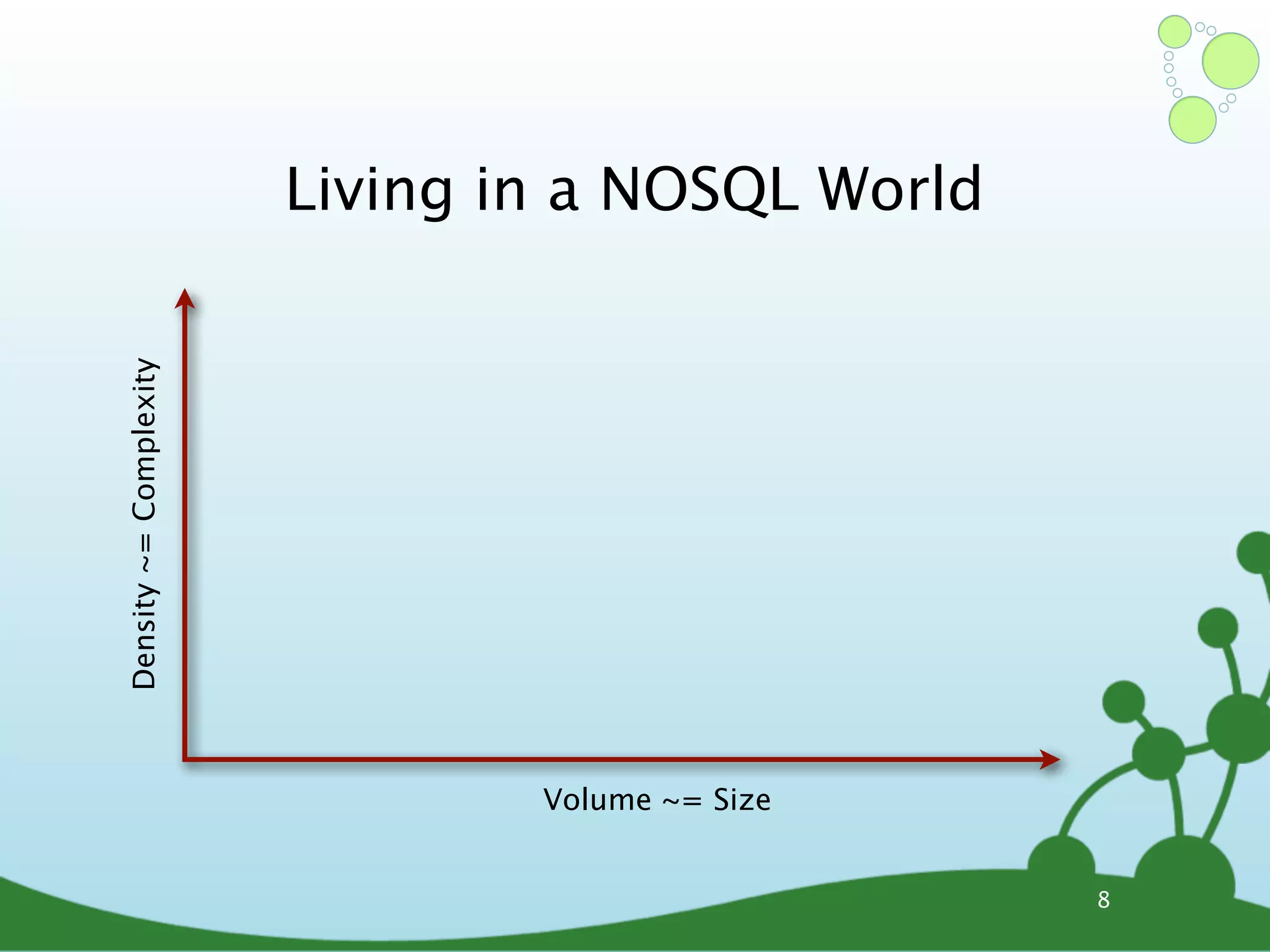
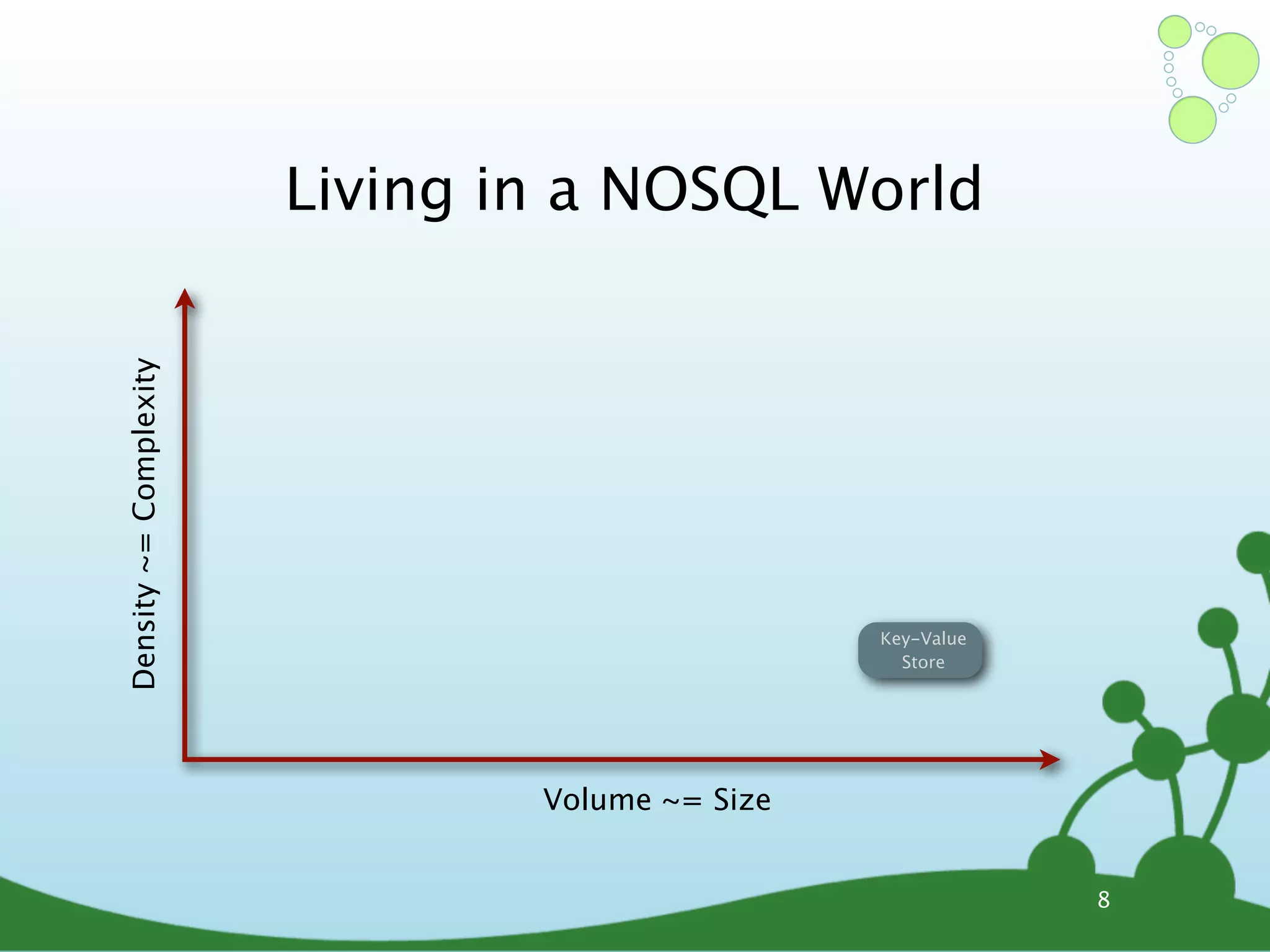
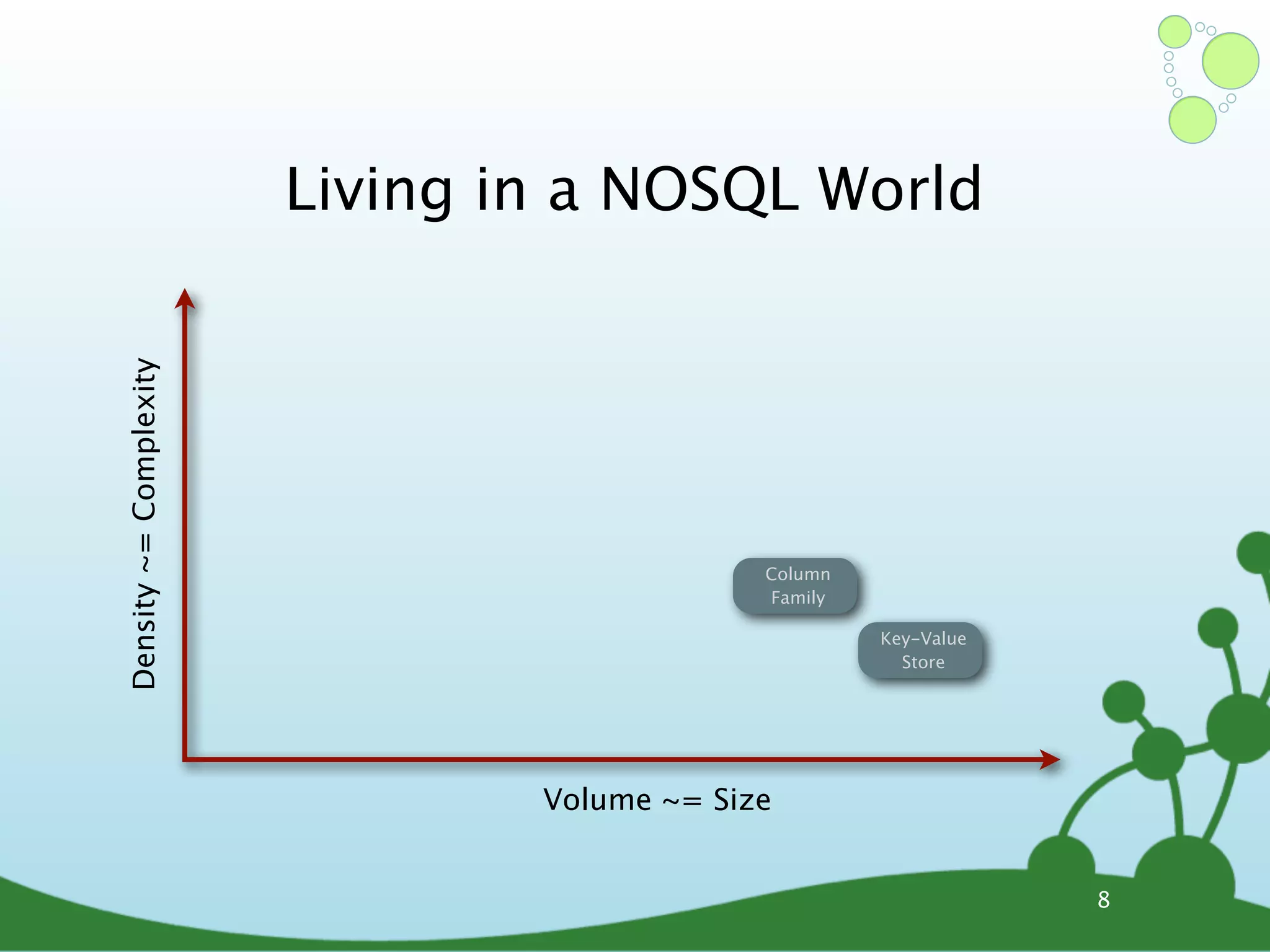
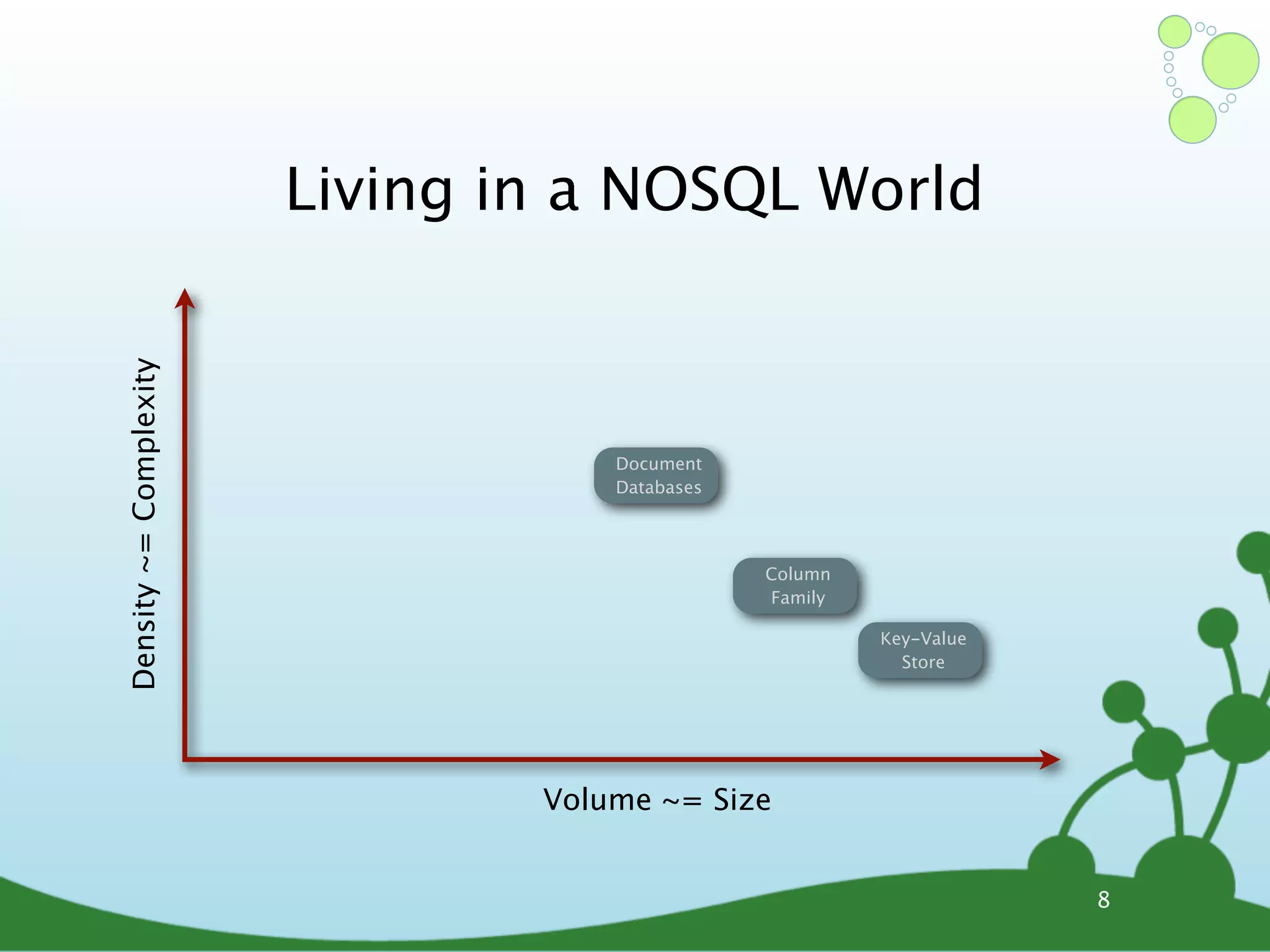
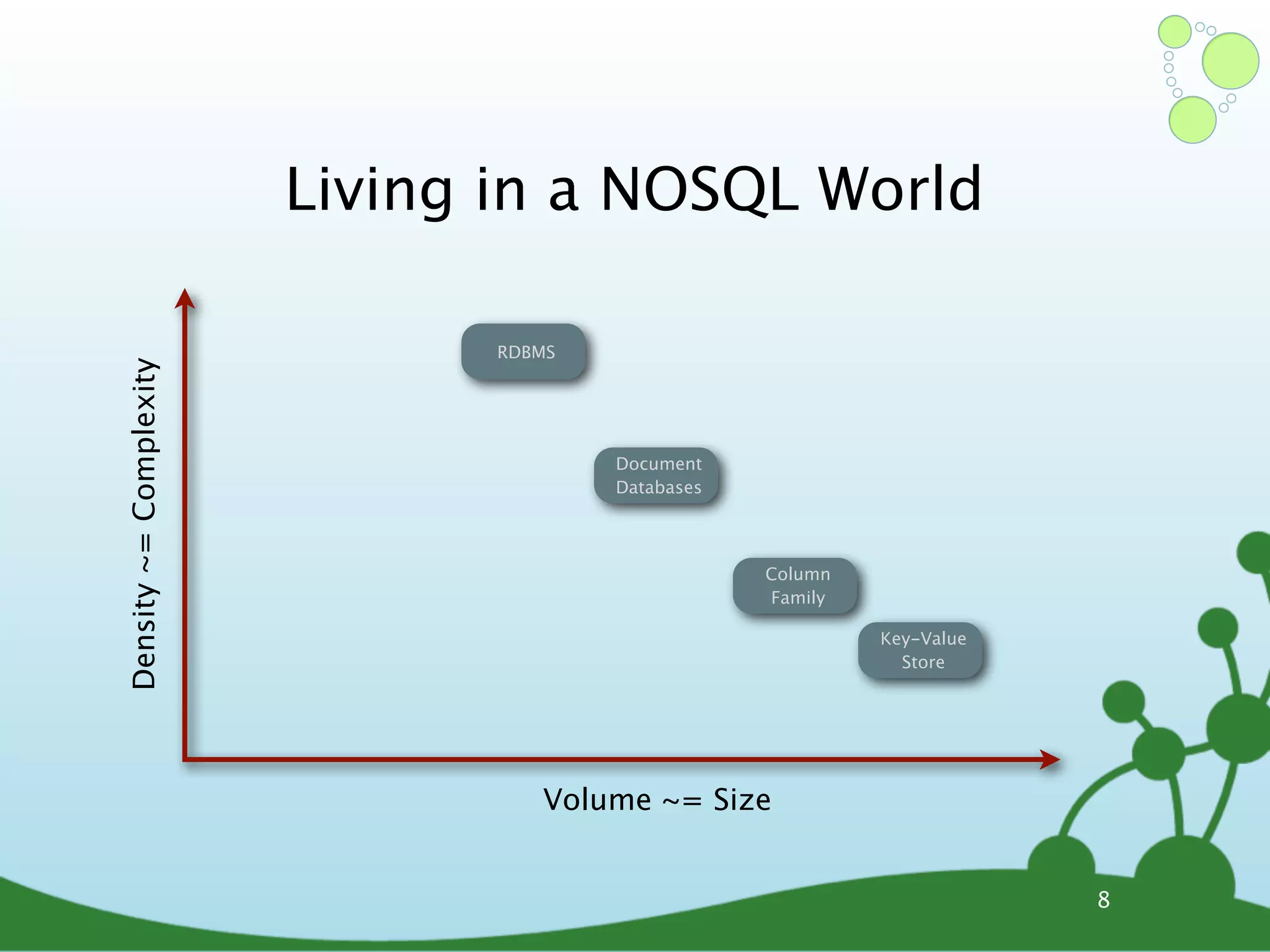
