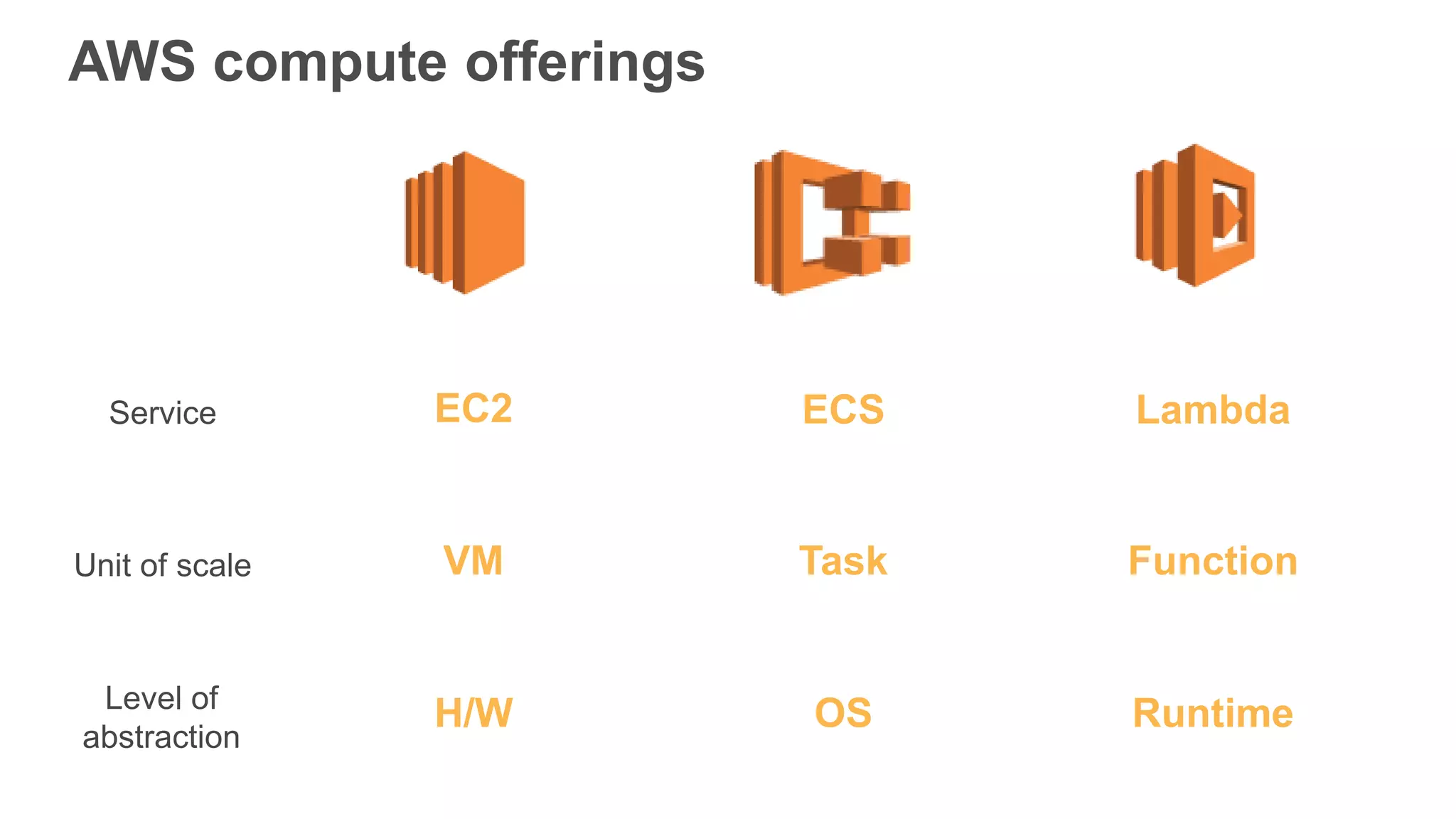
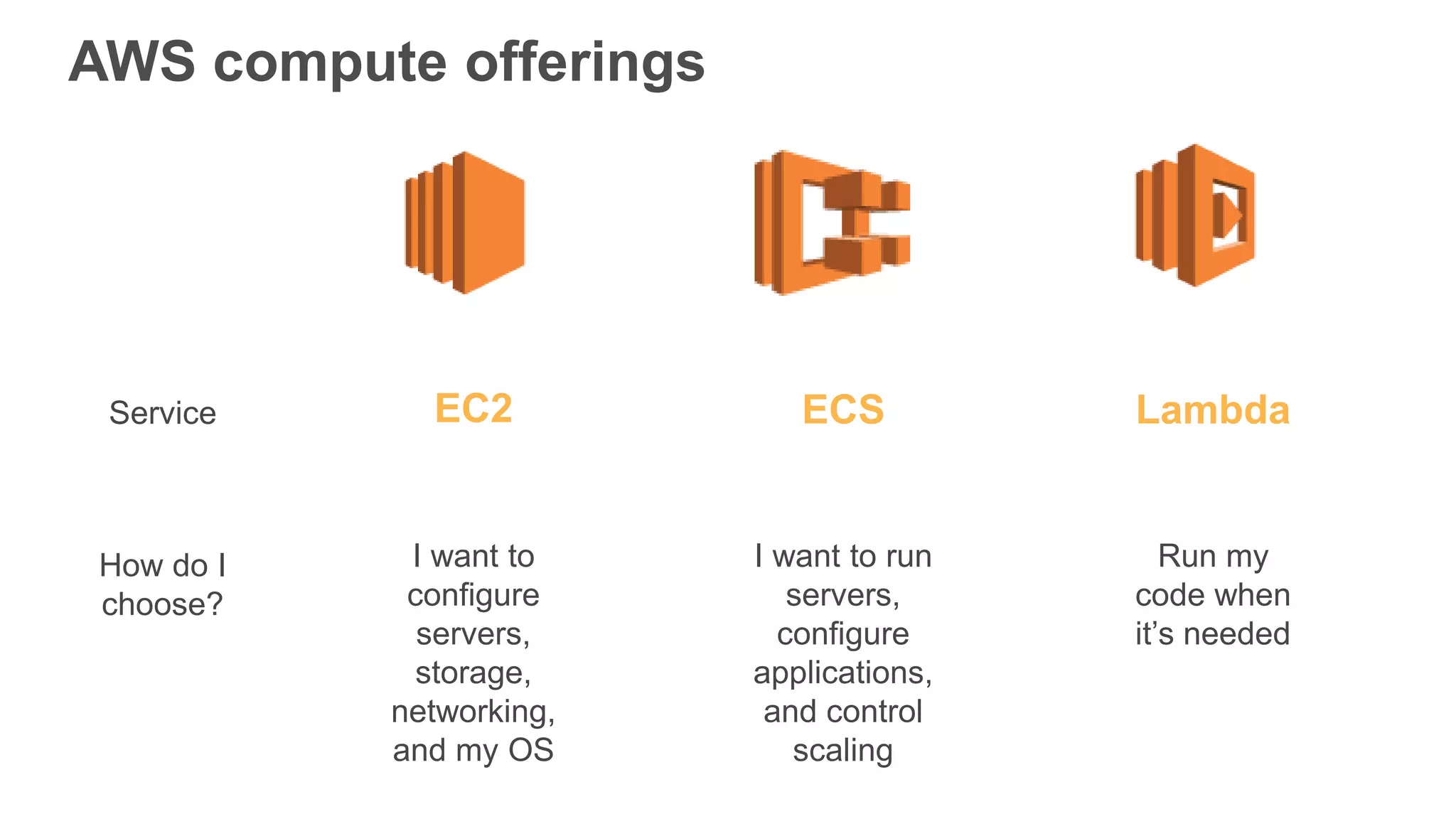
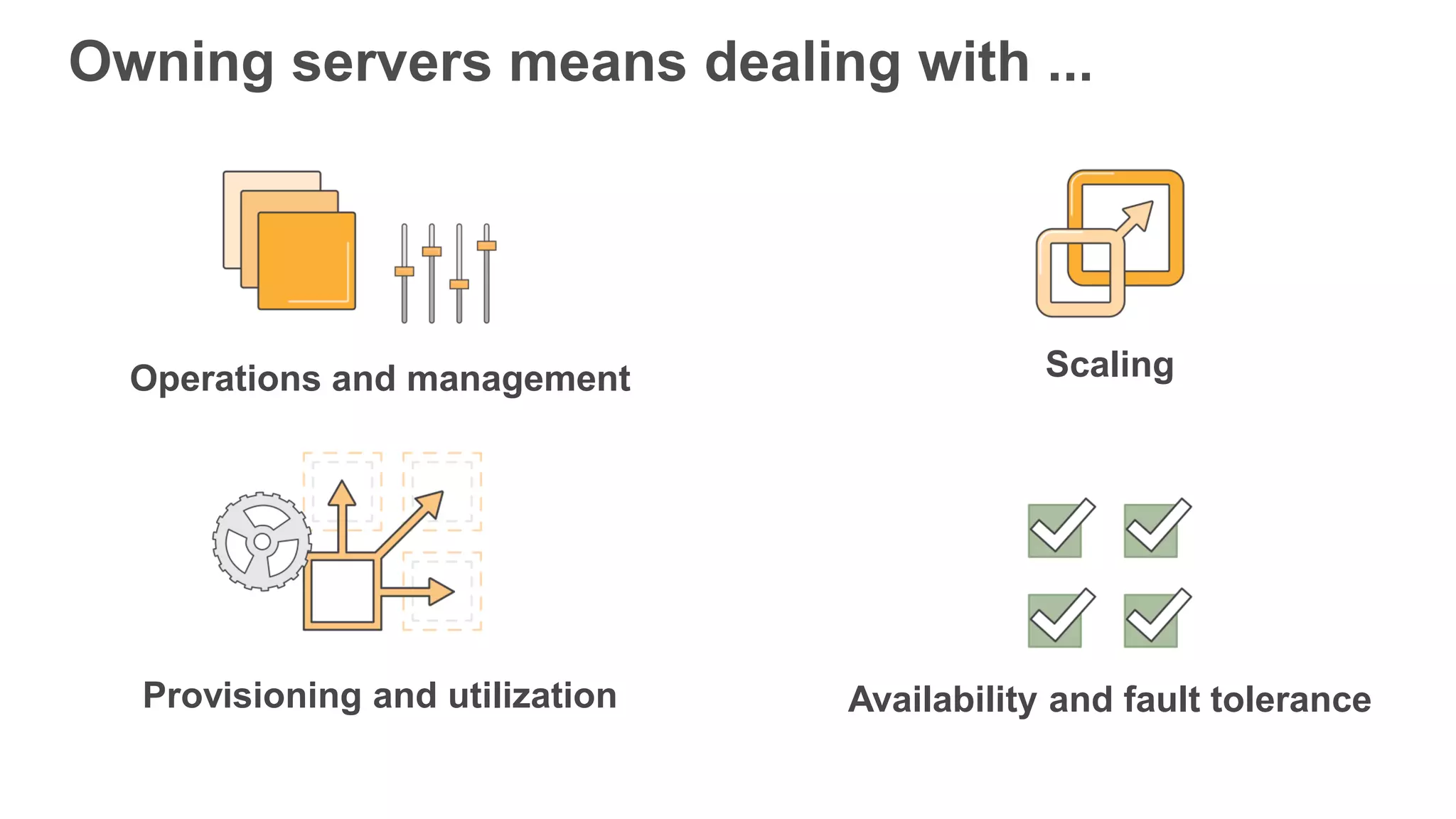
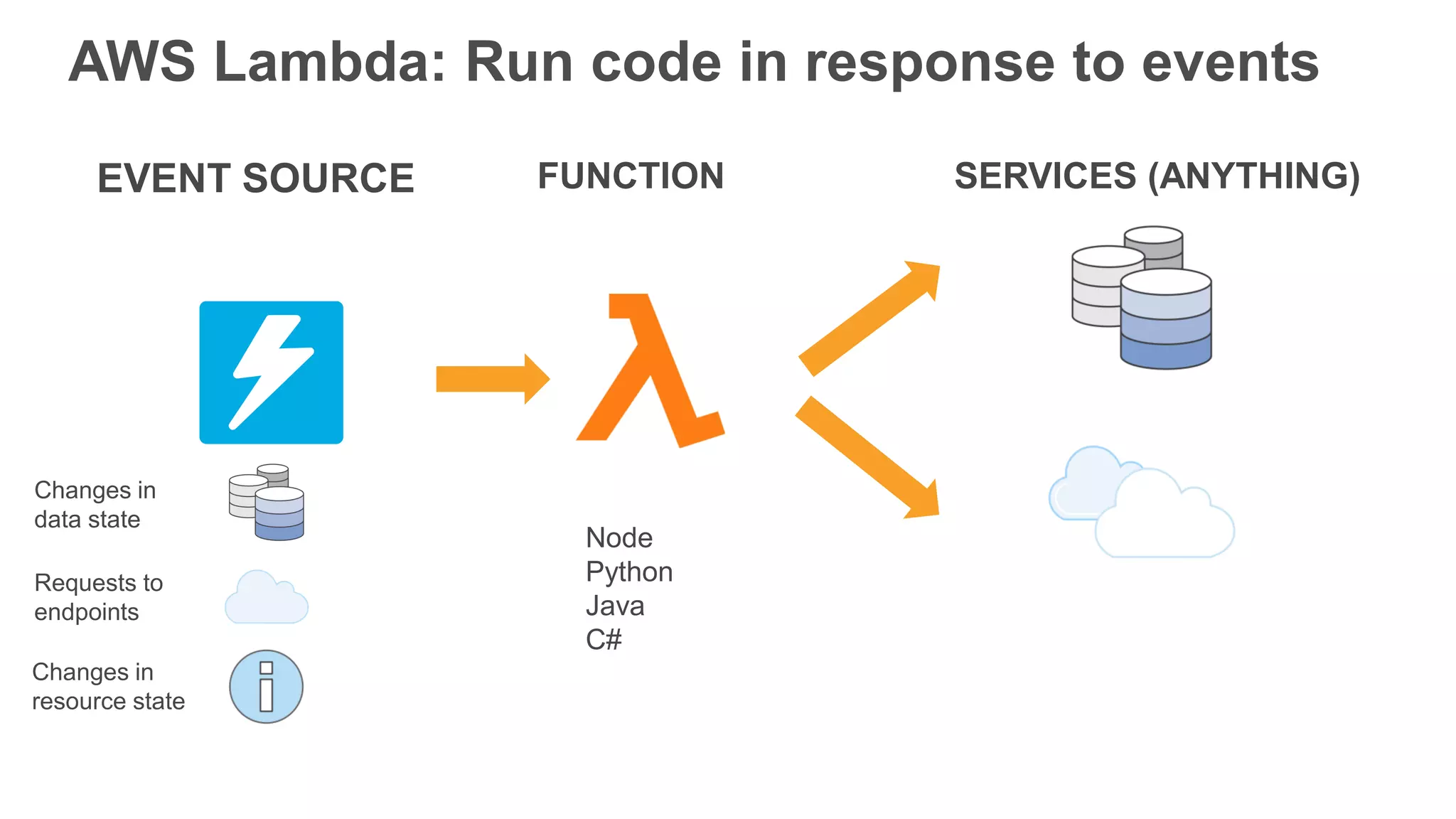
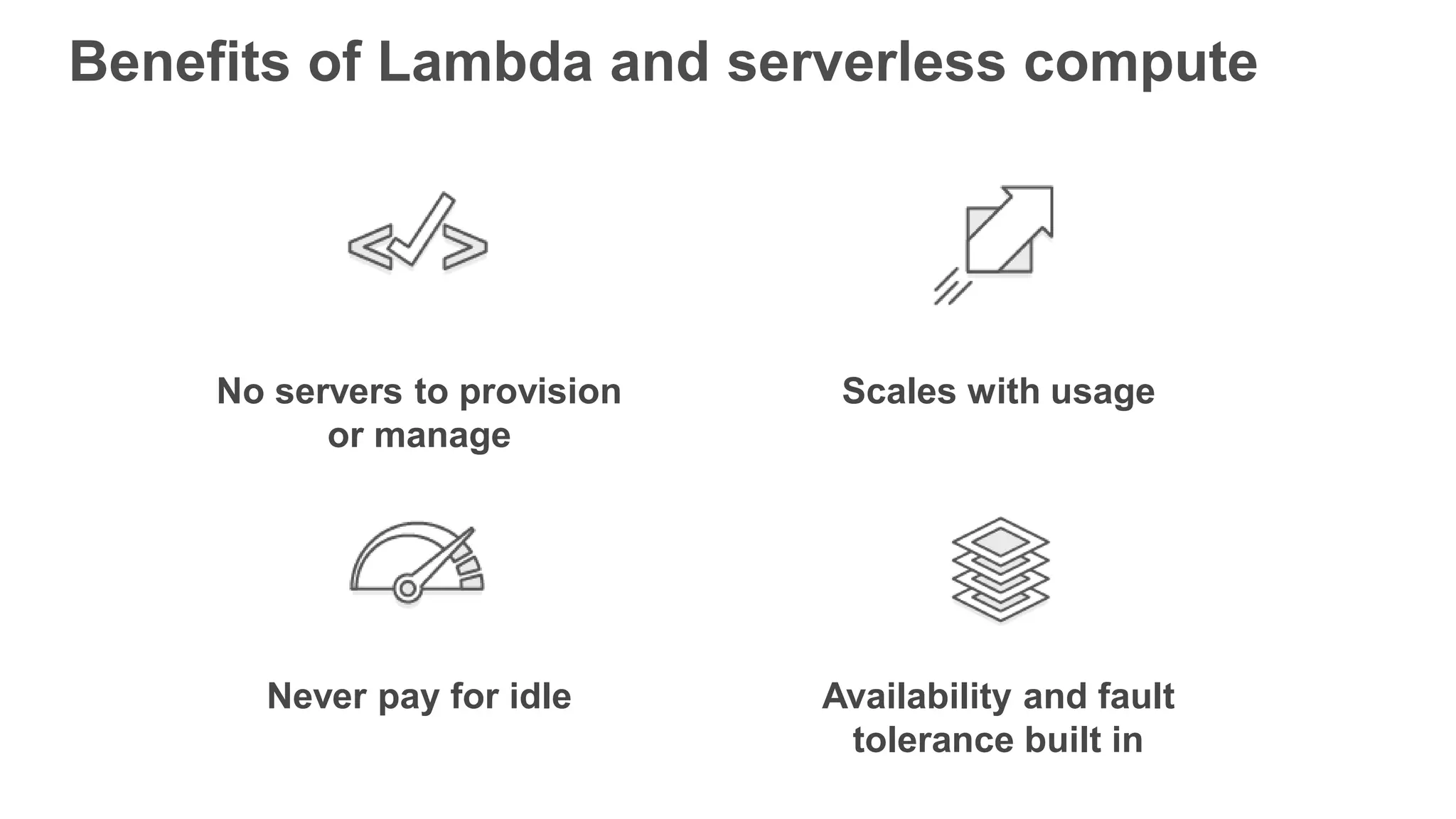
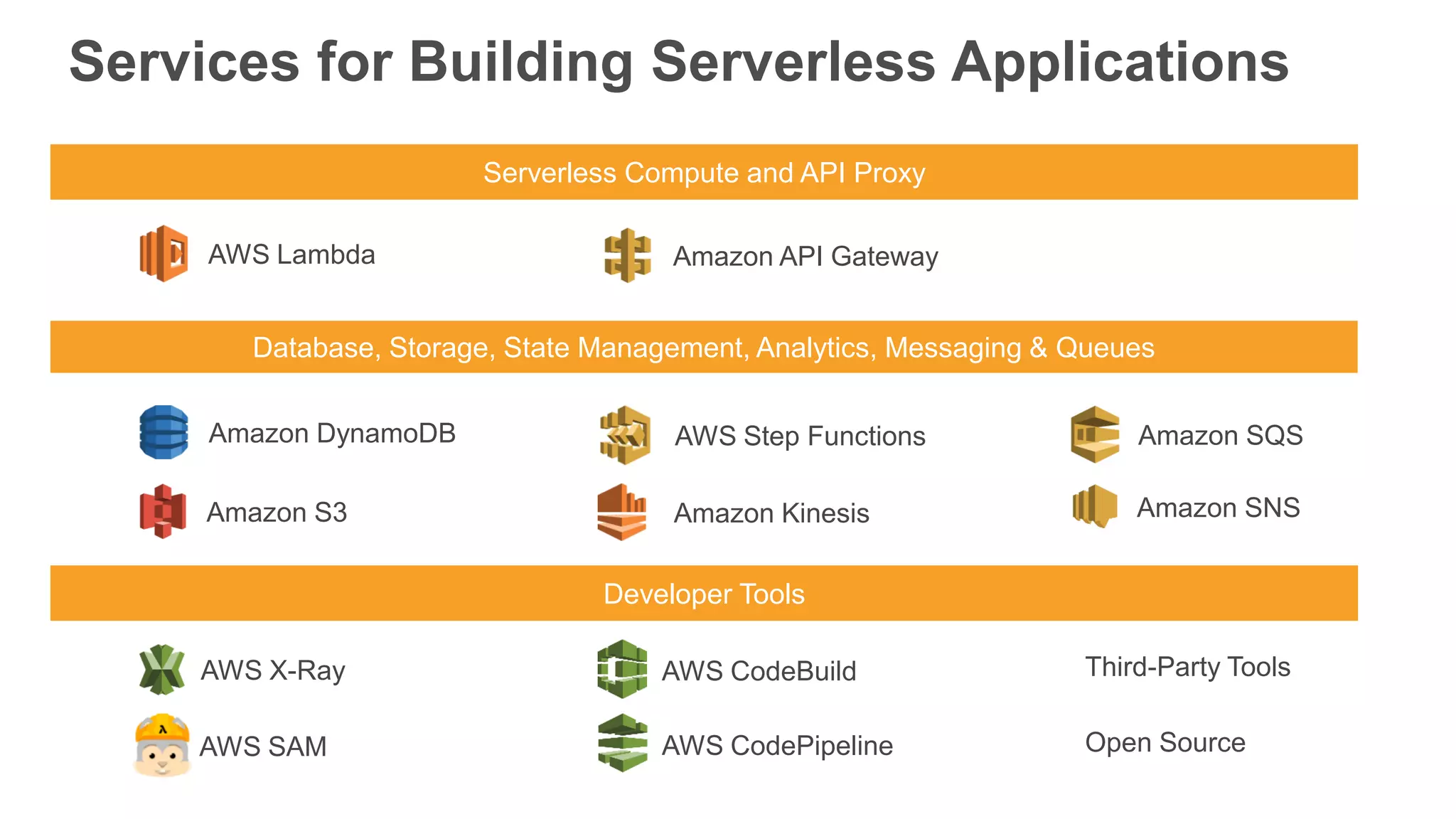
