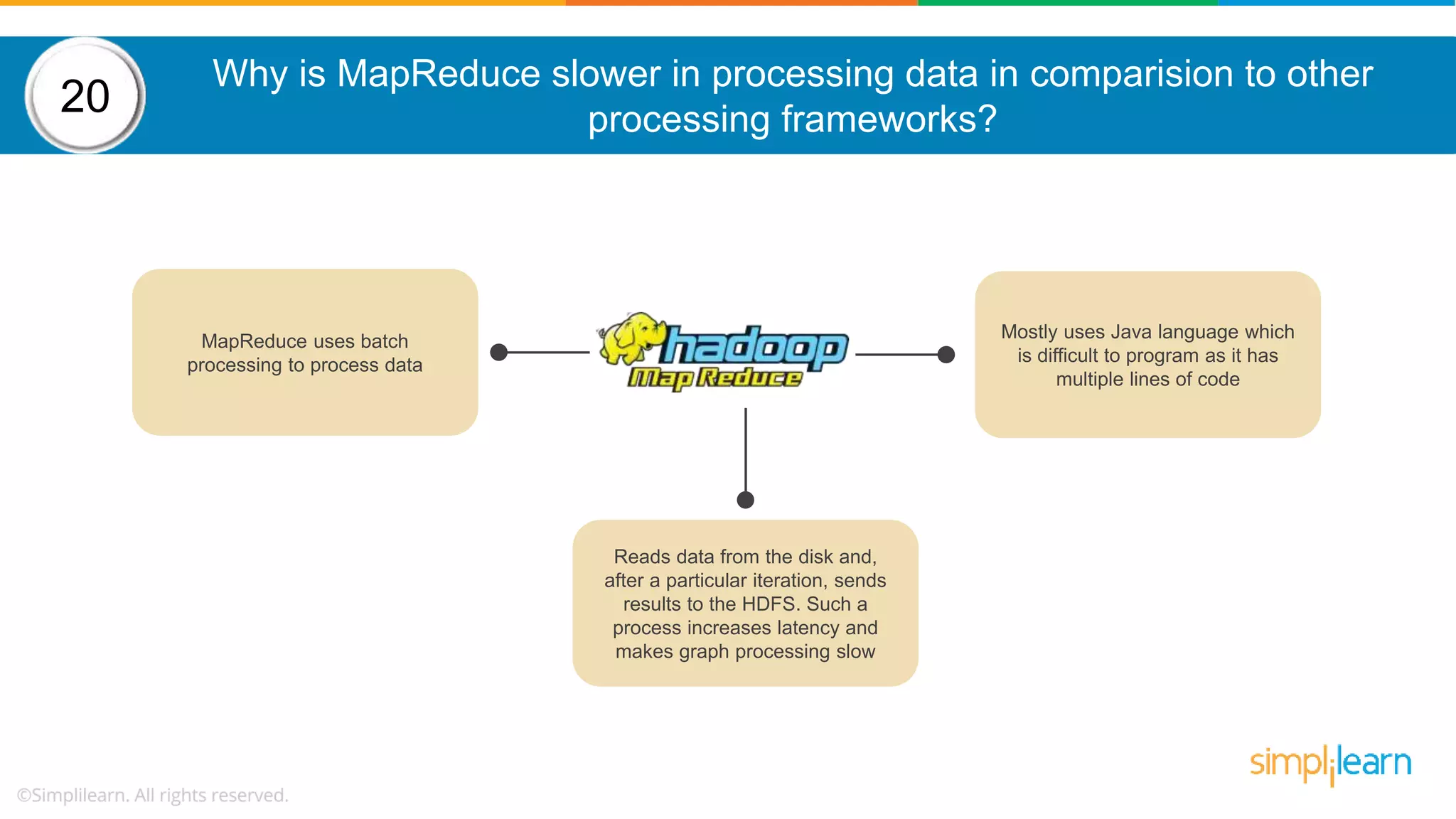
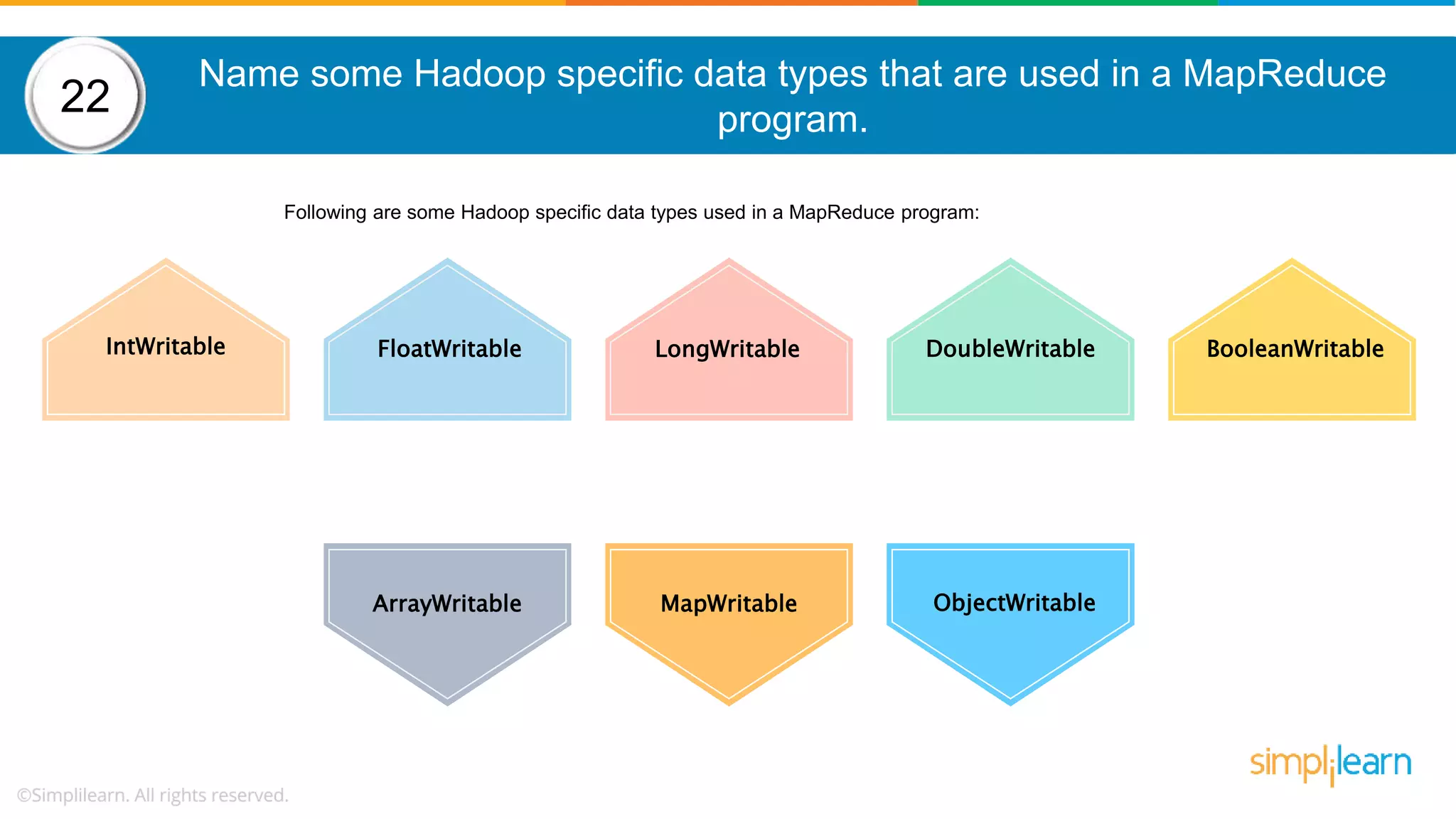
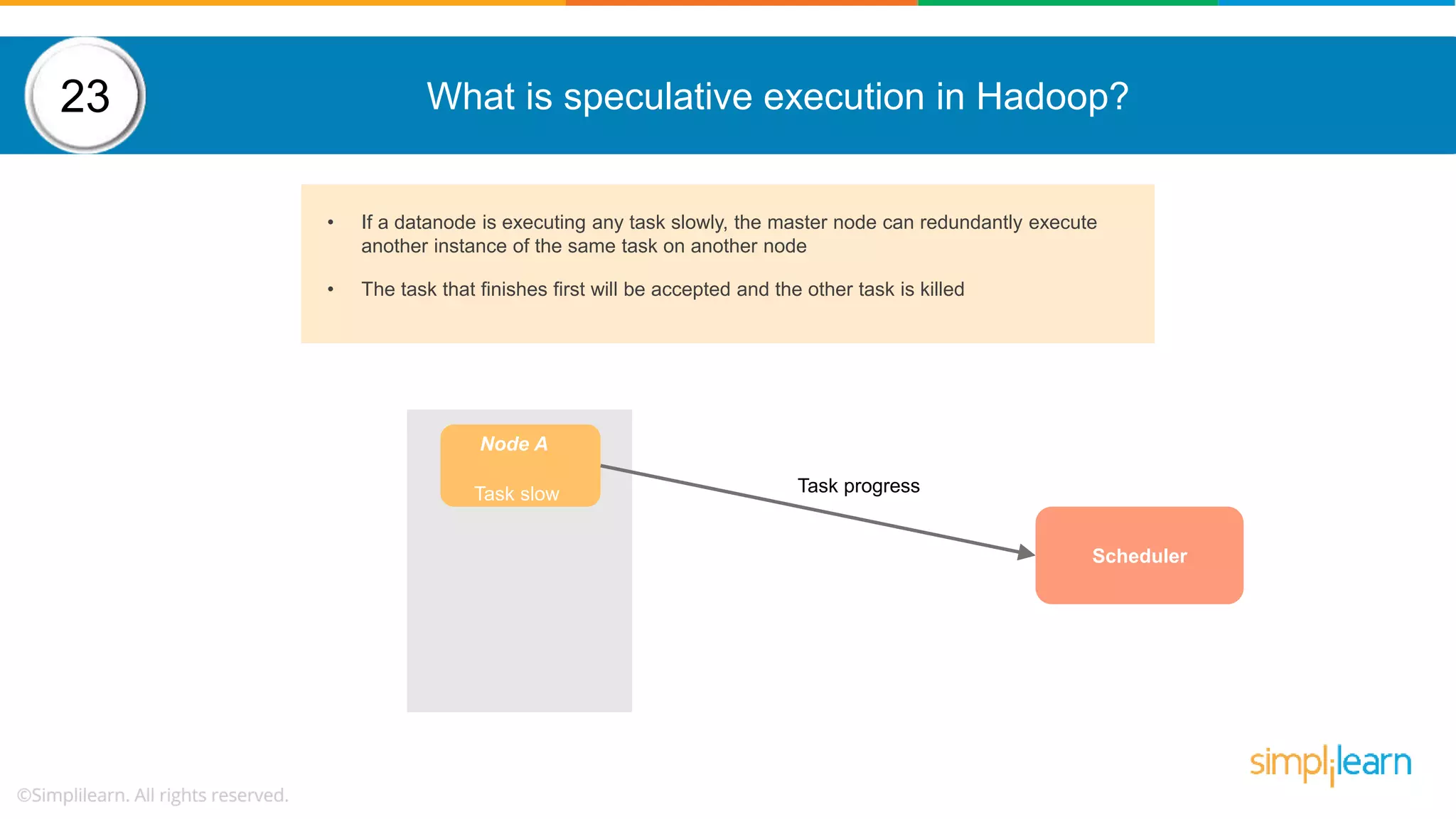
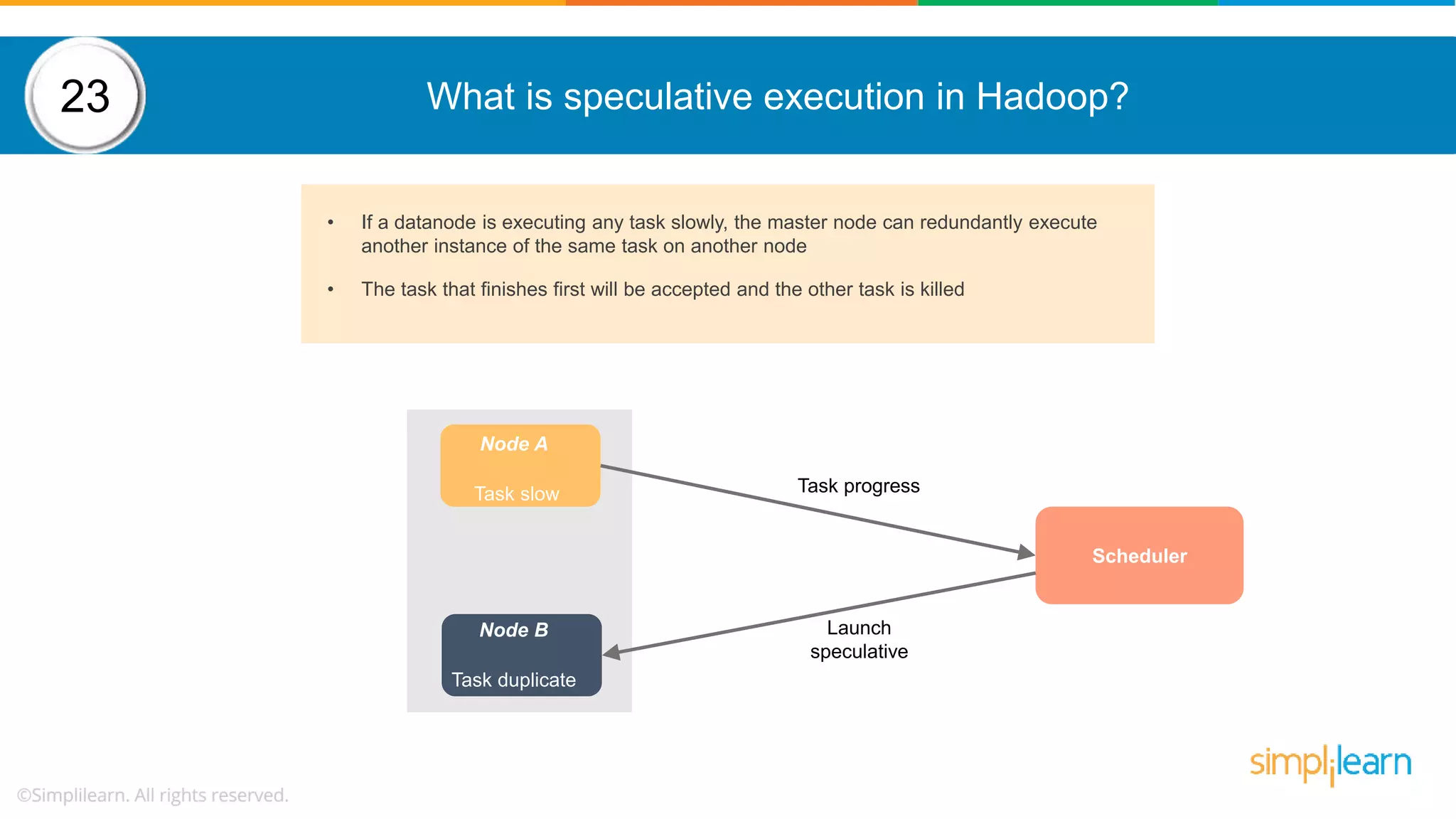
