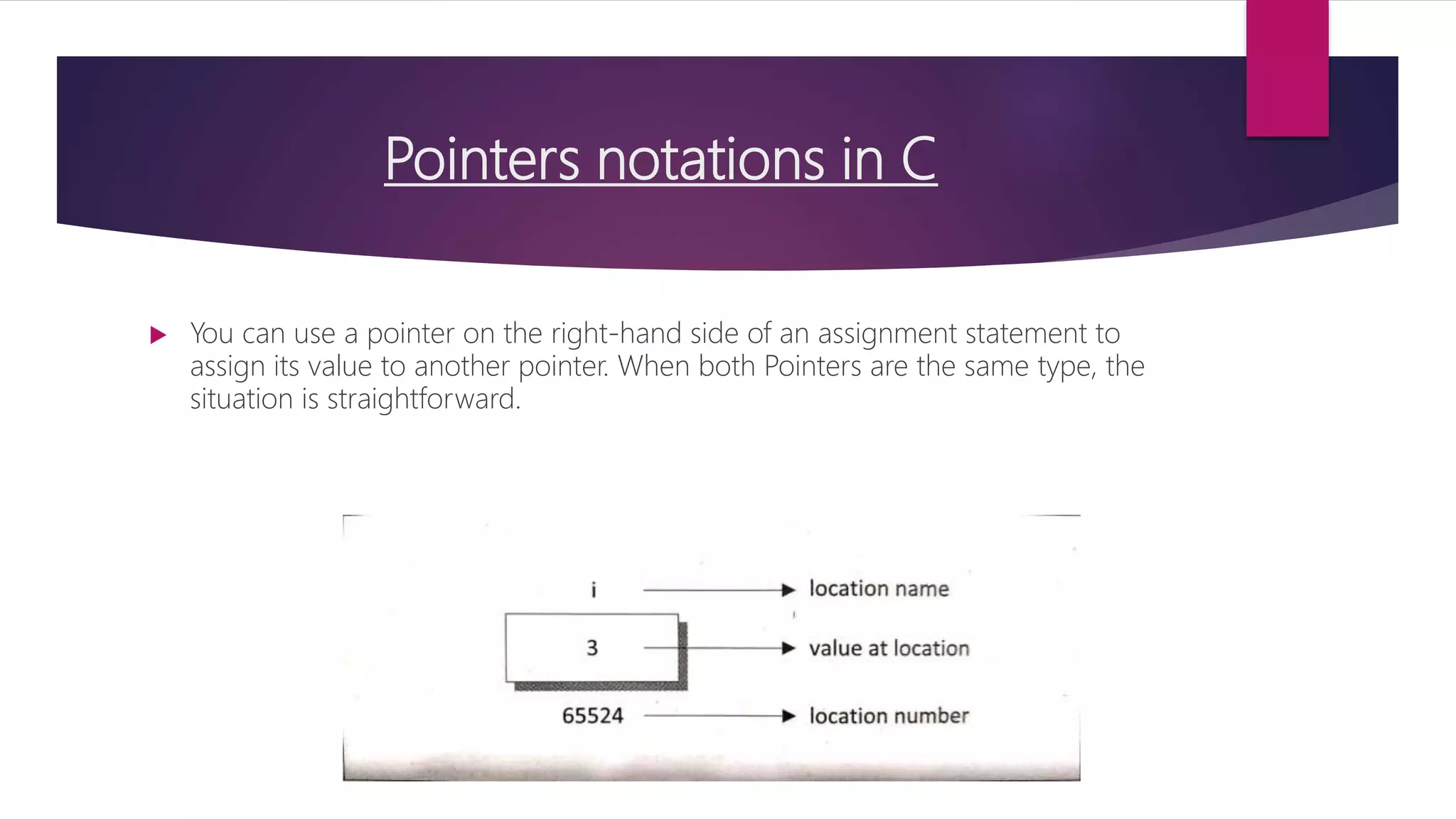
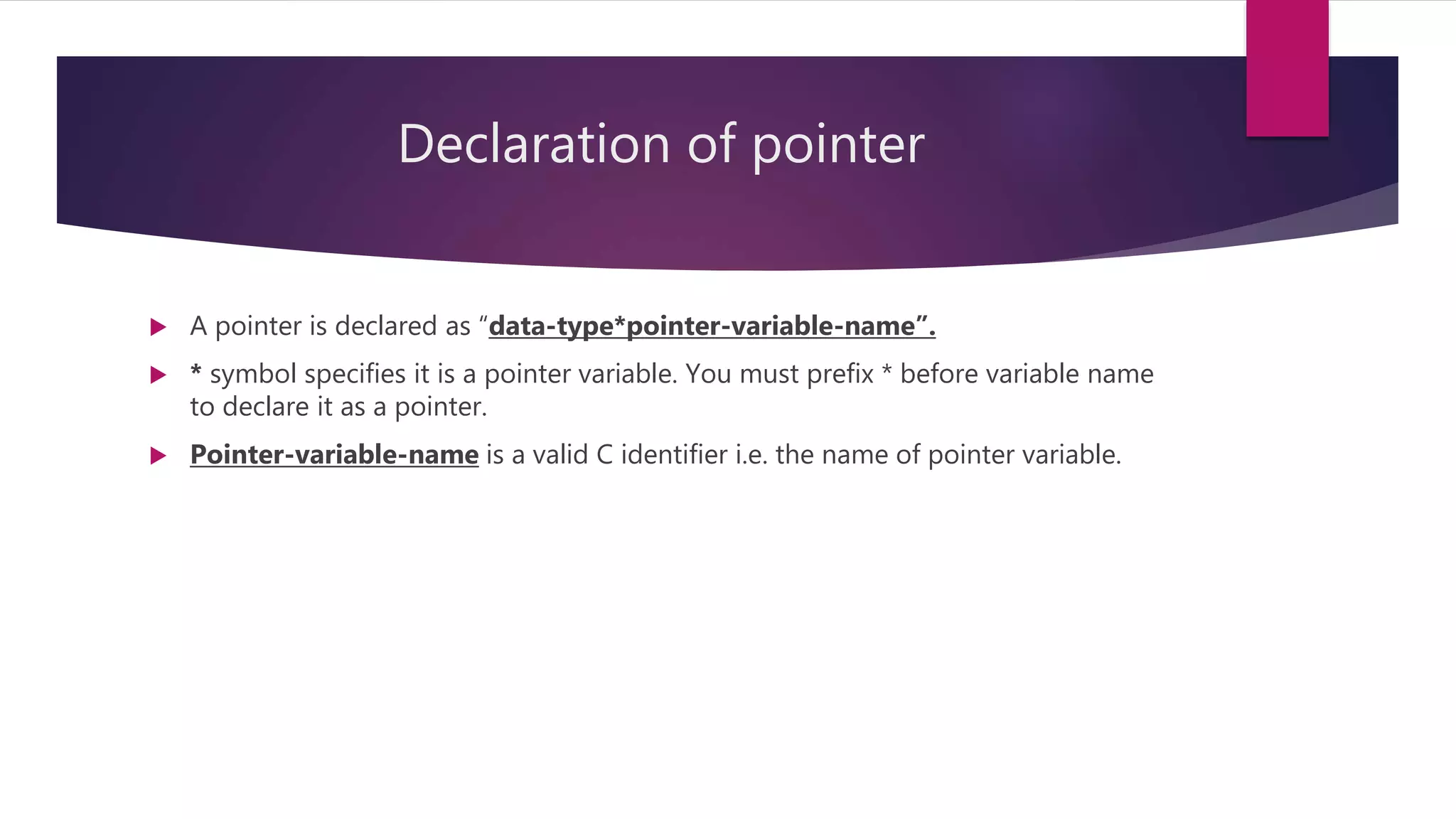
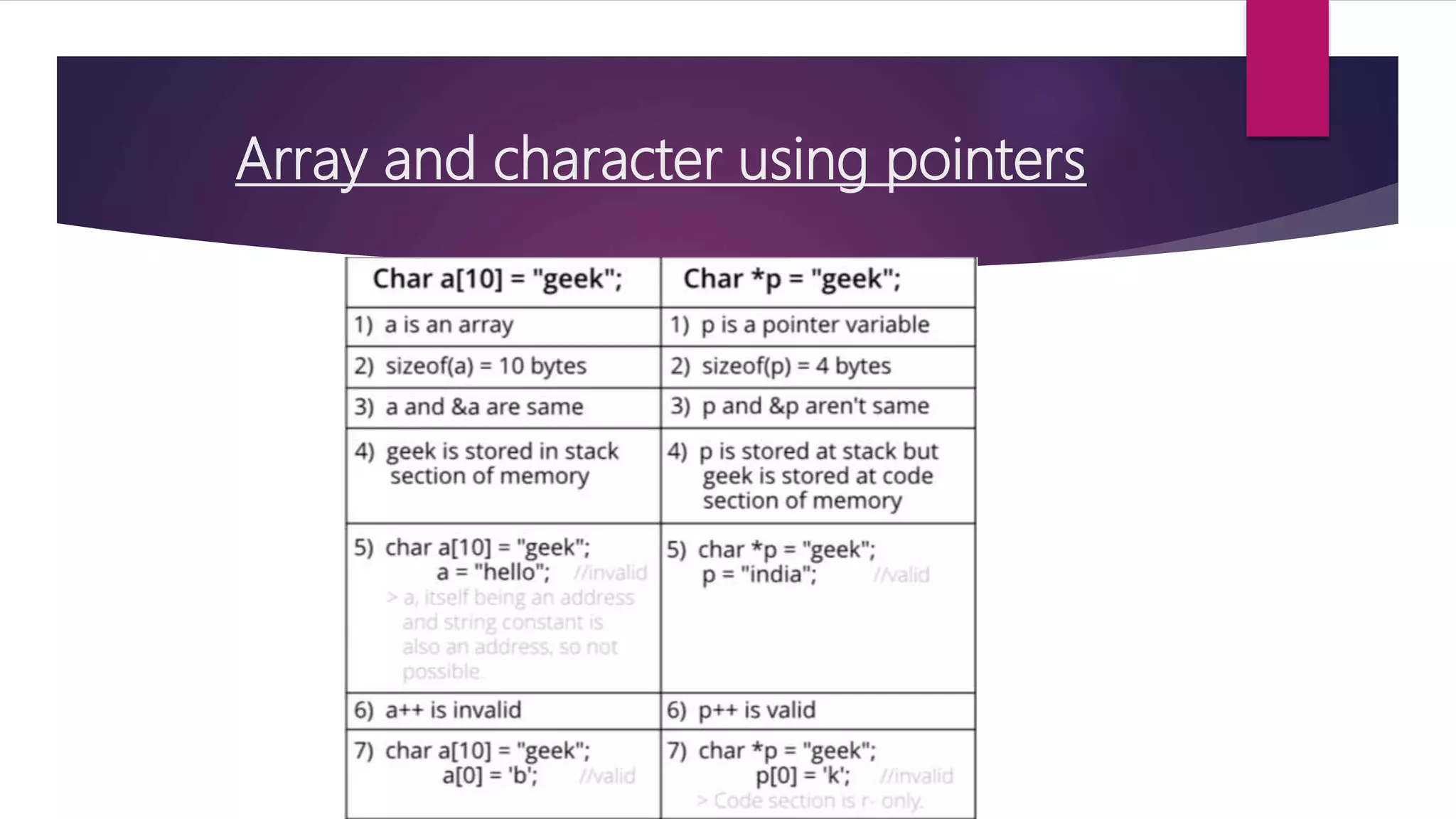
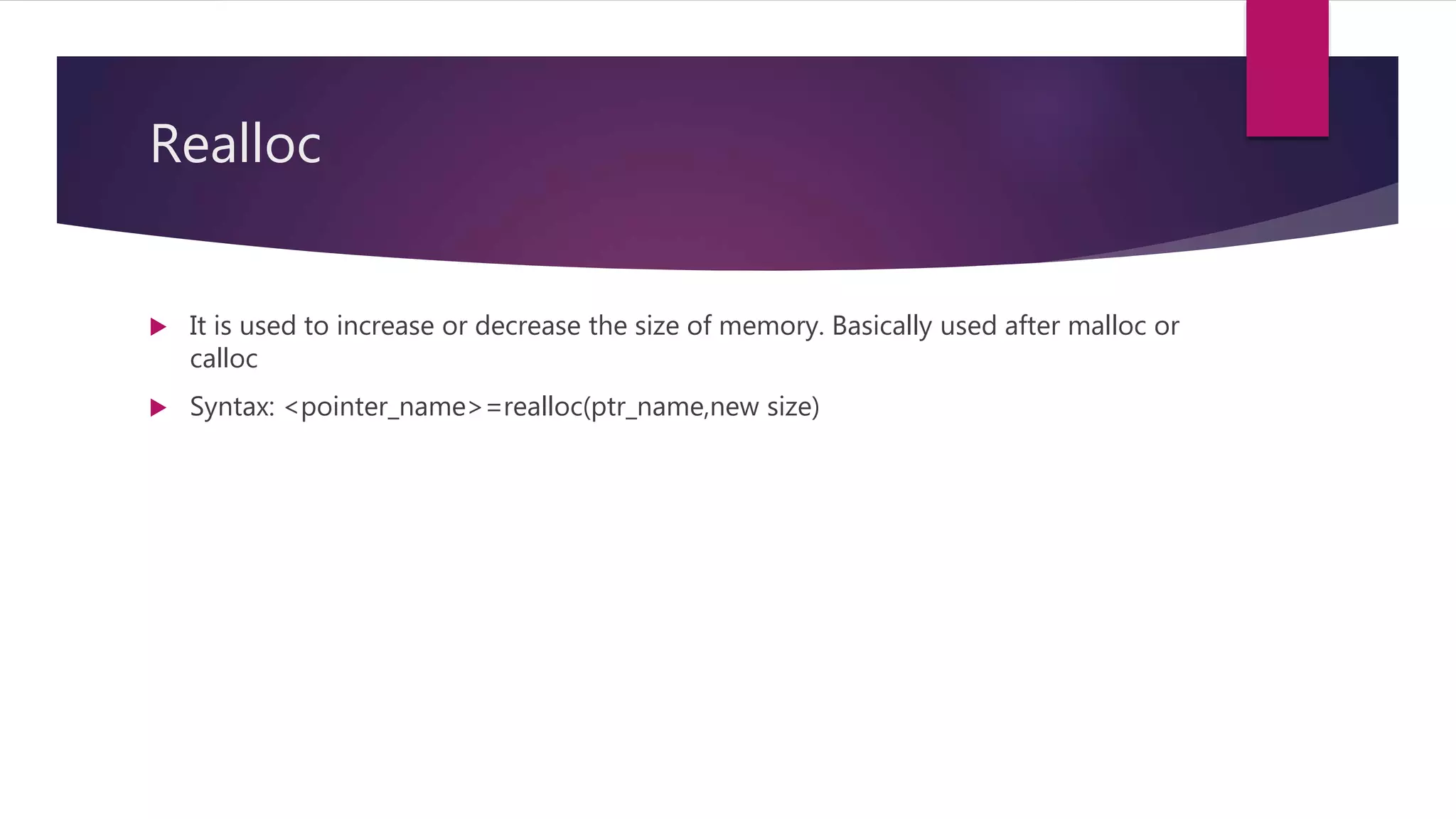
This document discusses pointers in C programming. It defines a pointer as a variable that stores a memory address, specifically the location of another object in memory. It describes how to declare pointers using data type asterisk pointer name syntax. It explains common pointer operations like assignment, value finding, incrementing, and comparing. Pointers allow for efficient handling of arrays and structures. They can also be used to return multiple values from functions and for dynamic memory allocation using functions like malloc, calloc, realloc, and free. Parameters can be passed by value, where the argument value is copied, or by reference, where the address of the argument is passed and its value can be modified.