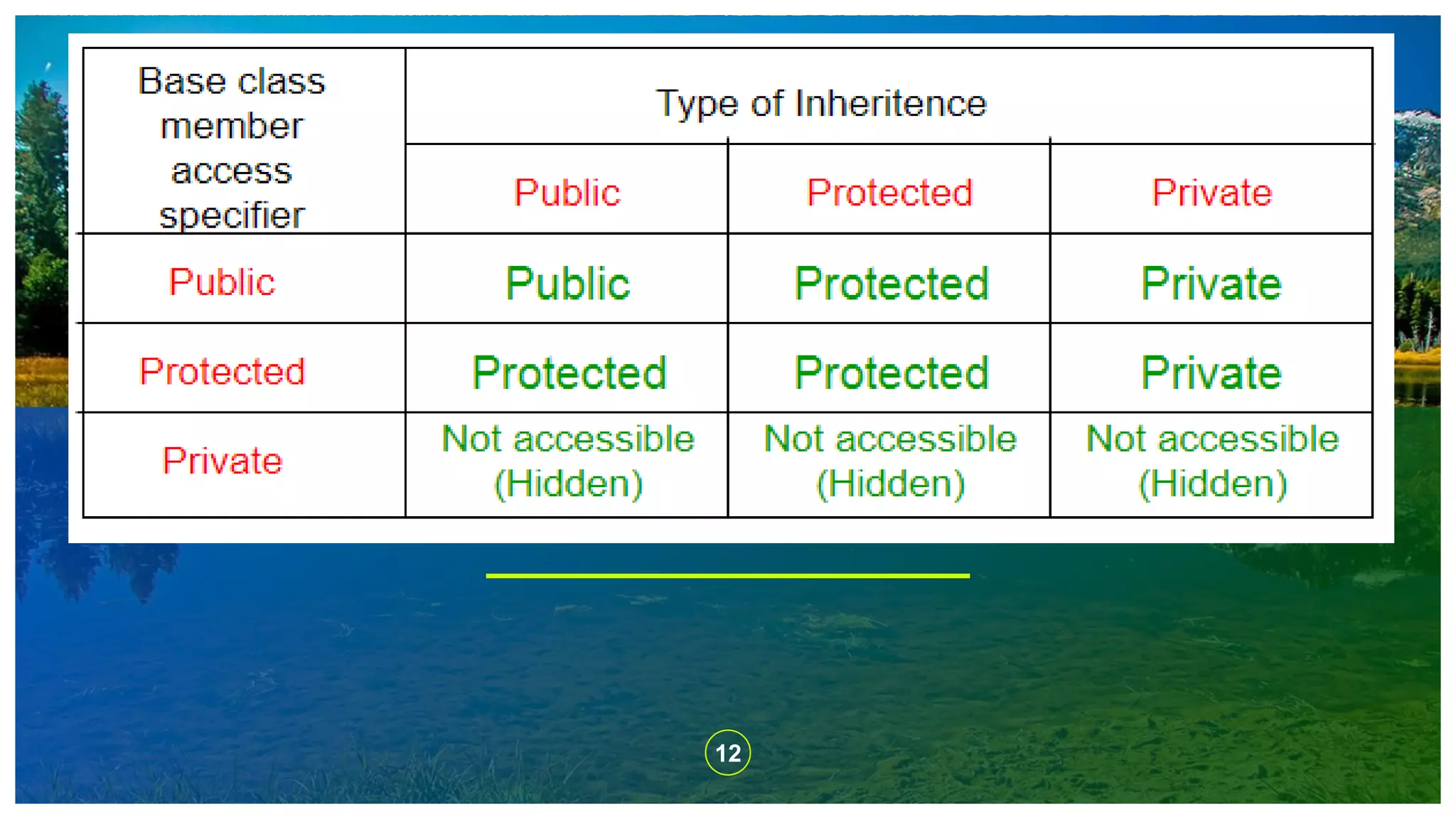
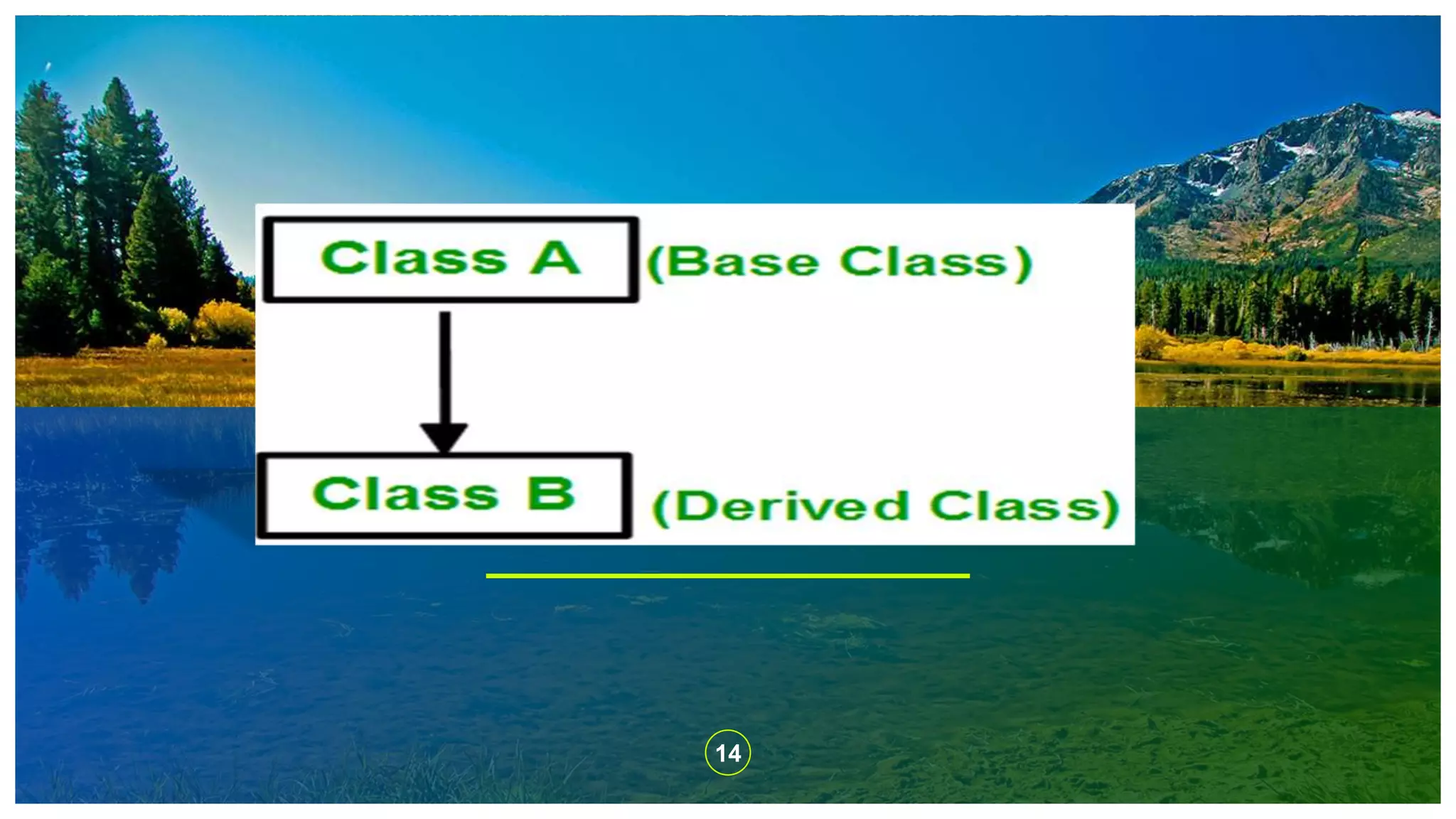
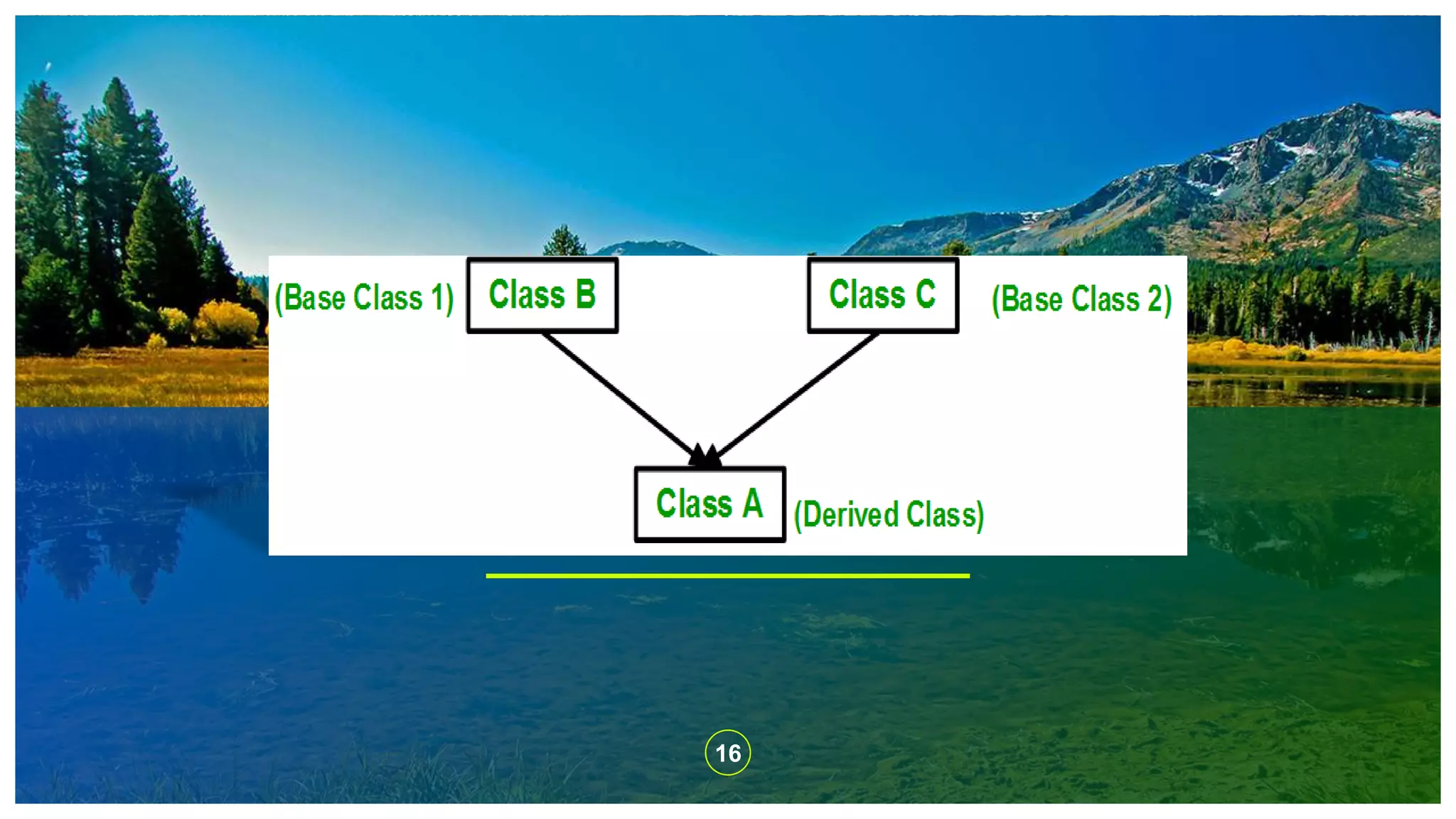
