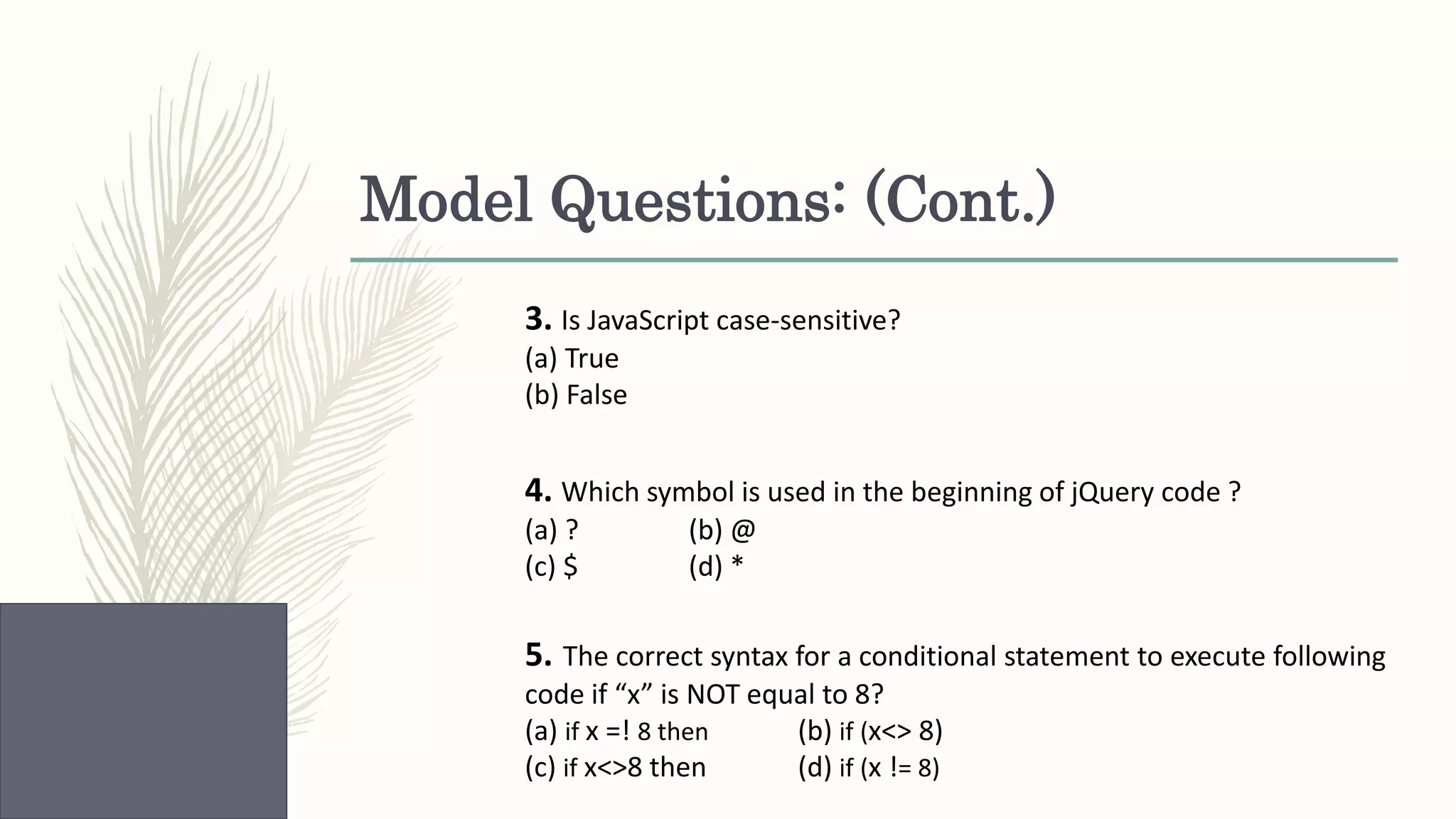
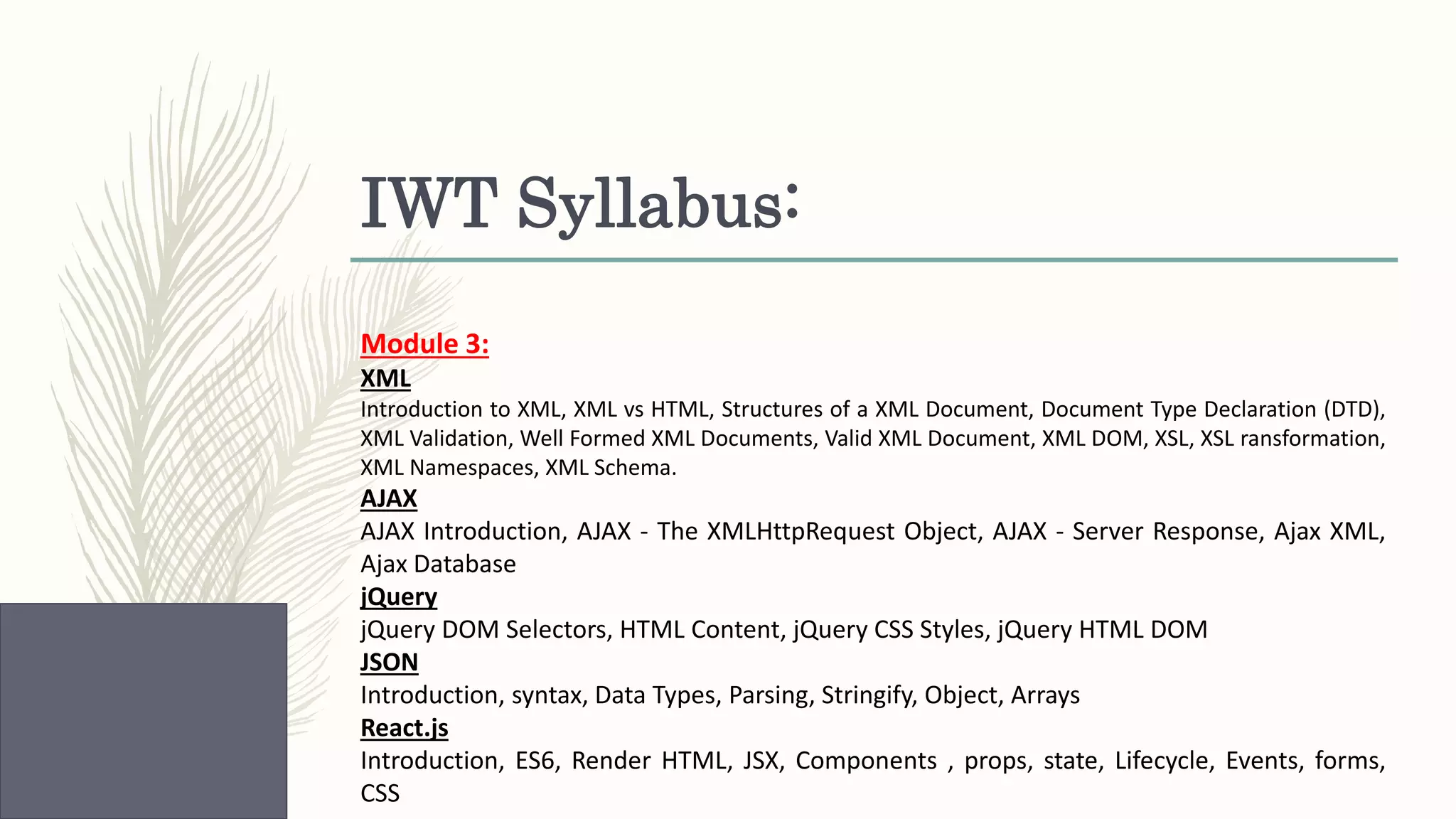
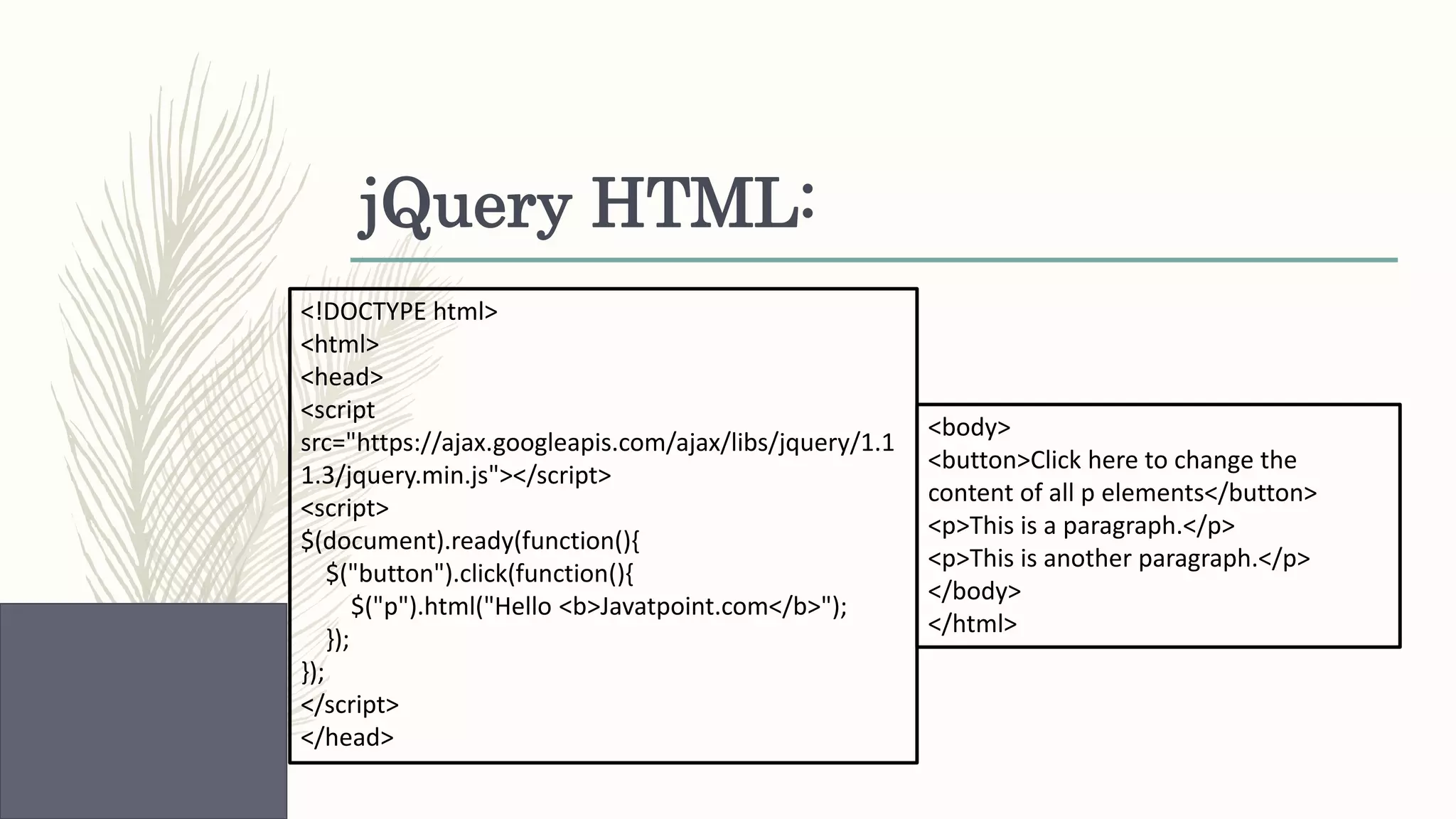
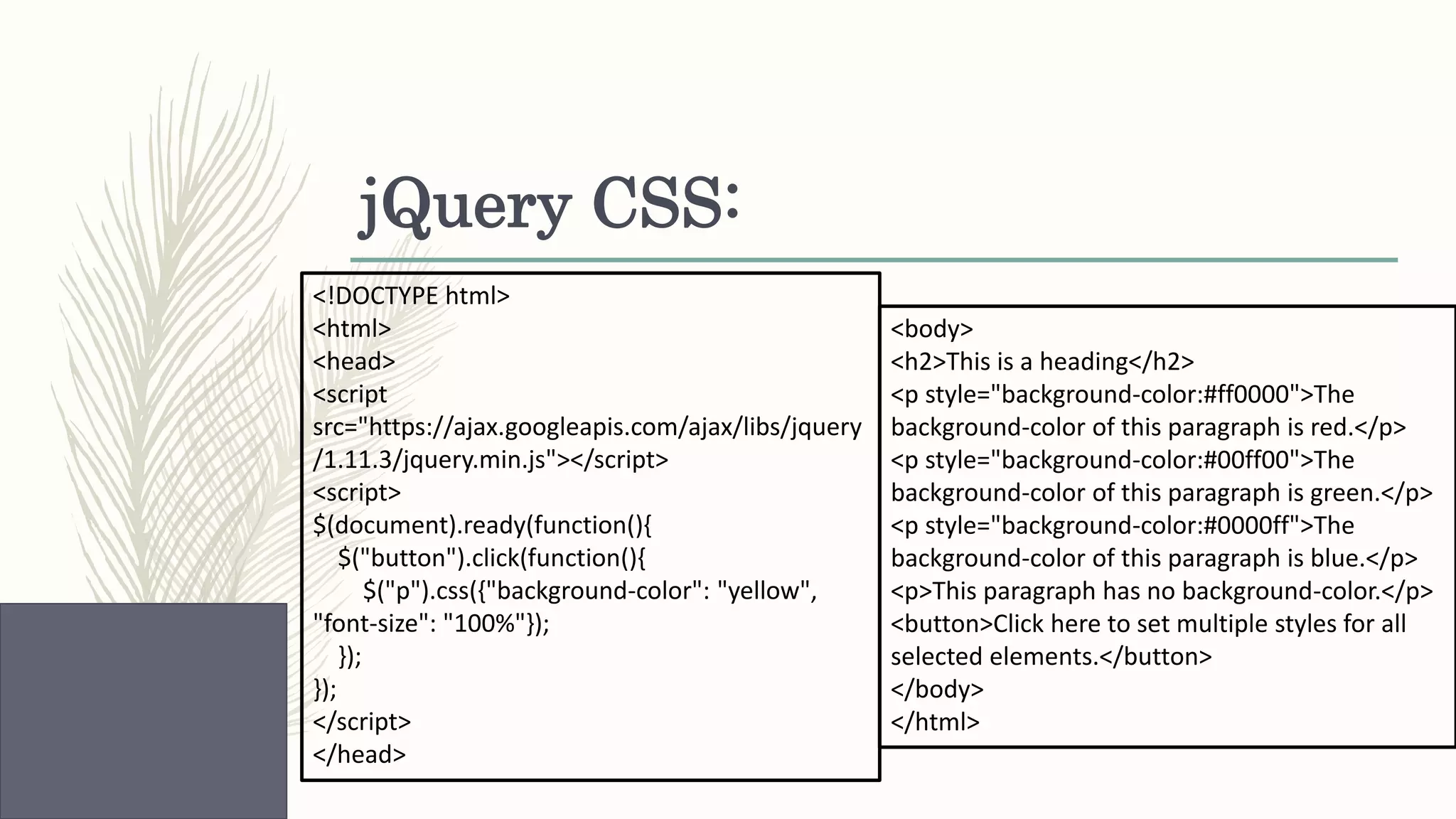
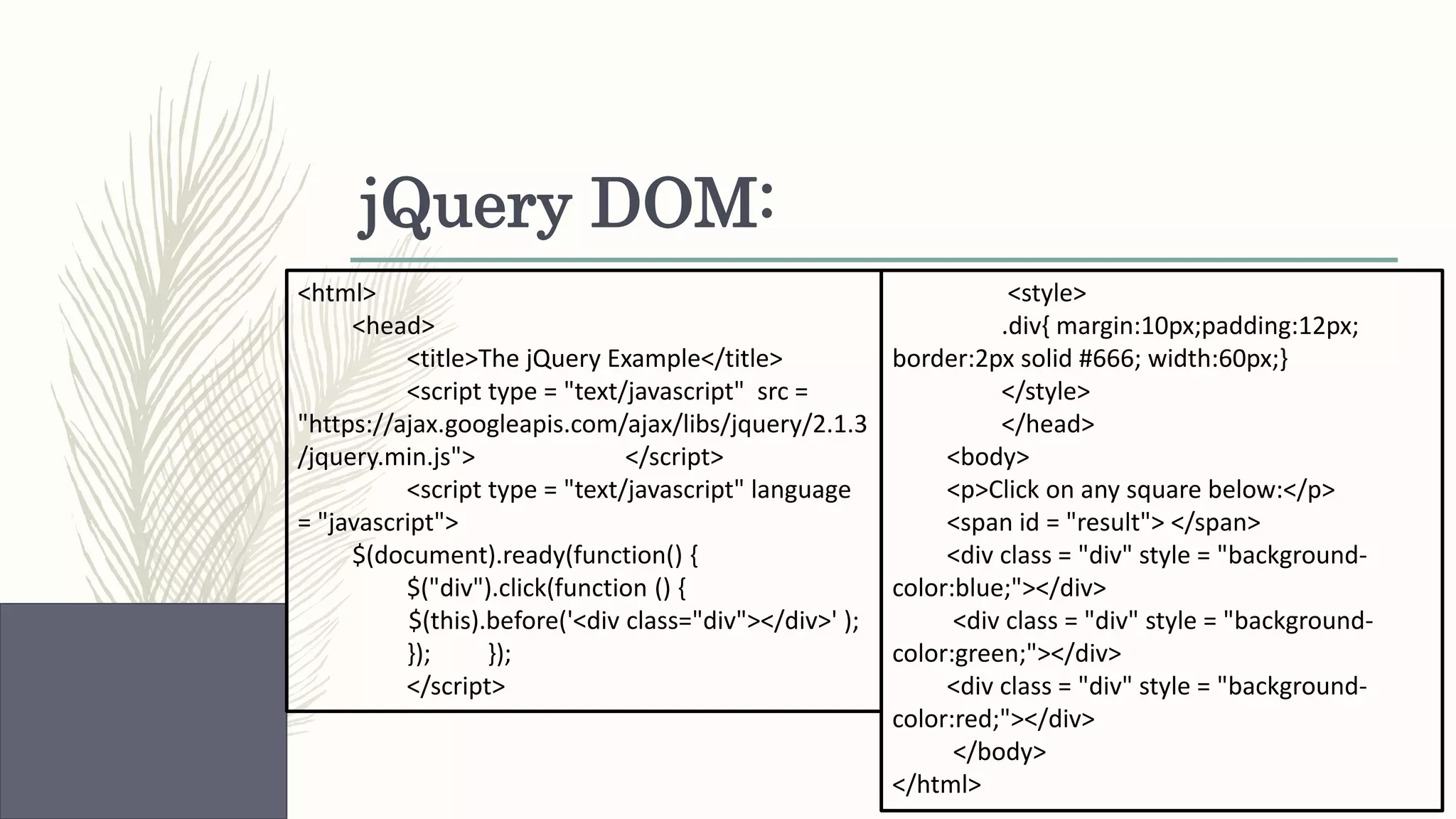
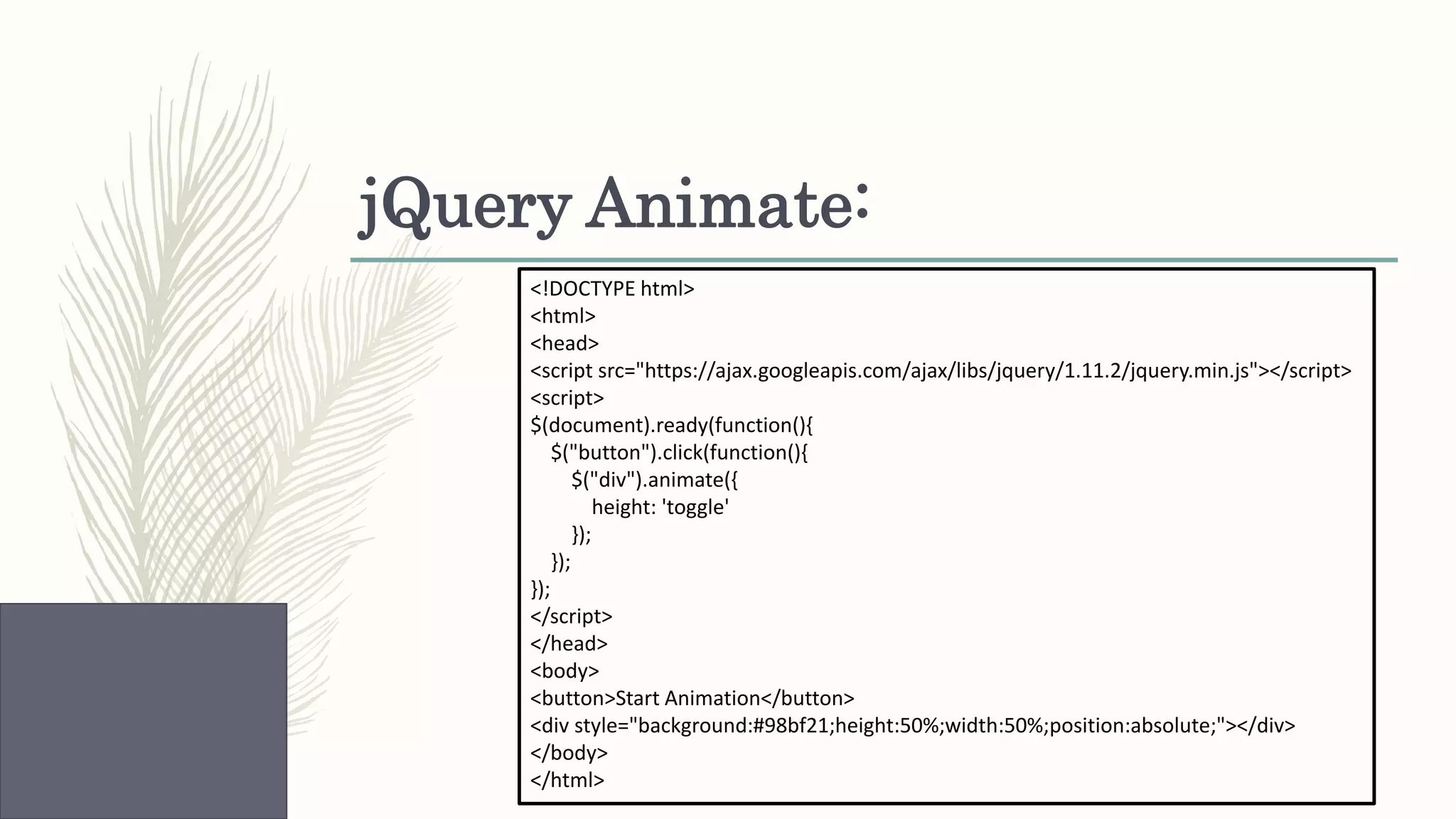
This document provides an overview of various web technologies including XML, AJAX, jQuery, JSON, and React.js. It discusses key concepts such as XML structures and validation, the