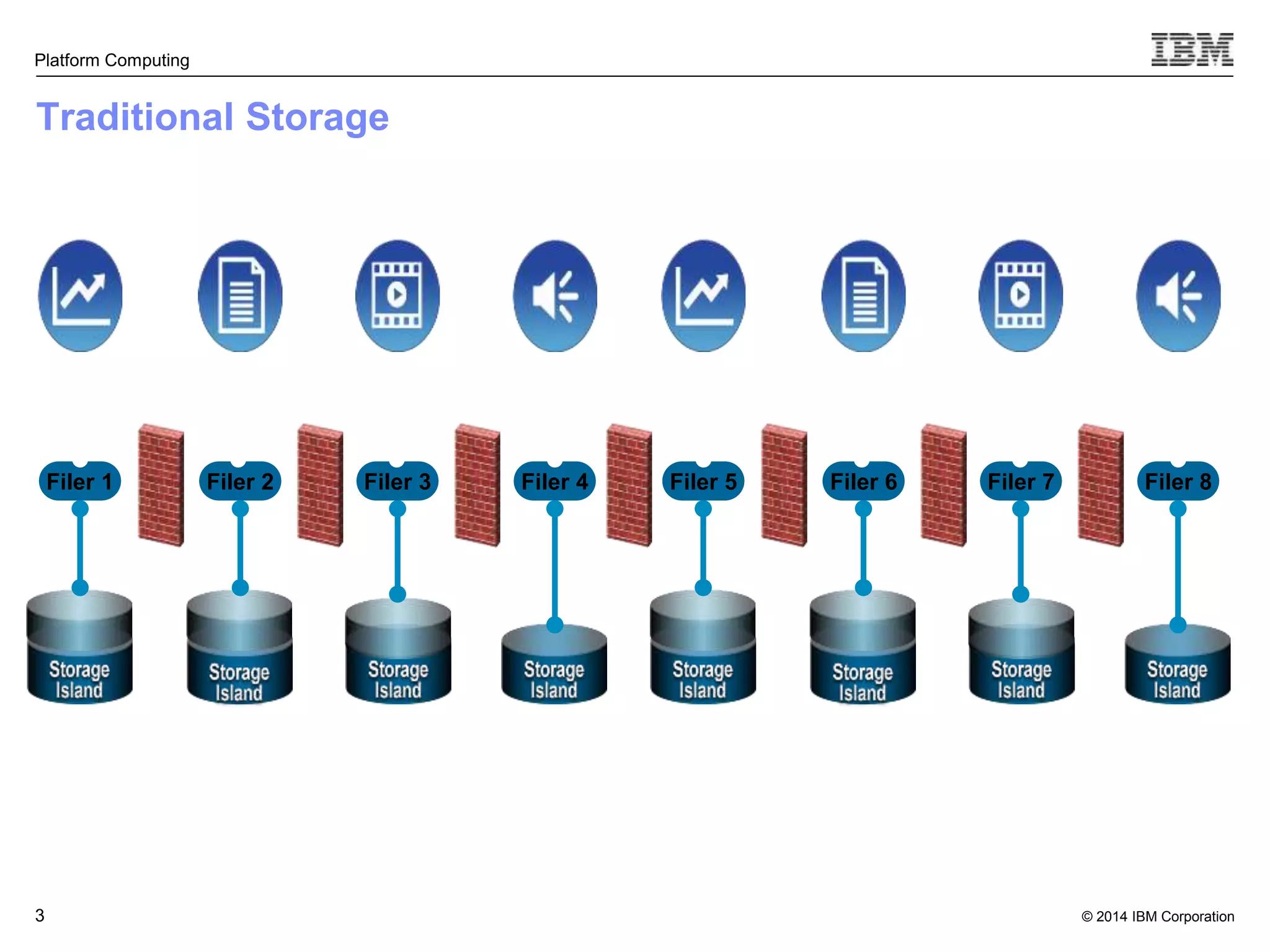
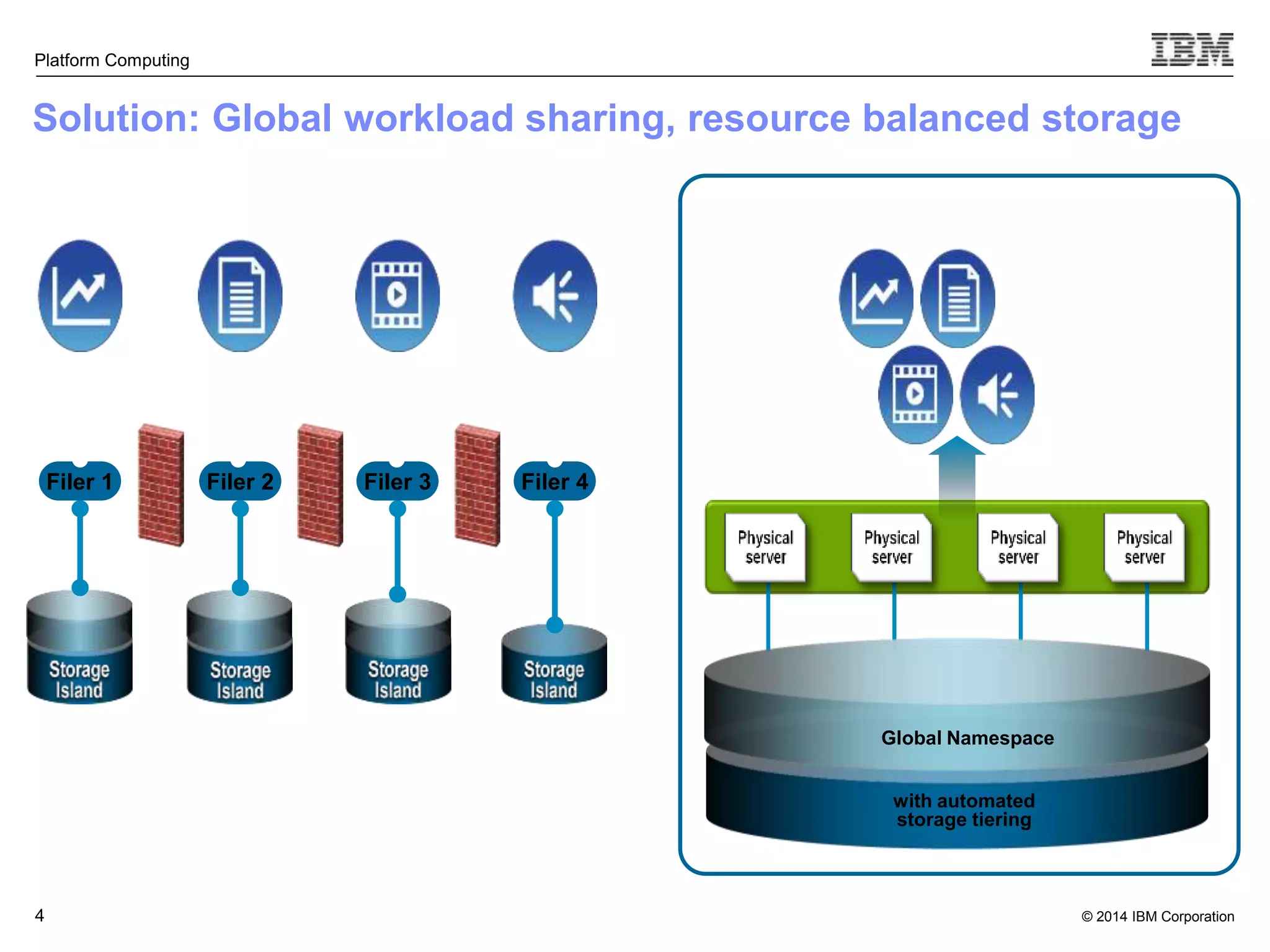
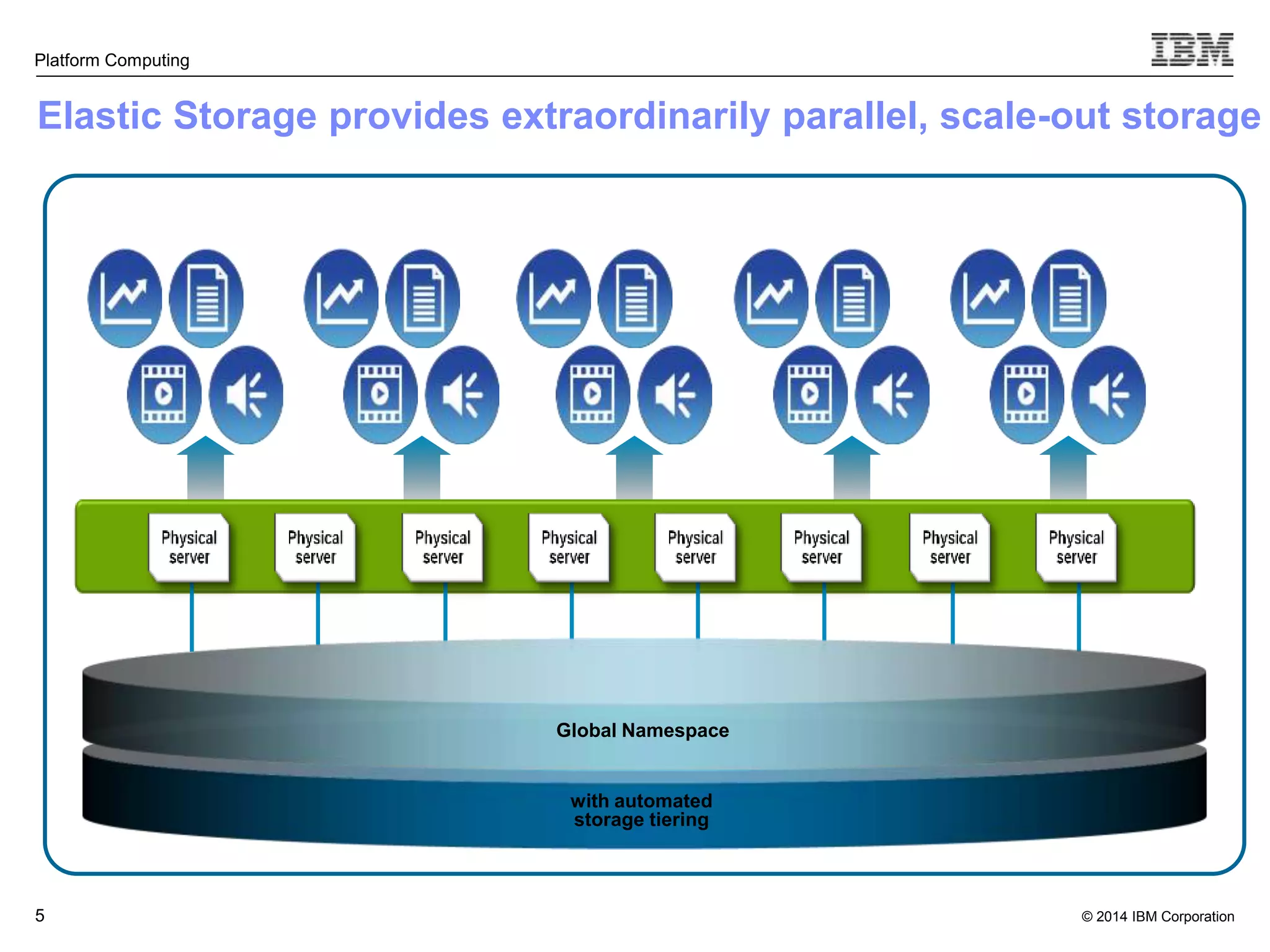
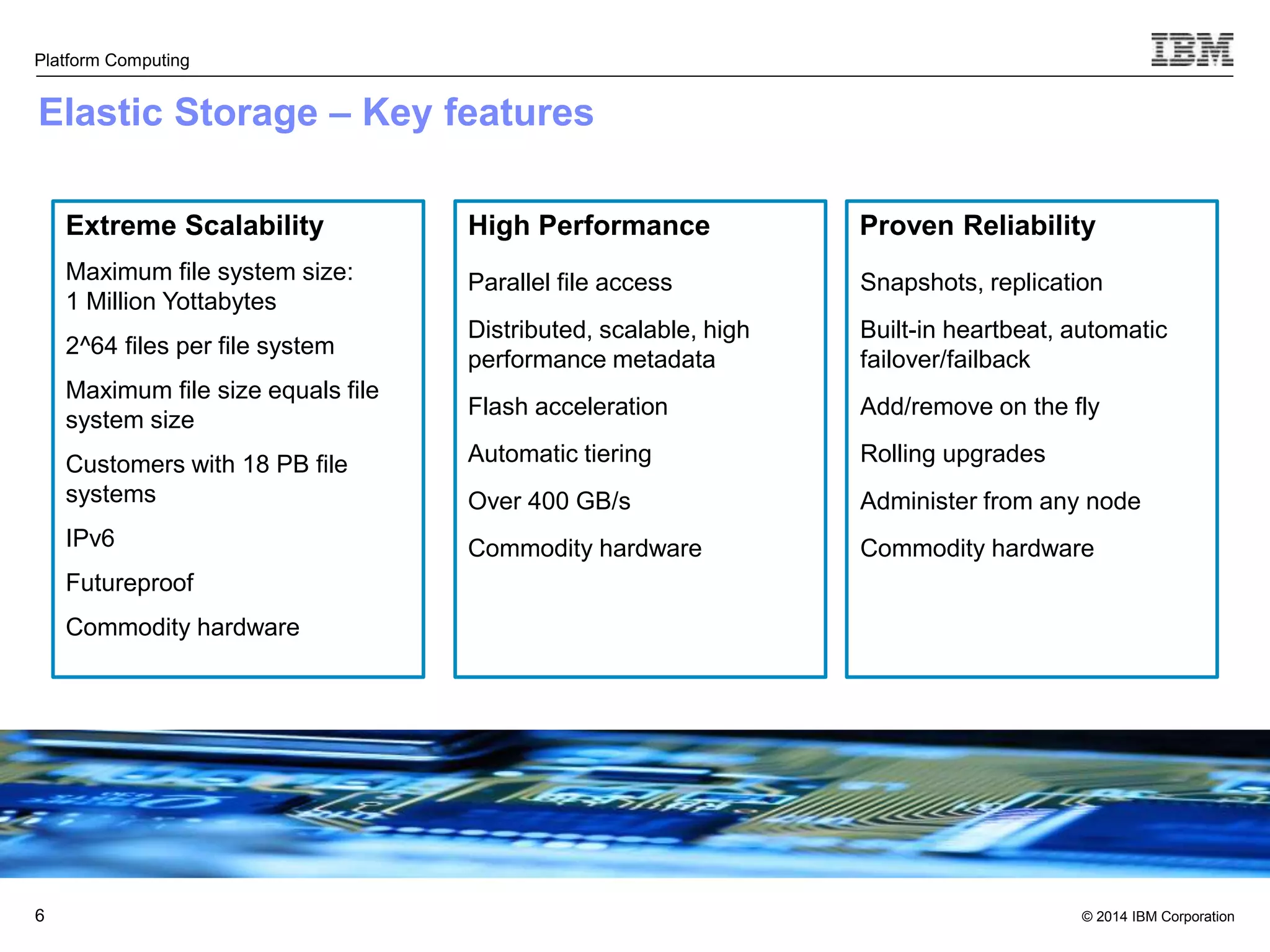
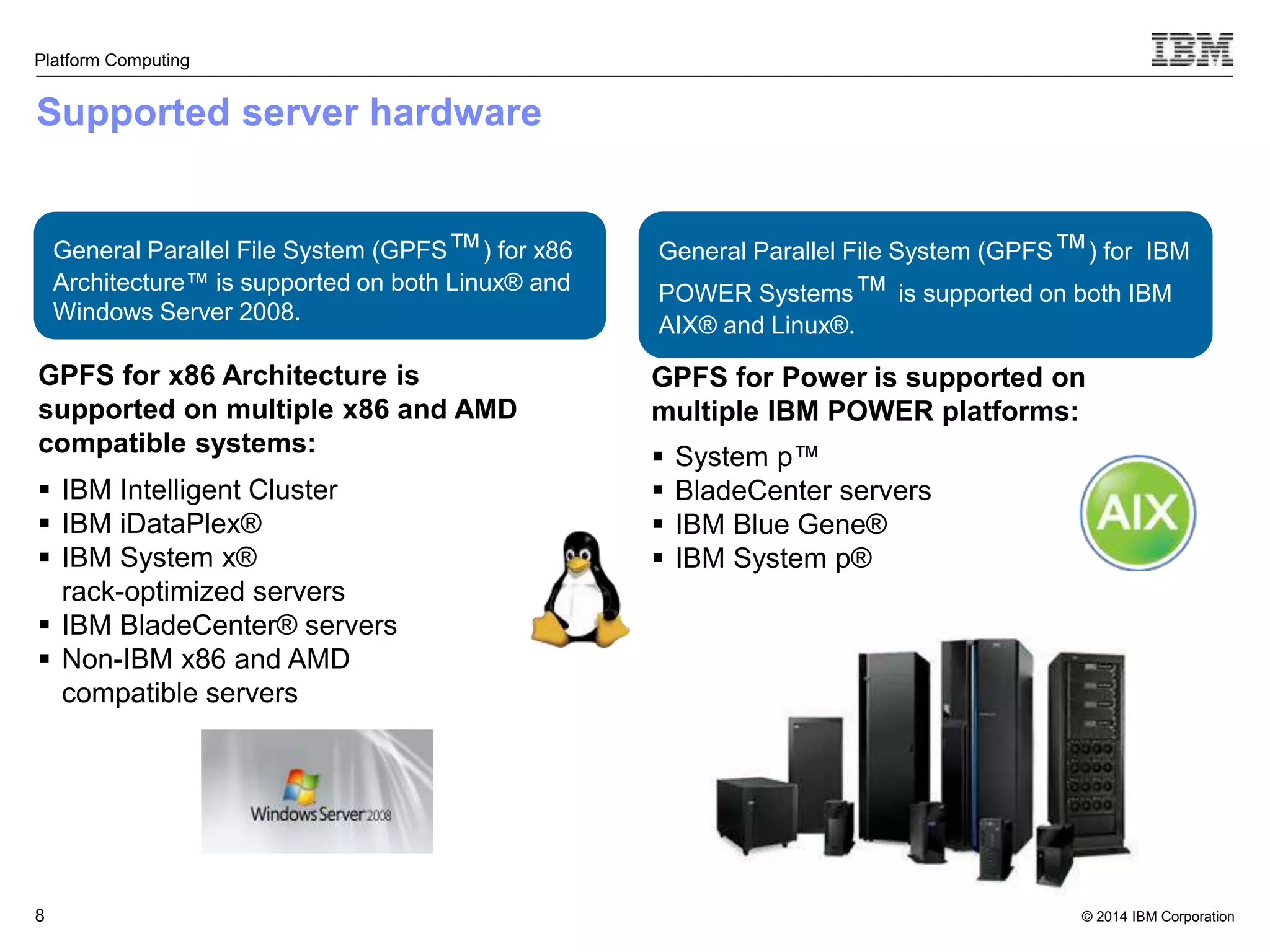
