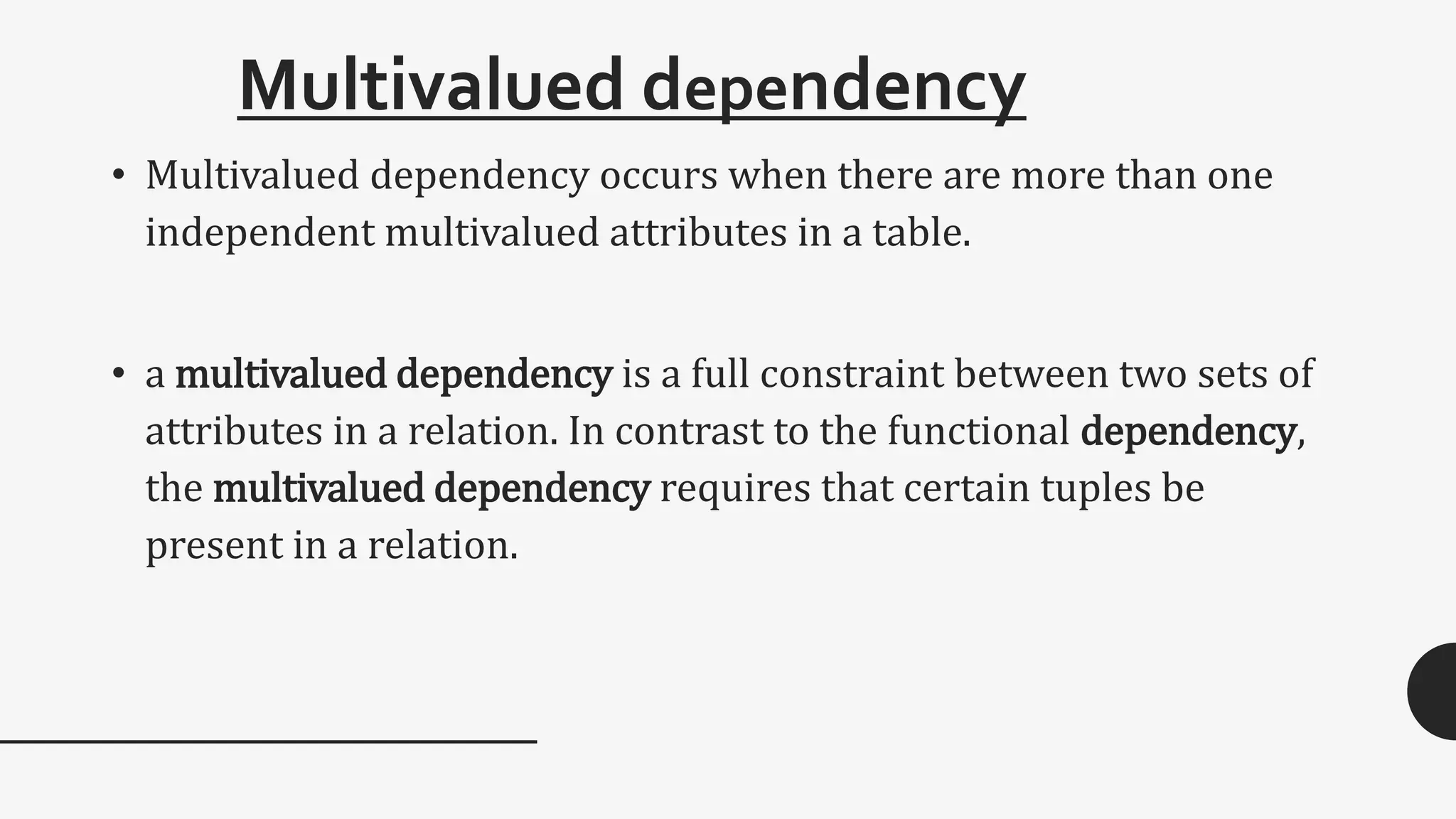
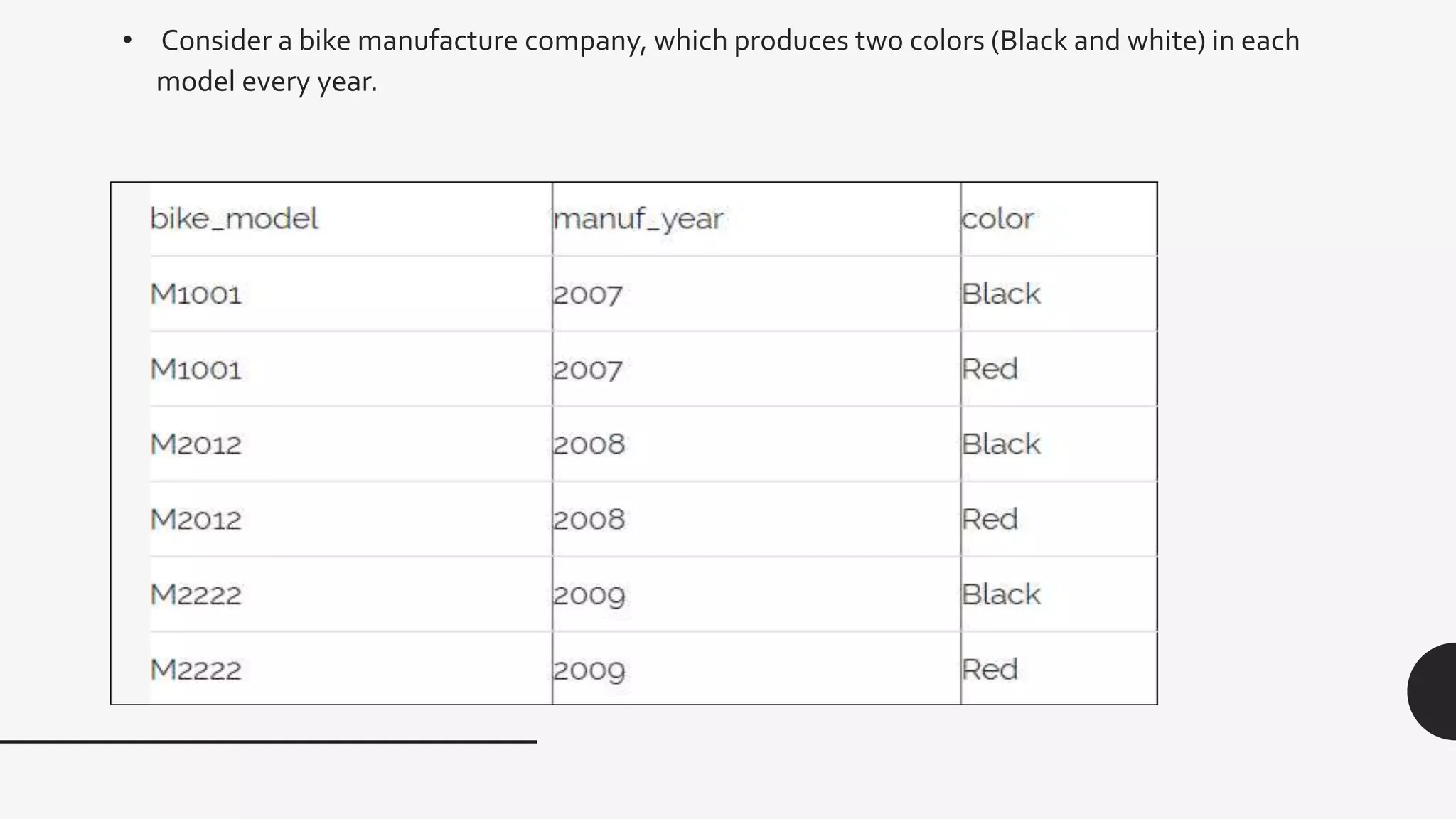
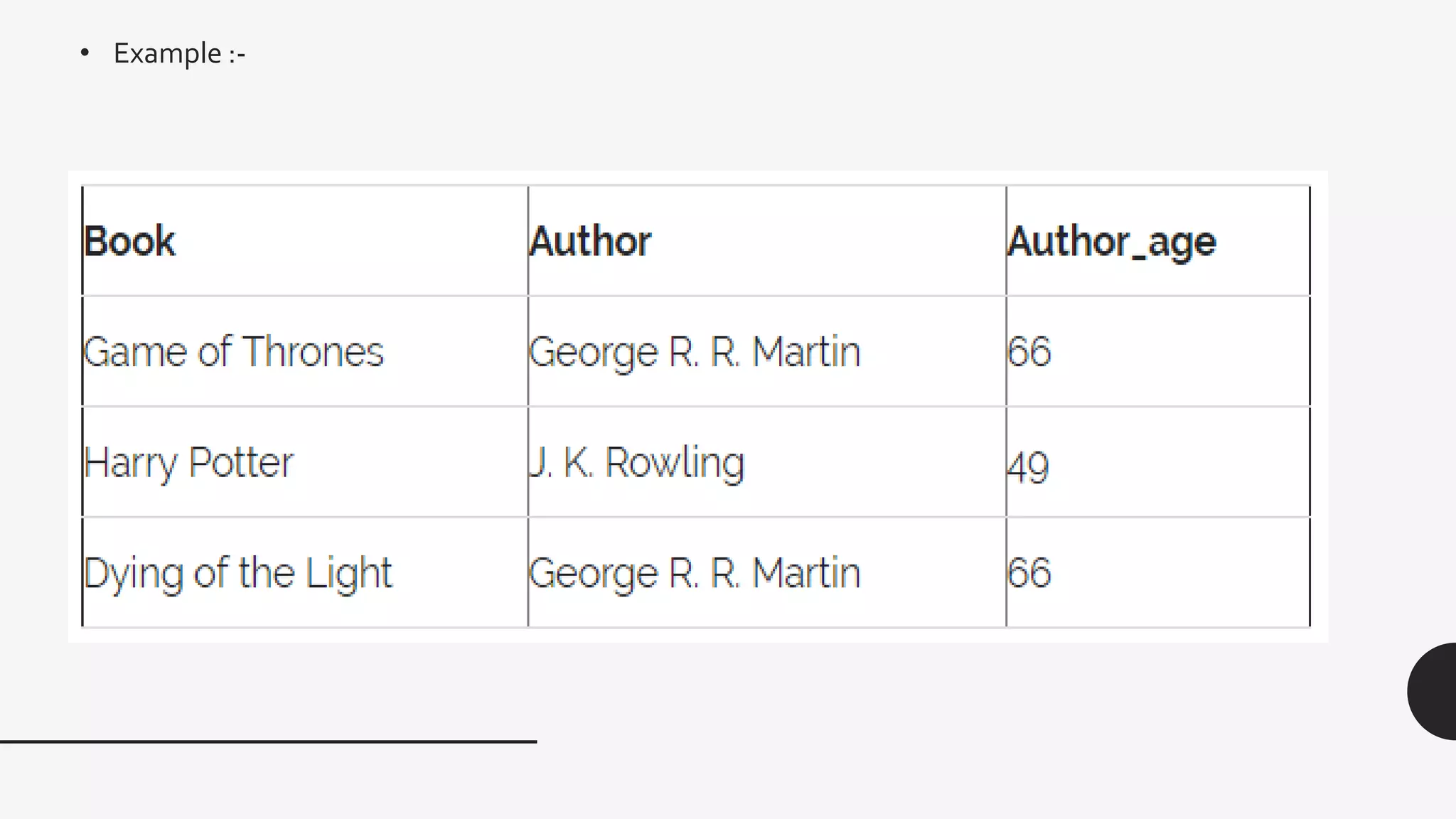
