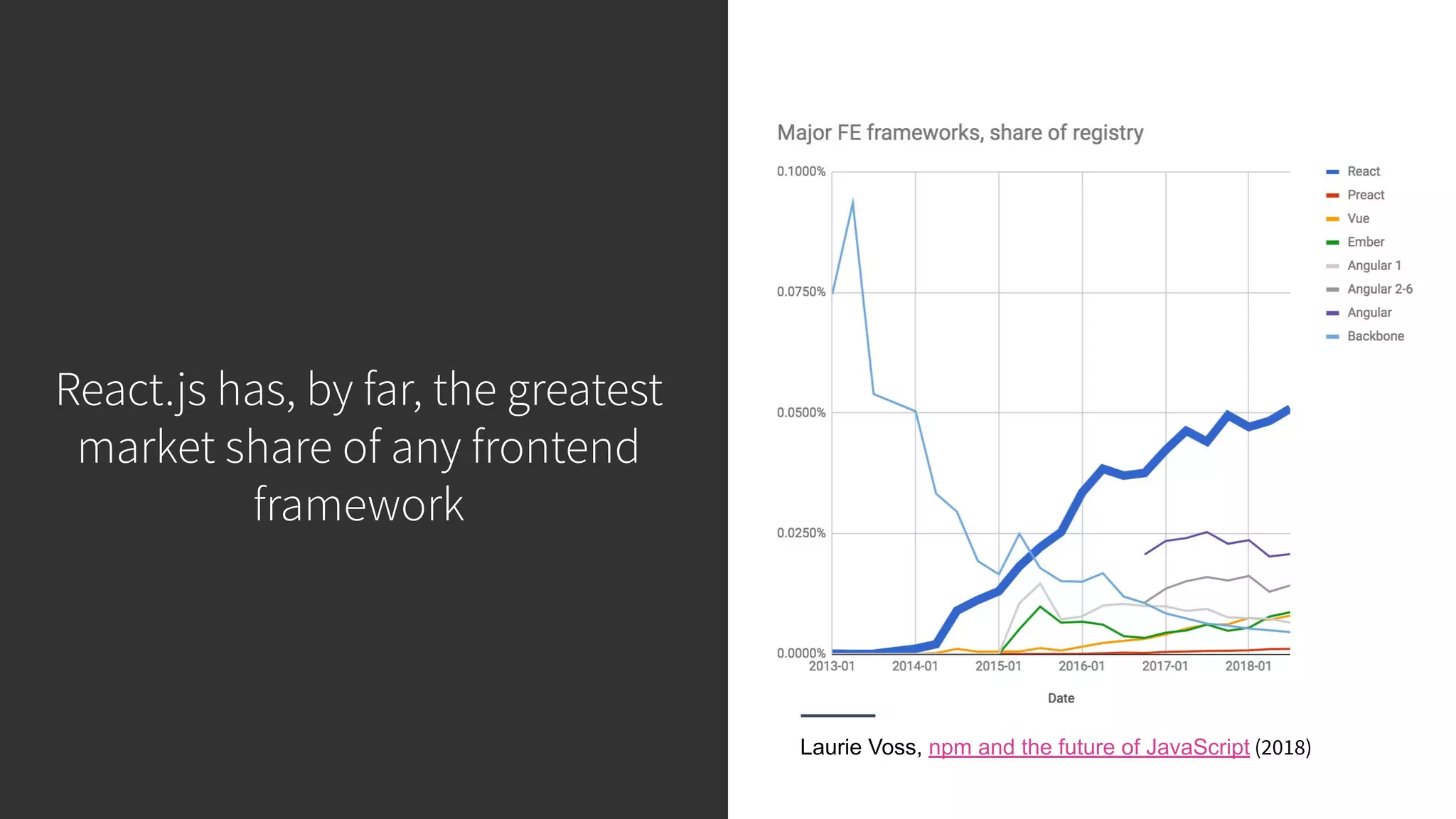
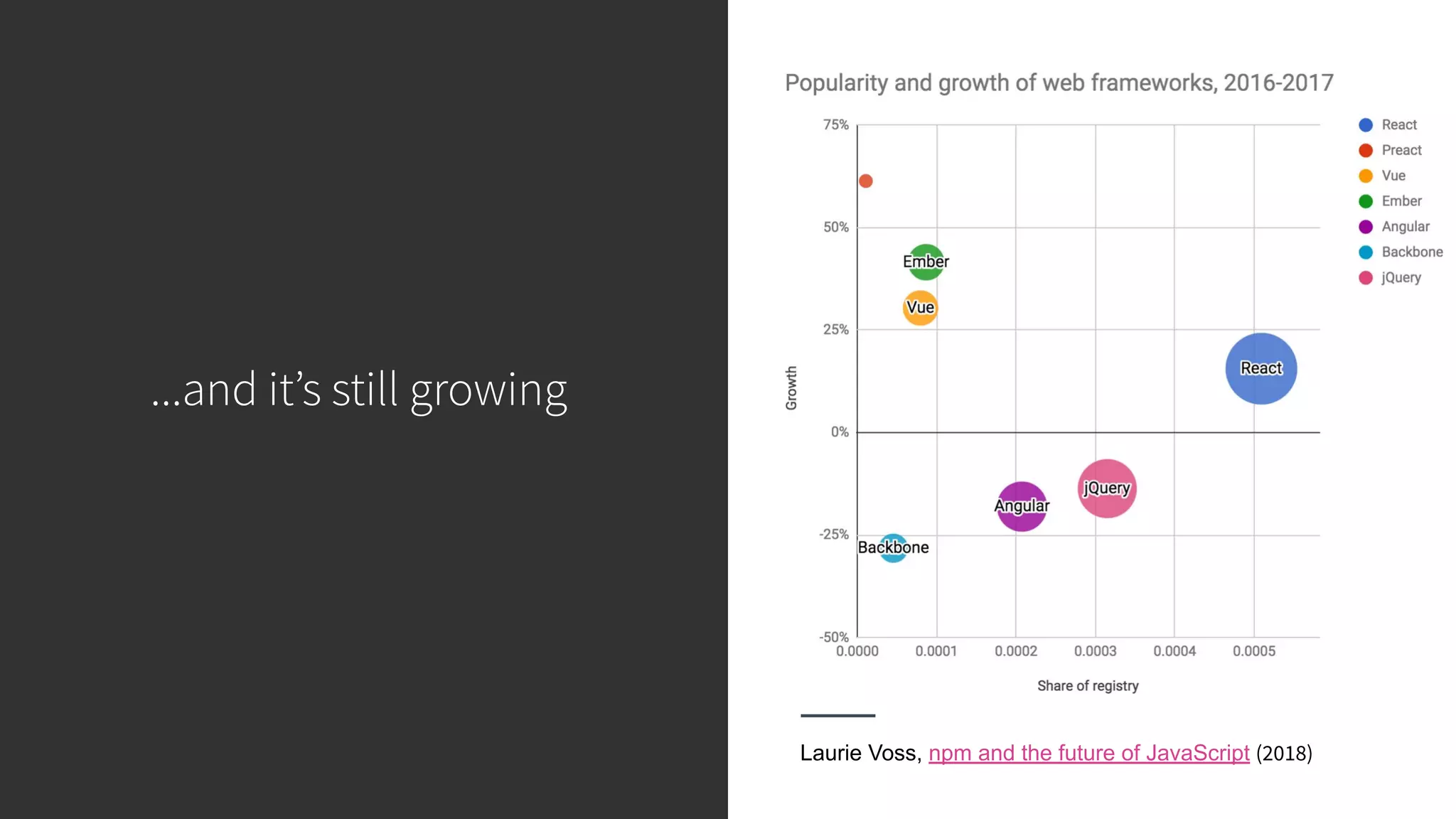
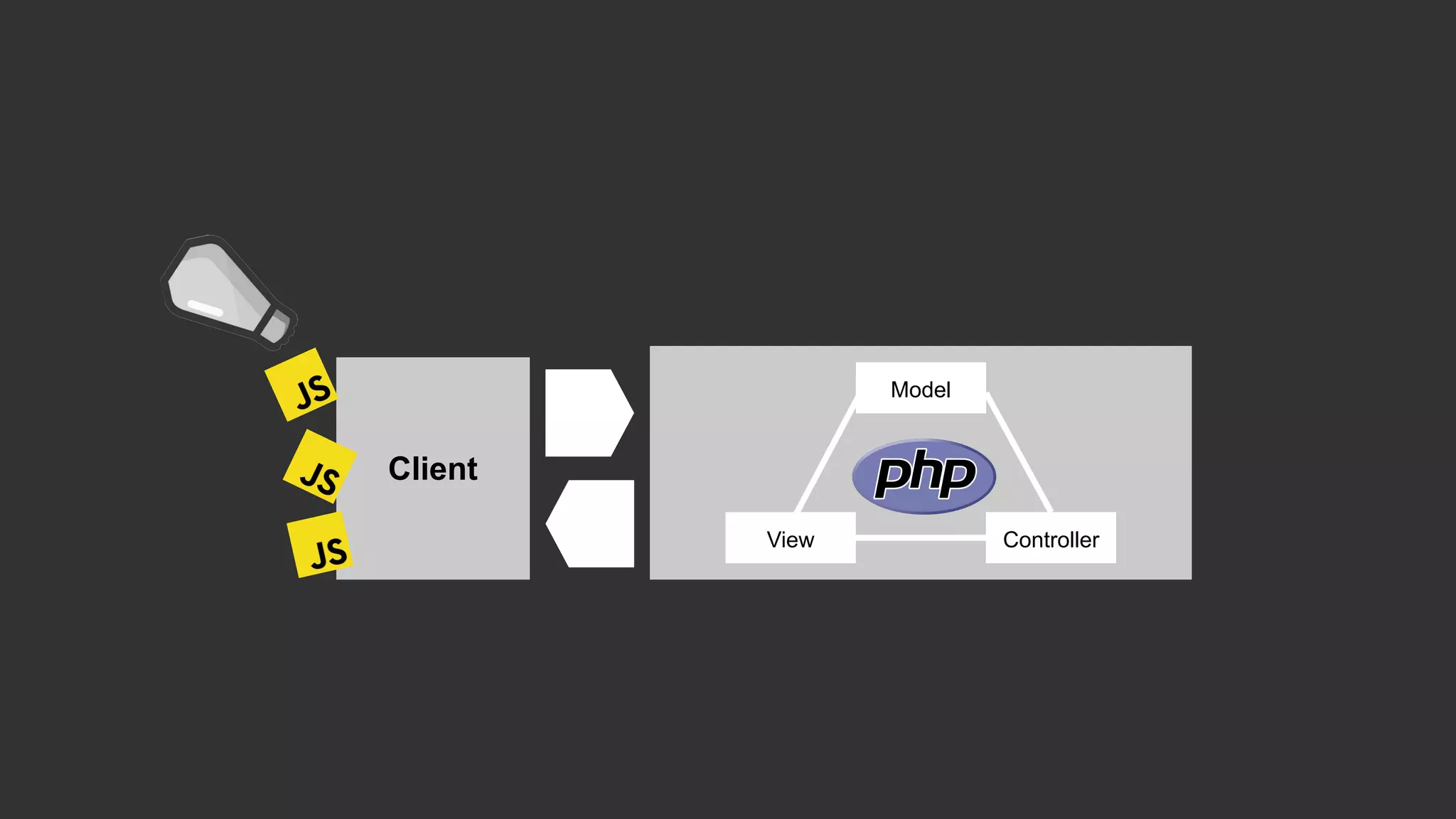
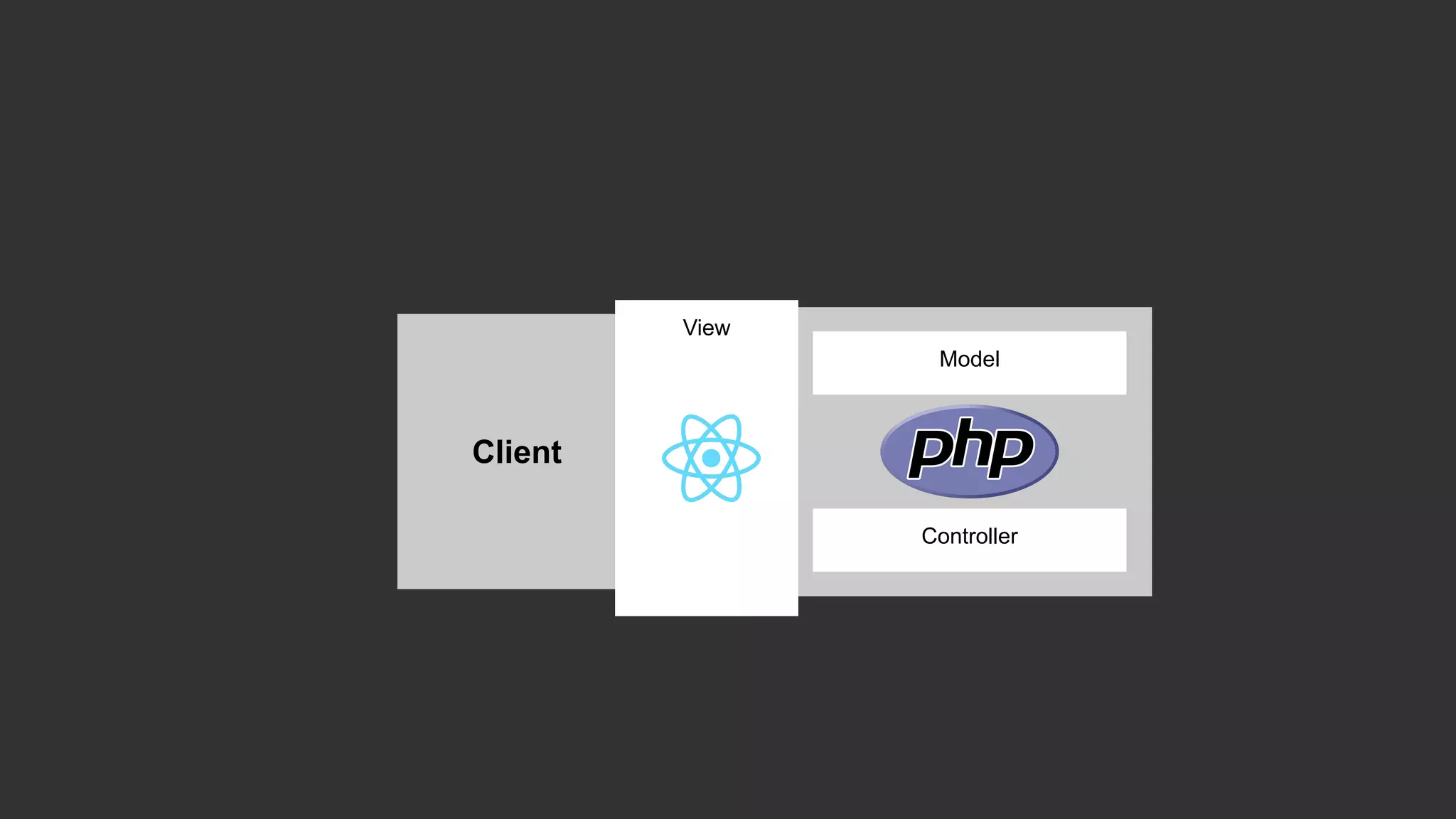