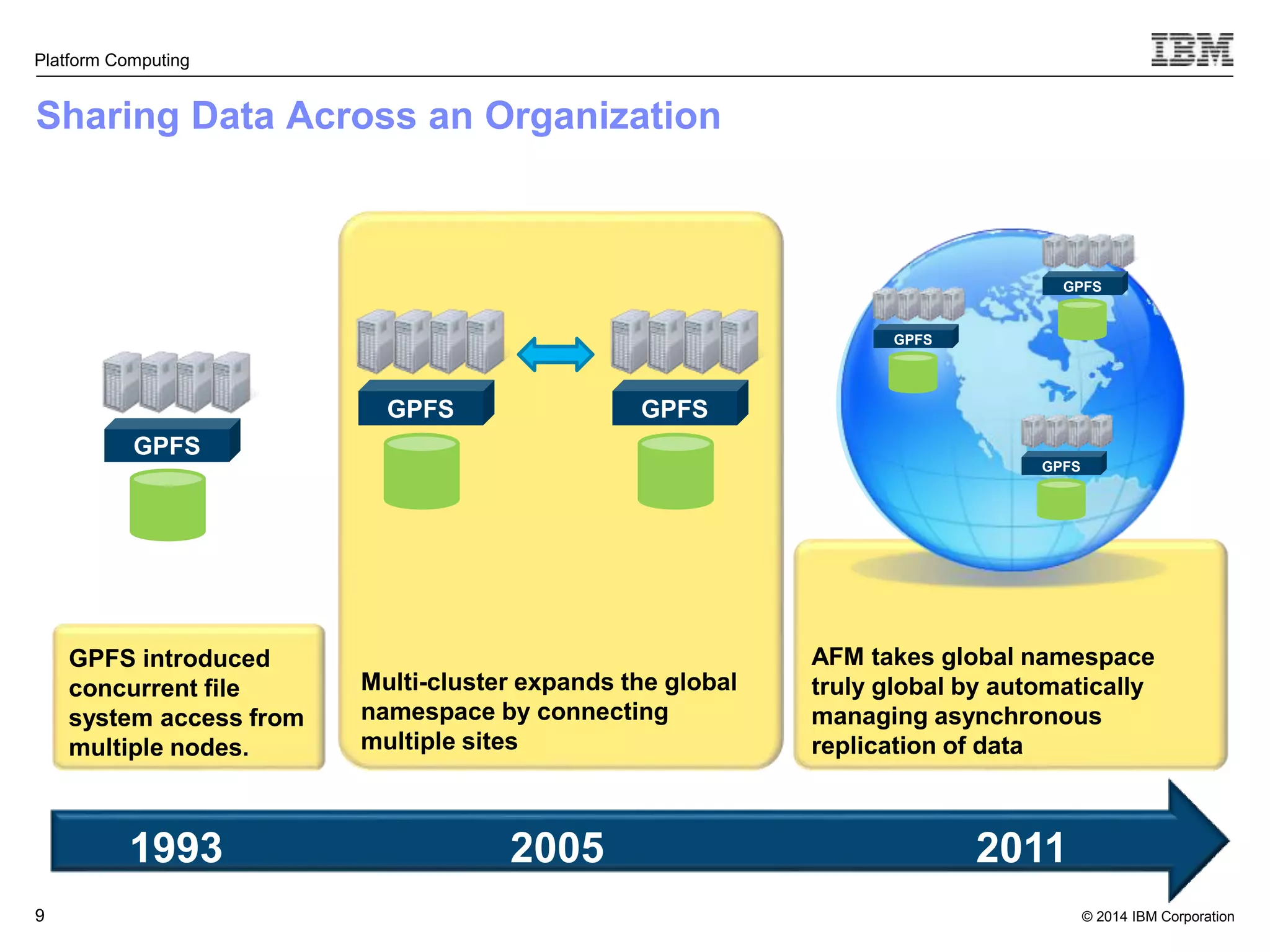
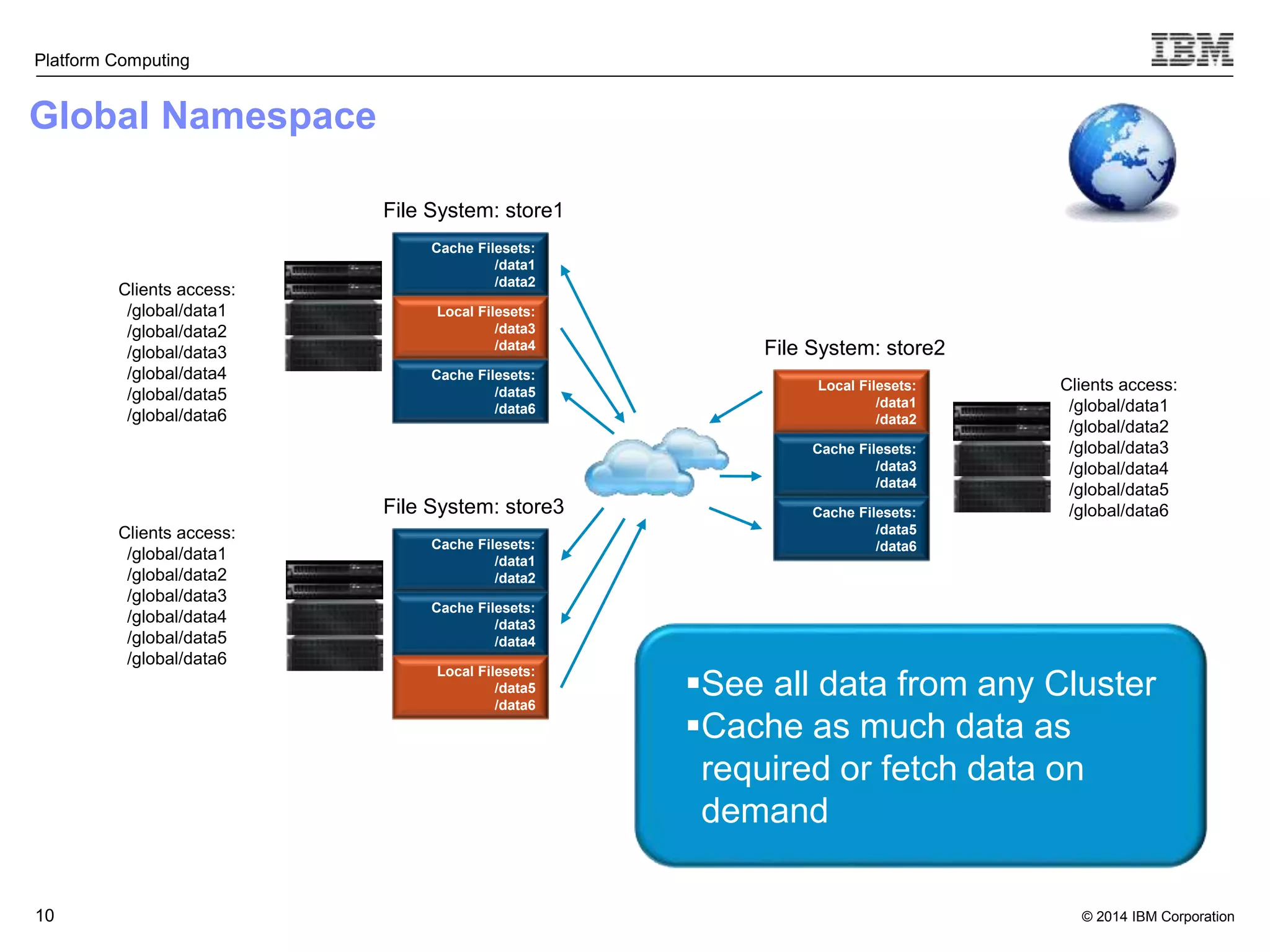
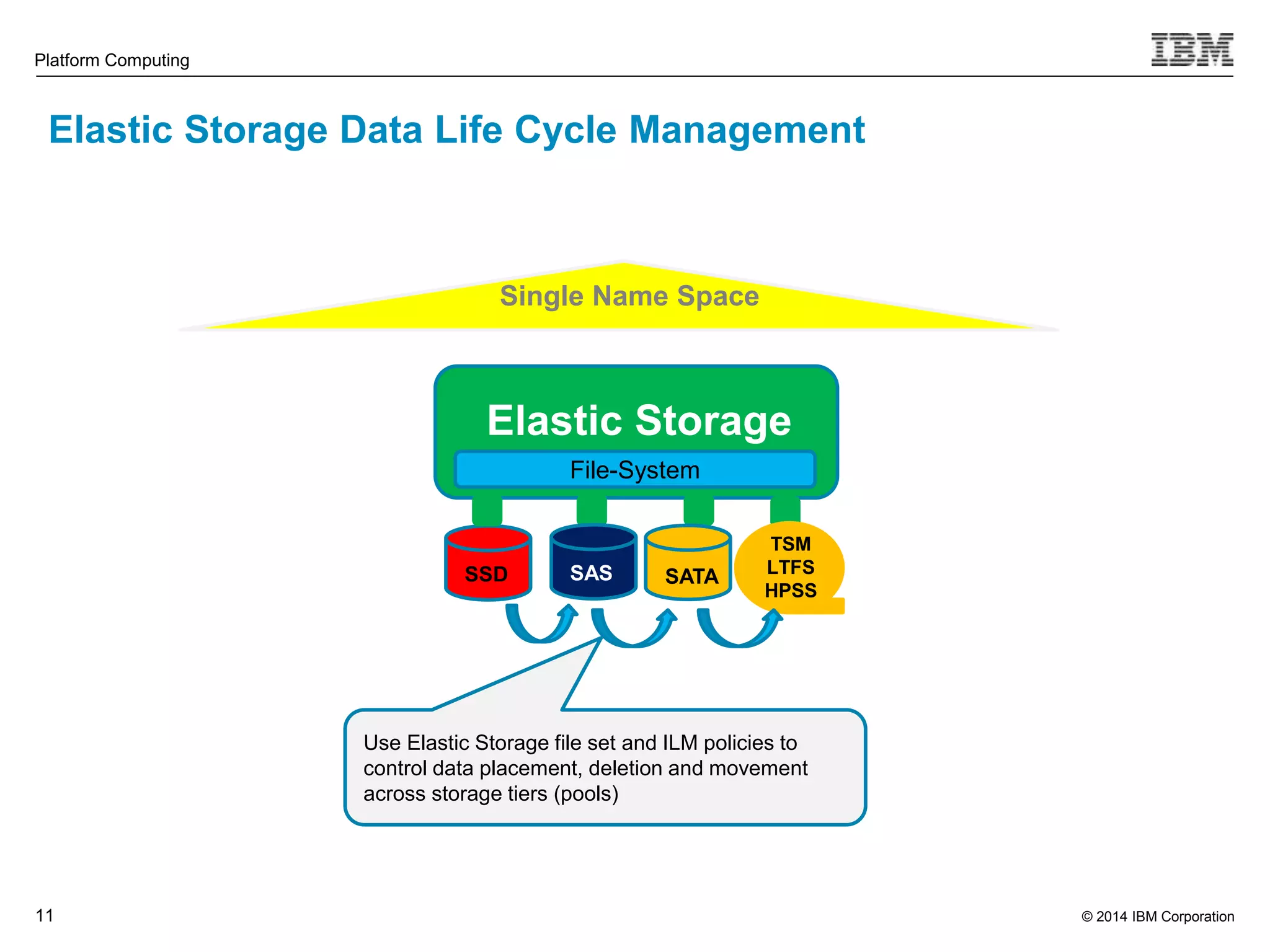
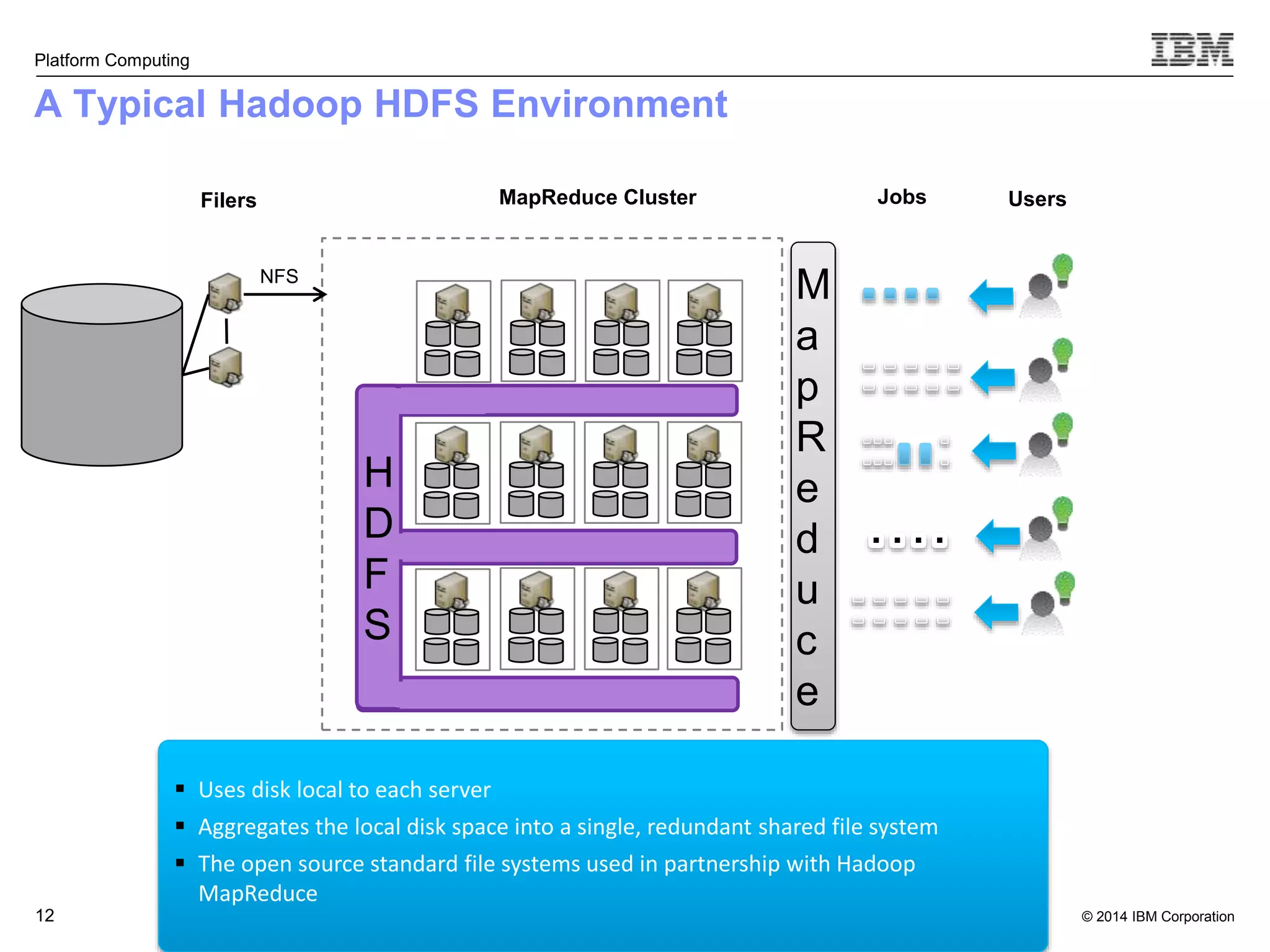
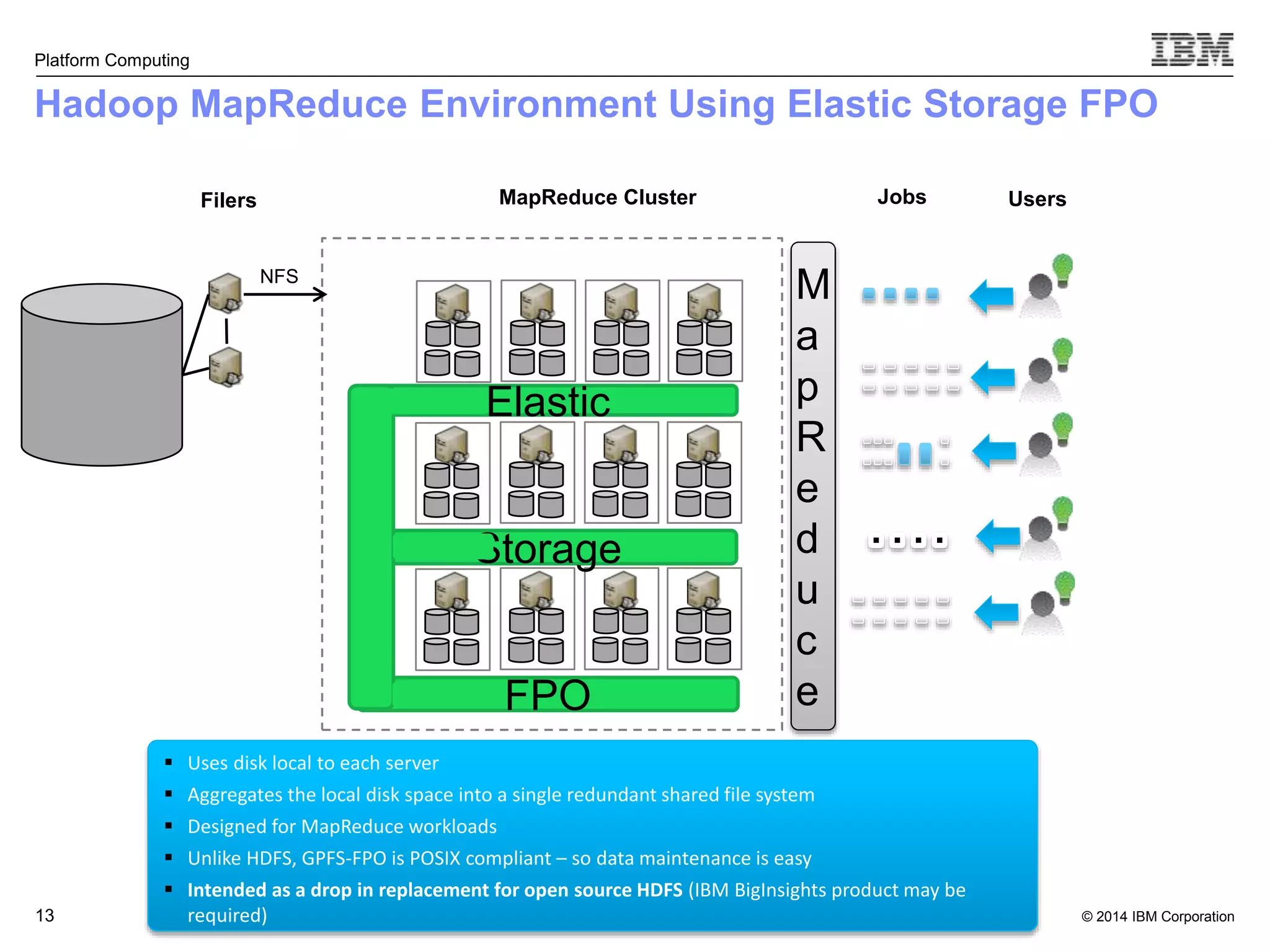
