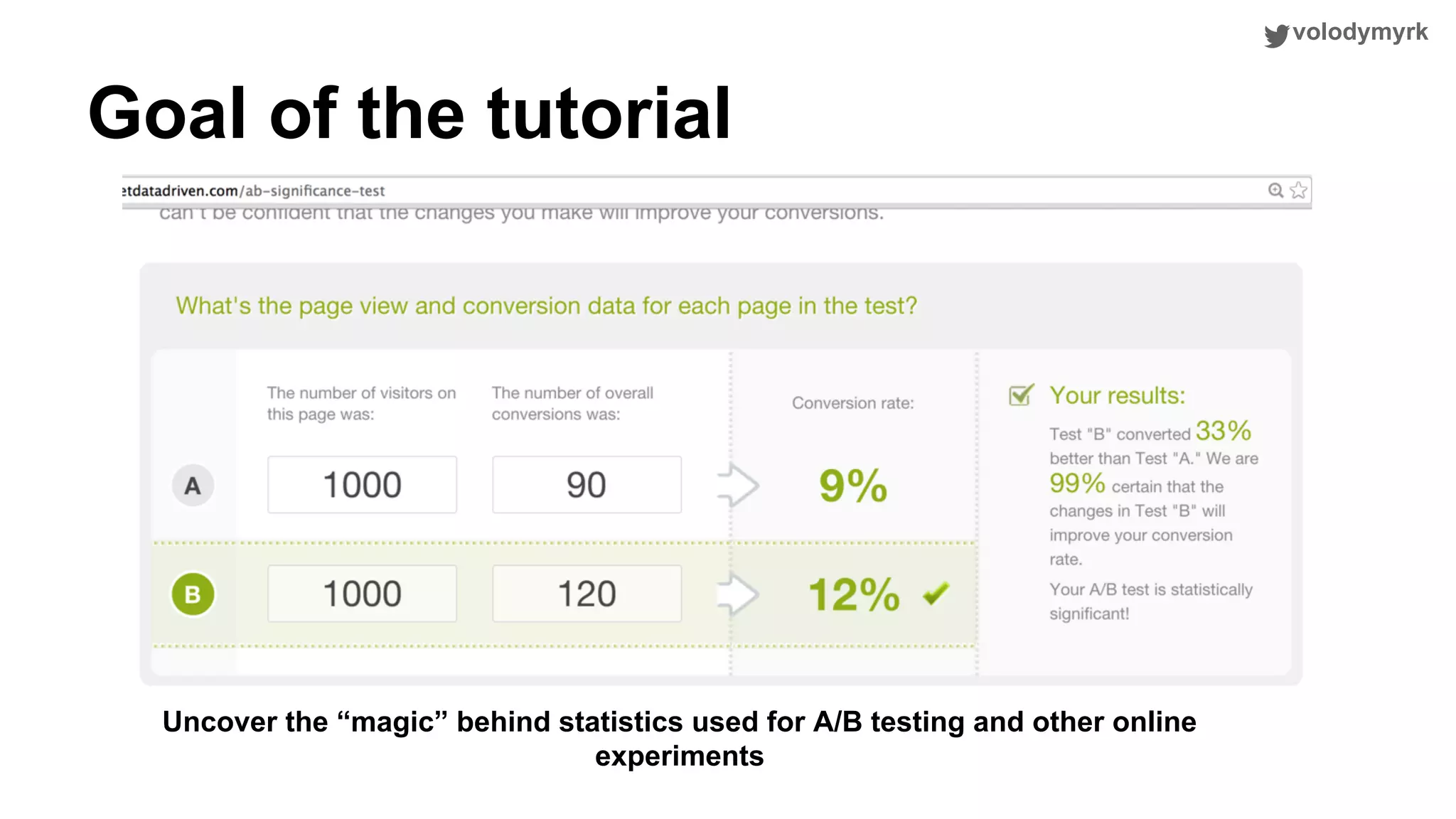
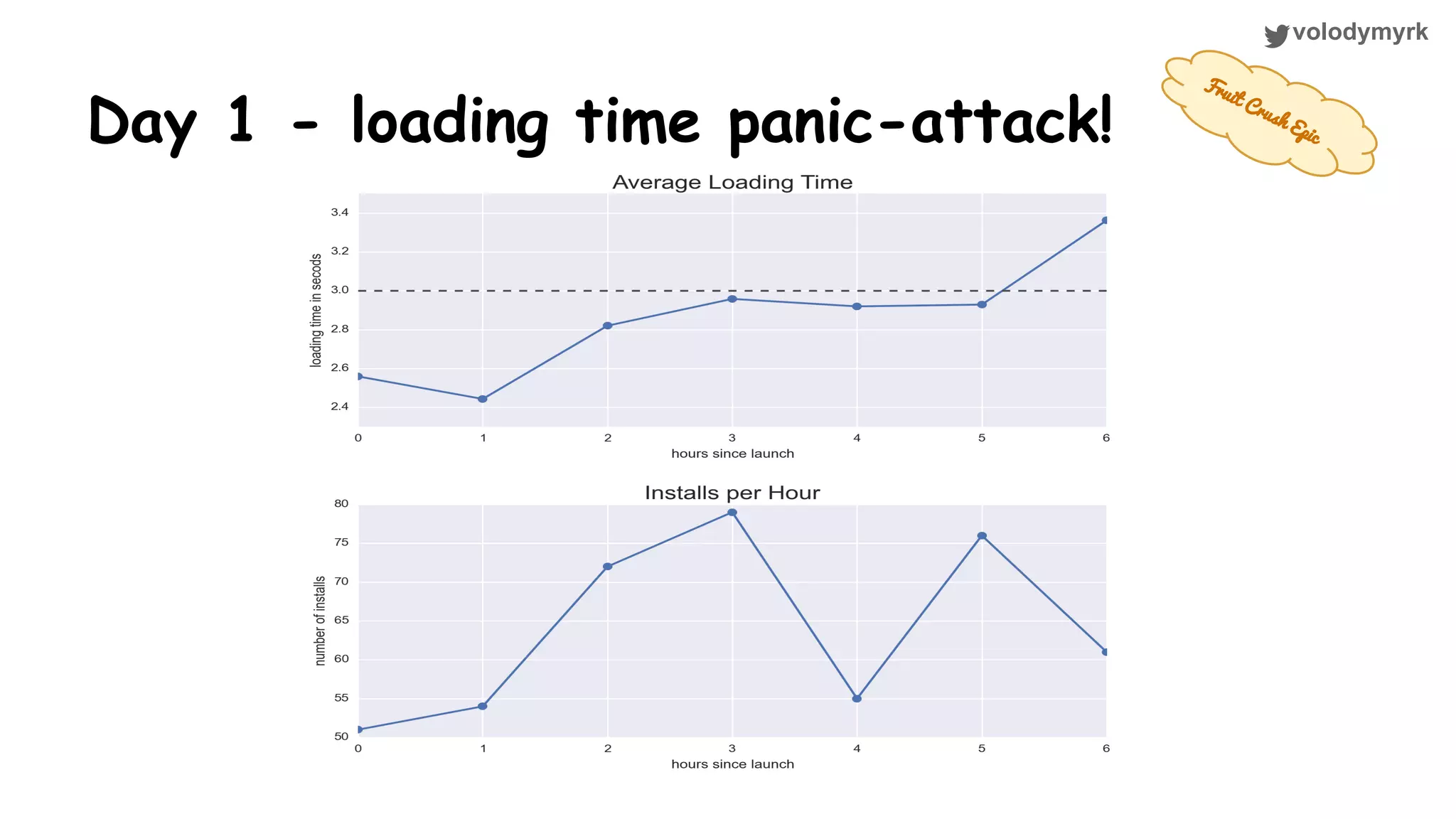
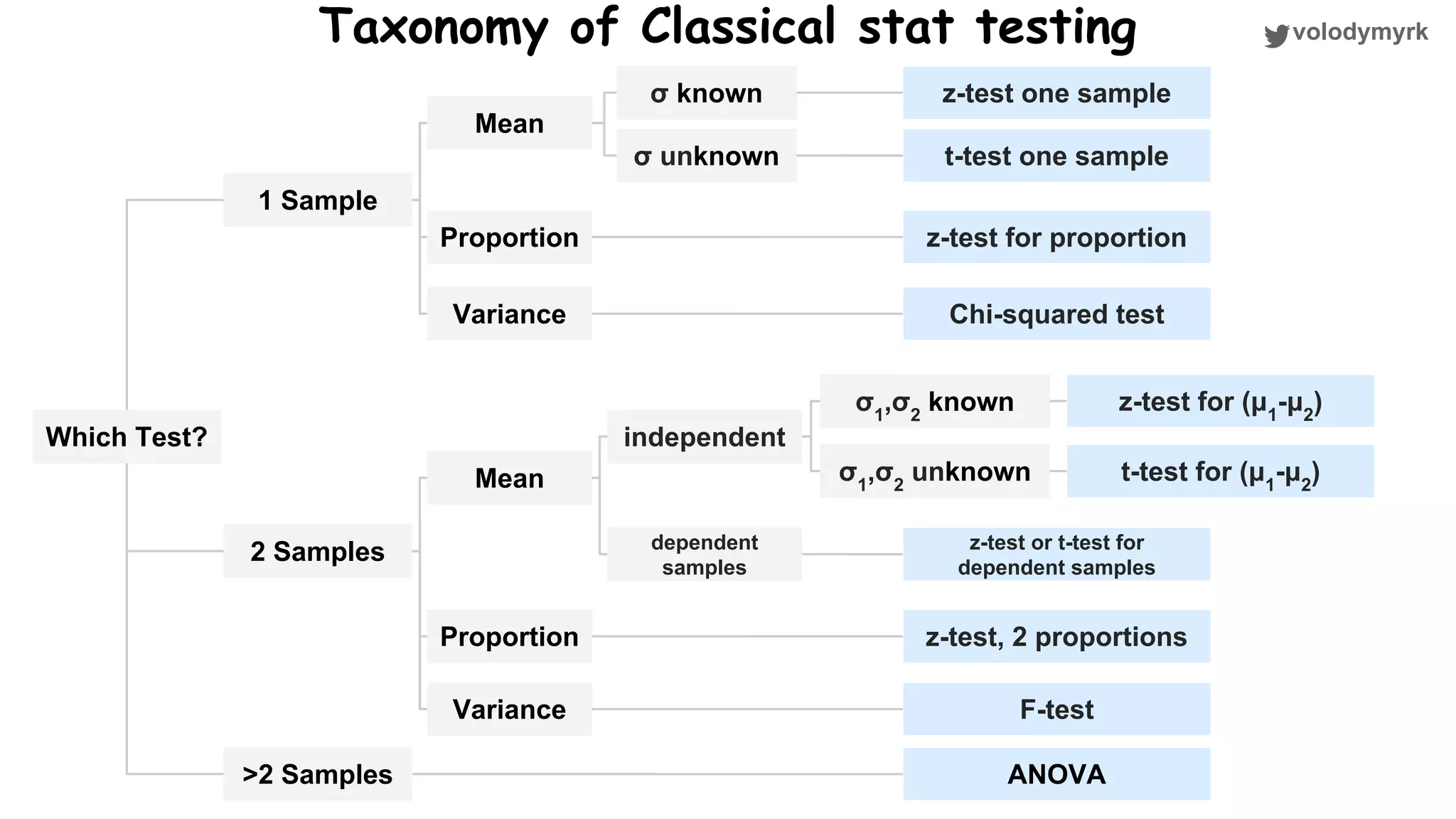
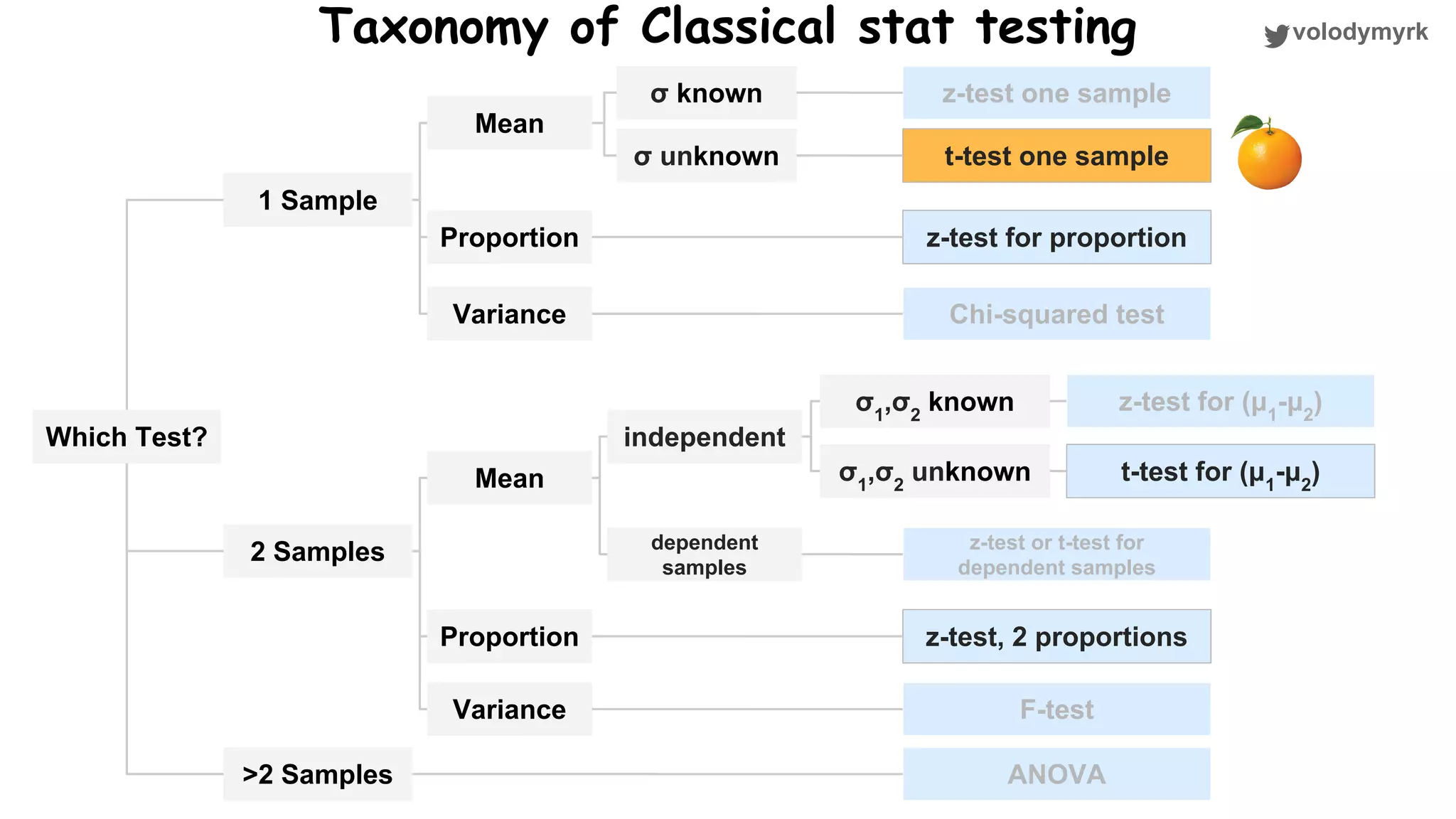
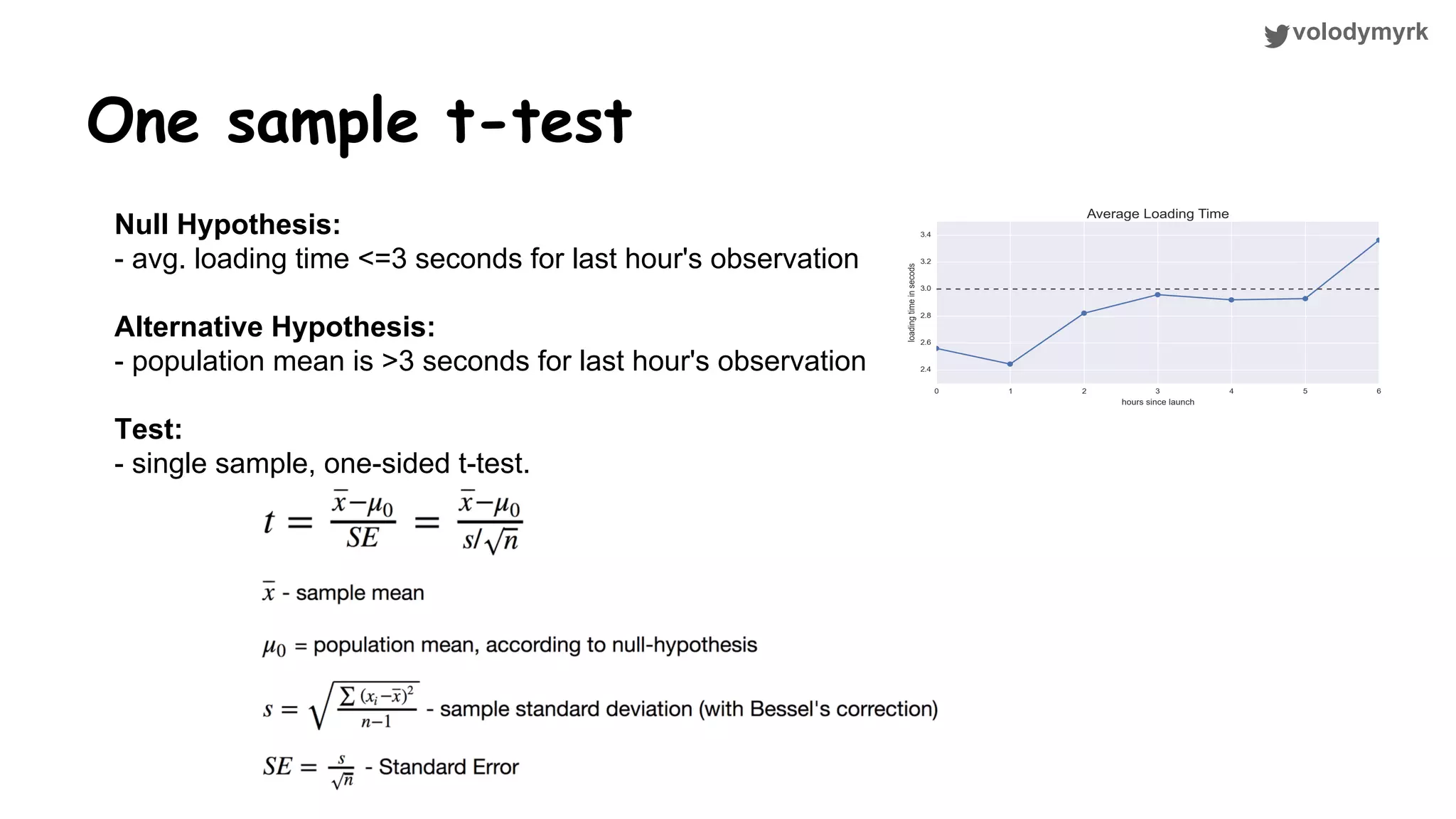
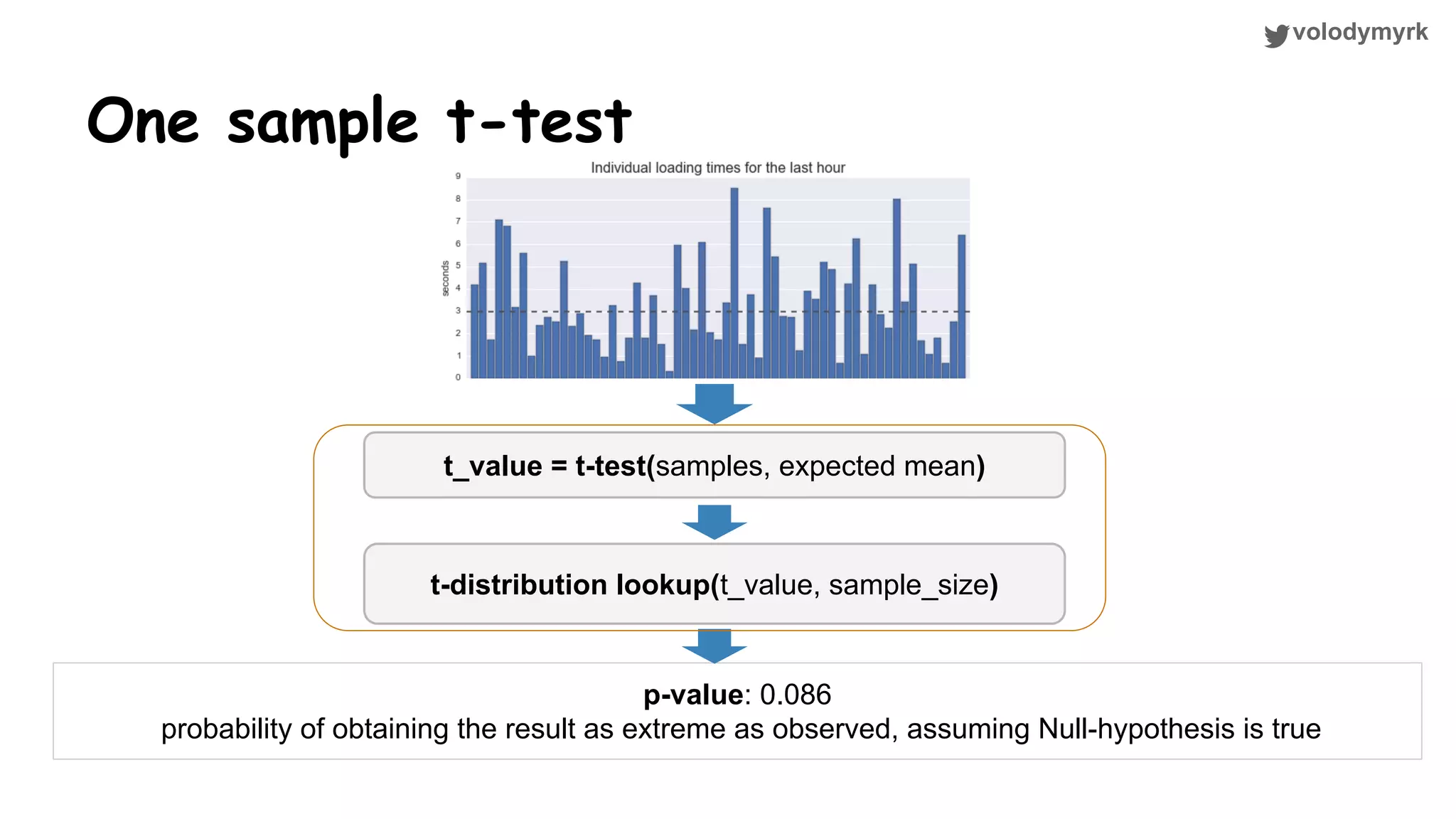