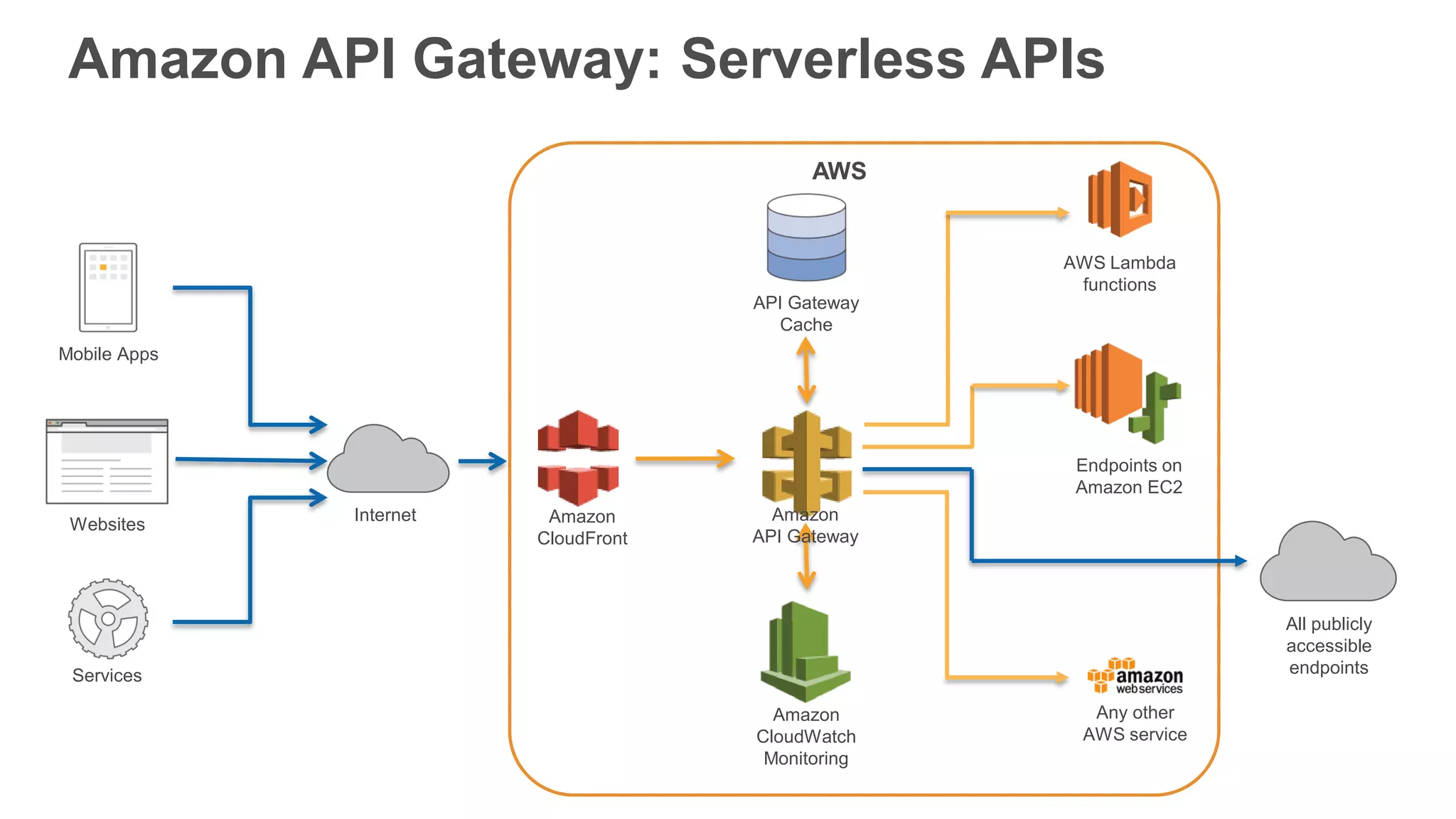
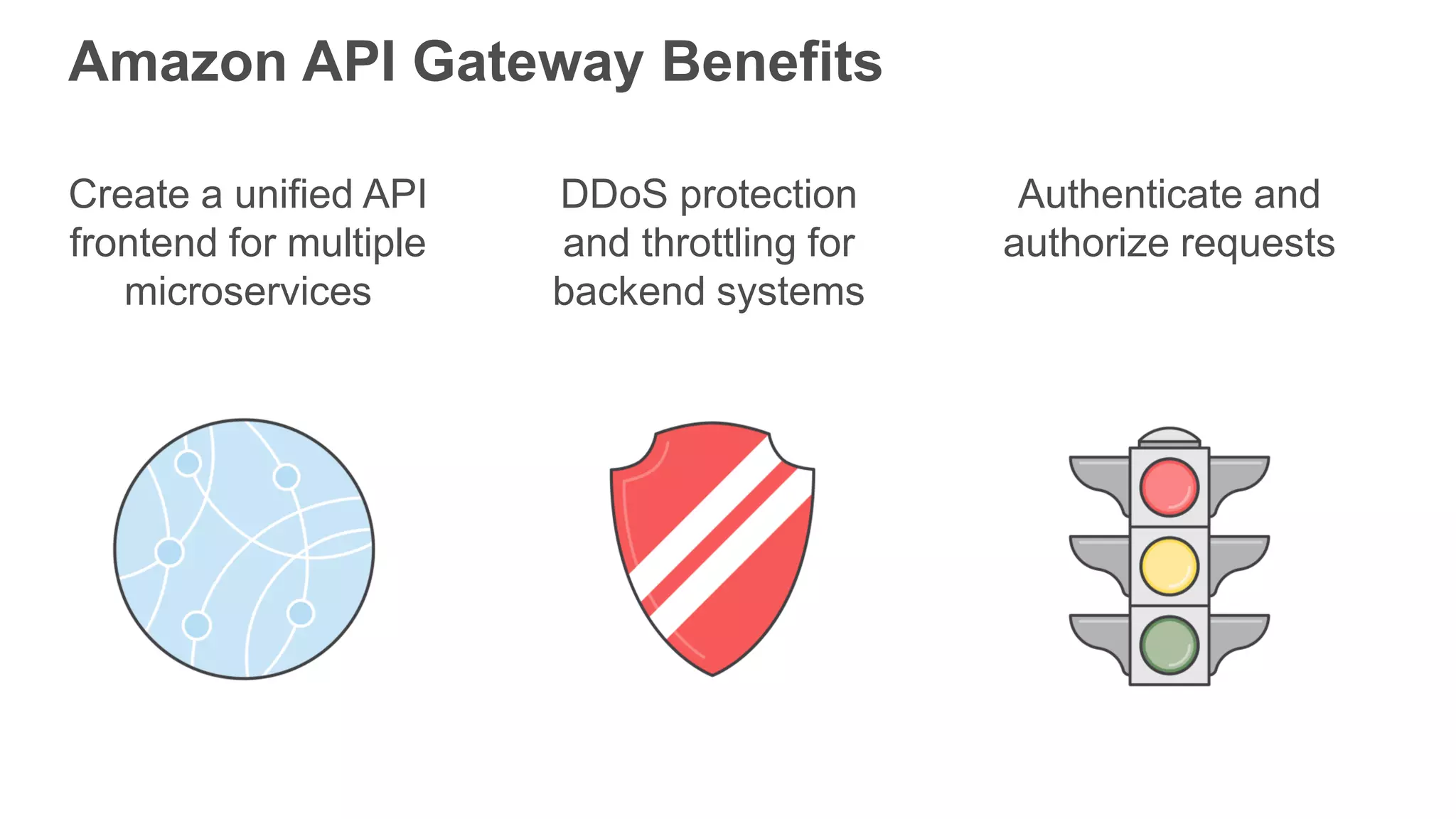
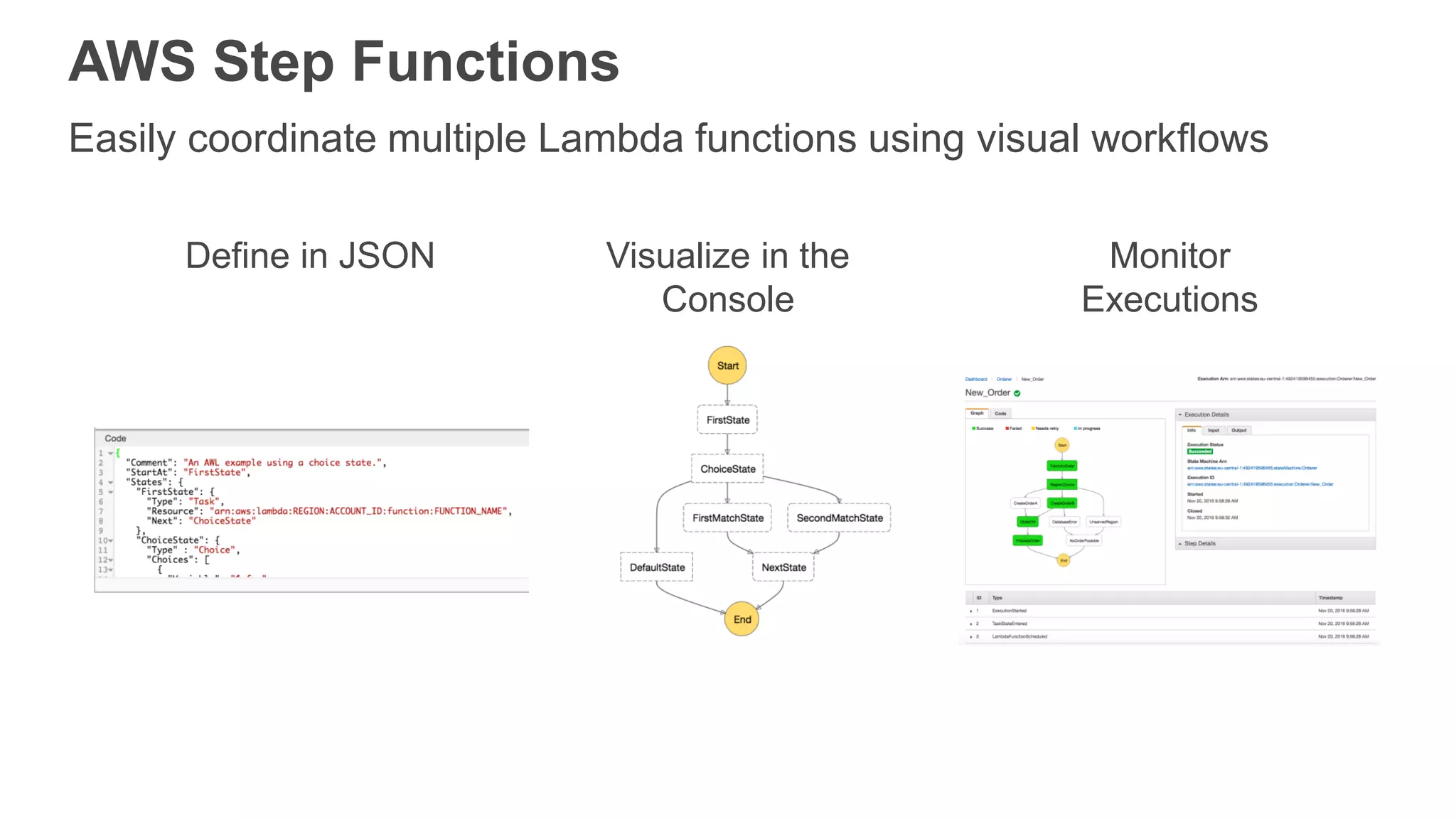
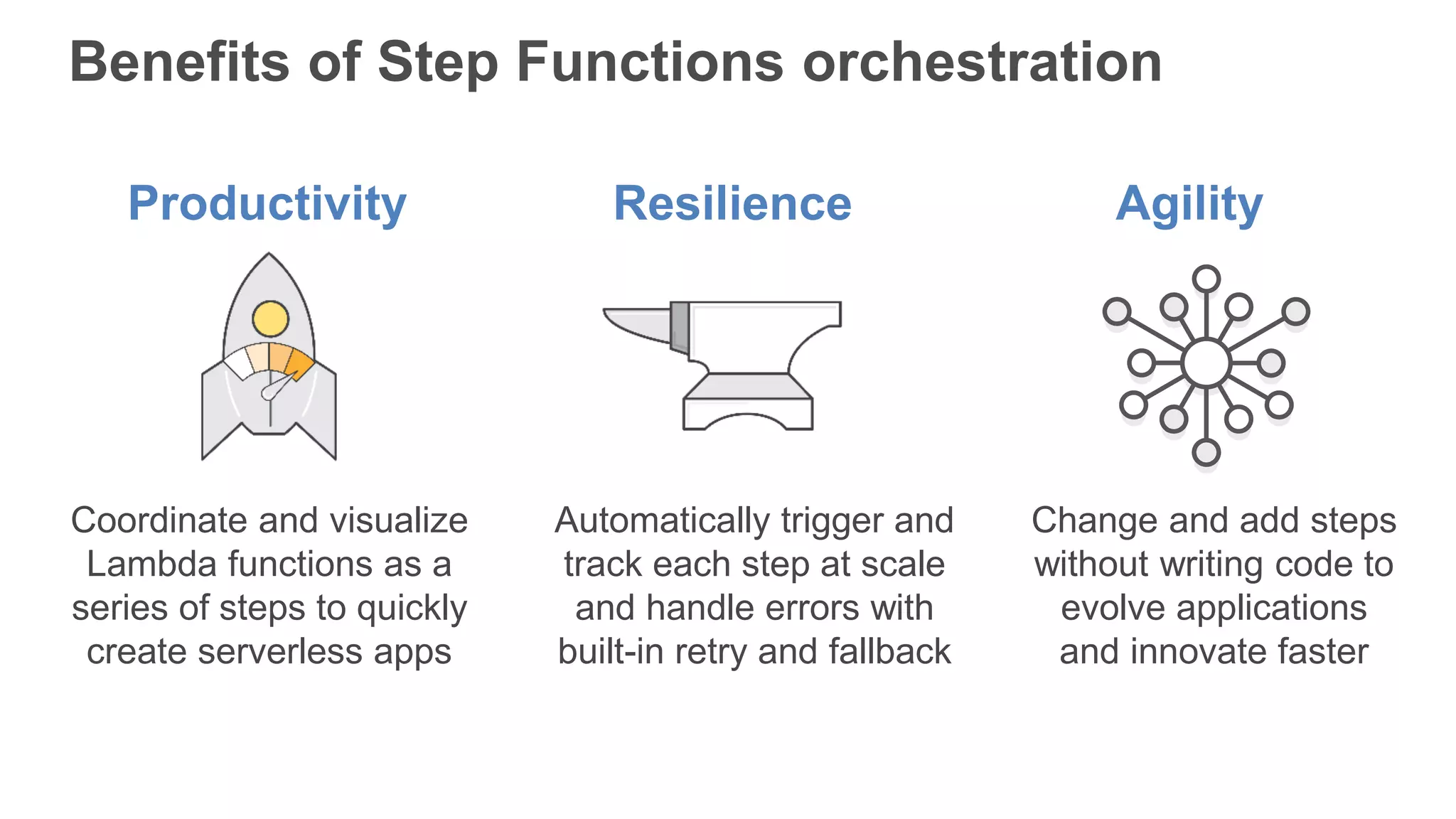
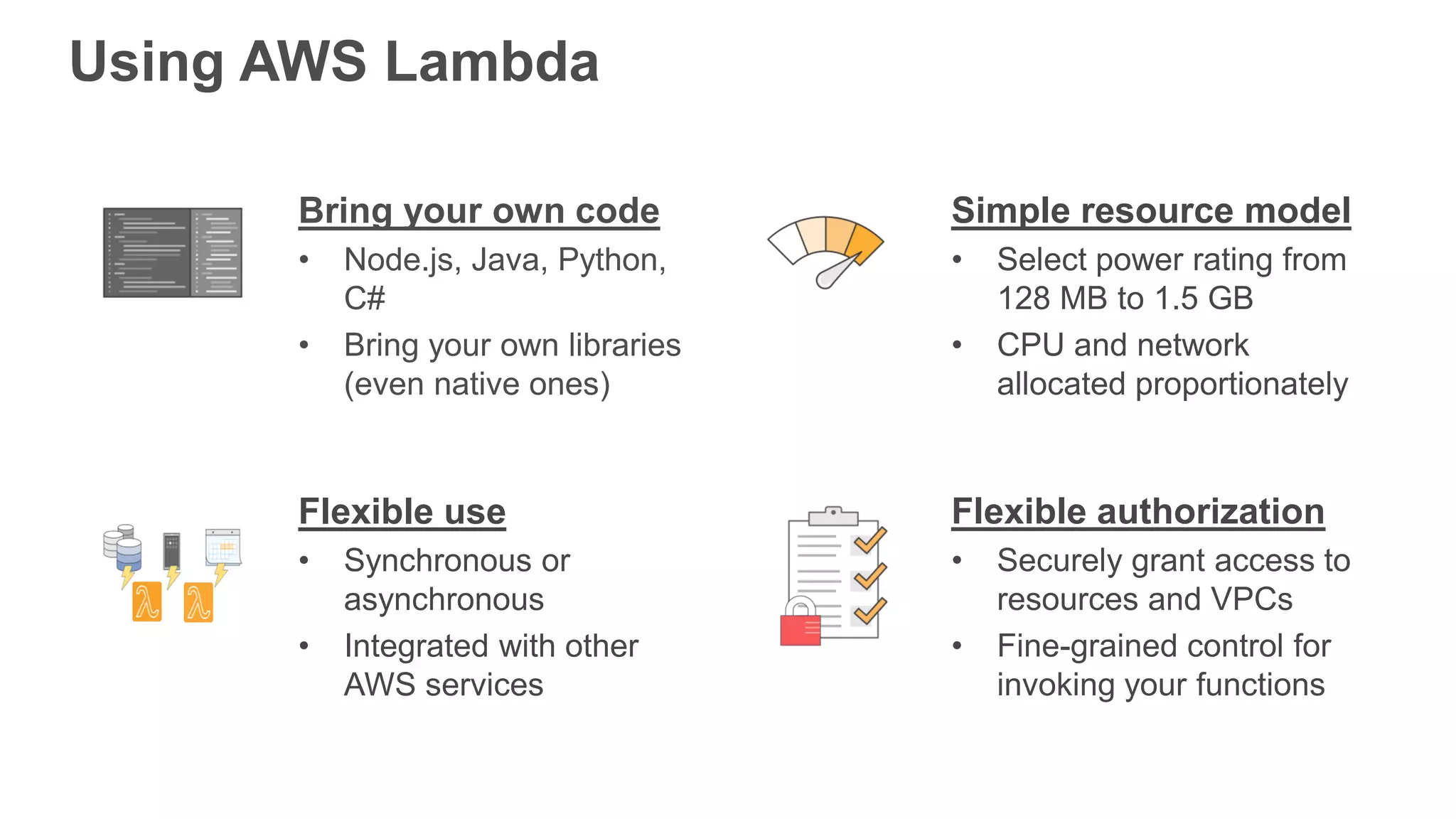
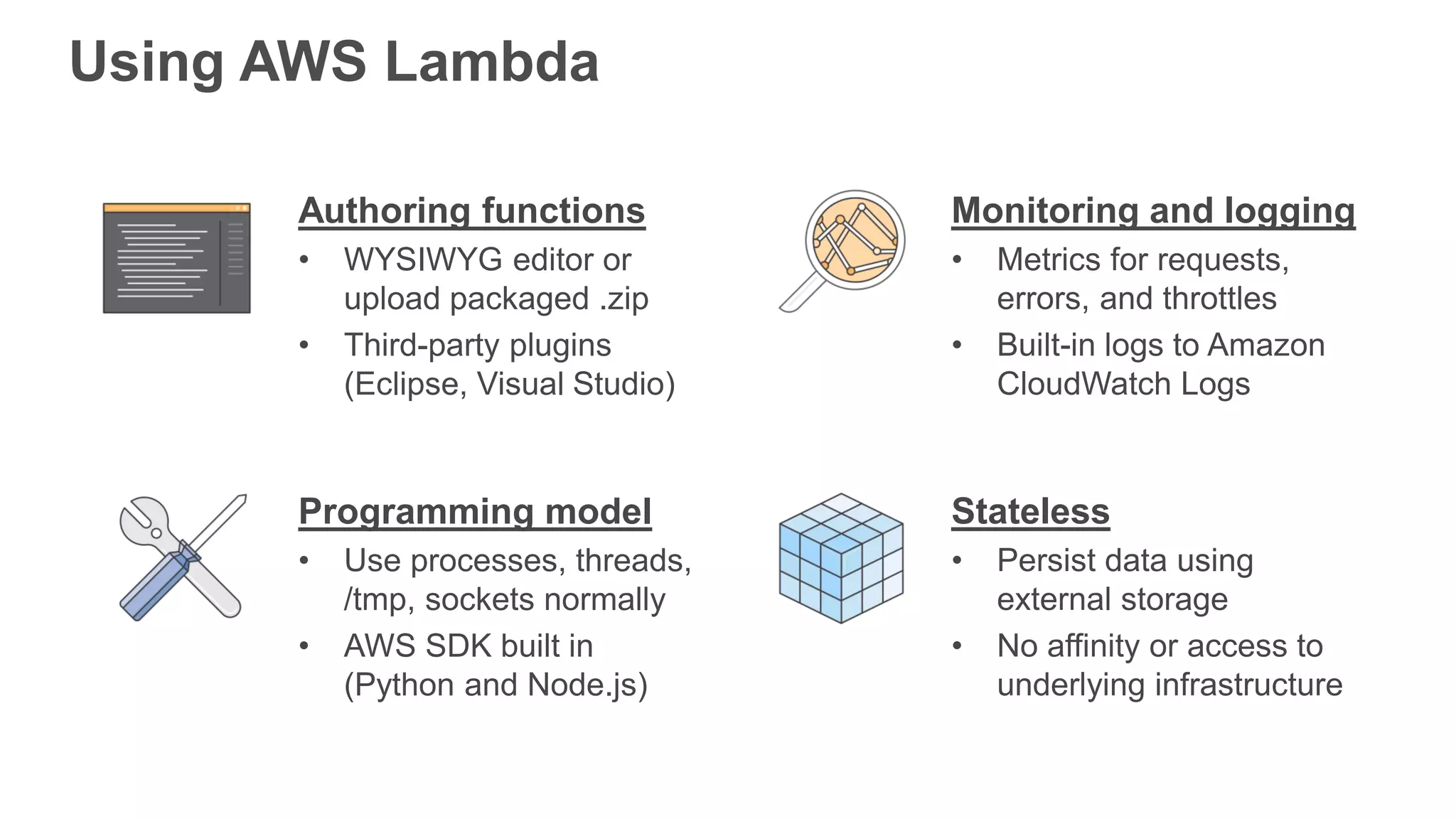