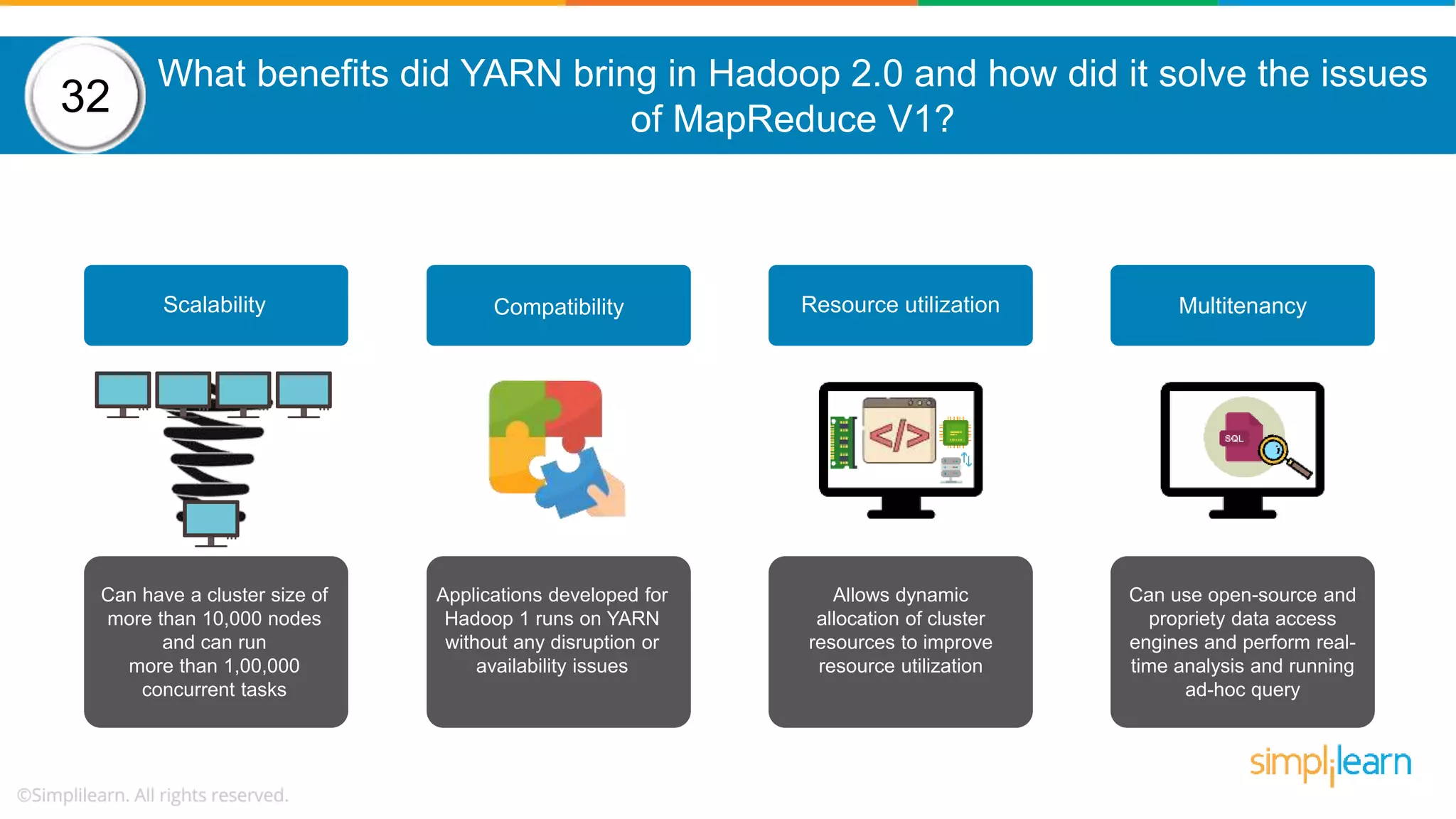
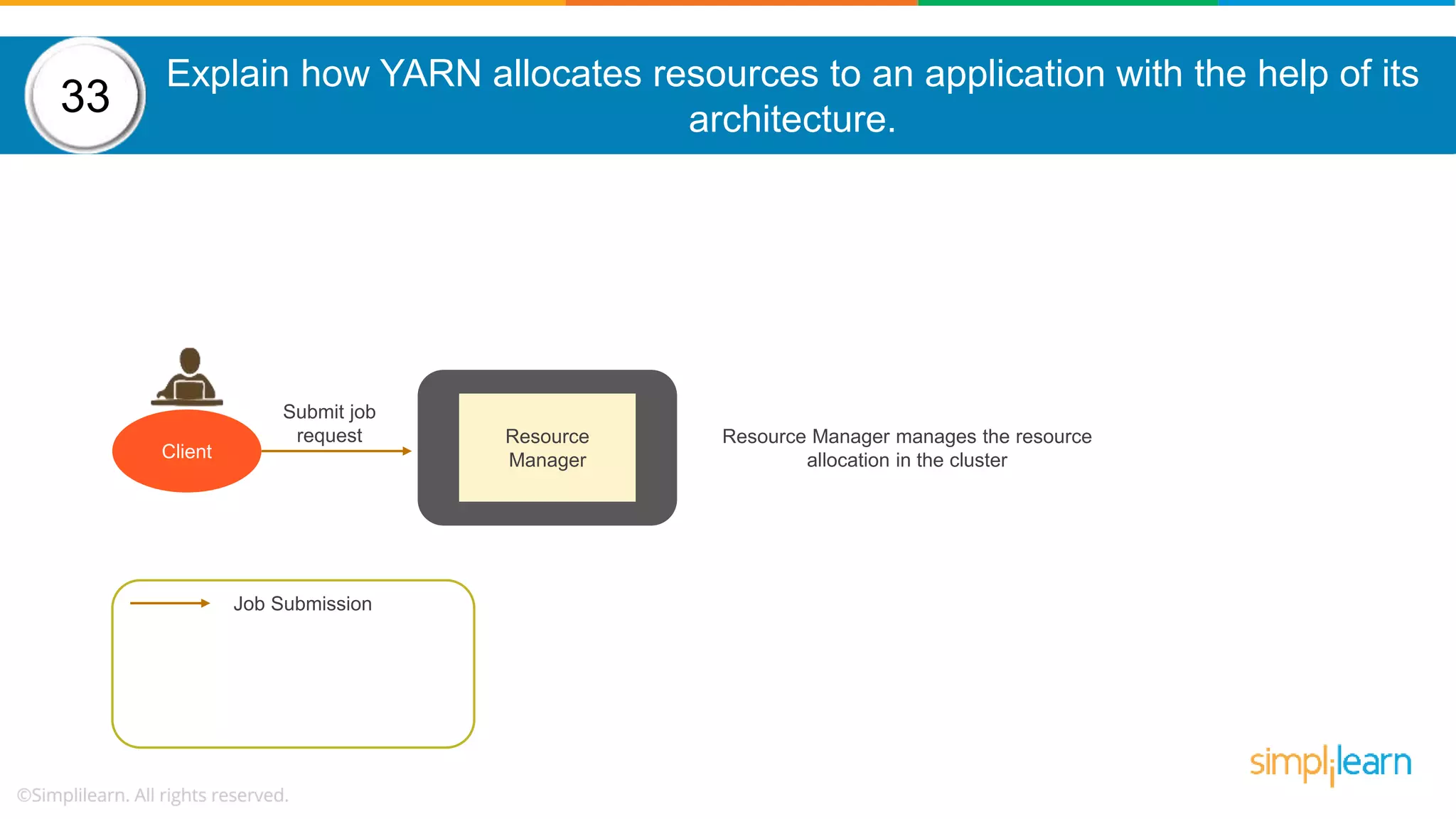
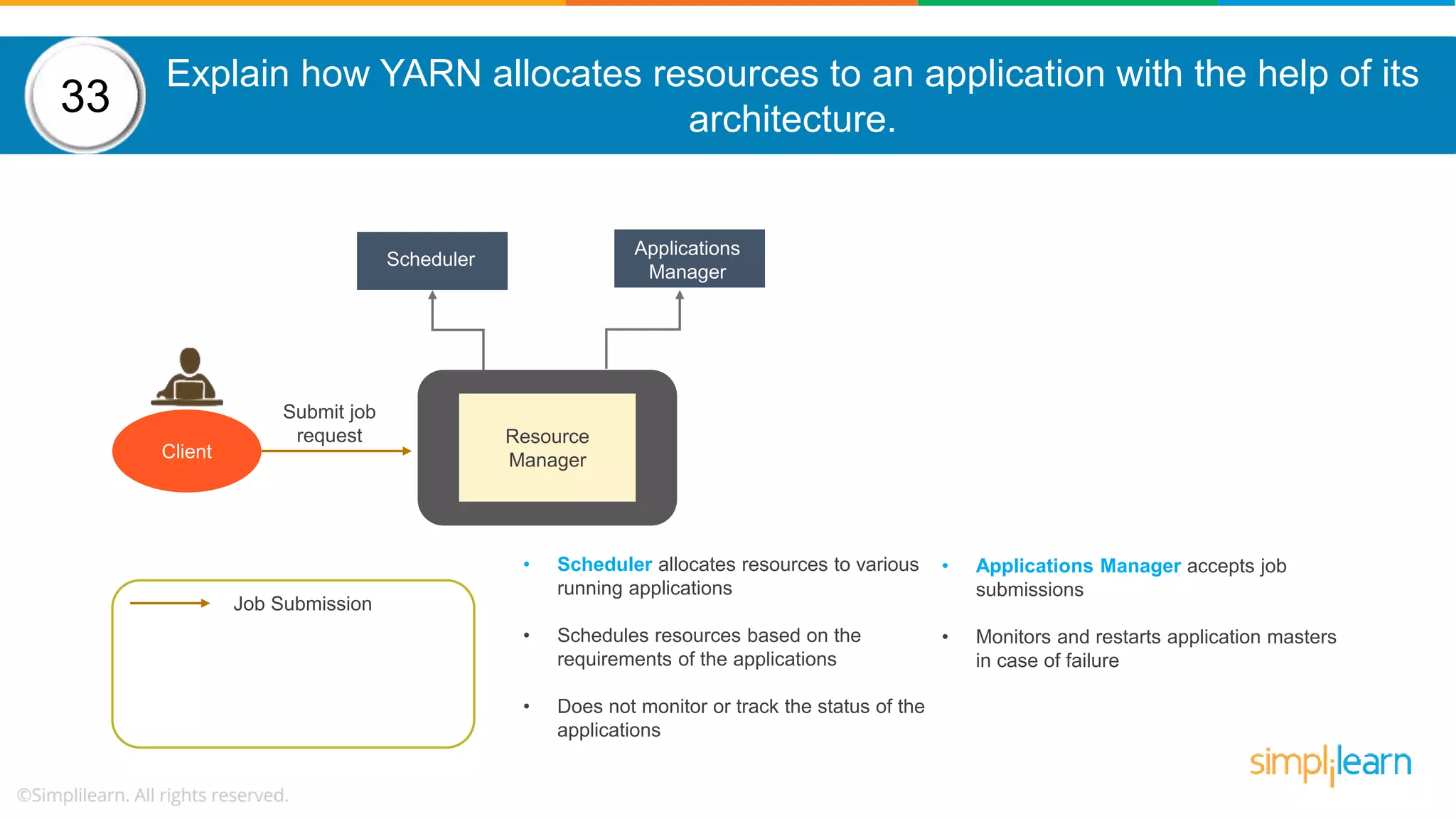
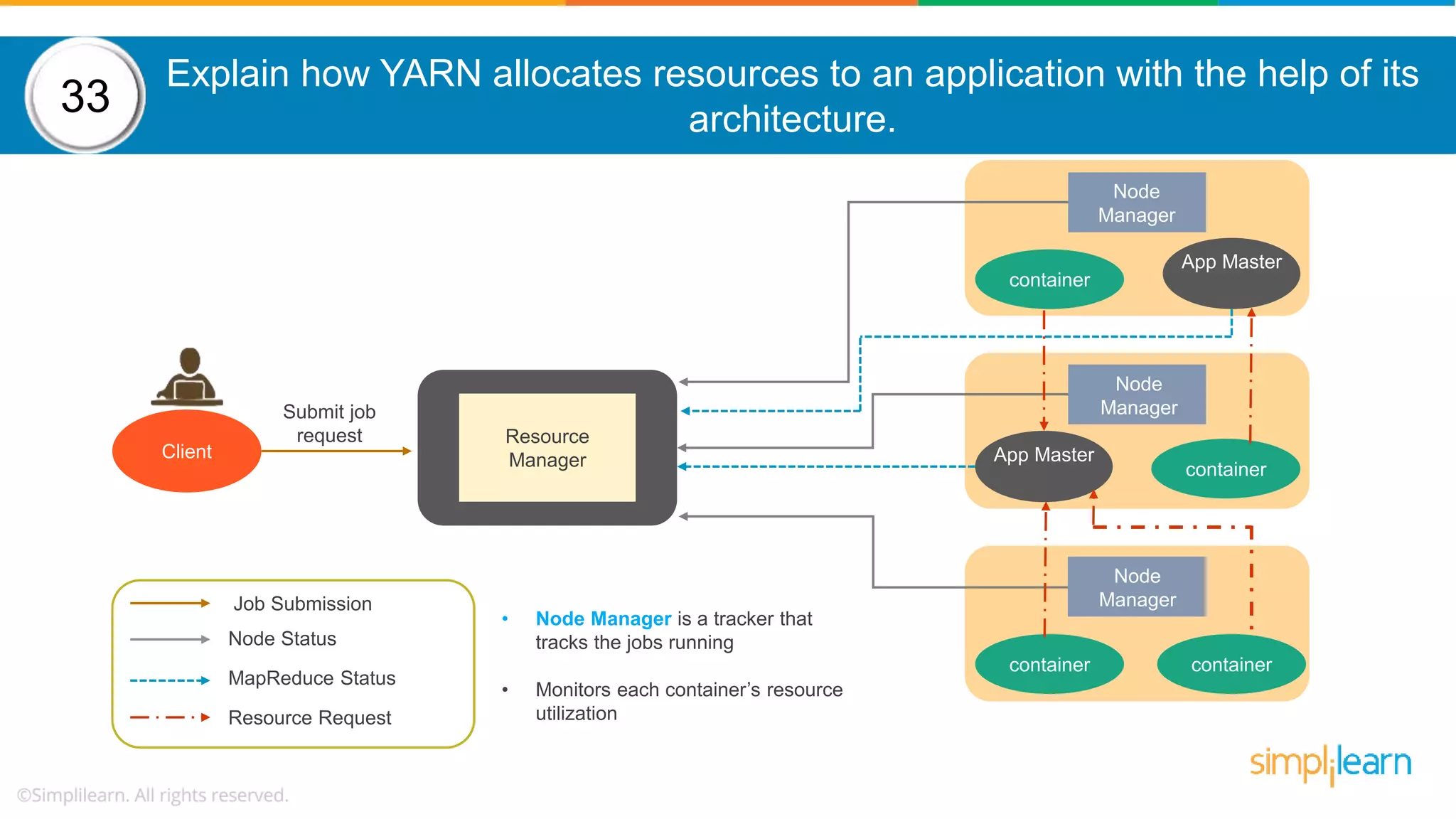
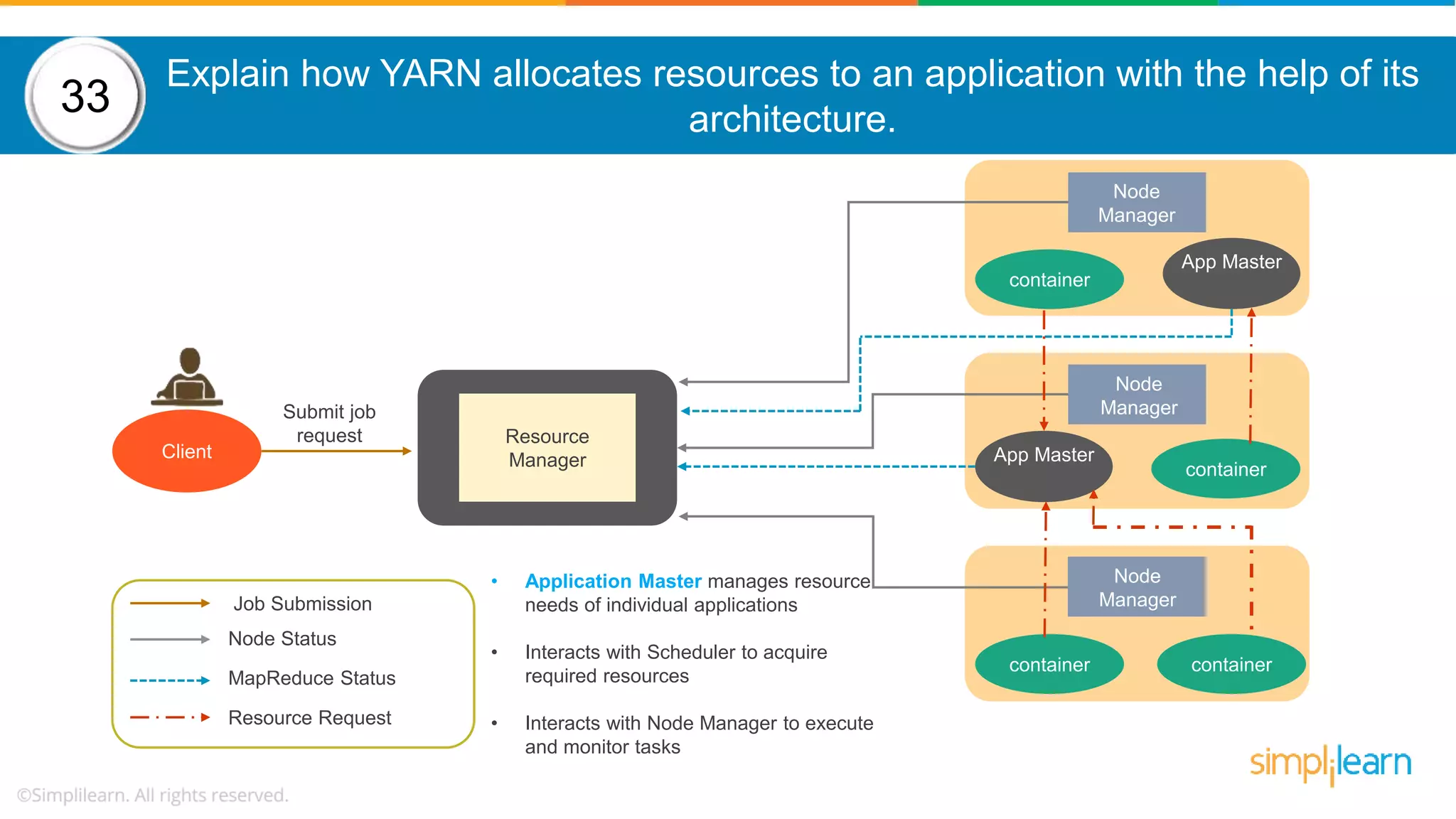