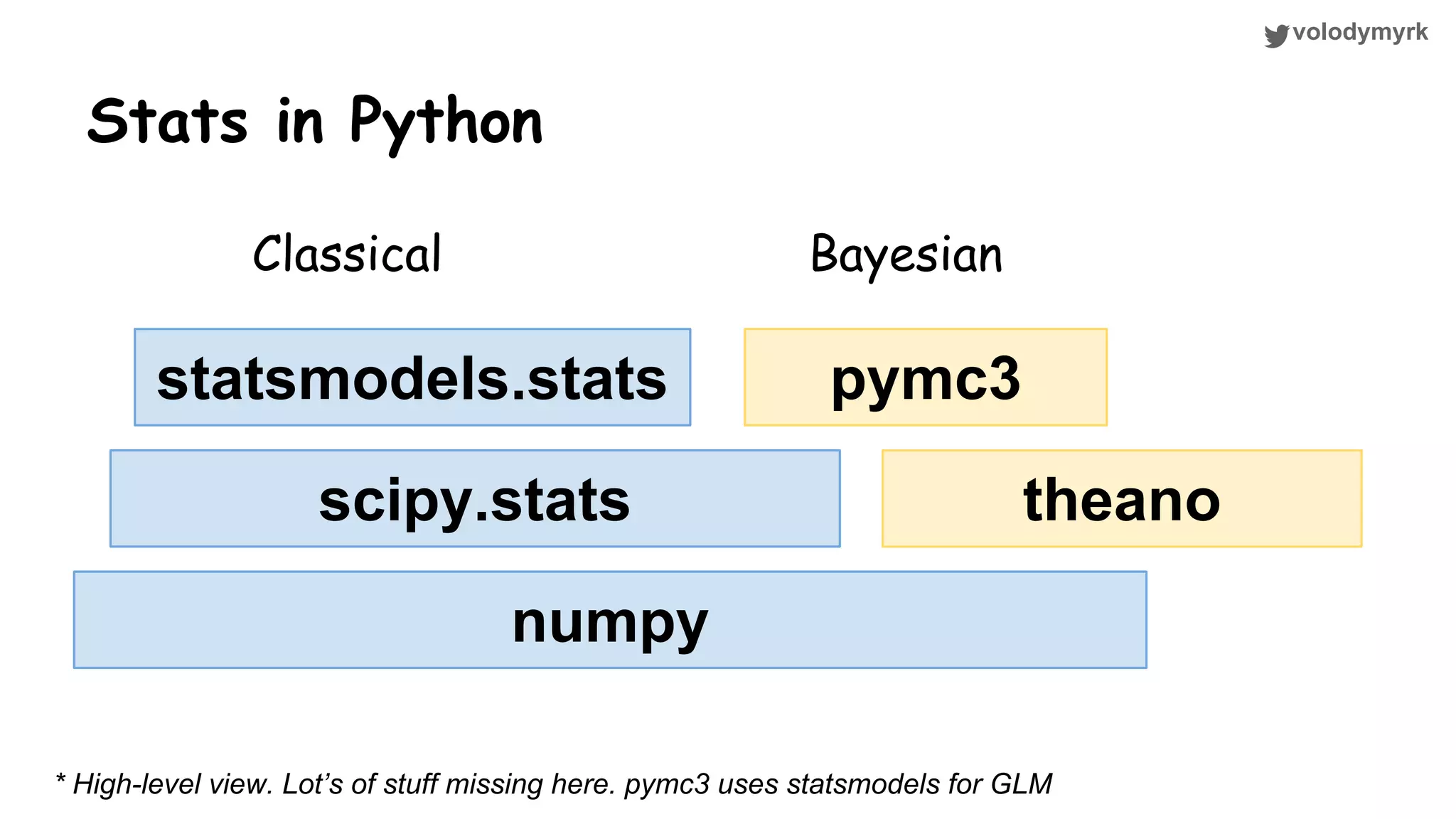
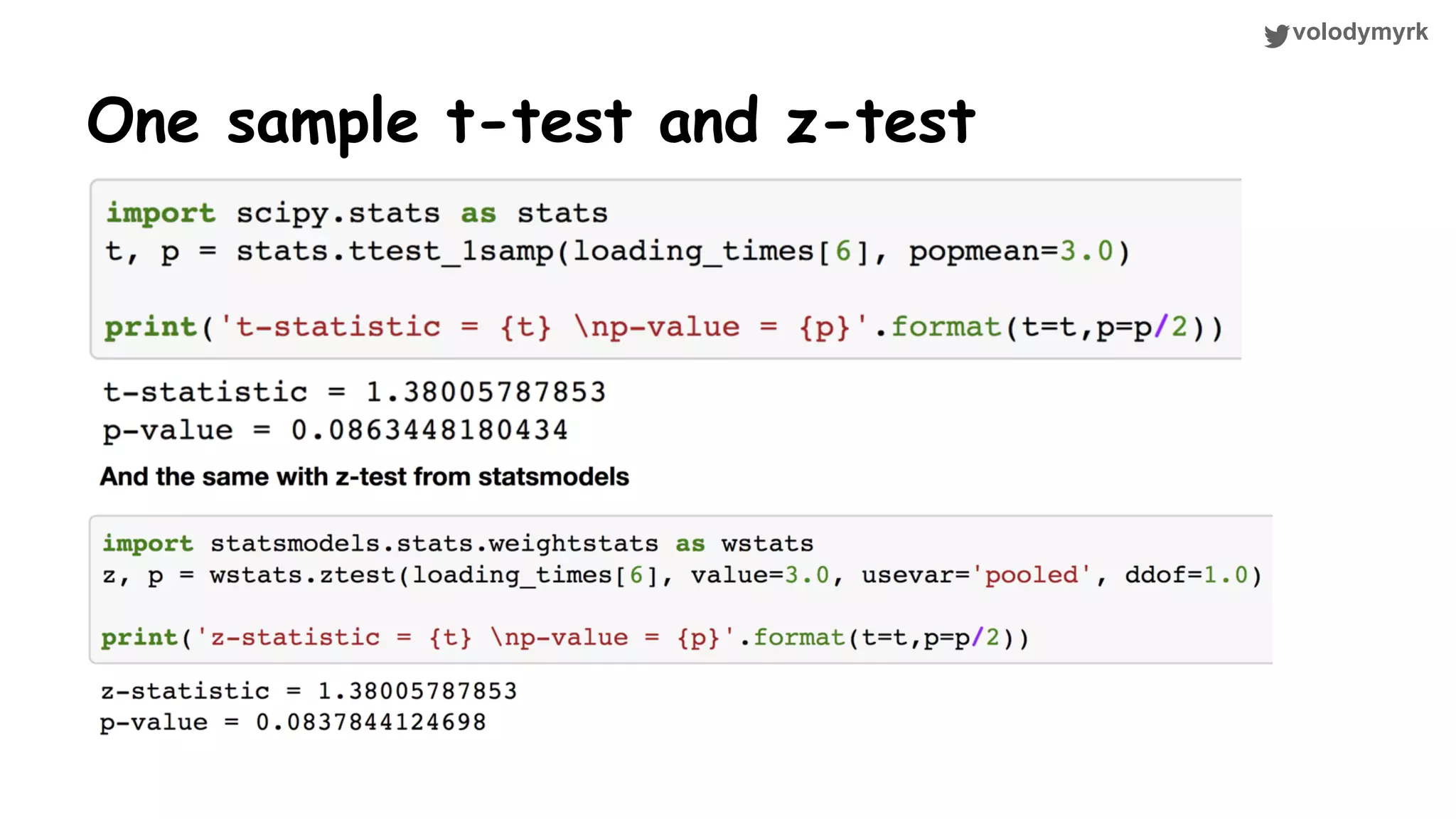
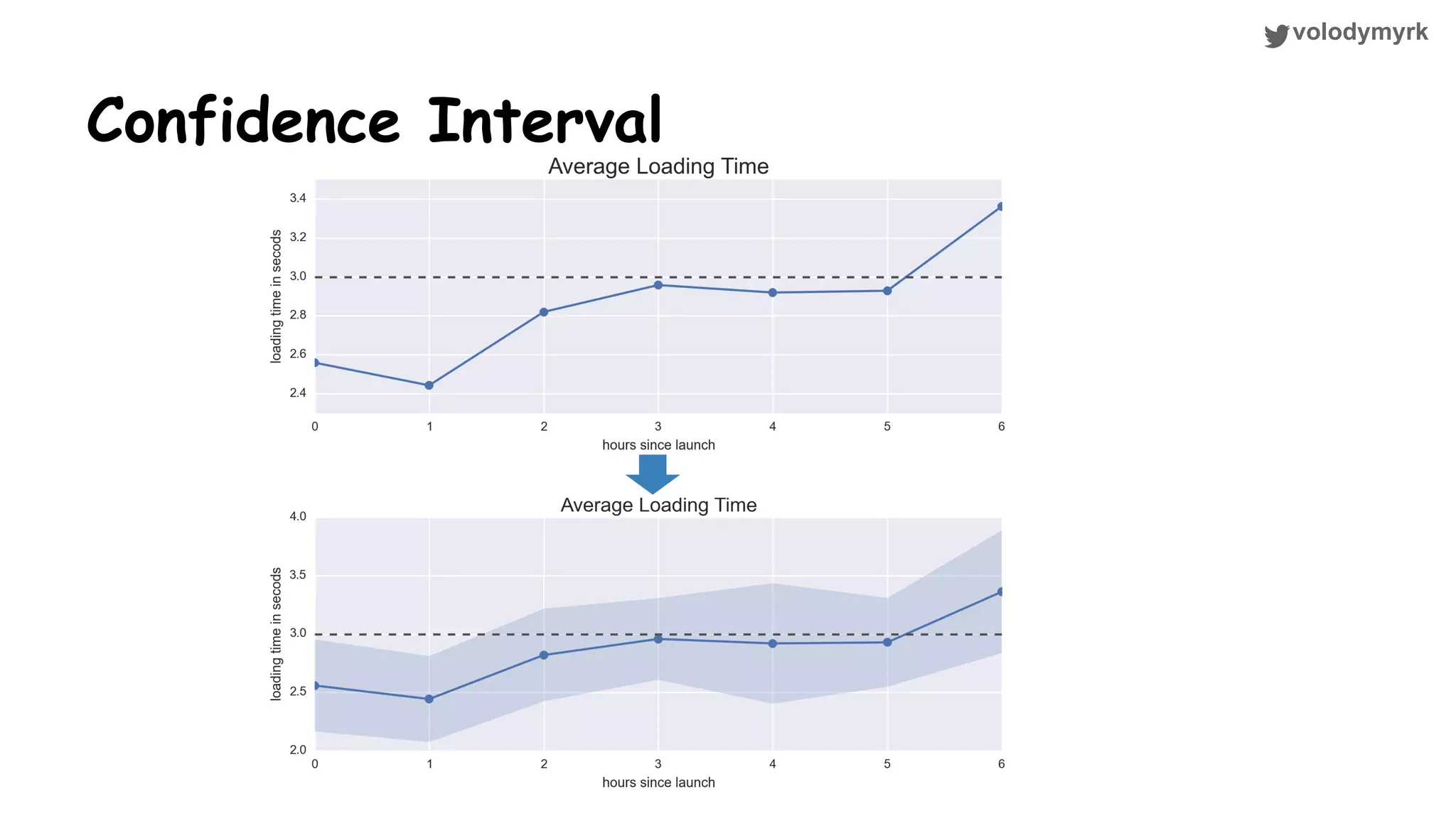
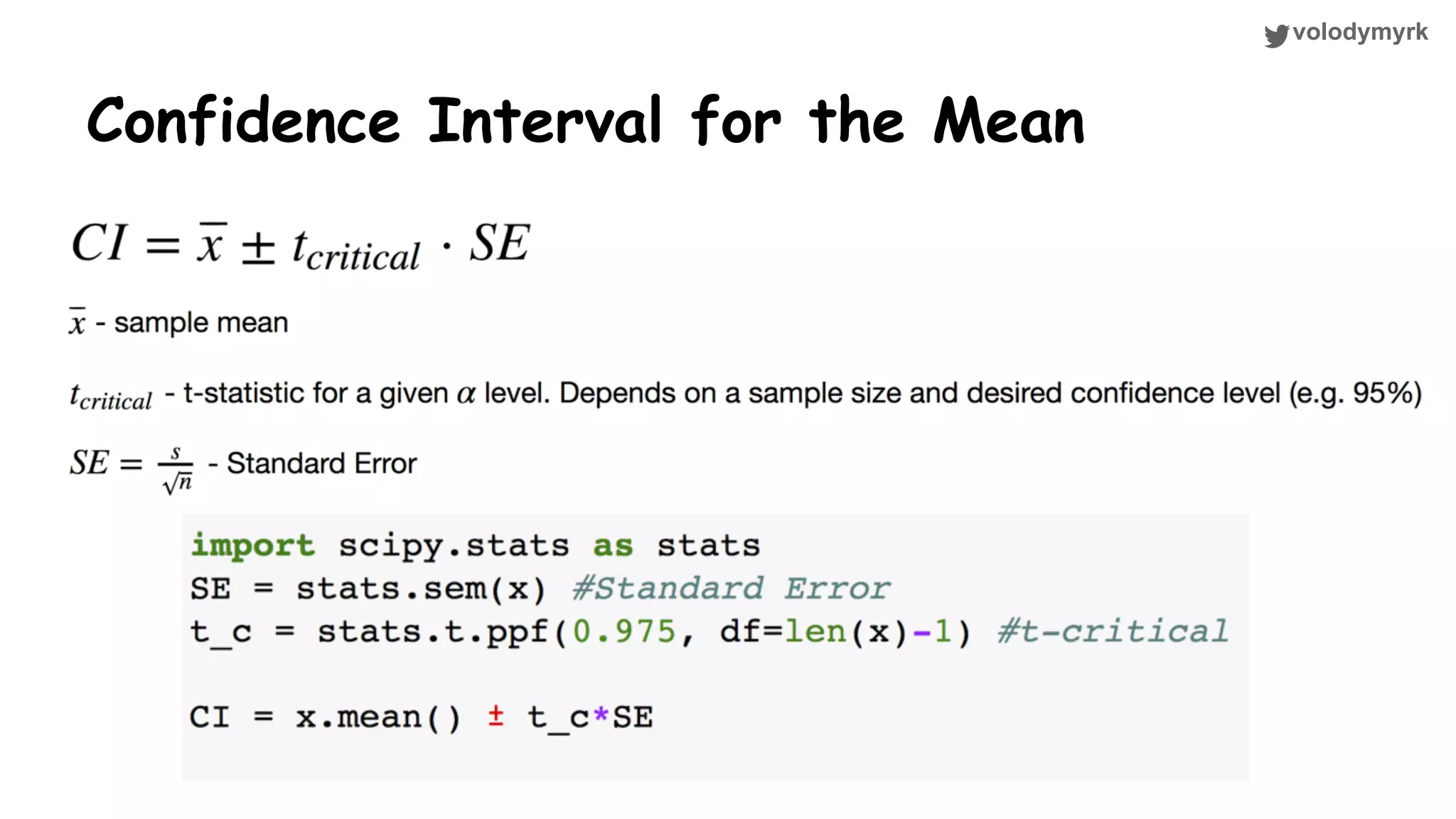
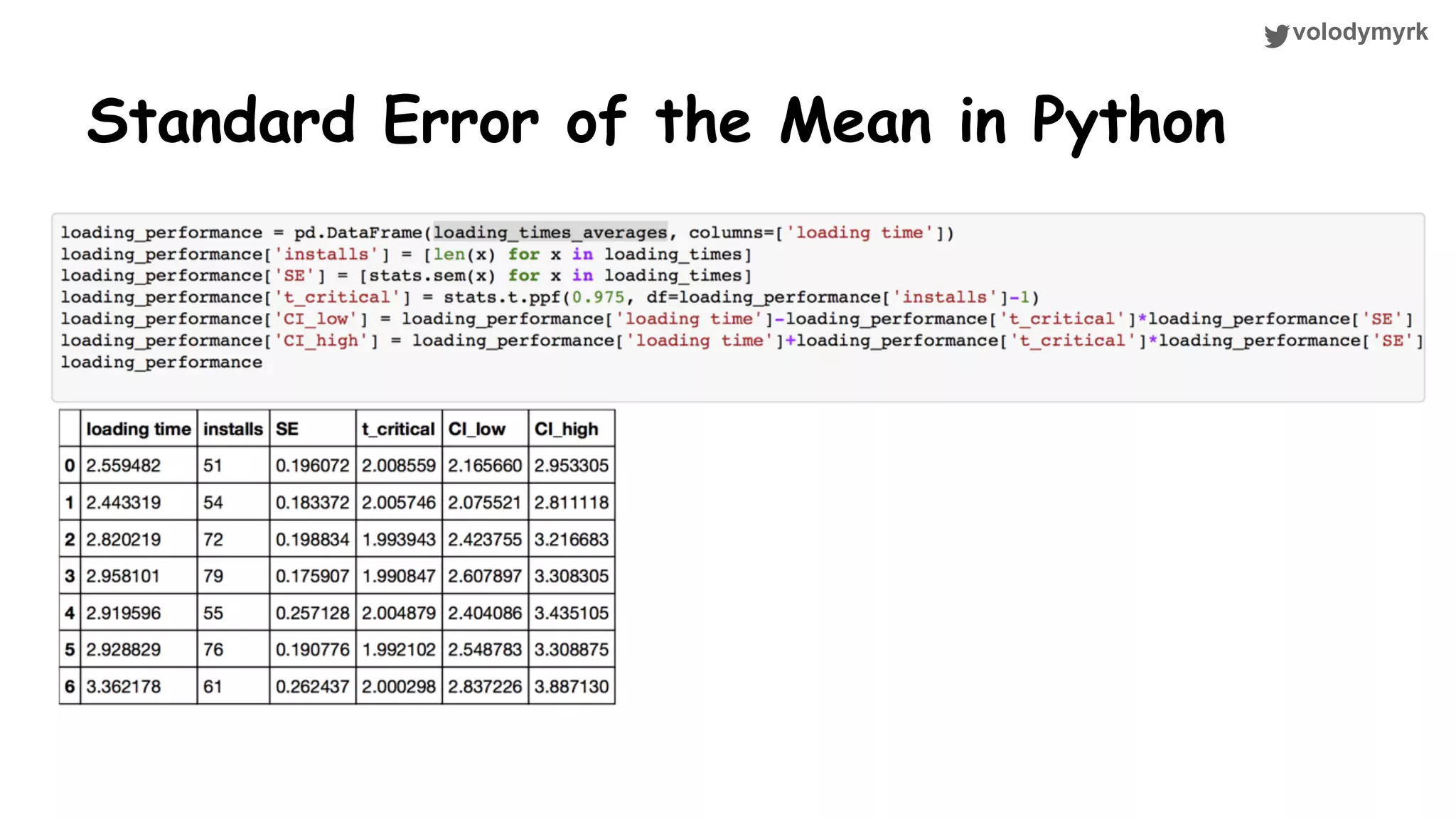
