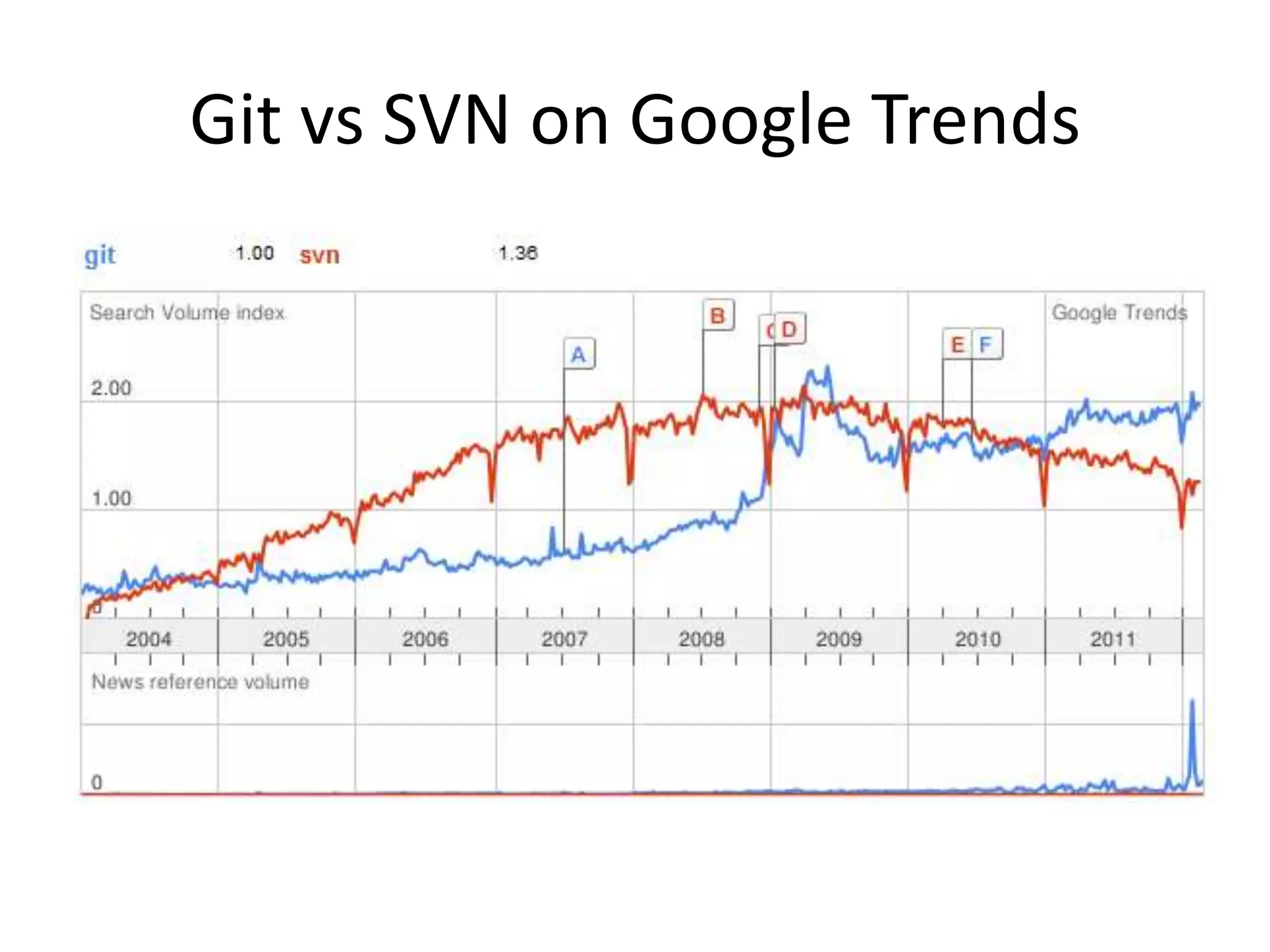
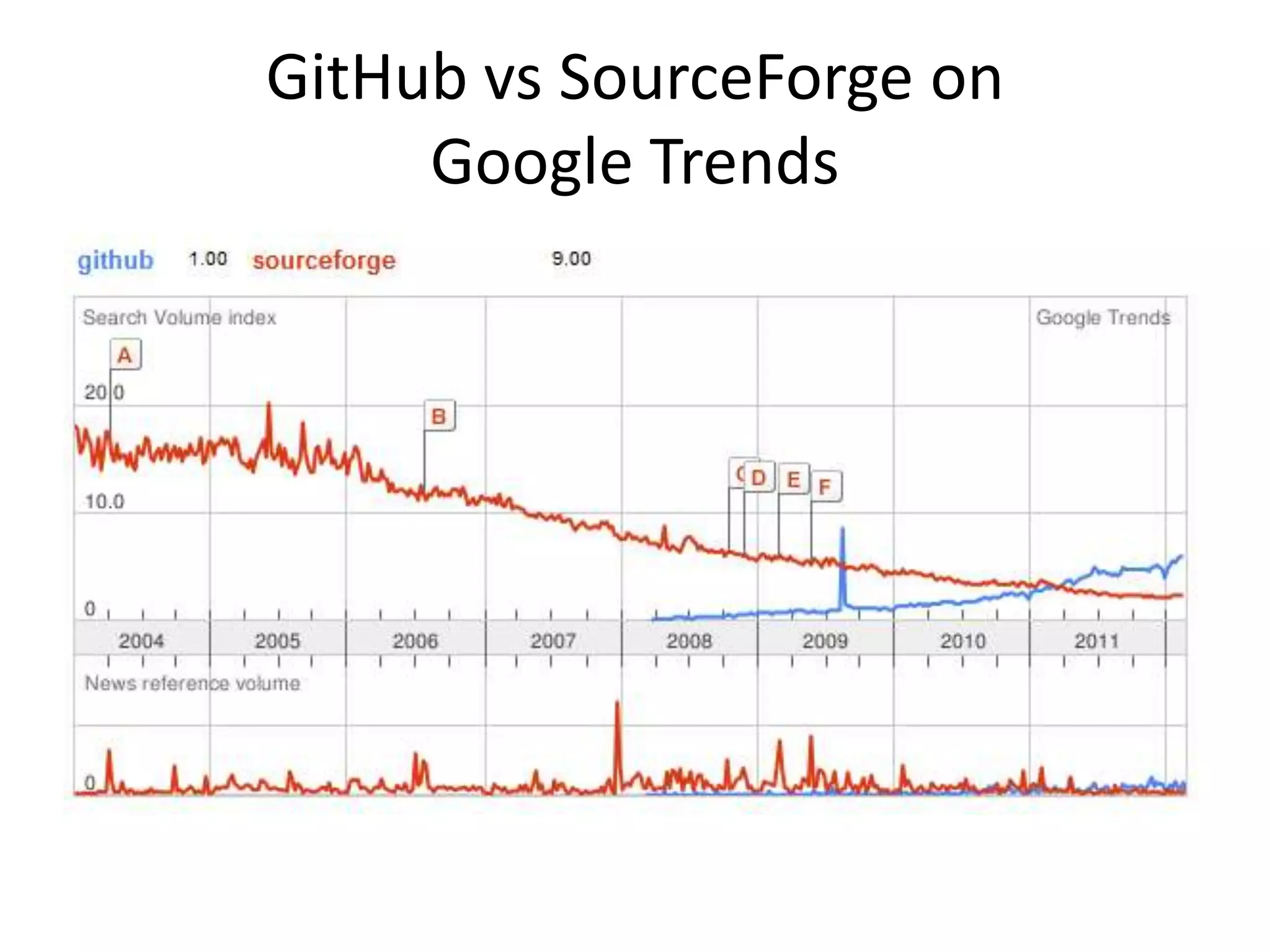
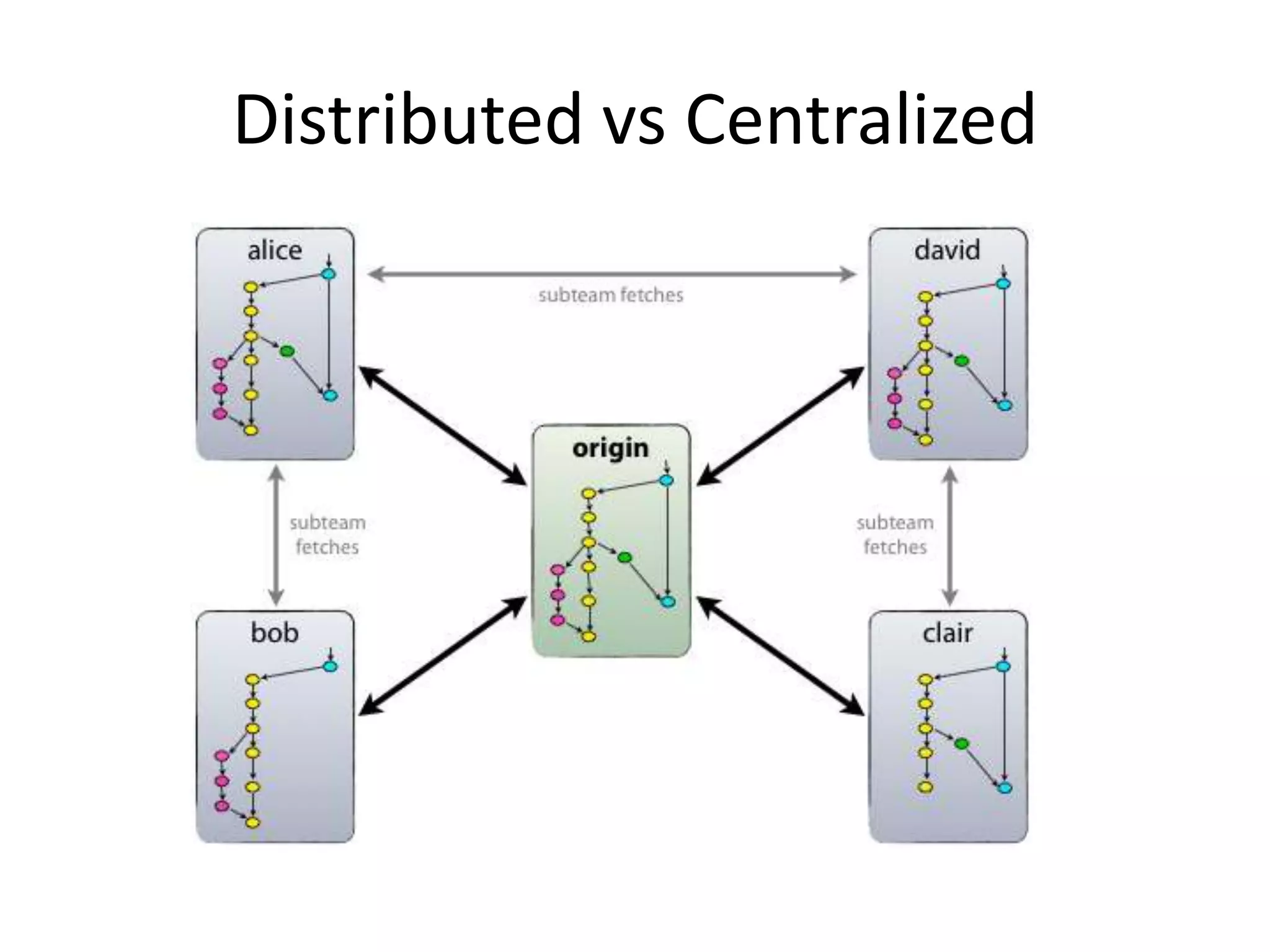