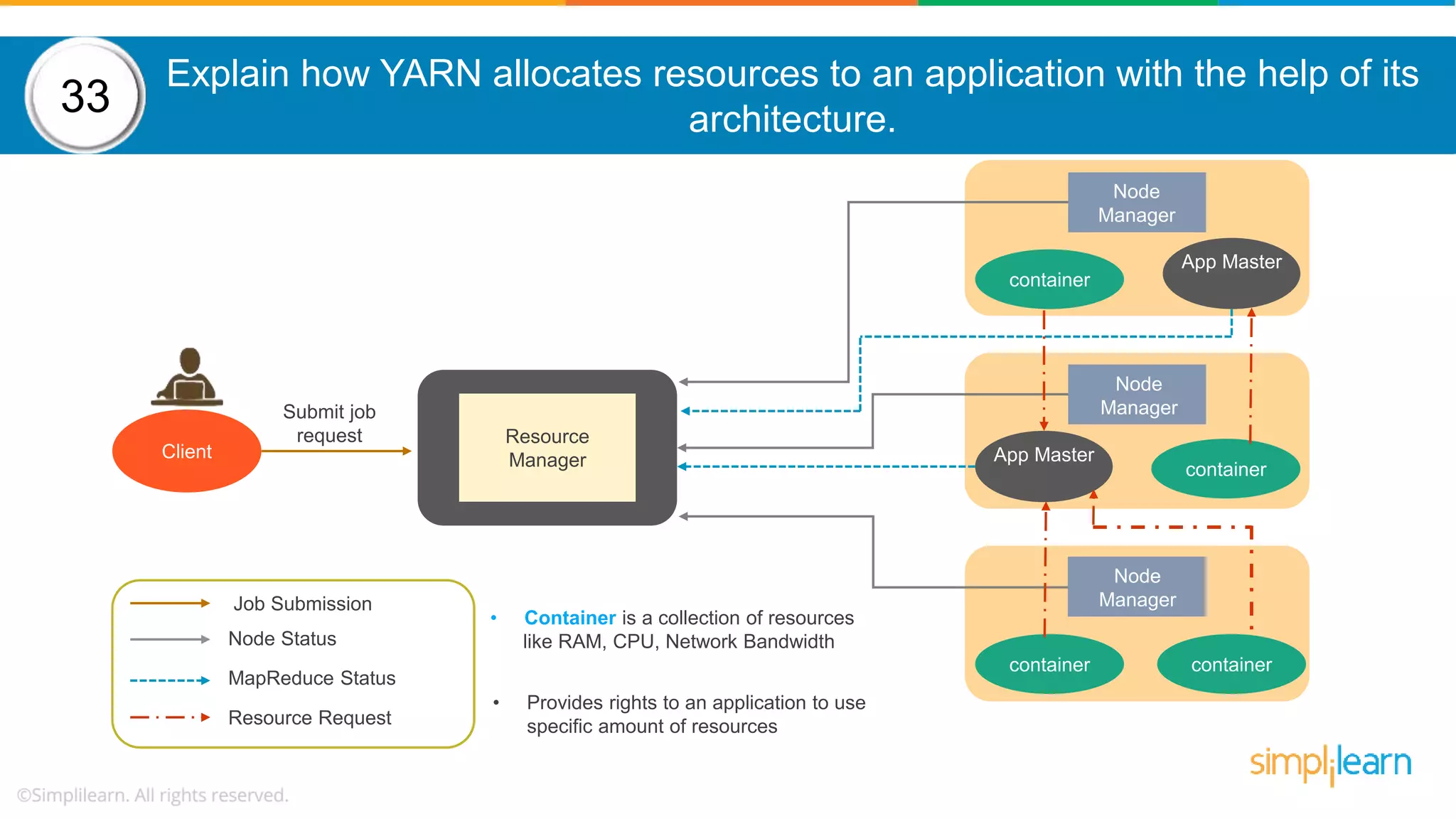
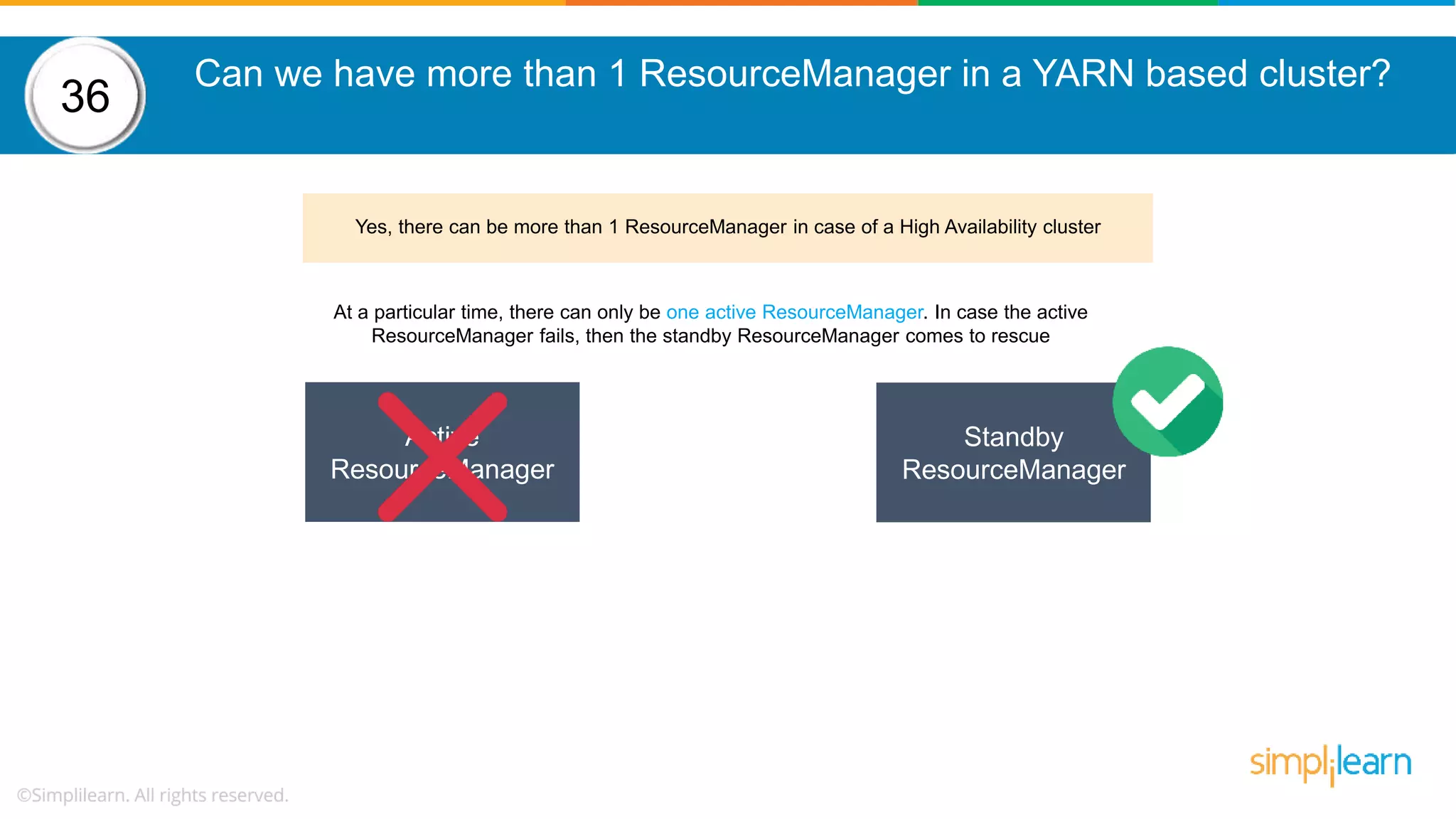
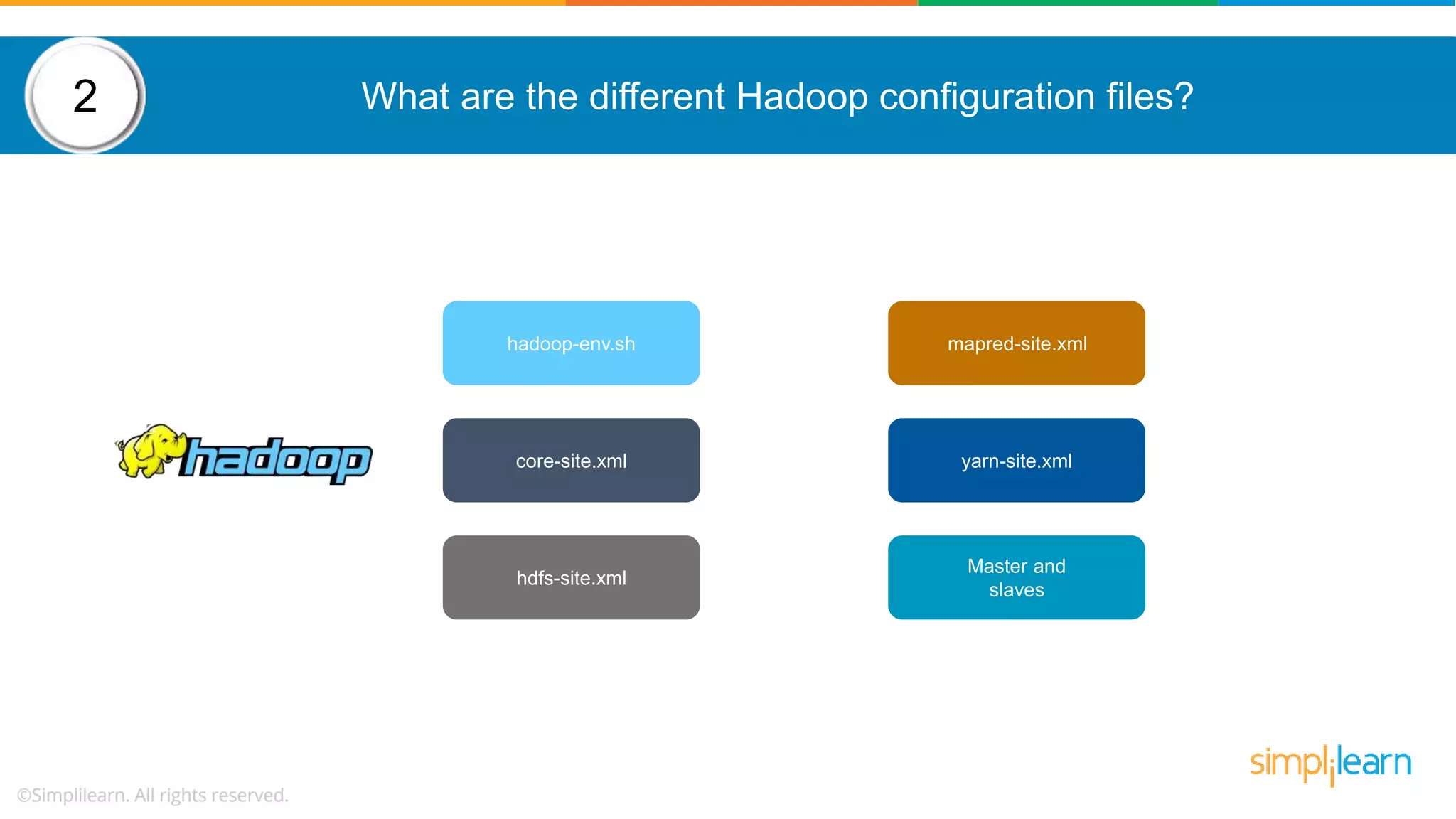
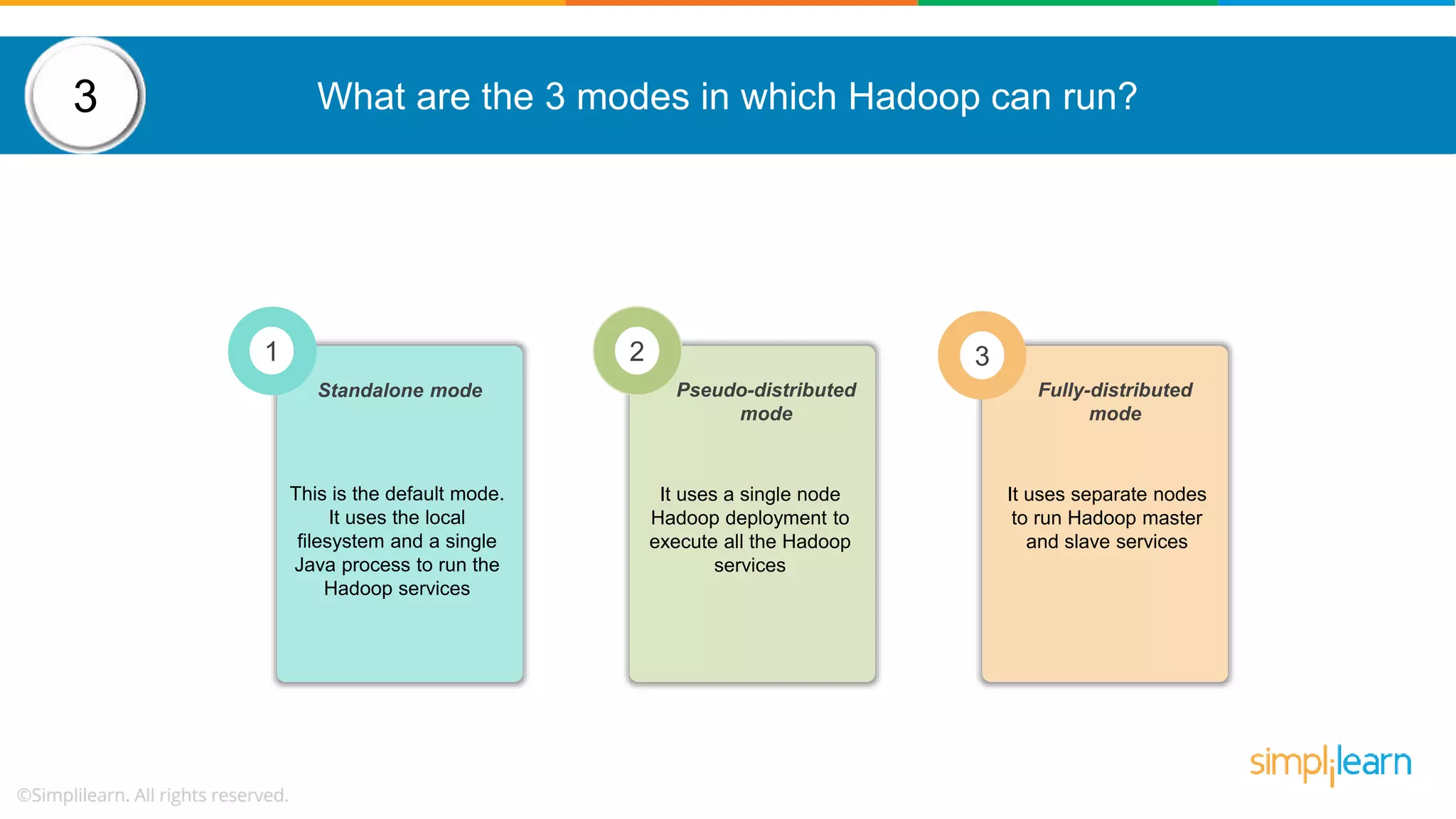