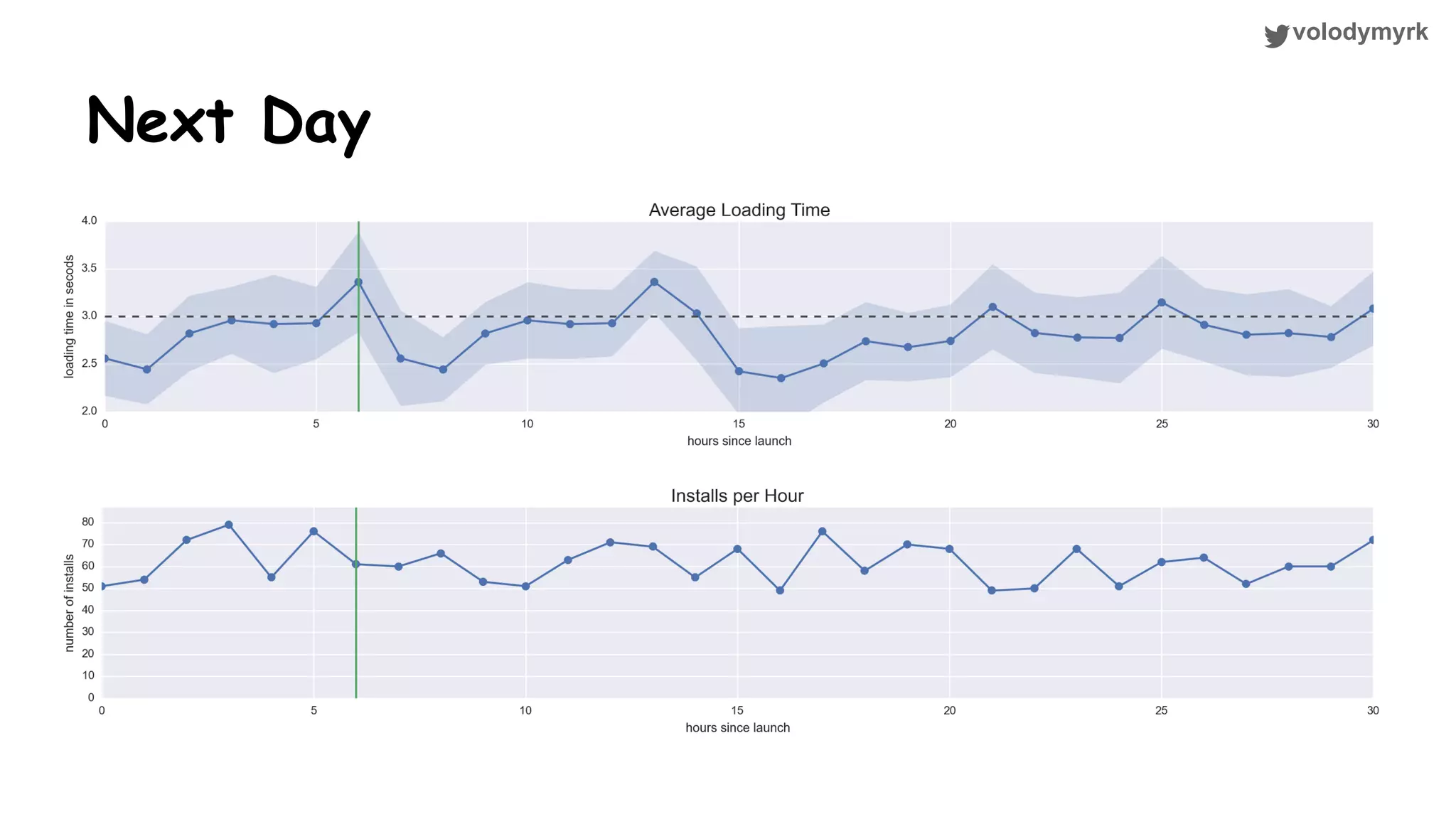
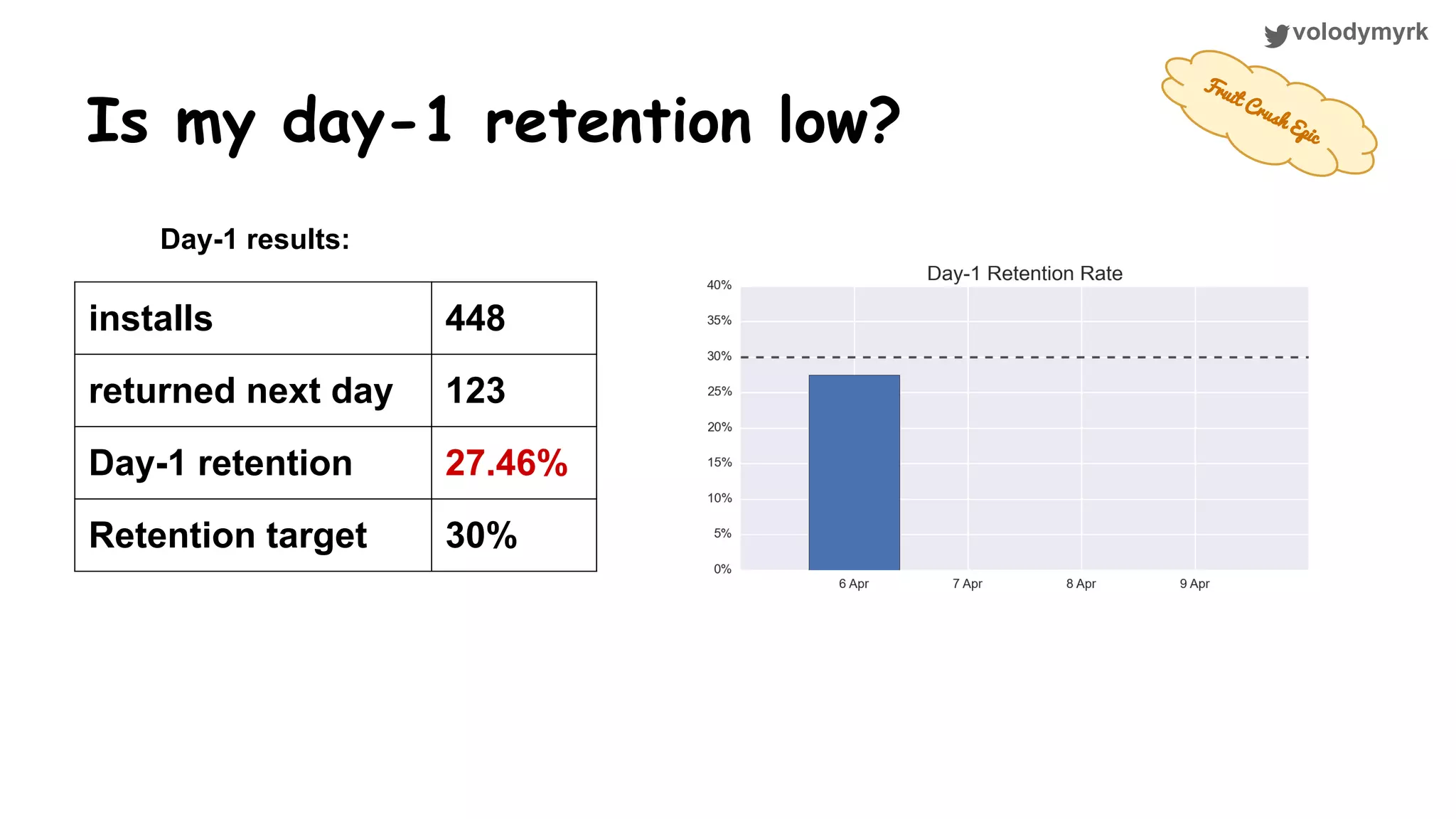
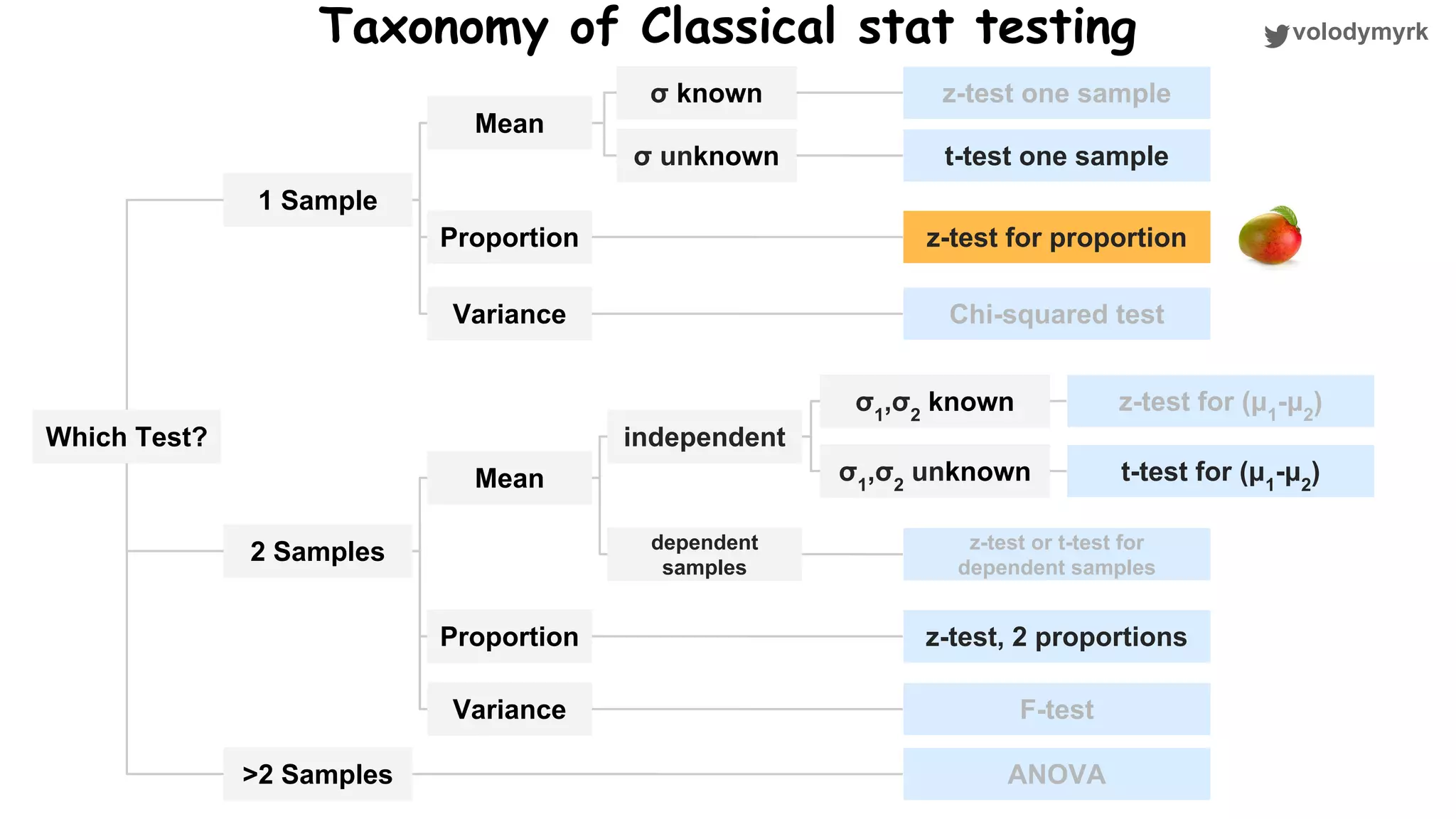
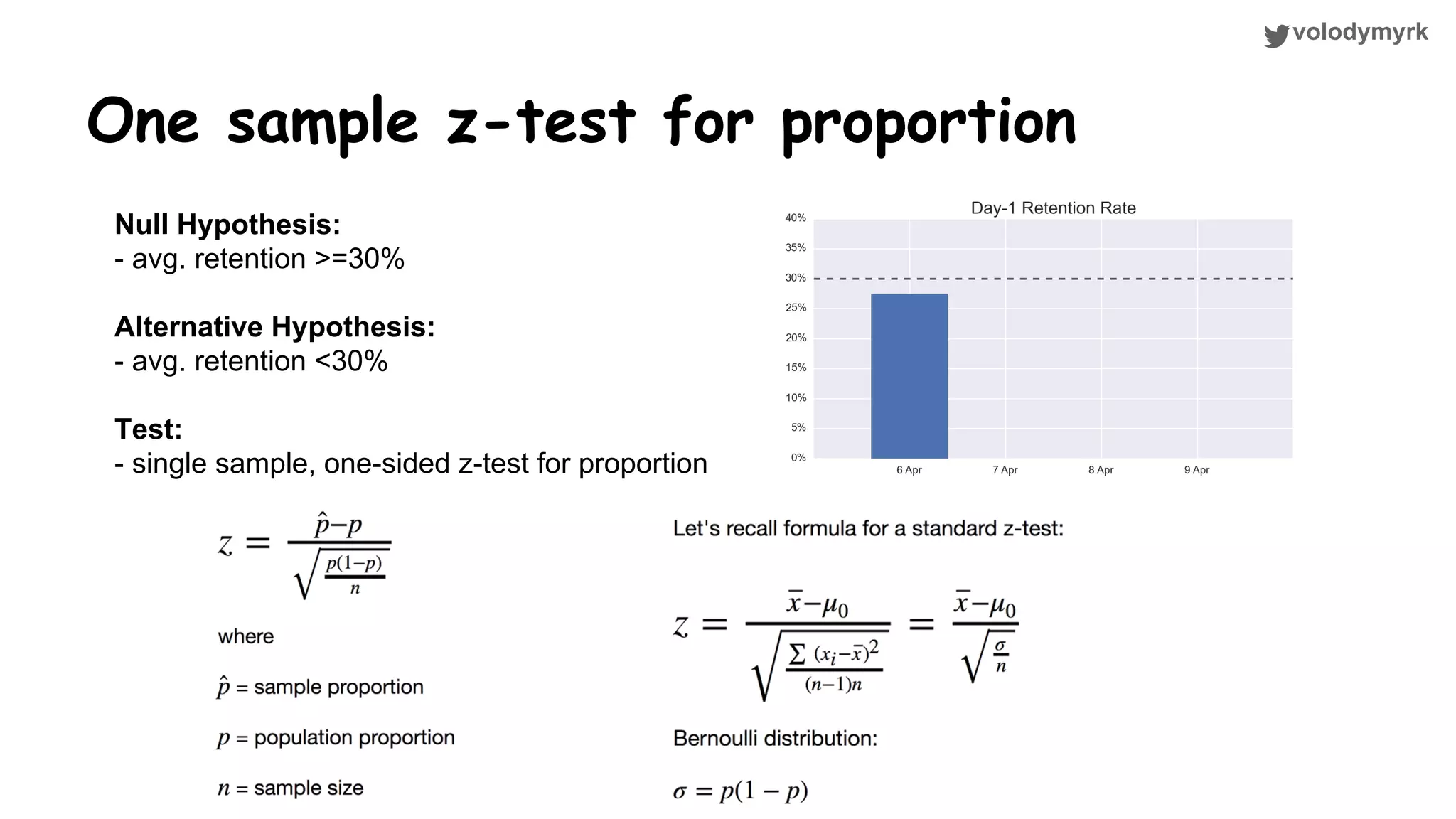
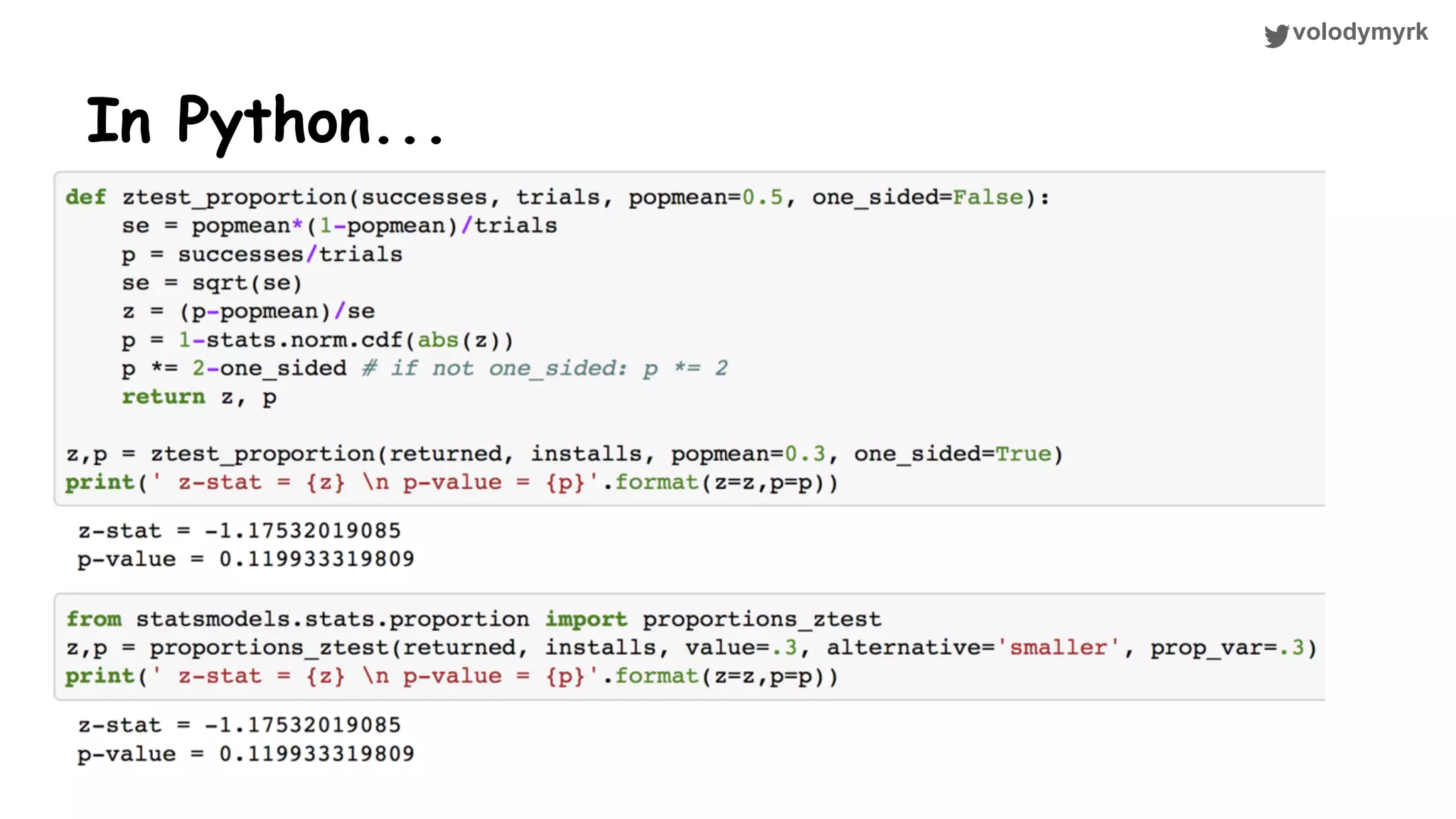
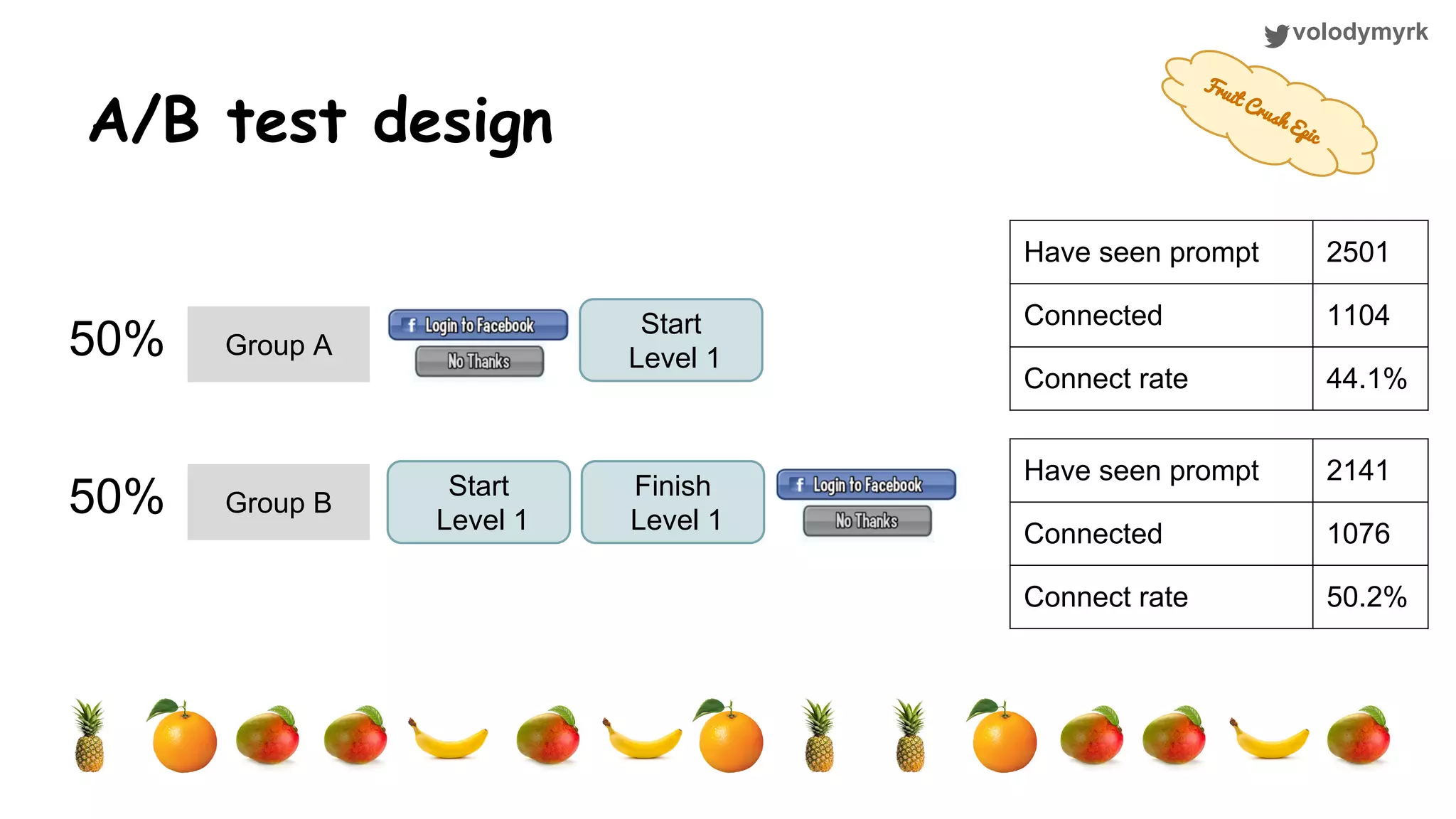
