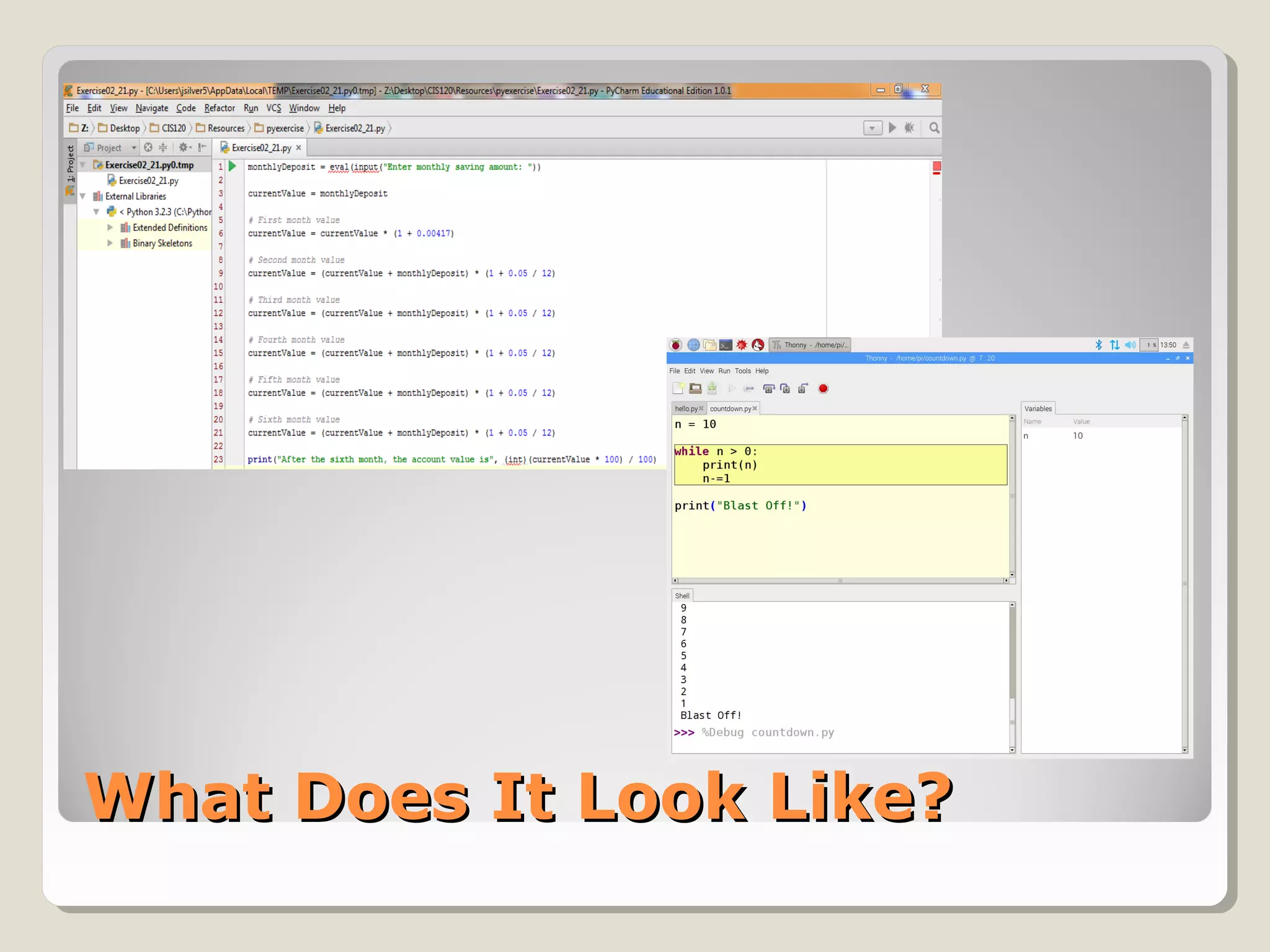
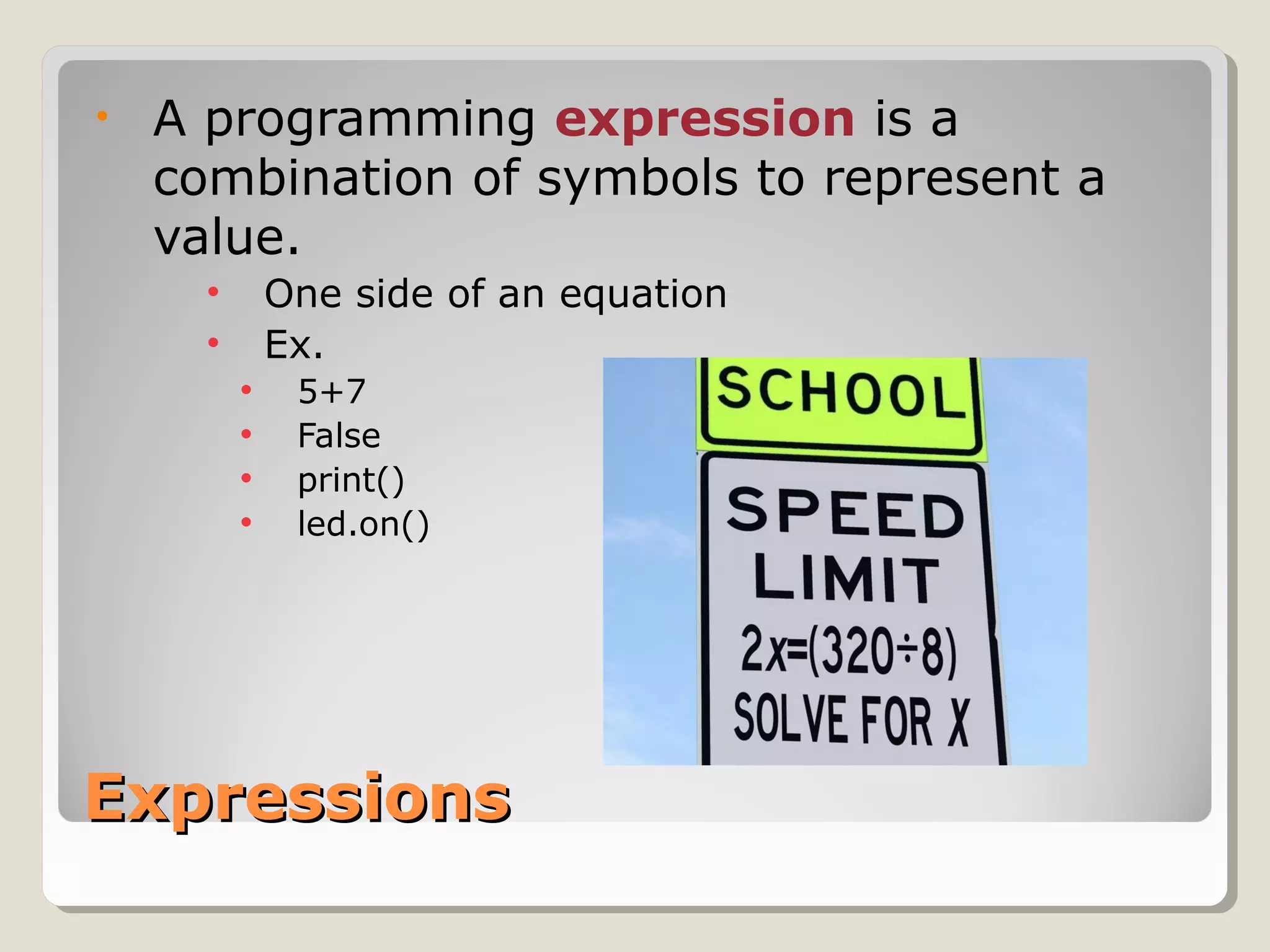
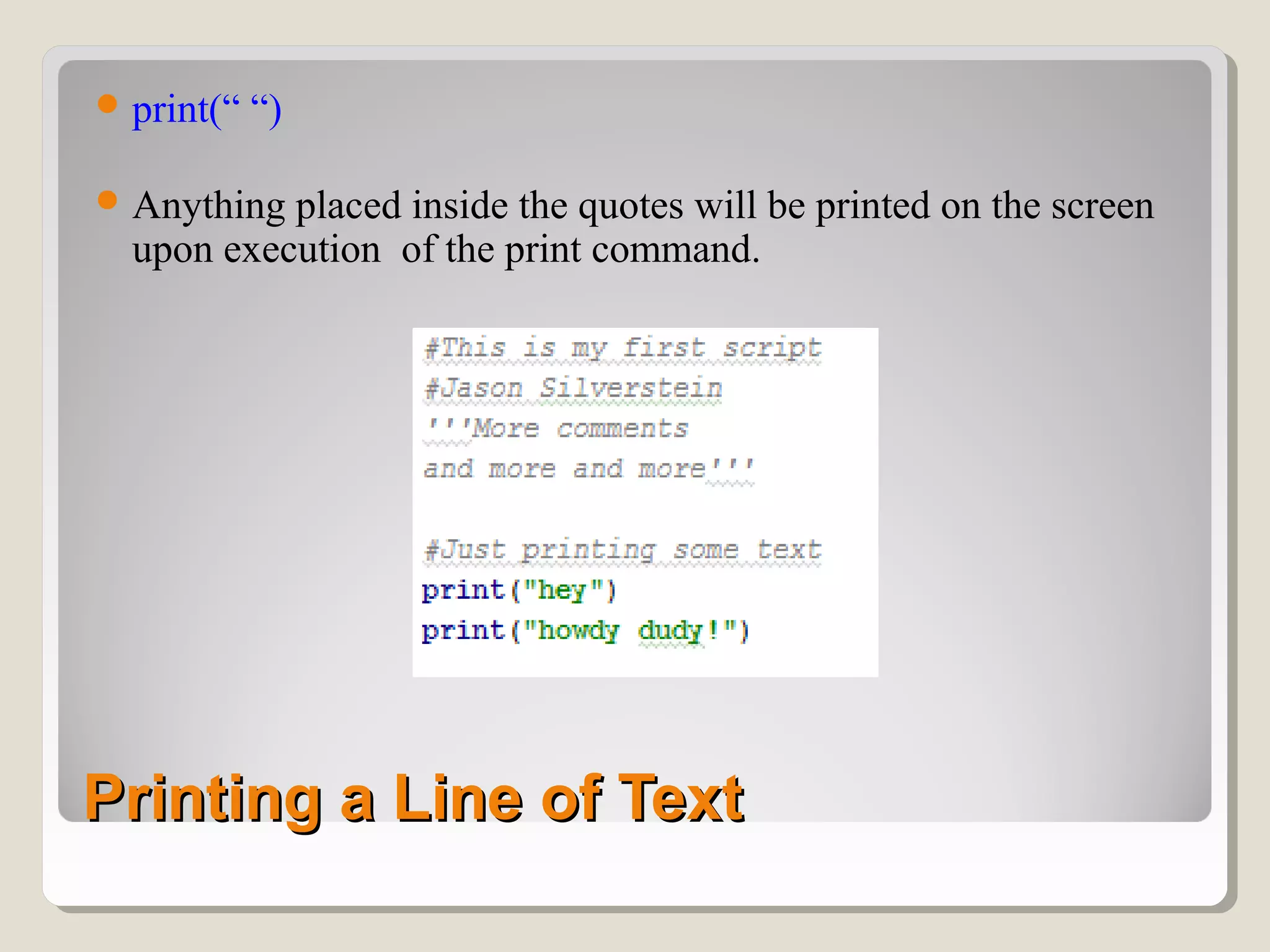
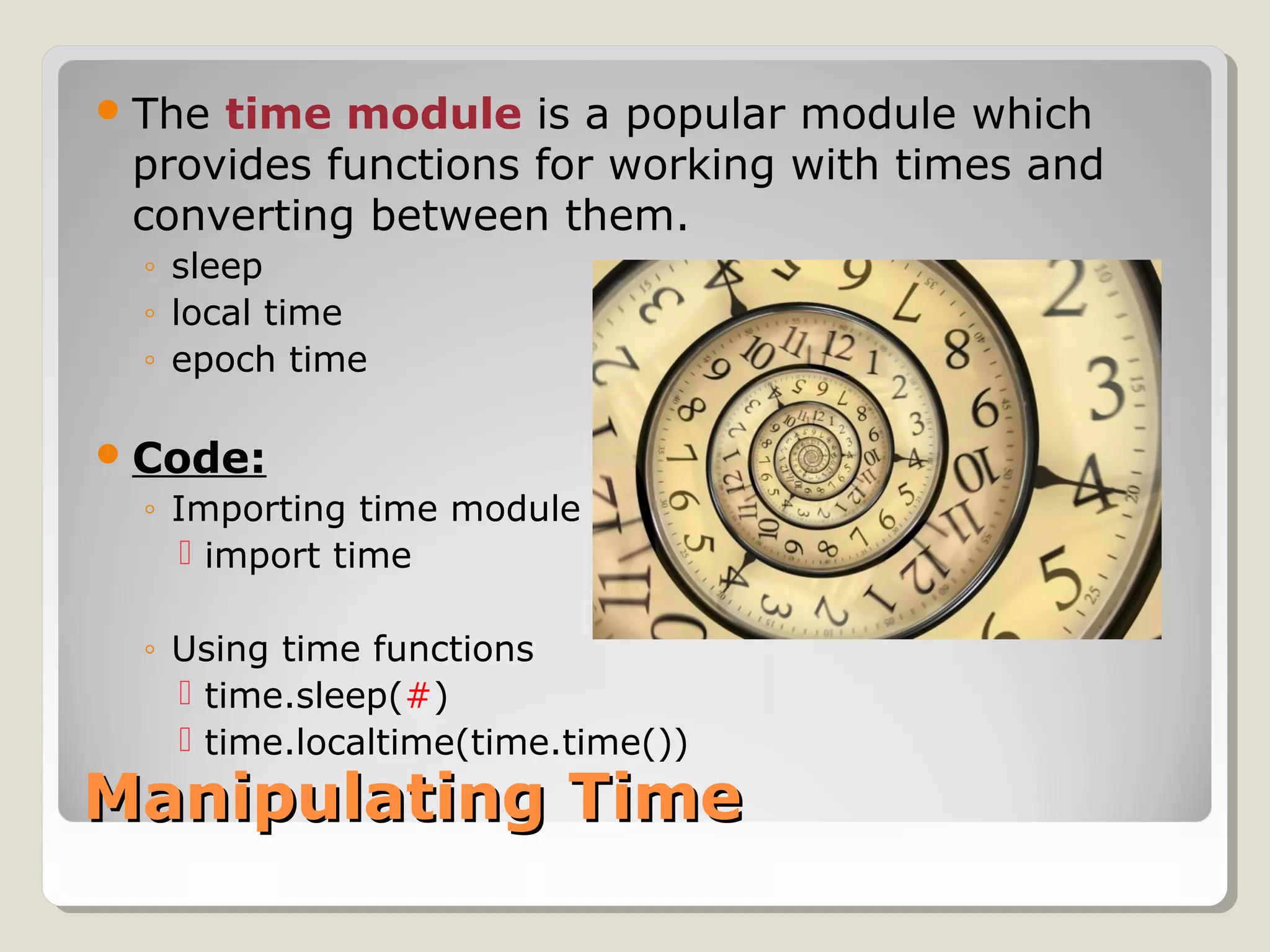
This document provides an introduction to Python programming. It discusses why Python is a useful language, how Python code is interpreted, the basic parts of a Python program including modules and main code, using comments and whitespace for readability, importing common modules like time and GPIOZero for working with times and LEDs, and basic expressions. Key terms defined include objects, modules, functions, and manipulating GPIO pins to control LEDs.