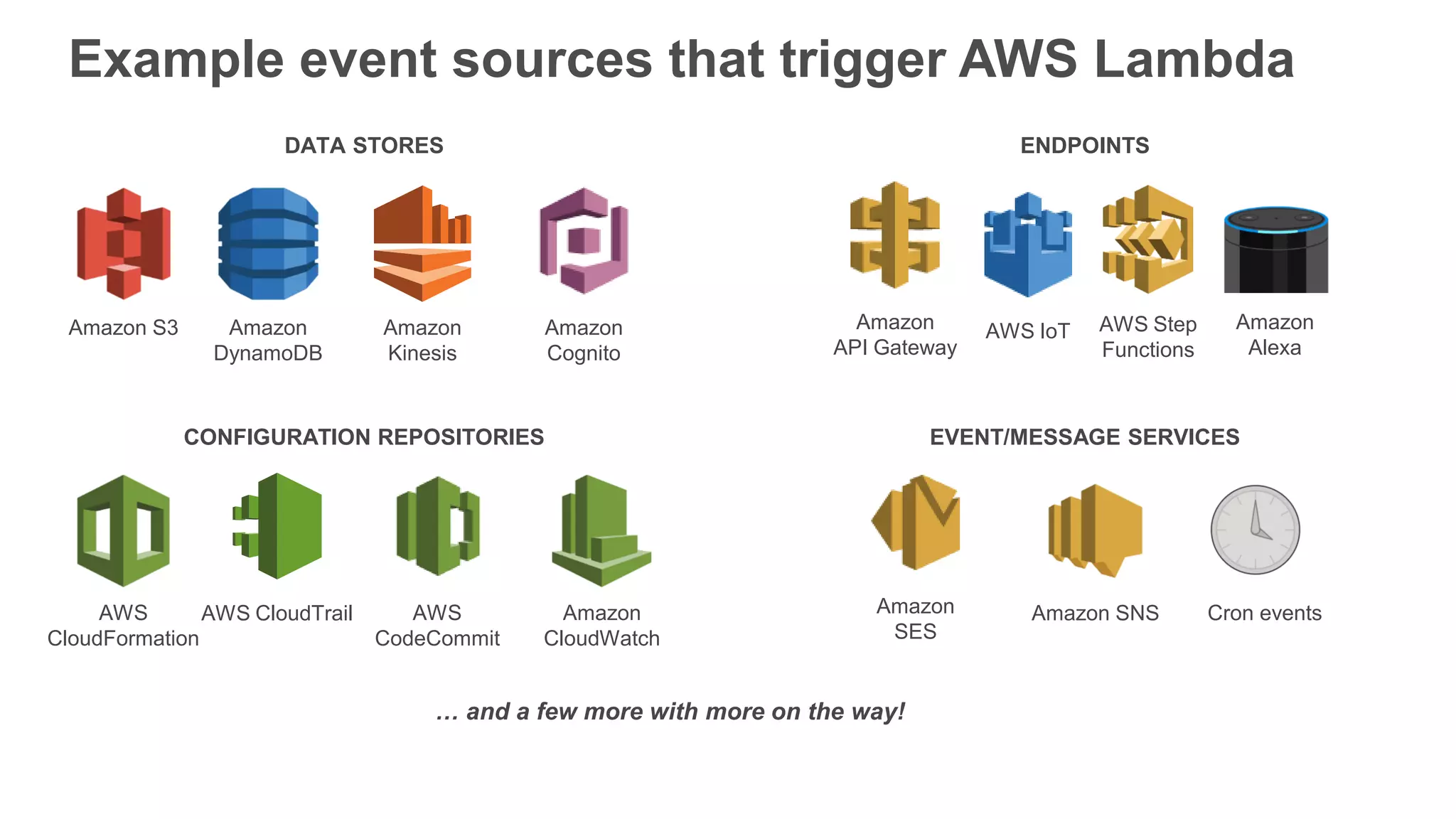
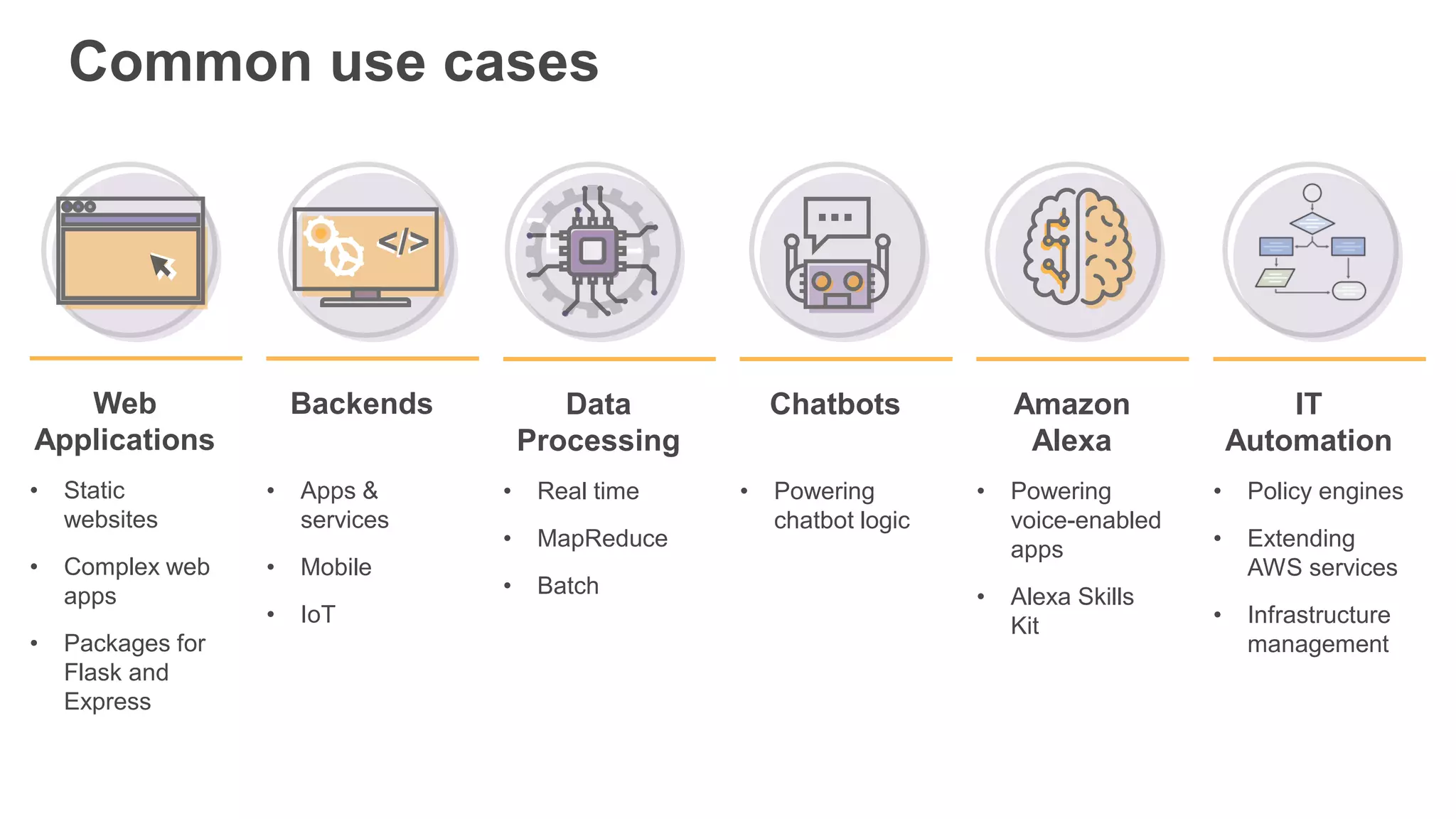
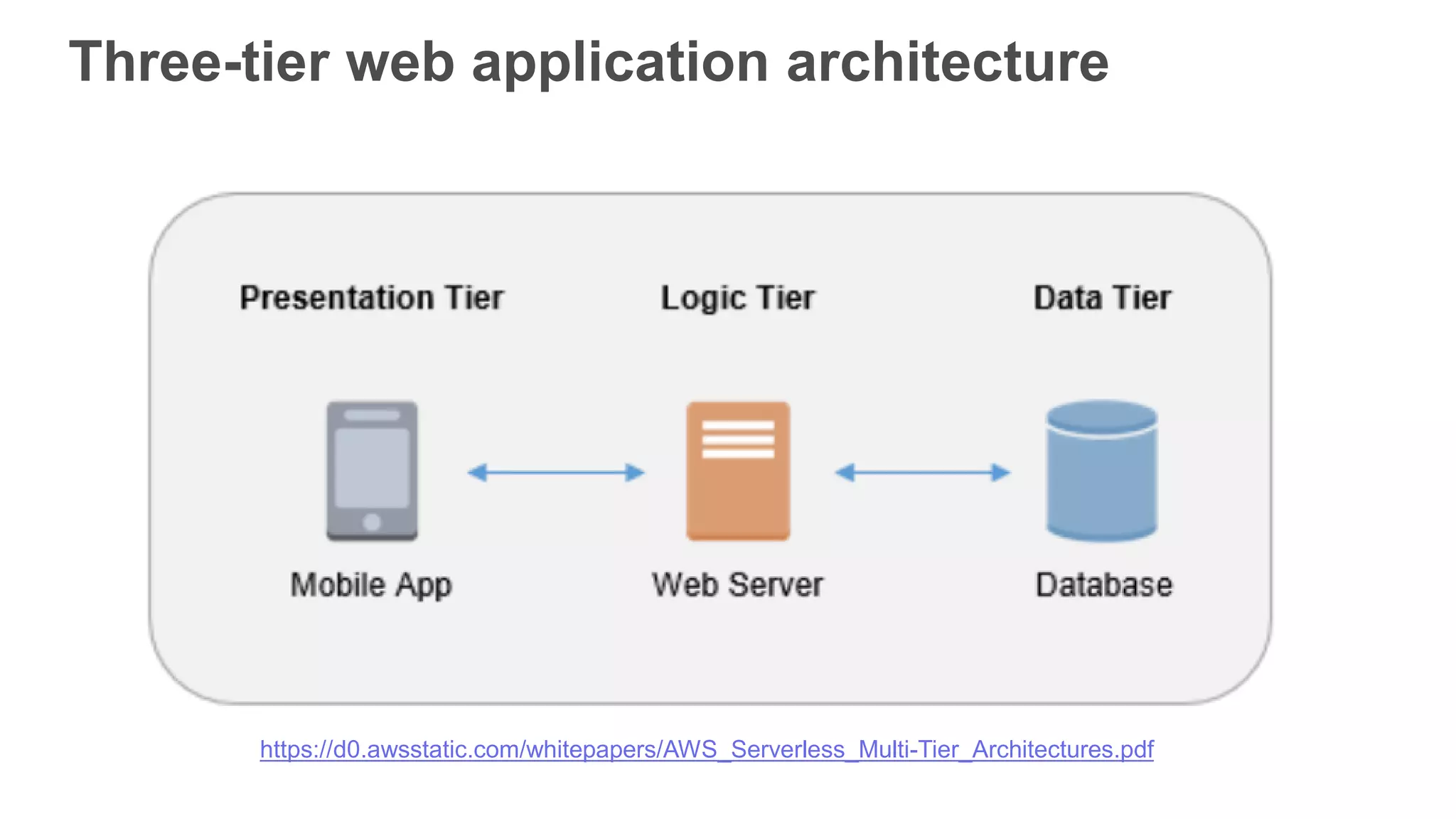
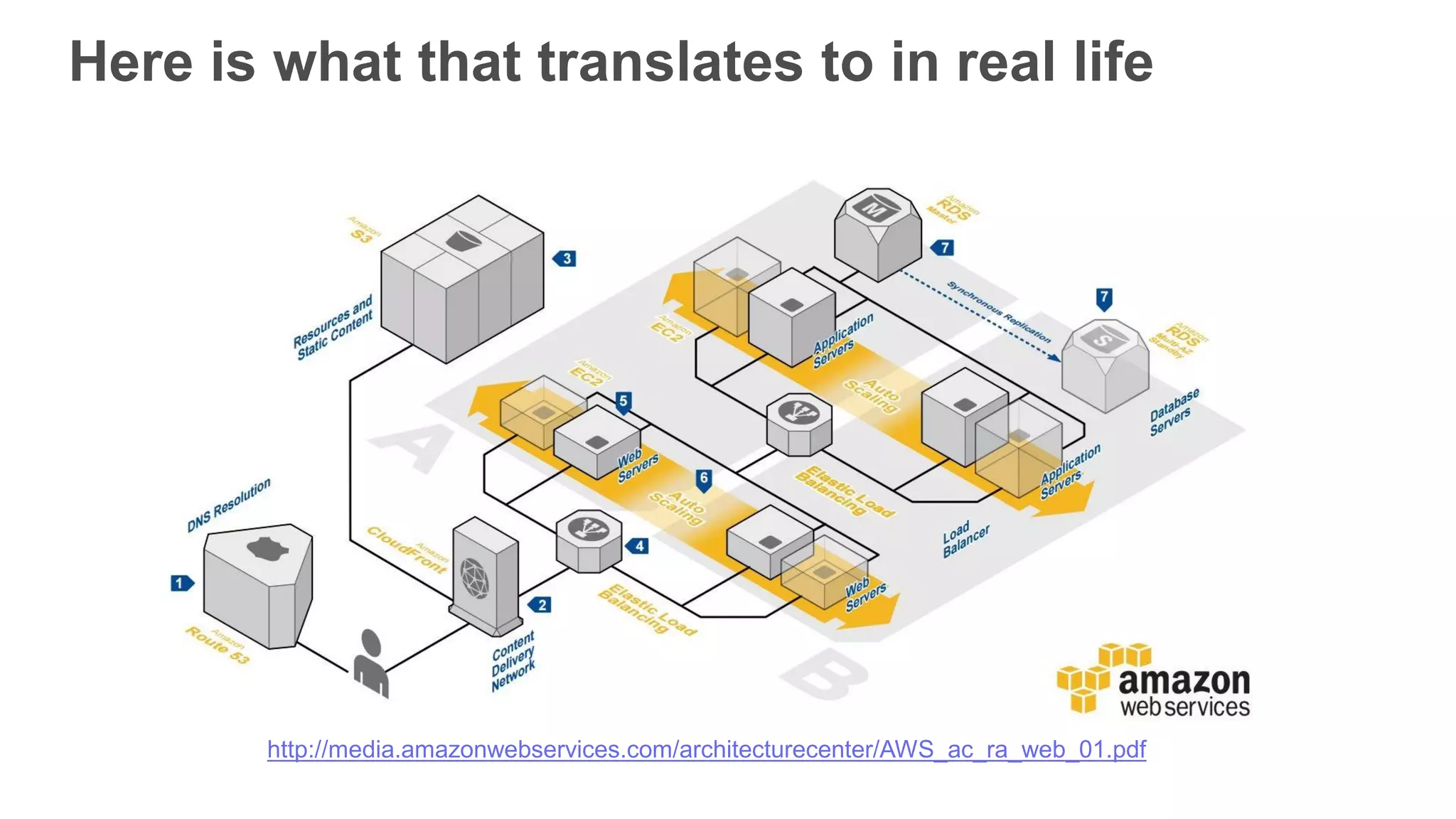
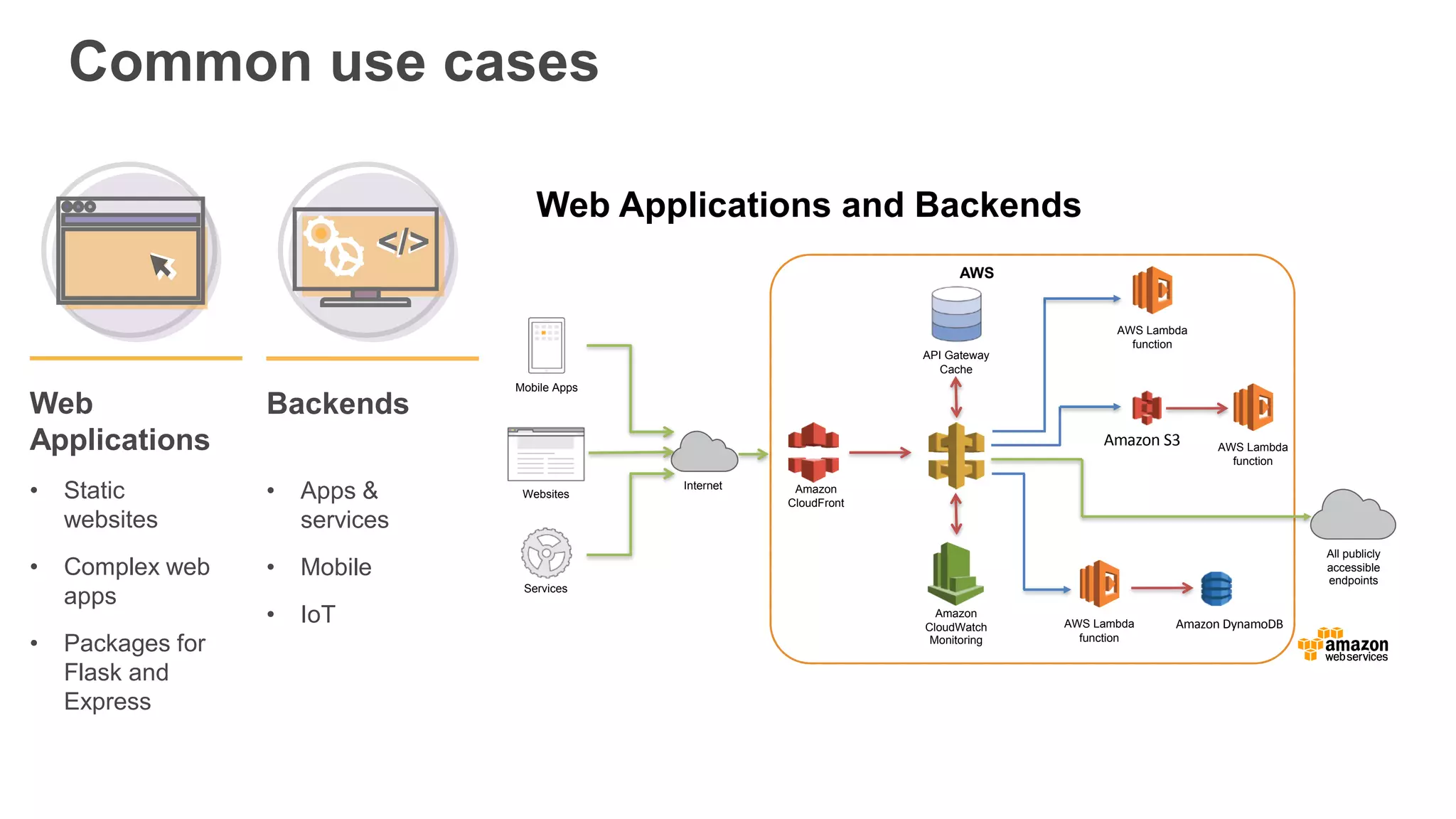
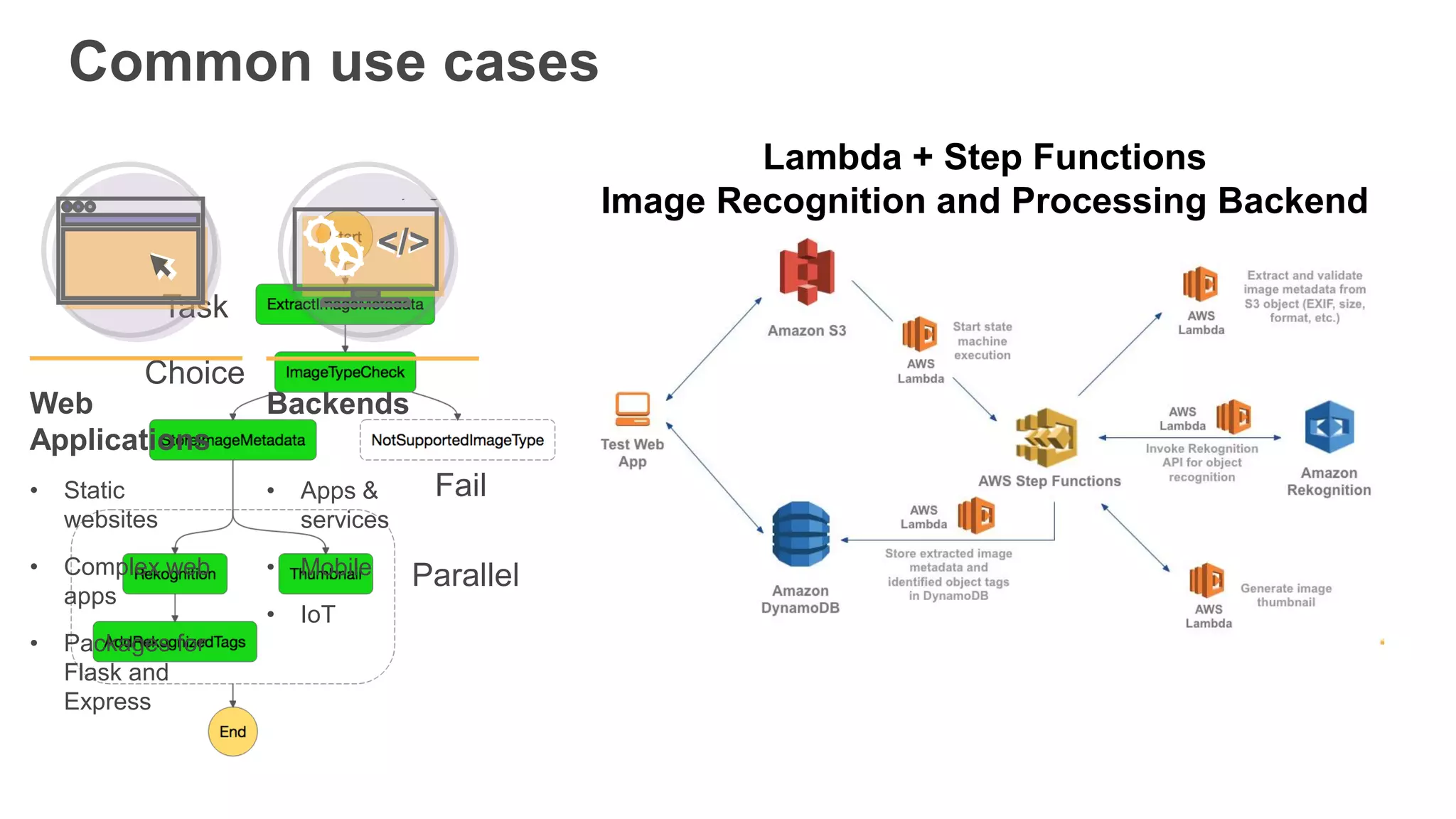