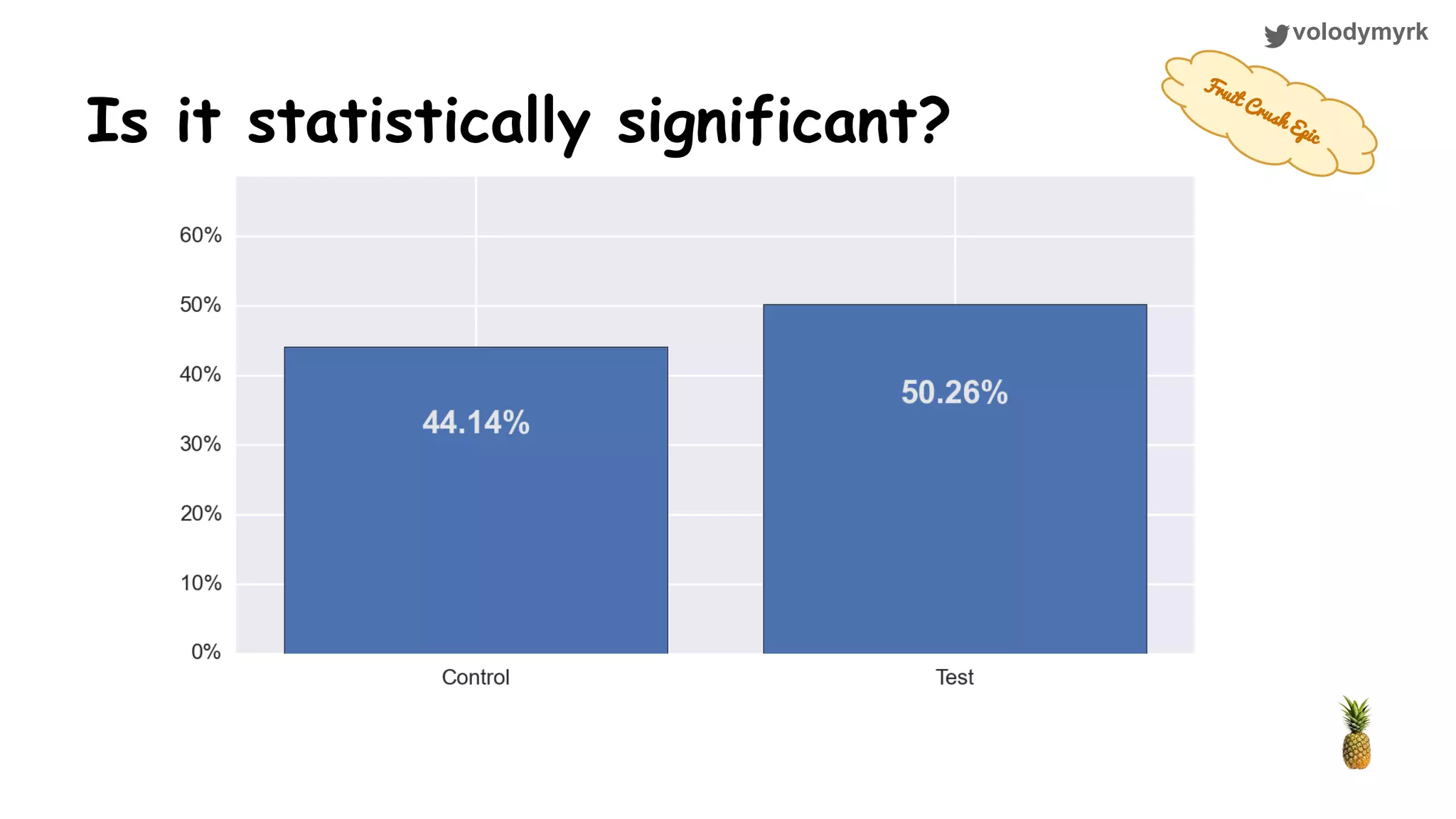
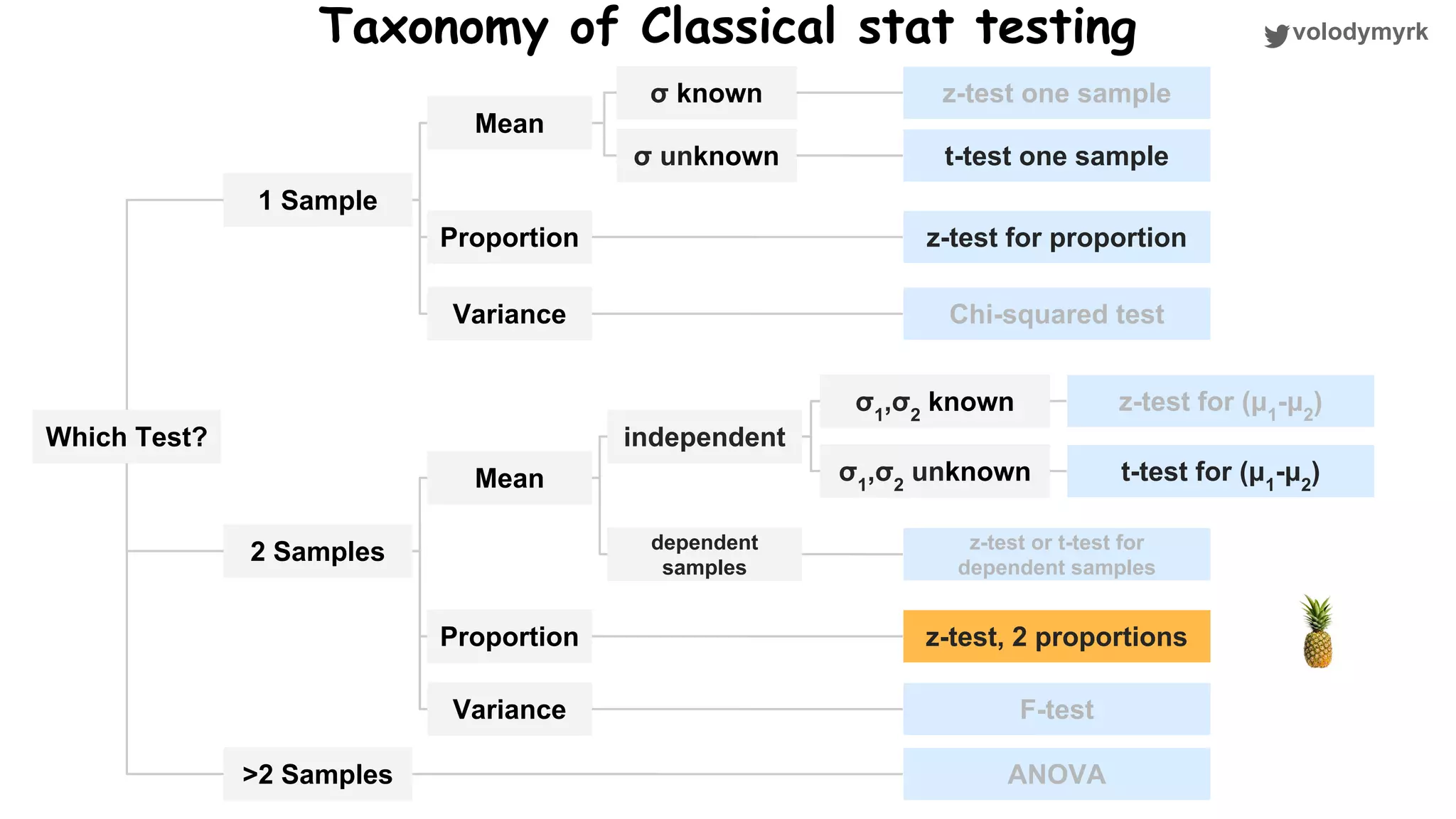
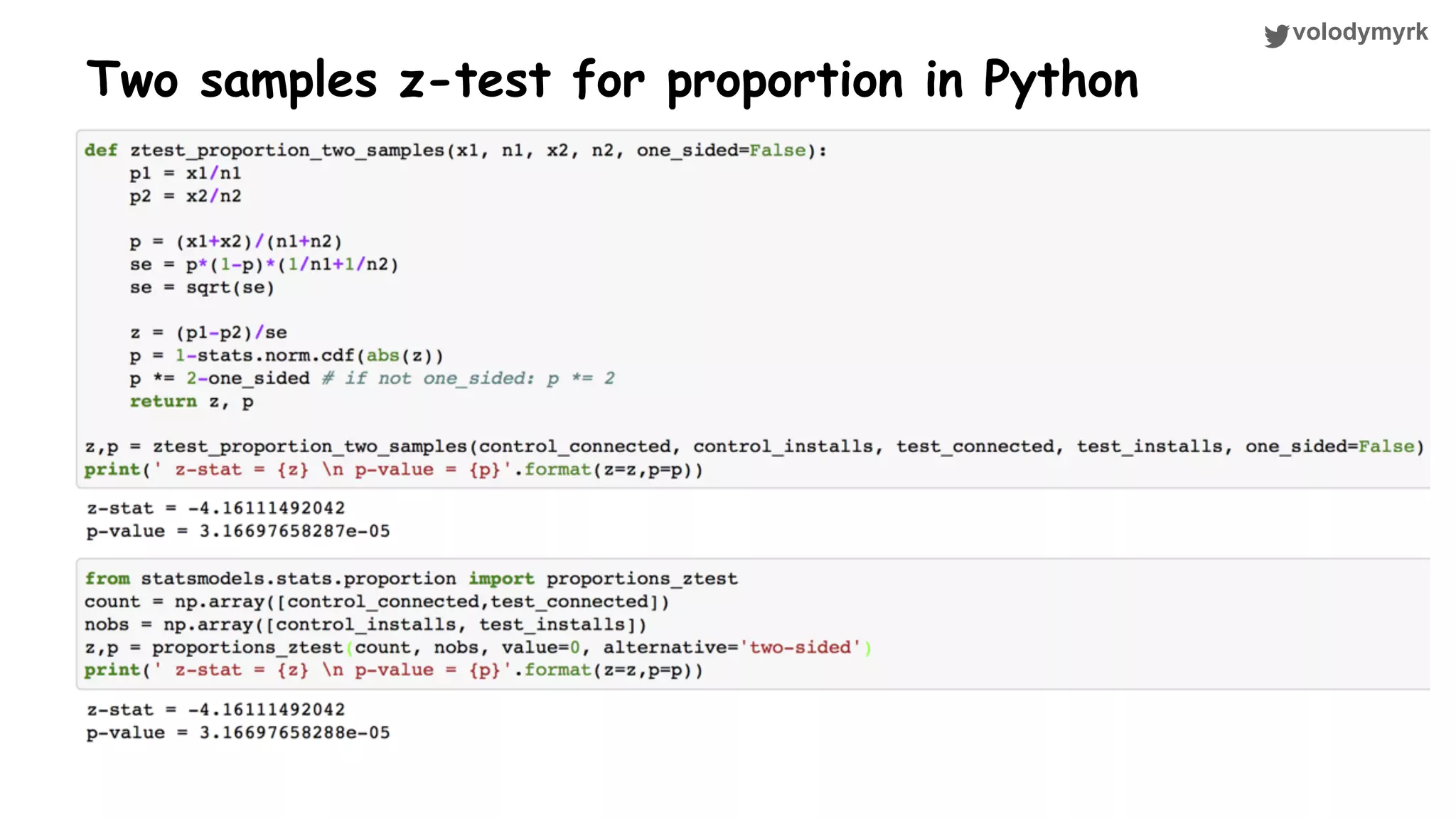
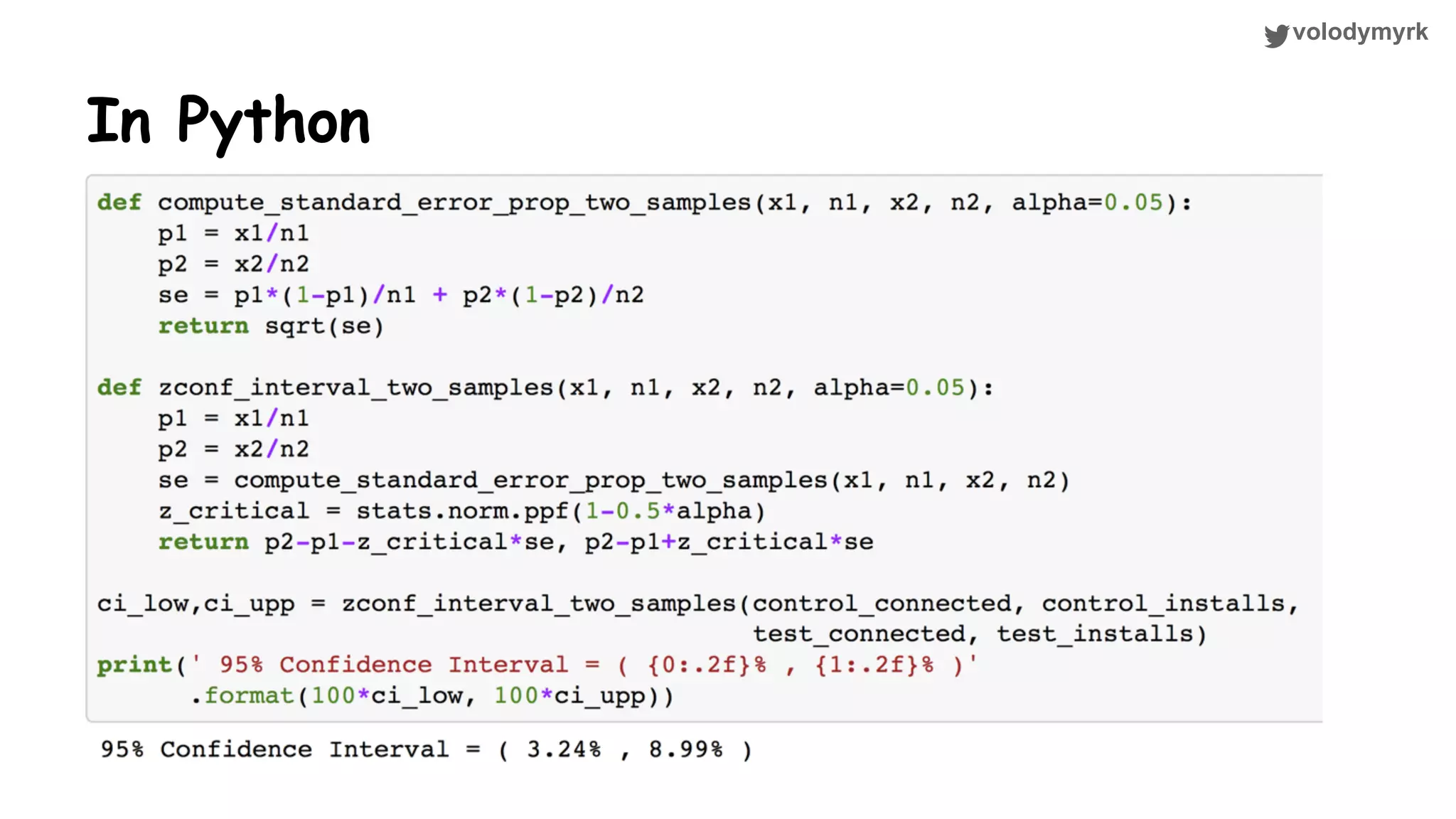
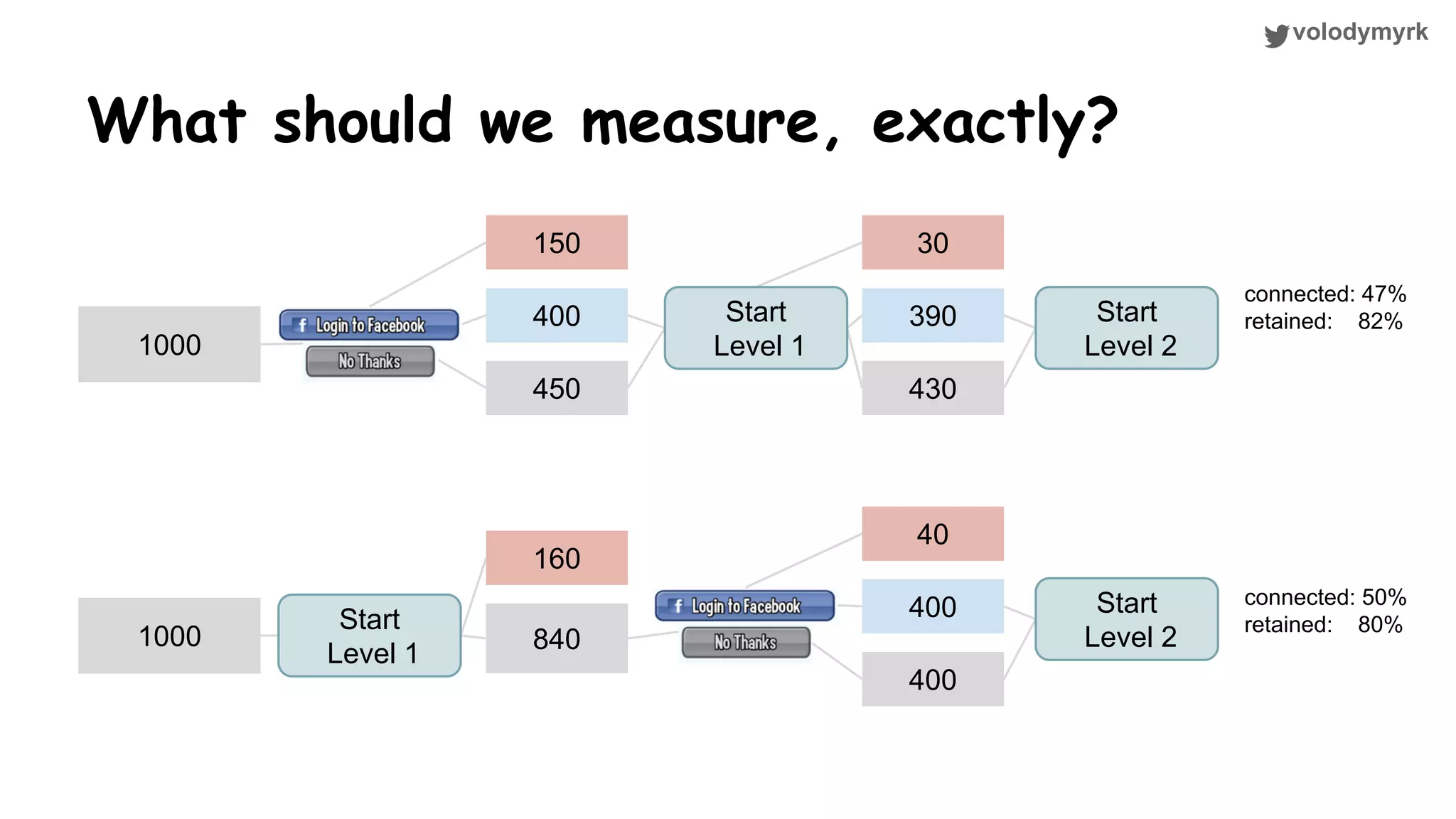
