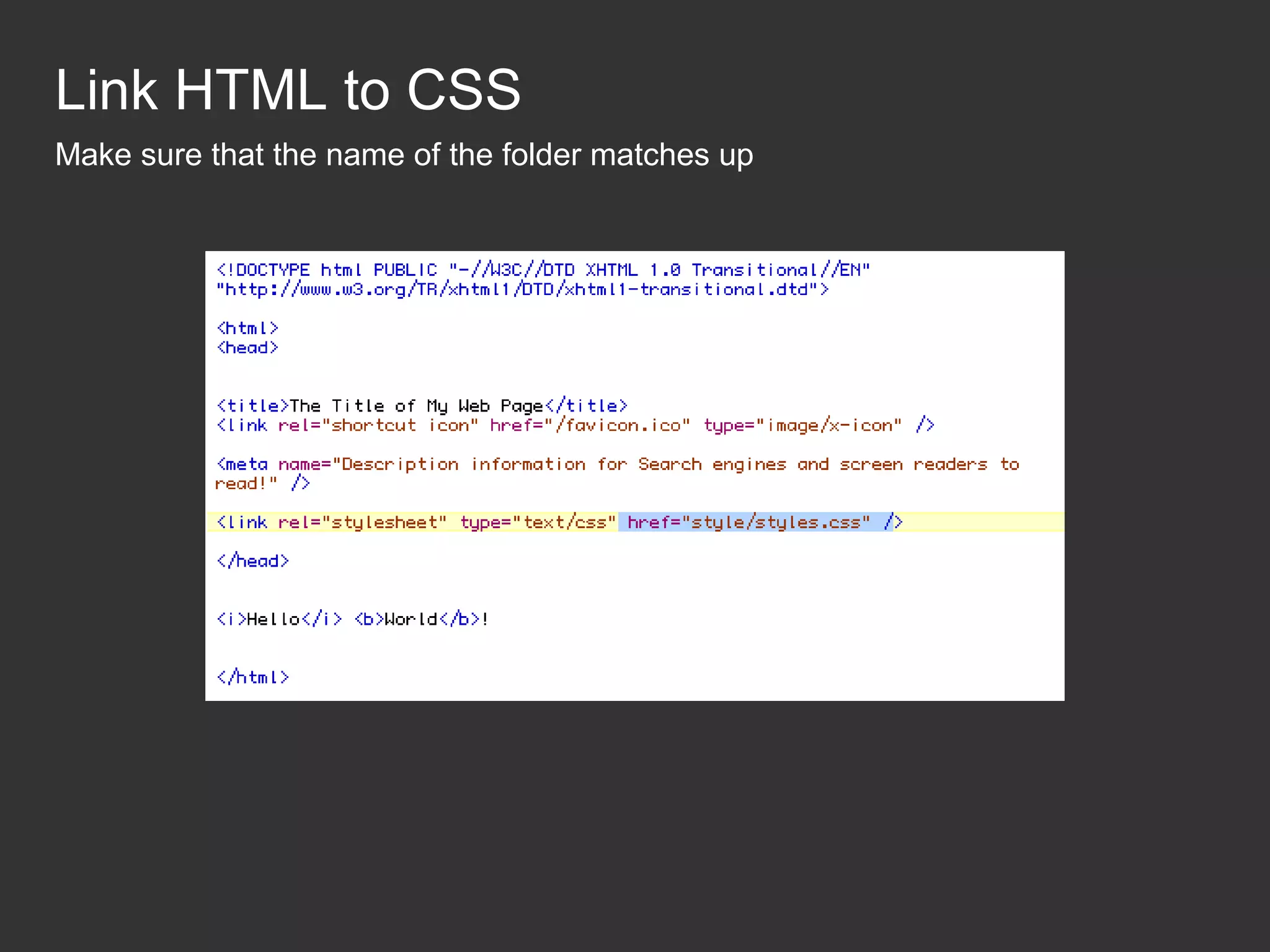
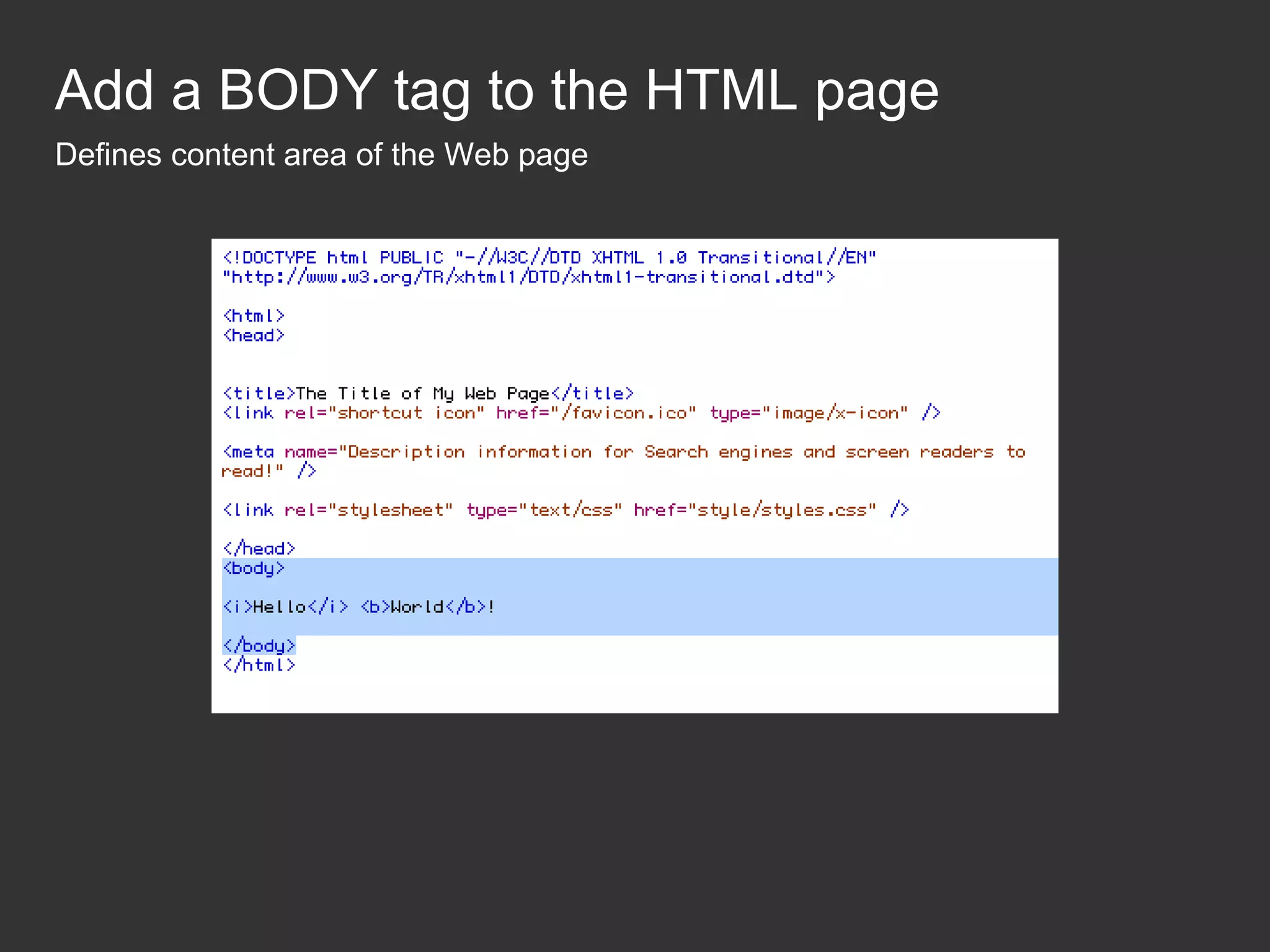
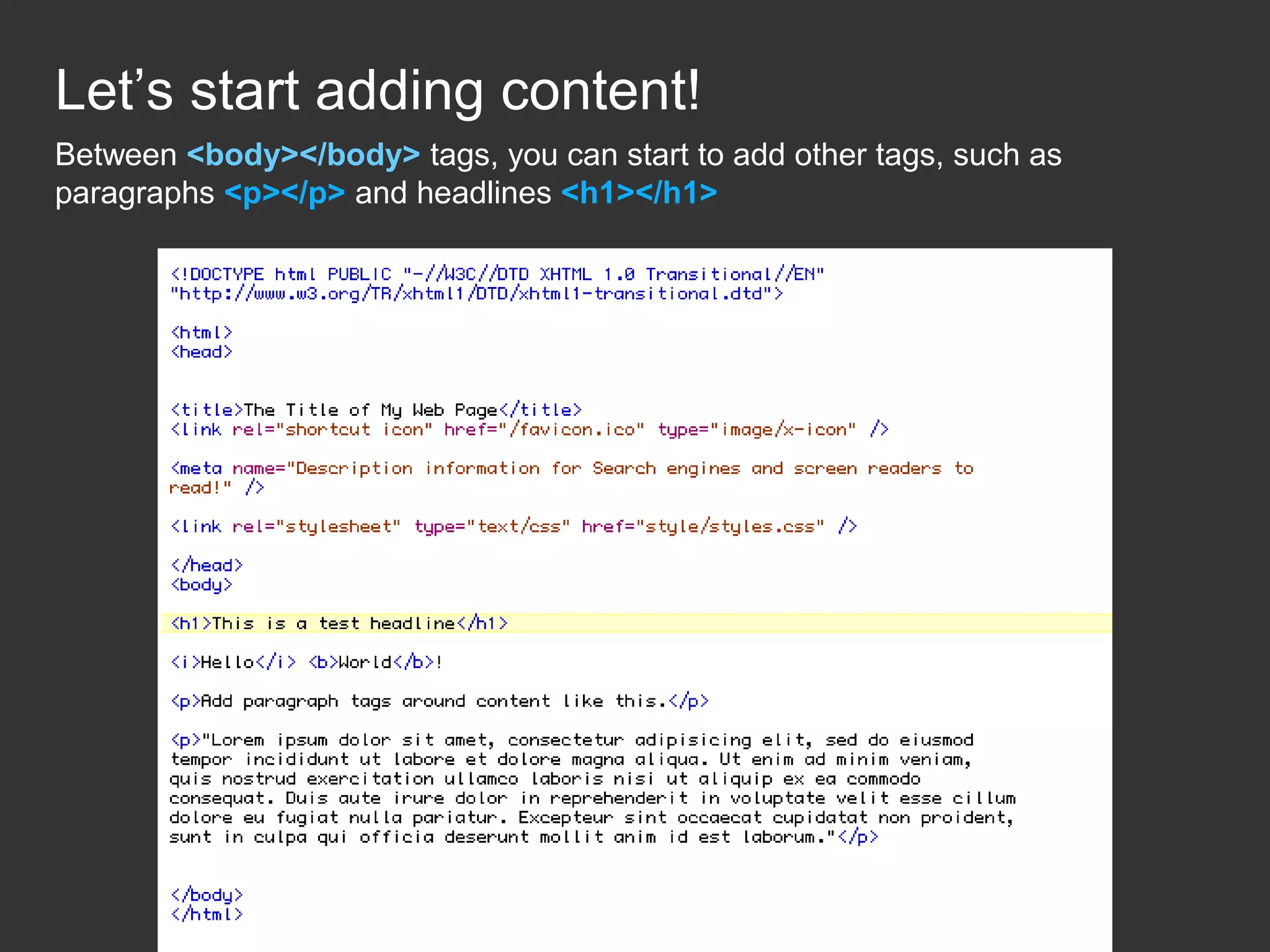