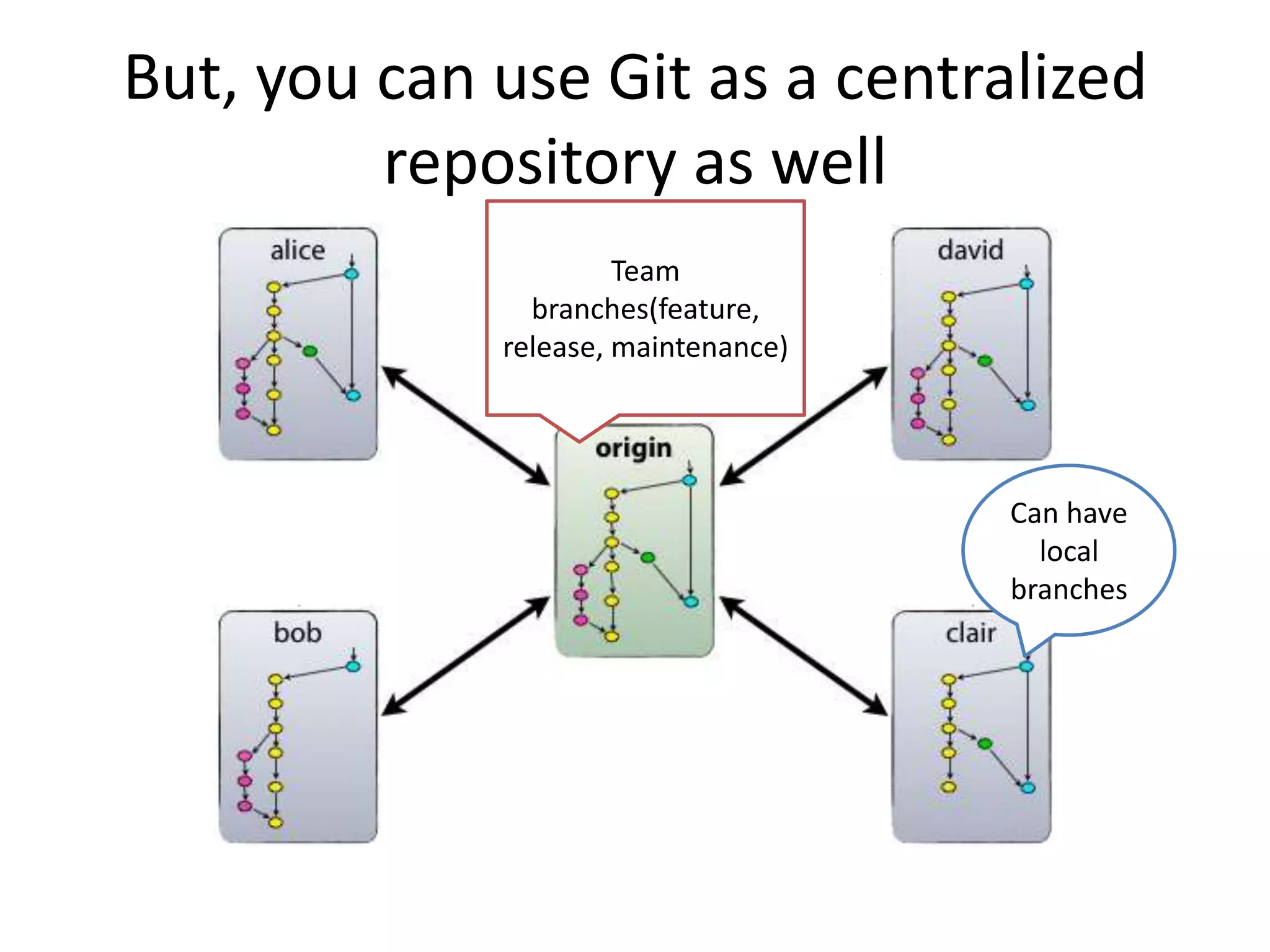
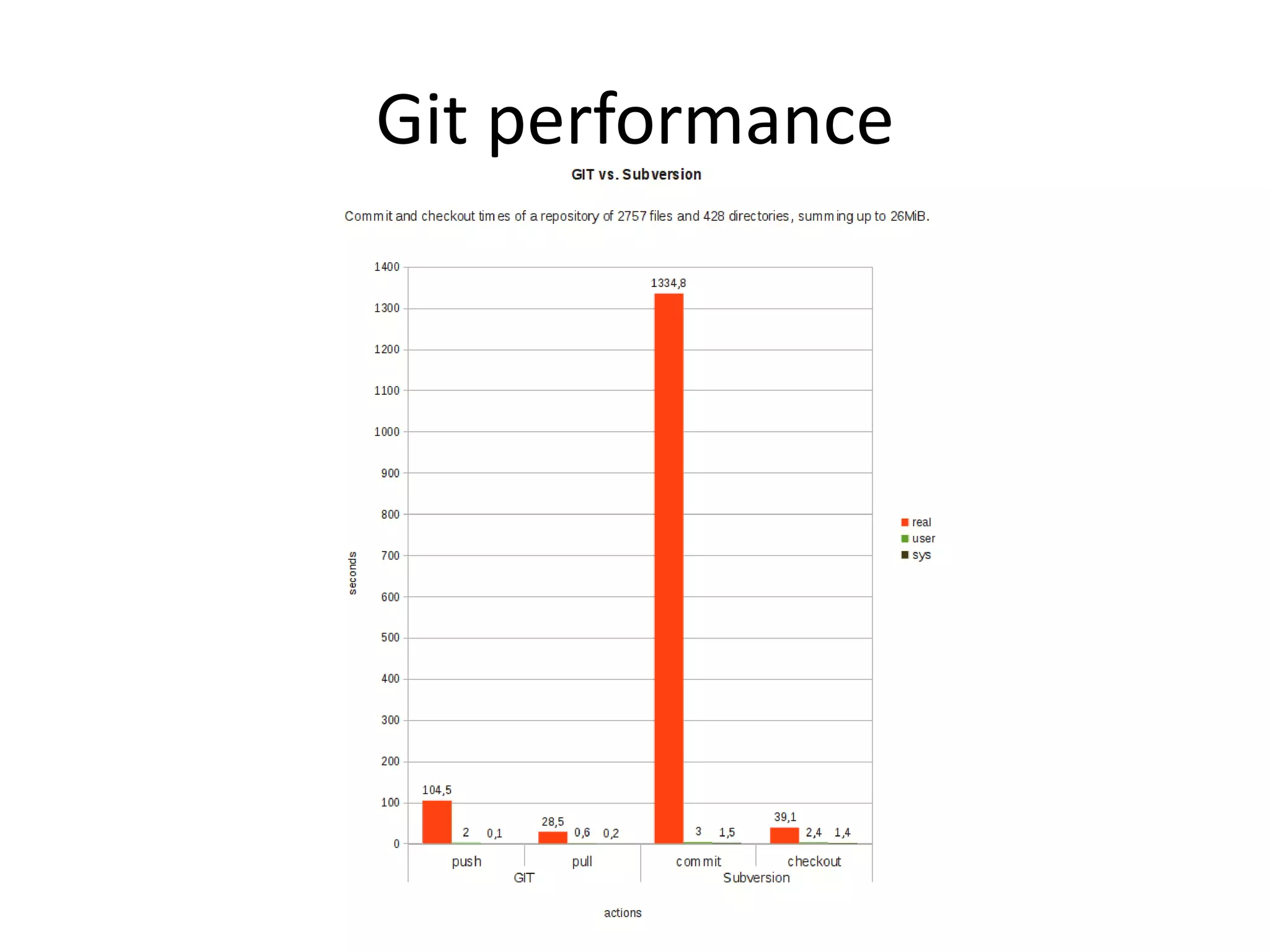
