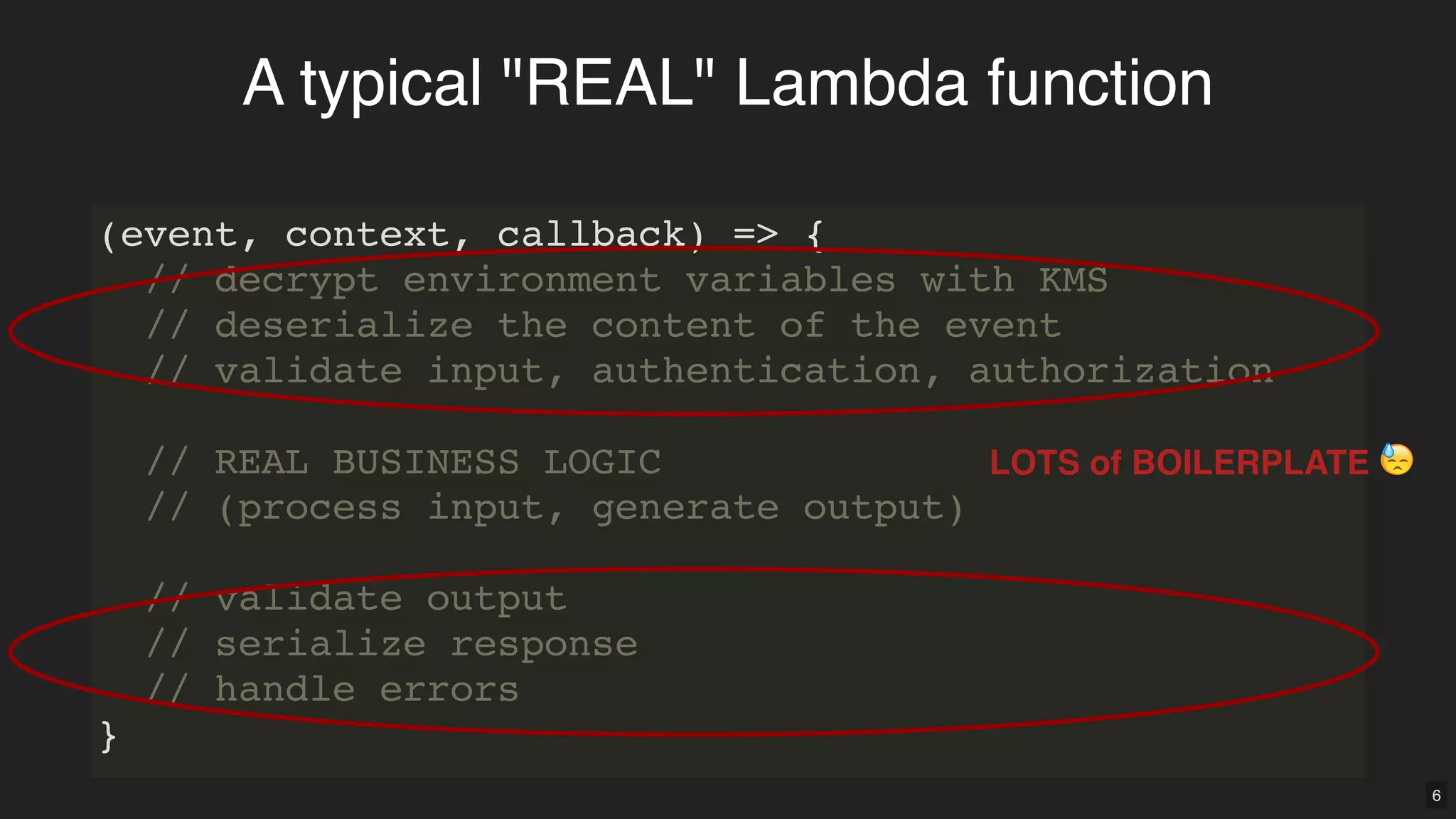
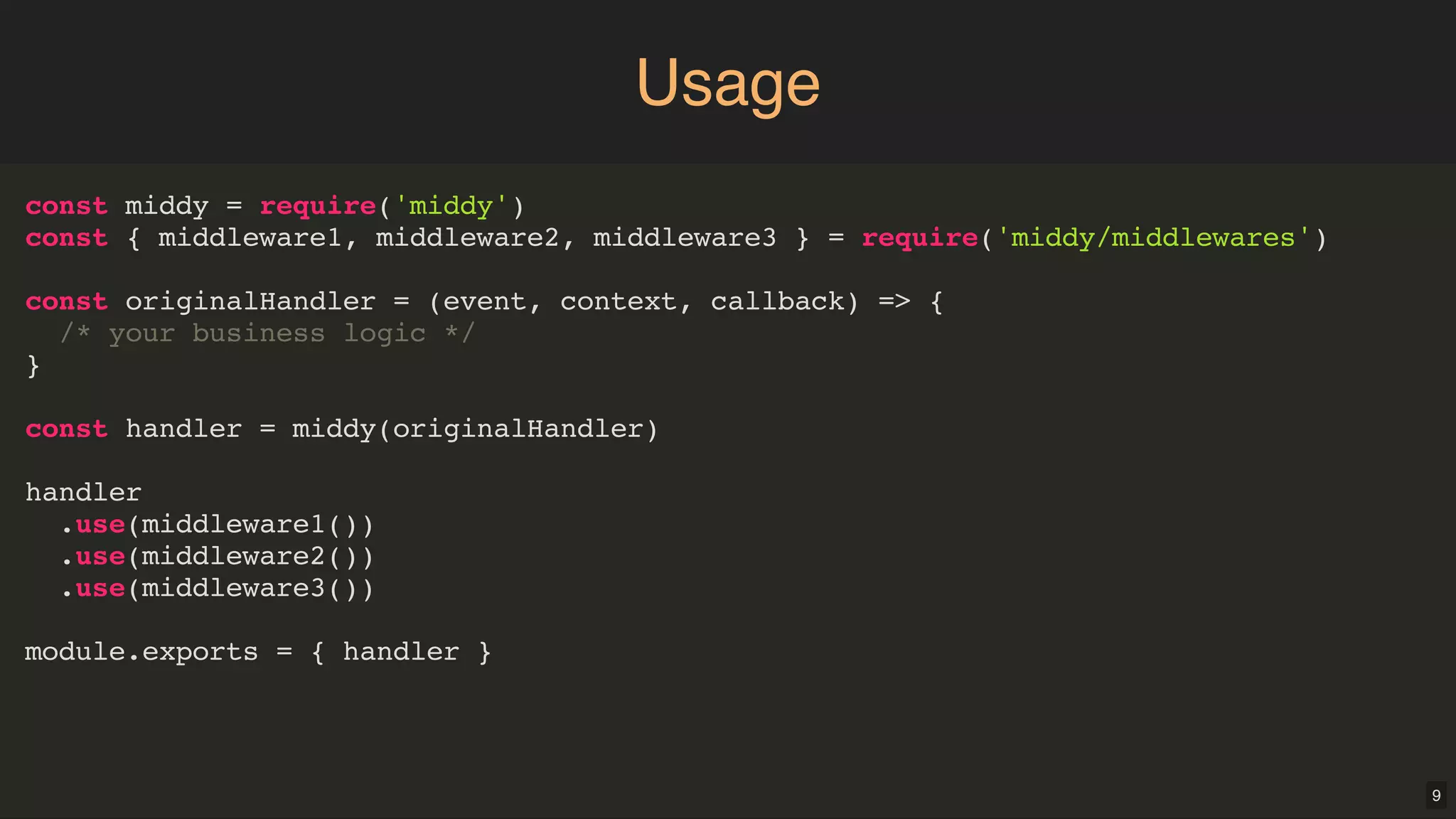
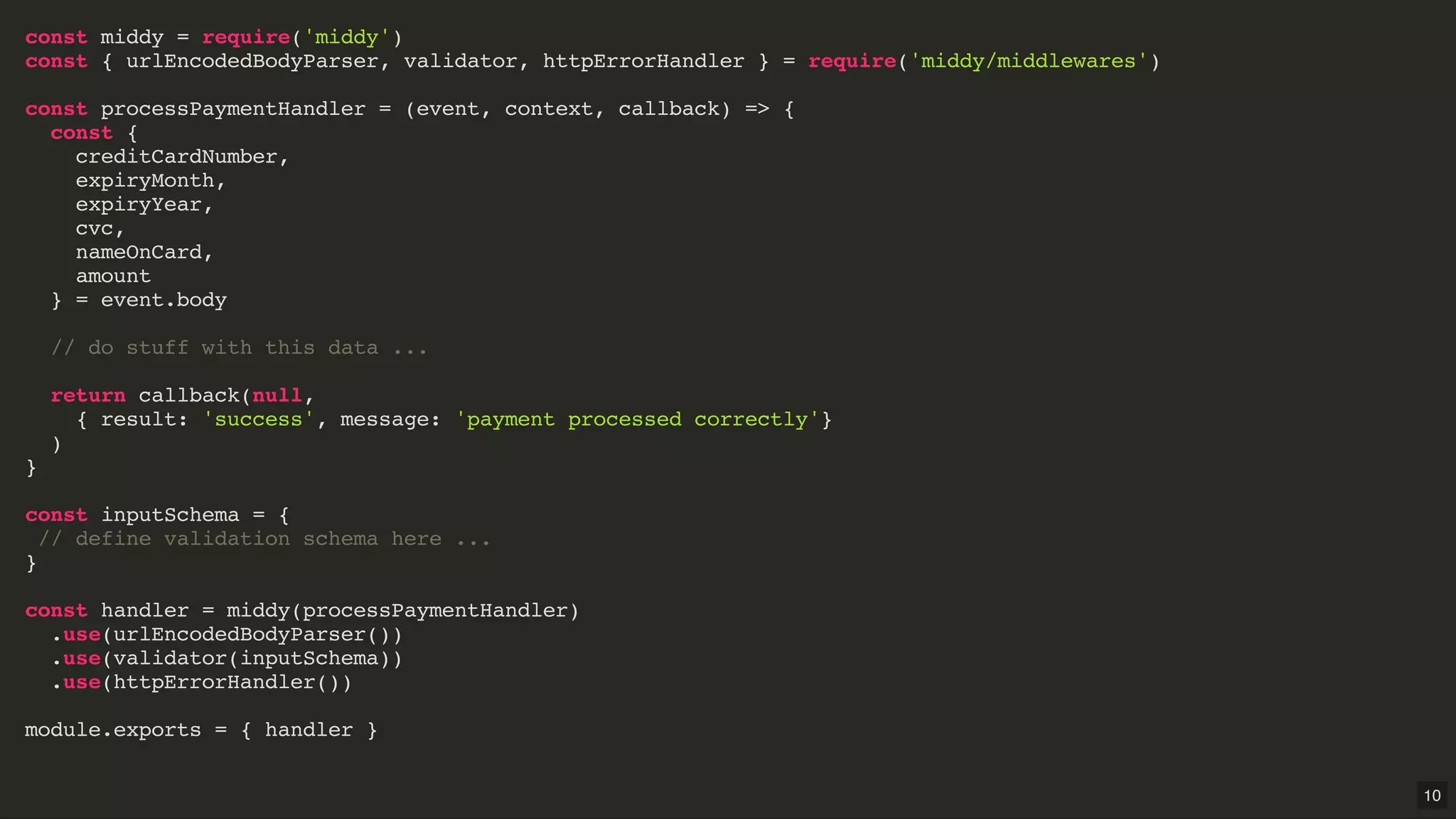