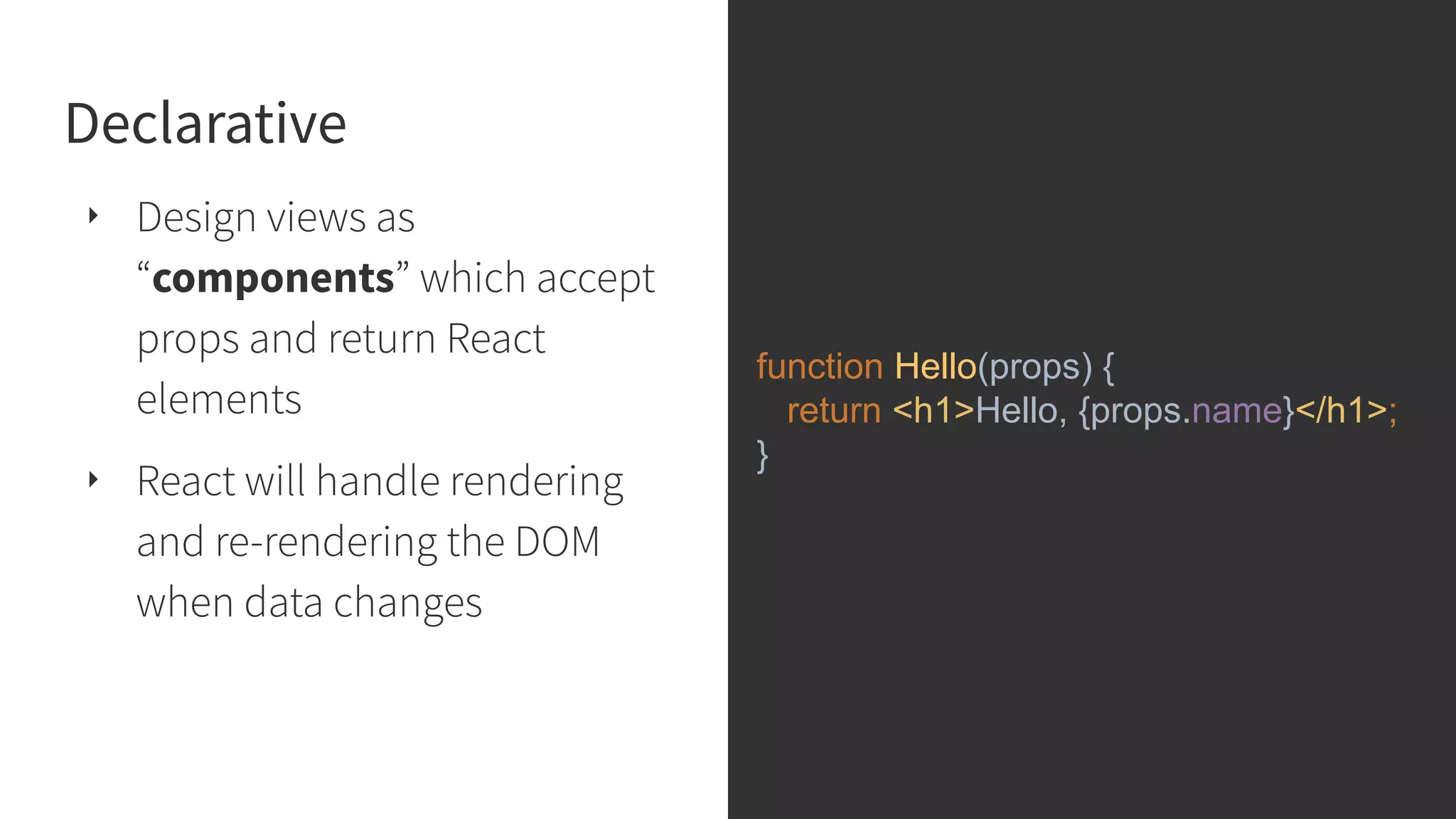
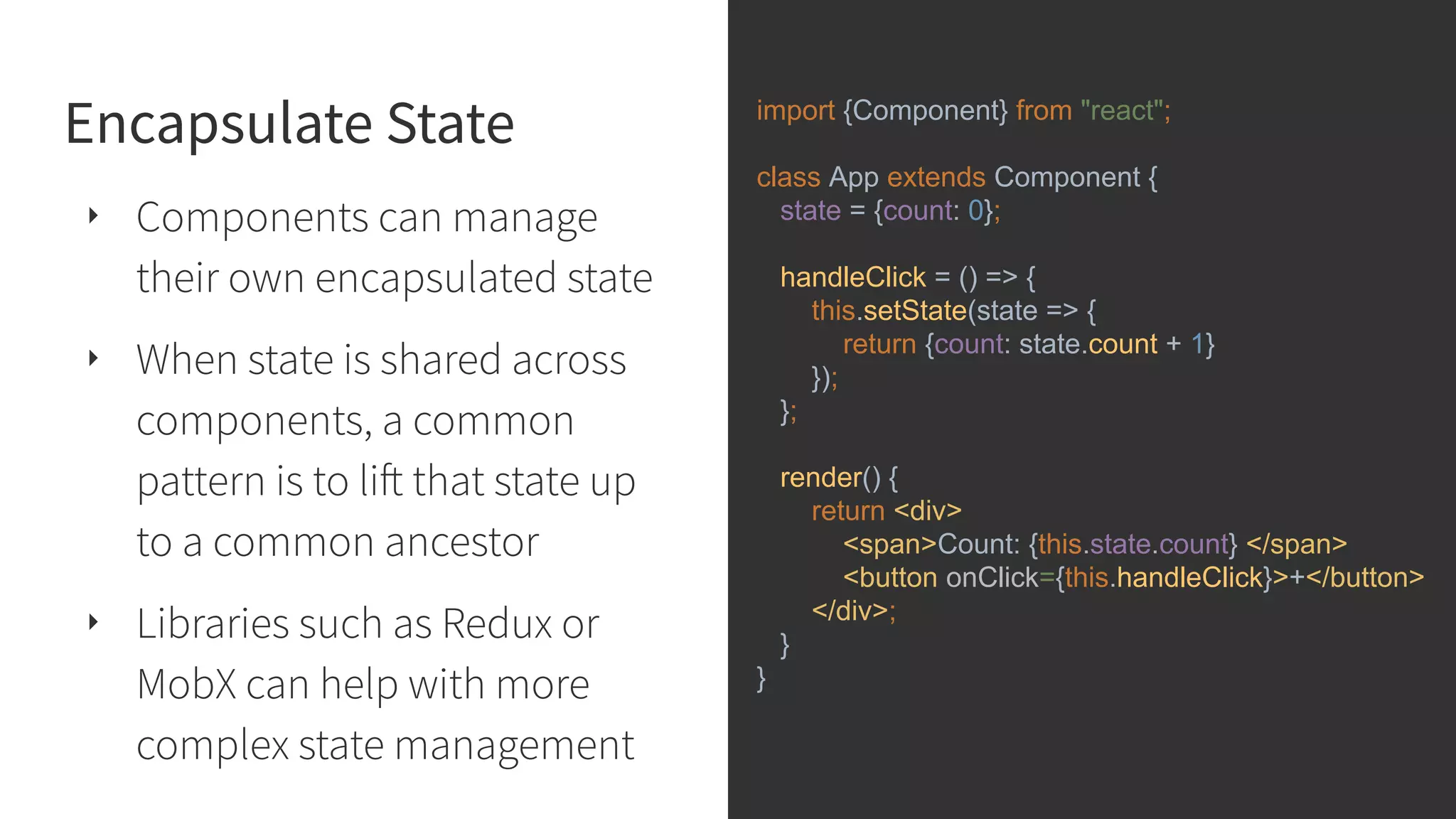
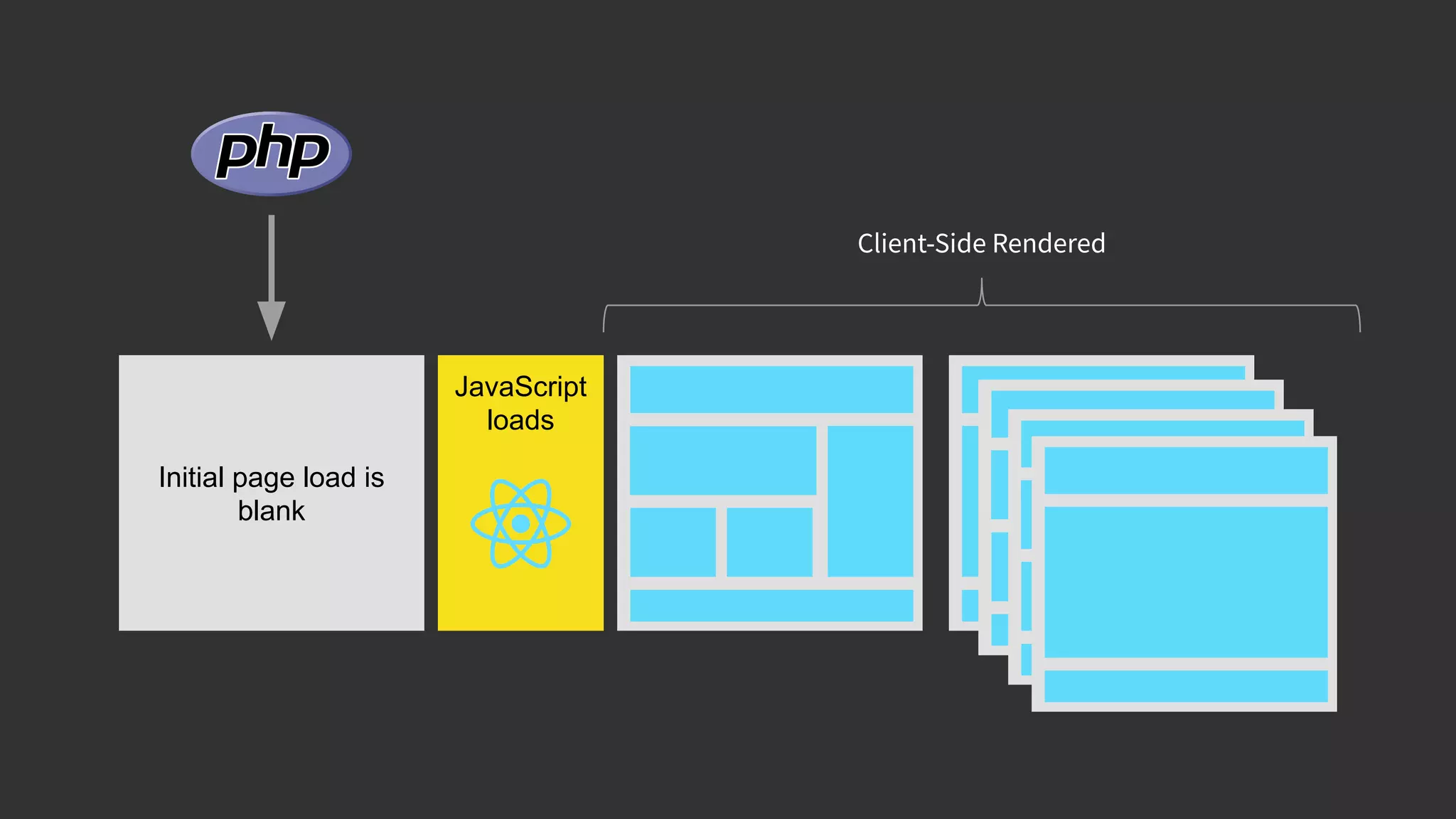
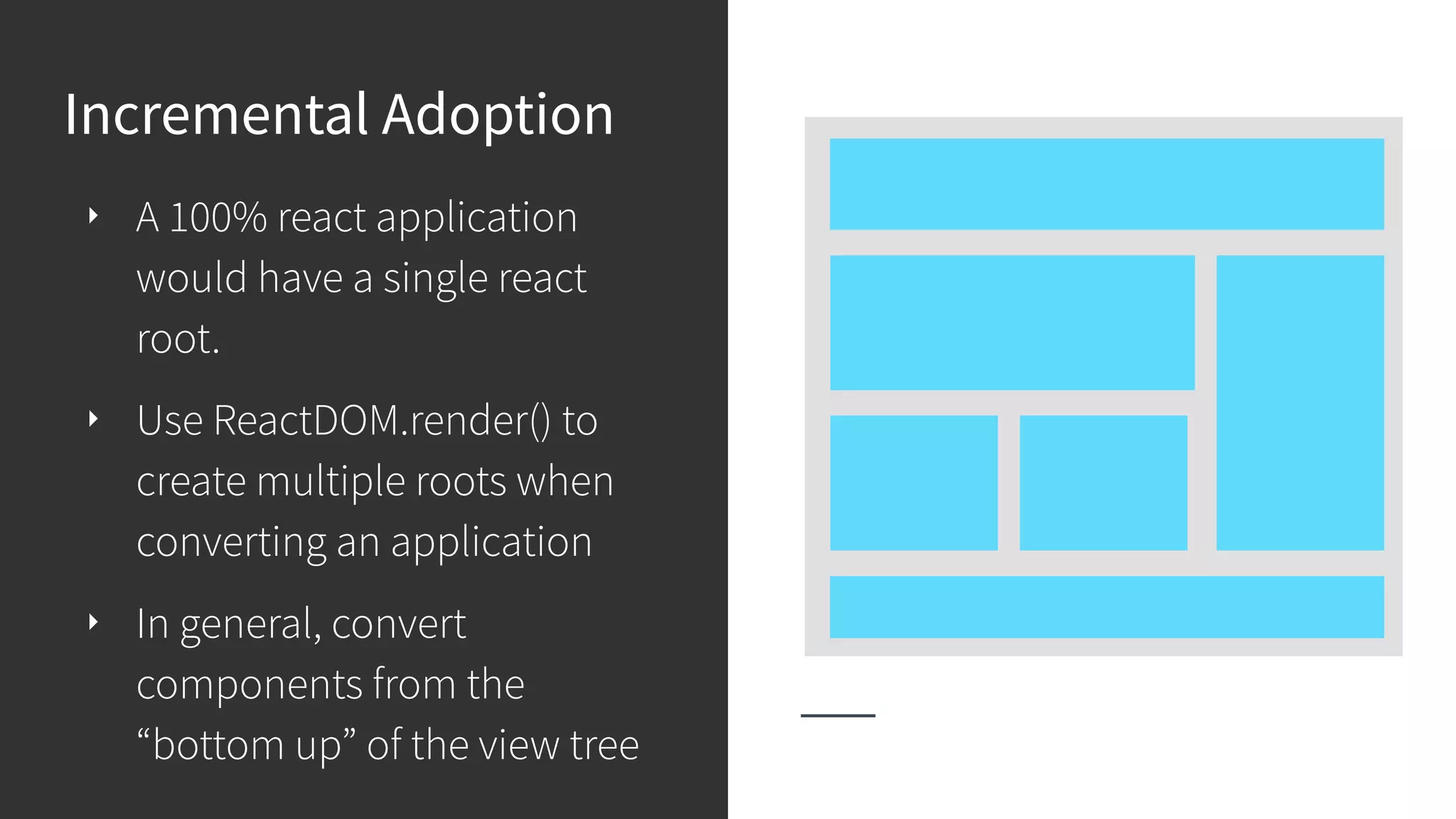
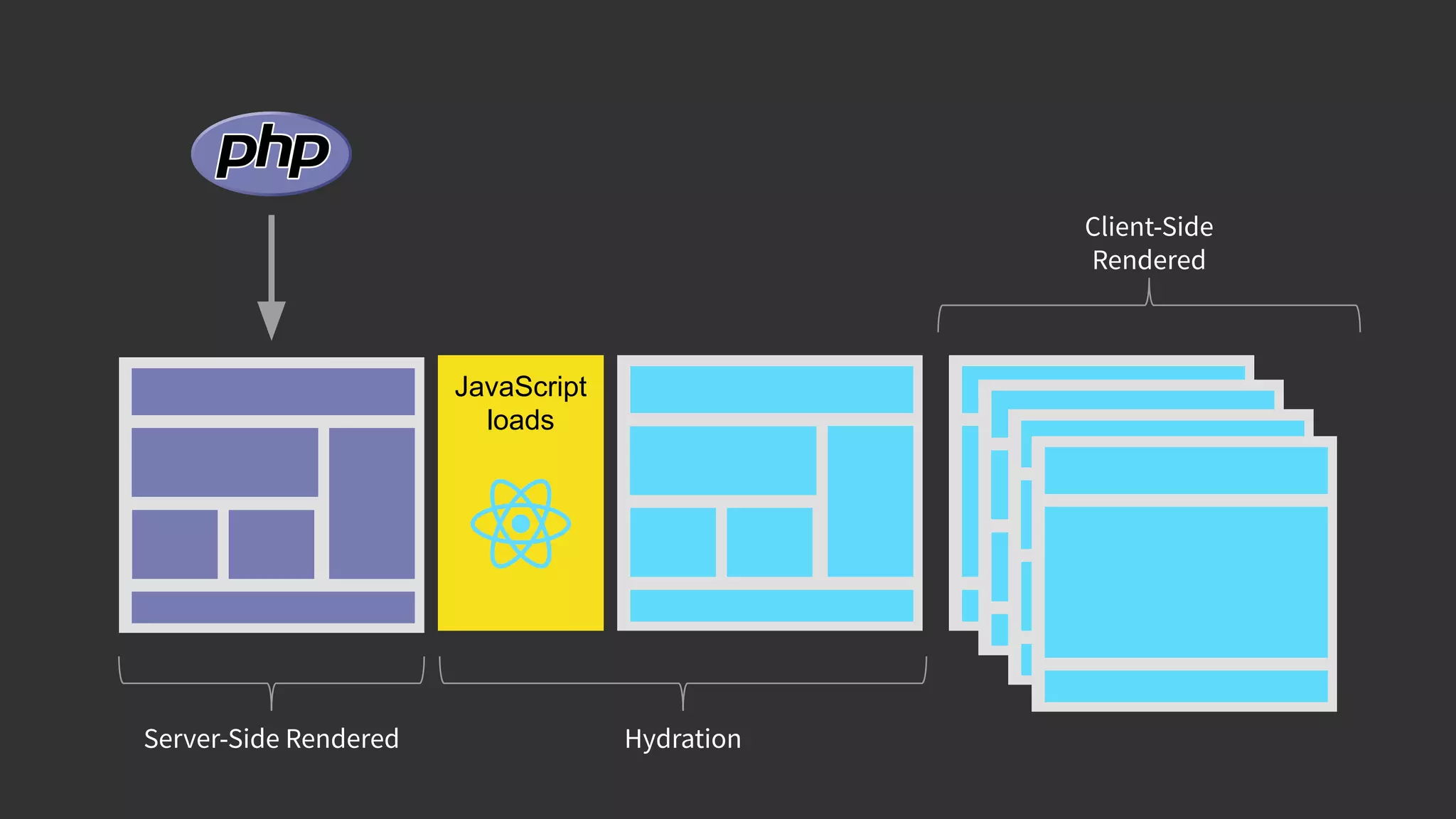