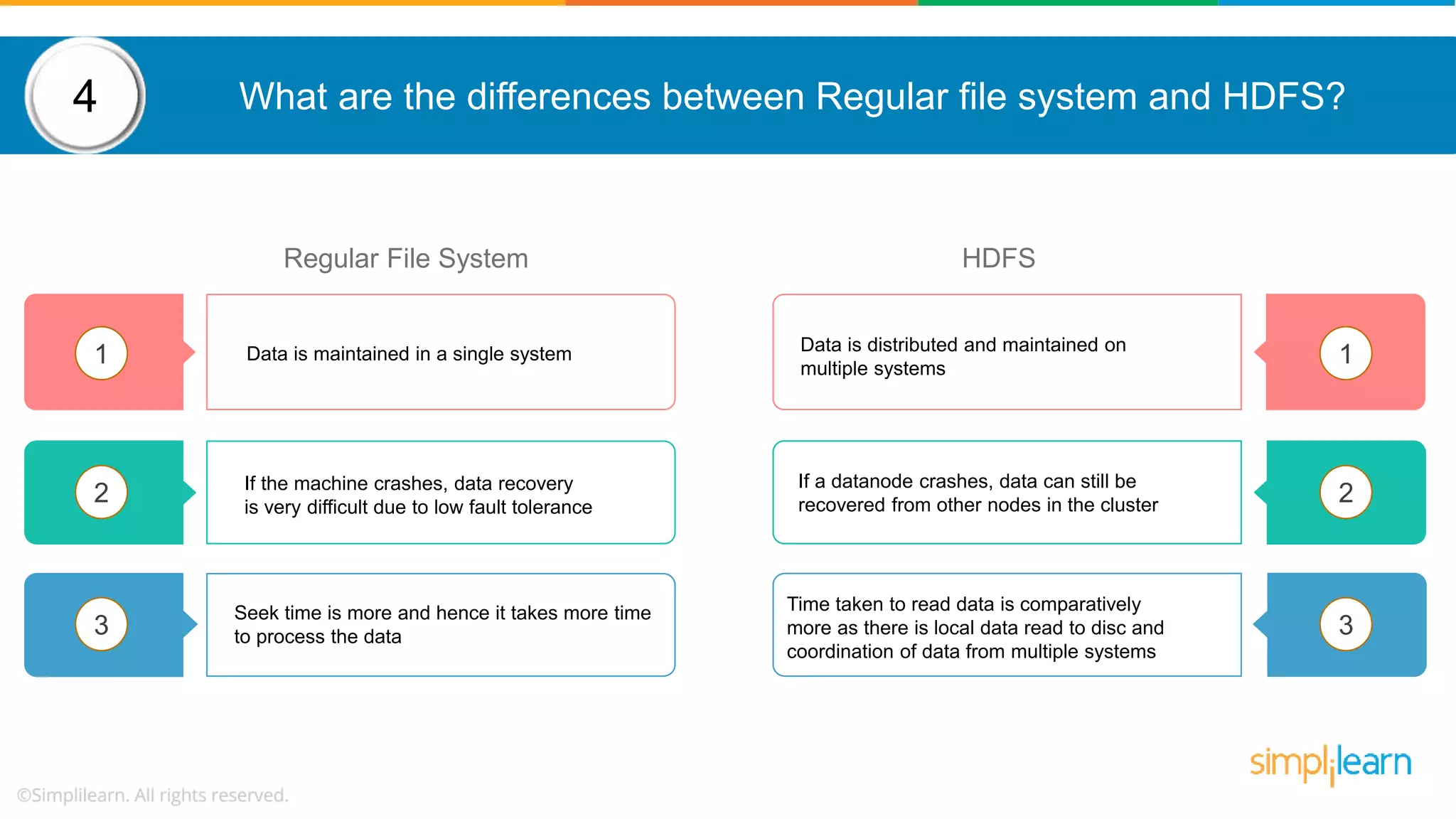
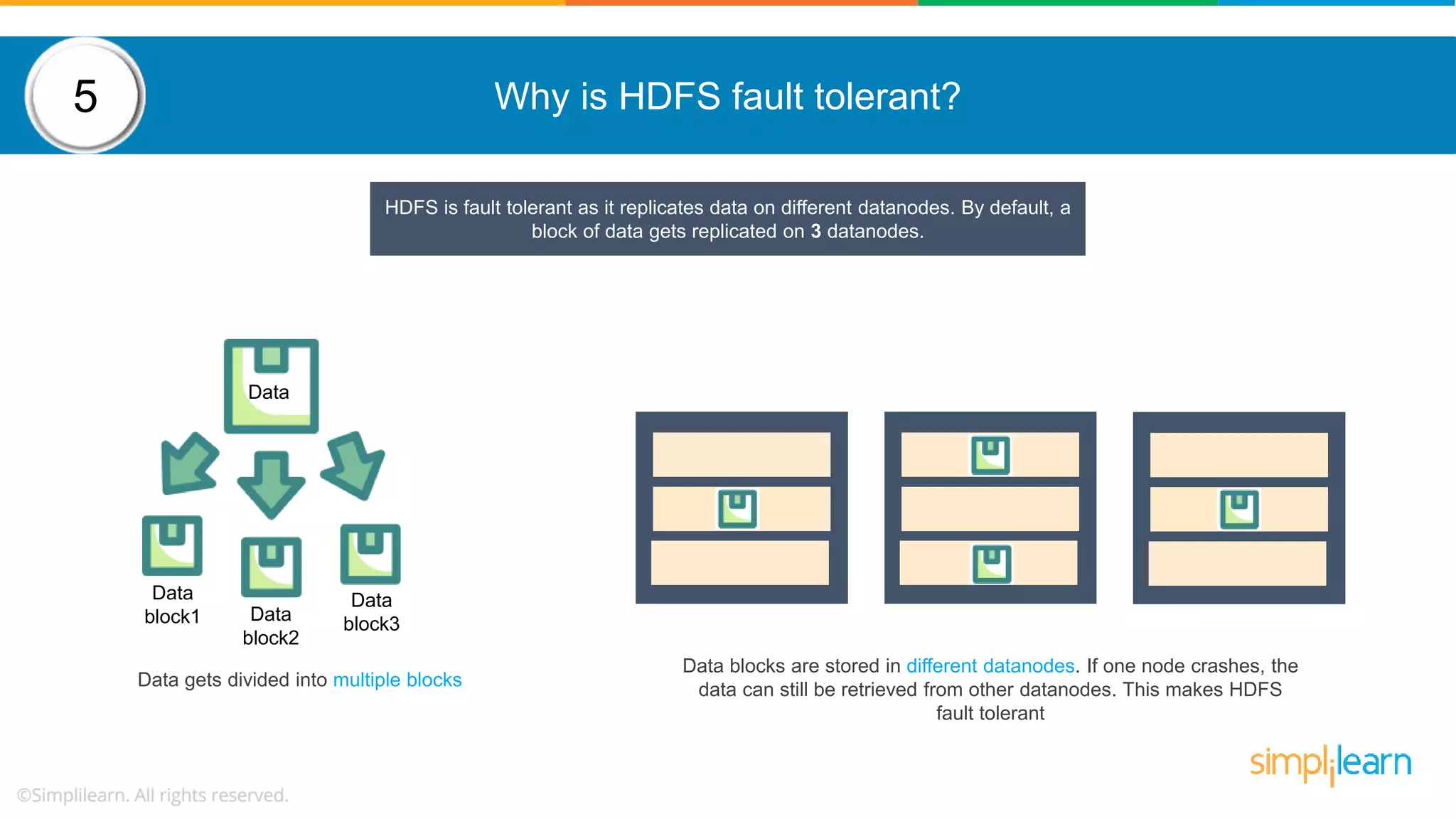
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Hadoop, including its architecture, configuration files, operation modes, and specific components such as HDFS and MapReduce. It addresses questions about data replication, fault tolerance, metadata management, and the roles of various entities in the Hadoop ecosystem. The document also covers practical commands and configurations for managing a Hadoop cluster and utilizing YARN for resource management.