XMLHttpRequest object, jQuery selectors and DOM manipulation, JSON syntax and parsing, and basic React introductions and components. Code examples are also provided to demonstrate jQuery DOM selection, CSS styling, animations, JSON parsing and arrays, and React rendering.



![JSON vs XML: {"employees":[ { "firstName":"John", "lastName":"Doe" }, { "firstName":"Anna", "lastName":"Smith" }, { "firstName":"Peter", "lastName":"Jones" } ]} <employees> <employee> <firstName>John</firstName> <lastName>Doe</lastName> </employee> <employee> <firstName>Anna</firstName> <lastName>Smith</lastName> </employee> <employee> <firstName>Peter</firstName> <lastName>Jones</lastName> </employee> </employees> Both JSON and XML are "self describing" (human readable). Both JSON and XML are hierarchical (values within values). Both JSON and XML can be parsed and used by lots of programming languages. Both JSON and XML can be fetched with an XMLHttpRequest. JSON doesn't use end tag JSON is shorter JSON is quicker to read and write JSON can use arrays JSON vs XML JSON is Like XML](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iwtclass-8-200721165112/75/Internet-and-Web-Technology-CLASS-8-jQuery-and-JSON-NIC-NIELIT-Web-Technology-10-2048.jpg)

![JSON Array: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p>Looping through an array using a for in loop:</p> <p id="demo"></p> <script> var myObj, i, x = ""; myObj = { "name":"John", "age":30, "cars":[ "Ford", "BMW", "Fiat" ] }; for (i in myObj.cars) { x += myObj.cars[i] + "<br>"; } document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = x; </script> </body> </html> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p>Access an array value of a JSON object.</p> <p id="demo"></p> <script> var myObj, x; myObj = { "name":"John", "age":30, "cars":[ "Ford", "BMW", "Fiat" ] }; x = myObj.cars[0]; document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = x; </script> </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iwtclass-8-200721165112/75/Internet-and-Web-Technology-CLASS-8-jQuery-and-JSON-NIC-NIELIT-Web-Technology-12-2048.jpg)