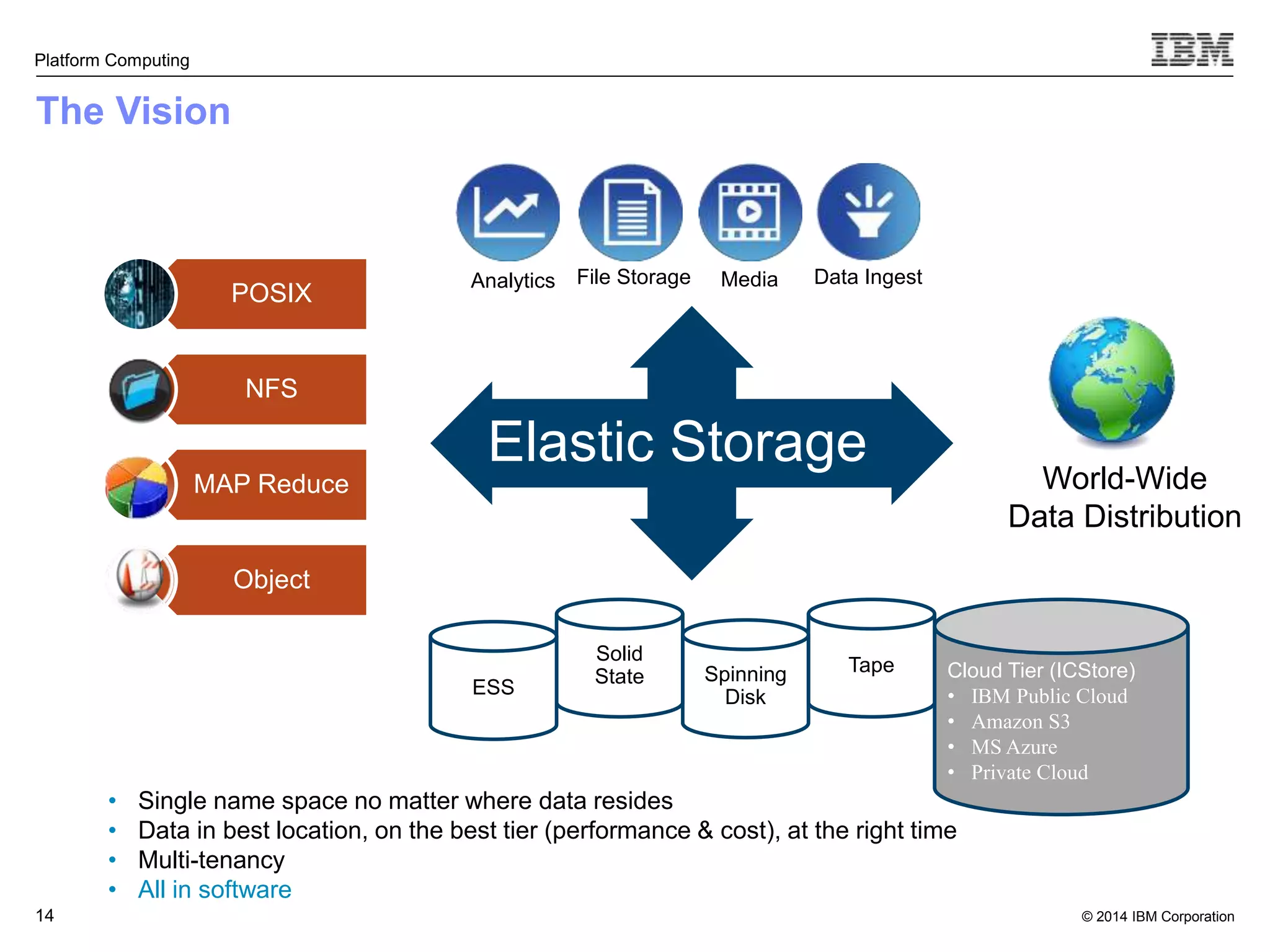
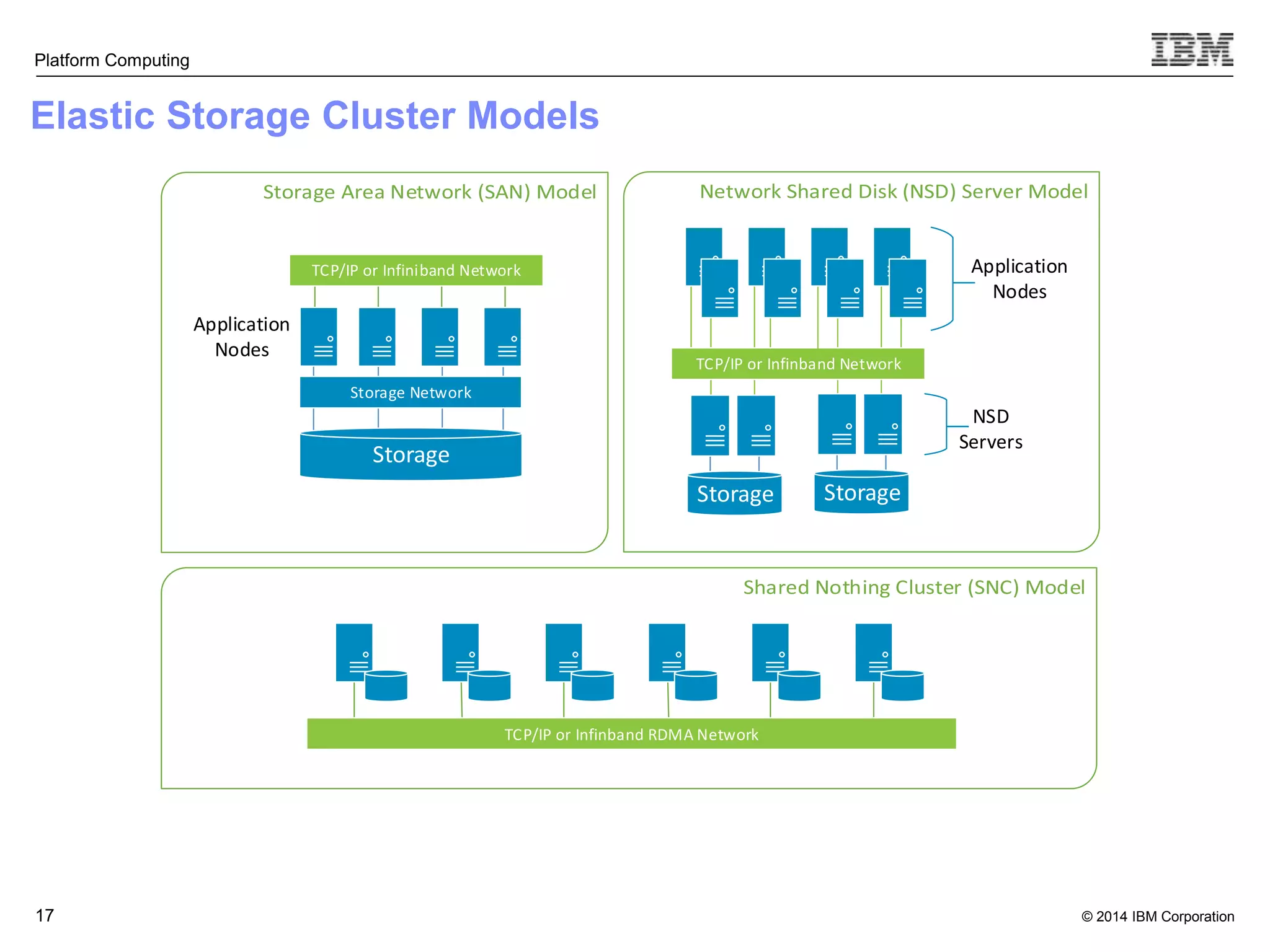
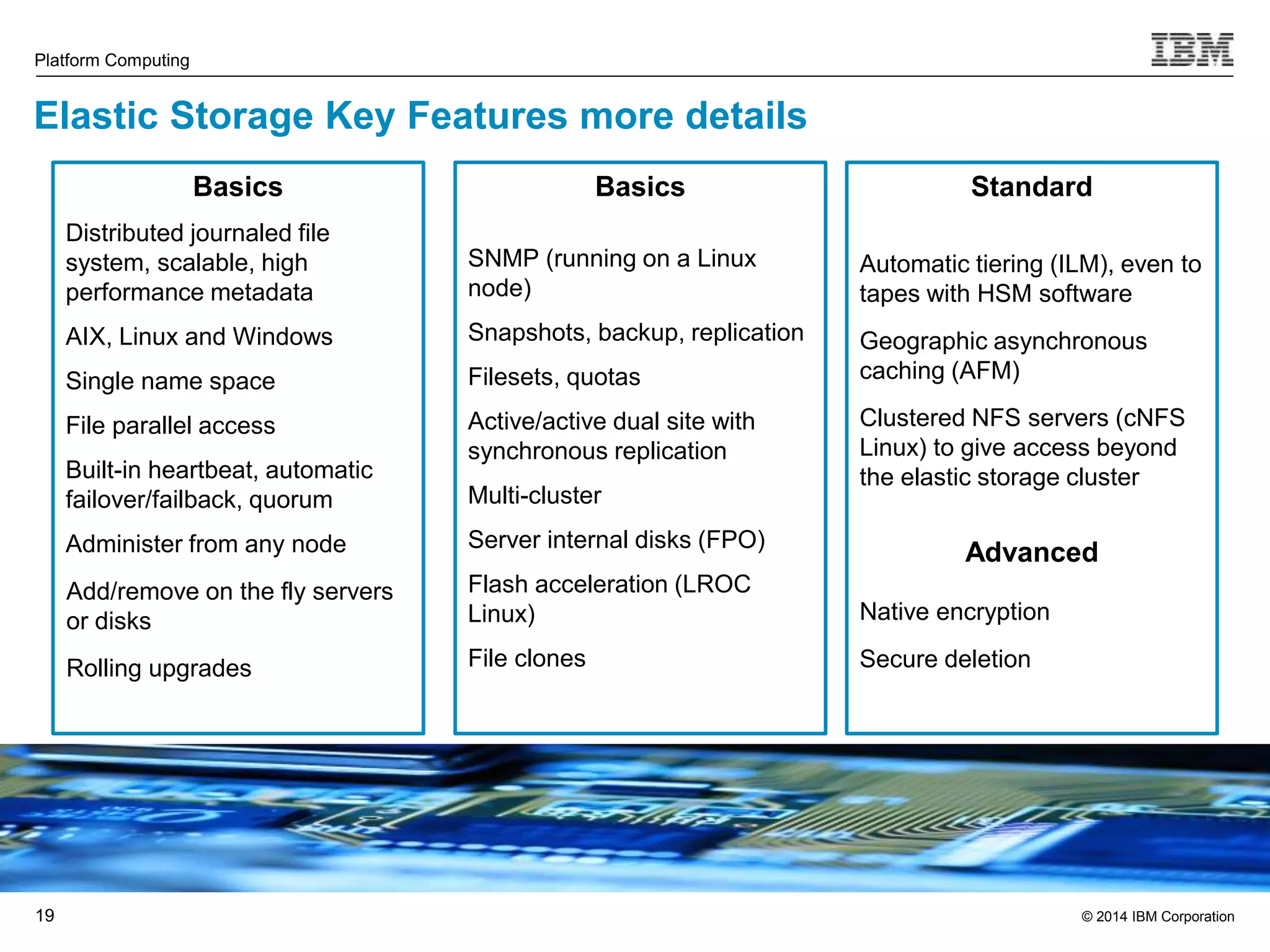
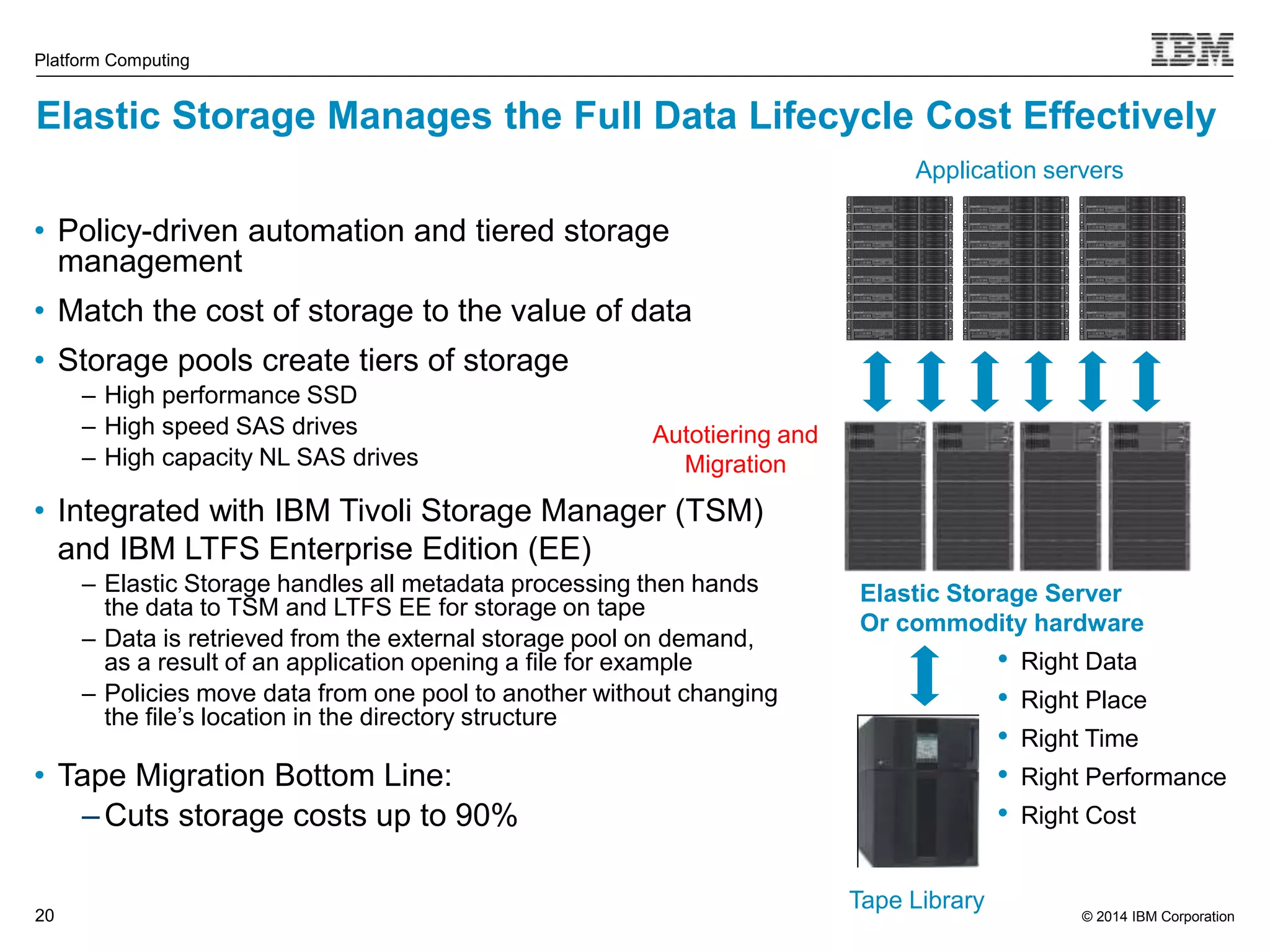