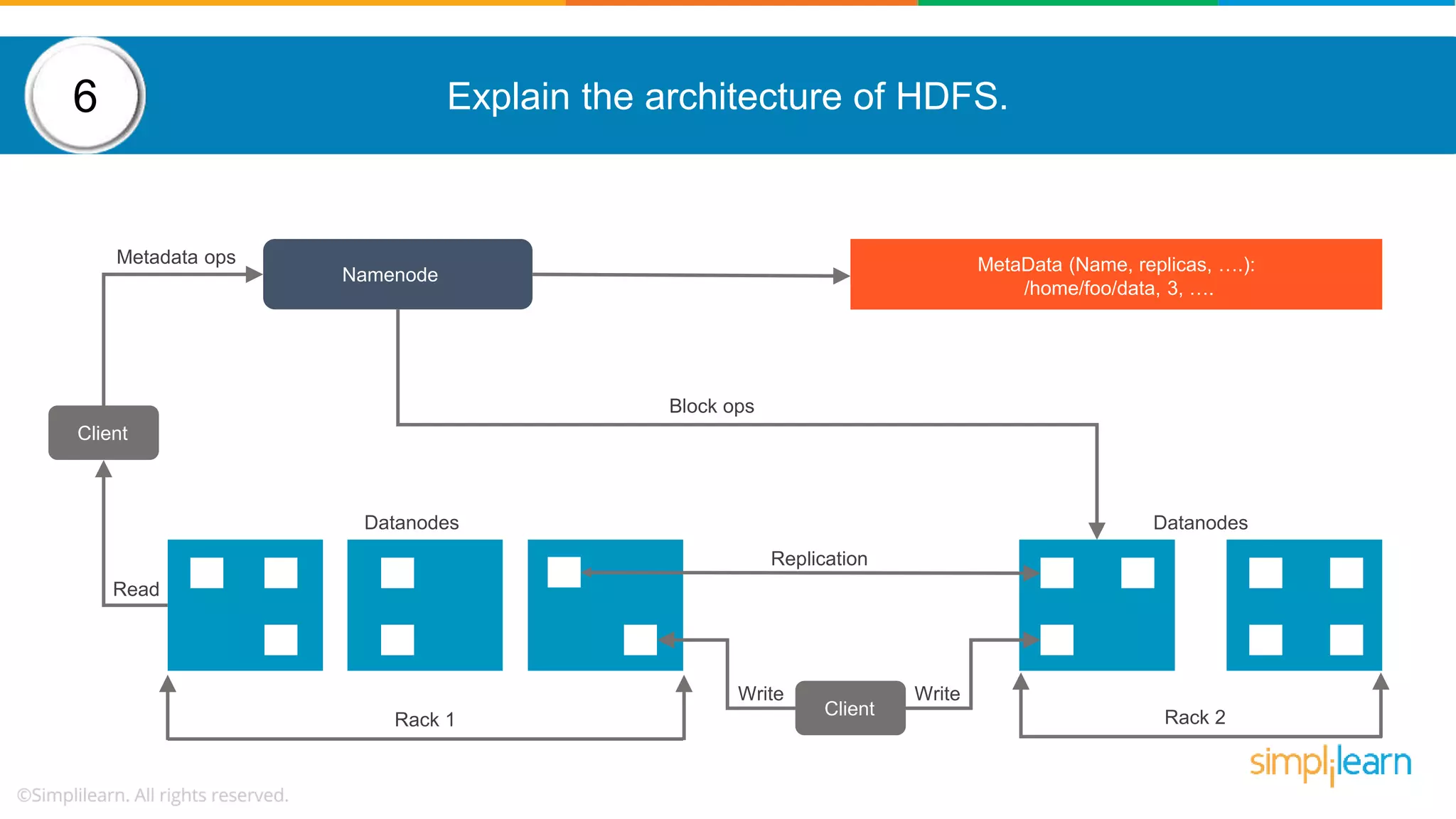
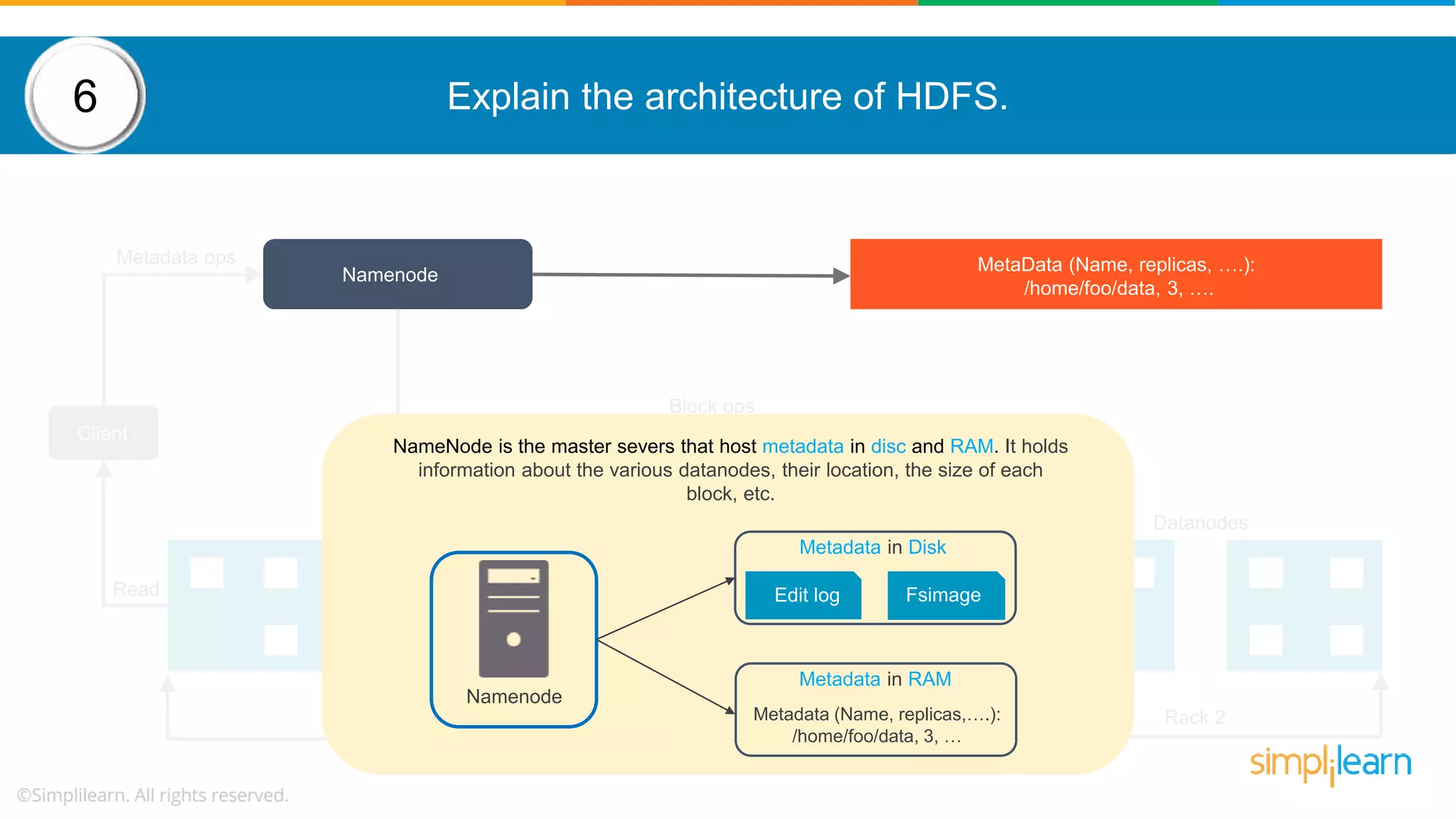
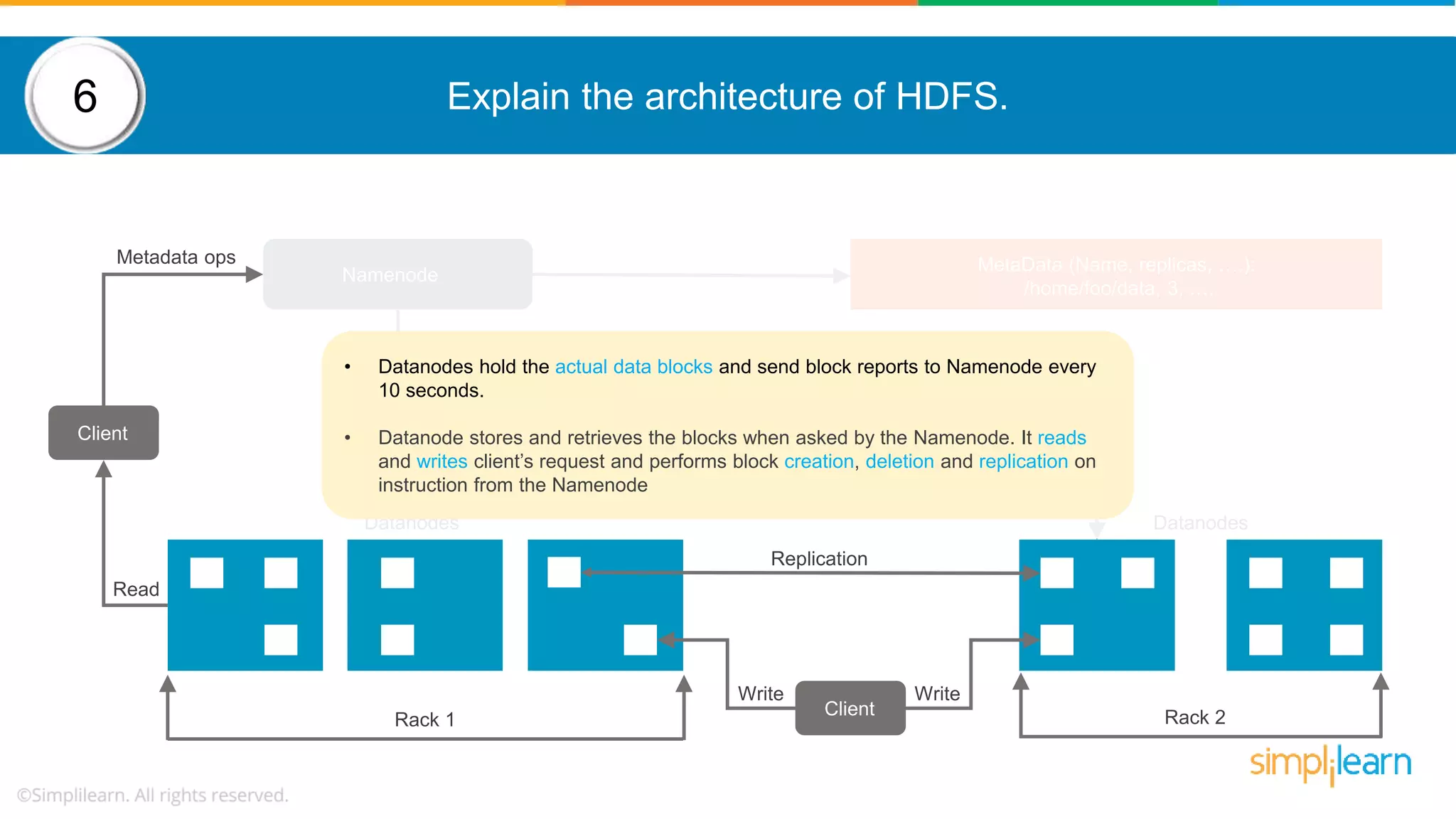
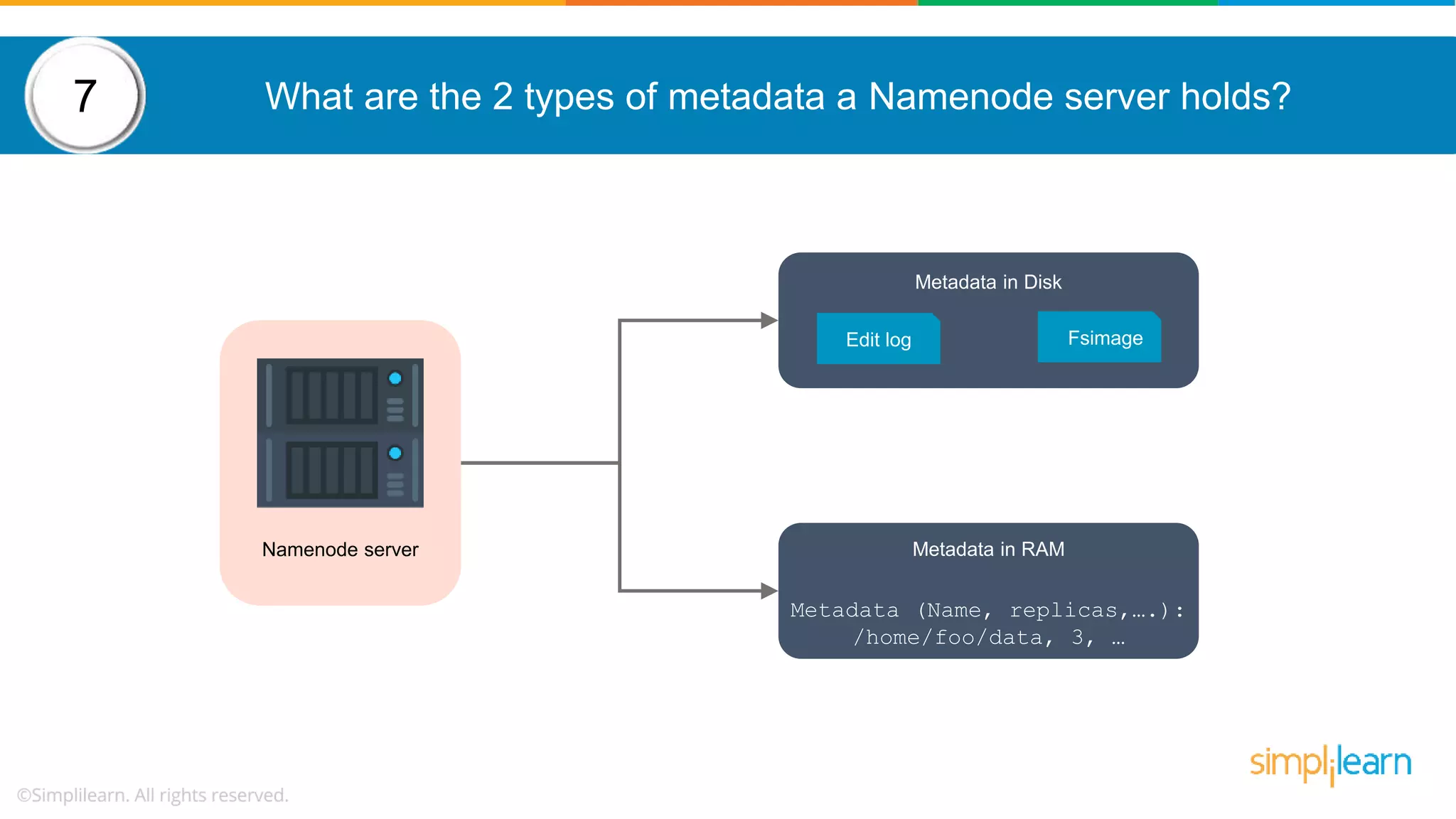



![How to copy data from local system on to HDFS? Following command helps to copy data from local file system into HDFS: hadoop fs –copyFromLocal [source] [destination] Example: hadoop fs –copyFromLocal /tmp/data.csv /user/test/data.csv 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hadoopinterviewquestions-part1-190531091226/75/Hadoop-Interview-Questions-And-Answers-Part-1-Big-Data-Interview-Questions-Answers-Simplilearn-22-2048.jpg)