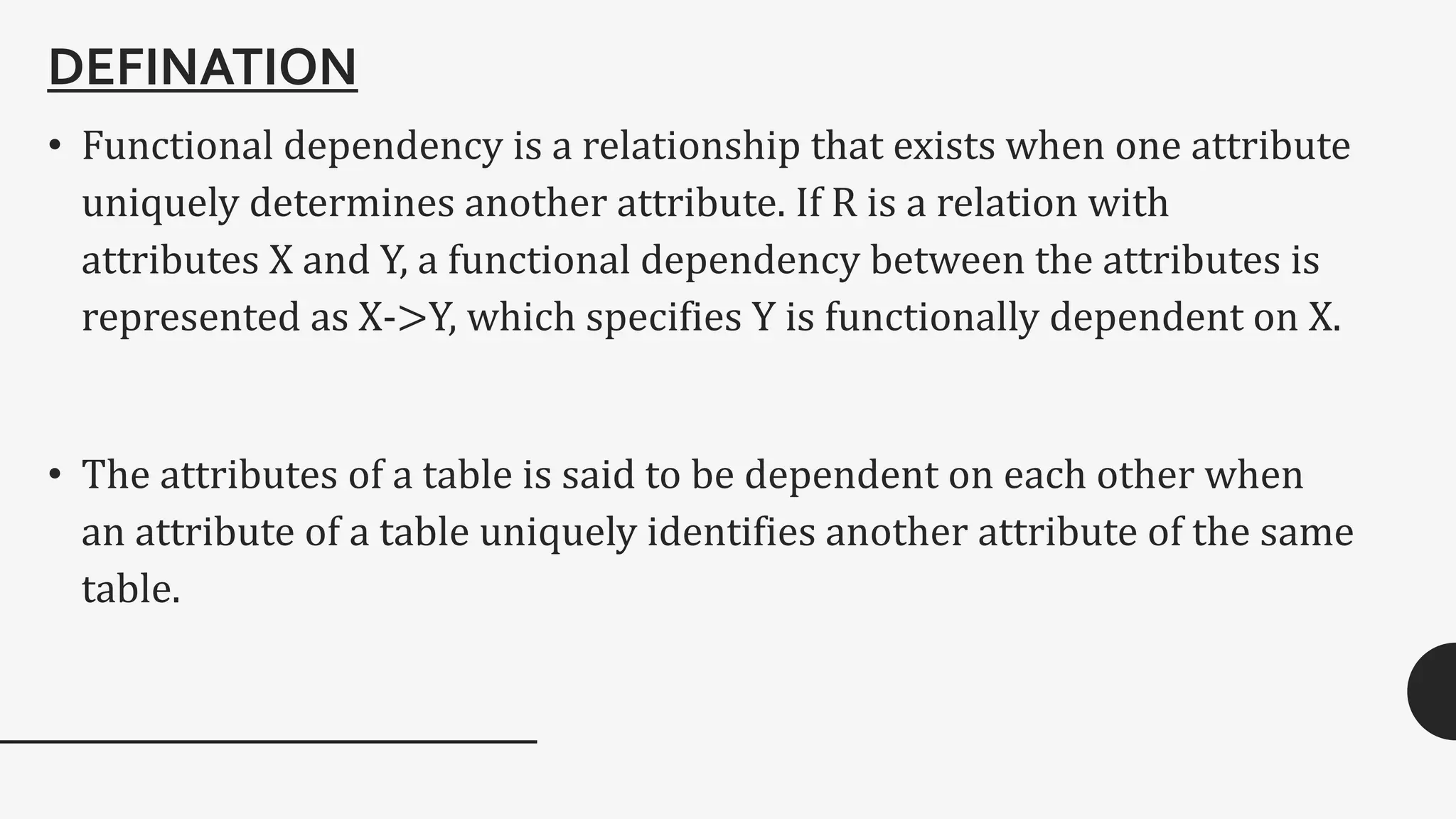
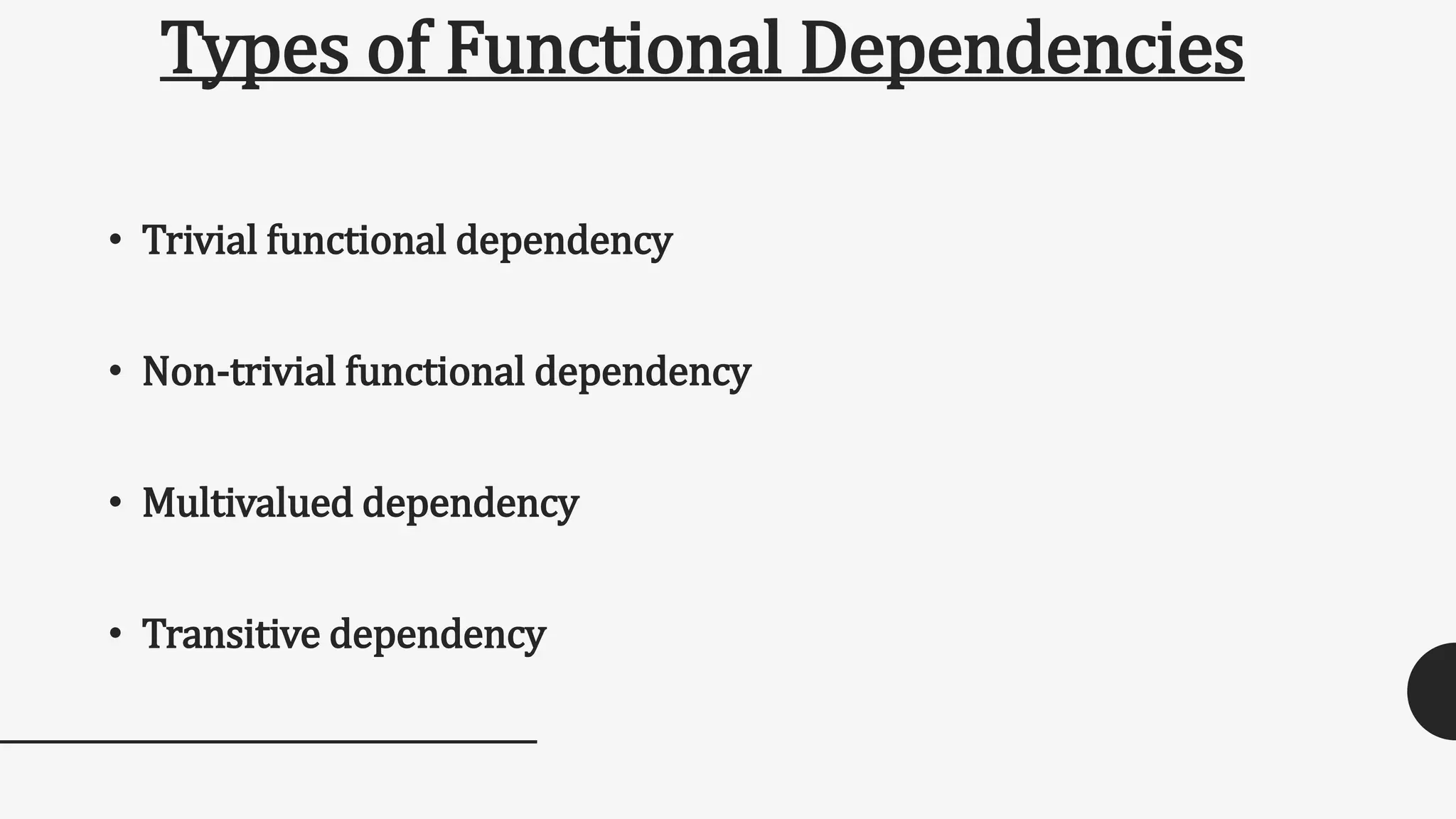
Functional dependency defines a relationship between attributes in a table where a set of attributes determine another attribute. There are different types of functional dependencies including trivial, non-trivial, multivalued, and transitive. An example given is a student table with attributes Stu_Id, Stu_Name, Stu_Age which has the functional dependency of Stu_Id->Stu_Name since the student ID uniquely identifies the student name.