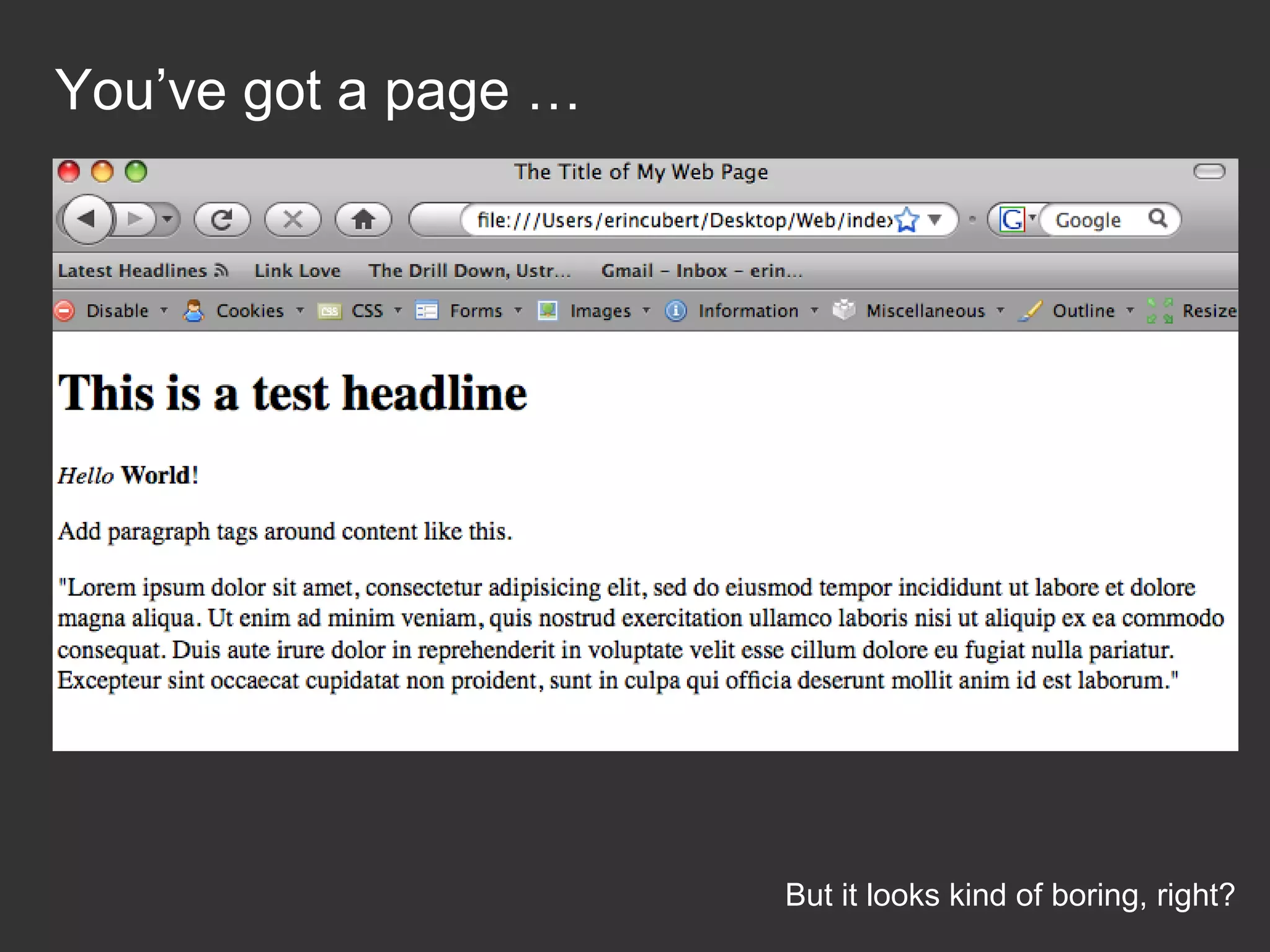
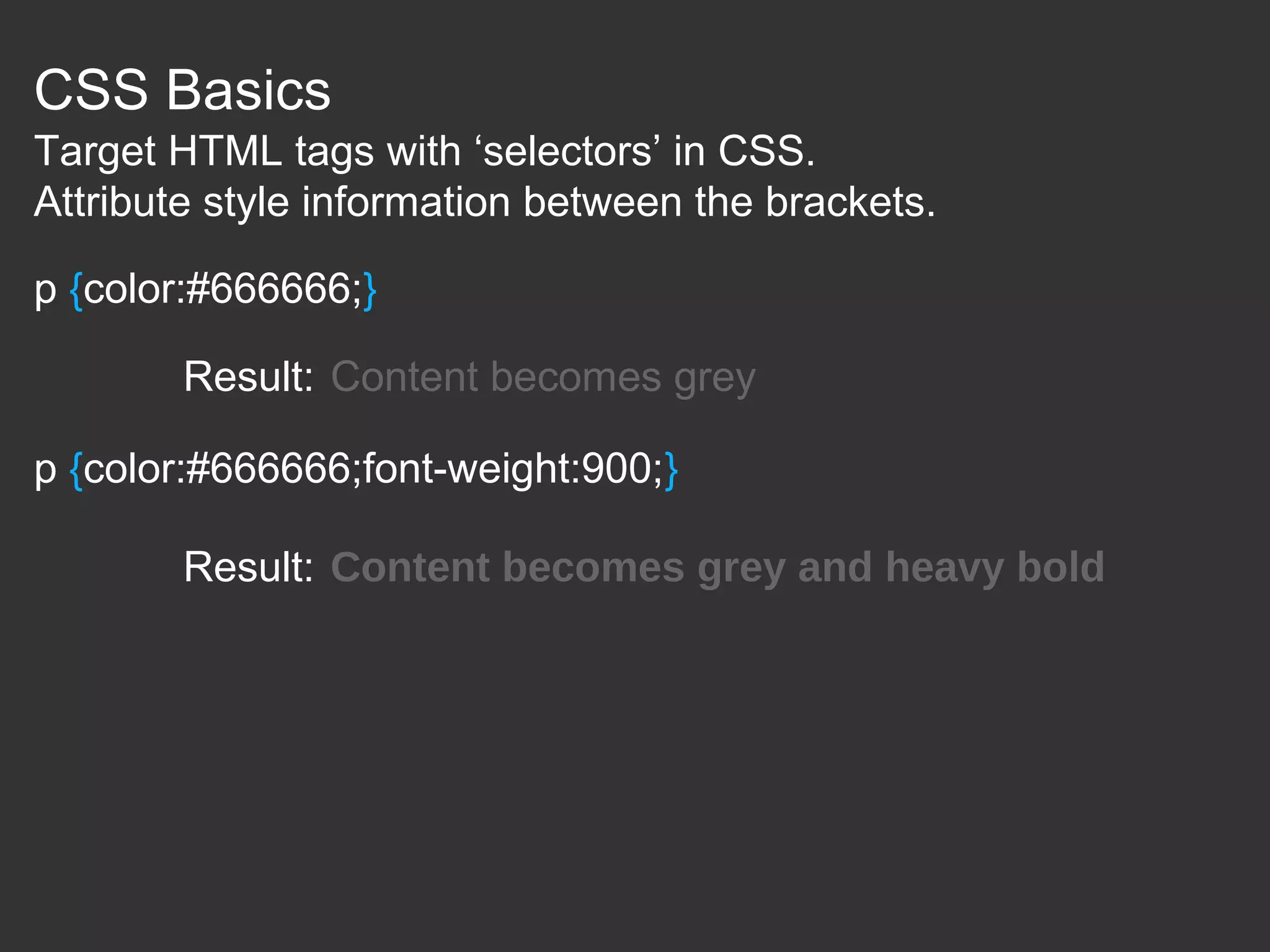
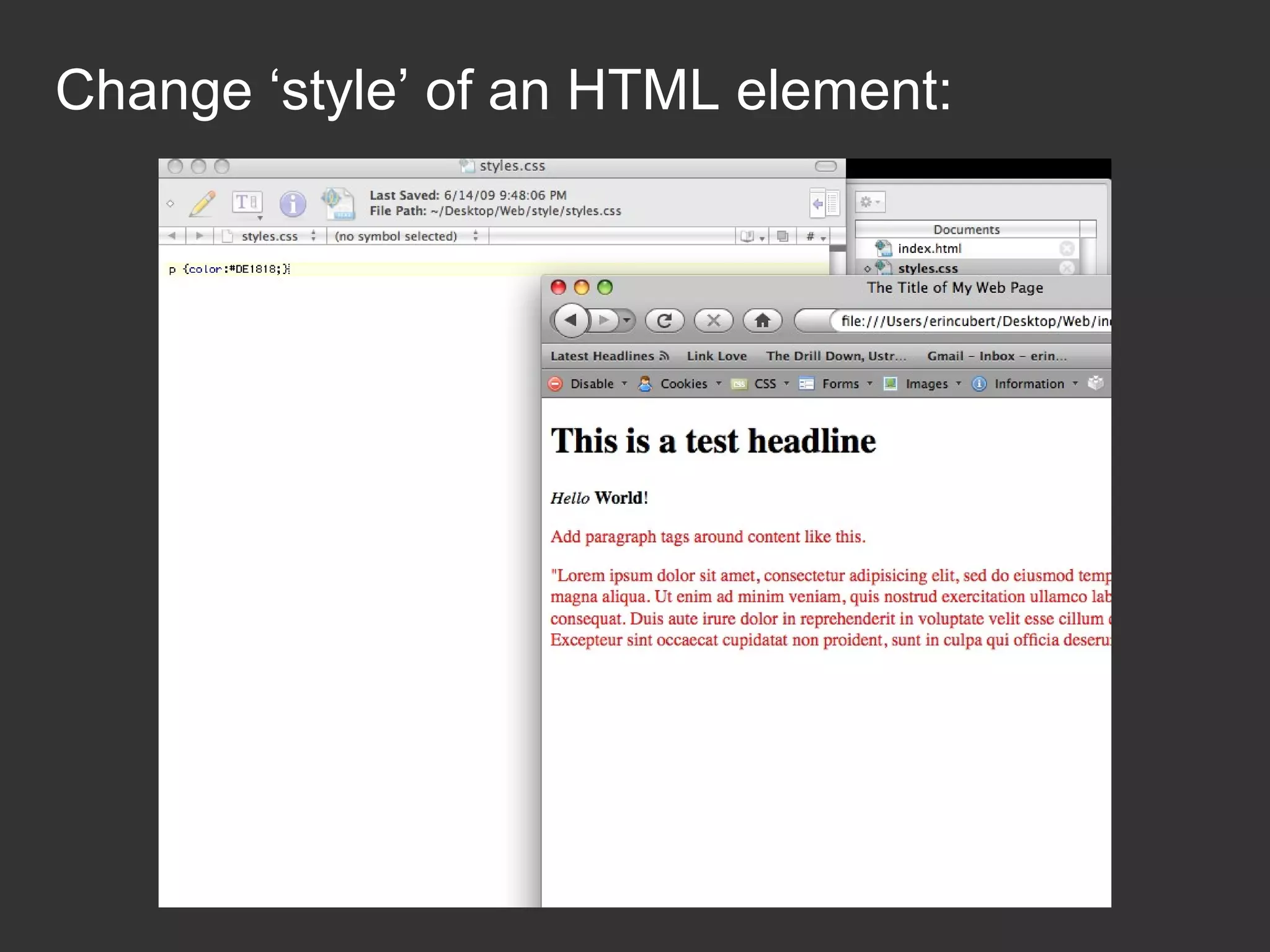
This document provides an introduction to HTML and CSS for web development. It explains that HTML is used for content and structure, describing elements like paragraphs and headings, while CSS is used to separate style from content and control formatting and layout. The document then gives examples of basic HTML tags and CSS rules to style text color and font weight. It encourages the reader to start creating their own HTML and CSS files to get hands-on experience with web development.