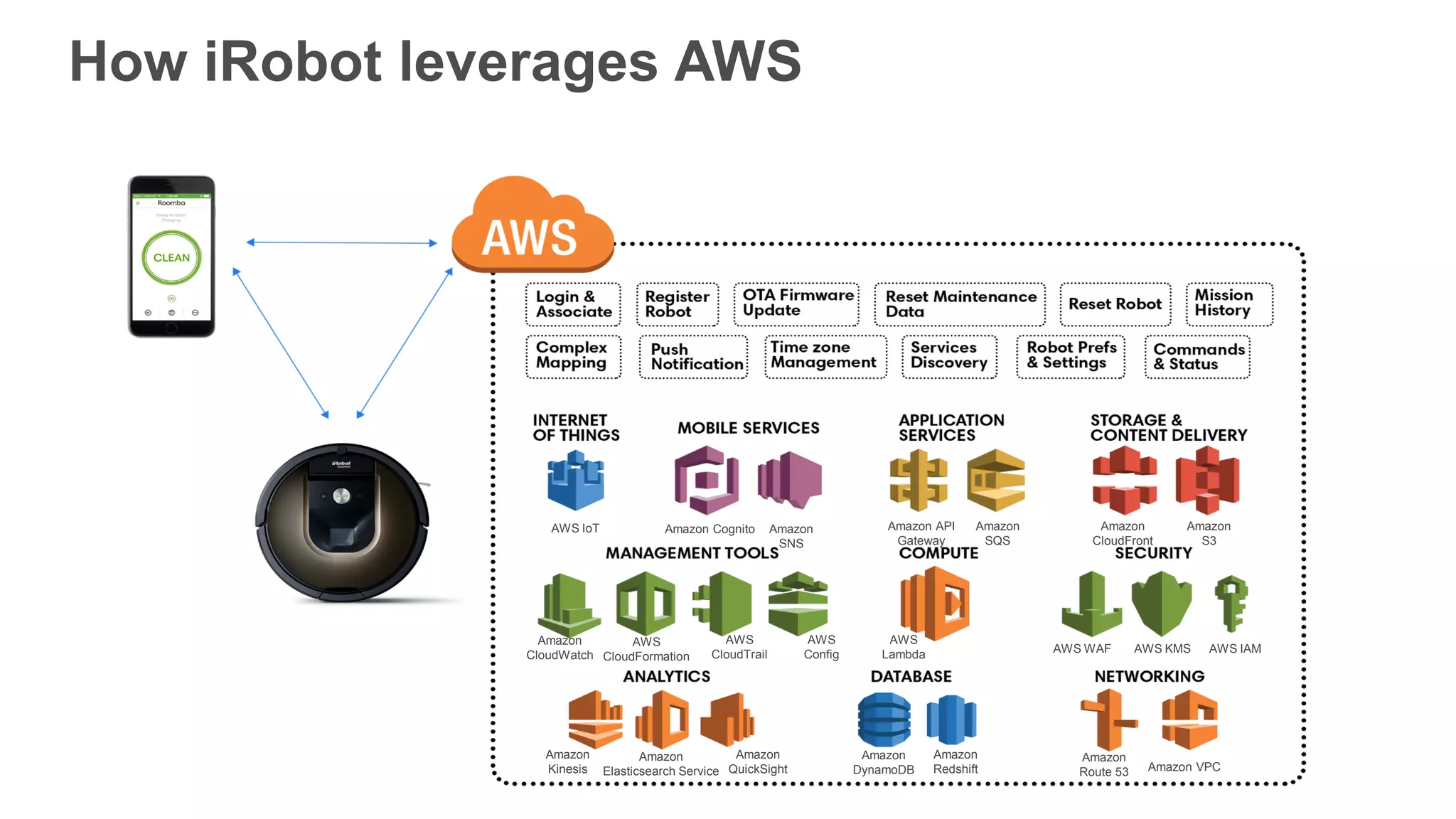
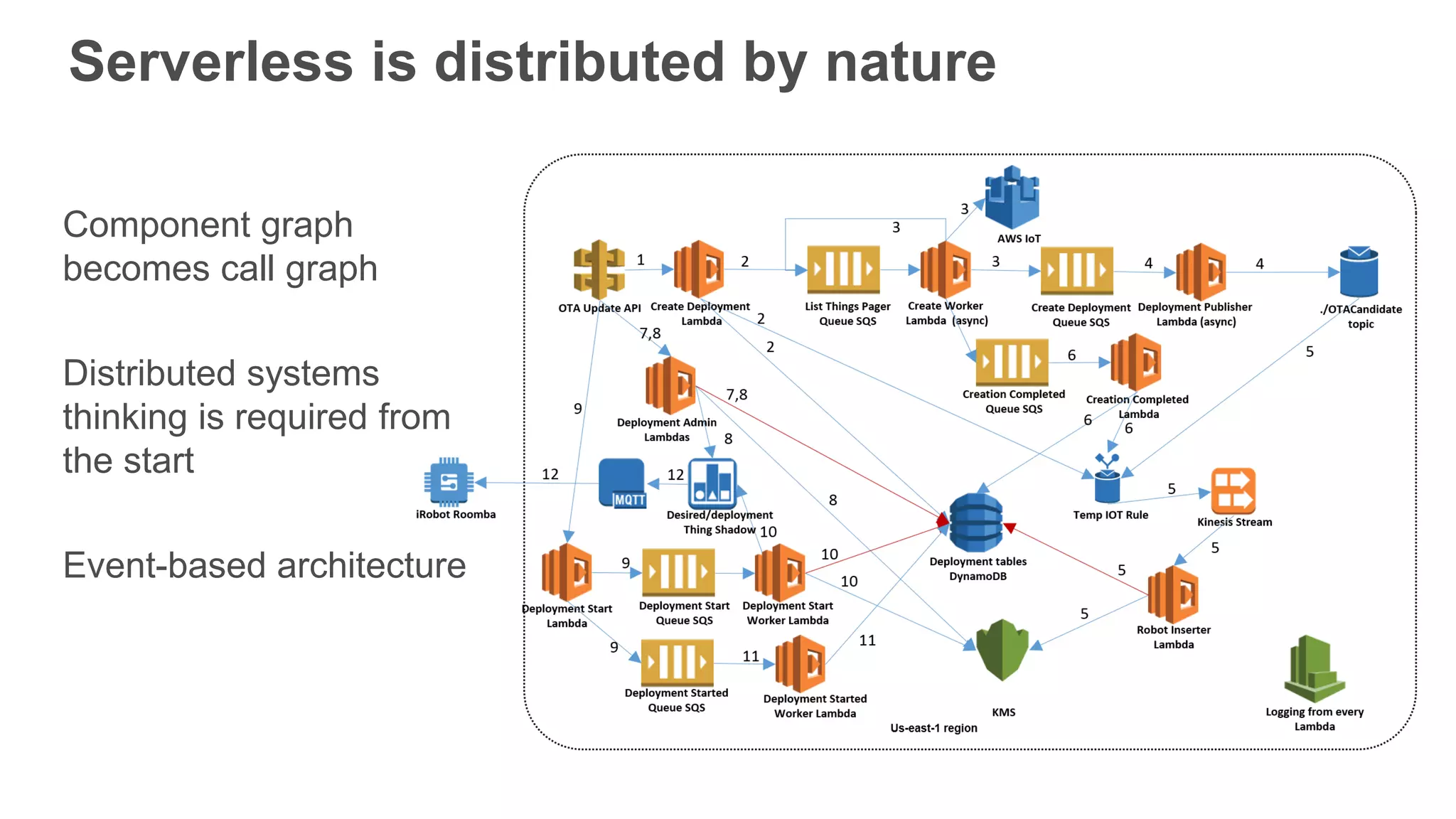
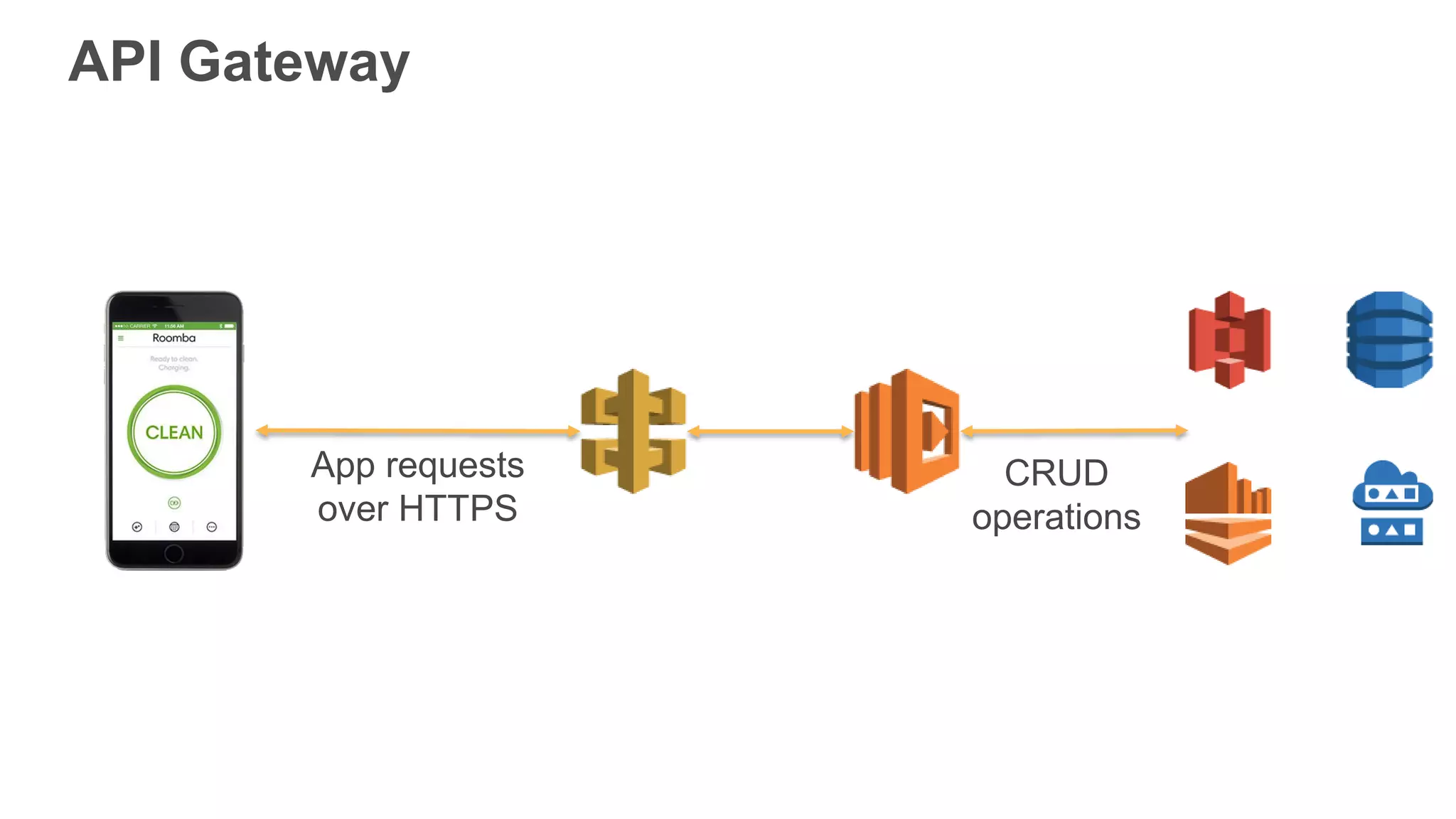
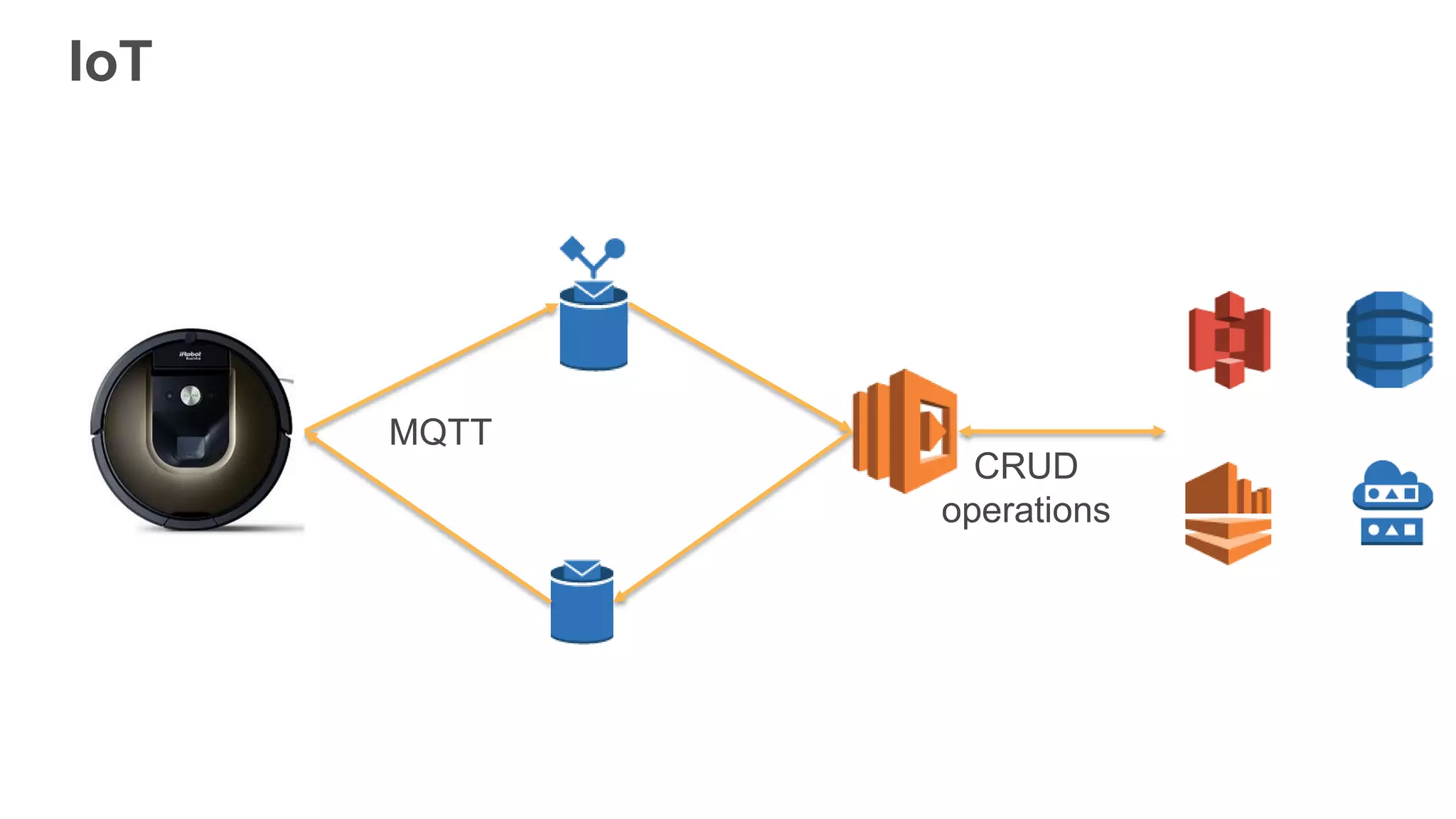
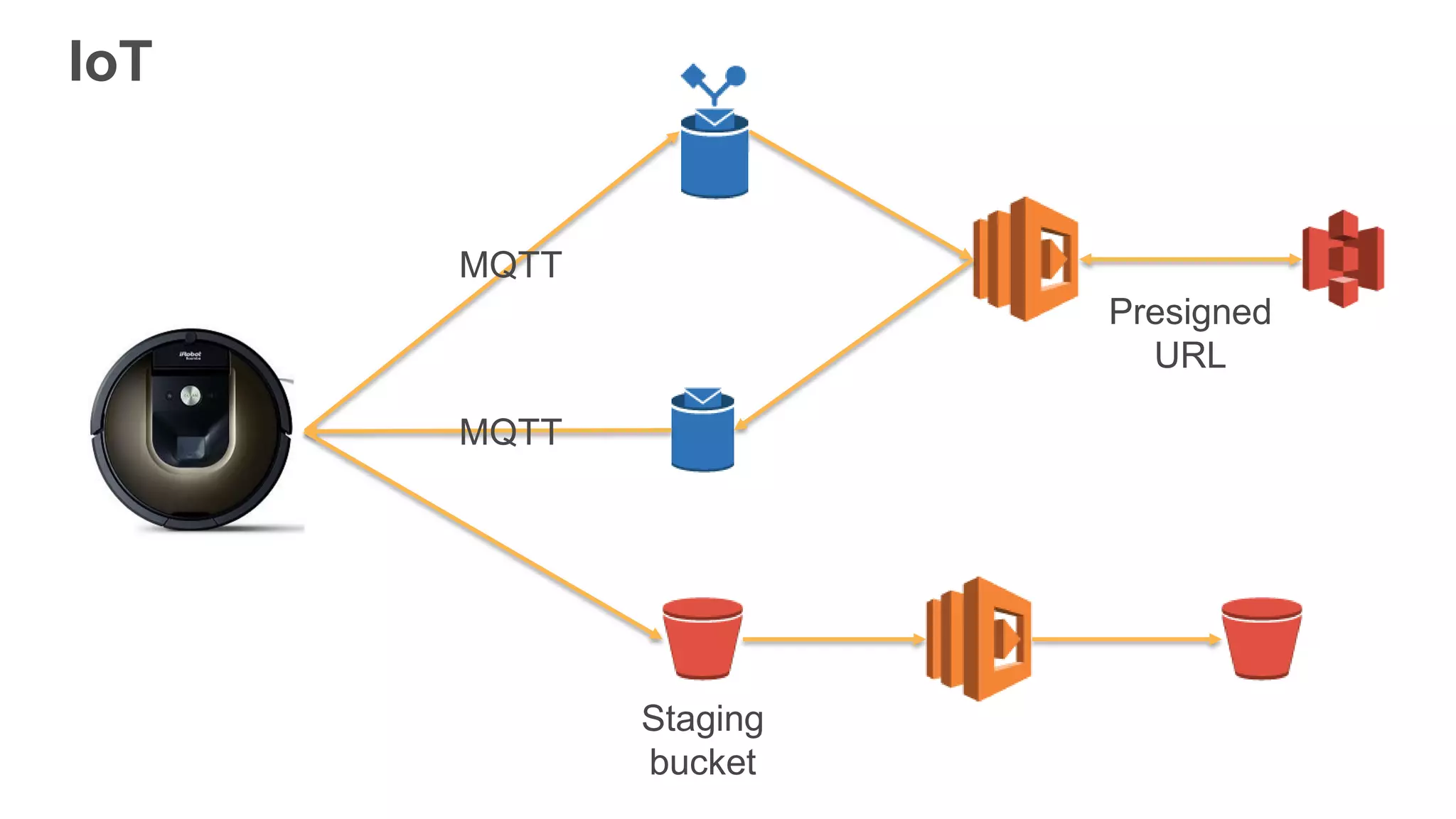
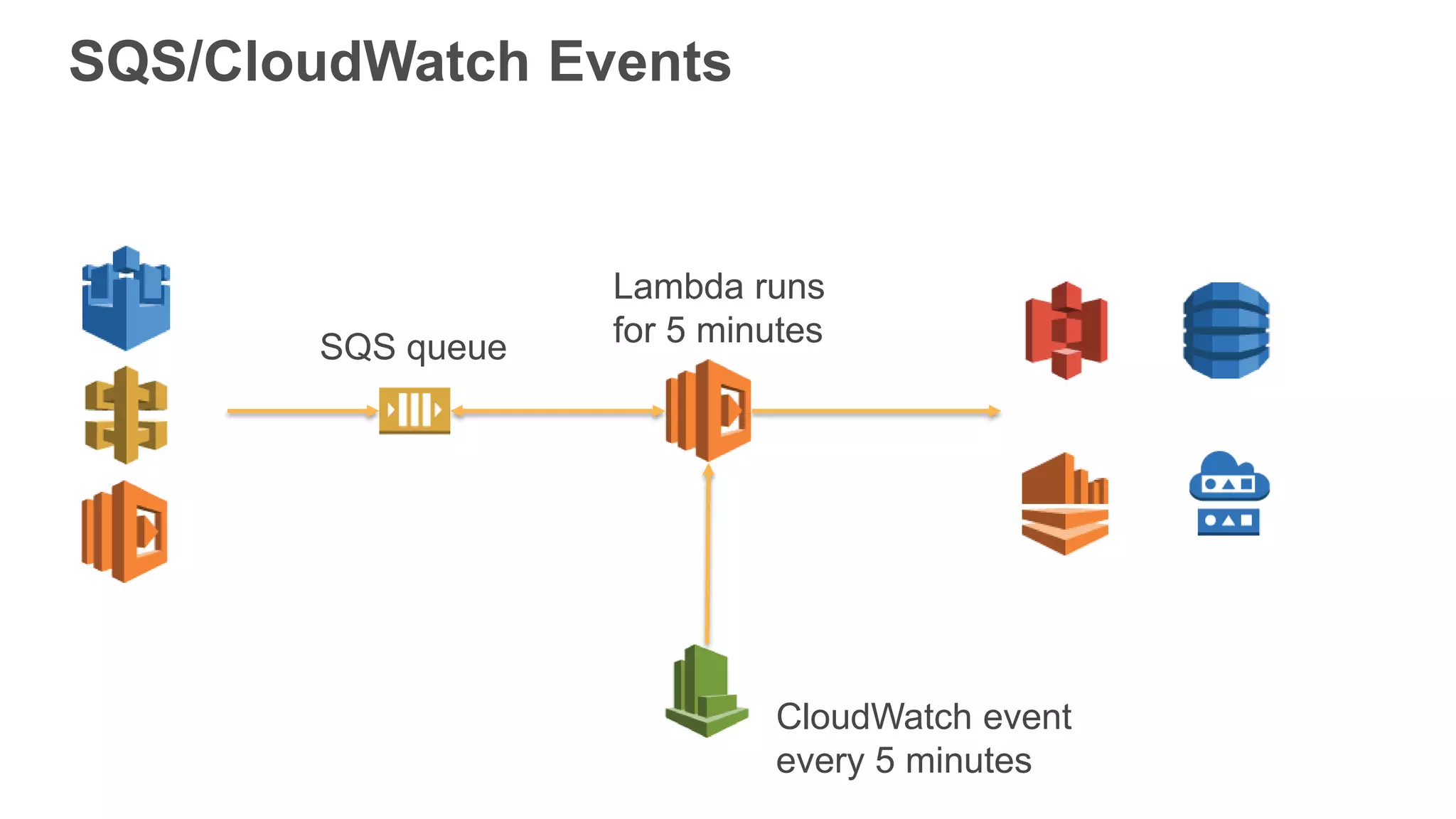