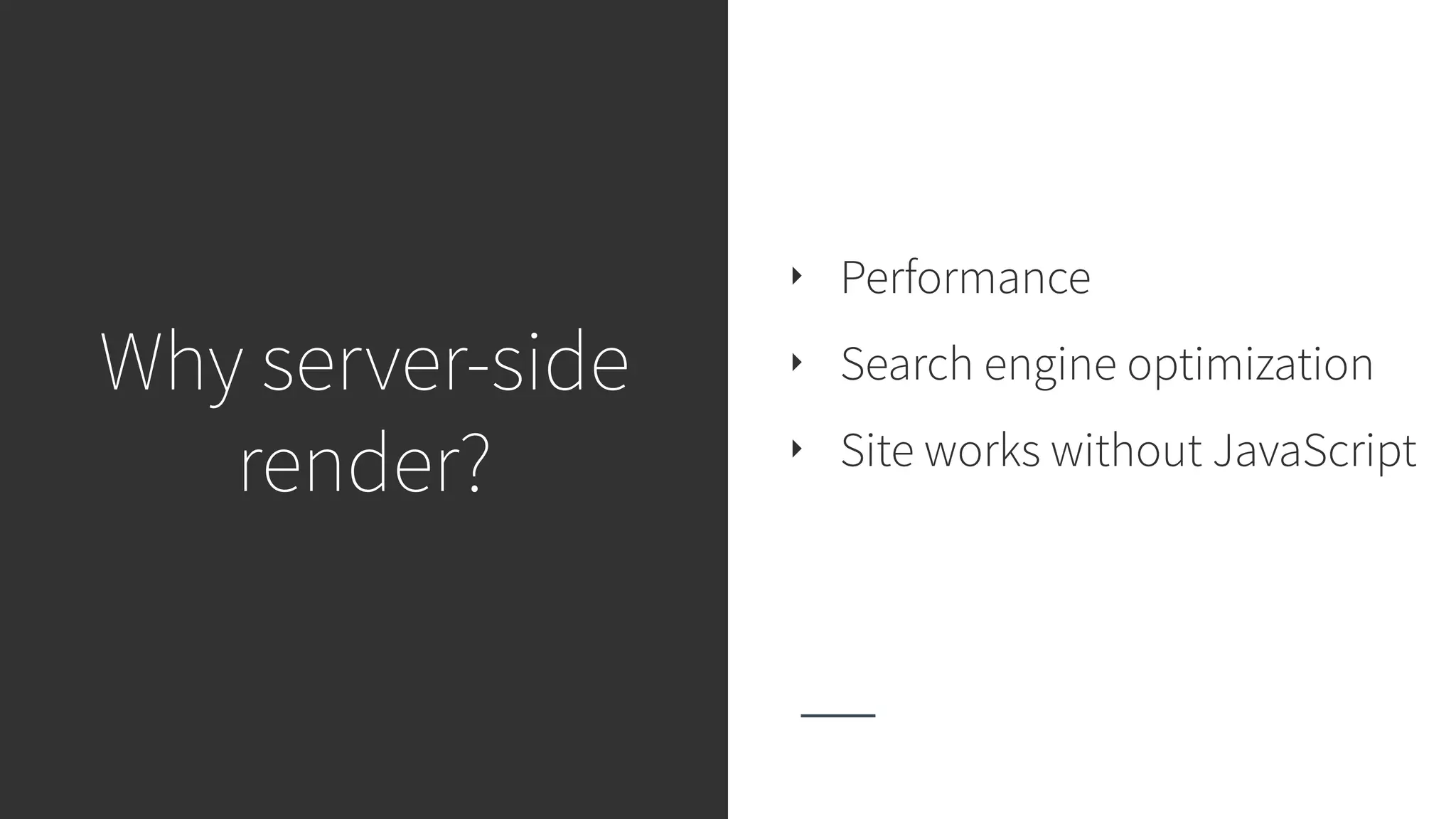
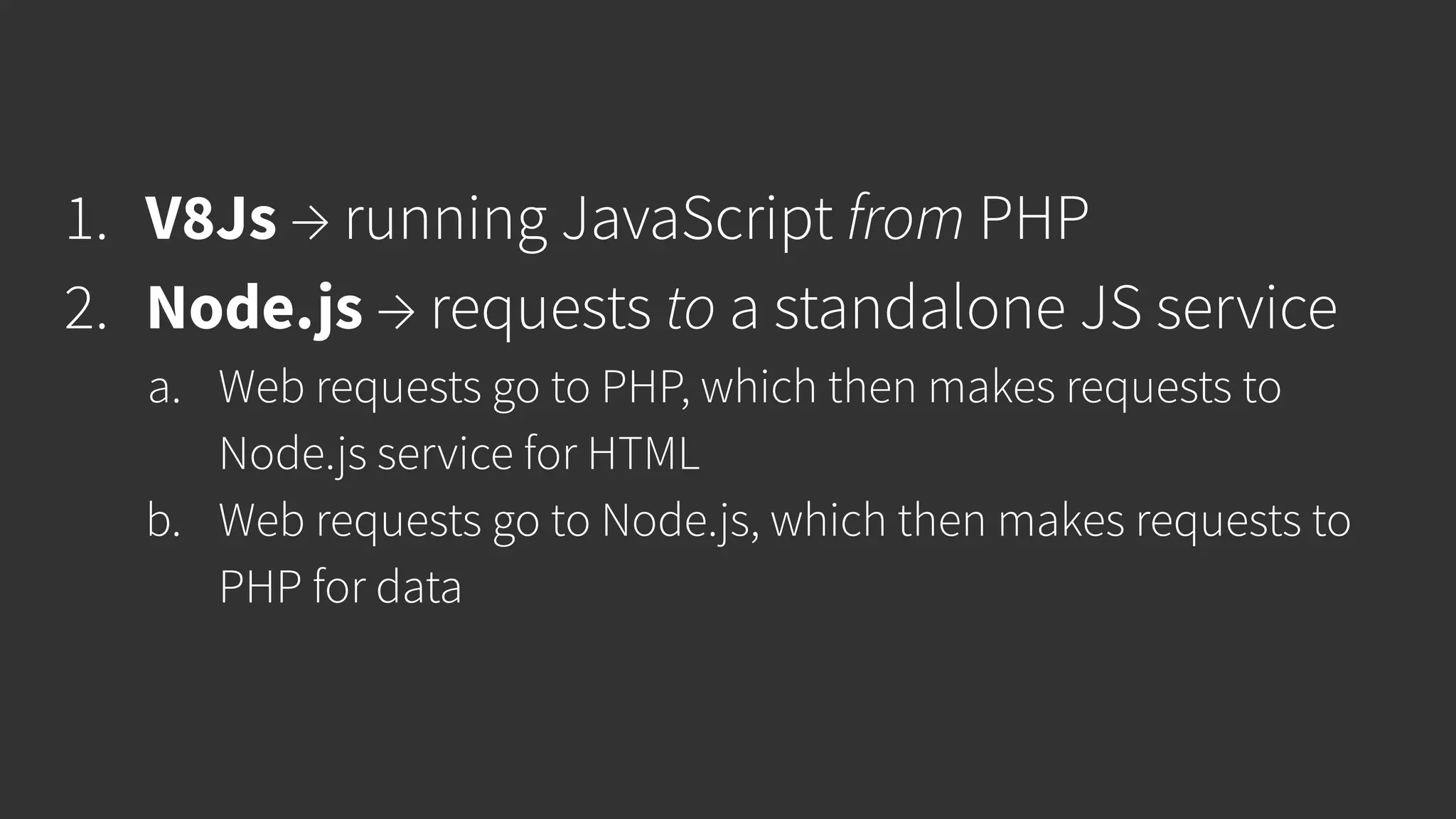
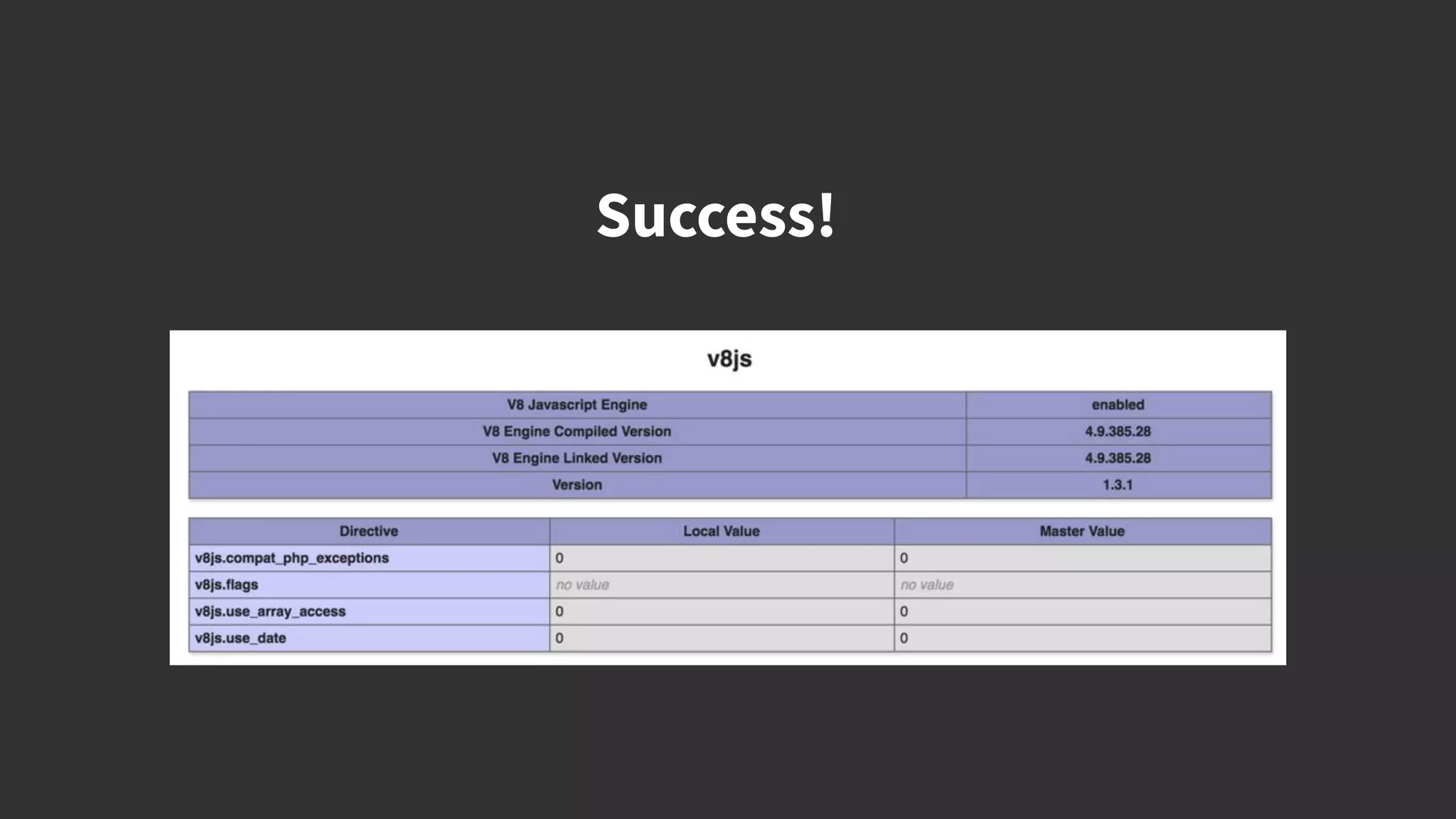
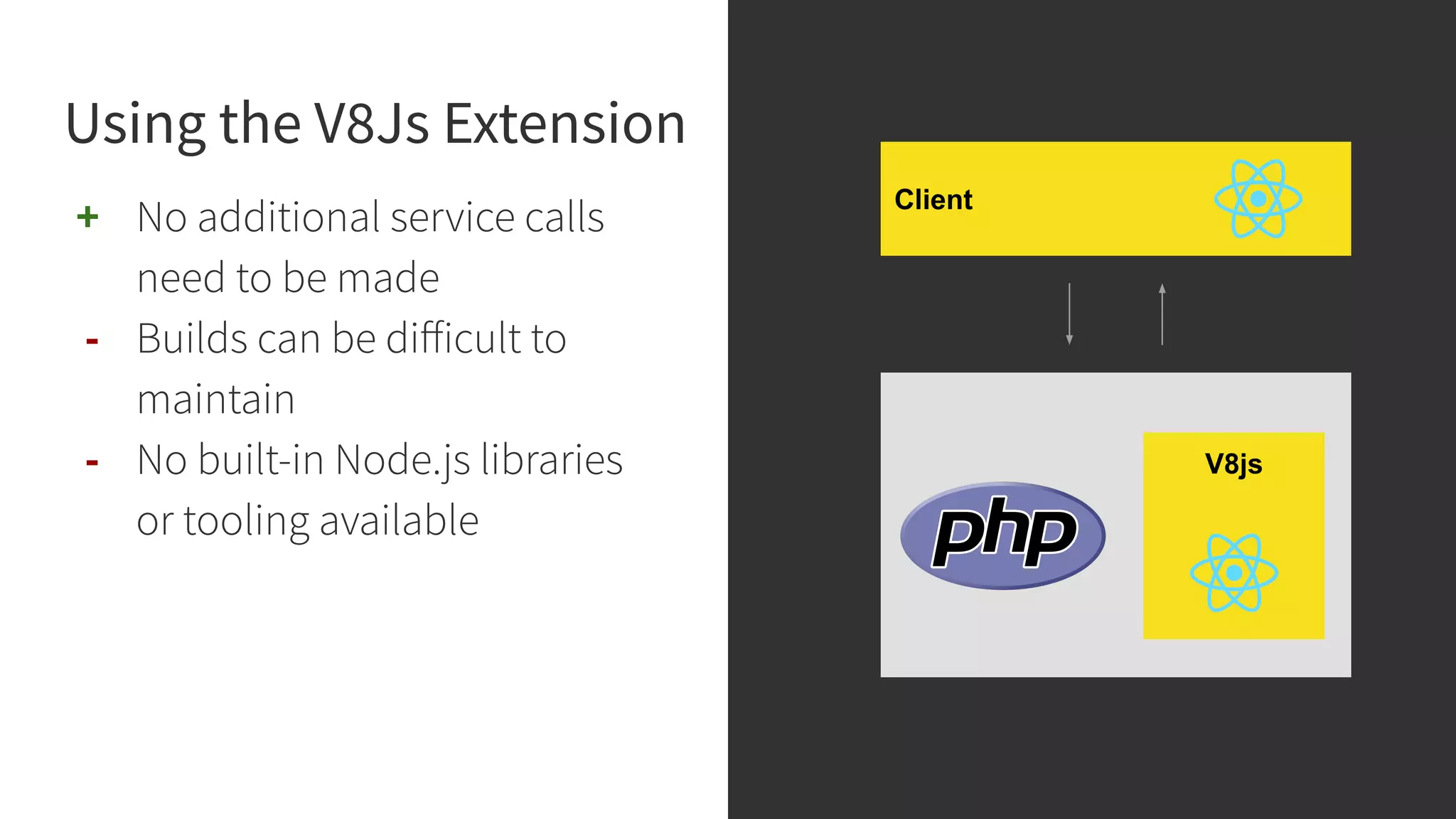