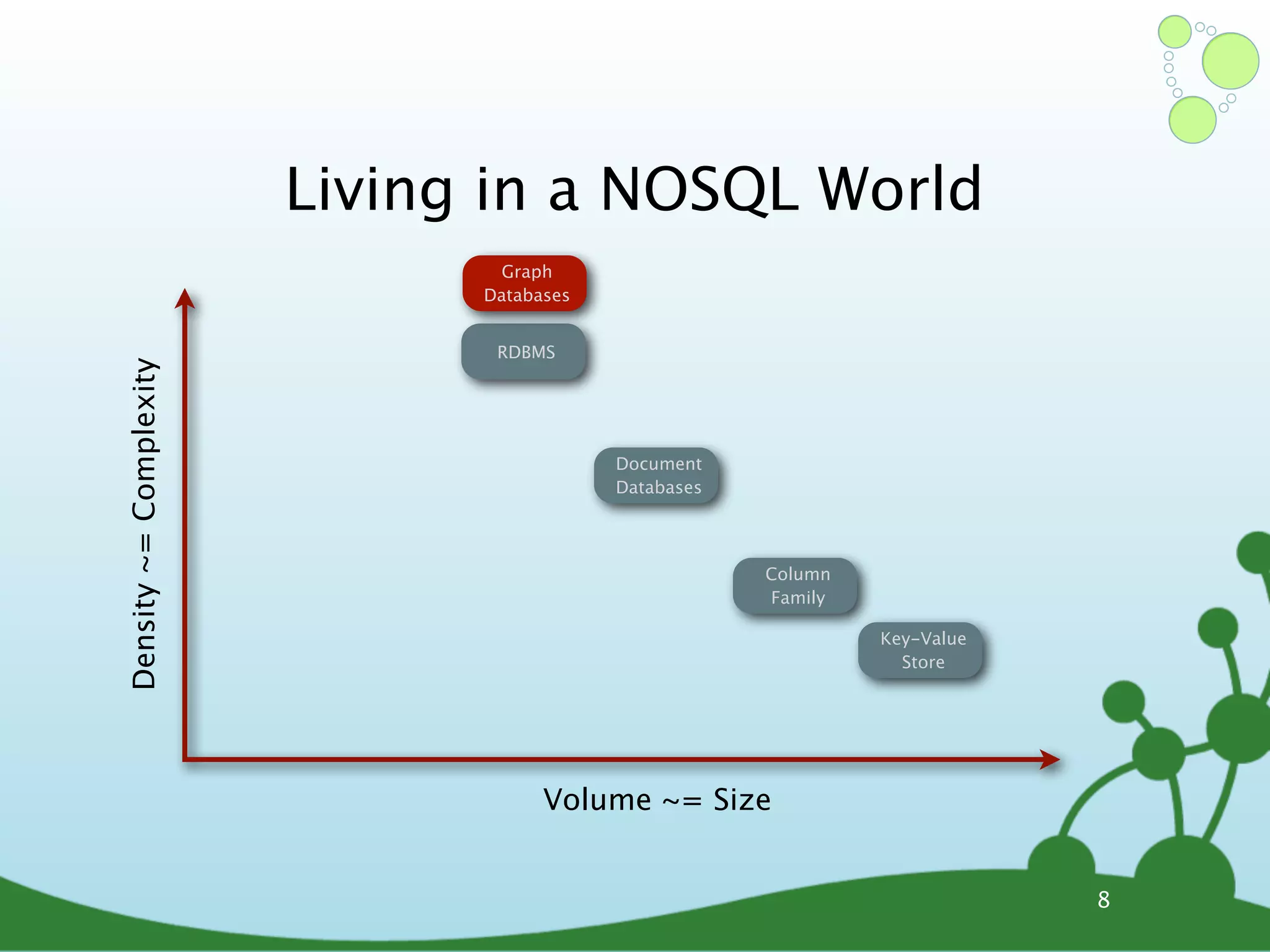
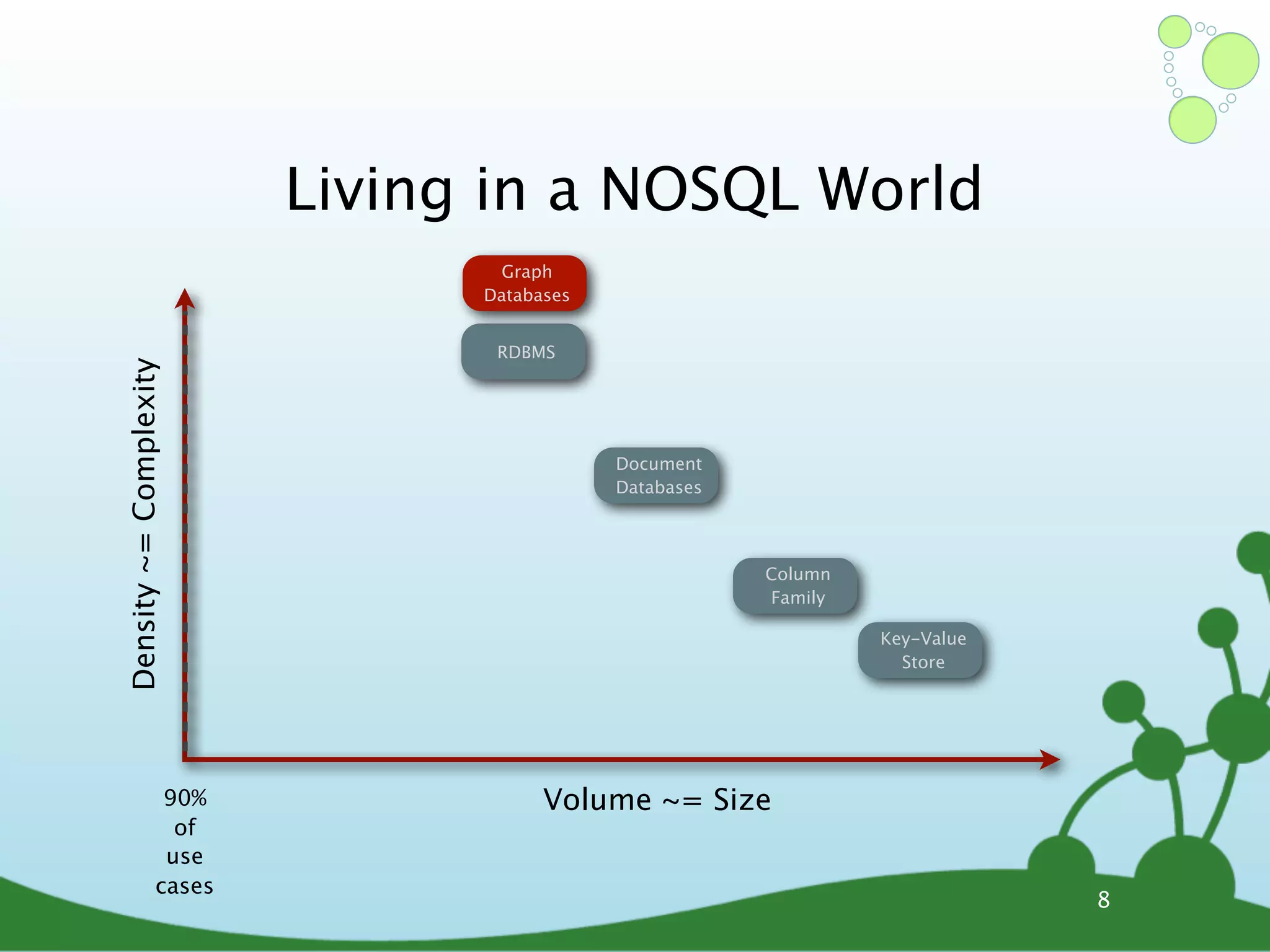
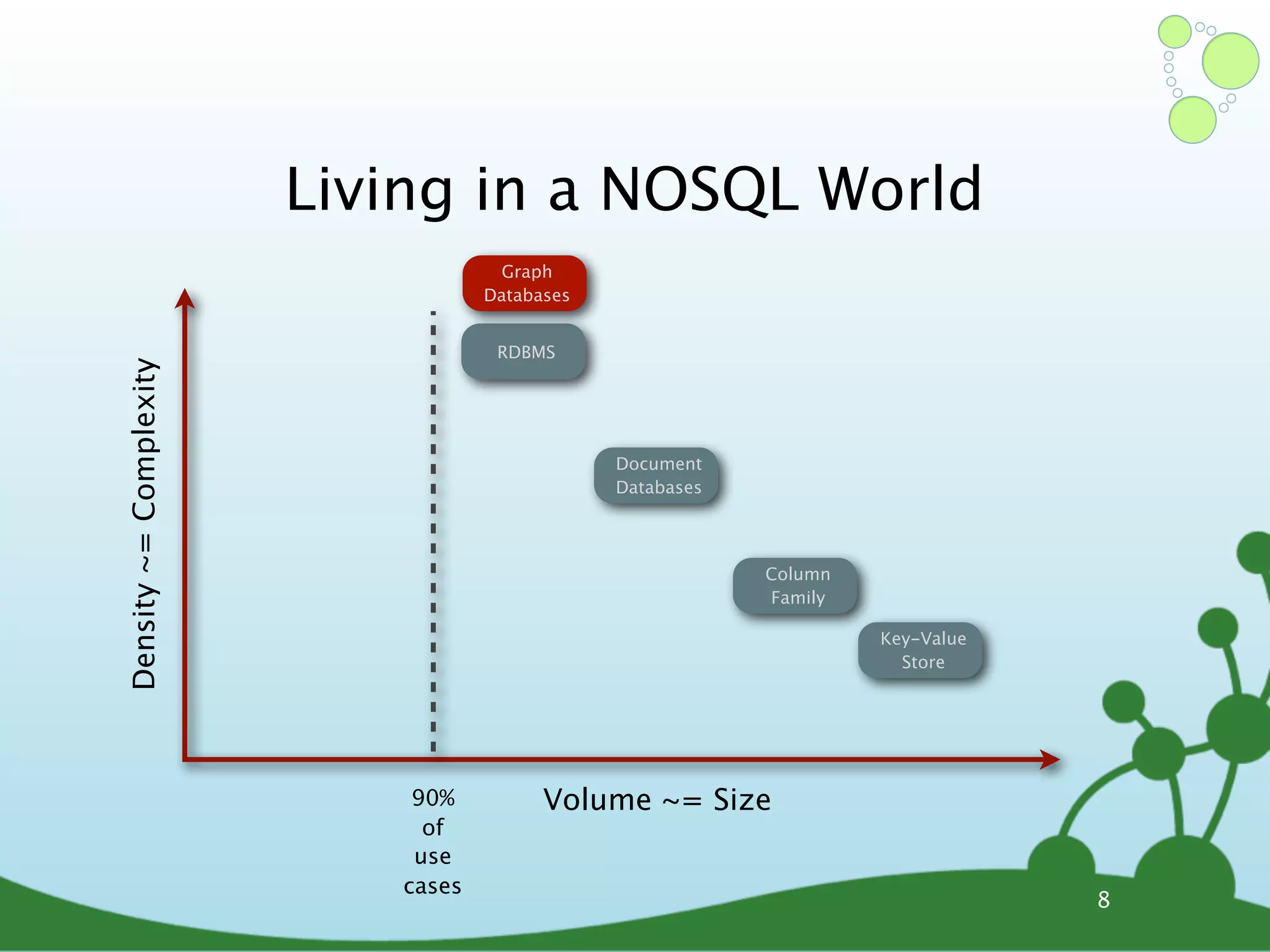
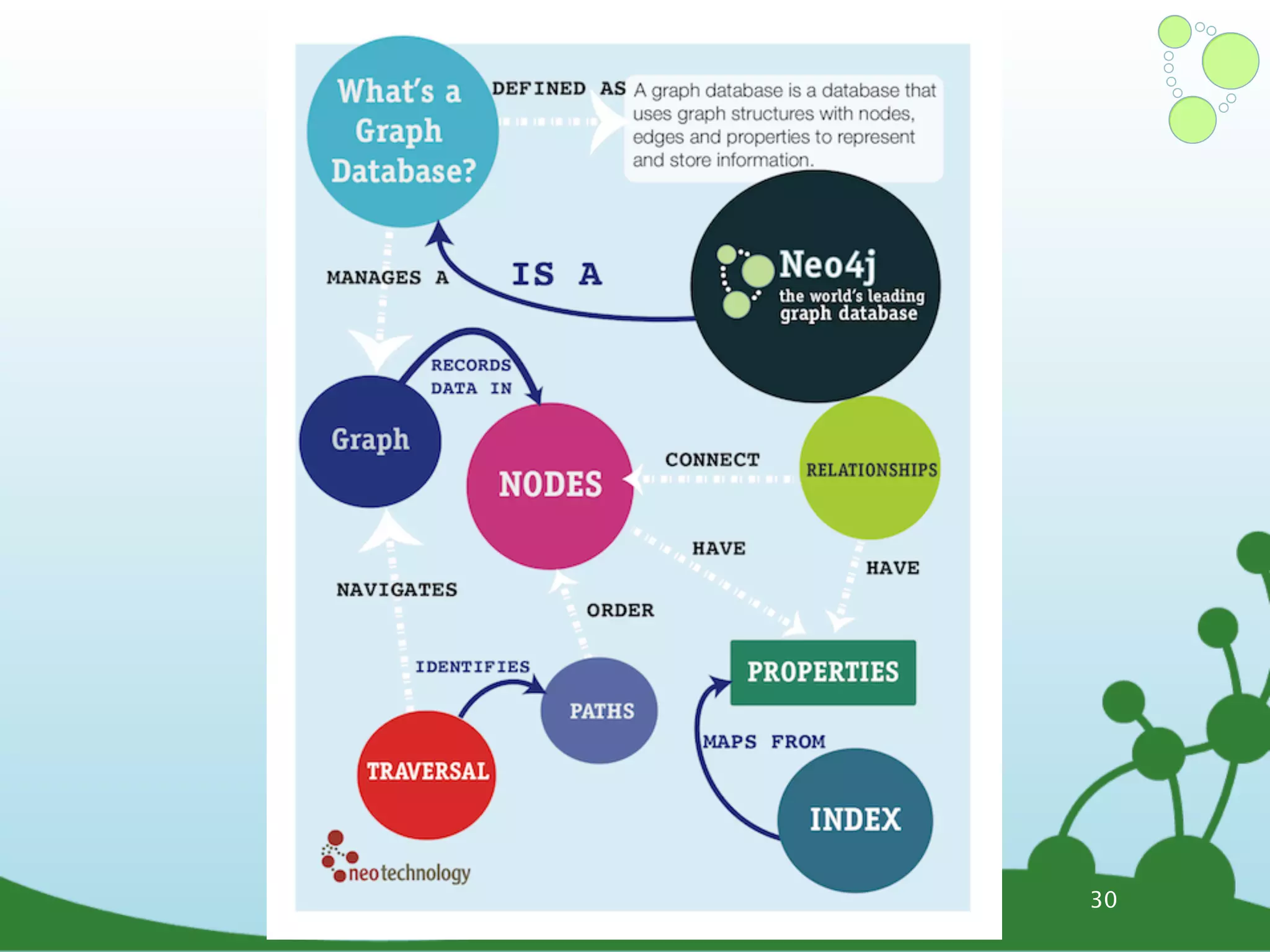
