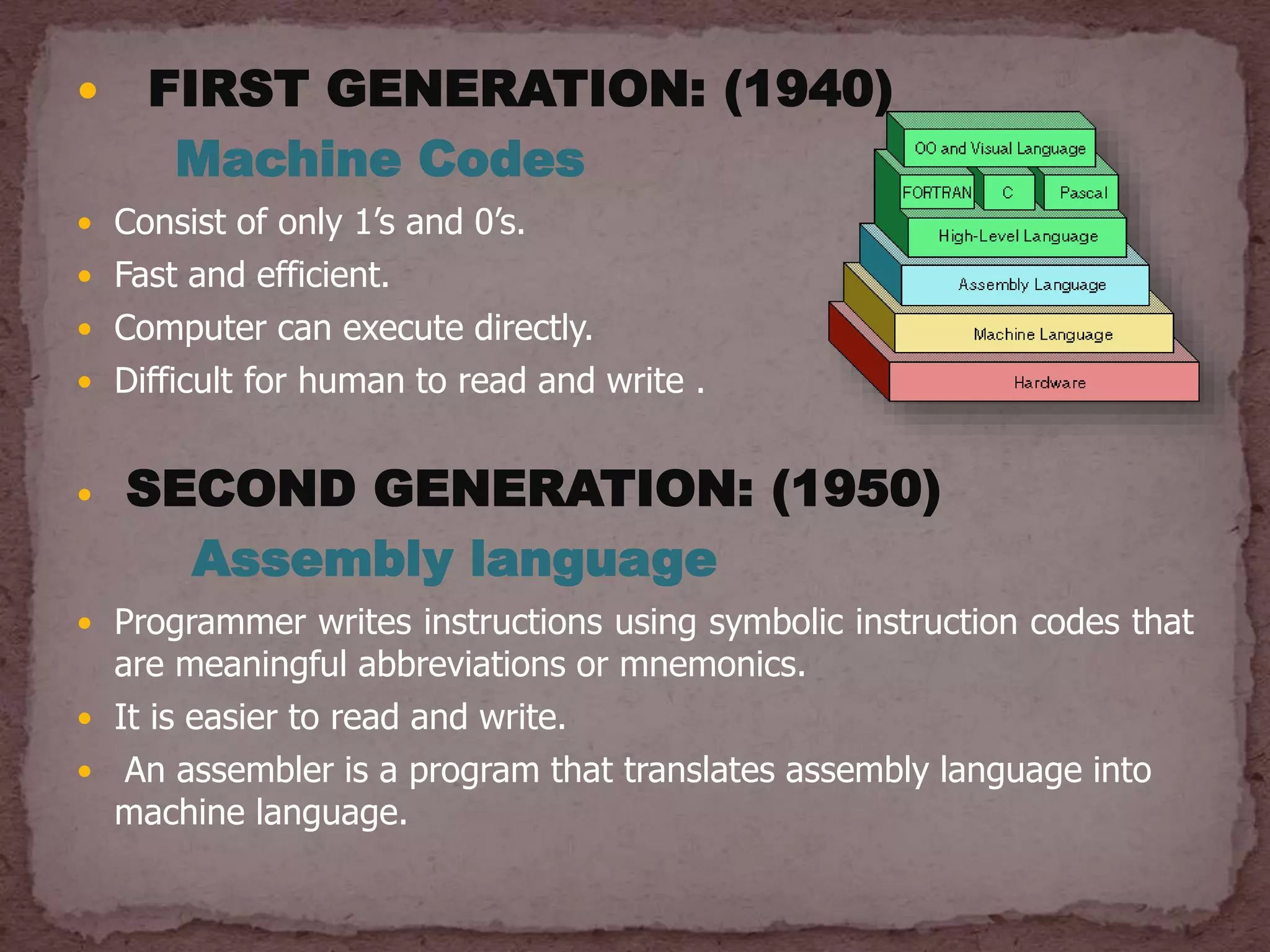
The document discusses the history and evolution of programming languages from the first to fifth generations. It notes that Charles Babbage proposed the first general-purpose computer called the Analytical Engine in 1837 and that Ada Lovelace was the first computer programmer. Programming languages have evolved from machine code consisting of 1s and 0s, to assembly languages using symbolic codes, to modern high-level languages that are closer to human languages like C++, Java, Python and SQL. Fifth generation languages allow solving problems by defining constraints rather than writing algorithms.