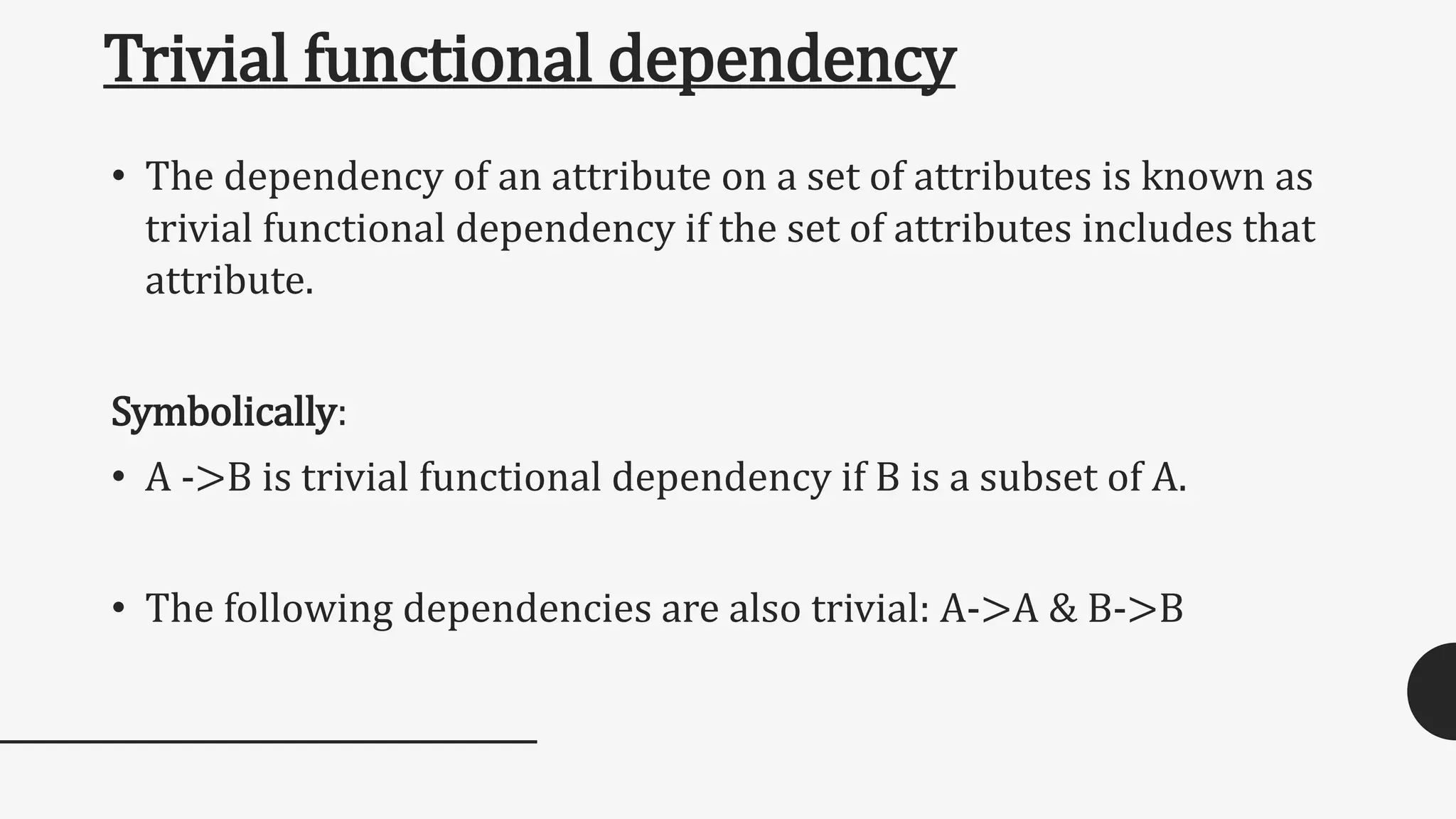

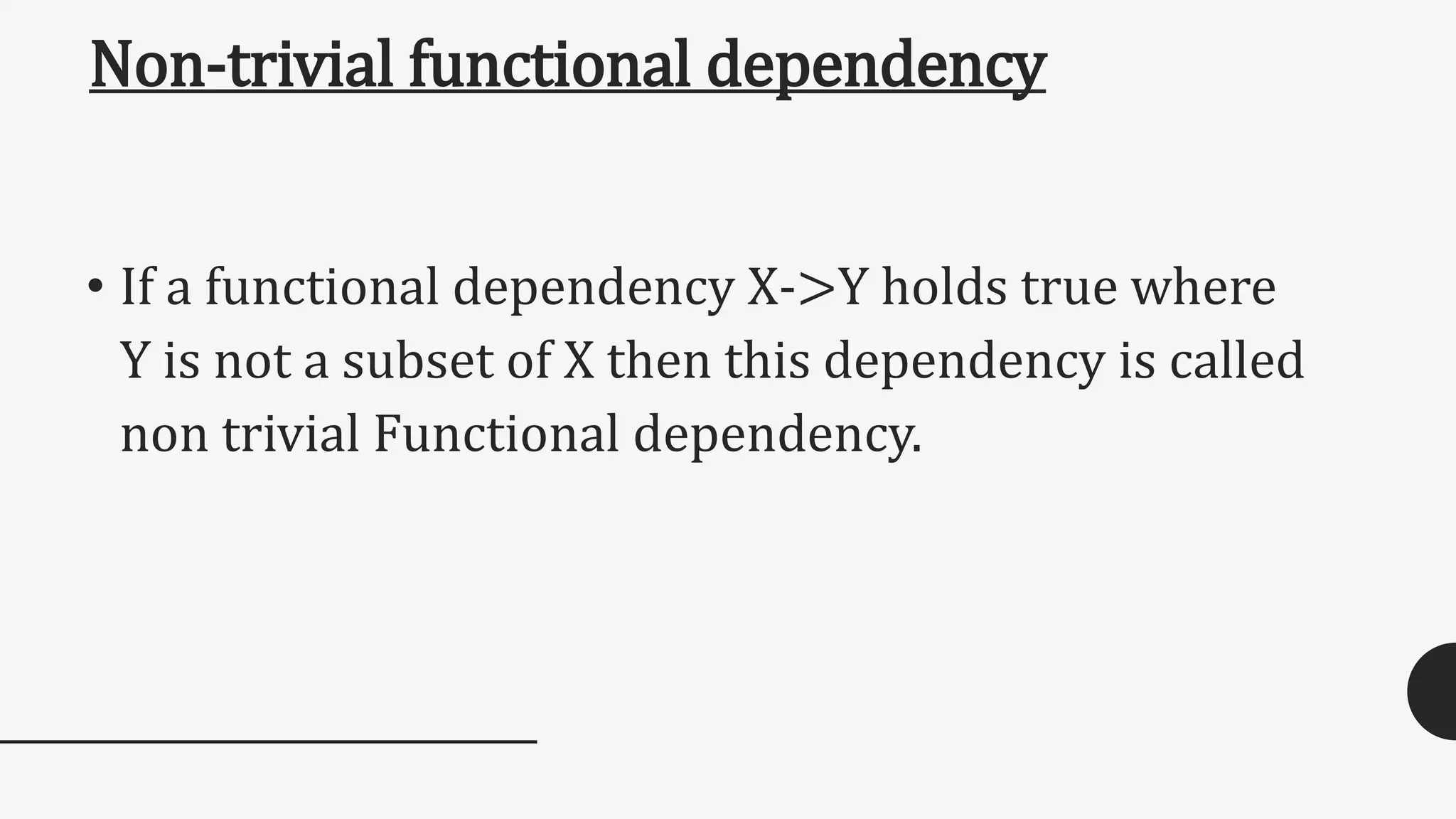

![• On the other hand, the following dependencies are trivial: {emp_id, emp_name} -> emp_name [emp_name is a subset of {emp_id, emp_name}] Completely non trivial FD: If a Functional dependency X->Y holds true where X intersection Y is Null then this dependency is said to be completely non trivial function dependency.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fd-161021045633/75/FUNCTION-DEPENDENCY-AND-TYPES-EXAMPLE-10-2048.jpg)