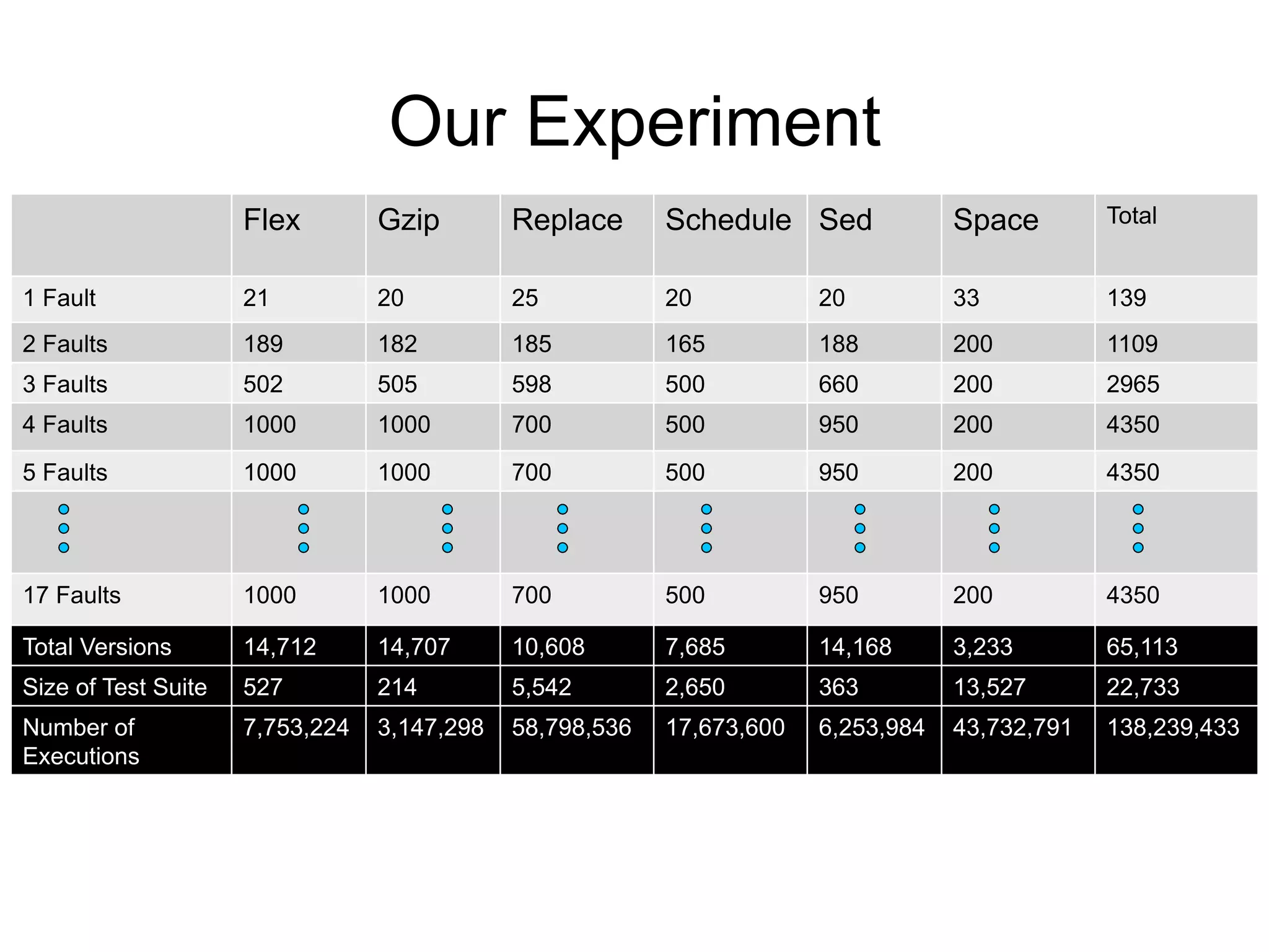
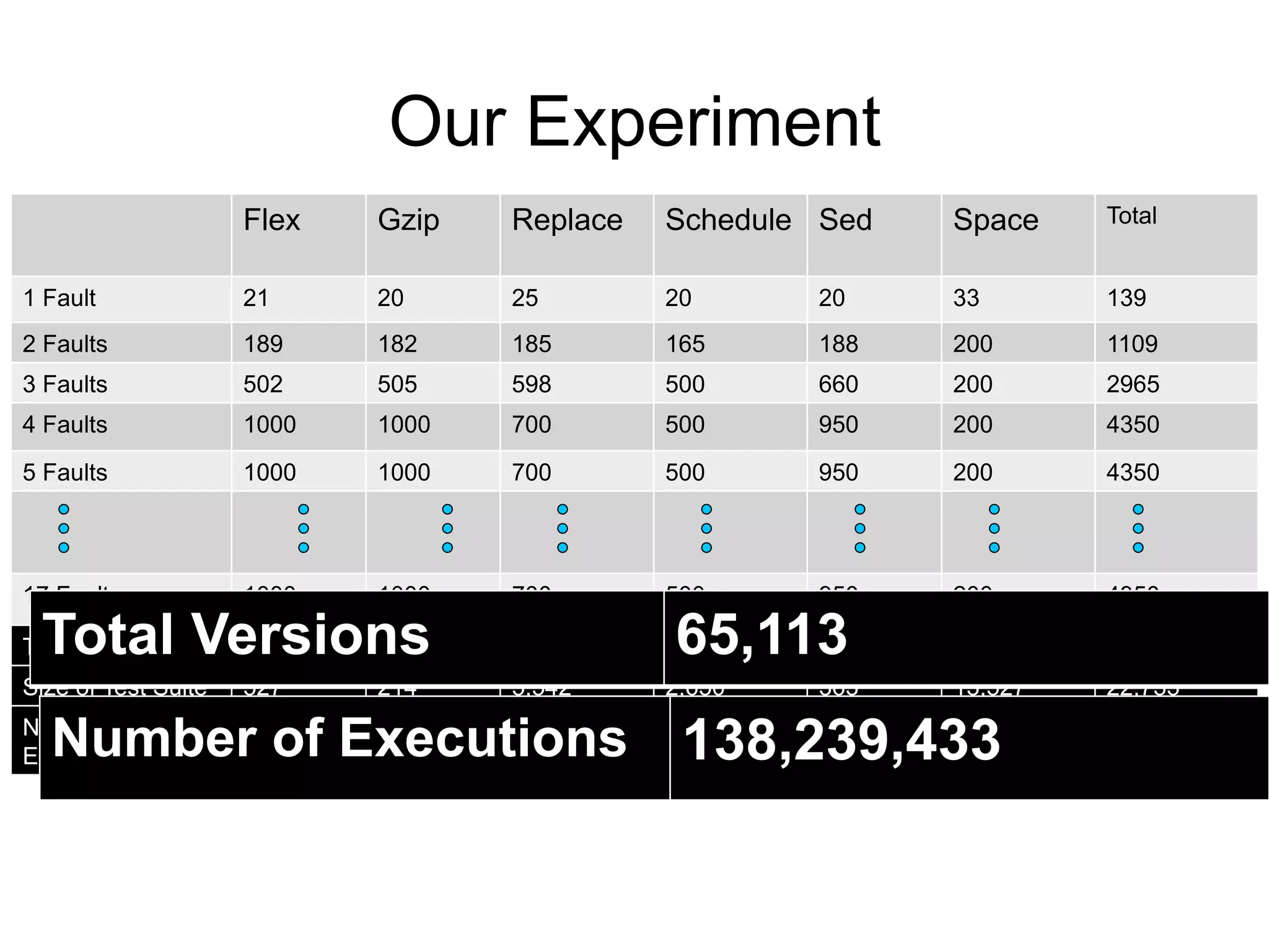
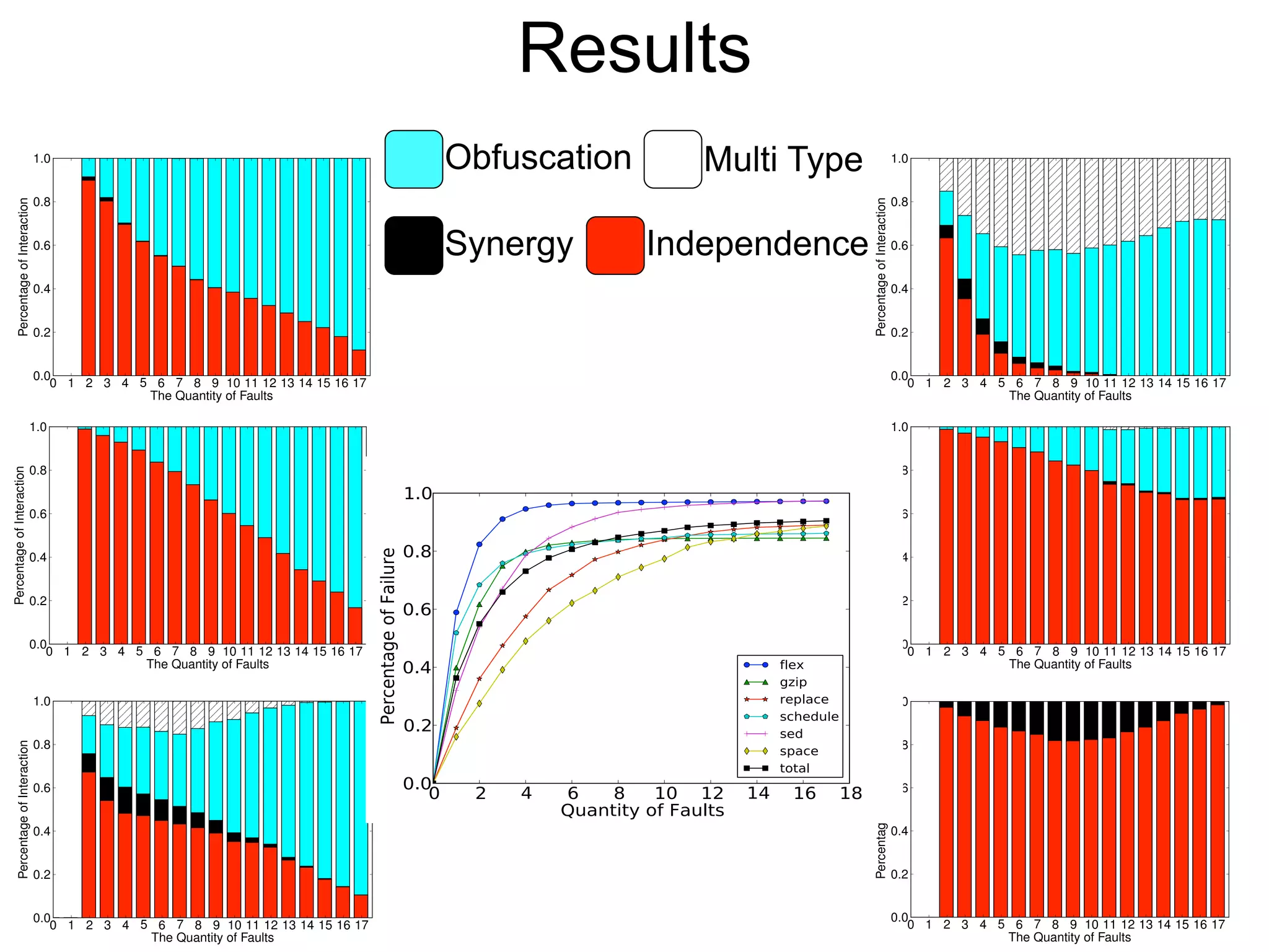
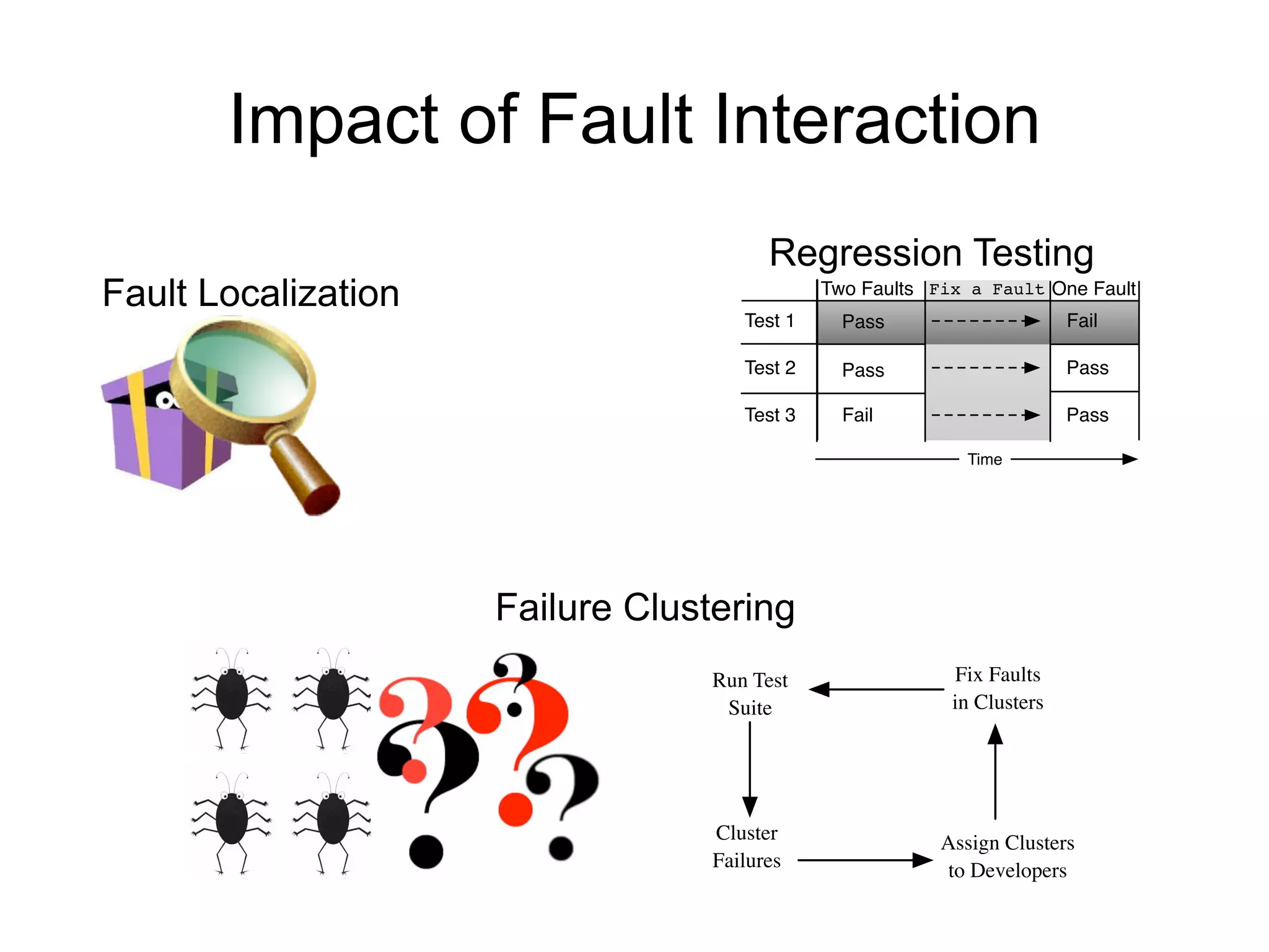
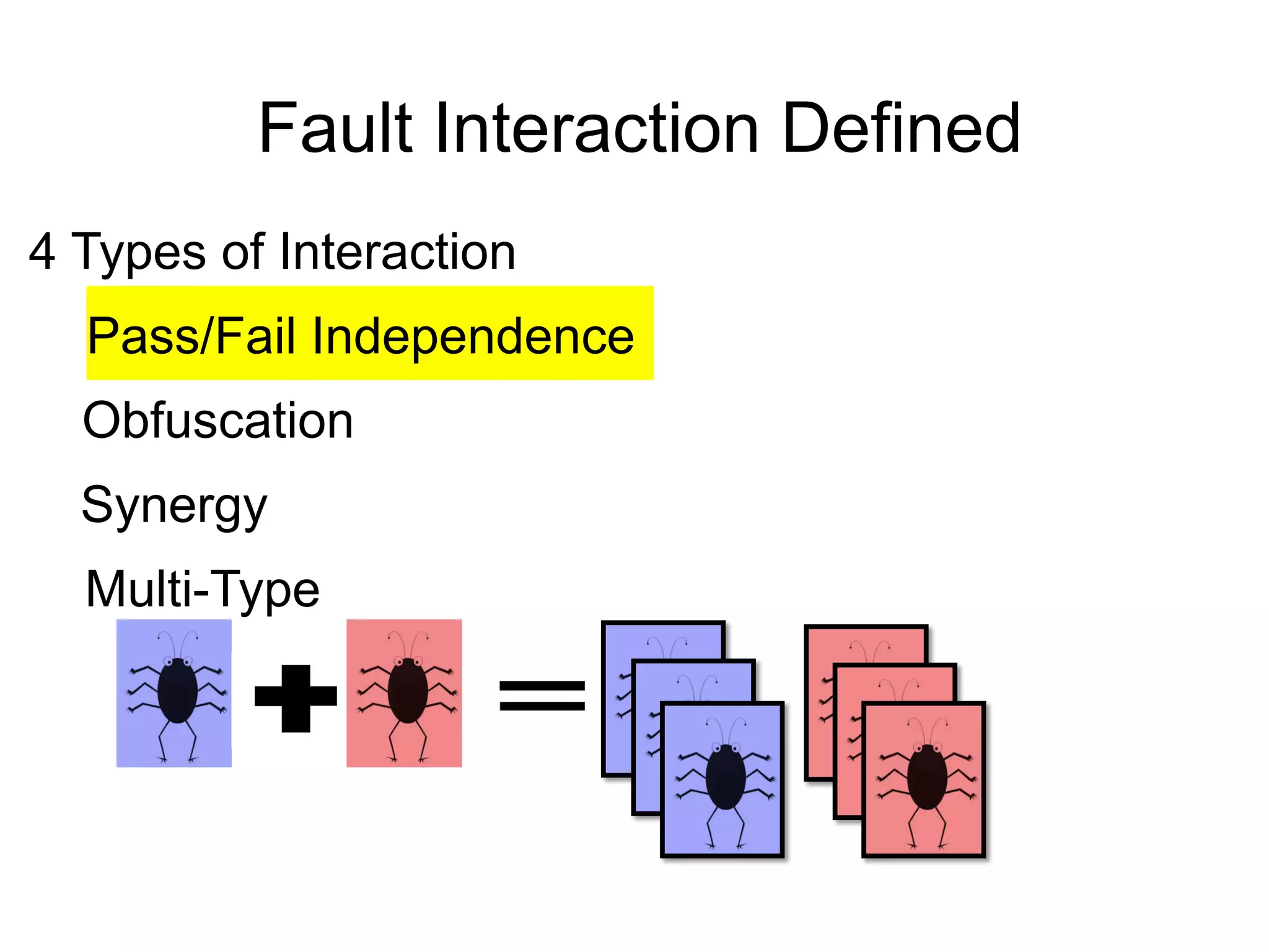
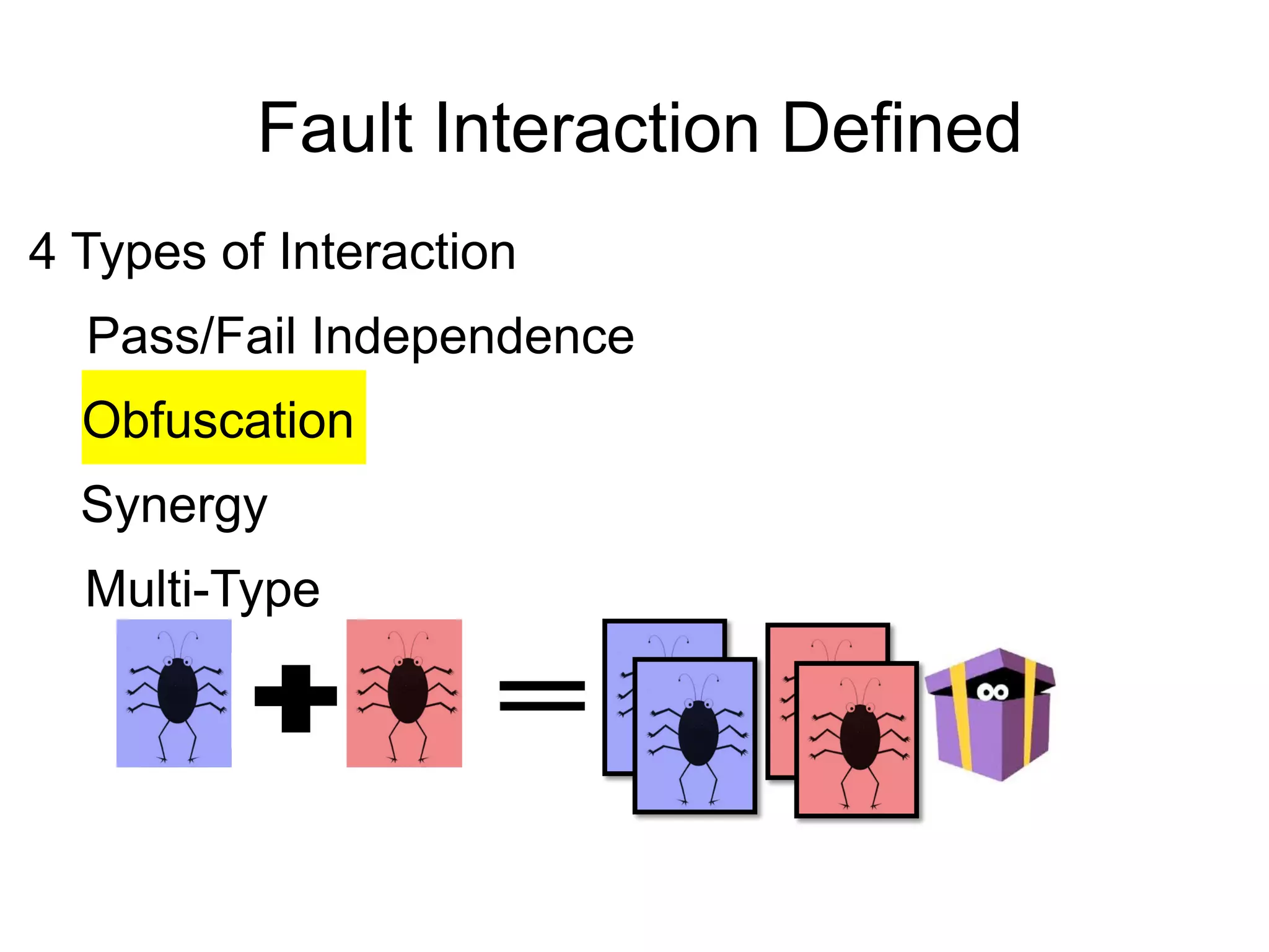
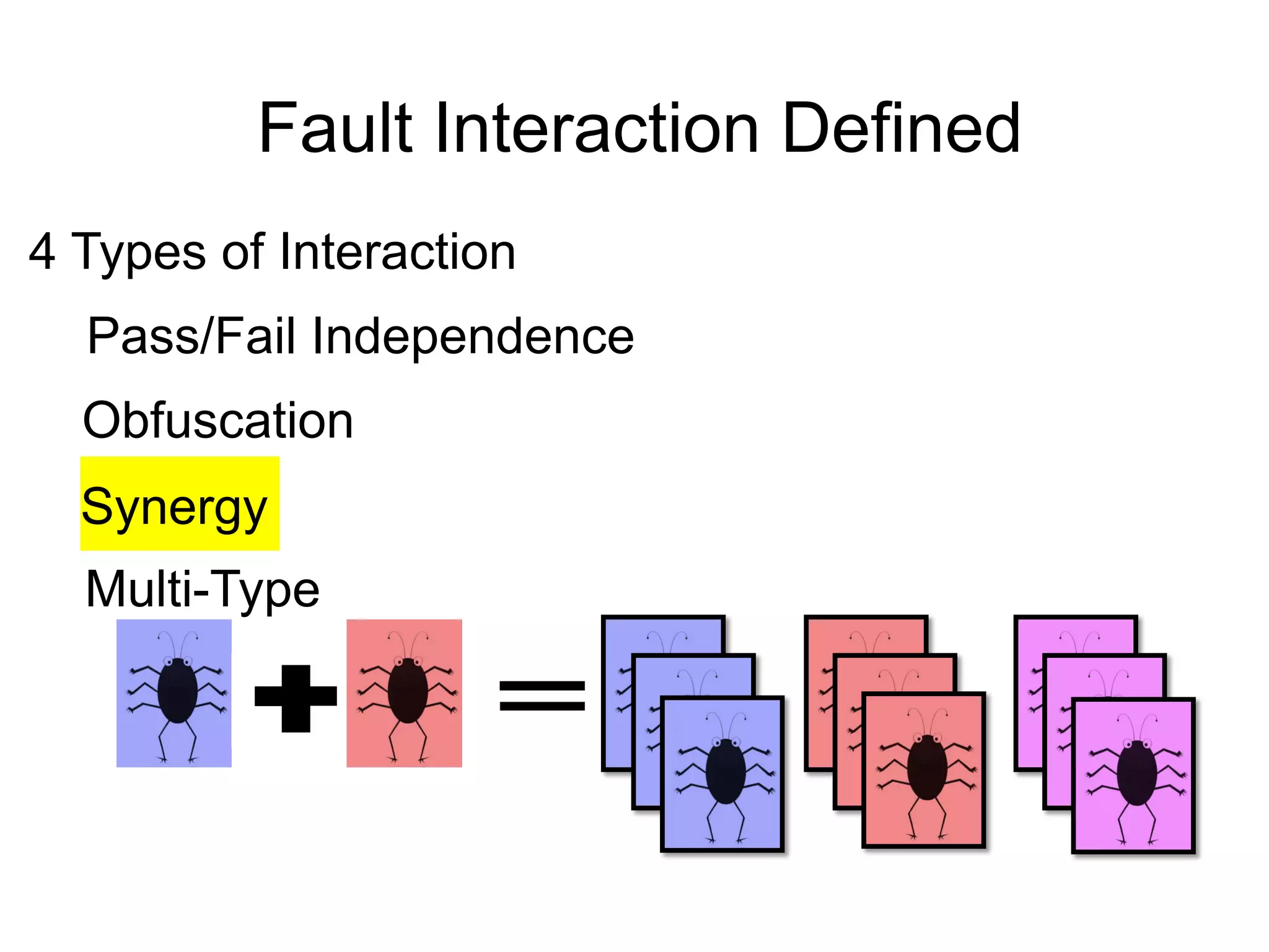