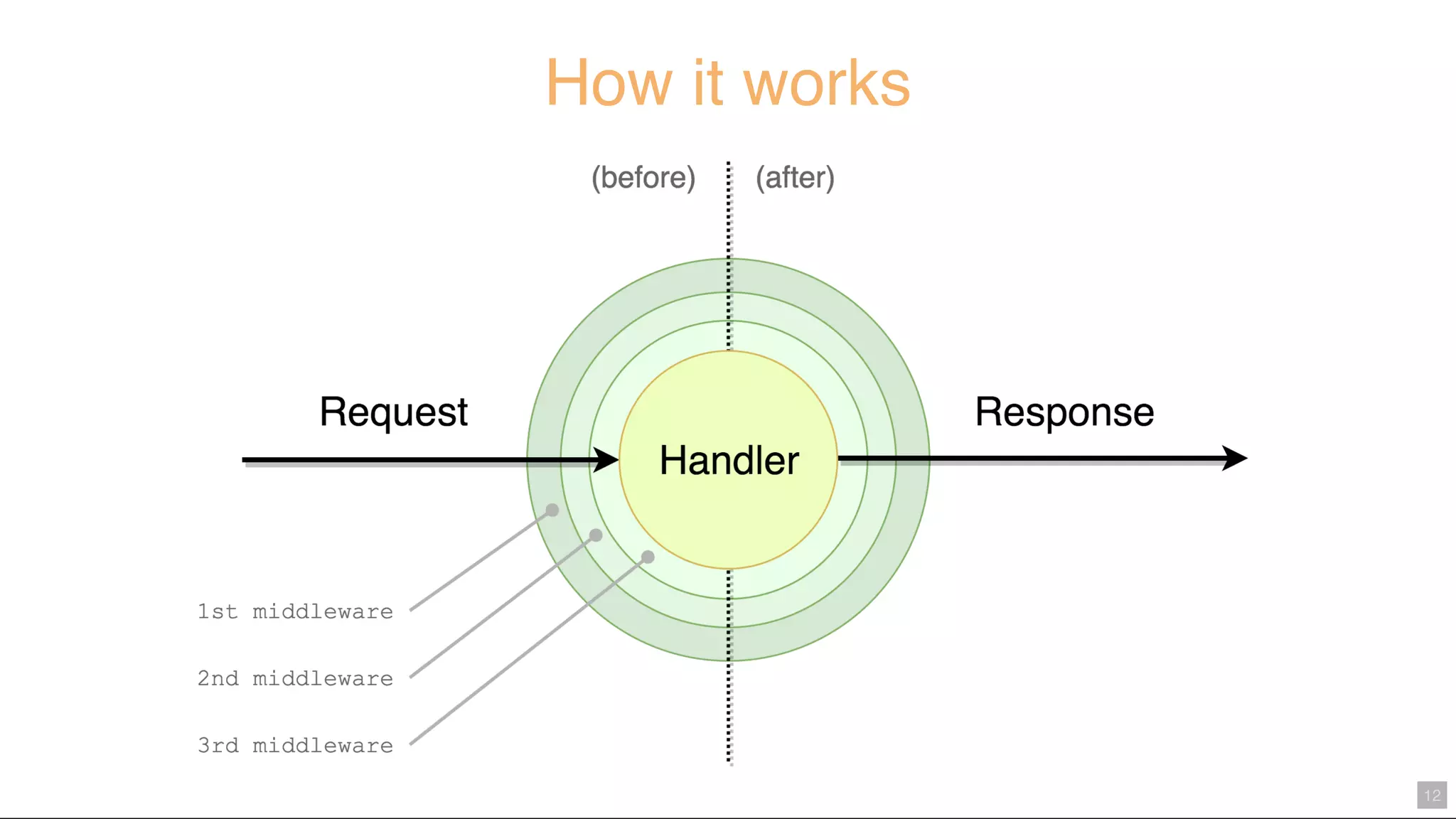
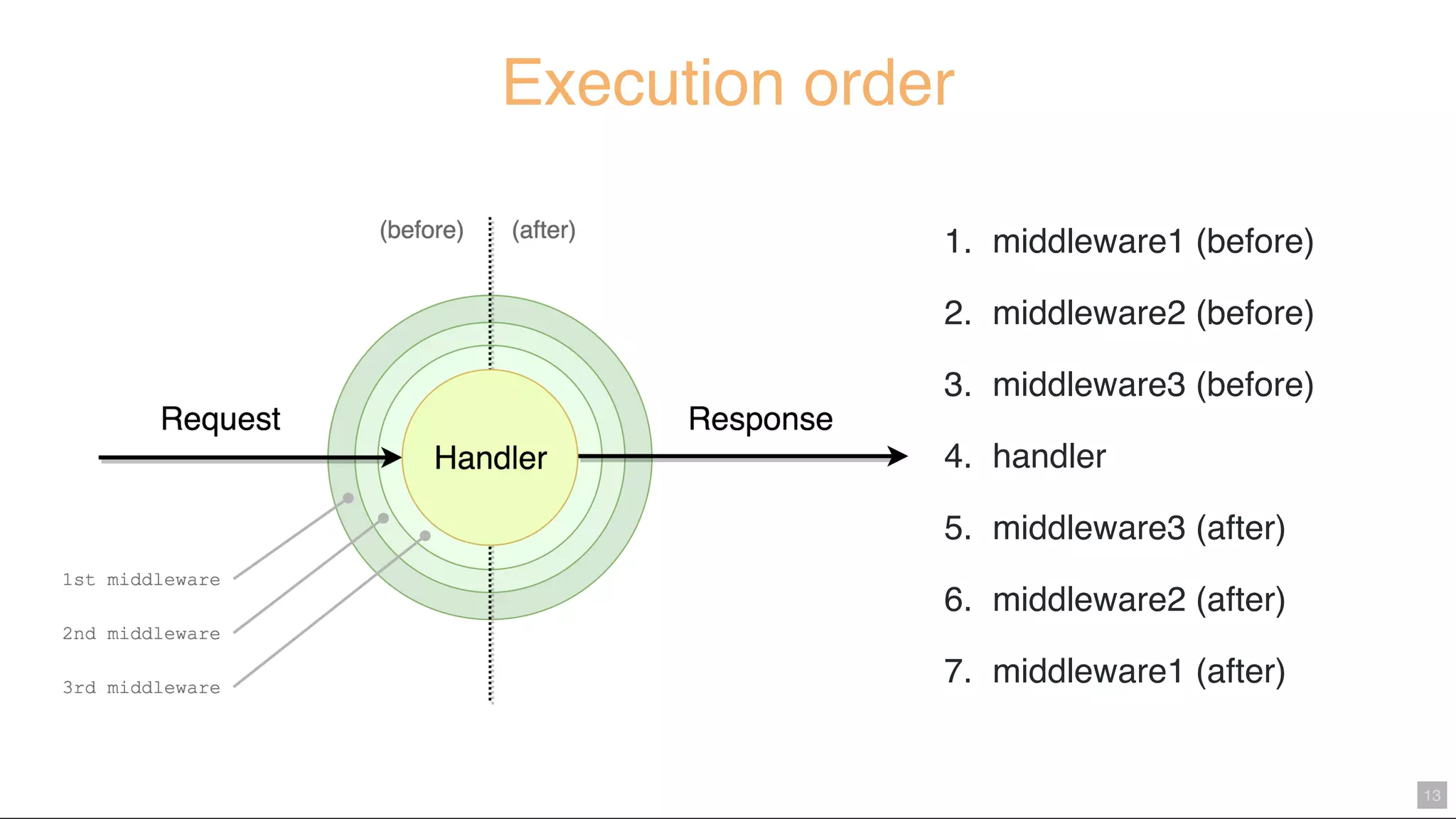
Middy.js is a middleware engine designed to simplify AWS Lambda functions written in Node.js by reducing boilerplate code and improving code organization. It allows developers to use reusable middleware for tasks such as input validation, error handling, and body parsing, enabling them to focus more on business logic. The document outlines how to implement Middy and some currently available middlewares that enhance Lambda function development.