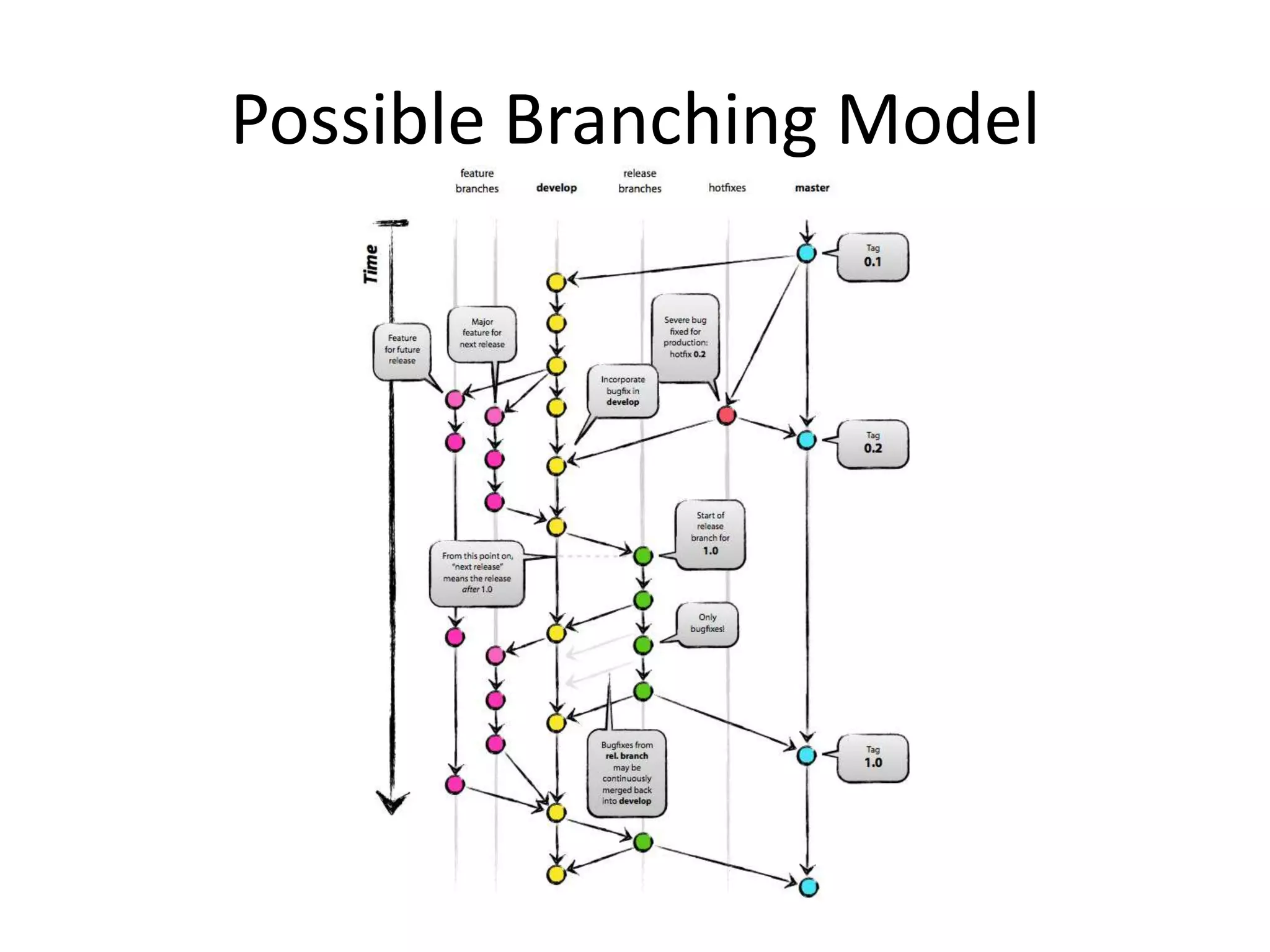
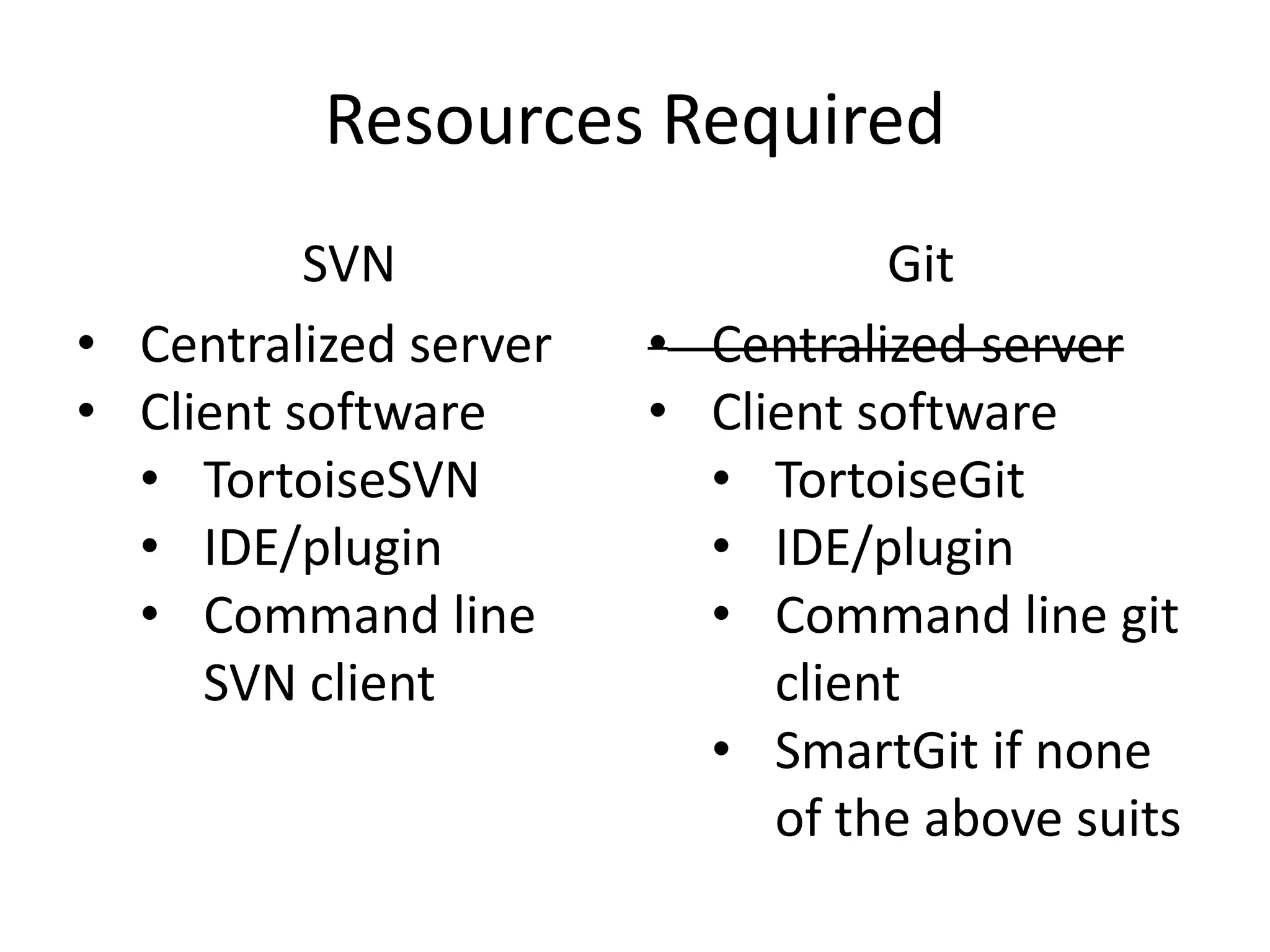
Git is a widely used distributed version control system that provides several advantages over centralized systems like SVN. It allows for distributed, offline development and easy branching and merging of code. Some key benefits include faster cloning and committing, smaller repository sizes, and easier integration of changes from multiple developers. While it has a steeper learning curve initially, Git usage is growing rapidly as more projects adopt it for version control.