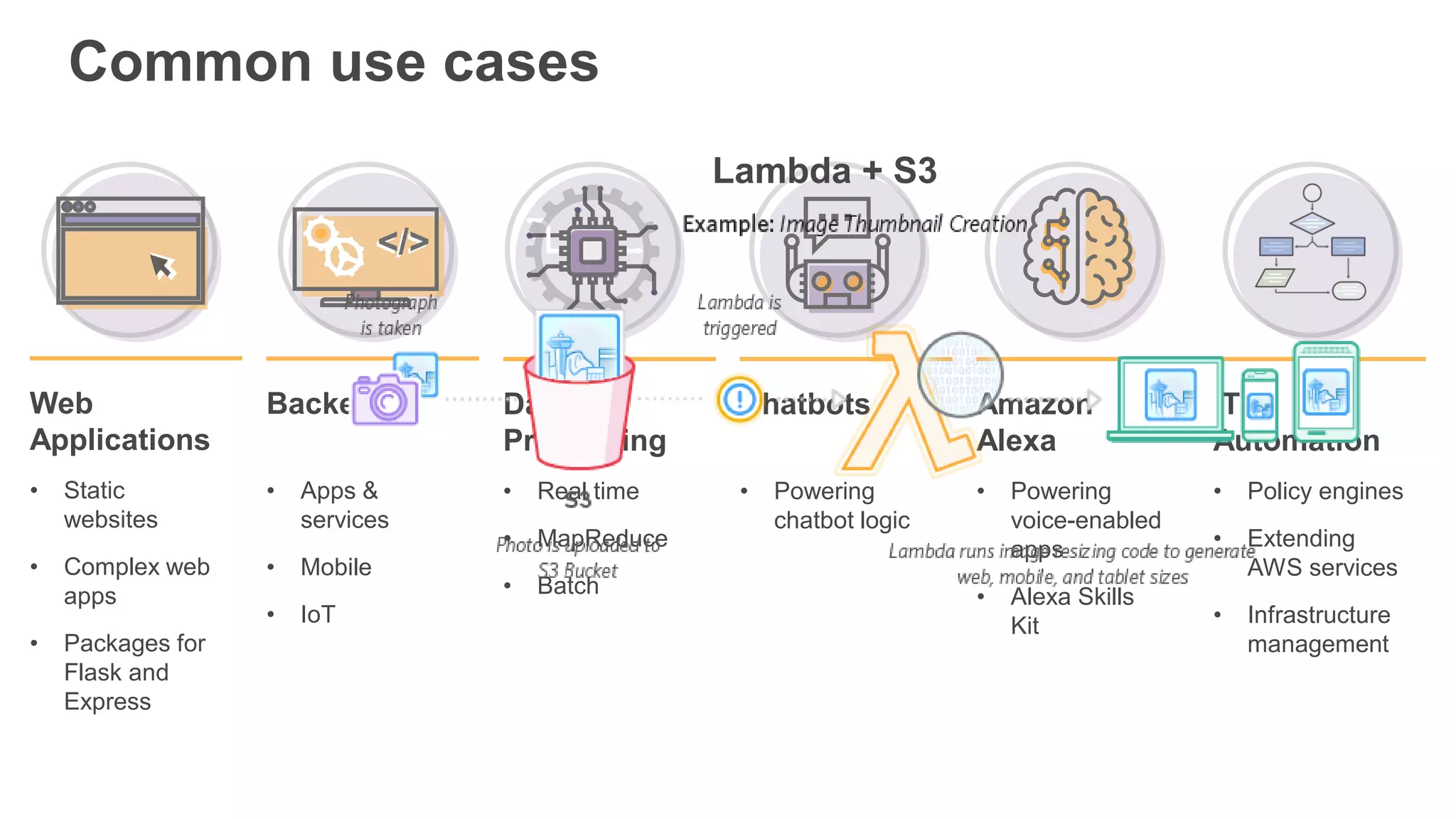
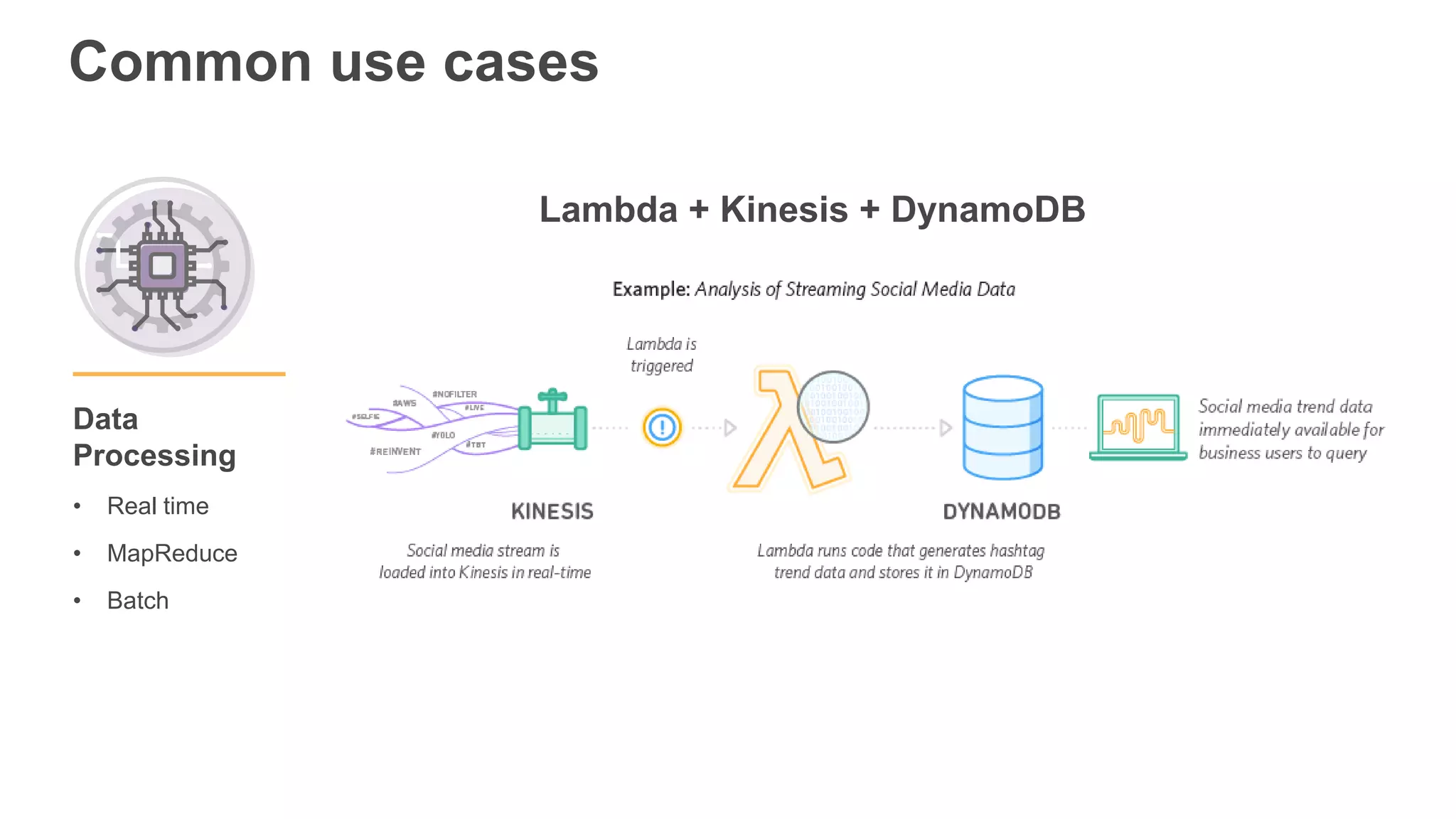
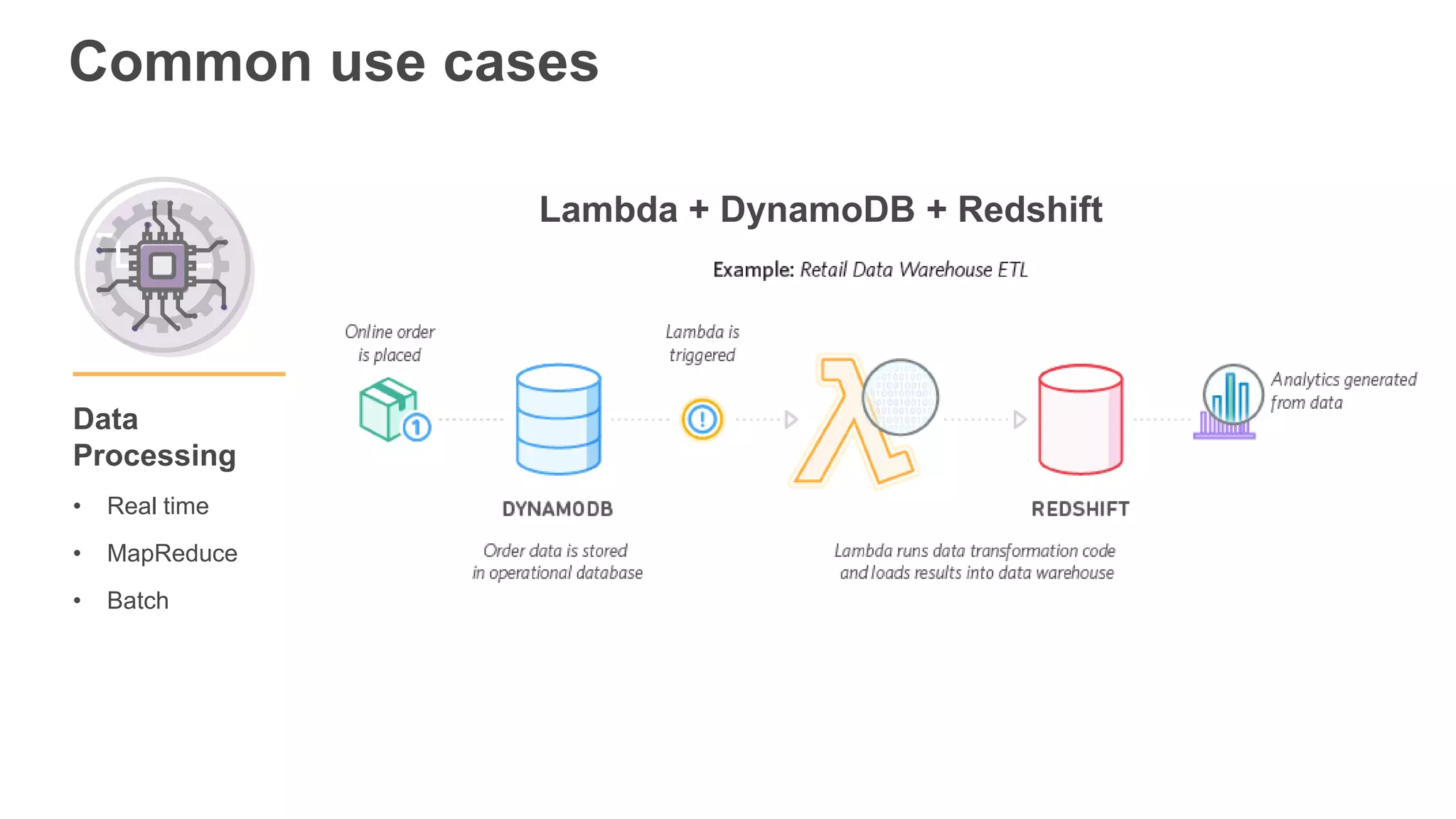
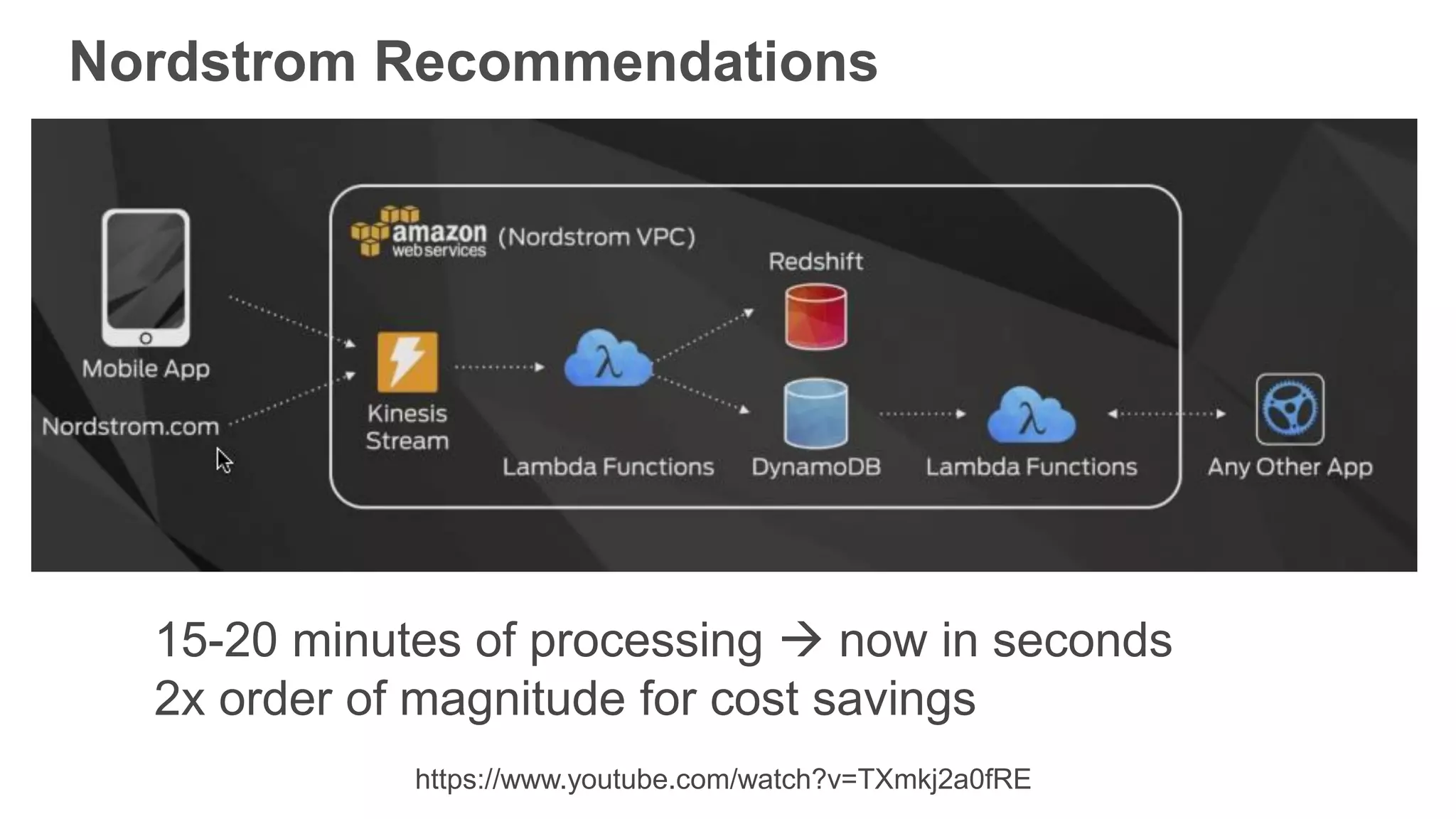
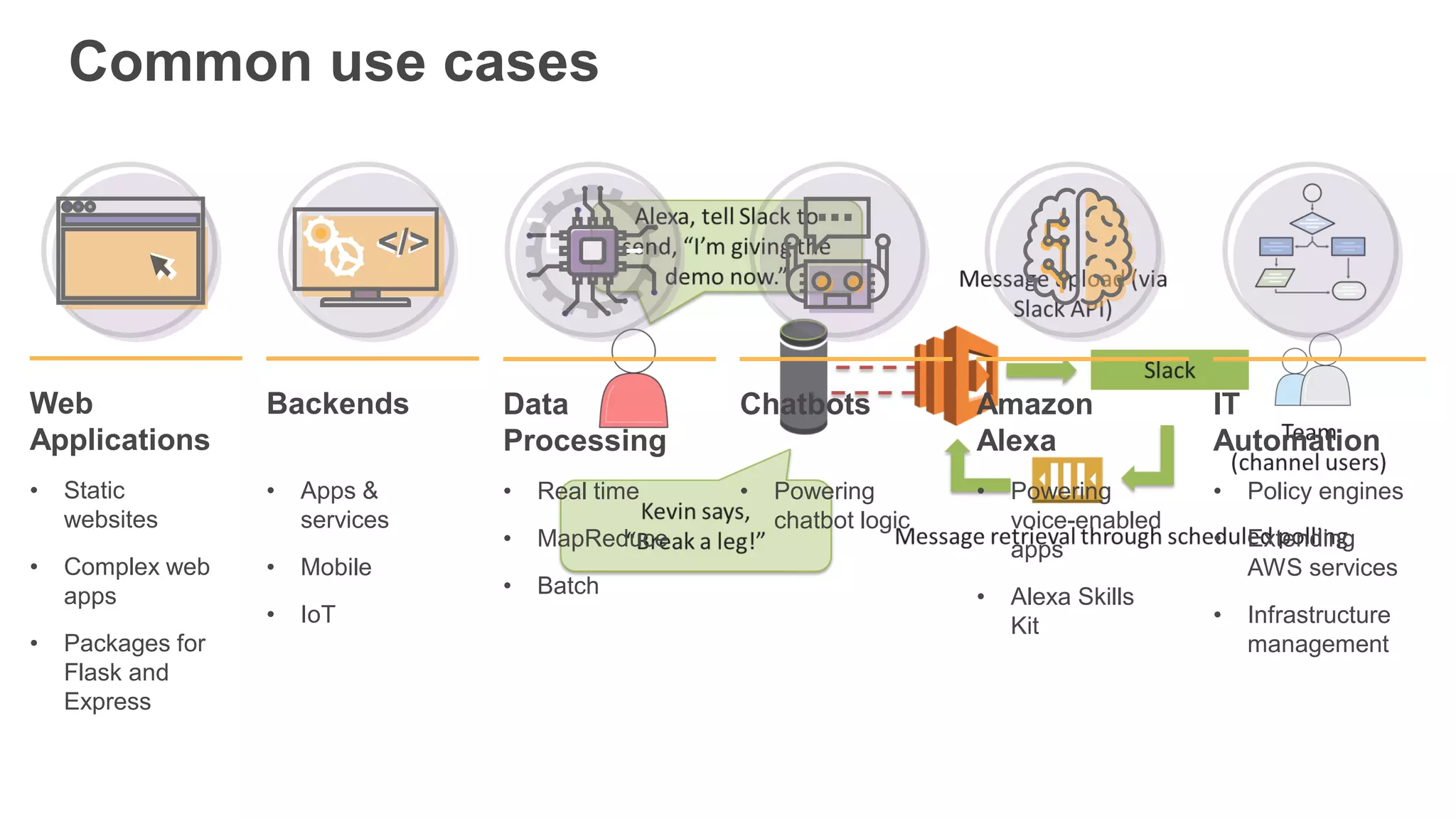
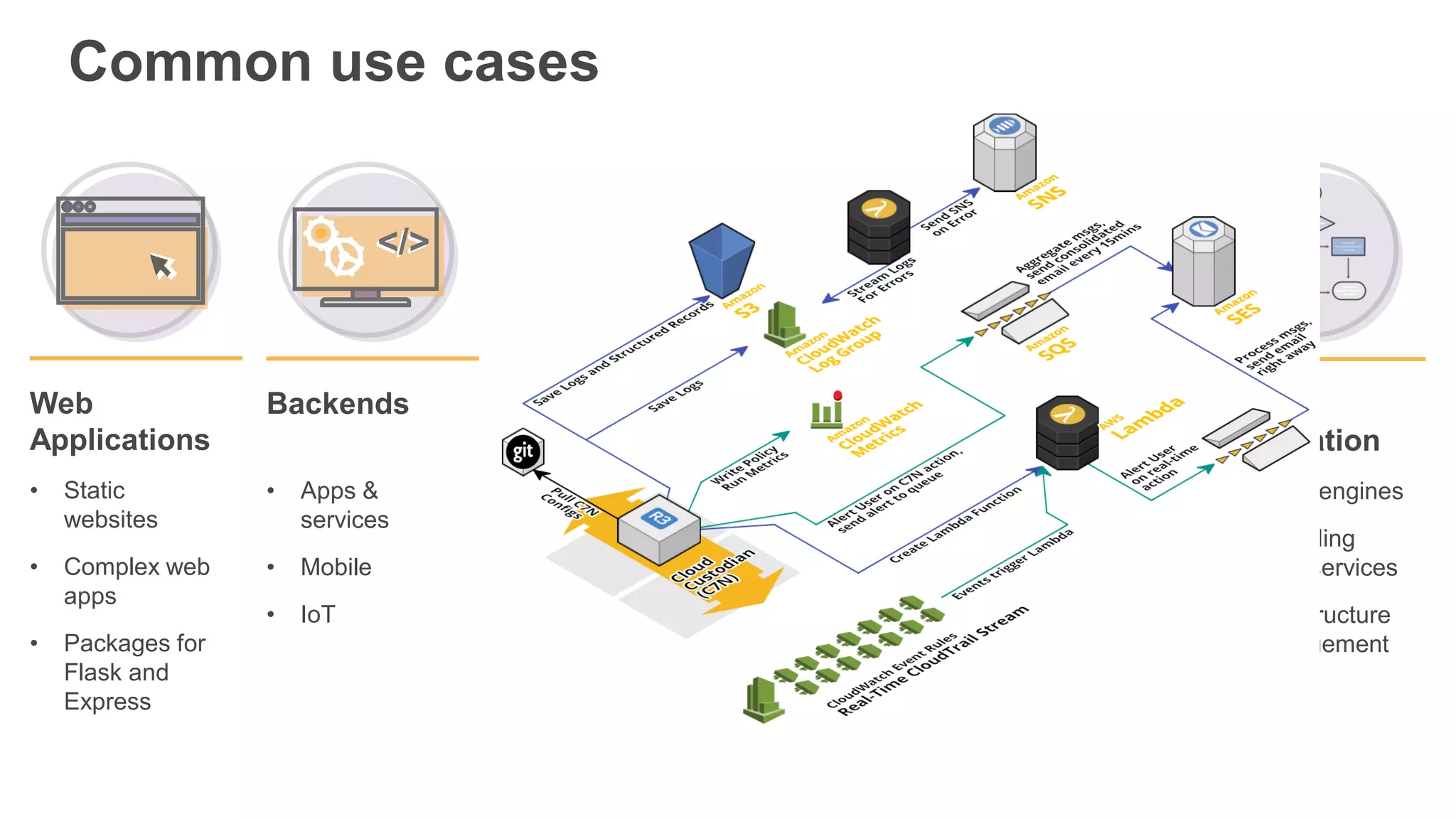