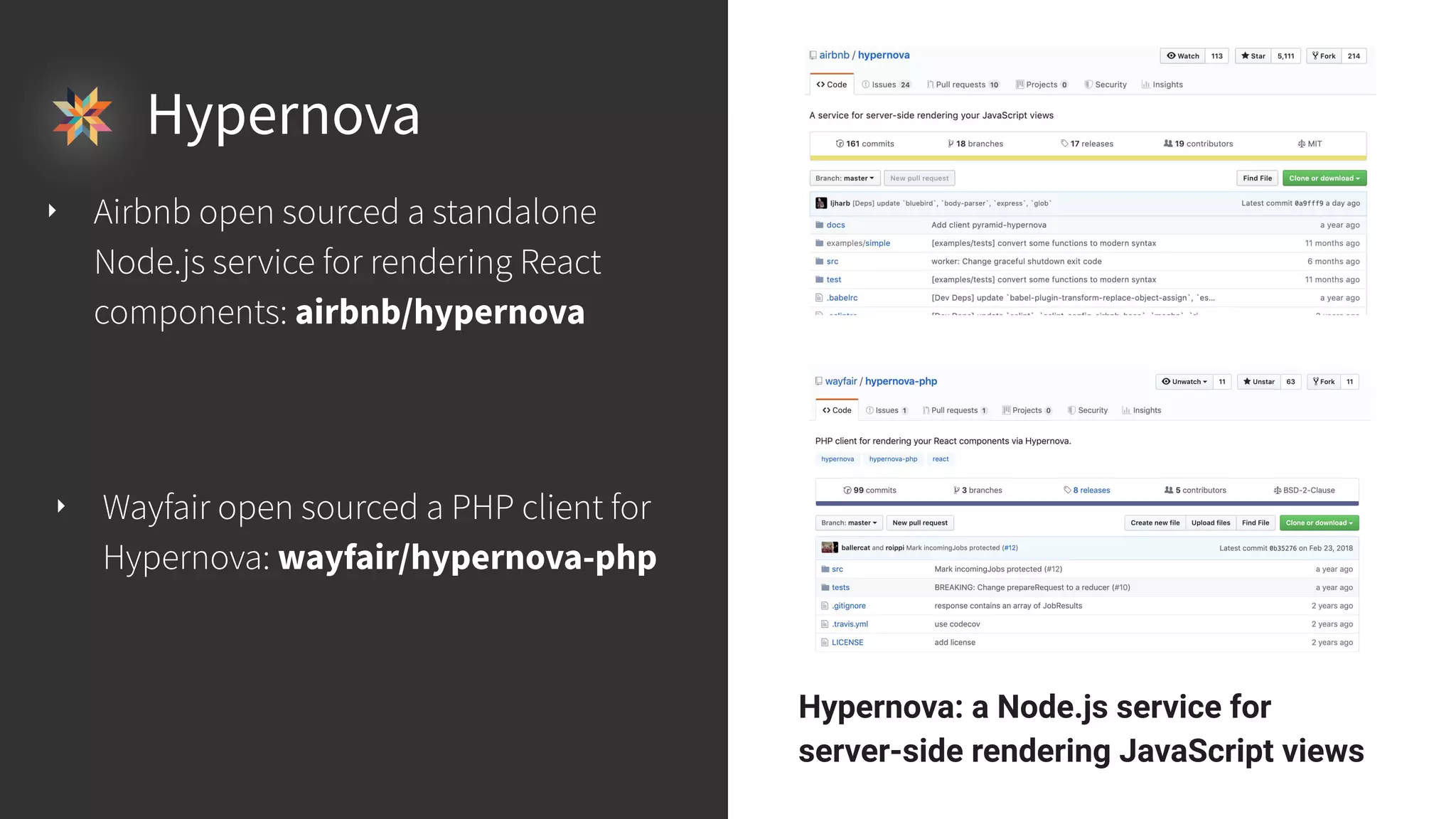
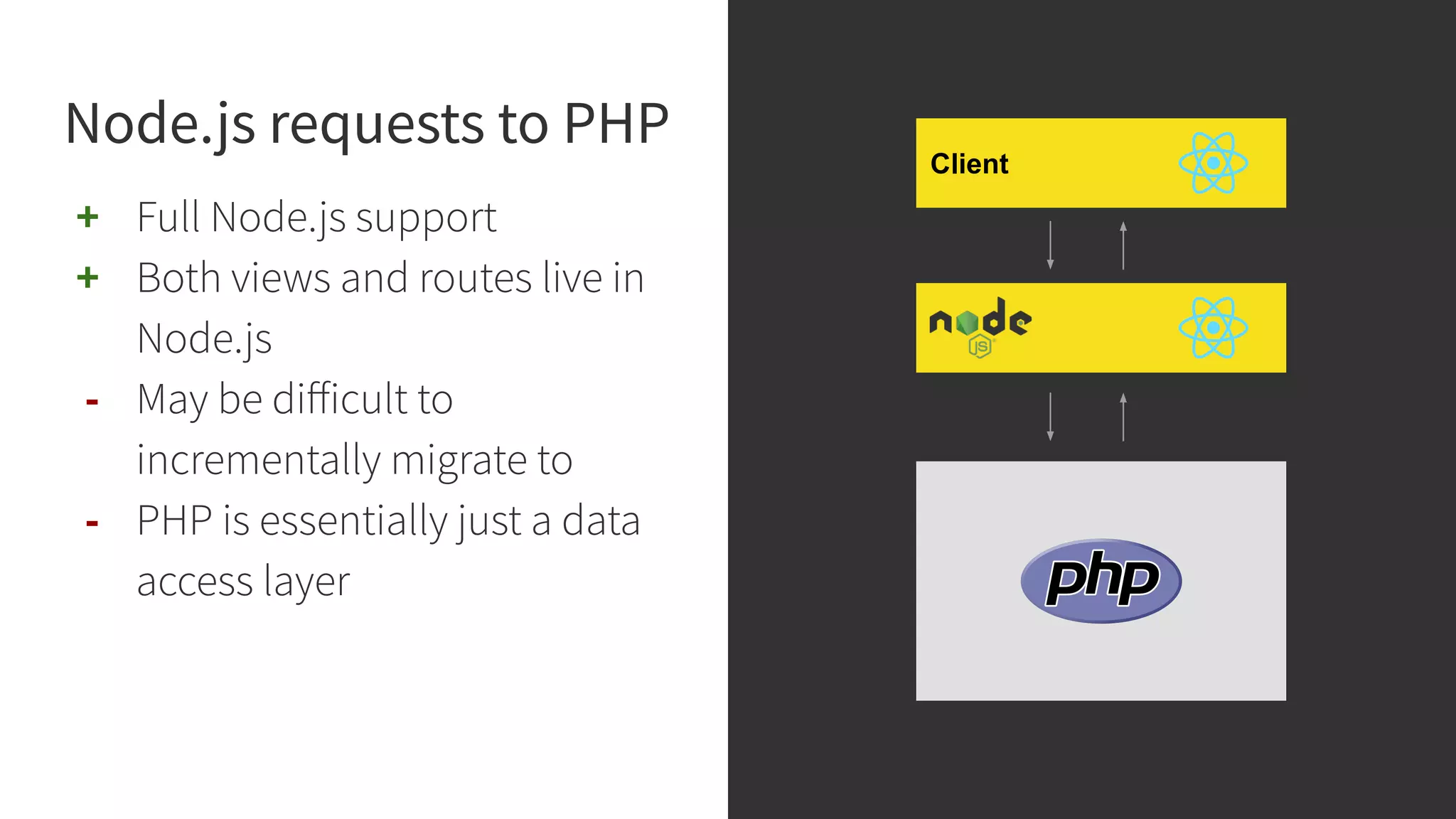
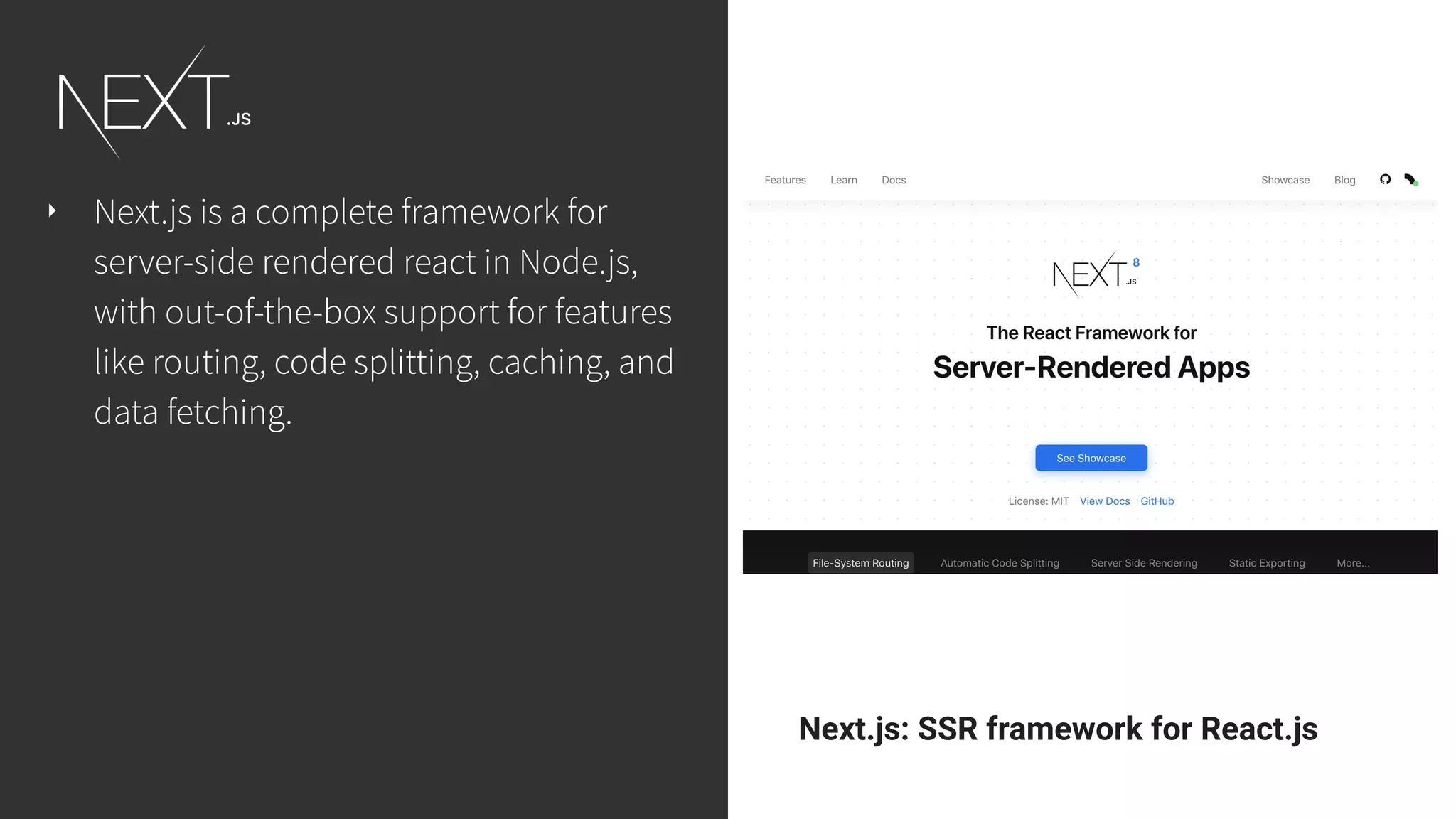
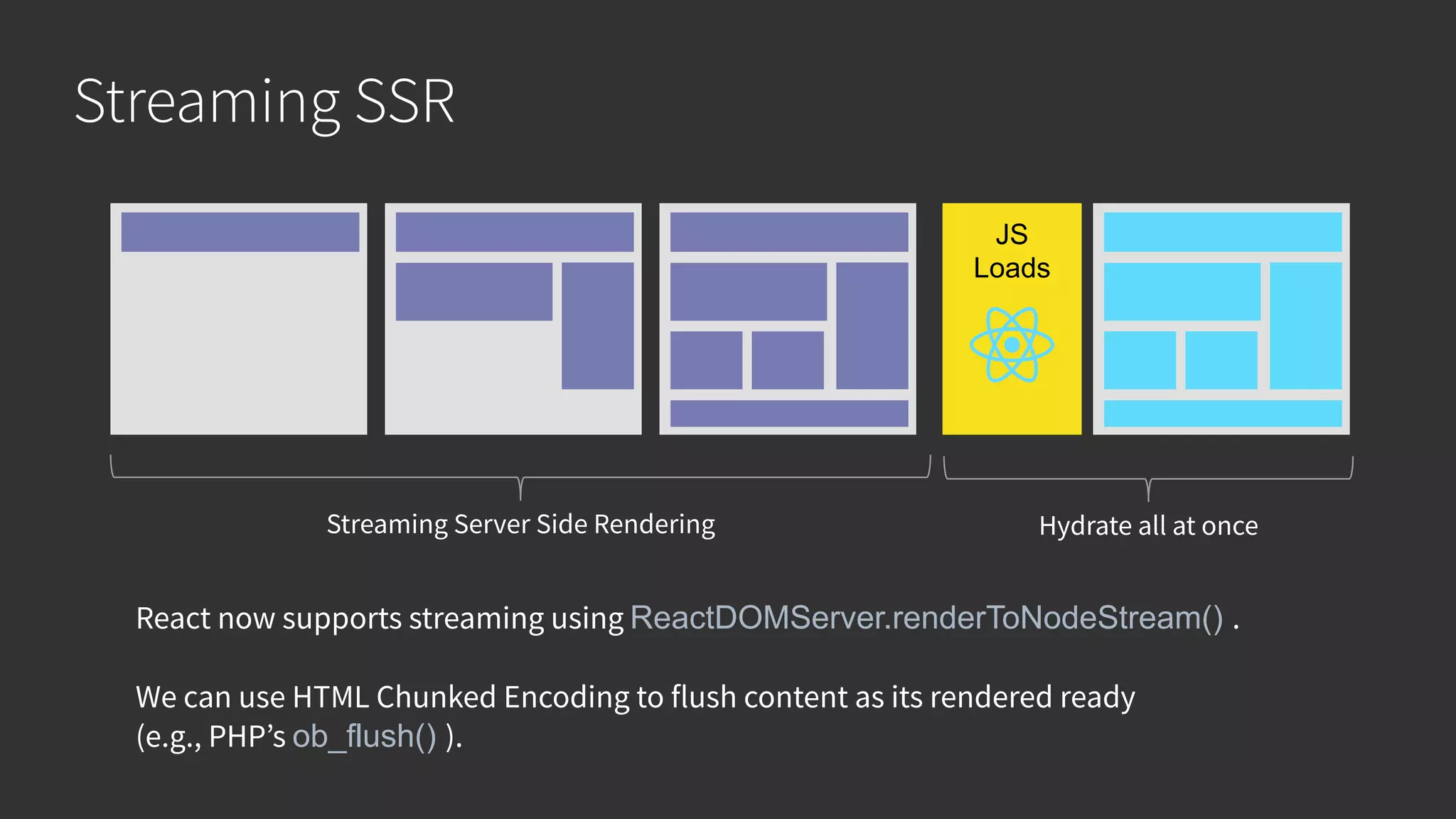
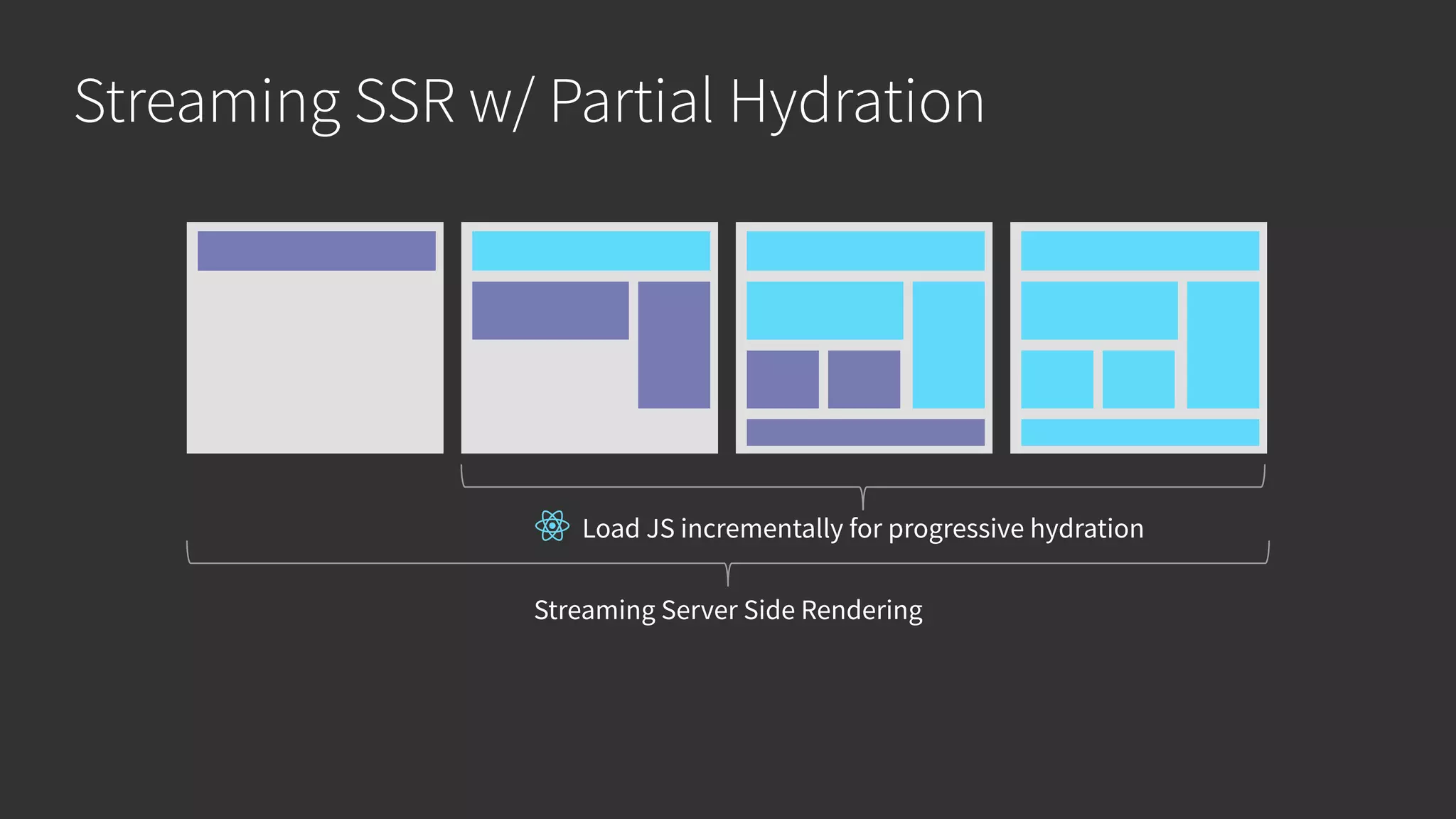