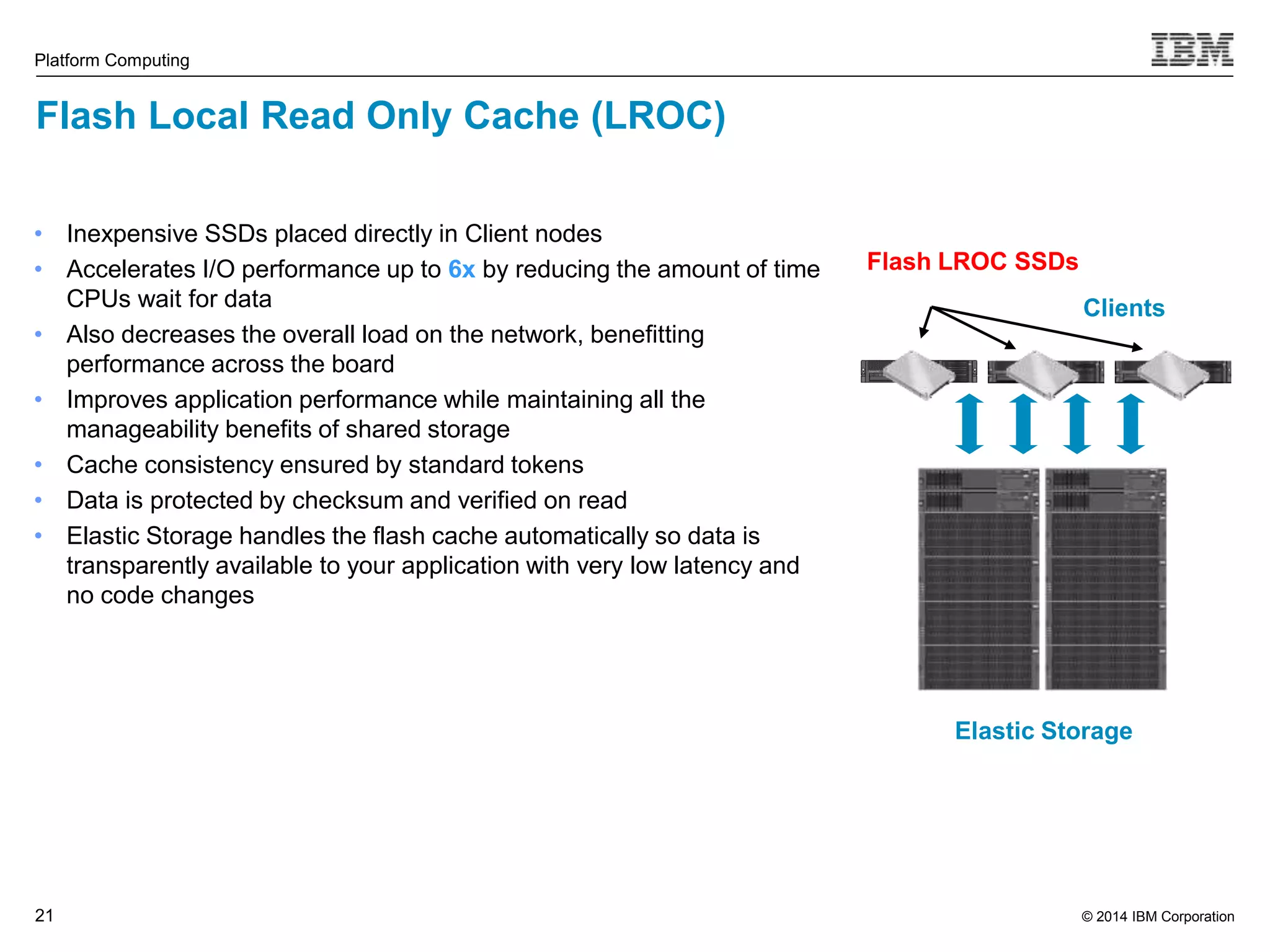
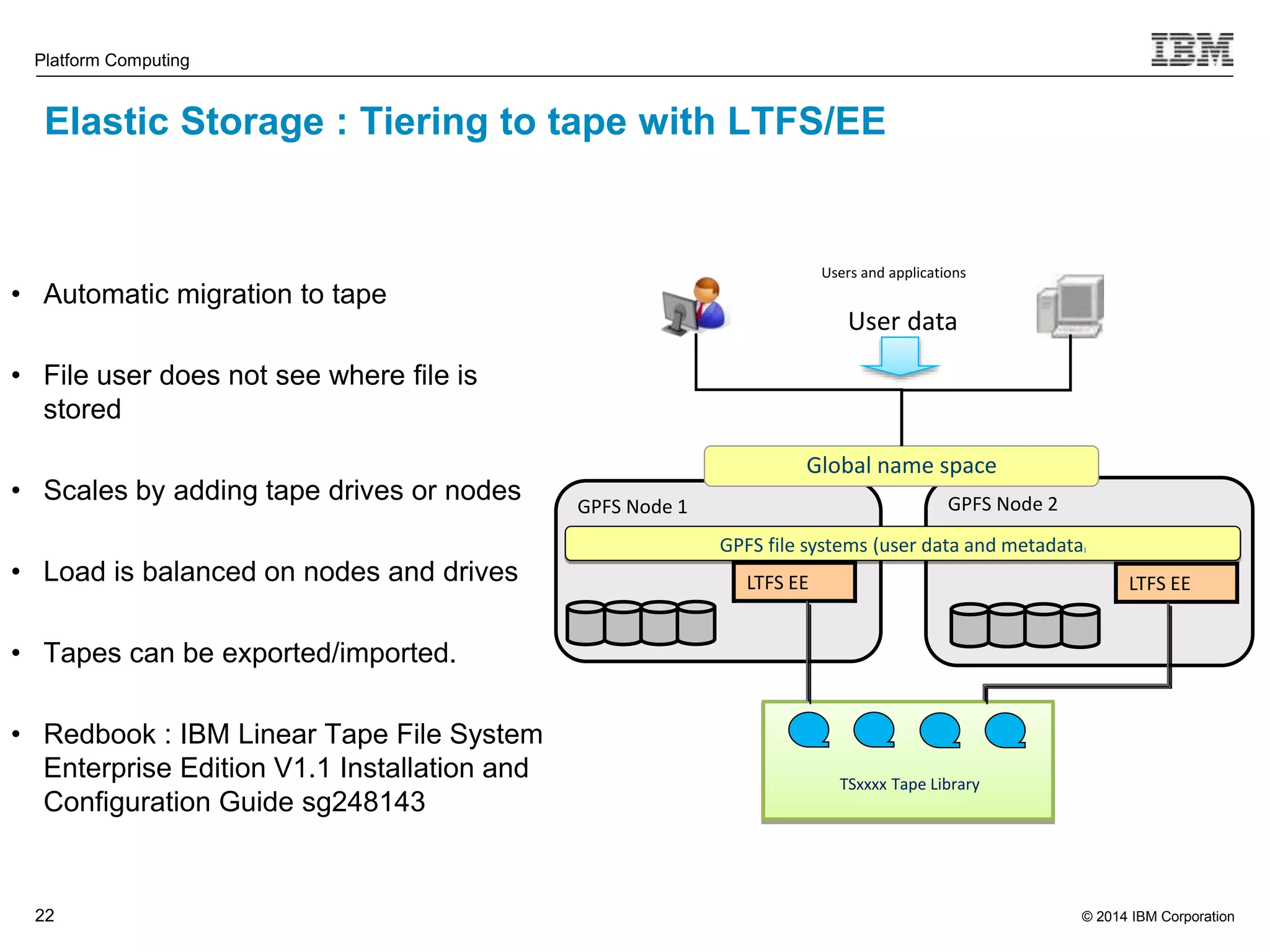
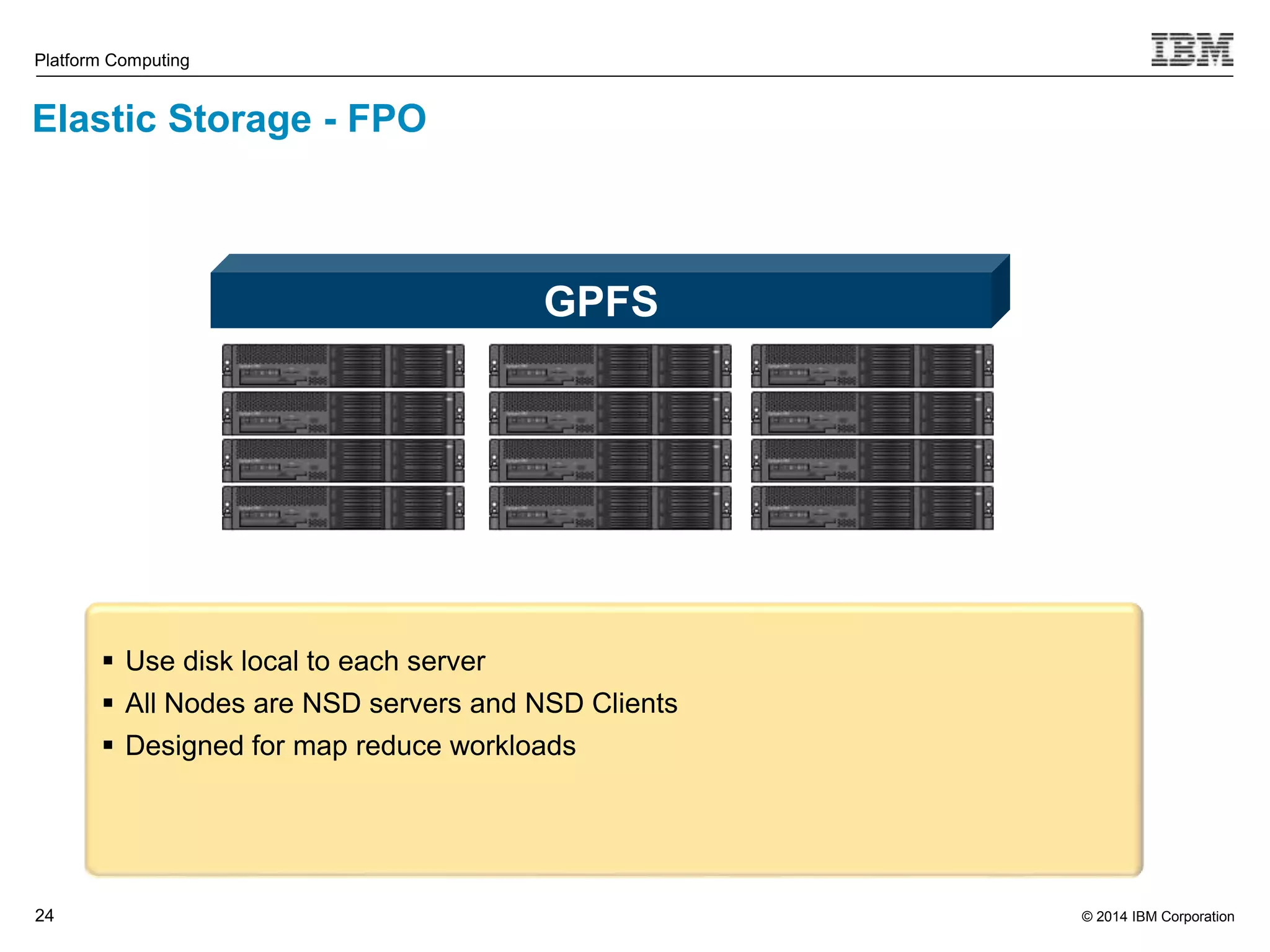
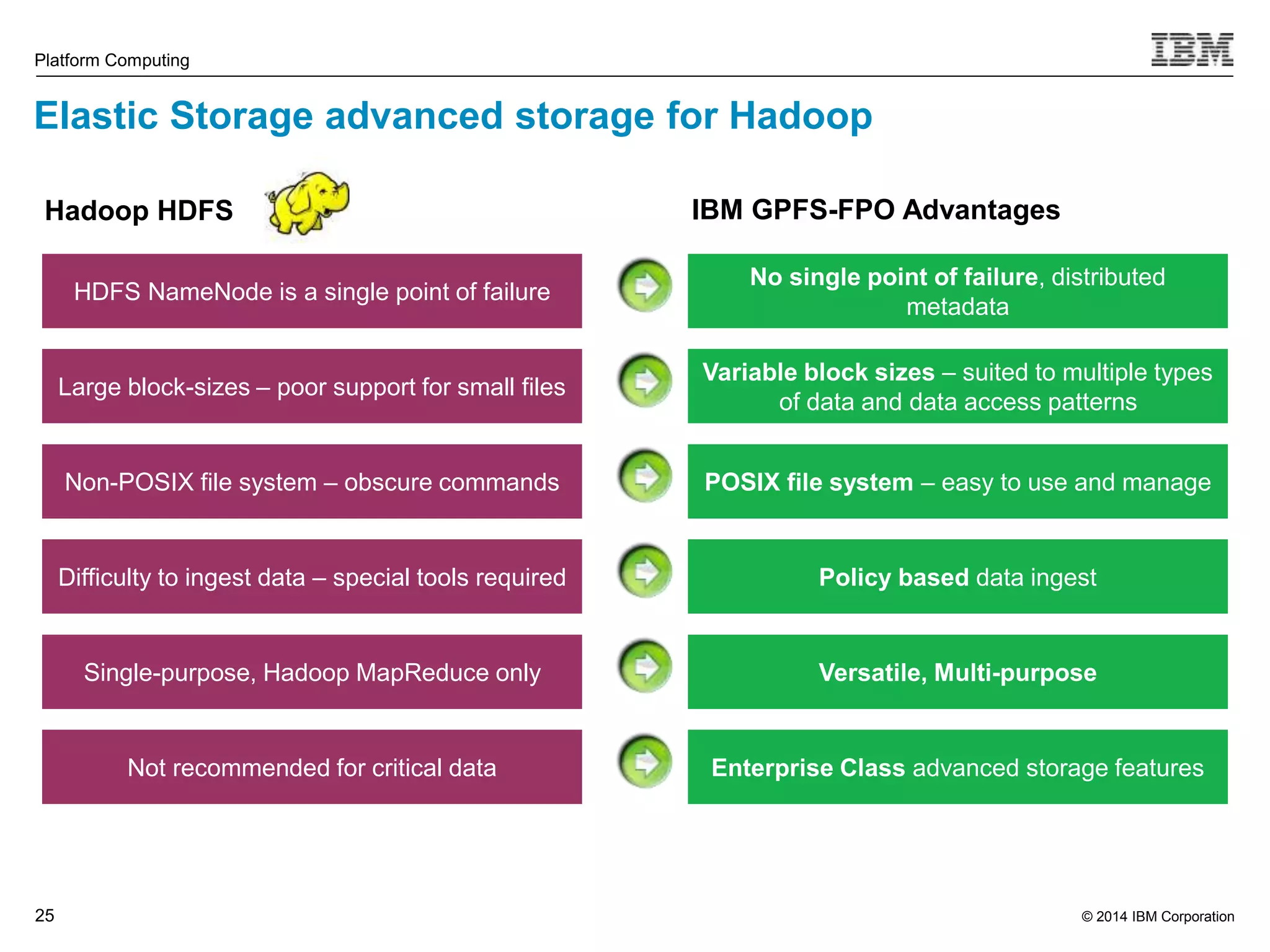
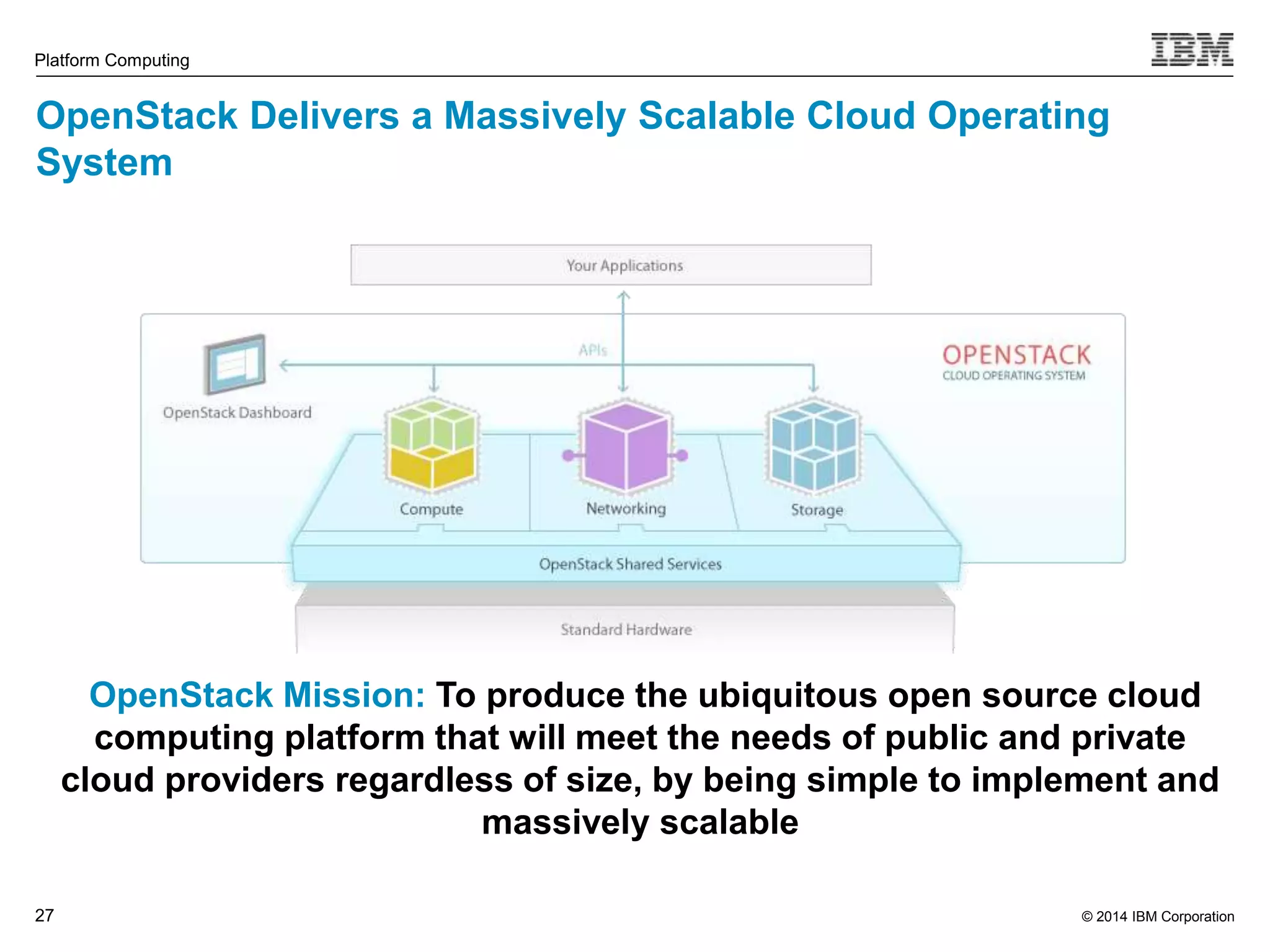
