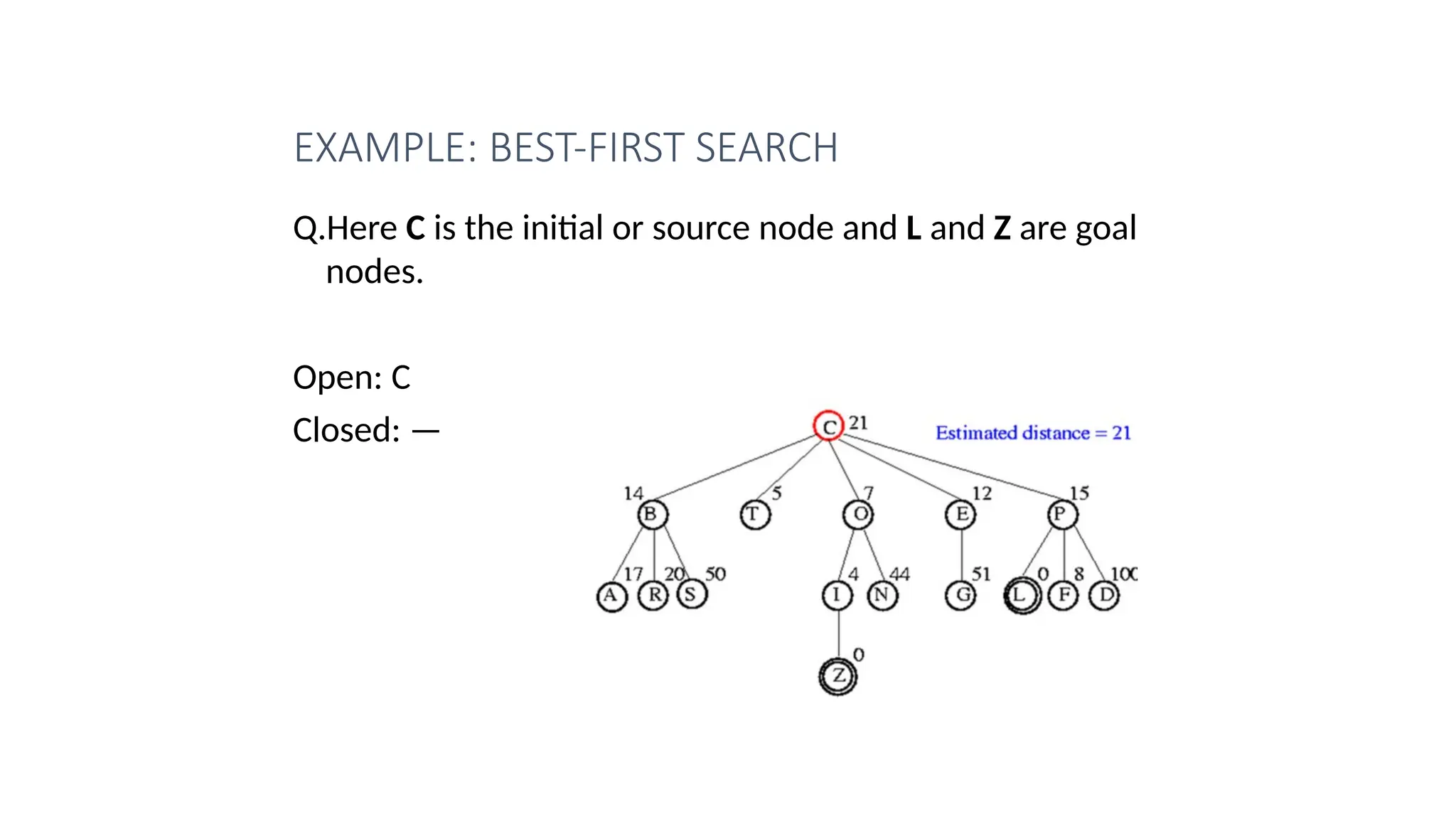
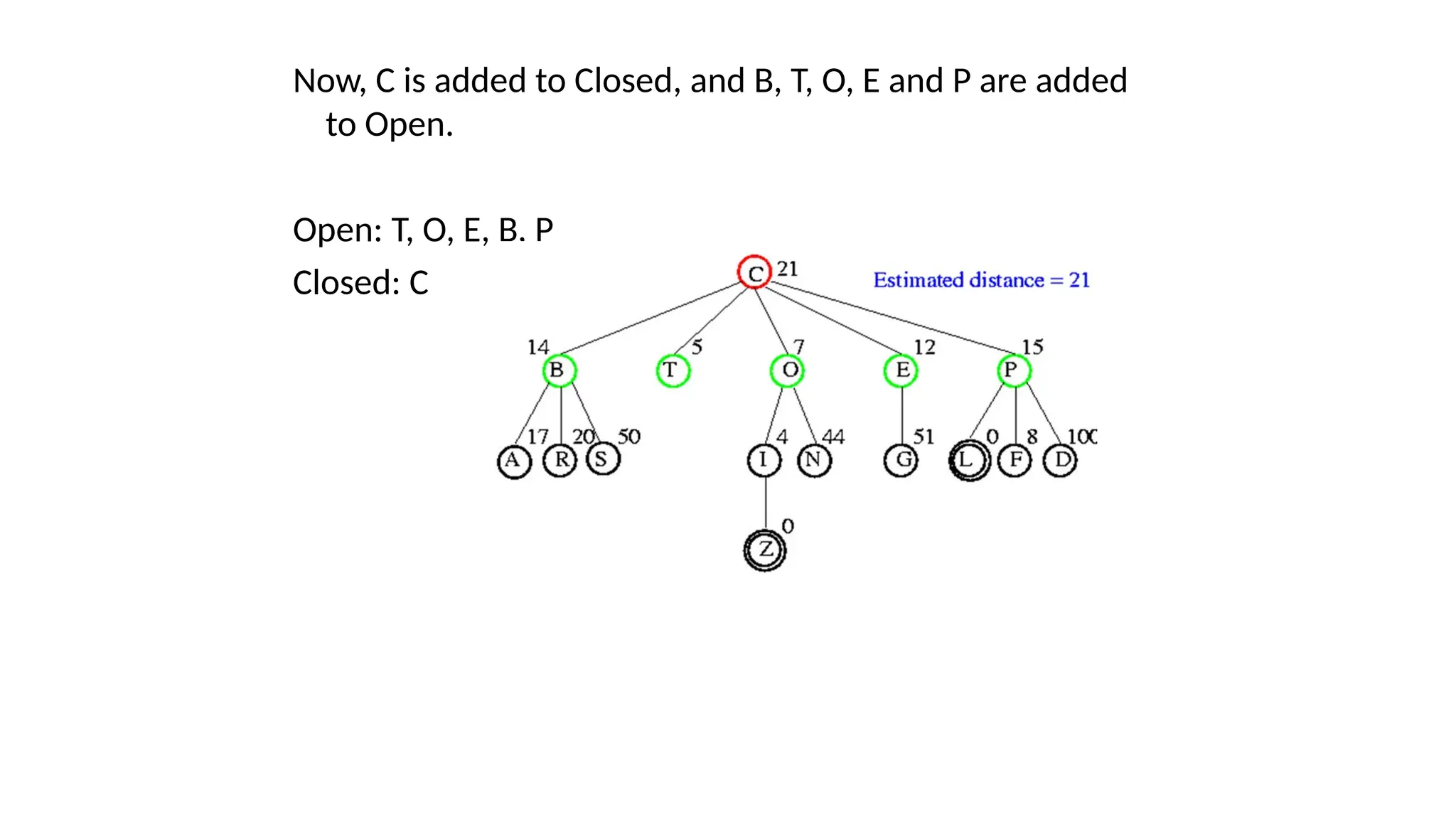
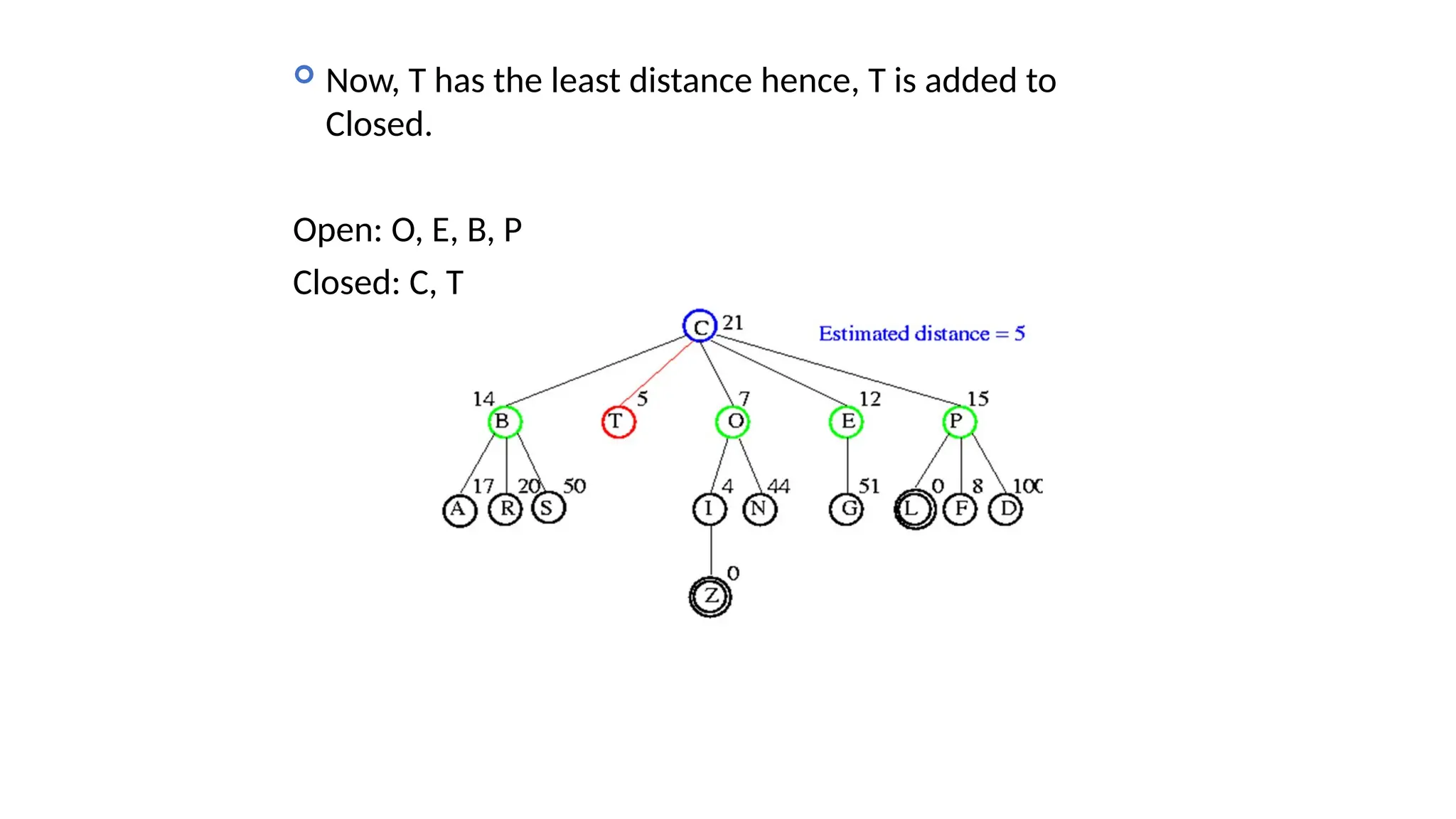