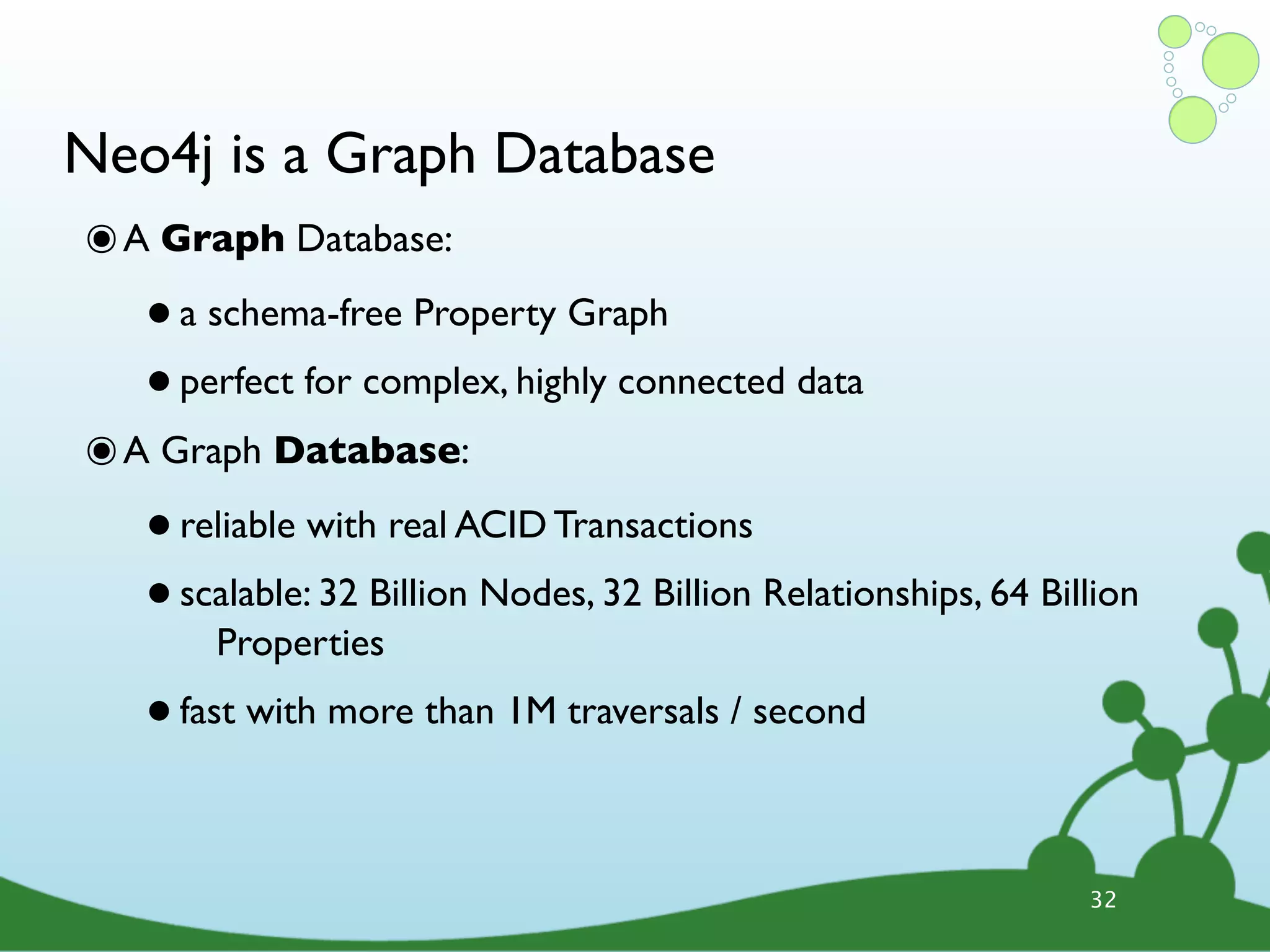
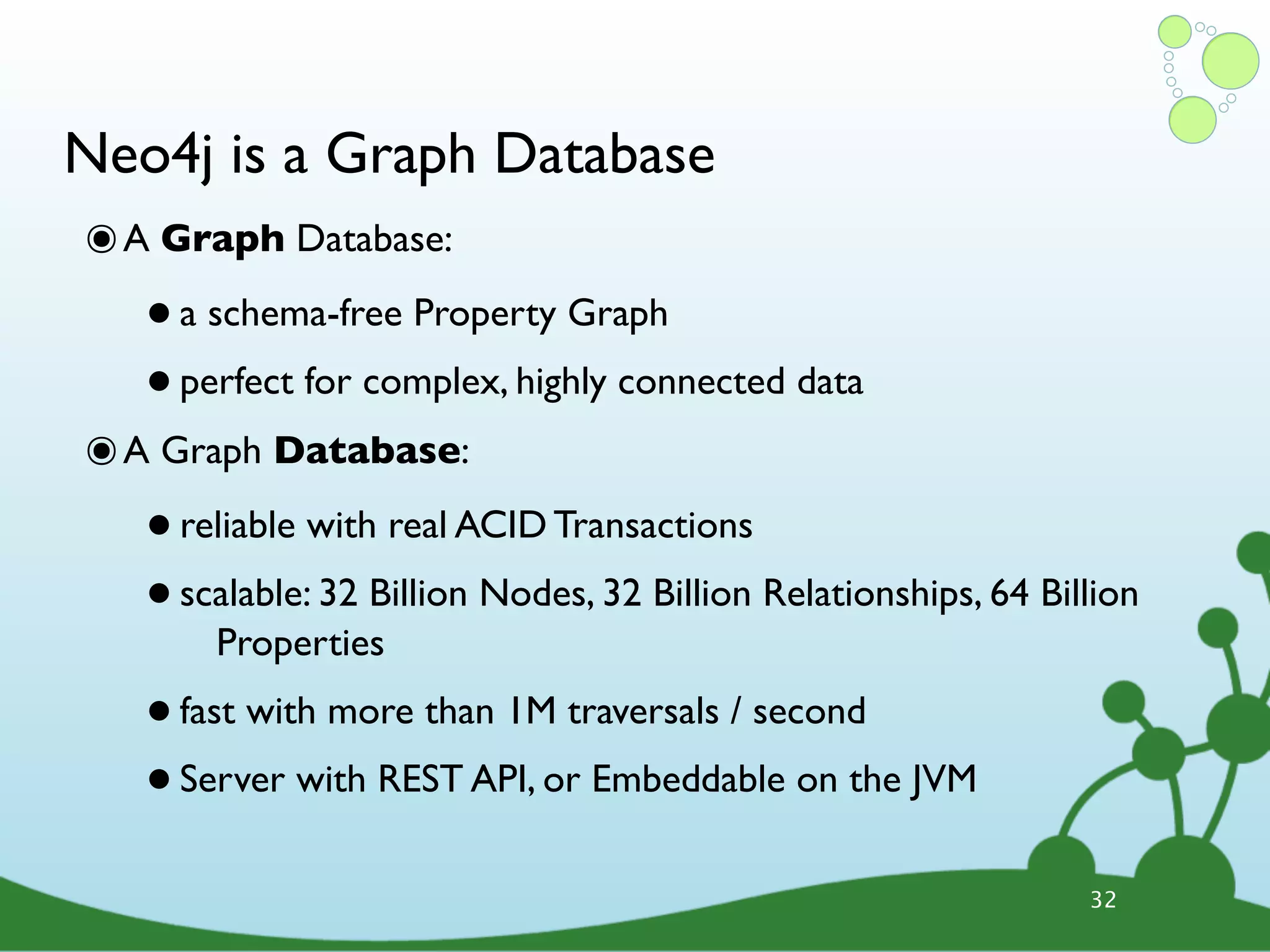
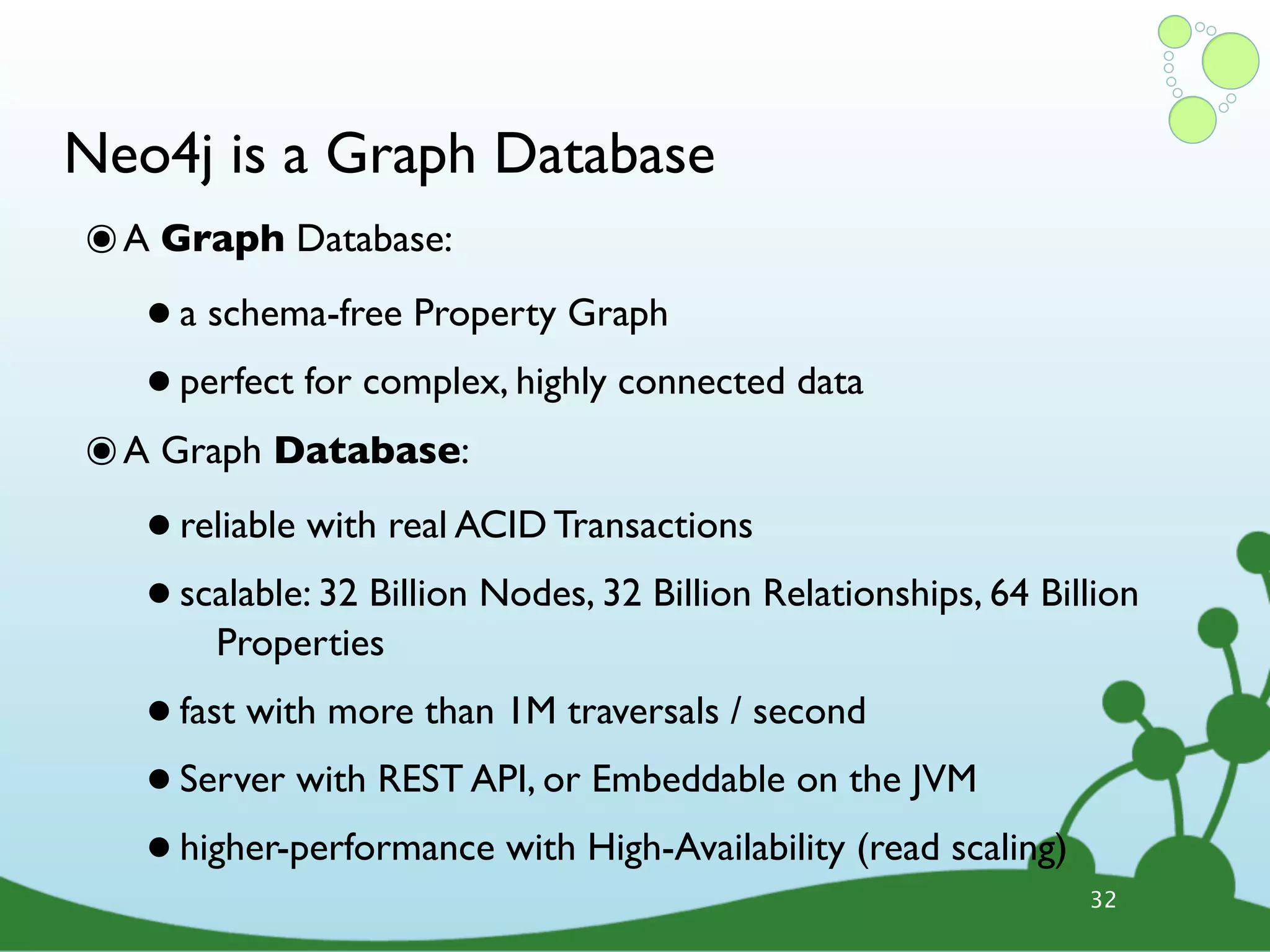
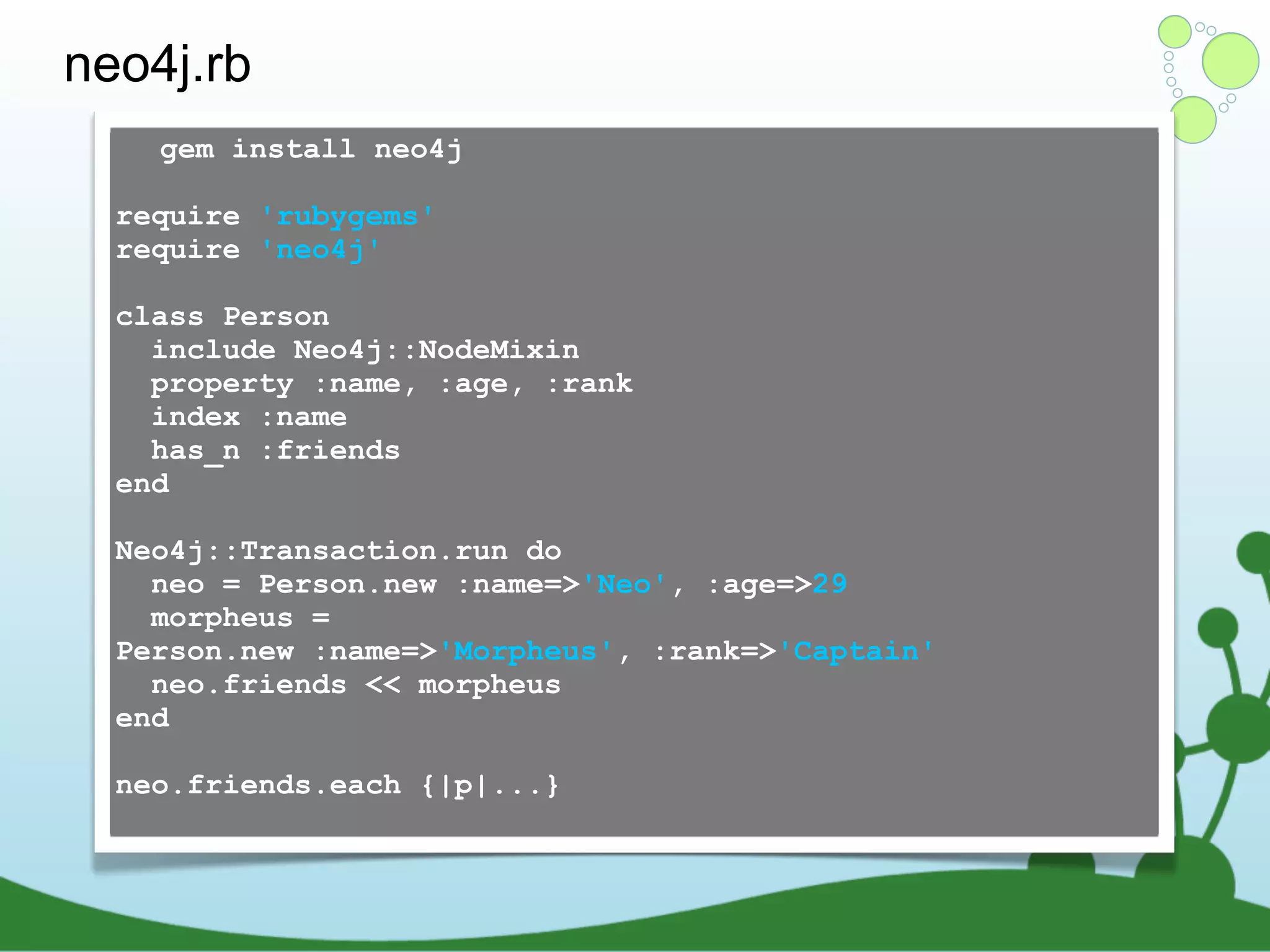
The document provides an introduction to Neo4j, a schema-free graph database designed for handling complex and highly connected data. It outlines the fundamentals of NoSQL databases, the advantages of graph data structures over traditional relational databases, and how to query data using Cypher language. Additionally, it discusses the scalability, performance, and flexibility of Neo4j in various application scenarios.