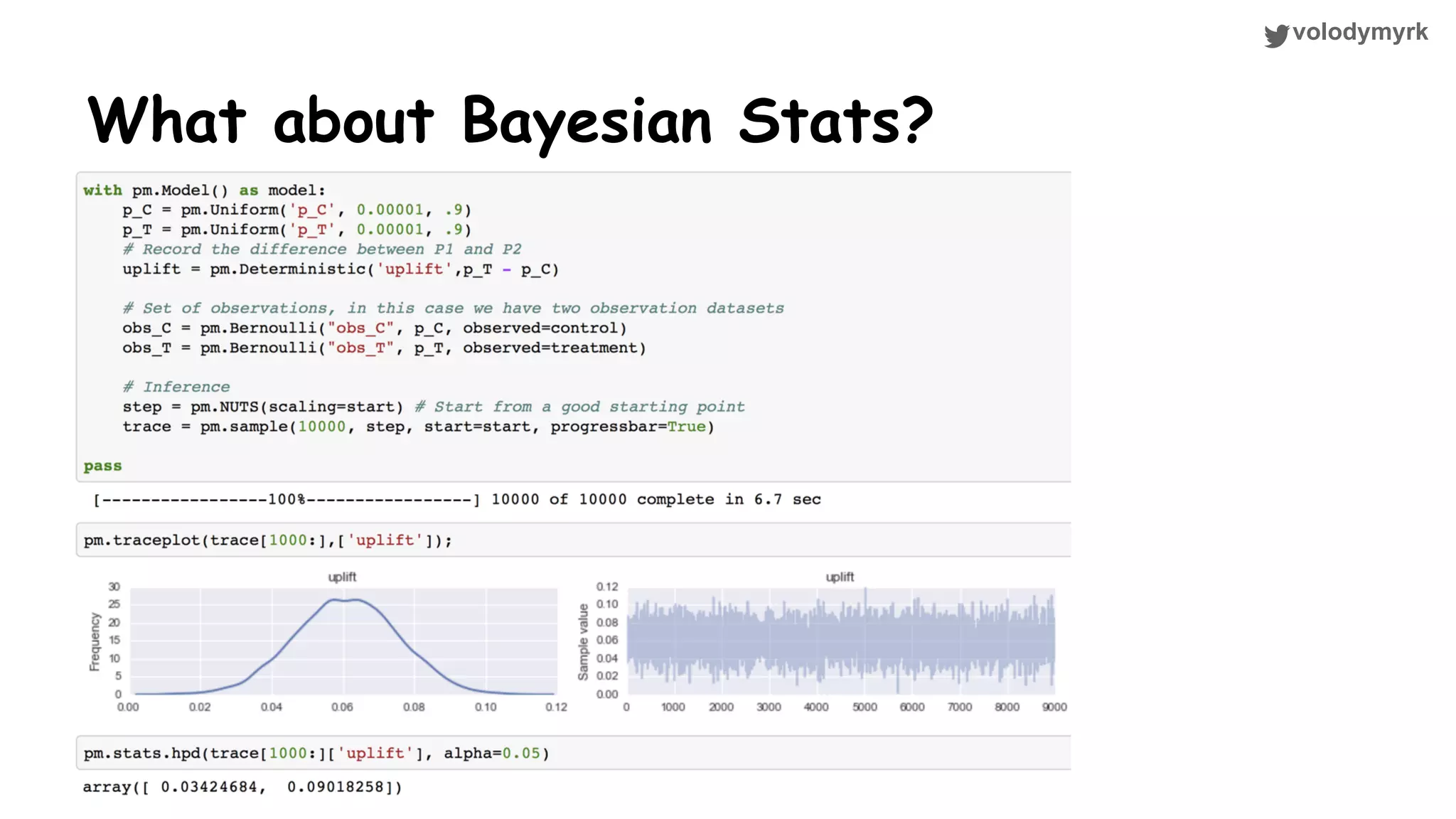
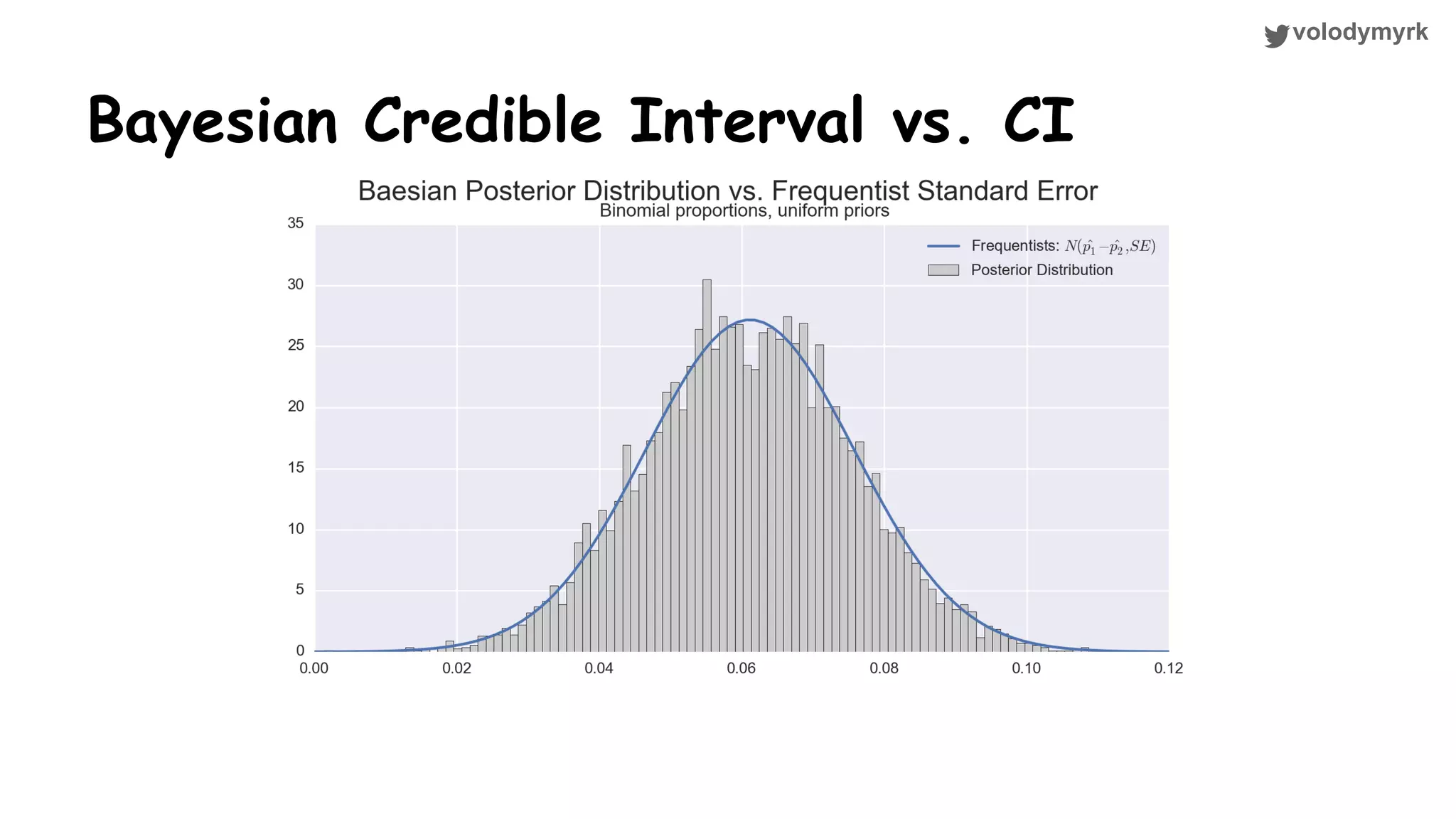
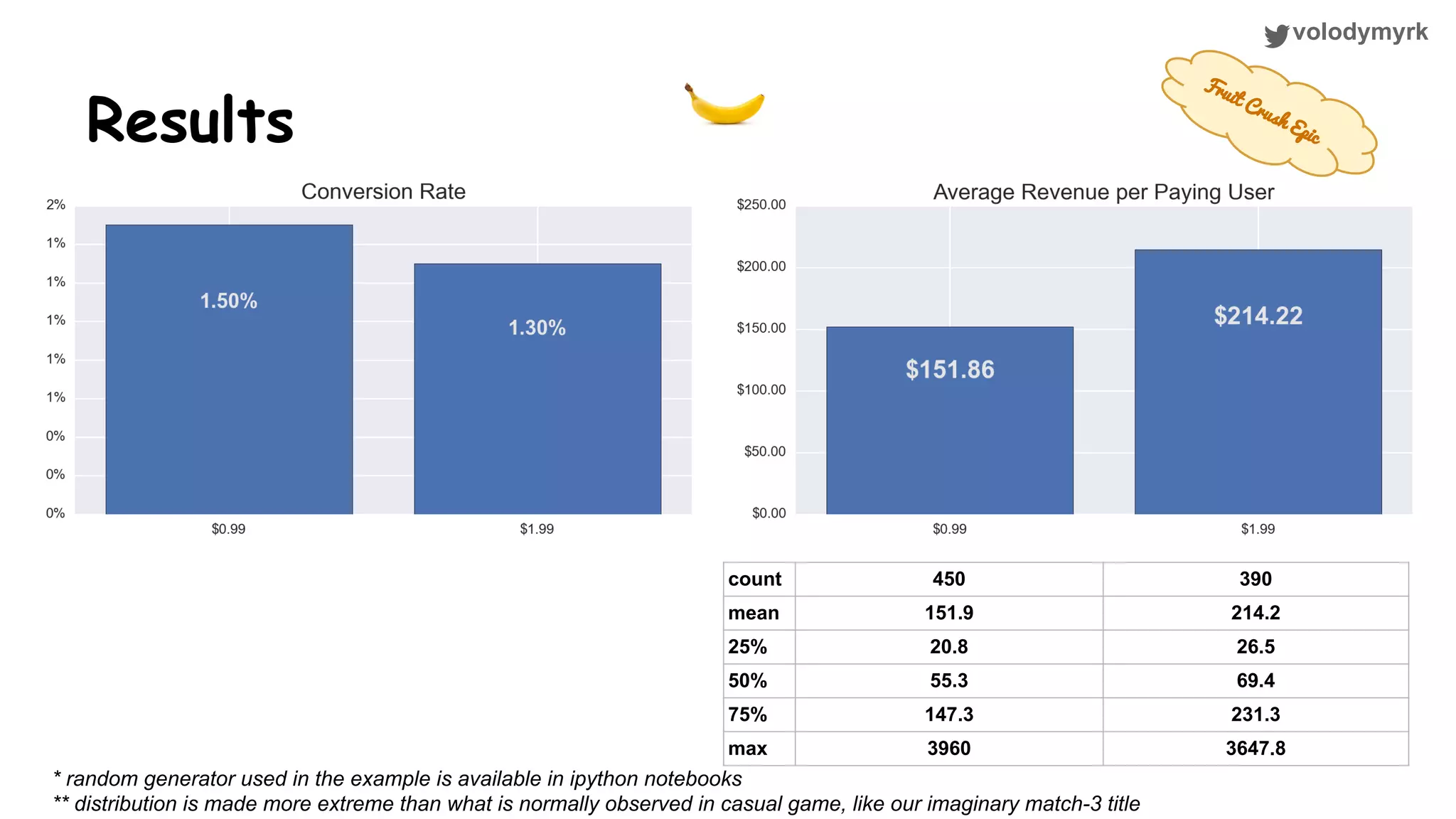
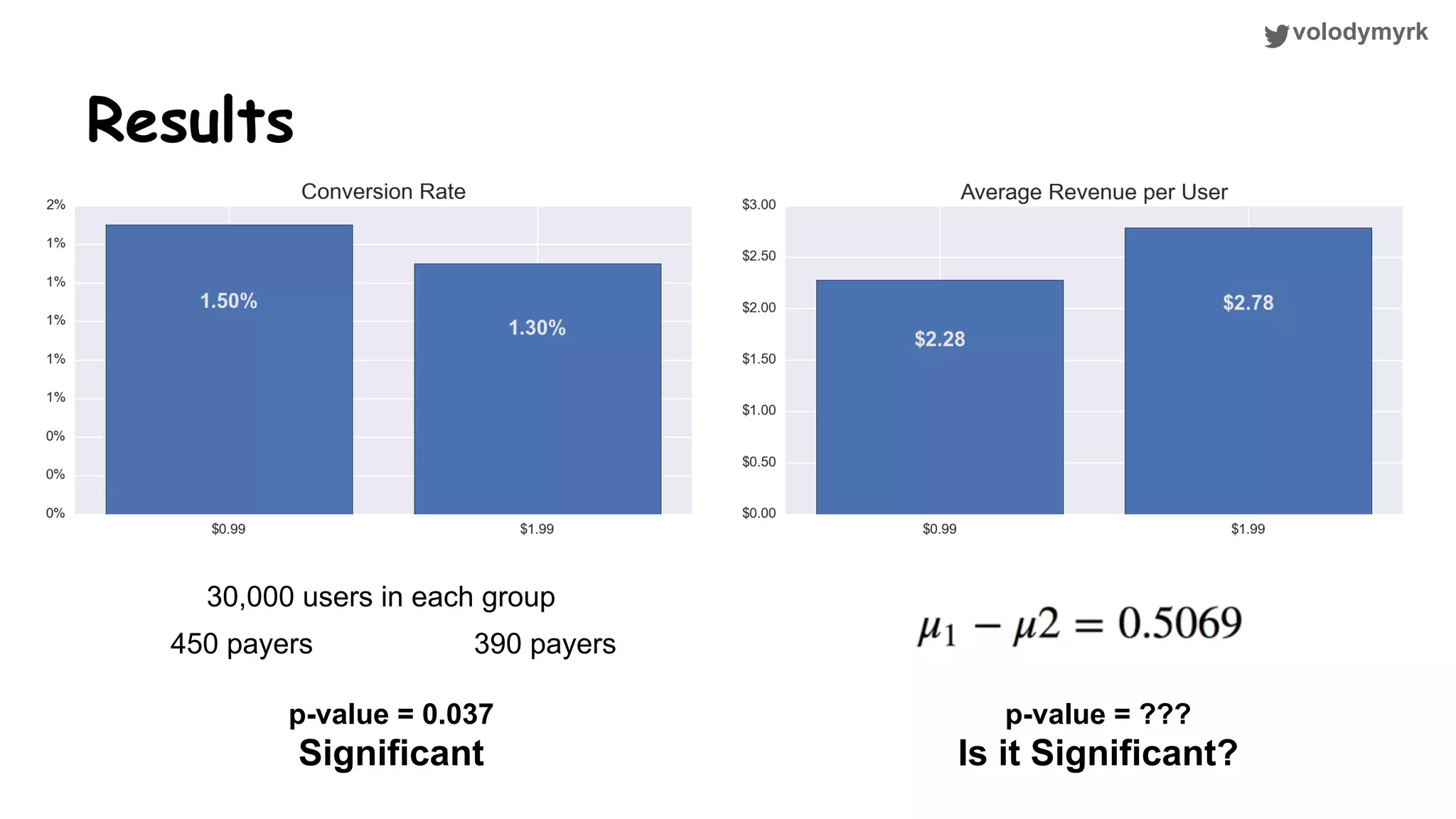
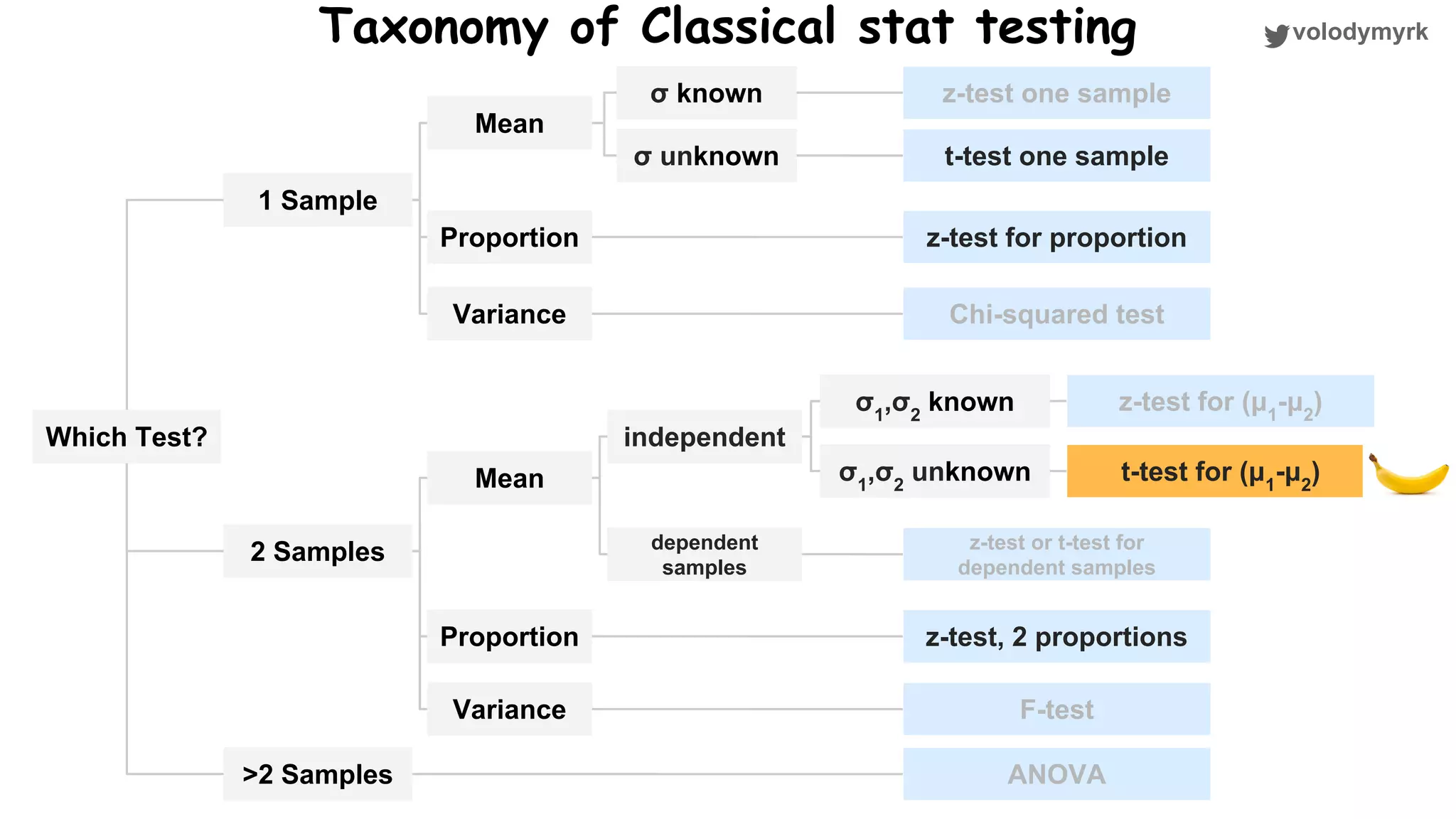
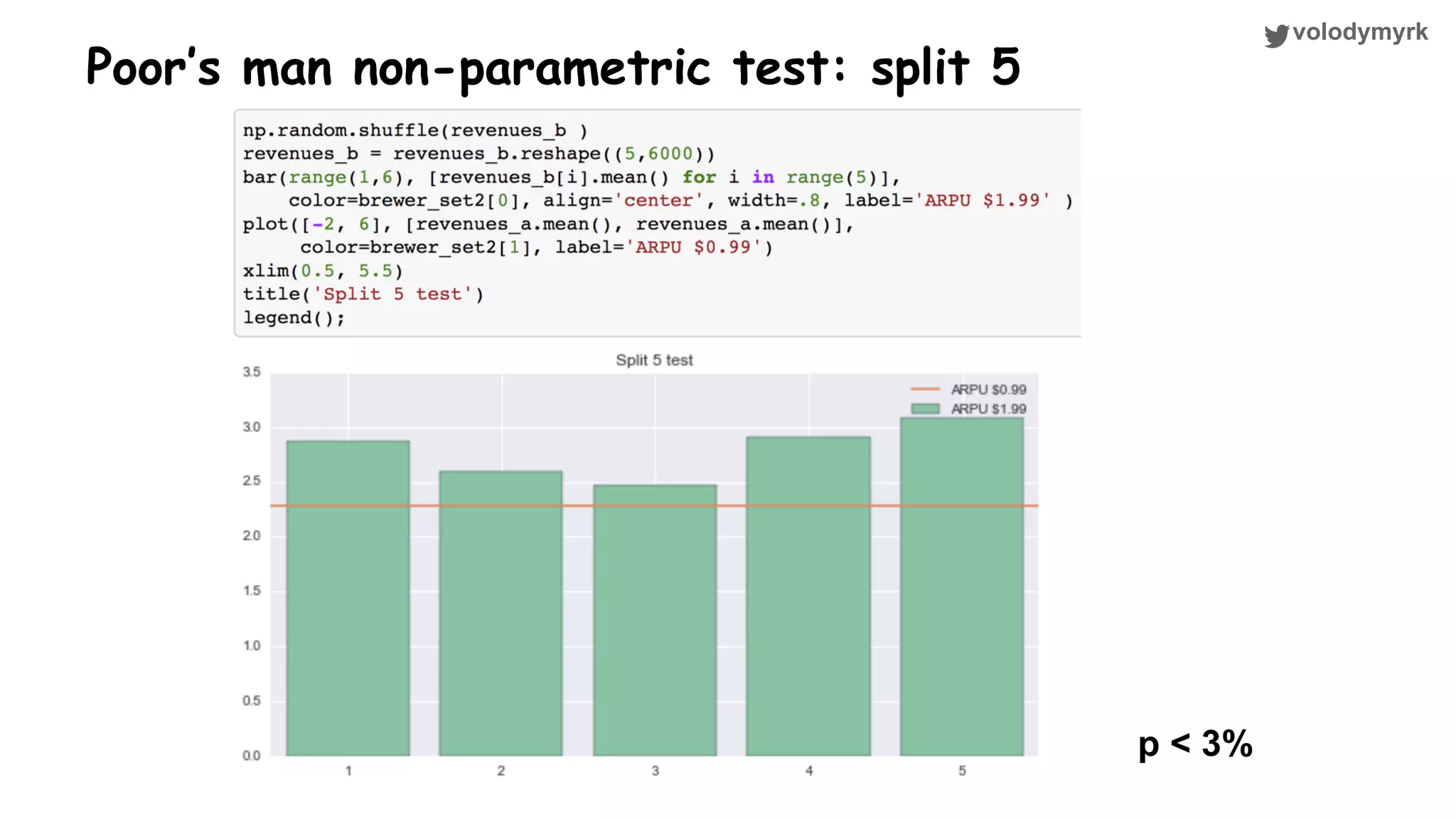
