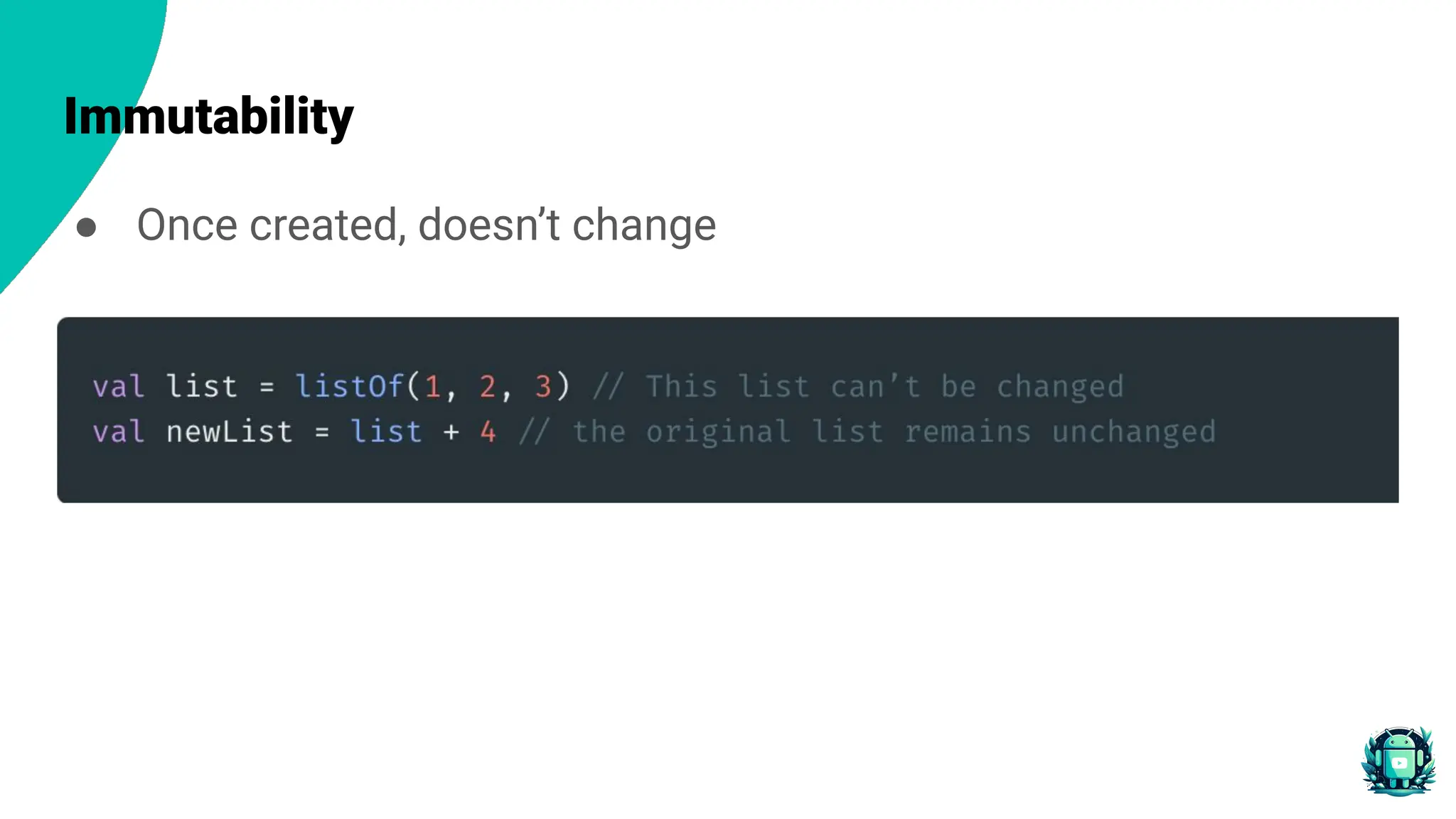
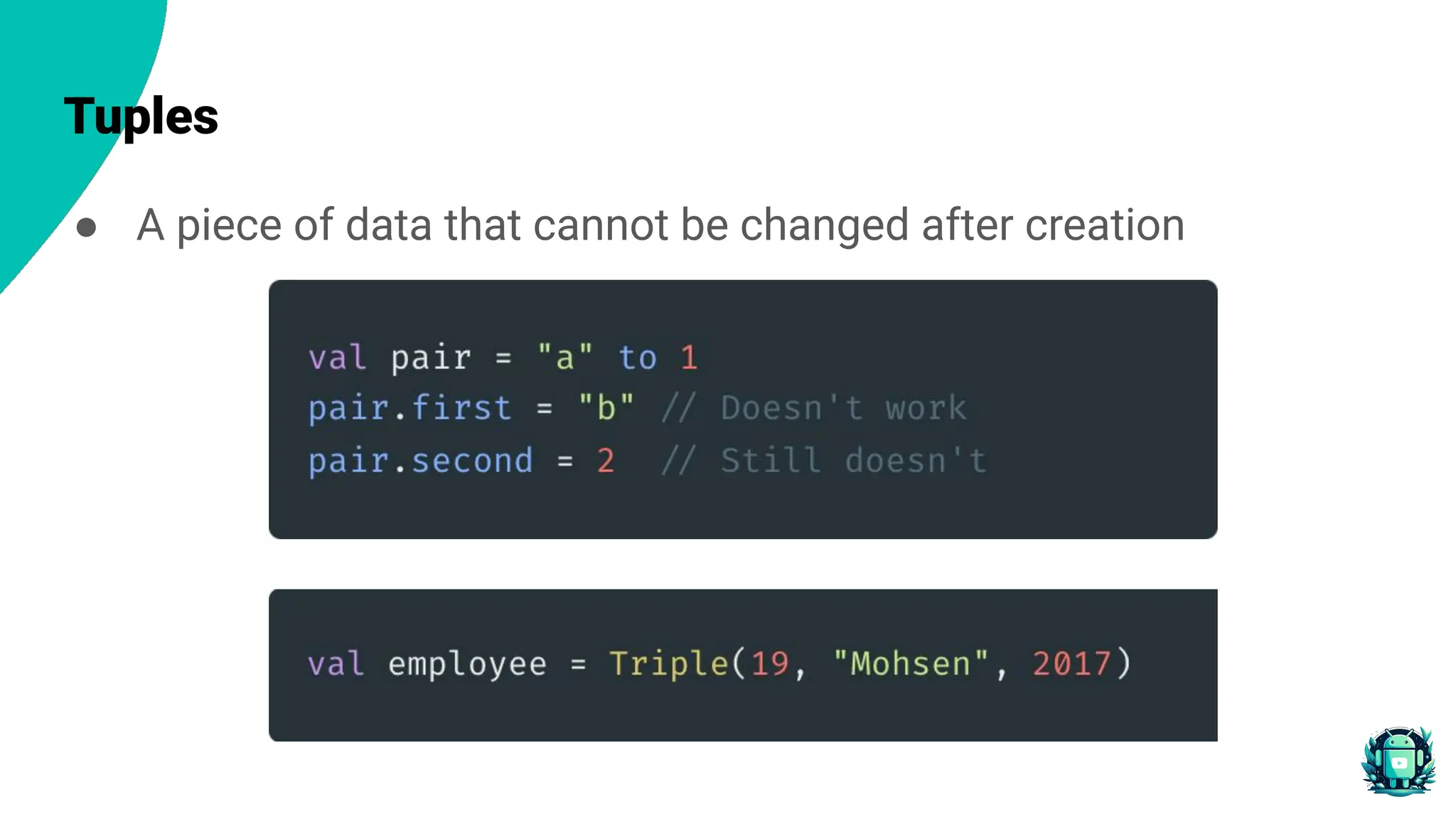
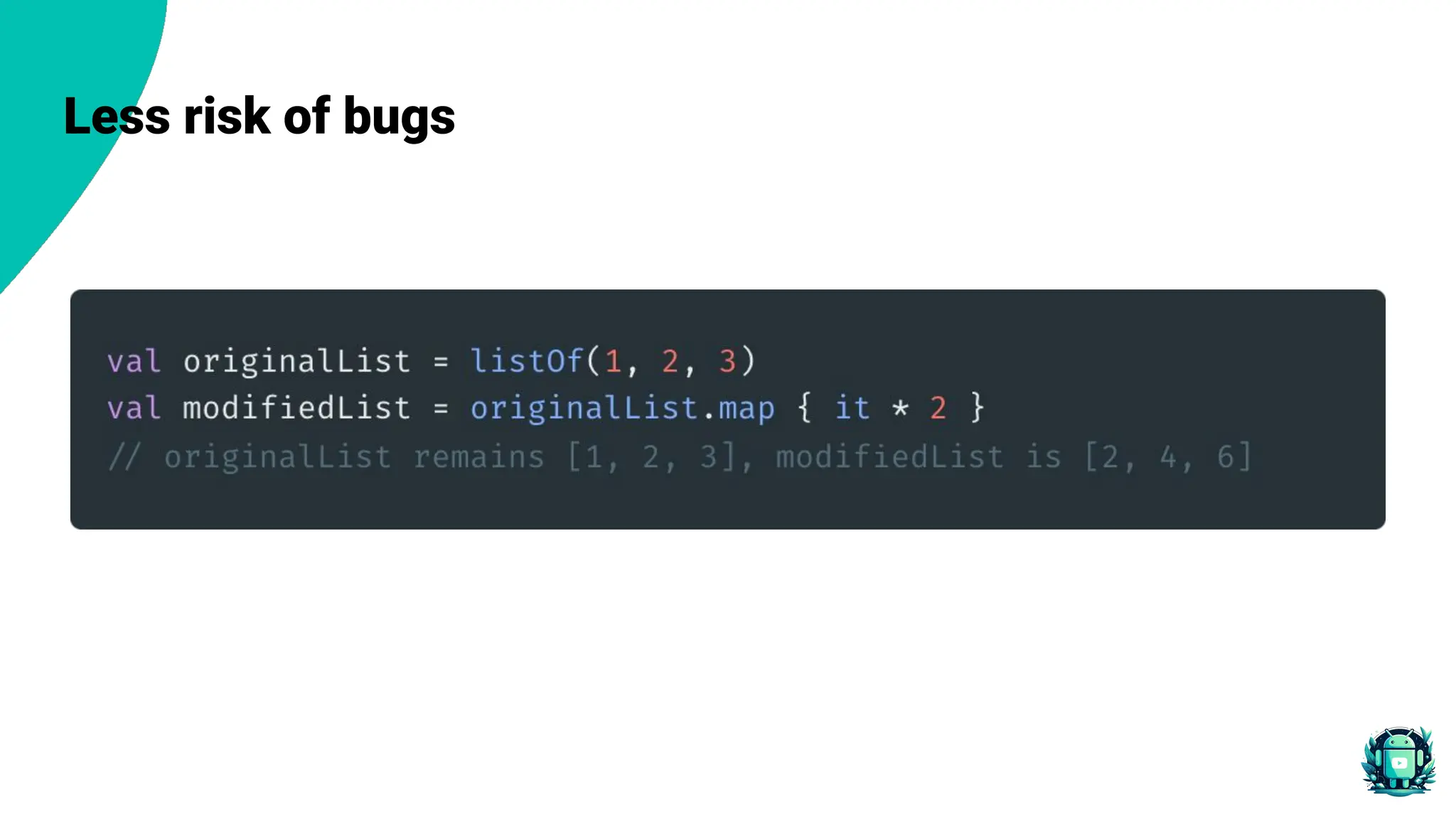
The document provides an overview of functional programming in Kotlin, emphasizing its core principles such as immutability, pure functions, and declarative approaches. It contrasts functional programming with imperative programming and introduces advanced concepts like function composition and currying. Additionally, it discusses the benefits of using functional programming in Android development, including improved code readability, maintainability, and reduced risk of bugs.