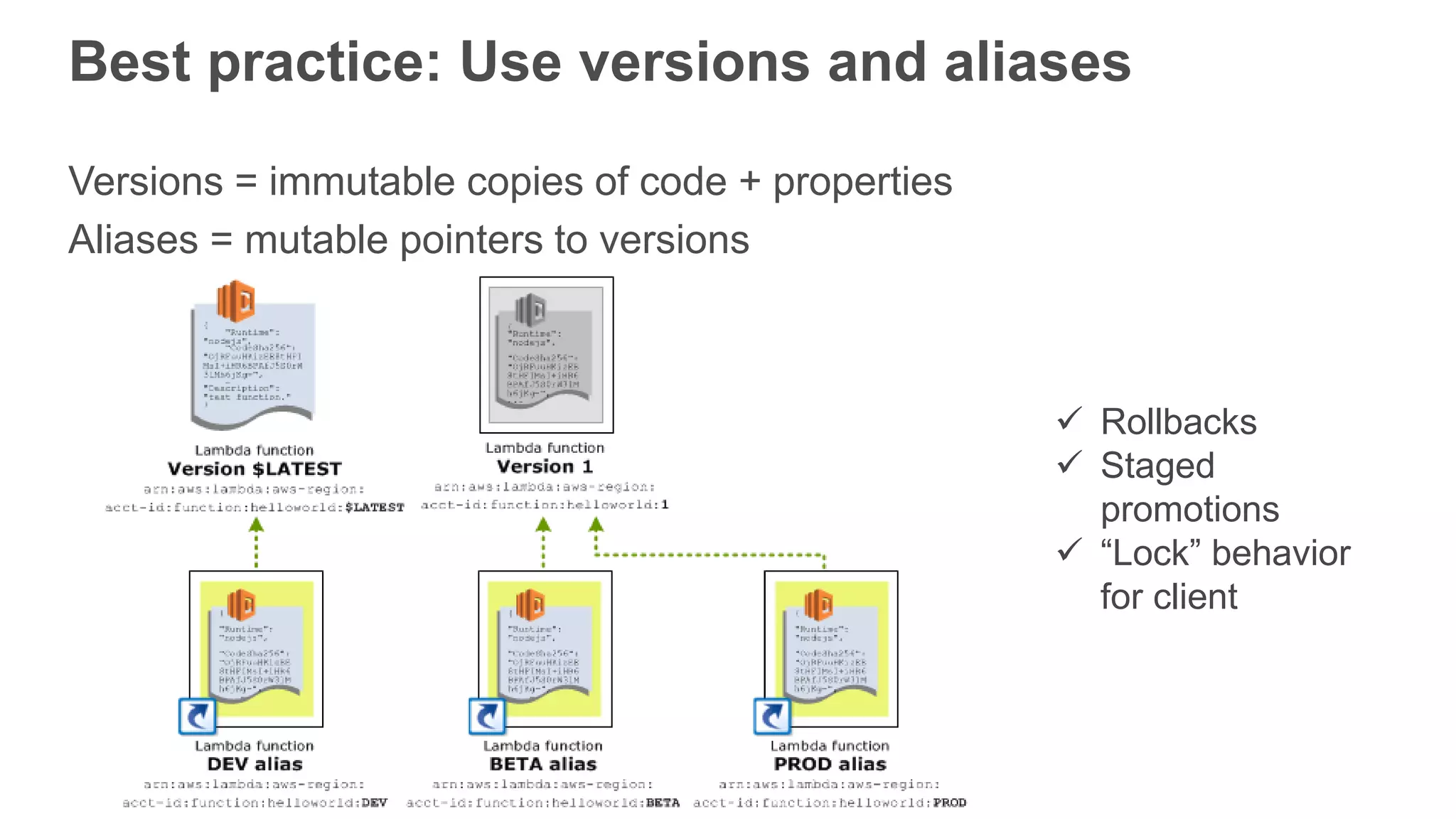
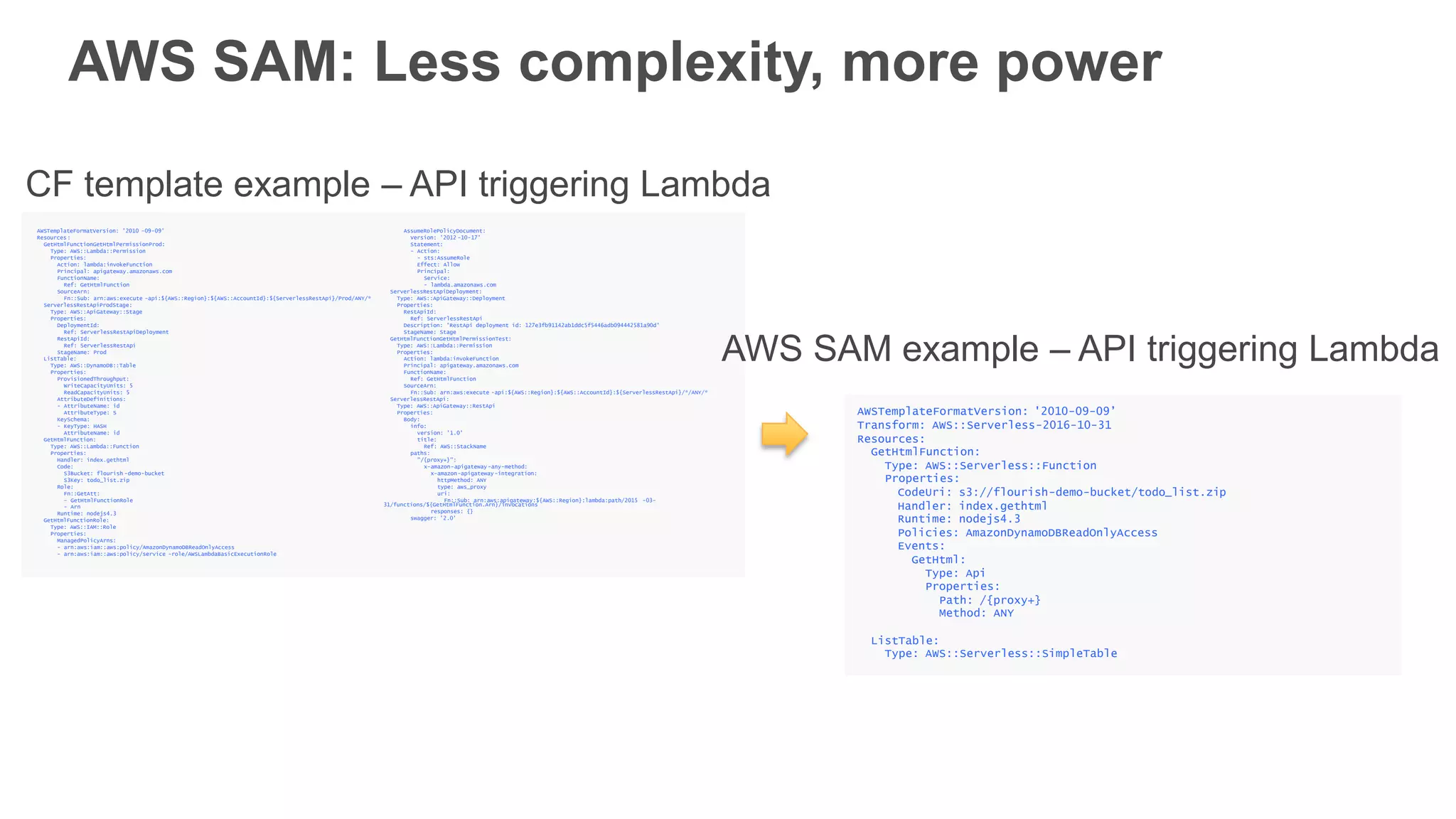
This document provides an overview of AWS Lambda and serverless computing. It discusses AWS compute offerings like EC2, ECS, and Lambda. Lambda allows running code in response to events without provisioning or managing servers. Benefits include automatic scaling, pay per use, and built-in availability. Common use cases for Lambda include web applications, backends, data processing, chatbots, and IT automation. Best practices for Lambda include limiting function size, parameterizing code, and using versions and aliases. The document also provides examples of serverless applications and architectures using Lambda along with other AWS services.