The document discusses fault interaction, defining four types: pass/fail, independence, obfuscation, and synergy, and exploring multi-type fault interactions. It emphasizes the significance of understanding fault interactions and their effects on software testing and fault localization, supported by empirical data and examples. The study concludes that fault interaction, especially obfuscation, is prominent and urges adaptation of techniques in practice and research.


![Motivating Example X = input [0] - 2 Y = input [0] - 2 If (X == Y) print 1 else print 0 Expected Actual Pass/Fail Results Results Status Test Case 1: input [0,0] 1 1 Pass Test Case 2: input [2,0] 0 1 Fail](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faultinteractionanditsrepercussions-111015111225-phpapp02/75/Faults-and-Regression-Testing-Fault-interaction-and-its-repercussions-7-2048.jpg)
![Motivating Example X = input [0] - 2 Y = input [1] / 2 If (X == Y) print 1 else print 0 Expected Actual Pass/Fail Results Results Status Test Case 1: input [0,0] 1 0 Fail Test Case 2: input [2,0] 0 1 Fail](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faultinteractionanditsrepercussions-111015111225-phpapp02/75/Faults-and-Regression-Testing-Fault-interaction-and-its-repercussions-8-2048.jpg)
![Motivating Example X = input [0] * 2 Y = input [1] / 2 If (X == Y) print 1 else print 0 Expected Actual Pass/Fail Results Results Status Test Case 1: input [0,0] 1 1 Pass Test Case 2: input [2,0] 0 0 Pass](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faultinteractionanditsrepercussions-111015111225-phpapp02/75/Faults-and-Regression-Testing-Fault-interaction-and-its-repercussions-9-2048.jpg)