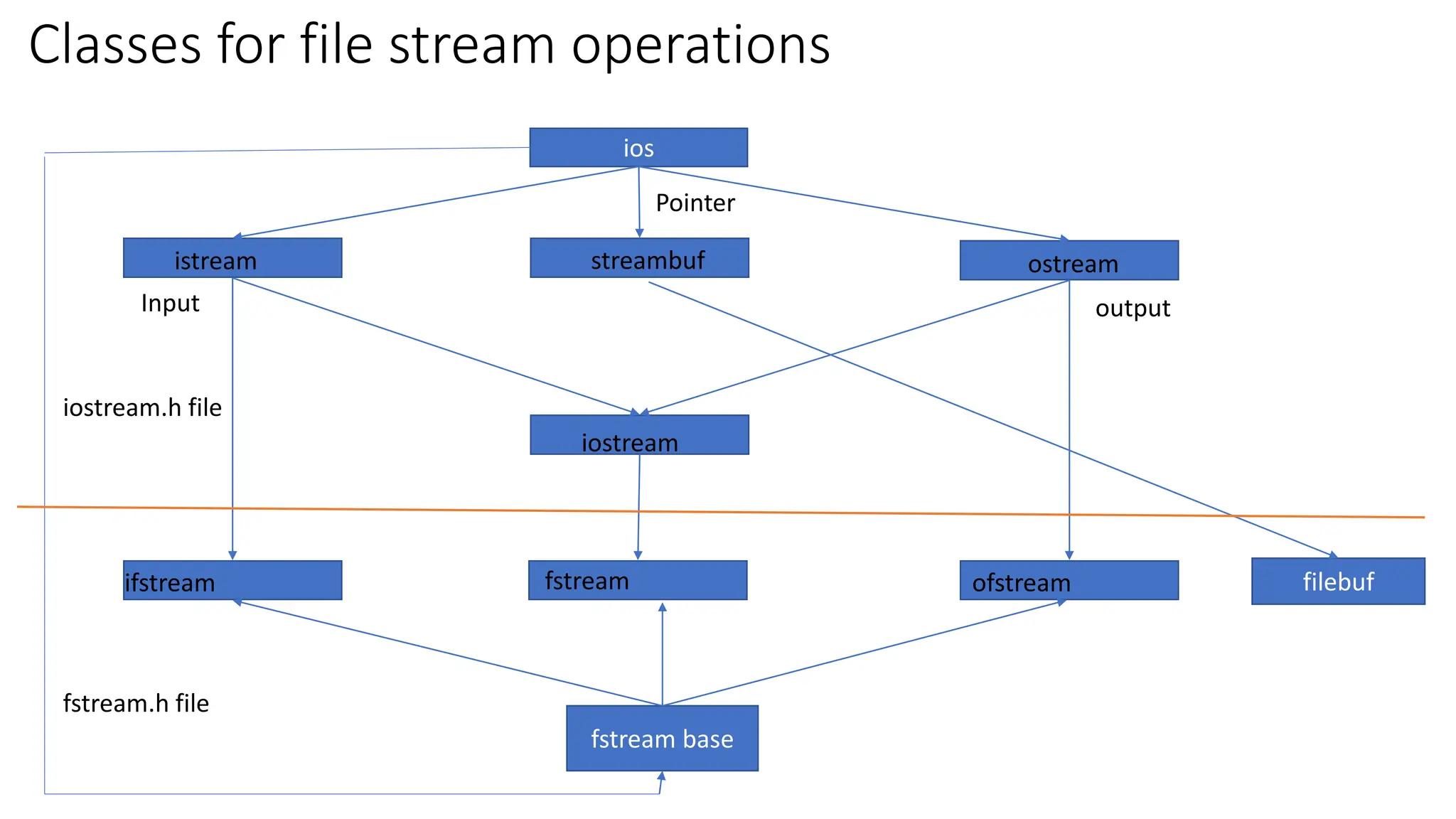
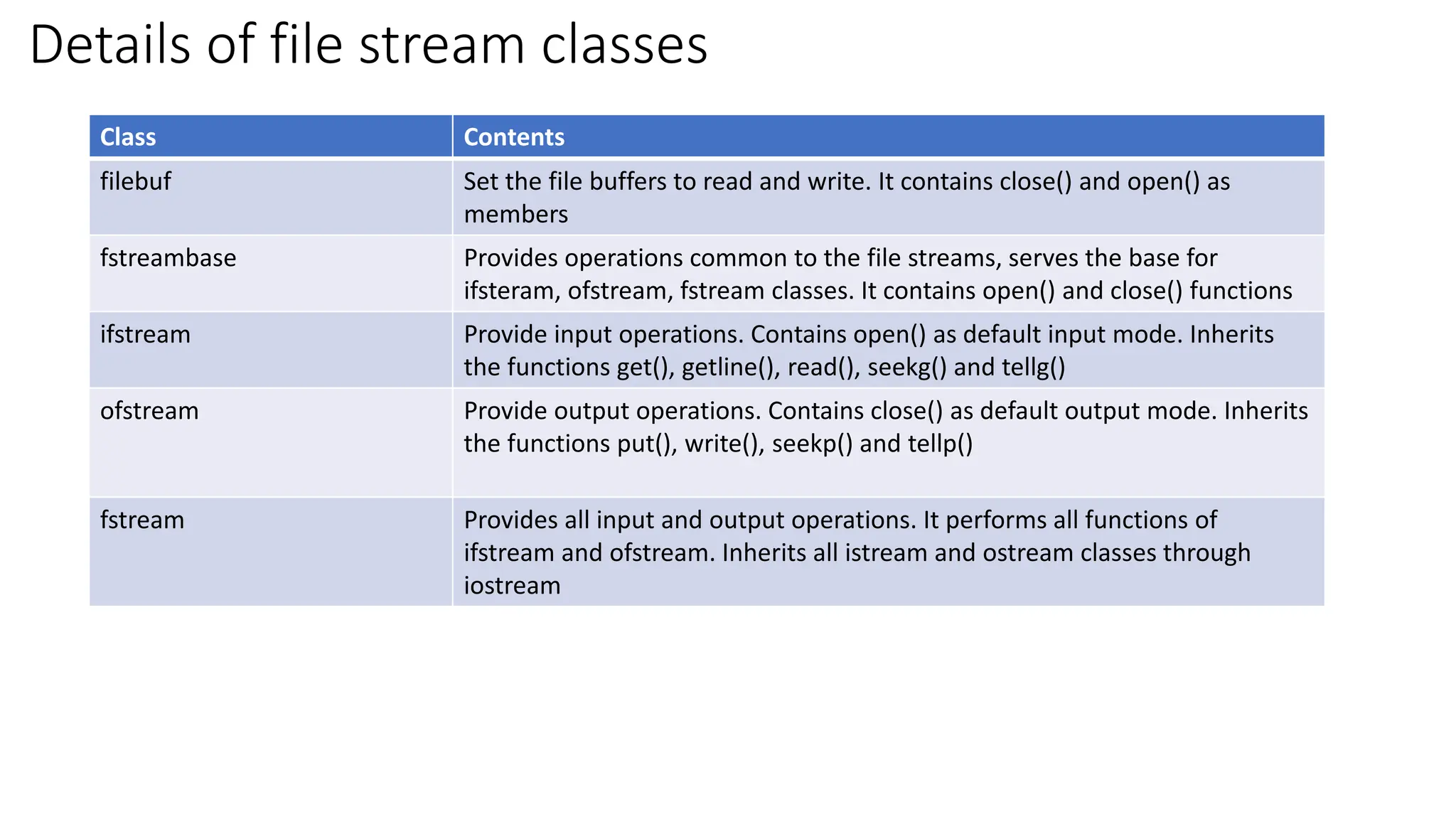
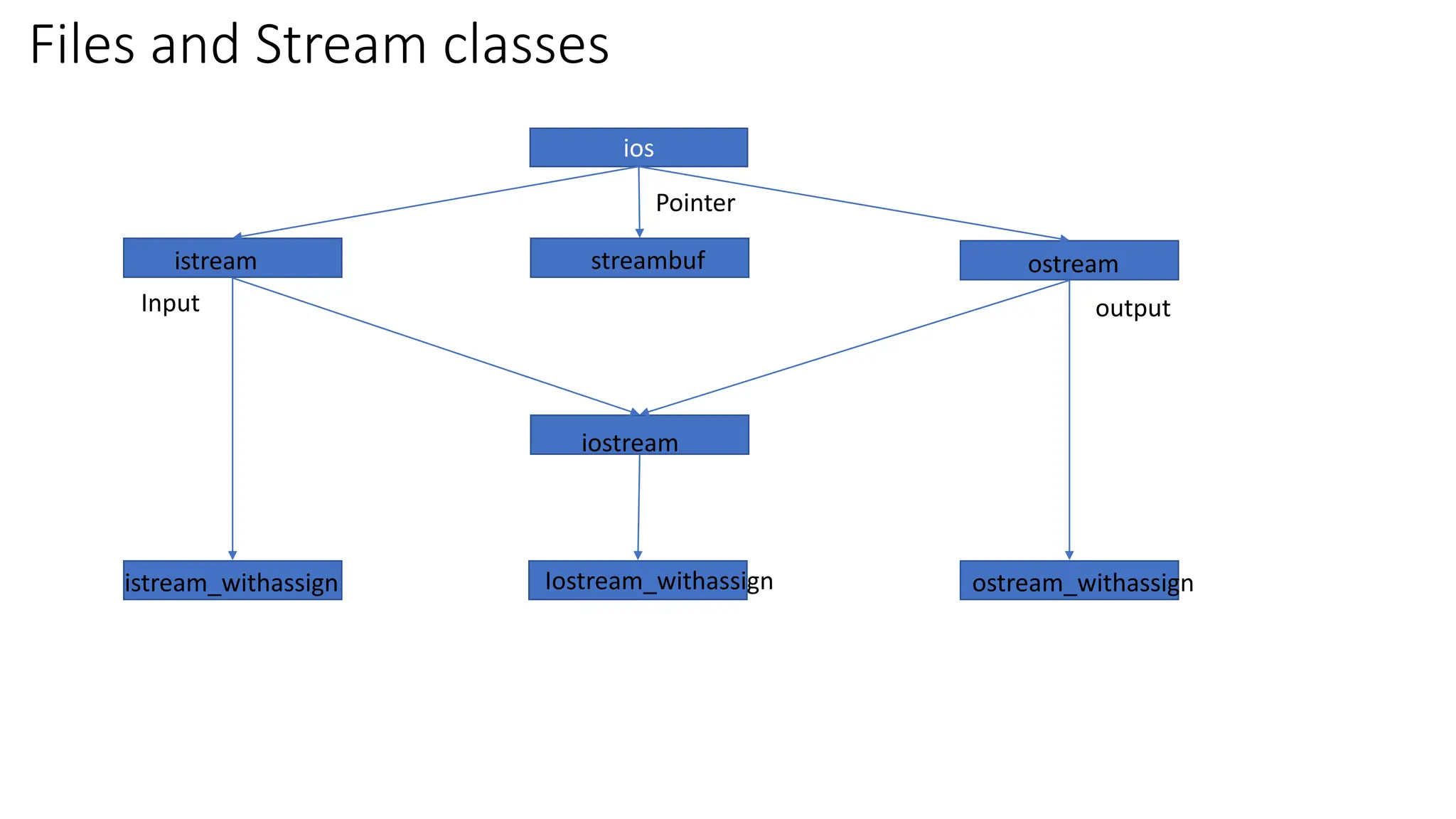
Files in C++ can be accessed using stream classes which provide an interface for input/output operations with files. The key stream classes are fstream, ifstream, and ofstream which allow reading from, writing to, and both reading and writing files. Files can be opened using constructors or the open() function, specifying a file name and open mode. File pointers track the current read/write position and can be manipulated using seekg(), seekp(), tellg(), and tellp() along with positions like ios::beg or ios::cur.