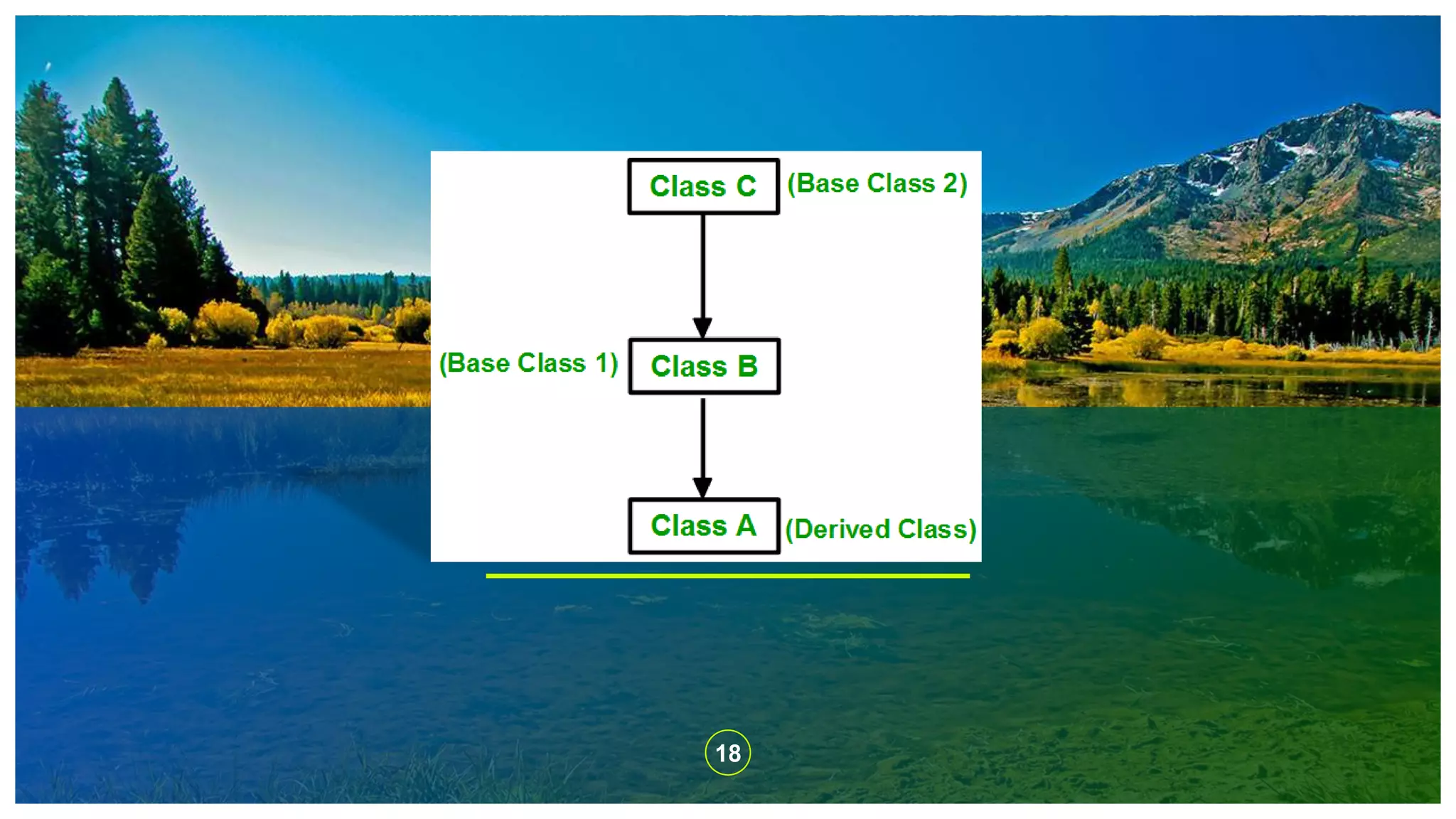
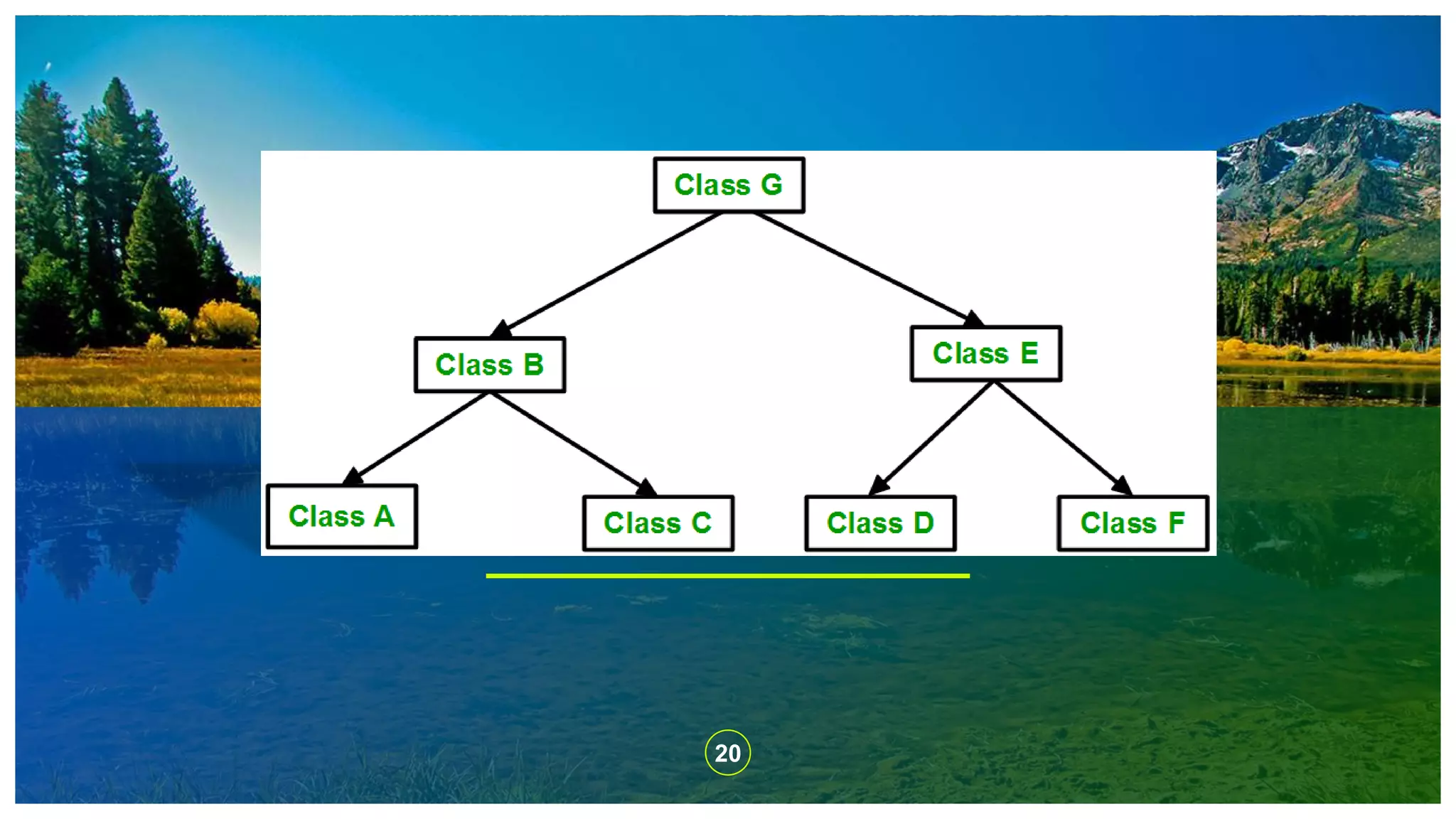
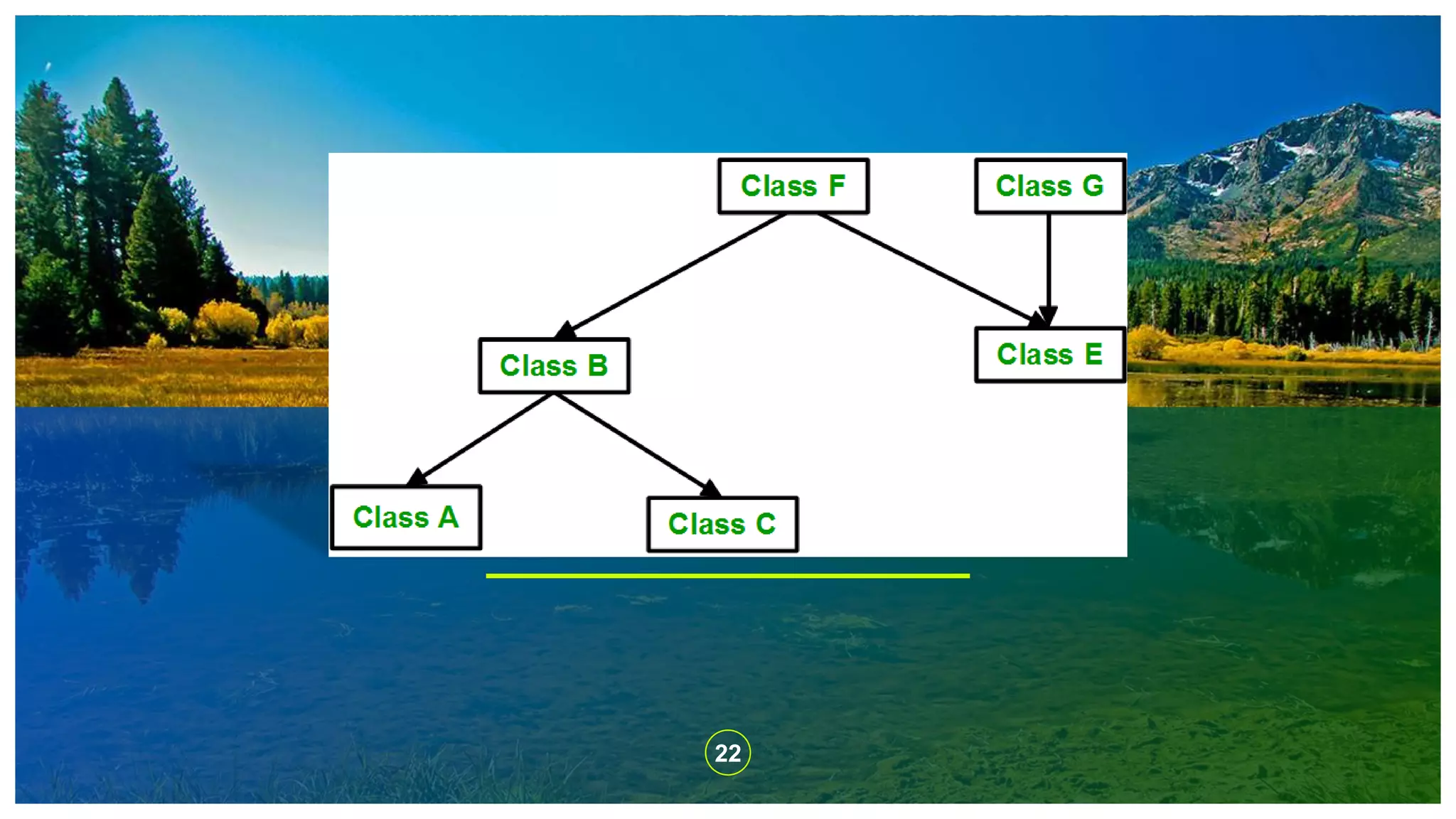
The document explains the concept of inheritance in C++, which allows a class (subclass) to derive properties from another class (superclass), improving code reusability and reducing redundancy. It details various types of inheritance, including single, multiple, multilevel, hierarchical, and hybrid inheritance, along with their practical implications. The content emphasizes the importance of inheritance in object-oriented programming to avoid duplicating code across multiple classes.