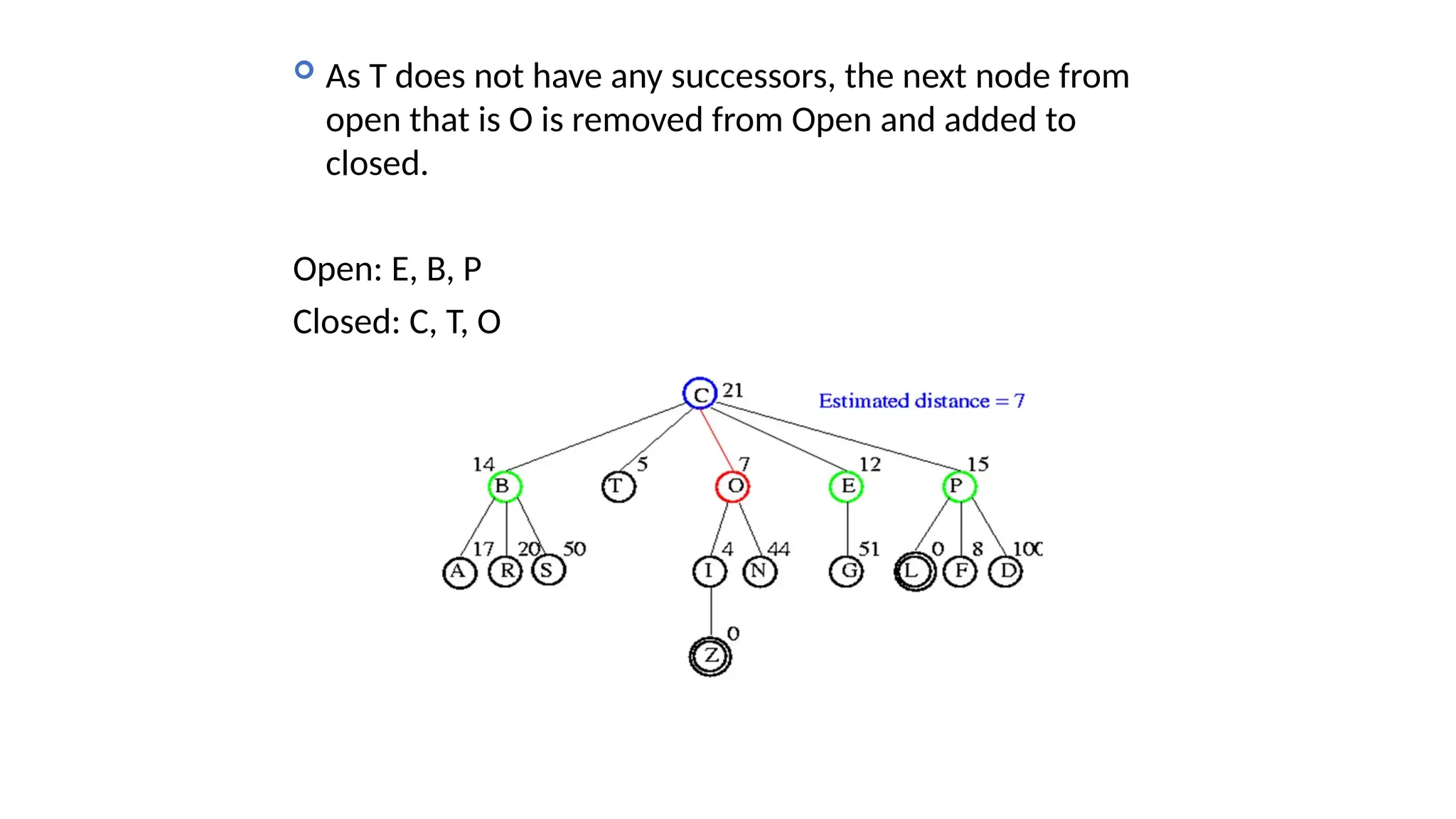
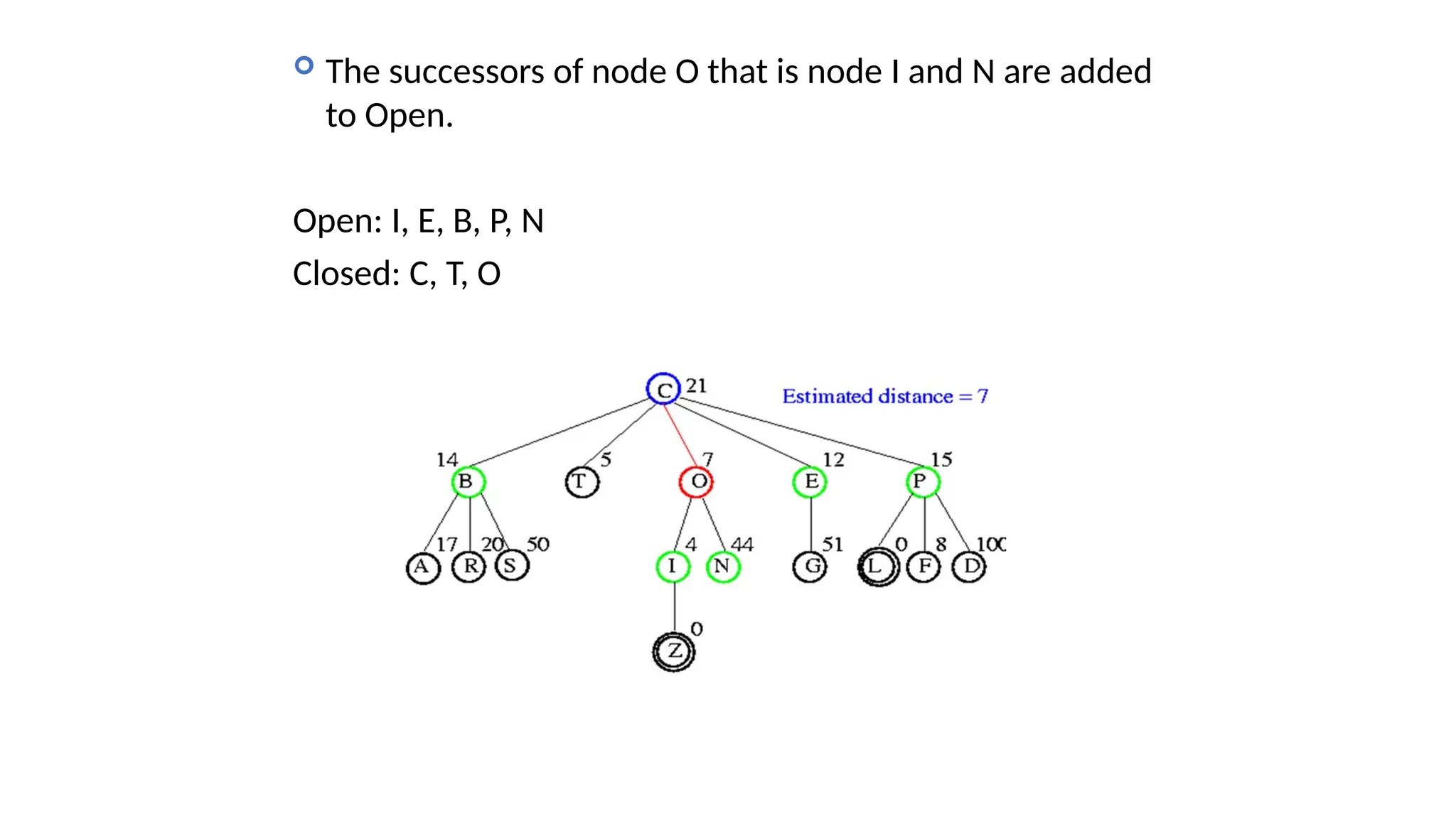