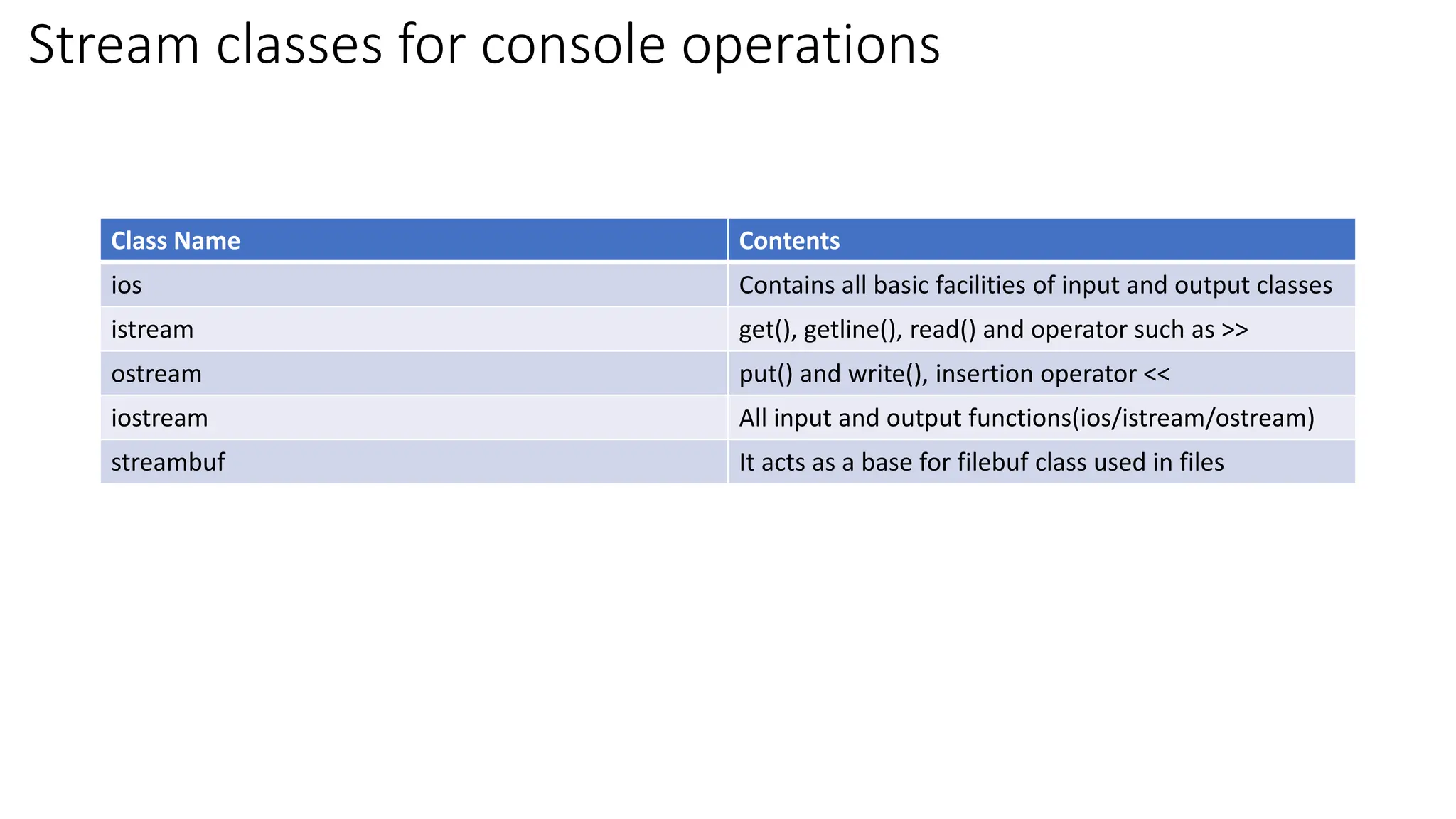

![Unformatted I/O operations getline() and write() The getline() reads a whole line of text end with newline character(or when we press return(enter) key) cin.getline(line, size); Eg; char name[20]; cin.getline(name, 20); cout.write(line, size); The write() displays/prints a whole line of text](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesinc-240118144142-73bfddd0/75/Files-in-C-pdf-is-the-notes-of-cpp-for-reference-6-2048.jpg)