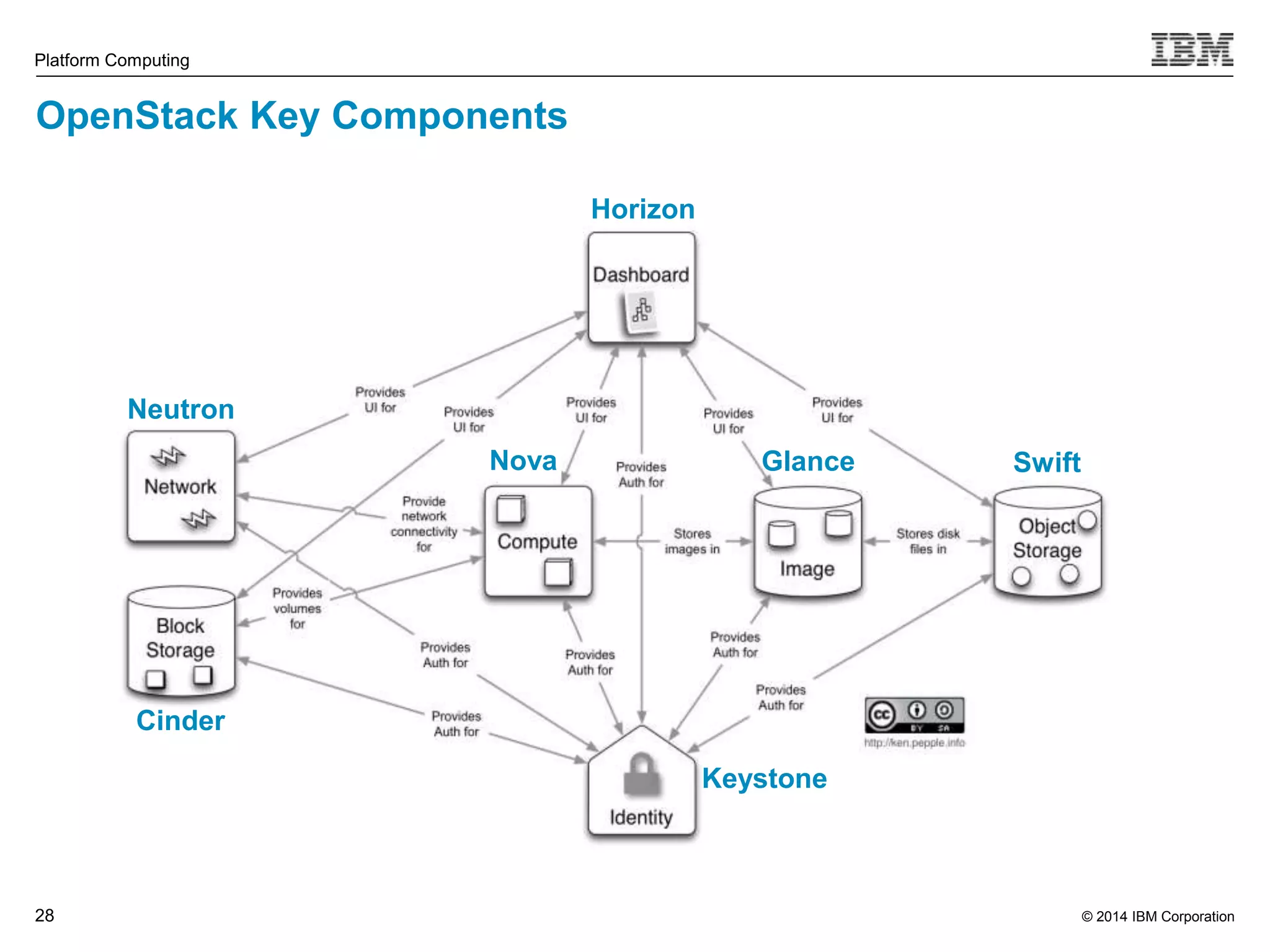
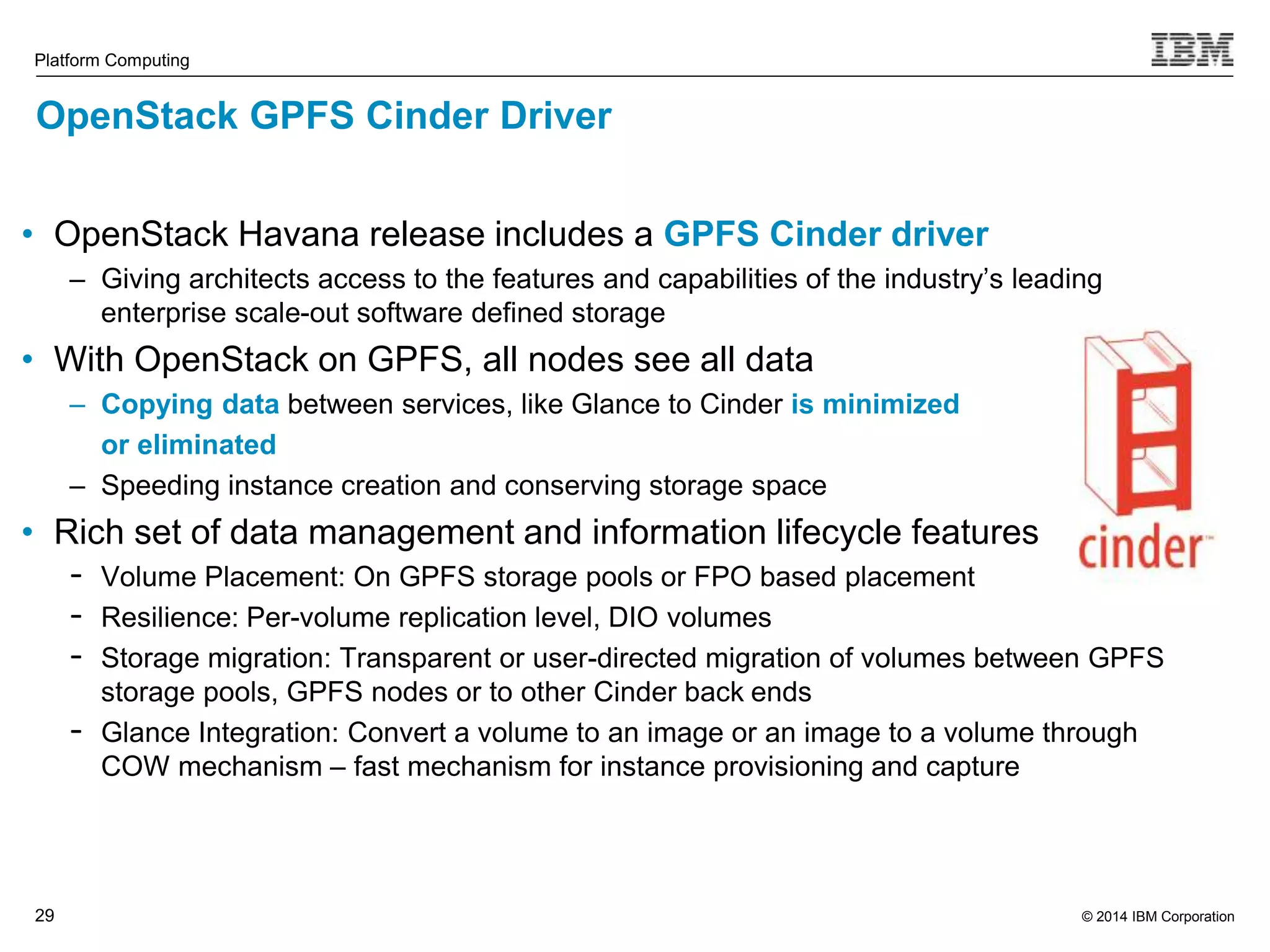
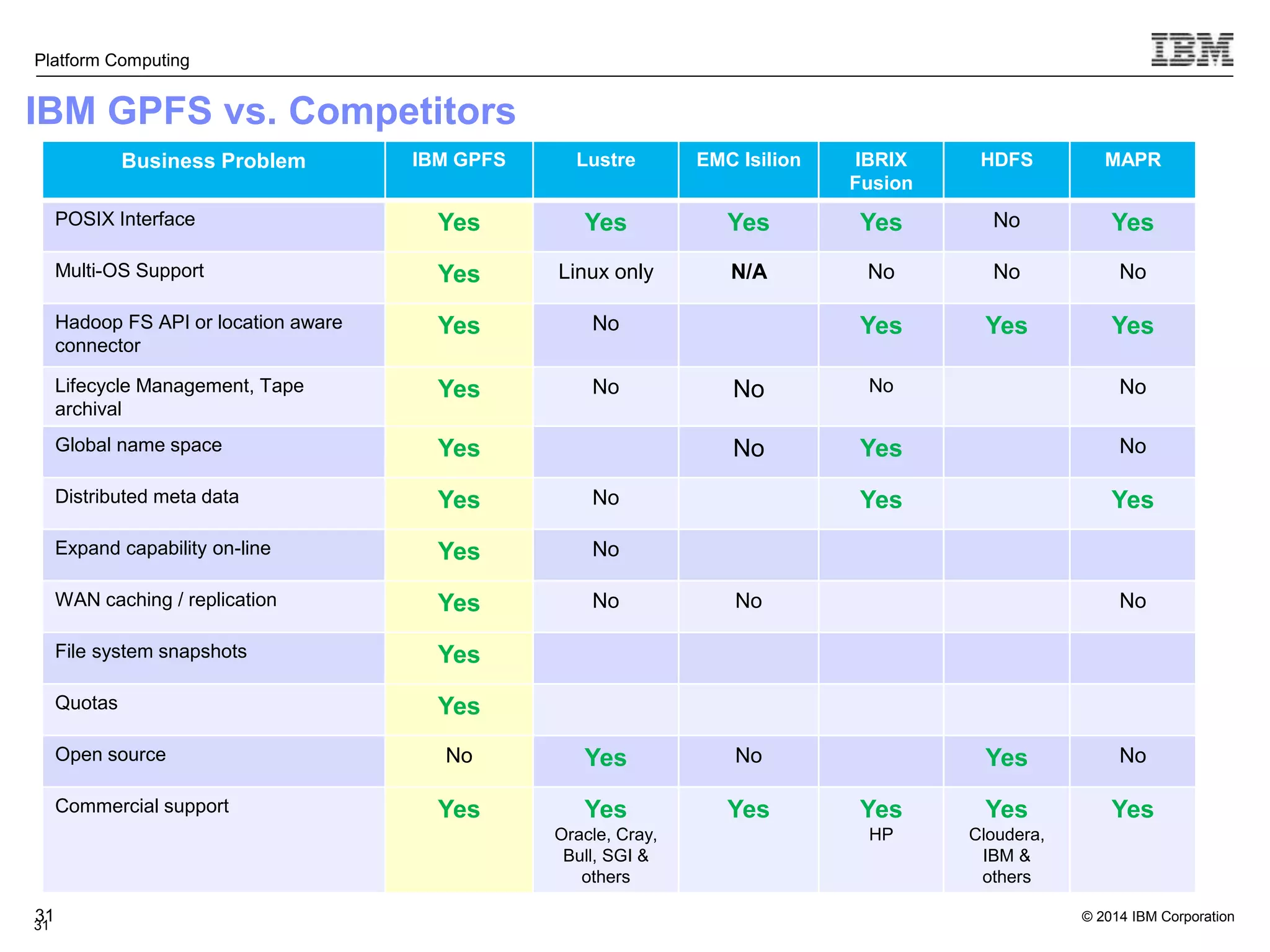
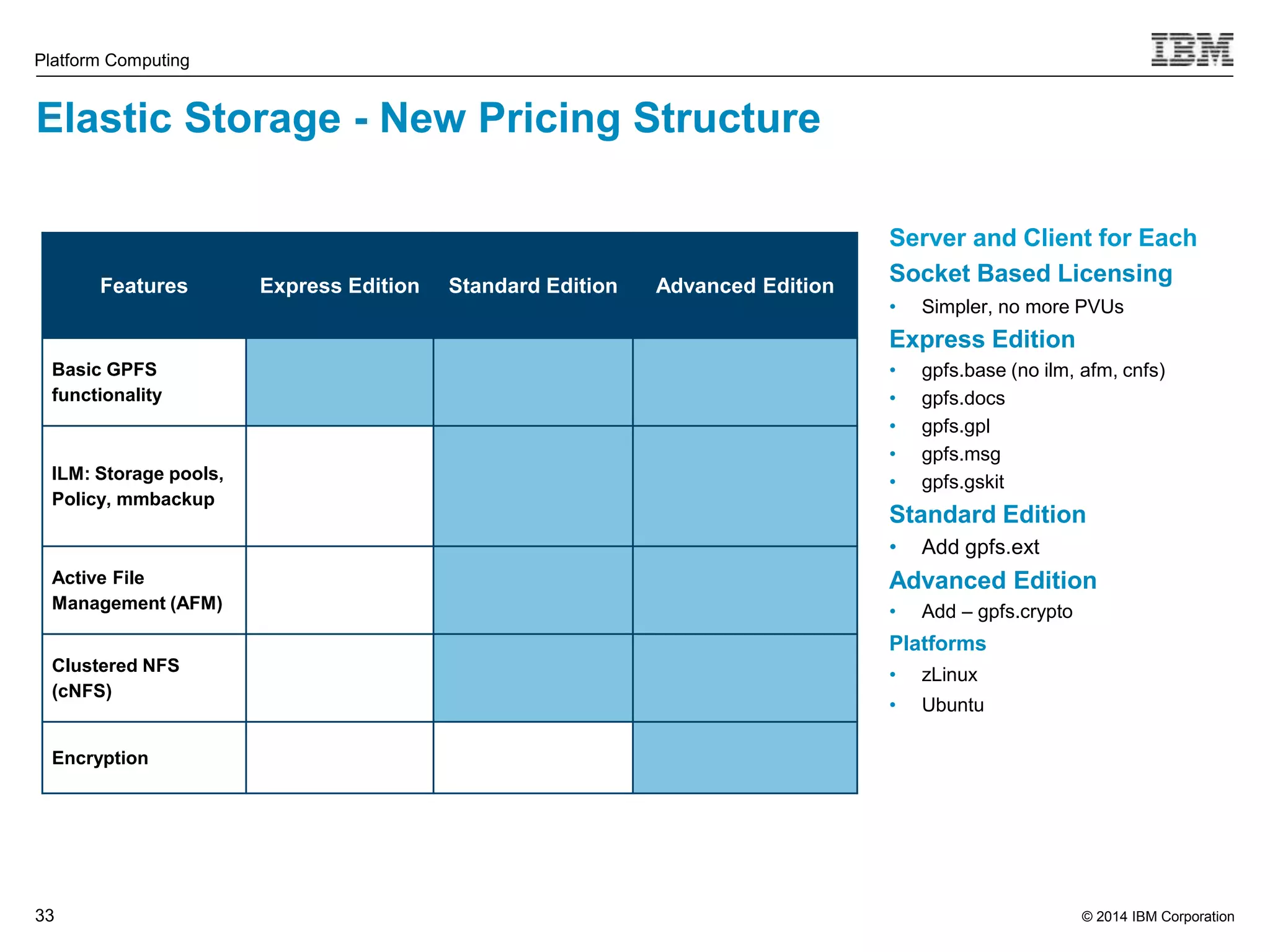
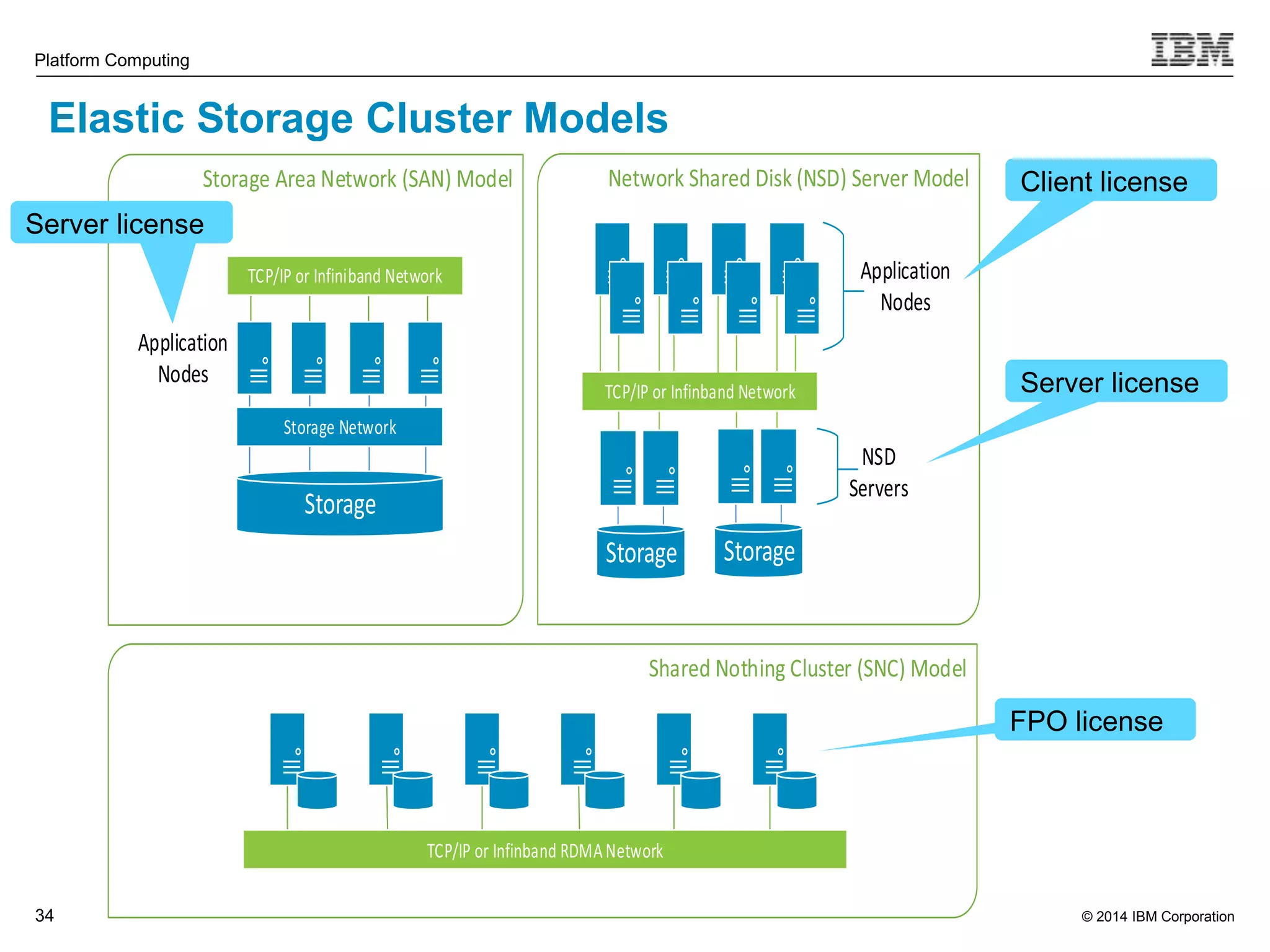