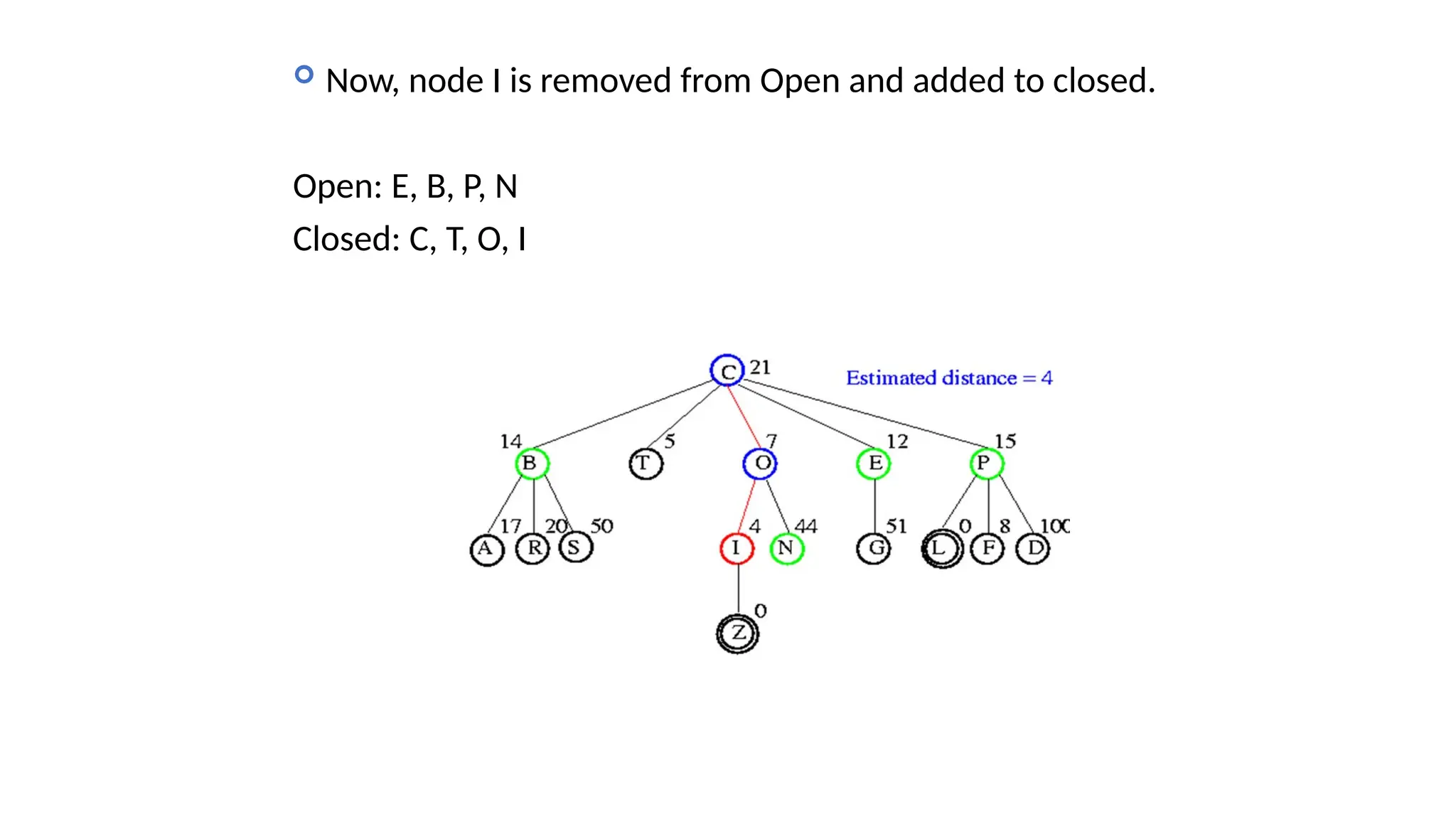
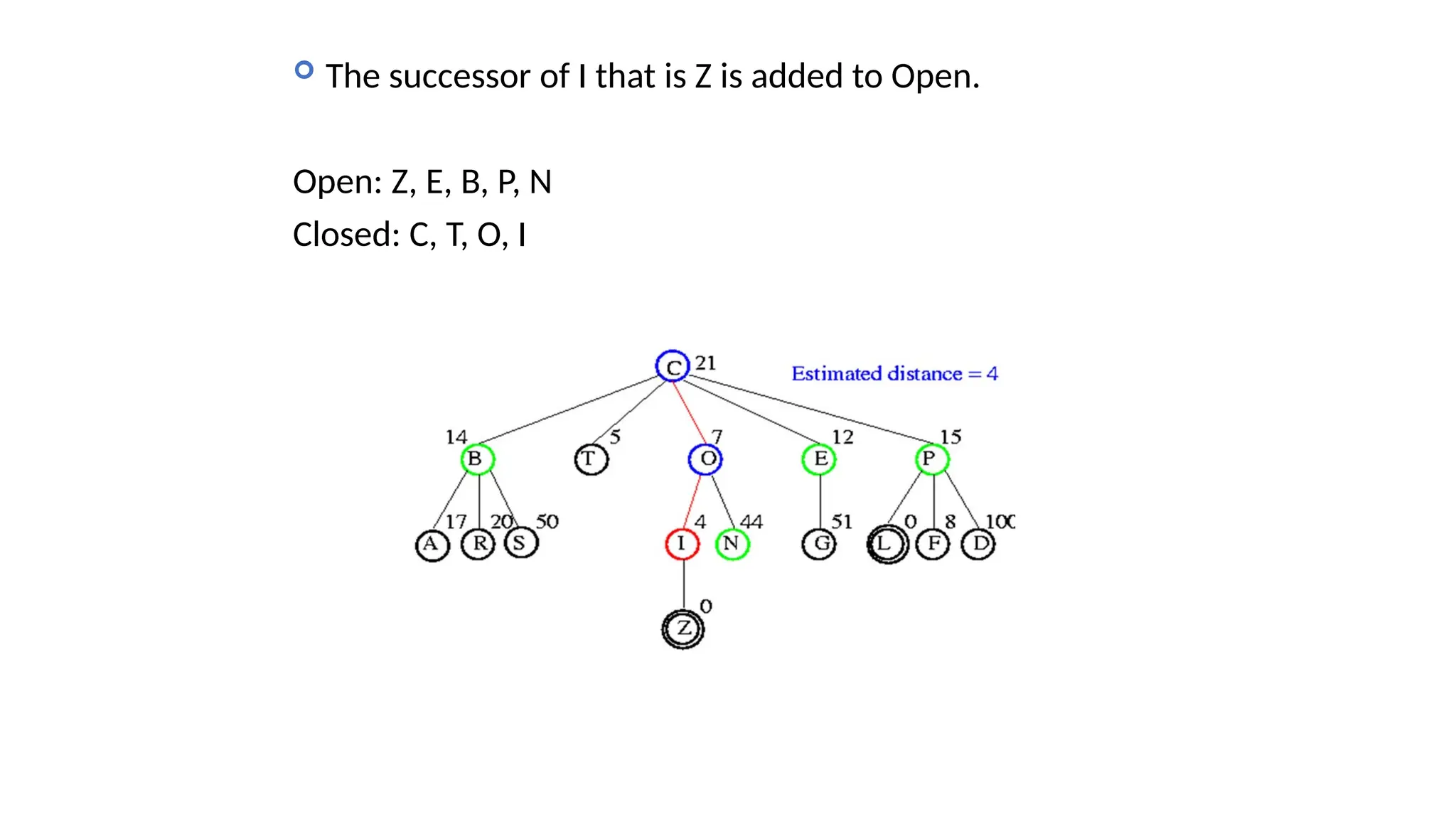
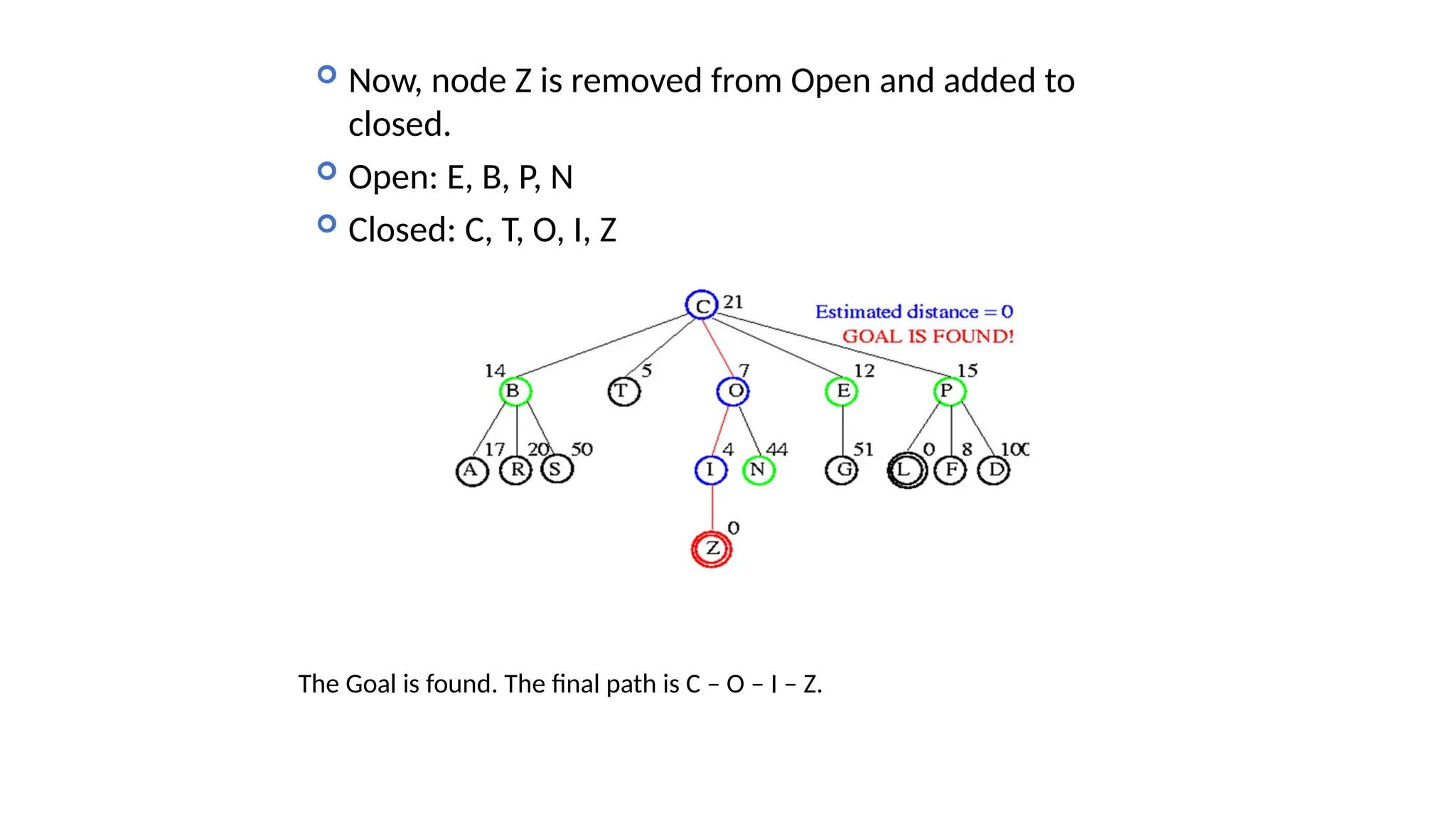
Informed search algorithms, also known as heuristic search algorithms, leverage domain-specific knowledge to enhance search efficiency, leading to quicker and optimal solutions. Greedy best-first search, a type of informed search, evaluates nodes based on their estimated cost to the goal, but may struggle with local optima and lacks a guarantee of finding the best solution. Despite its simplicity and efficiency, greedy best-first search requires a heuristic function and may not complete the search if it encounters complex problems.