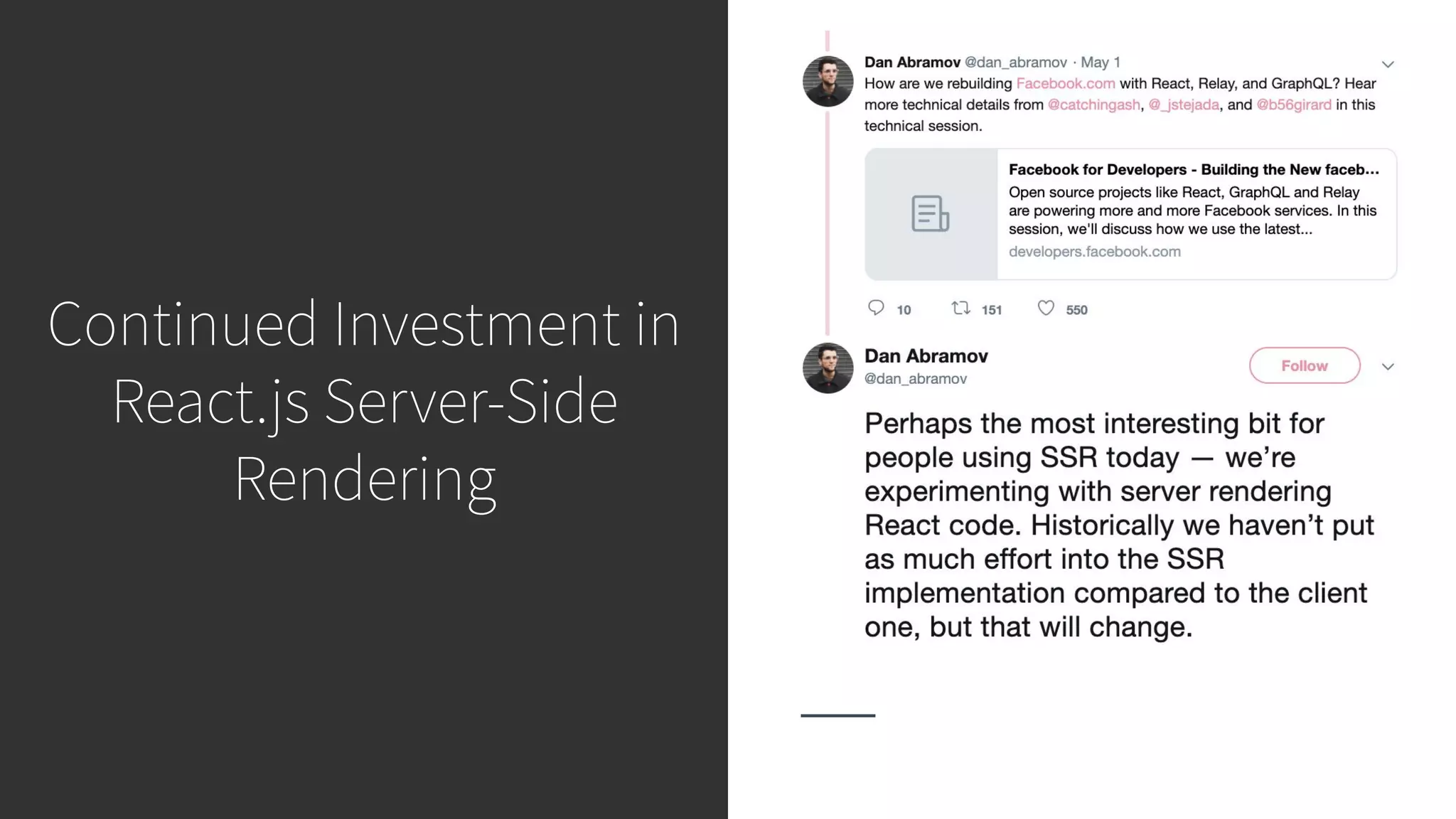
This document discusses integrating React.js into a PHP application. It provides an overview of React.js and its benefits for building user interfaces. It then covers different approaches to server-side rendering (SSR) with React in a PHP application, including using the V8Js PHP extension to run JavaScript, making requests from PHP to a Node.js service, and making requests from Node.js to PHP. It emphasizes that React.js and PHP can complement each other and discusses frameworks like Next.js that support SSR. The key takeaways are that React.js can enhance PHP applications, there are different SSR architectures to integrate them, and giving React.js a try can help modernize app views.