![(Michael) -[:WORKS_ON]-> (Neo4j) console Cypher community graph Community ME Server Spring Cloud 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innoq-export-120818045130-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-Neo4j-presentation-6-2048.jpg)
















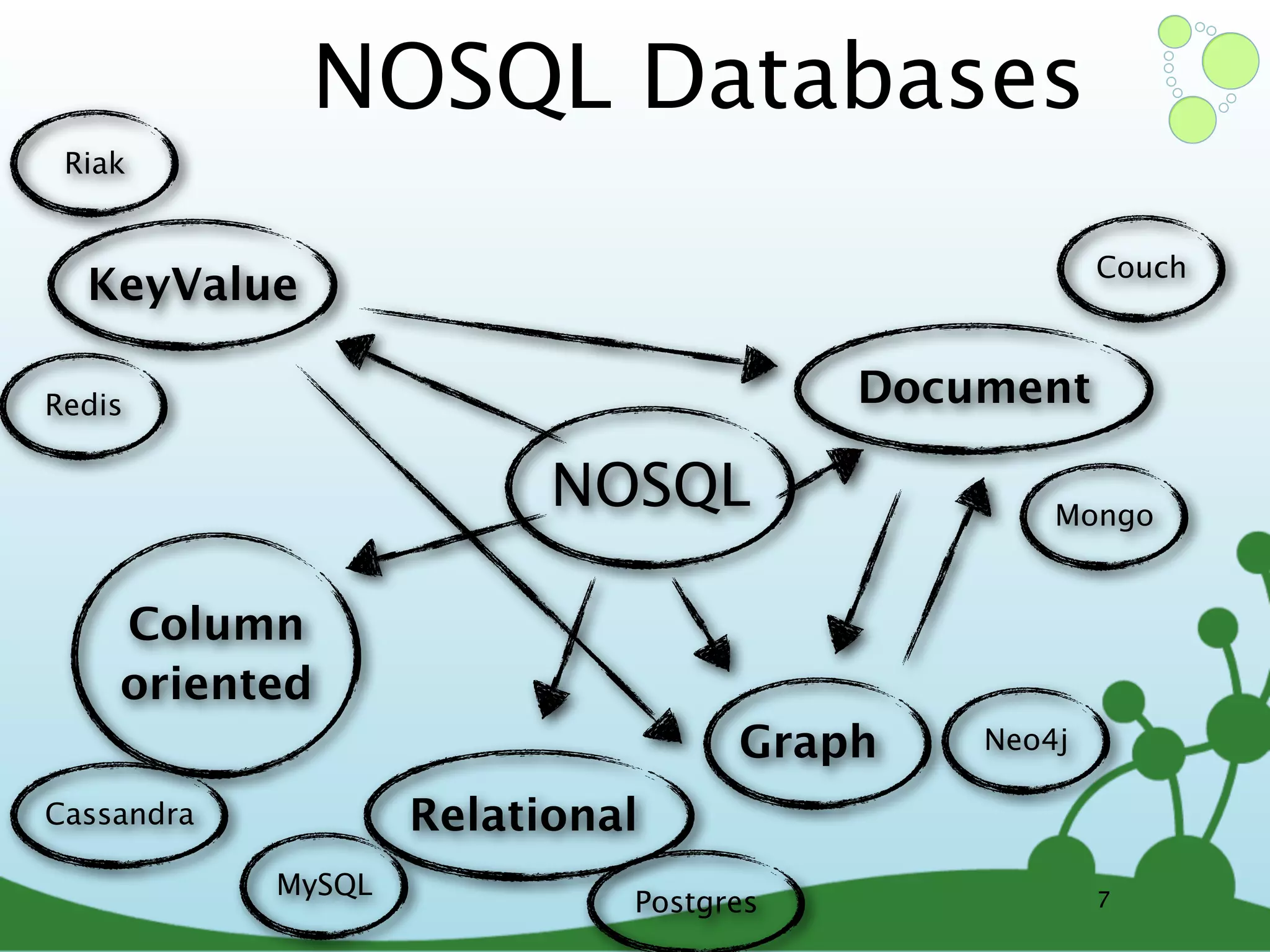


















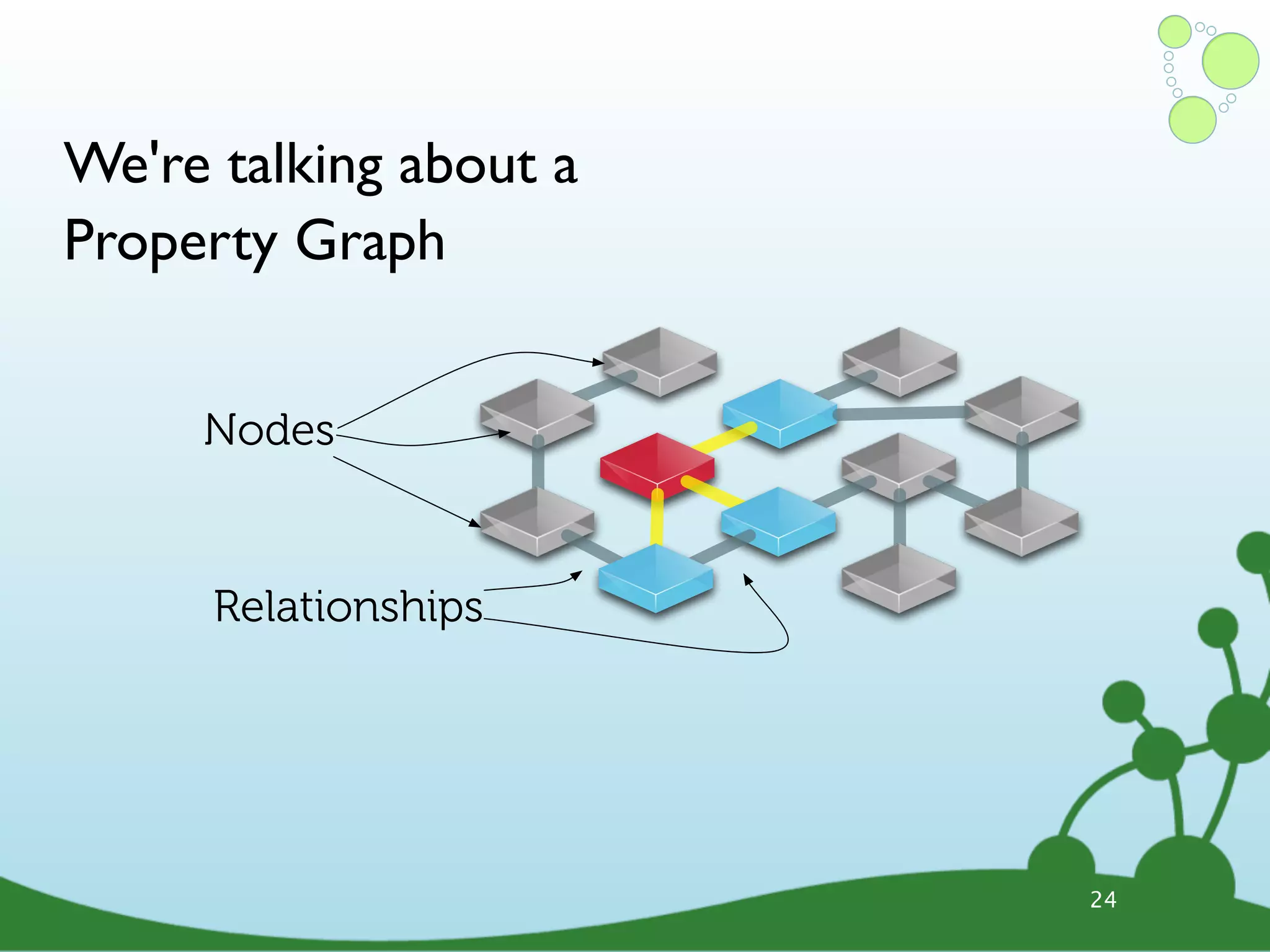
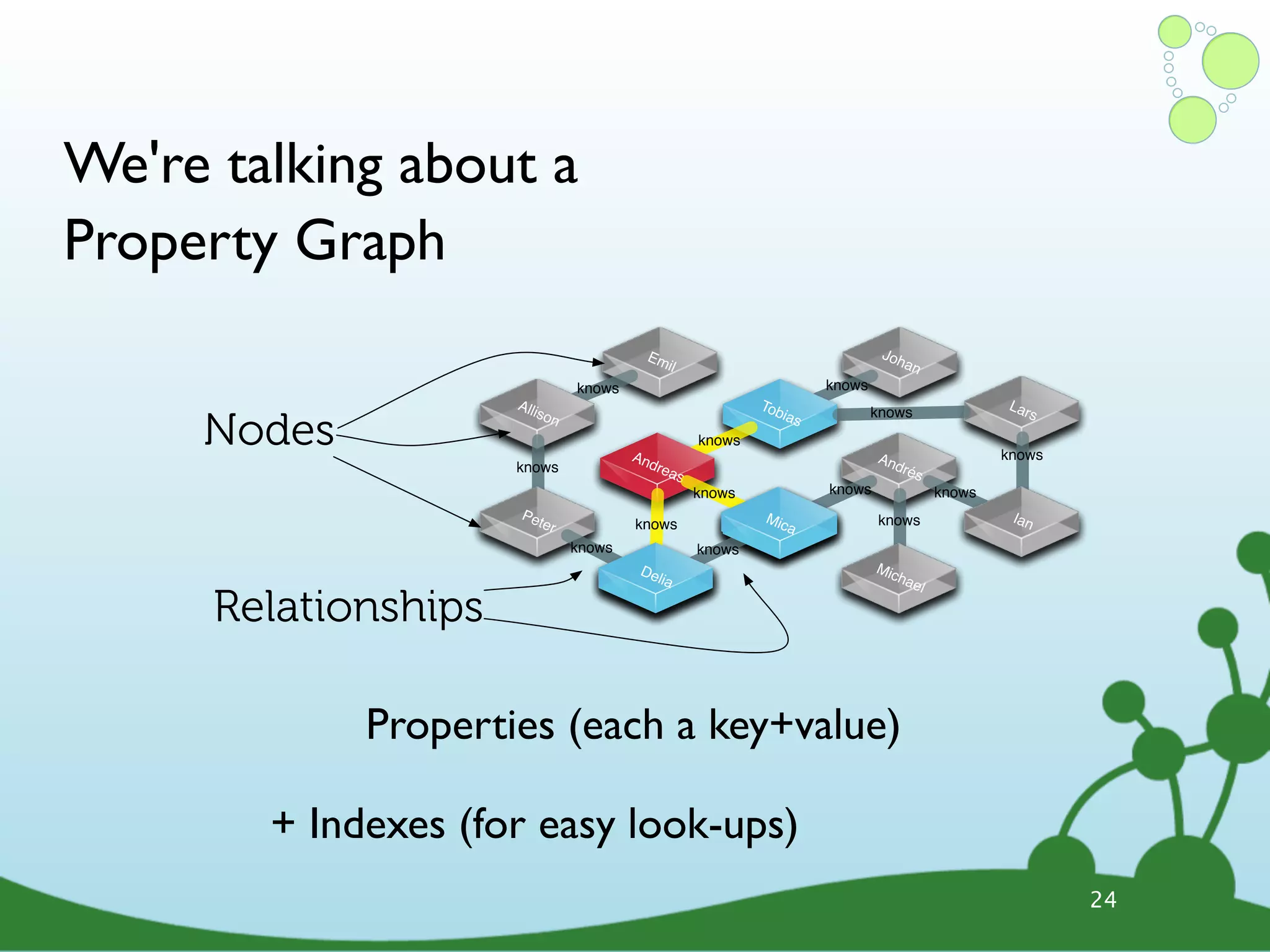



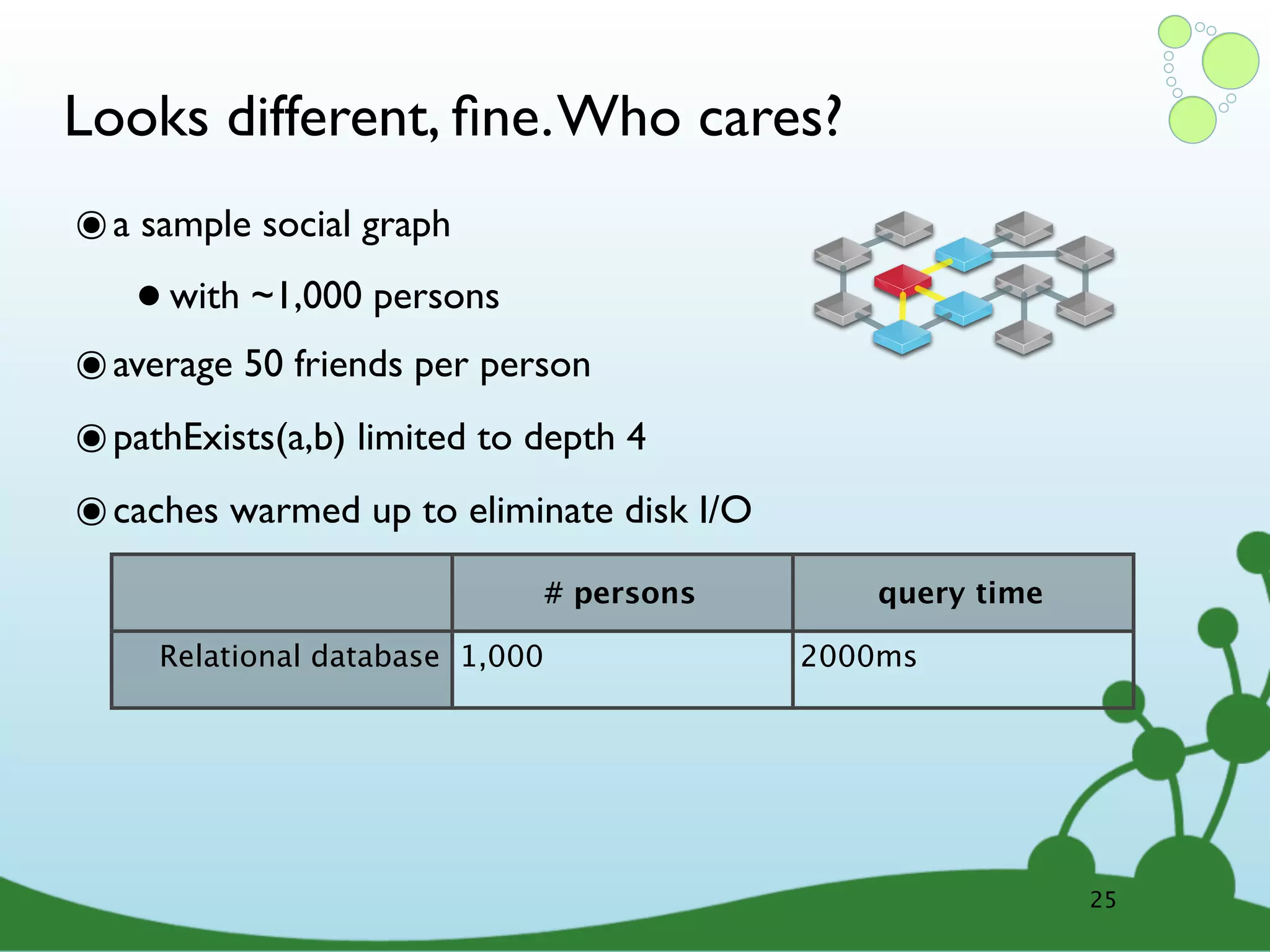





![(Neo4j) -[:IS_A]-> (Graph Database) Lucene Sharding 1 M/s Master/ Index LS Slave TRAVERSA HIG TES H_A VA RA G IL. TE IN PROVIDES ACID Server RUN S_A LI TX S CE NS ED _L