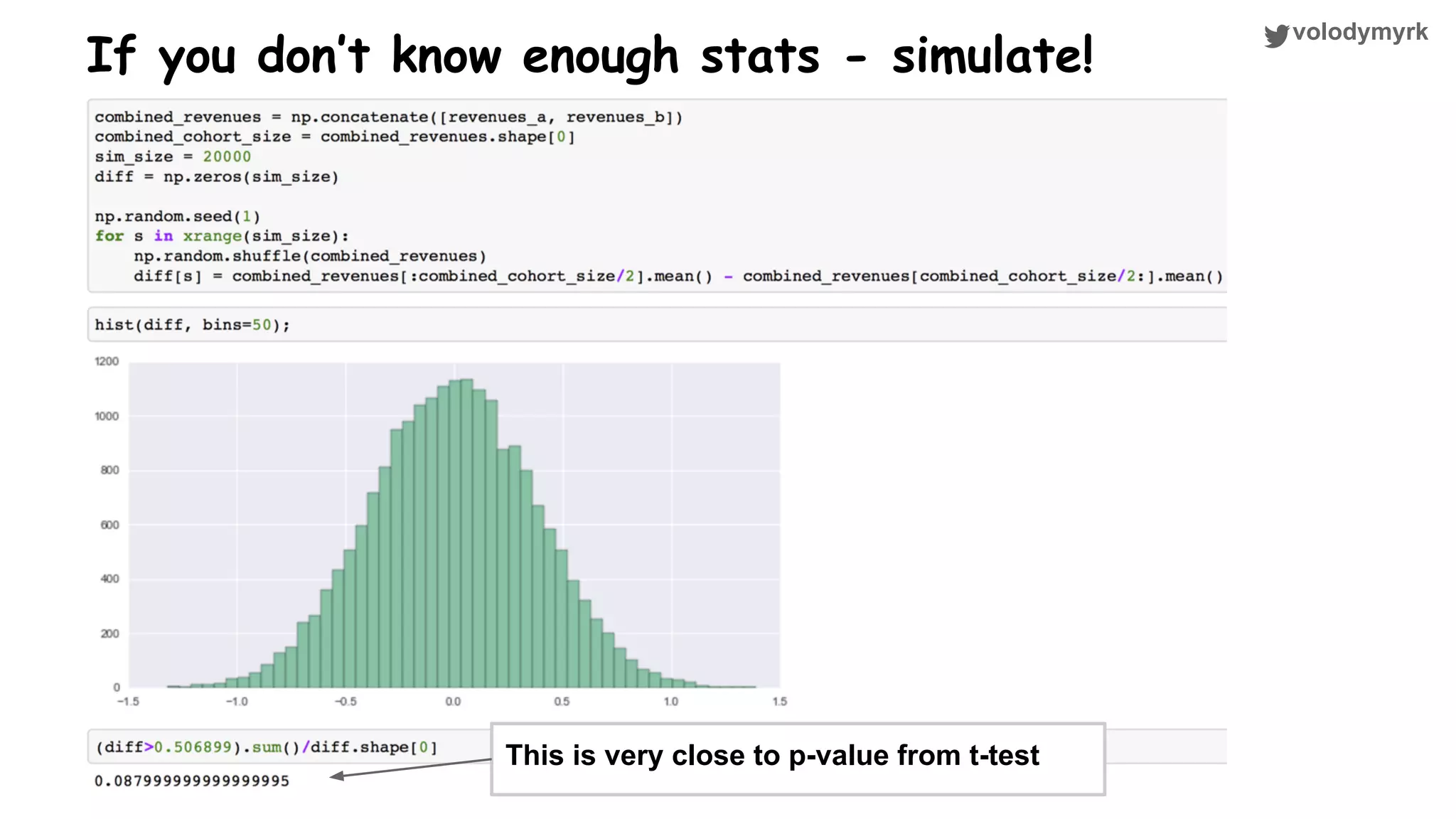
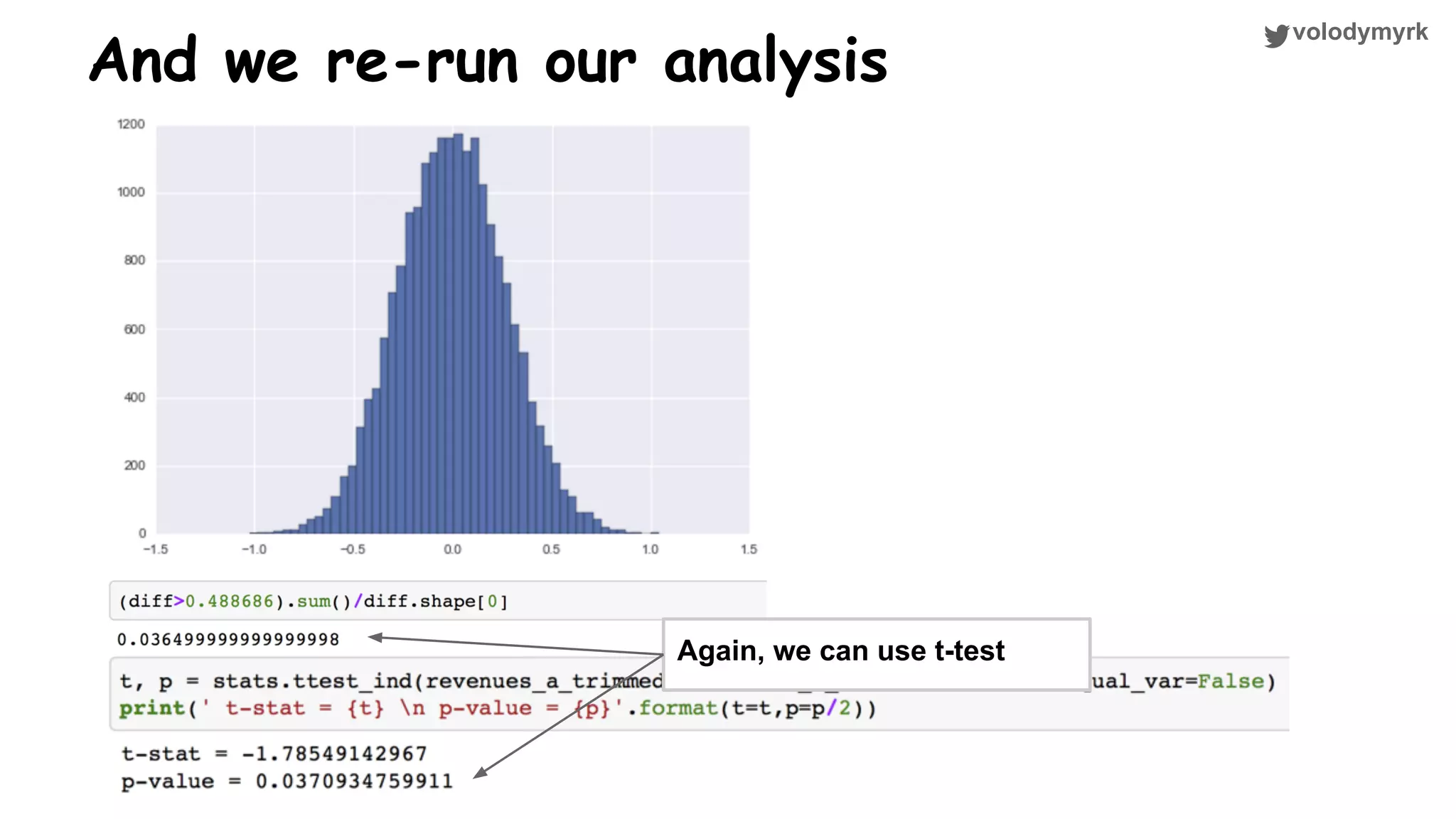
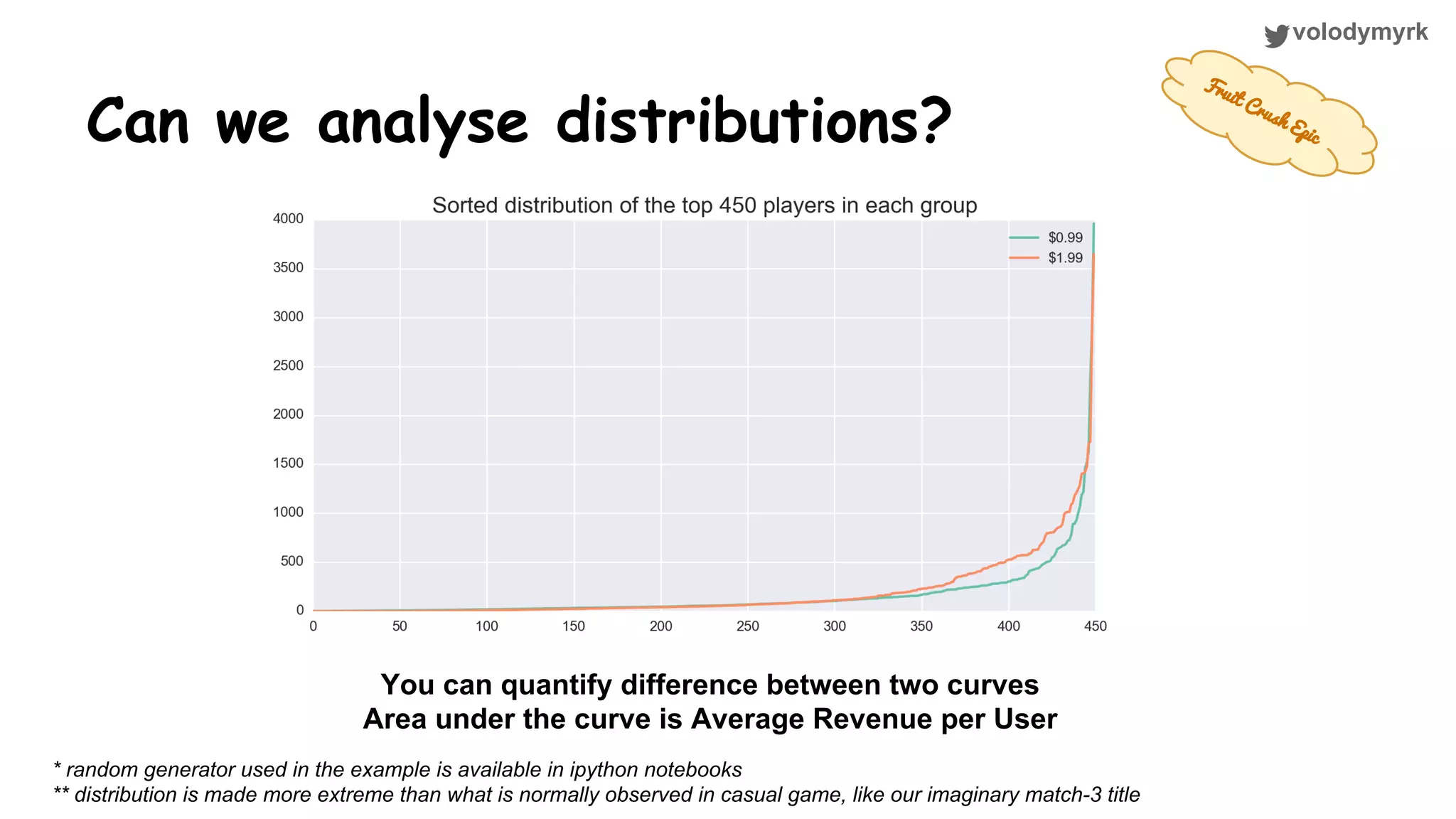
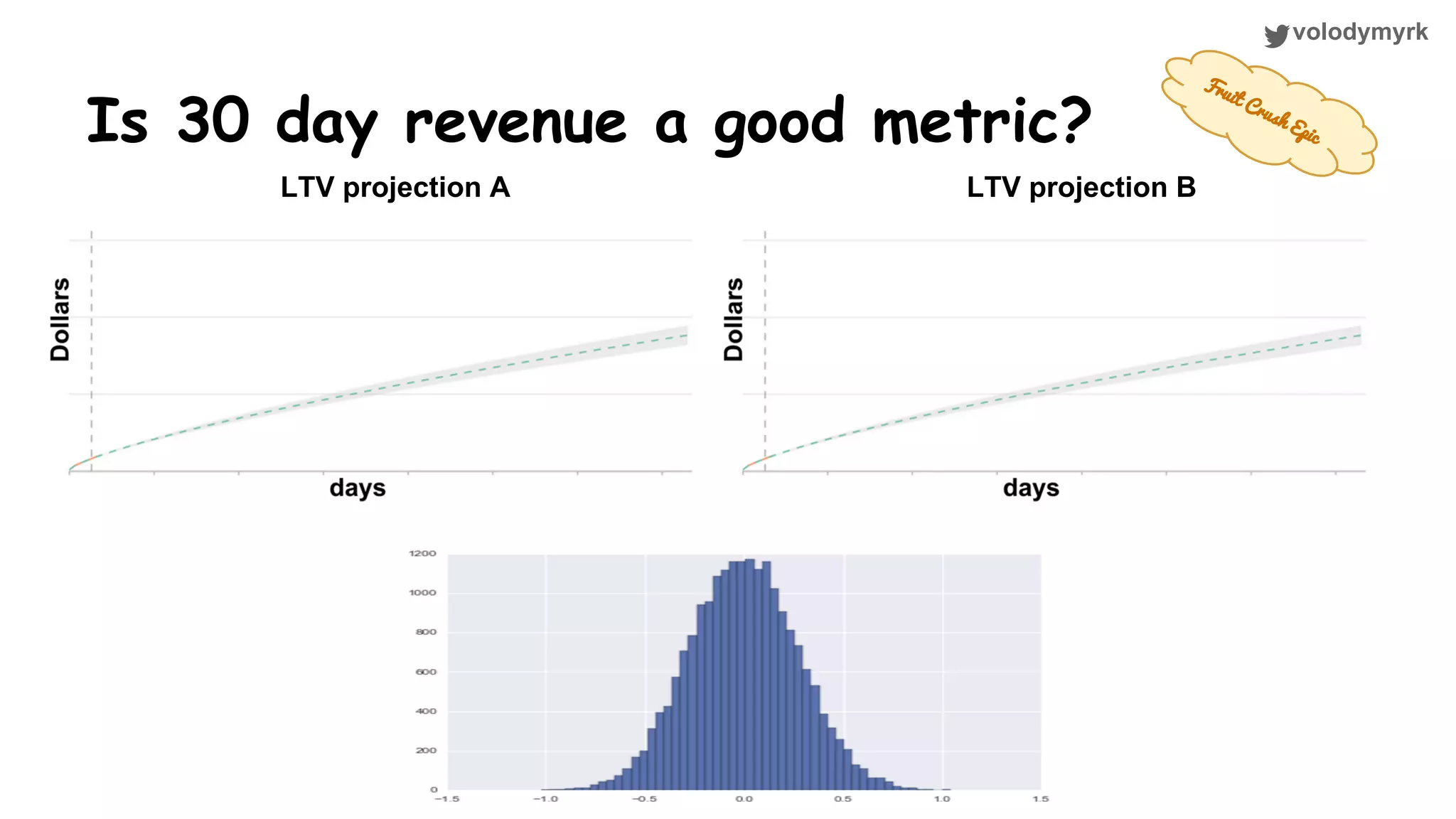
The document outlines a tutorial on conducting online experiments and A/B testing using Python, emphasizing the importance of statistical methods to analyze data and test hypotheses. It covers various statistical tests such as t-tests, z-tests, and their applications in assessing user retention and revenue strategies in gaming. Finally, it advocates for understanding both classical and Bayesian statistics, highlighting key takeaways for data scientists involved in product performance analysis.