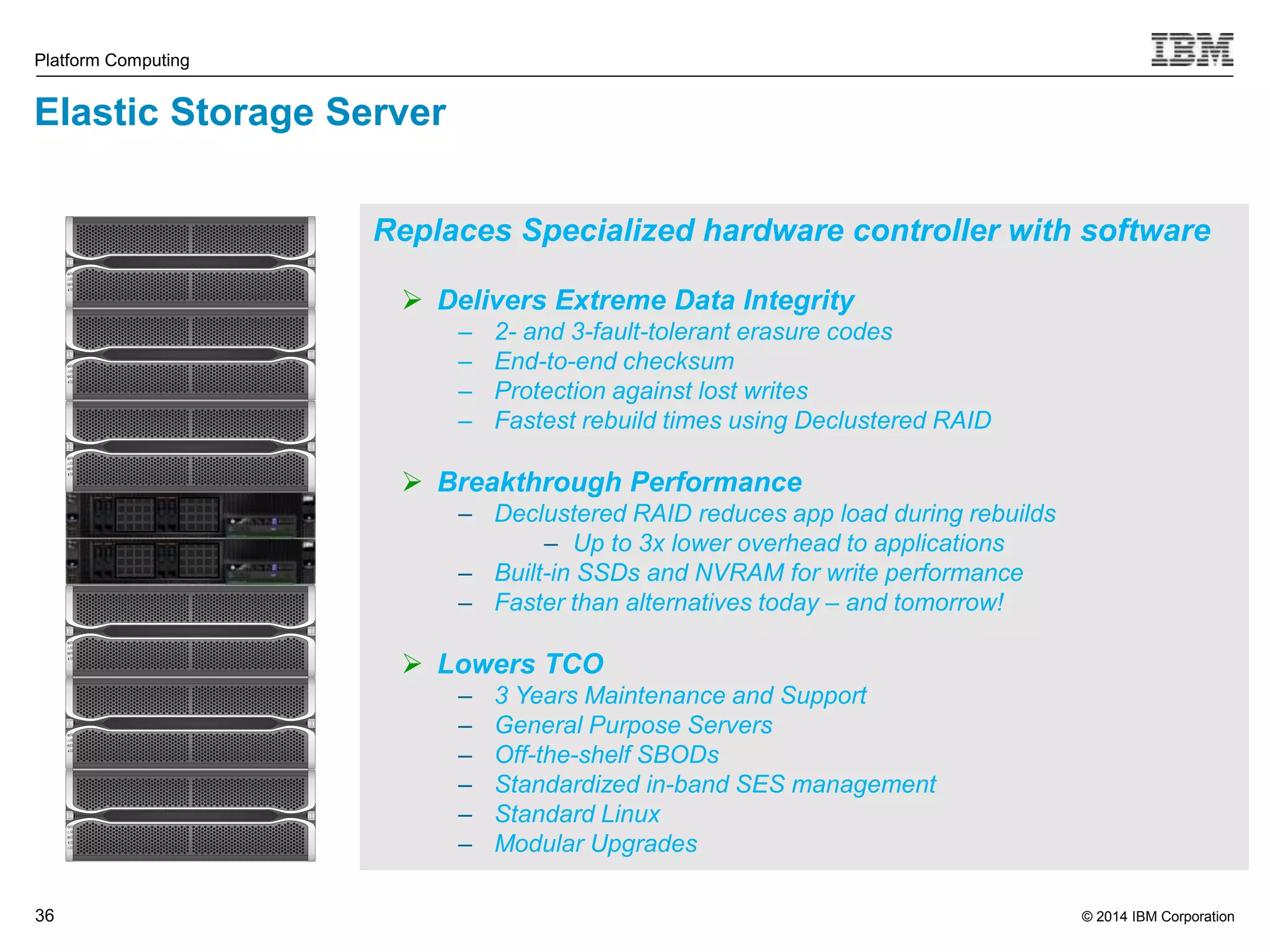
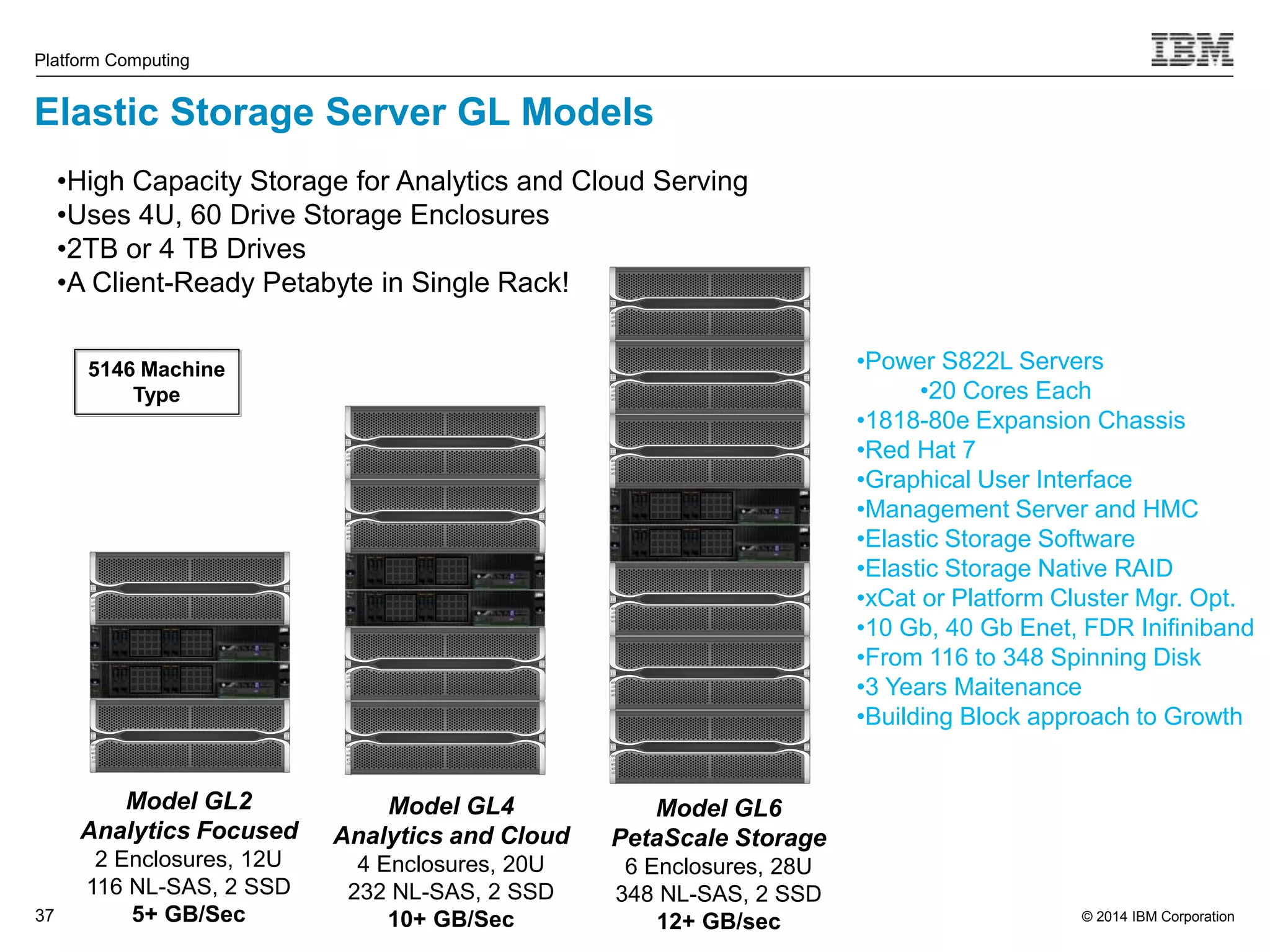
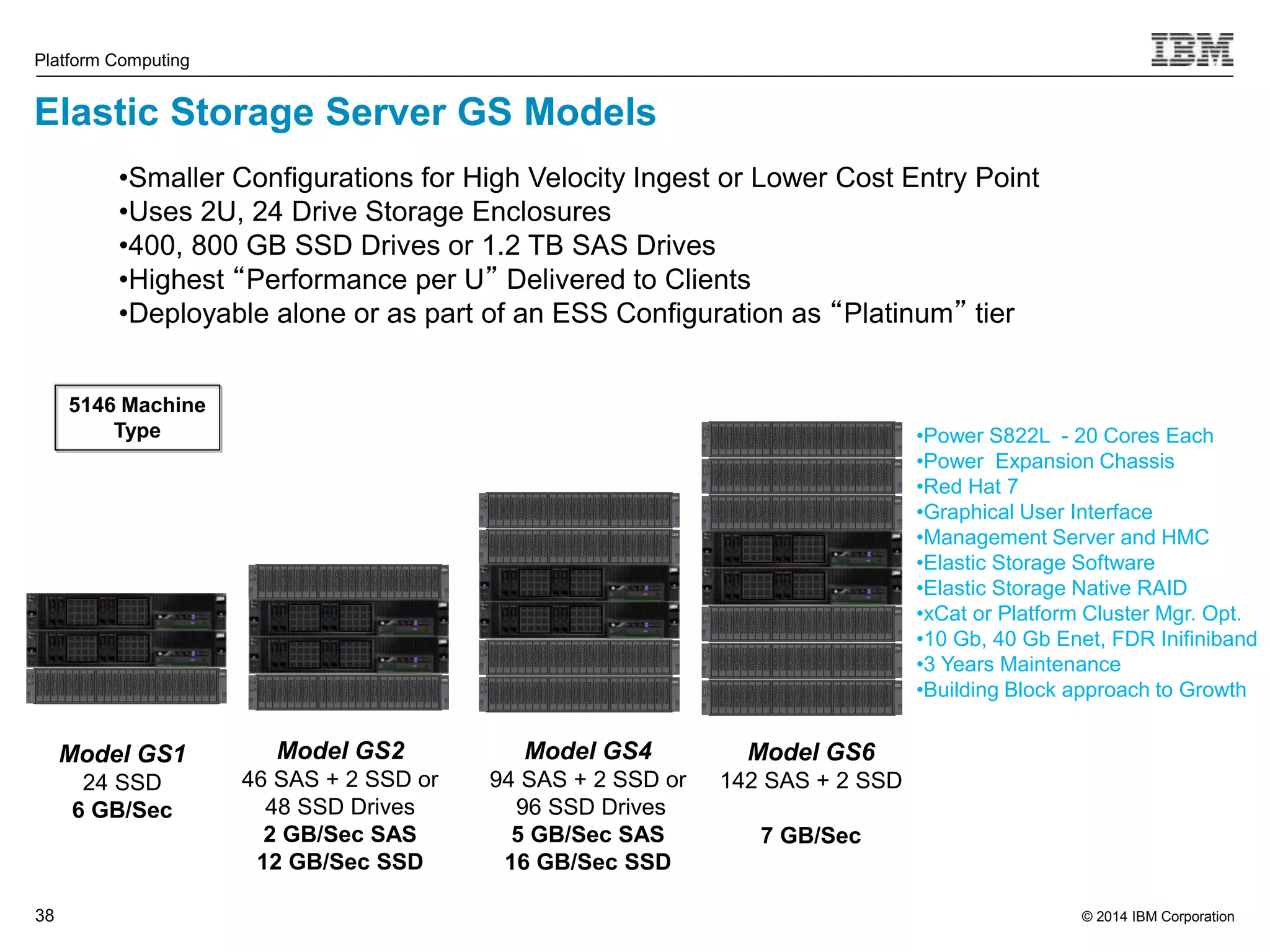
This document discusses IBM's Elastic Storage product. It provides an overview of Elastic Storage's key features such as extreme scalability, high performance, support for various operating systems and hardware, data lifecycle management capabilities, integration with Hadoop, and editions/pricing. It also compares Elastic Storage to alternative storage solutions and discusses how Elastic Storage can be used to build private and hybrid clouds with OpenStack.