ES_T Ruby IK RU JS E MySQL S _A NS SC AL O Clojure _O NS .net RU N Mongo 34bn embedded Heroku Nodes 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innoq-export-120818045130-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-Neo4j-presentation-104-2048.jpg)
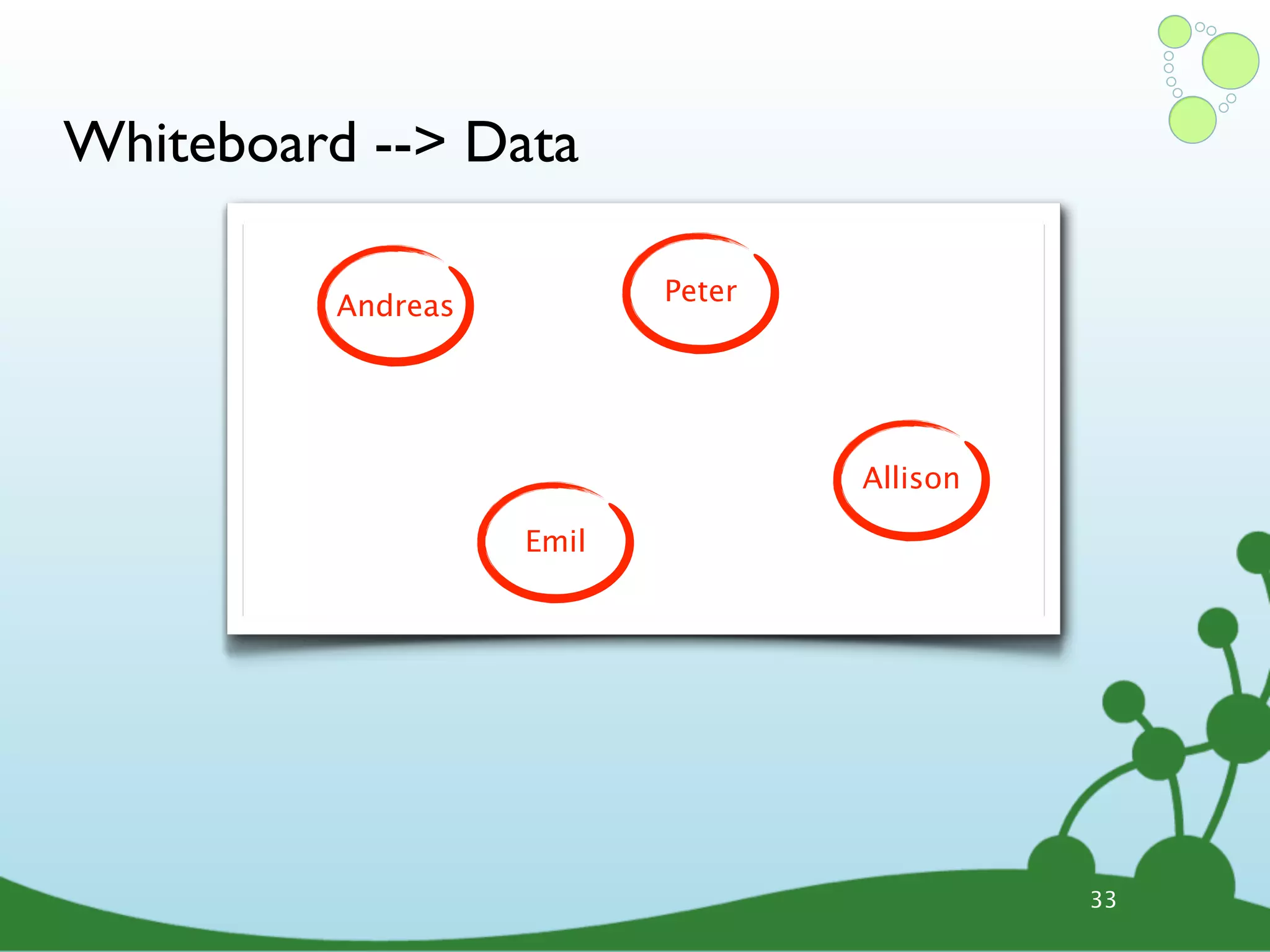
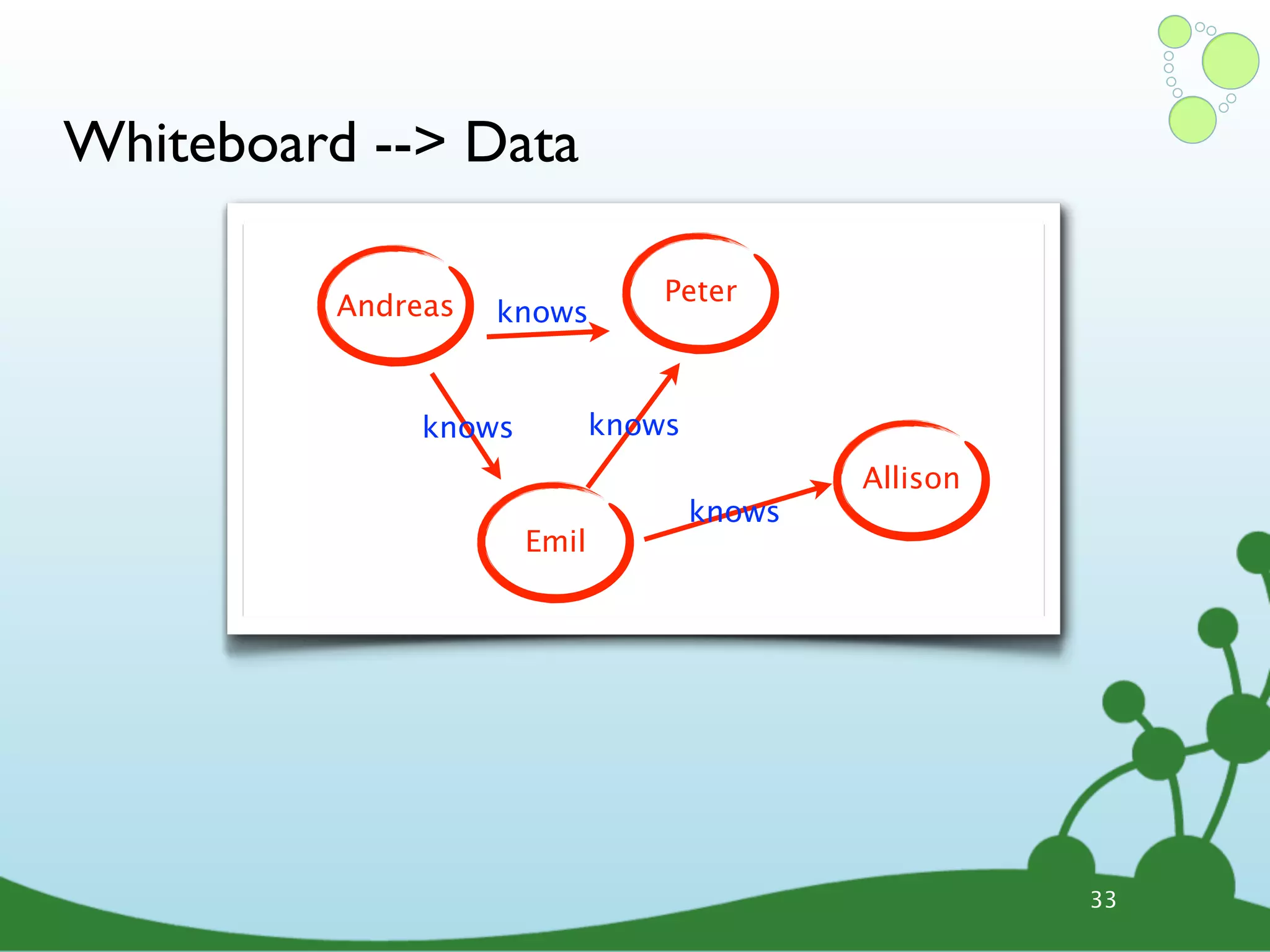
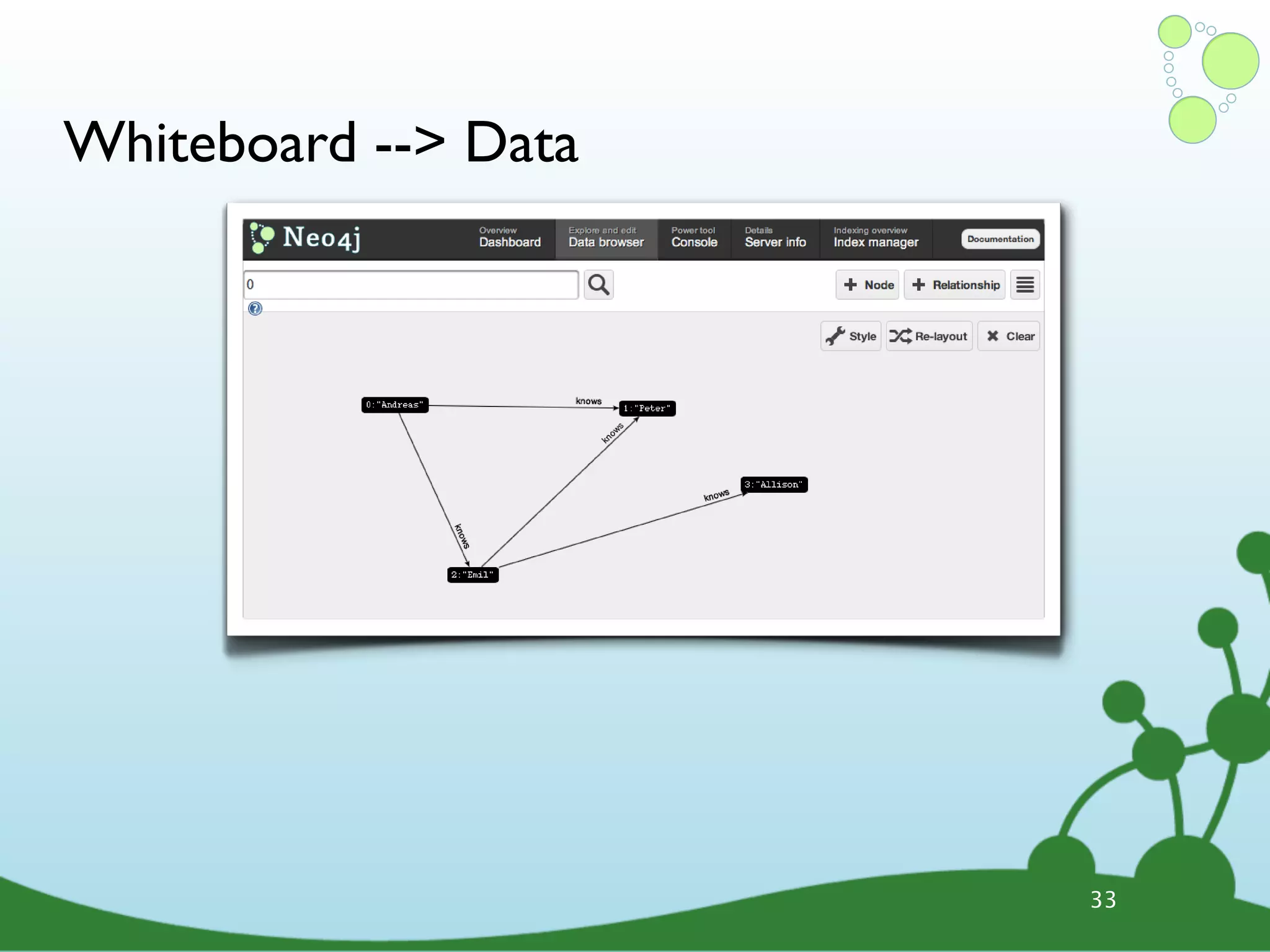
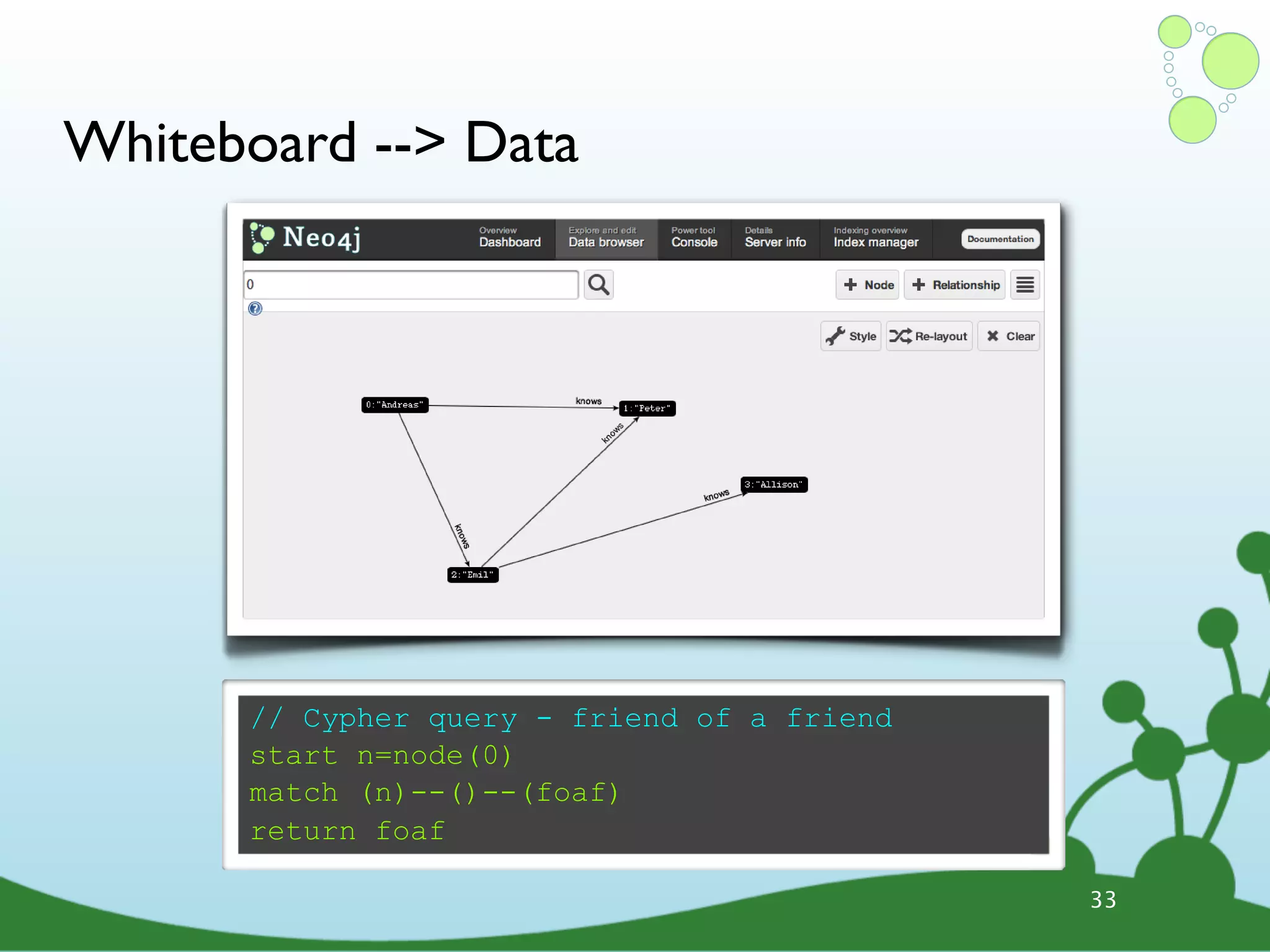










![Cypher Query Language ๏ Declarative query language • Describe what you want, not how • Based on pattern matching ๏ Examples: START david=node:people(name=”David”) # index lookup MATCH david-[:knows]-friends-[:knows]-new_friends WHERE new_friends.age > 18 RETURN new_friends START user=node(5, 15, 26, 28) # node IDs MATCH user--friend RETURN user, COUNT(friend), SUM(friend.money) 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innoq-export-120818045130-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-Neo4j-presentation-135-2048.jpg)
![Create Graph with Cypher CREATE (steve {name: “Steve Vinoski”}) -[:PRESENTED_WITH {date:{day}}]-> (michael {name: “Michael Hunger”})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innoq-export-120818045130-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-Neo4j-presentation-136-2048.jpg)